



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (2): 253-255. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020008 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020008
所属专题: 生物入侵
收稿日期:2020-01-08
接受日期:2020-02-20
出版日期:2020-02-20
发布日期:2020-03-31
通讯作者:
何维明
基金资助:Received:2020-01-08
Accepted:2020-02-20
Online:2020-02-20
Published:2020-03-31
Contact:
Weiming He
摘要:
生物入侵常常带来一系列负面影响, 如物种快速丧失、巨大经济损失、生态公益急剧降低、不可逆环境破坏等。正是这些负面影响引起科技界、政府和公众对生物入侵的极大关注。因此, 准确量化生物入侵的影响非常重要。然而, 广泛使用的生物入侵影响评估方法存在两个严重缺陷: 一是缺乏真实对照, 二是包含非入侵效应。这两个缺陷使得人们对生物入侵影响的了解相对粗略。为此, 作者提出两点建议: 一是在实验条件下设置真实对照, 二是考虑同步对照。评估方法的完善将有助于人们更加准确地理解生物入侵的影响。
何维明 (2020) 生物入侵的影响是否准确可知?. 生物多样性, 28, 253-255. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020008.
Weiming He (2020) Biological invasions: Are their impacts precisely knowable or not?. Biodiversity Science, 28, 253-255. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020008.
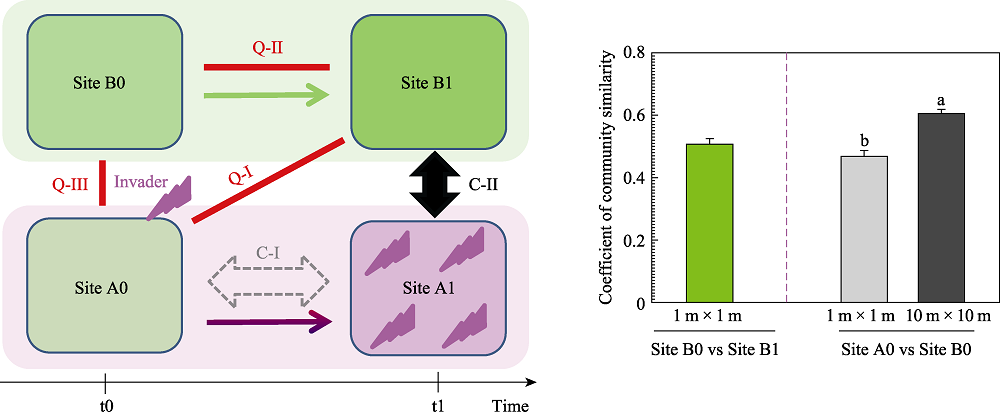
图1 生物入侵的影响评估示意图(左)和植物群落相似度(右)。在左图中, 单箭头表示立地A和B从时间t0到t1的转变, 双箭头表示立地之间的比较, 实线表示两个立地是否可替换这个问题。C: 比较; Q: 问题; Invader: 外来入侵生物。在右图中, 不同字母表示1 m × 1 m植物群落相似性与10 m × 10 m植物群落相似性之间存在差异(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 1 Graphic illustration of quantifying biological invasion impacts (left panel), and the related comparisons of plant community similarity coefficients between sites (right panel). At the left panel, single arrows indicate a shift of sites from t0 to t1, double arrows indicate a comparison between two sites, and solid lines indicate a question about whether two sites are substitutable. C: Comparison; Q: Question. At the right panel, different letters demonstrate a significant difference in similarity coefficients between 1 m × 1 m quadrats and 10 m × 10 m quadrats at the P < 0.05 level.
| [1] | Elton CS (1958) The Ecology of Invasions by Animals and Plants. Methuen Press, London. |
| [2] | Gaertner M, Breeyen AD, Hui C, Richardson DM (2009) Impacts of alien plant invasions on species richness in Mediterranean-type ecosystems: A meta-analysis. Progress in Physical Geography, 33, 319-338. |
| [3] | Lockwood JL, Hoopes MF, Marchetti MP (2013) Invasion Ecology. John Wiley & Sons, New York. |
| [4] |
Powell KI, Chase JM, Knight TM (2013) Invasive plants have scale-dependent effects on diversity by altering species-area relationships. Science, 339, 316-318.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] | Ricciardi A, Hoopes MF, Marchetti MP, Lockwood JL (2013) Progress toward understanding the ecological impacts of nonnative species. Ecological Monographs, 83, 263-282. |
| [6] | Richardson DM (2011) Fifty Years of Invasion Ecology: The Legacy of Charles Elton. Wiley-Blackwell, Chichester. |
| [7] |
van Kleunen M, Dawson W, Essl F, Pergl J, Winter M, Weber E, Kreft H, Weigelt P, Kartesz J, Nishino M, Antonova LA, Barcelona JF, Cabezas FJ, Cardenas D, Cardenas-Toro J, Castano N, Chacon E, Chatelain C, Ebel AL, Figueiredo E, Fuentes N, Groom QJ, Henderson L, Inderjit , Kupriyanov A, Masciadri S, Meerman J, Morozova O, Moser D, Nichrent DL, Patzelt A, Pelser PB, Baptiste MP, Poopath M, Schulze M, Seebens H, Shu W, Thomas J, Velayos M, Wieringa J, Pysek P (2015) Global exchange and accumulation of non-native plants. Nature, 525, 100-104.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] |
Vilà M, Espinar JL, Hejda M, Hulme PE, Jarošík V, Maron JL, Pergl J, Schaffner U, Sun Y, Pyšek P (2011) Ecological impacts of invasive alien plants: A meta-analysis of their effects on species, communities and ecosystems. Ecology Letters, 14, 702-708.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] | Yu HW, He WM (2019) Increased rainfall and nitrogen alter colonization and extinction during postgrazing steppe succession. Journal of Vegetation Science, 30, 75-85. |
| [1] | 原雪姣, 张渊媛, 张衍亮, 胡璐祎, 桑卫国, 杨峥, 陈颀. 基于飞机草历史分布数据拟合的物种分布模型及其预测能力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24288-. |
| [2] | 杜聪聪, 冯学宇, 陈志林. 桥头堡效应中气候生态位差异的缩小促进了红火蚁的入侵[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24276-. |
| [3] | 韩丽霞, 王永健, 刘宣. 外来物种入侵与本土物种分布区扩张的异同[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23396-. |
| [4] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [5] | 李钊丞, 张燕雪丹. 基于物种濒危状况评价与种群增长的一种新评估方法在水生野生动物保护司法中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22319-. |
| [6] | 魏博, 刘林山, 谷昌军, 于海彬, 张镱锂, 张炳华, 崔伯豪, 宫殿清, 土艳丽. 紫茎泽兰在中国的气候生态位稳定且其分布范围仍有进一步扩展的趋势[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 21443-. |
| [7] | 刘艳杰, 黄伟, 杨强, 郑玉龙, 黎绍鹏, 吴昊, 鞠瑞亭, 孙燕, 丁建清. 近十年植物入侵生态学重要研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22438-. |
| [8] | 严靖, 闫小玲, 李惠茹, 杜诚, 马金双. 华东地区归化植物的组成特征、引入时间及时空分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 428-438. |
| [9] | 张家真, 高春蕾, 李艳, 孙萍, 王宗灵. 江阴港口外来船舶压载舱沉积物中甲藻包囊种类及组成[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(2): 144-154. |
| [10] | 殷万东, 吴明可, 田宝良, 于宏伟, 王麒云, 丁建清. 生物入侵对黄河流域生态系统的影响及对策[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(12): 1533-1545. |
| [11] | 李晗溪, 黄雪娜, 李世国, 战爱斌. 基于环境DNA-宏条形码技术的水生生态系统入侵生物的早期监测与预警[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(5): 491-504. |
| [12] | 余文生, 郭耀霖, 江佳佳, 孙可可, 鞠瑞亭. 土著昆虫素毒蛾在本地植物芦苇与入侵植物互花米草上的生活史[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(4): 433-438. |
| [13] | 孙士国, 卢斌, 卢新民, 黄双全. 入侵植物的繁殖策略以及对本土植物繁殖的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(5): 457-467. |
| [14] | 孙燕, 周忠实, 王瑞, HeinzMüller-Schärer. 气候变化预计会减少东亚地区豚草的生物防治效果**[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(12): 1285-1294. |
| [15] | 张紫妍, 张致杰, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草对遮荫的可塑性反应:入侵地与原产地种群的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(1): 18-22. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()
