



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 23396. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023396 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023396
所属专题: 生物入侵
韩丽霞1,2( ), 王永健2,*(
), 王永健2,*( )(
)( ), 刘宣1,3,*(
), 刘宣1,3,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2023-10-19
接受日期:2023-12-27
出版日期:2024-01-20
发布日期:2024-01-25
通讯作者:
*E-mail: liuxuan@ioz.ac.cn;yongjianwang@126.com
基金资助:
Lixia Han1,2( ), Yongjian Wang2,*(
), Yongjian Wang2,*( )(
)( ), Xuan Liu1,3,*(
), Xuan Liu1,3,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-10-19
Accepted:2023-12-27
Online:2024-01-20
Published:2024-01-25
Contact:
*E-mail: liuxuan@ioz.ac.cn;yongjianwang@126.com
摘要:
当今全球变化背景下, 物种分布区正发生着快速变化, 一类是人类活动介导下的生物入侵过程, 另一类是本土物种的自然分布区扩张。两者之间既具有相似之处, 亦有明显差异。探讨两者间异同是发展外来入侵物种管控和本土物种保护策略的基础科学问题。本文以两栖爬行类、鸟类和哺乳类等陆栖脊椎动物为例, 在阐述外来物种入侵过程的基础上, 将其与本土物种的分布区变化进行比较并阐述了两者间的异同。我们发现, 伴随经济贸易发展和人口流动, 外来物种正在加剧入侵; 同时, 发生分布范围变化的本土物种数量也在迅速增加。两者在分布区变化过程中的驱动因子、时空尺度、发生速度、物种特征的预测能力以及对新分布区的影响方面具有明显差异: 人类活动介导下的外来物种入侵通常会经历长距离迁移, 甚至跨越生物地理区系, 并在入侵区快速扩散, 物种特征在预测外来物种入侵过程中起着重要作用, 对当地生物多样性造成严重威胁; 本土物种分布区扩张通常发生在原生范围的邻近区域, 发生速度较慢, 物种特征在预测分布区扩展中的作用有限, 且对新区域的负面影响较小。由于在短期内很难全面判定外来物种和发生分布区变化的本土物种的生态影响, 我们建议应对新分布区内的外来物种和本土物种进行密切监测和长期研究, 对其可能引发的生态学效应进行早期预警和评估, 以最大限度地限制其潜在危害并保护生物多样性。
中图分类号:
韩丽霞, 王永健, 刘宣 (2024) 外来物种入侵与本土物种分布区扩张的异同. 生物多样性, 32, 23396. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023396.
Lixia Han, Yongjian Wang, Xuan Liu (2024) Comparisons between non-native species invasion and native species range expansion. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23396. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023396.
| Box 1 本文中涉及生态位相关的专业词汇释义 | |
|---|---|
| 专业词汇 Specialized words | 释义 Understanding definitions |
| 生态位追踪 Niche tracking | 物种可以通过在地理空间上遵循环境边界(如向更高海拔或更高纬度方向移动)来保持在适宜环境空间中的分布(Monahan & Hijmans, |
| 气候生态位 Climatic niche | 物种能够生存的非生物条件, 特别指由温度、降水等气候因子来限制的环境空间(Pearman et al, |
| 生态位保守性 Niche conservatism | 物种在大的时空尺度下生态位趋于不变(Wiens & Graham, |
| 生态位偏移 Niche shift | 物种的生态位(哈钦森生态位)宽度和/或位置的变化(Pearman et al, |
| Box 1 本文中涉及生态位相关的专业词汇释义 | |
|---|---|
| 专业词汇 Specialized words | 释义 Understanding definitions |
| 生态位追踪 Niche tracking | 物种可以通过在地理空间上遵循环境边界(如向更高海拔或更高纬度方向移动)来保持在适宜环境空间中的分布(Monahan & Hijmans, |
| 气候生态位 Climatic niche | 物种能够生存的非生物条件, 特别指由温度、降水等气候因子来限制的环境空间(Pearman et al, |
| 生态位保守性 Niche conservatism | 物种在大的时空尺度下生态位趋于不变(Wiens & Graham, |
| 生态位偏移 Niche shift | 物种的生态位(哈钦森生态位)宽度和/或位置的变化(Pearman et al, |
| 外来物种入侵过程 Non-native species invasion | 本土物种分布区扩张过程 Native species range expansion | 参考文献 Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 驱动因子 Driving factors | 人类协助过程为主 Human-assisted processes | 环境变化驱动为主 Environmental change drivers | 2015 |
| 空间尺度 Spatial scales | 长距离, 通常跨地理区系 Long distance, often across geographic realm | 短/中距离 Short/medium distance | 2019 |
| 发生速度 Occurring rates | 较快 Faster | 较慢 Slower | 2021 |
| 物种特征 Species traits | 具有较强预测性 Higher predictability | 具有较低预测性 Lower predictability | 2021 |
| 对新分布区的影响 Impacts on new ranges | 负面影响较大 More negative impacts | 负面影响较小 Less negative impacts | 2022 |
表1 外来入侵物种与本土物种在分布区变化中的主要差异
Table 1 Differences between invasive non-native species and native species during range shift
| 外来物种入侵过程 Non-native species invasion | 本土物种分布区扩张过程 Native species range expansion | 参考文献 Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 驱动因子 Driving factors | 人类协助过程为主 Human-assisted processes | 环境变化驱动为主 Environmental change drivers | 2015 |
| 空间尺度 Spatial scales | 长距离, 通常跨地理区系 Long distance, often across geographic realm | 短/中距离 Short/medium distance | 2019 |
| 发生速度 Occurring rates | 较快 Faster | 较慢 Slower | 2021 |
| 物种特征 Species traits | 具有较强预测性 Higher predictability | 具有较低预测性 Lower predictability | 2021 |
| 对新分布区的影响 Impacts on new ranges | 负面影响较大 More negative impacts | 负面影响较小 Less negative impacts | 2022 |
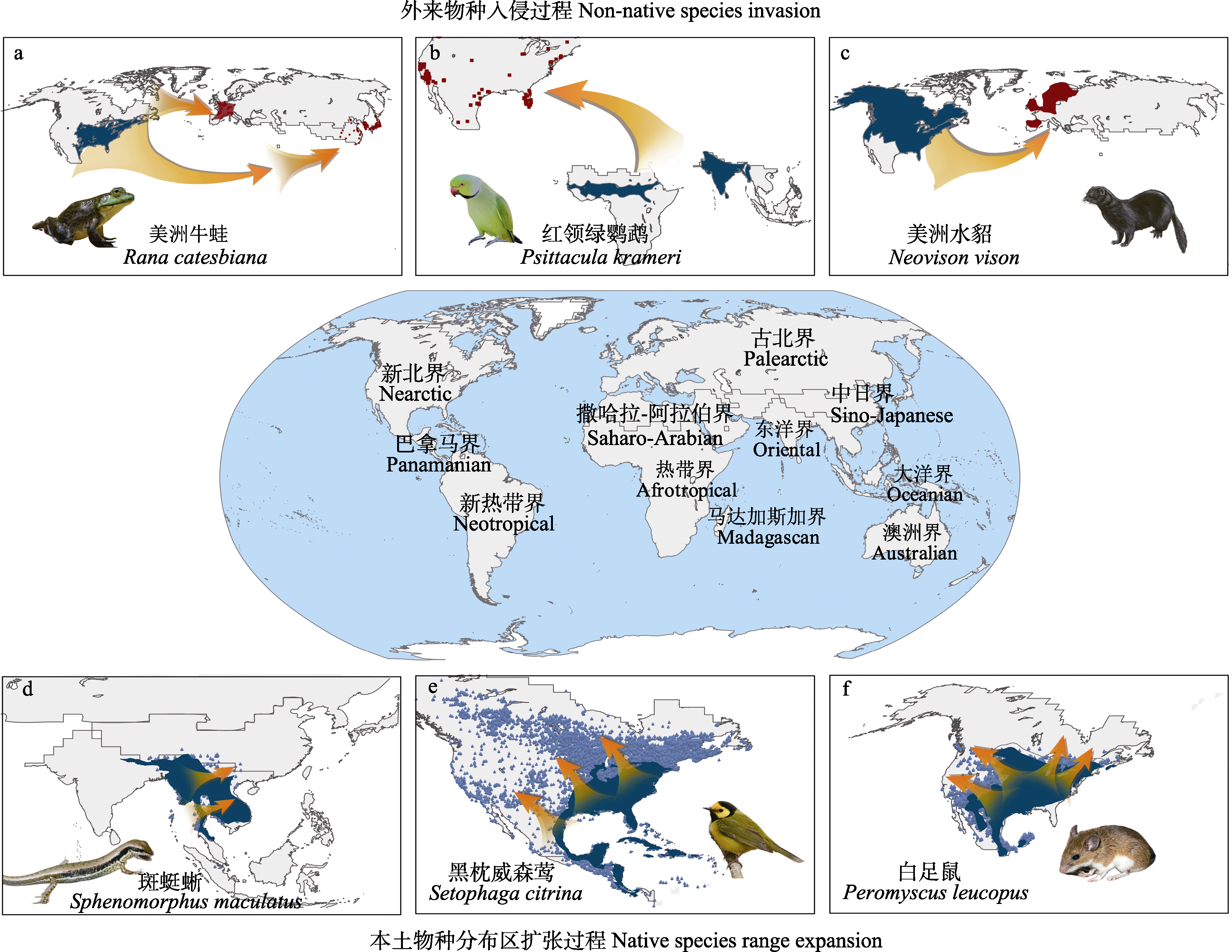
图1 典型的外来物种入侵与本土物种的分布区扩张案例。深蓝色区域代表物种历史自然分布区, 红色区域代表入侵区; 蓝色点和红色点分别代表扩张分布点和入侵区分布点。物种分布信息源自多个数据库(见附录1), 物种历史自然分布区源自世界自然保护联盟(IUCN, https://www.iucnredlist.org/); 地理区系源自Holt等(2013)。物种插图源自IUCN、全球生物多样性信息网络(GBIF, http://www.gbif.org/)和动物多样性网(ADW, https://animaldiversity.org/)。
Fig. 1 Typical examples on non-native species invasion and native species range expansion. Dark blue areas represent historical natural ranges, red areas represent invasive ranges; the blue and red dots represent the expansion and invasive distribution points, respectively. Species distribution information from multiple databases (see Appendix 1); historical natural range of species from the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN, https://www.iucnredlist.org/). The geographic realms from Holt et al, 2013. Species illustrations from IUCN, the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF, http://www.gbif.org/) and Animal Diversity Web (ADW, https://animaldiversity.org/).
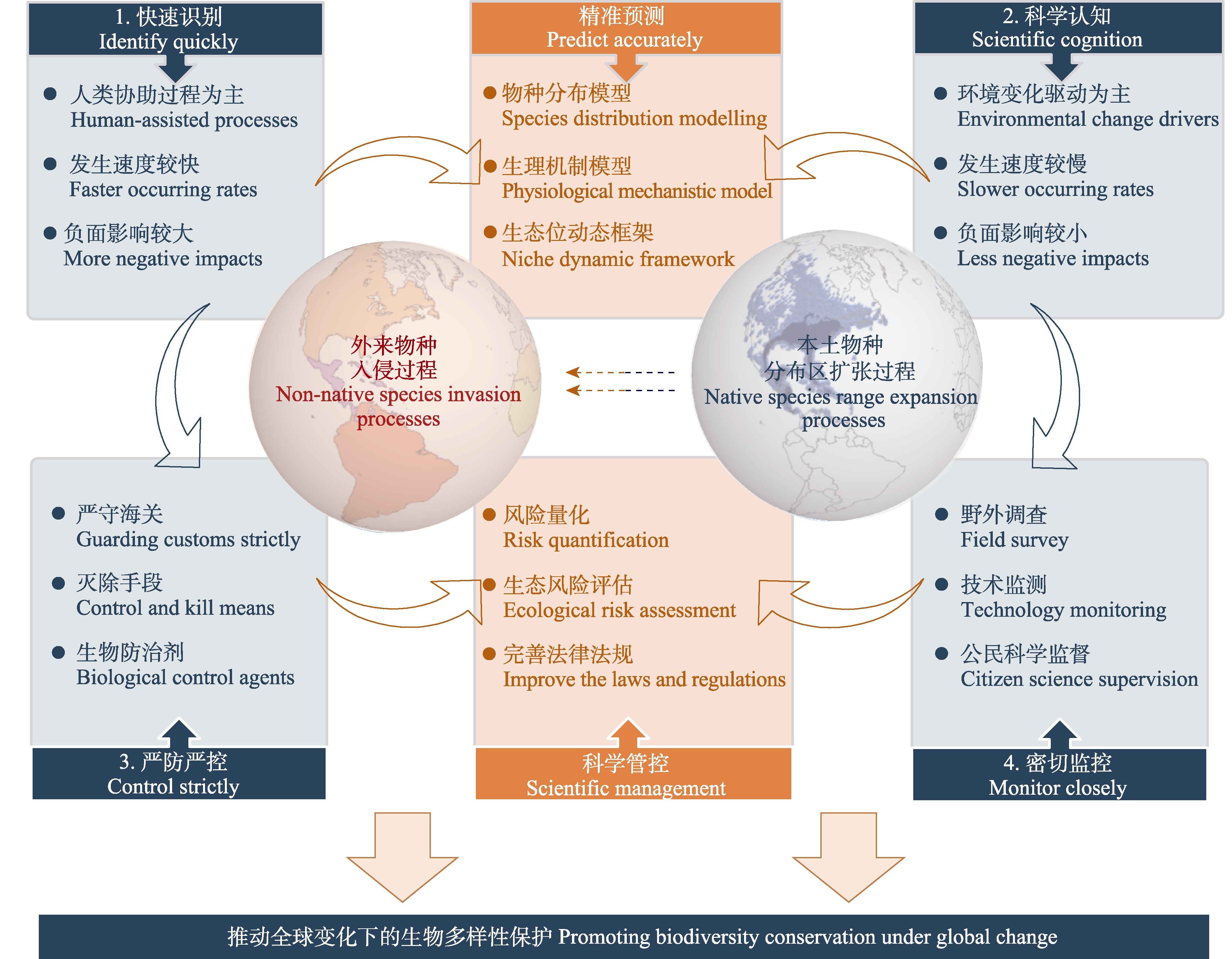
图2 全球变化下外来物种入侵过程和本土物种分布区扩张过程的管控建议
Fig. 2 Management suggestions of the non-native species invasion process and native species range expansion process under global change
| [1] | Abellán P, Tella JL, Carrete M, Cardador L, Anadón JD (2017) Climate matching drives spread rate but not establishment success in recent unintentional bird introductions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 114, 9385-9390. |
| [2] |
Allen MC, Nielsen AL, Peterson DL, Lockwood JL (2021) Terrestrial eDNA survey outperforms conventional approach for detecting an invasive pest insect within an agricultural ecosystem. Environmental DNA, 3, 1102-1112.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Allen WL, Street SE, Capellini I (2017) Fast life history traits promote invasion success in amphibians and reptiles. Ecology Letters, 20, 222-230.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Alves JM, Carneiro M, Day JP, Welch JJ, Duckworth JA, Cox TE, Letnic M, Strive T, Ferrand N, Jiggins FM (2022) A single introduction of wild rabbits triggered the biological invasion of Australia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 119, e2122734119. |
| [5] |
Alves RRDN, Nogueira EEG, Araujo HFP, Brooks SE (2010) Bird-keeping in the Caatinga, NE Brazil. Human Ecology, 38, 147-156.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Amand A (2000) Boiga irregularis (brown tree snakes) on Guam and its effect on fauna. Restoration and Reclamation Review, 6, 1-6. |
| [7] |
Angert AL, Crozier LG, Rissler LJ, Gilman SE, Tewksbury JJ, Chunco AJ (2011) Do species’ traits predict recent shifts at expanding range edges? Ecology Letters, 14, 677-689.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Bacher S, Blackburn TM, Essl F, Genovesi P, Heikkilä J, Jeschke JM, Jones G, Keller R, Kenis M, Kueffer C, Martinou AF, Nentwig W, Pergl J, Pyšek P, Rabitsch W, Richardson DM, Roy HE, Saul WC, Scalera R, Vilà M, Wilson JRU, Kumschick S (2018) Socio-economic impact classification of alien taxa (SEICAT). Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 9, 159-168.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Baker DJ, Garnett ST, O’Connor J, Ehmke G, Clarke RH, Woinarski JCZ, McGeoch MA (2019) Conserving the abundance of nonthreatened species. Conservation Biology, 33, 319-328.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Balmer DE, Gillings S, Caffrey B (2013) Bird Atlas 2007-2011: The Breeding and Wintering Birds of Britain and Ireland. British Trust for Ornithology, Thetford, Norfolk. |
| [11] |
Banks NC, Paini DR, Bayliss KL, Hodda M (2015) The role of global trade and transport network topology in the human-mediated dispersal of alien species. Ecology Letters, 18, 188-199.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Barnett LK, Prowse TAA, Peacock DE, Mutze GJ, Sinclair RG, Kovaliski J, Cooke BD, Bradshaw CJA (2018) Previous exposure to myxoma virus reduces survival of European rabbits during outbreaks of rabbit haemorrhagic disease. Journal of Applied Ecology, 55, 2954-2962.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Bates AE, Pecl GT, Frusher S, Hobday AJ, Wernberg T, Smale DA, Sunday JM, Hill NA, Dulvy NK, Colwell RK, Holbrook NJ, Fulton EA, Slawinski D, Feng M, Edgar GJ, Radford BT, Thompson PA, Watson RA (2014) Defining and observing stages of climate-mediated range shifts in marine systems. Global Environmental Change, 26, 27-38.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Beissinger SR, Riddell EA (2021) Why are species’ traits weak predictors of range shifts? Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 52, 47-66.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Bellard C, Rysman JF, Leroy B, Claud C, Mace GM (2017) A global picture of biological invasion threat on islands. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 1, 1862-1869. |
| [16] |
Berg MP, Kiers ET, Driessen G, van der Heijden M, Kooi BW, Kuenen F, Liefting M, Verhoef HA, Ellers J (2010) Adapt or disperse: Understanding species persistence in a changing world. Global Change Biology, 16, 587-598.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Bertelsmeier C, Keller L (2018) Bridgehead effects and role of adaptive evolution in invasive populations. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 33, 527-534.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Bertelsmeier C, Ollier S (2021) Bridgehead effects distort global flows of alien species. Diversity and Distributions, 27, 2180-2189.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Bertelsmeier C, Ollier S, Liebhold A, Keller L (2017) Recent human history governs global ant invasion dynamics. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 1, 0184. |
| [20] |
Birzu G, Matin S, Hallatschek O, Korolev KS (2019) Genetic drift in range expansions is very sensitive to density dependence in dispersal and growth. Ecology Letters, 22, 1817-1827.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Blackburn TM, Pyšek P, Bacher S, Carlton JT, Duncan RP, Jarošík V, Wilson JRU, Richardson DM (2011) A proposed unified framework for biological invasions. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 26, 333-339.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Bonesi L, Palazon S (2007) The American mink in Europe: Status, impacts, and control. Biological Conservation, 134, 470-483.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Broennimann O, Treier UA, Müller-Schärer H, Thuiller W, Peterson AT, Guisan A (2007) Evidence of climatic niche shift during biological invasion. Ecology Letters, 10, 701-709.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Capinha C, Essl F, Seebens H, Moser D, Pereira HM (2015) The dispersal of alien species redefines biogeography in the Anthropocene. Science, 348, 1248-1251.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Carter J, Leonard B (2002) A review of the literature on the worldwide distribution, spread of, and efforts to eradicate the coypu (Myocastor coypus). Wildlife Society Bulletin, 30, 162-175. |
| [26] | Cassey P, Blackburn TM, Sol D, Duncan RP, Lockwood JL (2004) Global patterns of introduction effort and establishment success in birds. Proceedings: Biological Sciences, 271, S405-S408. |
| [27] |
Catullo RA, Ferrier S, Hoffmann AA (2015) Extending spatial modelling of climate change responses beyond the realized niche: Estimating, and accommodating, physiological limits and adaptive evolution. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 24, 1192-1202.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Chen IC, Hill JK, Ohlemüller R, Roy DB, Thomas CD (2011) Rapid range shifts of species associated with high levels of climate warming. Science, 333, 1024-1026. |
| [29] | Chen IC, Shiu HJ, Benedick S, Holloway JD, Chey VK, Barlow HS, Hill JK, Thomas CD (2009) Elevation increases in moth assemblages over 42 years on a tropical mountain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 106, 1479-1483. |
| [30] |
Chen MH, Zhang C, Wang JD, Zhan ZJ, Chen JZ, Luan XF (2023) Distribution and niche overlap of American mink and Eurasian otter in Northeast China. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22289. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[陈敏豪, 张超, 王嘉栋, 湛振杰, 陈君帜, 栾晓峰 (2023) 北美水貂和欧亚水獭在东北地区的分布与生态位重叠. 生物多样性, 31, 22289.]
DOI |
|
| [31] |
Chen Y, Zhao L, Teng HJ, Shi CM, Liu QS, Zhang JX, Zhang YH (2021) Population genomics reveal rapid genetic differentiation in a recently invasive population of Rattus norvegicus. Frontiers in Zoology, 18, 6.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | Connallon T, Sgrò CM (2018) In search of a general theory of species’ range evolution. PLoS Biology, 16, e2006735. |
| [33] | Devictor V, van Swaay C, Brereton T, Brotons L, Chamberlain D, Heliölä J, Herrando S, Julliard R, Kuussaari M, Lindström Å, Reif J, Roy DB, Schweiger O, Settele J, Stefanescu C, van Strien A, van Turnhout C, Vermouzek Z, WallisDeVries M, Wynhoff I, Jiguet F (2012) Differences in the climatic debts of birds and butterflies at a continental scale. Nature Climate Change, 2, 121-124. |
| [34] |
Diagne C, Leroy B, Vaissière AC, Gozlan RE, Roiz D, Jarić I, Salles JM, Bradshaw CJA, Courchamp F (2021) High and rising economic costs of biological invasions worldwide. Nature, 592, 571-576.
DOI |
| [35] | Dorcas ME, Willson JD, Reed RN, Snow RW, Rochford MR, Miller MA, Meshaka WE Jr, Andreadis PT, Mazzotti FJ, Romagosa CM, Hart KM (2012) Severe mammal declines coincide with proliferation of invasive Burmese pythons in Everglades National Park. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 109, 2418-2422. |
| [36] | Du YB, Tu WS, Yang L, Gu DE, Guo BC, Liu X (2023) Review of the impacts of invasive alien vertebrates on biodiversity. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 53, 1035-1054. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杜元宝, 涂炜山, 杨乐, 顾党恩, 郭宝成, 刘宣 (2023) 外来入侵脊椎动物对生物多样性危害的研究进展. 中国科学: 生命科学, 53, 1035-1054.] | |
| [37] | Du YB, Xi YH, Yang ZX, Gu DE, Zhang ZX, Tu WS, Zeng Y, Cui RN, Yan Z, Xin YS, Jin WJ, Zhang Y, Yang L, Guo BC, Ke ZW, Rohr JR, Liu X (2024a) High risk of biological invasion from prayer animal release in China. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, e2647. |
| [38] | Du YB, Wang XY, Ashraf S, Tu WS, Xi YH, Cui RN, Chen SN, Yu JJ, Han LX, Xin YS, Qu YH, Liu X (2024b) Climate match is key to predict range expansion of the world’s worst invasive terrestrial vertebrates. Global Change Biology, 30, e17137. |
| [39] |
Duncan RP (2021) Time lags and the invasion debt in plant naturalisations. Ecology Letters, 24, 1363-1374.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Early R, Sax DF (2014) Climatic niche shifts between species’ native and naturalized ranges raise concern for ecological forecasts during invasions and climate change. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 23, 1356-1365.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Essl F, Dullinger S, Genovesi P, Hulme PE, Jeschke JM, Katsanevakis S, Kühn I, Lenzner B, Pauchard A, Pyšek P, Rabitsch W, Richardson DM, Seebens H, van Kleunen M, van der Putten WH, Vilà M, Bacher S (2019) A conceptual framework for range-expanding species that track human-induced environmental change. BioScience, 69, 908-919.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Estrada A, Morales-Castilla I, Caplat P, Early R (2016) Usefulness of species traits in predicting range shifts. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 31, 190-203.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Evans T, Kumschick S, Blackburn TM (2016) Application of the environmental impact classification for alien taxa (EICAT) to a global assessment of alien bird impacts. Diversity and Distributions, 22, 919-931.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Ficetola GF, Thuiller W, Miaud C (2007) Prediction and validation of the potential global distribution of a problematic alien invasive species—The American bullfrog. Diversity and Distributions, 13, 476-485.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Fournier A, Penone C, Pennino MG, Courchamp F (2019) Predicting future invaders and future invasions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 116, 7905-7910. |
| [46] |
Gervazoni P, Minuti G, Fuentes-Rodriguez D, Coetzee J, Sosa A, Sabater L, Franceschini C (2023) Citizen science improves the known and potential distribution of a strong wetland invader: Implications for niche modeling and invasion management. Environmental Management, 71, 1176-1187.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Gilman SE, Urban MC, Tewksbury J, Gilchrist GW, Holt RD (2010) A framework for community interactions under climate change. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 25, 325-331.
DOI URL |
| [48] | Gu SM, Qi TY, Rohr JR, Liu X (2023) Meta-analysis reveals less sensitivity of non-native animals than natives to extreme weather worldwide. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 7, 2004-2027. |
| [49] |
Guo FY, Lenoir J, Bonebrake TC (2018) Land-use change interacts with climate to determine elevational species redistribution. Nature Communications, 9, 1315.
DOI PMID |
| [50] |
Han LX, Zhang ZX, Tu WS, Zhang Q, Hong YH, Chen SN, Lin ZQ, Gu SM, Du YB, Wu ZJ, Liu X (2023) Preferred prey reduce species realized niche shift and improve range expansion prediction. Science of the Total Environment, 859, 160370.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Hanslowe E, Duquesnel J, Snow R, Falk B, Yackel Adams A, Metzger E, Collier M, Reed R (2018) Exotic predators may threaten another island ecosystem: A comprehensive assessment of python and boa reports from the Florida Keys. Management of Biological Invasions, 9, 369-377.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Hawkins CL, Bacher S, Essl F, Hulme PE, Jeschke JM, Kühn I, Kumschick S, Nentwig W, Pergl J, Pyšek P, Rabitsch W, Richardson DM, Vilà M, Wilson JRU, Genovesi P, Blackburn TM (2015) Framework and guidelines for implementing the proposed IUCN Environmental Impact Classification for Alien Taxa (EICAT). Diversity and Distributions, 21, 1360-1363.
DOI URL |
| [53] | Hickling R, Roy DB, Hill JK, Fox R, Thomas CD (2006) The distributions of a wide range of taxonomic groups are expanding polewards. Global Change Biology, 12, 450-455. |
| [54] |
Hitch AT, Leberg PL (2007) Breeding distributions of North American bird species moving north as a result of climate change. Conservation Biology, 21, 534-539.
PMID |
| [55] |
Holt BG, Lessard JP, Borregaard MK, Fritz SA, Araújo MB, Dimitrov D, Fabre PH, Graham CH, Graves GR, Jønsson KA, Nogués-Bravo D, Wang ZH, Whittaker RJ, Fjeldså J, Rahbek C (2013) An update of Wallace’s zoogeographic regions of the world. Science, 339, 74-78.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Hong YH, He YH, Lin ZQ, Du YB, Chen SN, Han LX, Zhang Q, Gu SM, Tu WS, Hu SW, Yuan ZY, Liu X (2022) Complex origins indicate a potential bridgehead introduction of an emerging amphibian invader (Eleutherodactylus planirostris) in China. NeoBiota, 77, 23-37.
DOI URL |
| [57] | Hurley BP, Robertson MP, Rouget M, Wilson JRU, Faulkner KT (2017) The balance of trade in alien species between South Africa and the rest of Africa. Bothalia-African Biodiversity & Conservation, 47, 1-16. |
| [58] | IPBES (2023) Summary for Policymakers of the Thematic Assessment Report on Invasive Alien Species and their Control of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. IPBES Secretariat, Bonn, Germany. |
| [59] | IPBES (2023) Climate Change 2023:Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC, Geneva, Switzerland. |
| [60] | Jackson HA (2021) Global invasion success of the rose-ringed parakeet. In: Naturalized Parrots of the World (ed. Pruett-Jones S), pp. 159-172. Princeton University Press, New Jersey, USA. |
| [61] | Jeschke JM, Strayer DL (2005) Invasion success of vertebrates in Europe and North America. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 102, 7198-7202. |
| [62] |
Kosoy M, Khlyap L, Cosson JF, Morand S (2015) Aboriginal and invasive rats of genus Rattus as hosts of infectious agents. Vector Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 15, 3-12.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Kraus F (2015) Impacts from invasive reptiles and amphibians. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 46, 75-97.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Kraus F, Campbell EW (2002) Human-mediated escalation of a formerly eradicable problem: The invasion of Caribbean frogs in the Hawaiian Islands. Biological Invasions, 4, 327-332.
DOI URL |
| [65] | Lenoir J, Bertrand R, Comte L, Bourgeaud L, Hattab T, Murienne J, Grenouillet G (2020) Species better track climate warming in the oceans than on land. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 4, 1044-1059. |
| [66] |
Lenoir J, Svenning JC (2015) Climate-related range shifts—A global multidimensional synthesis and new research directions. Ecography, 38, 15-28.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Leung B, Roura-Pascual N, Bacher S, Heikkilä J, Brotons L, Burgman MA, Dehnen-Schmutz K, Essl F, Hulme PE, Richardson DM, Sol D, Vilà M, Rejmanek M (2012) TEASIng apart alien species risk assessments: A framework for best practices. Ecology Letters, 15, 1475-1493.
DOI PMID |
| [68] |
Li S, Wang DJ, Chen XH, Bu HL, Liu XG, Jin T (2021) The wildlife camera-trapping dataset of Laohegou Protected Area, Sichuan Province (2011-2015). Biodiversity Science, 29, 1170-1174. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [李晟, 王大军, 陈祥辉, 卜红亮, 刘小庚, 靳彤 (2021) 四川老河沟保护地2011-2015年野生动物红外相机监测数据集. 生物多样性, 29, 1170-1174.] | |
| [69] |
Li YM, Liu X, Li XP, Petitpierre B, Guisan A (2014) Residence time, expansion toward the equator in the invaded range and native range size matter to climatic niche shifts in non-native species. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 23, 1094-1104.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Lin ZQ, Hong YH, Chen SN, Zhang Q, Han LX, Tu WS, Du YB, Gu SM, Yuan ZY, Hu SW, Liu X (2023) Emerging non-native amphibians require immediate prevention management in a megacity of South China. BioInvasions Records, 12, 731-744.
DOI URL |
| [71] | Liu CL, Wolter C, Xian WW, Jeschke JM (2020) Most invasive species largely conserve their climatic niche. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 117, 23643-23651. |
| [72] |
Liu X, Li XP, Liu ZT, Tingley R, Kraus F, Guo ZW, Li YM (2014) Congener diversity, topographic heterogeneity and human-assisted dispersal predict spread rates of alien herpetofauna at a global scale. Ecology Letters, 17, 821-829.
DOI PMID |
| [73] | Liu X, Li YM (2009) Aquaculture enclosures relate to the establishment of feral populations of introduced species. PLoS ONE, 4, e6199. |
| [74] |
Liu X, Rohr JR, Li XP, Deng T, Li WH, Li YM (2021) Climate extremes, variability, and trade shape biogeographical patterns of alien species. Current Zoology, 67, 393-402.
DOI URL |
| [75] | Liu X, Rohr JR, Li YM (2013) Climate, vegetation, introduced hosts and trade shape a global wildlife pandemic. Proceedings: Biological Sciences, 280, 20122506. |
| [76] | Lovell RS, Blackburn TM, Dyer EE, Pigot AL (2021) Environmental resistance predicts the spread of alien species. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 5, 322-329. |
| [77] | Lowe S, Browne M, Boudjelas S, Poorter MD (2000) 100 of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species: A Selection from the Global Invasive Species Database. Invasive Species Specialist Group, Auckland. |
| [78] |
Ma L, Conradie SR, Crawford CL, Gardner AS, Kearney MR, Maclean IM, McKechnie AE, Mi CR, Senior RA, Wilcove DS (2023) Global patterns of climate change impacts on desert bird communities. Nature Communications, 14, 211.
DOI PMID |
| [79] | Ma M (2010) Bird expansion to east and the variation of geography distribution in Xinjiang, China: Cases of the invasive species as greenfinch and myna. Arid Land Geography, 33, 540-546. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马鸣 (2010) 鸟类“东扩”现象与地理分布格局变迁——以入侵种欧金翅和家八哥为例. 干旱区地理, 33, 540-546.] | |
| [80] | MacLean IMD, Wilson RJ (2011) Recent ecological responses to climate change support predictions of high extinction risk. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108, 12337-12342. |
| [81] |
MacLean SA, Beissinger SR (2017) Species’ traits as predictors of range shifts under contemporary climate change: A review and meta-analysis. Global Change Biology, 23, 4094-4105.
DOI PMID |
| [82] |
Magalhães ALB, Azevedo-Santos VM, Pelicice FM (2021) Caught in the act: Youtube™ reveals invisible fish invasion pathways in Brazil. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 37, 125-128.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
Malcolm JR, Liu CR, Neilson RP, Hansen L, Hannah L (2006) Global warming and extinctions of endemic species from biodiversity hotspots. Conservation Biology, 20, 538-548.
DOI PMID |
| [84] | McDonald J, McCormack PC, Fleming AJ, Harris RMB, Lockwood M (2016) Rethinking legal objectives for climate-adaptive conservation. Ecology and Society, 21, art25. |
| [85] |
Melbourne-Thomas J, Audzijonyte A, Brasier MJ, Cresswell KA, Fogarty HE, Haward M, Hobday AJ, Hunt HL, Ling SD, McCormack PC, Mustonen T, Mustonen K, Nye JA, Oellermann M, Trebilco R, van Putten I, Villanueva C, Watson RA, Pecl GT (2021) Poleward bound: Adapting to climate-driven species redistribution. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 32, 231-251.
DOI |
| [86] | Menchetti M, Mori E, Angelici FM (2016) Effects of the recent world invasion by ring-necked parakeets Psittacula krameri. In: Problematic Wildlife: A Cross-disciplinary Approach (ed. Angelici FM), pp. 253-266. Springer International Publishing, Cham. |
| [87] |
Monahan WB, Hijmans RJ (2008) Ecophysiological constraints shape autumn migratory response to climate change in the North American field sparrow. Biology Letters, 4, 595-598.
DOI PMID |
| [88] |
Moreno-Rueda G, Pleguezuelos JM, Pizarro M, Montori A (2012) Northward shifts of the distributions of Spanish reptiles in association with climate change. Conservation Biology, 26, 278-283.
DOI PMID |
| [89] |
Moscarella RA, Hoffman SMG, Myers P, Yahnke CJ, Lundrigan BL (2019) Genetic and demographic analysis of invasive Peromyscus leucopus in the Northern Great Lakes Region. Journal of Mammalogy, 100, 345-353.
DOI |
| [90] | Mungomery RW (1935) The giant American toad (Bufo marinus). Cane Growers Quarterly Bulletin, 3, 21-27. |
| [91] |
Myers P, Lundrigan BL, Hoffman SMG, Haraminac AP, Seto SH (2009) Climate-induced changes in the small mammal communities of the Northern Great Lakes Region. Global Change Biology, 15, 1434-1454.
DOI URL |
| [92] |
O’Hanlon SJ, Rieux A, Farrer RA, Rosa GM, Waldman B, Bataille A, Kosch TA, Murray KA, Brankovics B, Fumagalli M, Martin MD, Wales N, Alvarado-Rybak M, Bates KA, Berger L, Böll S, Brookes L, Clare F, Courtois EA, Cunningham AA, Doherty-Bone TM, Ghosh P, Gower DJ, Hintz WE, Höglund J, Jenkinson TS, Lin CF, Laurila A, Loyau A, Martel A, Meurling S, Miaud C, Minting P, Pasmans F, Schmeller DS, Schmidt BR, Shelton JMG, Skerratt LF, Smith F, Soto-Azat C, Spagnoletti M, Tessa G, Toledo LF, Valenzuela-Sánchez A, Verster R, Vörös J, Webb RJ, Wierzbicki C, Wombwell E, Zamudio KR, Aanensen DM, James TY, Gilbert MTP, Weldon C, Bosch J, Balloux F, Garner TWJ, Fisher MC (2018) Recent Asian origin of chytrid fungi causing global amphibian declines. Science, 360, 621-627.
DOI PMID |
| [93] |
Pagad S, Genovesi P, Carnevali L, Scalera R, Clout M (2015) IUCN SSC Invasive Species Specialist Group: Invasive alien species information management supporting practitioners, policy makers and decision takers. Management of Biological Invasions, 6, 127-135.
DOI URL |
| [94] |
Parmesan C, Yohe G (2003) A globally coherent fingerprint of climate change impacts across natural systems. Nature, 421, 37-42.
DOI |
| [95] |
Pearman PB, Guisan A, Broennimann O, Randin CF (2008) Niche dynamics in space and time. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 23, 149-158.
DOI URL |
| [96] | Pecl GT, Araújo MB, Bell JD, Blanchard J, Bonebrake TC, Chen IC, Clark TD, Colwell RK, Danielsen F, Evengård B, Falconi L, Ferrier S, Frusher S, Garcia RA, Griffis RB, Hobday AJ, Janion-Scheepers C, Jarzyna MA, Jennings S, Lenoir J, Linnetved HI, Martin VY, McCormack PC, McDonald J, Mitchell NJ, Mustonen T, Pandolfi JM, Pettorelli N, Popova E, Robinson SA, Scheffers BR, Shaw JD, Sorte CJB, Strugnell JM, Sunday JM, Tuanmu MN, Vergés A, Villanueva C, Wernberg T, Wapstra E, Williams SE (2017) Biodiversity redistribution under climate change: Impacts on ecosystems and human well-being. Science, 355, eaai9214. |
| [97] |
Peterson AT (2011) Ecological niche conservatism: A time-structured review of evidence. Journal of Biogeography, 38, 817-827.
DOI URL |
| [98] |
Phillips BL, Brown GP, Greenlees M, Webb JK, Shine R (2007) Rapid expansion of the cane toad (Bufo marinus) invasion front in tropical Australia. Austral Ecology, 32, 169-176.
DOI URL |
| [99] |
Platts PJ, Mason SC, Palmer G, Hill JK, Oliver TH, Powney GD, Fox R, Thomas CD (2019) Habitat availability explains variation in climate-driven range shifts across multiple taxonomic groups. Scientific Reports, 9, 15039.
DOI PMID |
| [100] |
Poloczanska ES, Brown CJ, Sydeman WJ, Kiessling W, Schoeman DS, Moore PJ, Brander K, Bruno JF, Buckley LB, Burrows MT, Duarte CM, Halpern BS, Holding J, Kappel CV, O’Connor MI, Pandolfi JM, Parmesan C, Schwing F, Thompson SA, Richardson AJ (2013) Global imprint of climate change on marine life. Nature Climate Change, 3, 919-925.
DOI |
| [101] | Pyšek P, Richardson DM (2007) Traits associated with invasiveness in alien plants: Where do we stand? Biological Invasions, 193, 97-125. |
| [102] |
Rew LJ, McDougall KL, Alexander JM, Daehler CC, Essl F, Haider S, Kueffer C, Lenoir J, Milbau A, Nuñez MA, Pauchard A, Rabitsch W (2020) Moving up and over: Redistribution of plants in alpine, Arctic, and Antarctic ecosystems under global change. Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research, 52, 651-665.
DOI URL |
| [103] |
Robertson PA, Adriaens T, Lambin X, Mill A, Roy S, Shuttleworth CM, Sutton-Croft M (2017) The large-scale removal of mammalian invasive alien species in Northern Europe. Pest Management Science, 73, 273-279.
DOI PMID |
| [104] |
Robertson PA, Mill A, Novoa A, Jeschke JM, Essl F, Gallardo B, Geist J, Jarić I, Lambin X, Musseau C, Pergl J, Pyšek P, Rabitsch W, von Schmalensee M, Shirley M, Strayer DL, Stefansson RA, Smith K, Booy O (2020) A proposed unified framework to describe the management of biological invasions. Biological Invasions, 22, 2633-2645.
DOI |
| [105] | Rushing CS, Royle JA, Ziolkowski DJ Jr, Pardieck KL (2020) Migratory behavior and winter geography drive differential range shifts of eastern birds in response to recent climate change. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 117, 12897-12903. |
| [106] |
Sales LP, Rebouças R, Toledo LF (2021) Native range climate is insufficient to predict anuran invasive potential. Biological Invasions, 23, 2635-2647.
DOI |
| [107] |
Sax DF, Early R, Bellemare J (2013) Niche syndromes, species extinction risks, and management under climate change. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 28, 517-523.
DOI URL |
| [108] |
Scheffers BR, Pecl G (2019) Persecuting, protecting or ignoring biodiversity under climate change. Nature Climate Change, 9, 581-586.
DOI |
| [109] | Schloss CA, Nuñez TA, Lawler JJ (2012) Dispersal will limit ability of mammals to track climate change in the Western Hemisphere. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 109, 8606-8611. |
| [110] |
Schulz AN, Lucardi RD, Marsico TD (2019) Successful invasions and failed biocontrol: The role of antagonistic species interactions. BioScience, 69, 711-724.
DOI URL |
| [111] |
Seebens H, Bacher S, Blackburn TM, Capinha C, Dawson W, Dullinger S, Genovesi P, Hulme PE, van Kleunen M, Kühn I, Jeschke JM, Lenzner B, Liebhold AM, Pattison Z, Pergl J, Pyšek P, Winter M, Essl F (2021) Projecting the continental accumulation of alien species through to 2050. Global Change Biology, 27, 970-982.
DOI URL |
| [112] |
Seebens H, Blackburn TM, Dyer EE, Genovesi P, Hulme PE, Jeschke JM, Pagad S, Pyšek P, Winter M, Arianoutsou M, Bacher S, Blasius B, Brundu G, Capinha C, Celesti-Grapow L, Dawson W, Dullinger S, Fuentes N, Jäger H, Kartesz J, Kenis M, Kreft H, Kühn I, Lenzner B, Liebhold A, Mosena A, Moser D, Nishino M, Pearman D, Pergl J, Rabitsch W, Rojas-Sandoval J, Roques A, Rorke S, Rossinelli S, Roy HE, Scalera R, Schindler S, Štajerová K, Tokarska-Guzik B, van Kleunen M, Walker K, Weigelt P, Yamanaka T, Essl F (2017) No saturation in the accumulation of alien species worldwide. Nature Communications, 8, 14435.
DOI PMID |
| [113] |
Shine R (2010) The ecological impact of invasive cane toads (Bufo marinus) in Australia. The Quarterly Review of Biology, 85, 253-291.
DOI URL |
| [114] |
Simberloff D (2009a) The role of propagule pressure in biological invasions. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 40, 81-102.
DOI URL |
| [115] |
Simberloff D (2009b) We can eliminate invasions or live with them. Successful management projects. Biological Invasions, 11, 149-157.
DOI URL |
| [116] |
Simberloff D, Martin JL, Genovesi P, Maris V, Wardle DA, Aronson J, Courchamp F, Galil B, García-Berthou E, Pascal M, Pyšek P, Sousa R, Tabacchi E, Vilà M (2013) Impacts of biological invasions: What’s what and the way forward. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 28, 58-66.
DOI URL |
| [117] |
Sohrabi S, Pergl J, Pyšek P, Foxcroft LC, Gherekhloo J (2021) Quantifying the potential impact of alien plants of Iran using the Generic Impact Scoring System (GISS) and Environmental Impact Classification for Alien Taxa (EICAT). Biological Invasions, 23, 2435-2449.
DOI |
| [118] | Spatz DR, Zilliacus KM, Holmes ND, Butchart SHM, Genovesi P, Ceballos G, Tershy BR, Croll DA (2017) Globally threatened vertebrates on islands with invasive species. Science Advances, 3, e1603080. |
| [119] |
Spiegel CS, Hart PJ, Woodworth BL, Tweed EJ, Lebrun JJ (2006) Distribution and abundance of forest birds in low-altitude habitat on Hawai'i Island: Evidence for range expansion of native species. Bird Conservation International, 16, 175-185.
DOI URL |
| [120] |
Steinbauer MJ, Grytnes JA, Jurasinski G, Kulonen A, Lenoir J, Pauli H, Rixen C, Winkler M, Bardy-Durchhalter M, Barni E, Bjorkman AD, Breiner FT, Burg S, Czortek P, Dawes MA, Delimat A, Dullinger S, Erschbamer B, Felde VA, Fernández-Arberas O, Fossheim KF, Gómez-García D, Georges D, Grindrud ET, Haider S, Haugum SV, Henriksen H, Herreros MJ, Jaroszewicz B, Jaroszynska F, Kanka R, Kapfer J, Klanderud K, Kühn I, Lamprecht A, Matteodo M, di Cella UM, Normand S, Odland A, Olsen SL, Palacio S, Petey M, Piscová V, Sedlakova B, Steinbauer K, Stöckli V, Svenning JC, Teppa G, Theurillat JP, Vittoz P, Woodin SJ, Zimmermann NE, Wipf S (2018) Accelerated increase in plant species richness on mountain summits is linked to warming. Nature, 556, 231-234.
DOI |
| [121] |
Stenberg JA, Sundh I, Becher PG, Björkman C, Dubey M, Egan PA, Friberg H, Gil JF, Jensen DF, Jonsson M, Karlsson M, Khalil S, Ninkovic V, Rehermann G, Vetukuri RR, Viketoft M (2021) When is it biological control? A framework of definitions, mechanisms, and classifications. Journal of Pest Science, 94, 665-676.
DOI |
| [122] | Stringham OC, Lockwood JL (2021) Managing propagule pressure to prevent invasive species establishments: Propagule size, number, and risk-release curve. Ecological Applications, 31, e02314. |
| [123] |
Strubbe D, Broennimann O, Chiron F, Matthysen E (2013) Niche conservatism in non-native birds in Europe: Niche unfilling rather than niche expansion. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 22, 962-970.
DOI URL |
| [124] |
Strubbe D, Jiménez L, Barbosa AM, Davis AJS, Lens L, Rahbek C (2023) Mechanistic models project bird invasions with accuracy. Nature Communications, 14, 2520.
DOI PMID |
| [125] |
Stuart KC, Hofmeister NR, Zichello JM, Rollins LA (2023) Global invasion history and native decline of the common starling: Insights through genetics. Biological Invasions, 25, 1291-1316.
DOI |
| [126] |
Sullivan BL, Aycrigg JL, Barry JH, Bonney RE, Bruns N, Cooper CB, Damoulas T, Dhondt AA, Dietterich T, Farnsworth A, Fink D, Fitzpatrick JW, Fredericks T, Gerbracht J, Gomes C, Hochachka WM, Iliff MJ, Lagoze C, La Sorte FA, Merrifield M, Morris W, Phillips TB, Reynolds M, Rodewald AD, Rosenberg KV, Trautmann NM, Wiggins A, Winkler DW, Wong WK, Wood CL, Yu J, Kelling S (2014) The eBird enterprise: An integrated approach to development and application of citizen science. Biological Conservation, 169, 31-40.
DOI URL |
| [127] |
Thomas CD, Lennon JJ (1999) Birds extend their ranges northwards. Nature, 399, 213.
DOI URL |
| [128] | Titley MA, Butchart SHM, Jones VR, Whittingham MJ, Willis SG (2021) Global inequities and political borders challenge nature conservation under climate change. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 118, e2011204118. |
| [129] |
Urban MC (2015) Accelerating extinction risk from climate change. Science, 348, 571-573.
DOI PMID |
| [130] |
Urban MC (2020) Climate-tracking species are not invasive. Nature Climate Change, 10, 382-384.
DOI |
| [131] |
van Kleunen M, Weber E, Fischer M (2010) A meta-analysis of trait differences between invasive and non-invasive plant species. Ecology Letters, 13, 235-245.
DOI PMID |
| [132] |
Vilà M, Basnou C, Pyšek P, Josefsson M, Genovesi P, Gollasch S, Nentwig W, Olenin S, Roques A, Roy D, Hulme PE, Partners D (2010) How well do we understand the impacts of alien species on ecosystem services? A pan-European, cross-taxa assessment. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 8, 135-144.
DOI URL |
| [133] |
Wallingford PD, Morelli TL, Allen JM, Beaury EM, Blumenthal DM, Bradley BA, Dukes JS, Early R, Fusco EJ, Goldberg DE, Ibáñez I, Laginhas BB, Vilà M, Sorte CJB (2020) Adjusting the lens of invasion biology to focus on the impacts of climate-driven range shifts. Nature Climate Change, 10, 398-405.
DOI |
| [134] |
Wan FH, Guo JY, Wang DH (2002) Alien invasive species in China: Their damages and management strategies. Biodiversity Science, 10, 119-125. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[万方浩, 郭建英, 王德辉 (2002) 中国外来入侵生物的危害与管理对策. 生物多样性, 10, 119-125.]
DOI |
|
| [135] | Wang KB, Zhou SL, Li ZQ, Yang L (2019) Exotic bird species in breeding birds in typical urban parks in Tibet. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 31(5), 31-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汪开宝, 周生灵, 李忠秋, 杨乐 (2019) 西藏典型城市公园繁殖鸟类中的外来鸟种. 环境监测管理与技术, 31(5), 31-34.] | |
| [136] |
Wang XY, Yi T, Li WH, Xu CX, Wang SP, Wang YP, Li YM, Liu X (2022) Anthropogenic habitat loss accelerates the range expansion of a global invader. Diversity and Distributions, 28, 1610-1619.
DOI URL |
| [137] |
Wessely J, Hülber K, Gattringer A, Kuttner M, Moser D, Rabitsch W, Schindler S, Dullinger S, Essl F (2017) Habitat-based conservation strategies cannot compensate for climate-change-induced range loss. Nature Climate Change, 7, 823-827.
DOI |
| [138] |
Wiens JJ, Graham CH (2005) Niche conservatism: Integrating evolution, ecology, and conservation biology. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 36, 519-539.
DOI URL |
| [139] |
Williams JW, Jackson ST (2007) Novel climates, no-analog communities, and ecological surprises. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 5, 475-482.
DOI URL |
| [140] |
Wilson JRU, García-Díaz P, Cassey P, Richardson DM, Pyšek P, Blackburn TM (2016) Biological invasions and natural colonisations are different—The need for invasion science. NeoBiota, 31, 87-98.
DOI URL |
| [141] |
Wu JG (2016) Can changes in the distribution of lizard species over the past 50 years be attributed to climate change? Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 125, 785-798.
DOI URL |
| [142] |
Wu ZJ, Wang YP, Li YM (2004) Natural populations of bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) and their potential threat in the east of Zhejiang Province. Biodiversity Science, 12, 441-446. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[武正军, 王彦平, 李义明 (2004) 浙江东部牛蛙的自然种群及潜在危害. 生物多样性, 12, 441-446.]
DOI |
|
| [143] | Xia ZQ, Gu JN, Wen Y, Cao XK, Gao YC, Li SG, Haffner GD, MacIsaac HJ, Zhan AB (2023) eDNA-based detection reveals invasion risks of a biofouling bivalve in the world’s largest water diversion project. Ecological Applications, 34, e2826. |
| [144] | Xin YS, Yang ZX, Du YB, Cui RN, Xi YH, Liu X (2023) Vulnerability of protected areas to future climate change, land use modification, and biological invasions in China. Ecological Applications, 34, e2831. |
| [145] |
Yan Z, Hu SH, Du YB, Liang J, Chen SN, Han LX, Hong YH, Lin ZQ, Tu WS, Li YX, Wang YC, Yu JJ, Qi TY, Li WJ, Zhao PY, Xi YH, Zhang Q, Cui RN, Gu SM, Liu X (2024) Social media unveils the hidden but high magnitude of human-mediated biological invasions in China. Current Biology, 34, R47-R49.
DOI URL |
| [146] |
Zhang L, Rohr J, Cui RN, Xin YS, Han LX, Yang XN, Gu SM, Du YB, Liang J, Wang XY, Wu ZJ, Hao Q, Liu X (2022) Biological invasions facilitate zoonotic disease emergences. Nature Communications, 13, 1762.
DOI PMID |
| [147] |
Zhang Q, Wang YP, Liu X (2024) Risk of introduction and establishment of alien vertebrate species in transboundary neighboring areas. Nature Communications, 15, 870.
DOI PMID |
| [148] |
Zu KL, Wang ZH (2022) Research progress on the elevational distribution of mountain species in response to climate change. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21451. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[祖奎玲, 王志恒 (2022) 山地物种海拔分布对气候变化响应的研究进展. 生物多样性, 30, 21451.]
DOI |
| [1] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [2] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [3] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [4] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [5] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| [6] | 周志华, 金效华, 罗颖, 李迪强, 岳建兵, 刘芳, 何拓, 李希, 董晖, 罗鹏. 中国林草部门落实《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》的机制、成效分析及建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24487-. |
| [7] | 刘立, 臧明月, 马月, 万雅琼, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 刘燕. 央地协同推动国家生物多样性战略和行动计划执行的措施、进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24532-. |
| [8] | 刘淑琪, 崔东, 江智诚, 刘江慧, 闫江超. 短期氮、水添加和刈割减弱了苦豆子型退化草地土壤生物多样性与生态系统多功能性的联系[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24305-. |
| [9] | 宋阳, 柳军, 何少林, 徐薇, 程琛, 刘博, 余绩庆. 我国能源企业生物多样性保护主流化管理路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24345-. |
| [10] | 陈楠, 张全国. 实验进化研究途径[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24171-. |
| [11] | 苏荣菲, 陈睿山, 俞霖琳, 吴婧彬, 康燕. 基于红外相机调查的上海市长宁区社区生境花园生物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24068-. |
| [12] | 董云伟, 鲍梦幻, 程娇, 陈义永, 杜建国, 高养春, 胡利莎, 李心诚, 刘春龙, 秦耿, 孙进, 王信, 杨光, 张崇良, 张雄, 张宇洋, 张志新, 战爱斌, 贺强, 孙军, 陈彬, 沙忠利, 林强. 中国海洋生物地理学研究进展和热点: 物种分布模型及其应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23453-. |
| [13] | 蔡颖莉, 朱洪革, 李家欣. 中国生物多样性保护政策演进、主要措施与发展趋势[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23386-. |
| [14] | 鄢德奎. 中国生物多样性保护政策的共同要素、不足和优化建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23293-. |
| [15] | 刘荆州, 钱易鑫, 张燕雪丹, 崔凤. 基于潜在迪利克雷分布(LDA)模型的旗舰物种范式研究进展与启示[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23439-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()