



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (2): 144-154. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019253 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019253
所属专题: 生物入侵
张家真1, 高春蕾1,2,3,*( ), 李艳1,2,3, 孙萍1,2,3, 王宗灵1,2,3
), 李艳1,2,3, 孙萍1,2,3, 王宗灵1,2,3
收稿日期:2019-08-14
接受日期:2019-12-17
出版日期:2020-02-20
发布日期:2019-12-24
通讯作者:
高春蕾
基金资助:
Jiazhen Zhang1, Chunlei Gao1,2,3,*( ), Yan Li1,2,3, Ping Sun1,2,3, Zongling Wang1,2,3
), Yan Li1,2,3, Ping Sun1,2,3, Zongling Wang1,2,3
Received:2019-08-14
Accepted:2019-12-17
Online:2020-02-20
Published:2019-12-24
Contact:
Chunlei Gao
摘要:
为了探究外来船舶压载舱沉积物中甲藻休眠包囊的种类组成及外来甲藻入侵风险, 本文根据包囊及其萌发细胞的形态特征辅以分子生物学信息对江阴港5艘外来船舶压载舱沉积物中的活体甲藻休眠包囊的种类进行鉴定和分析。共鉴定出甲藻休眠包囊29种(不含3种未鉴定种), 包括膝沟藻类、钙甲藻类、裸甲藻类、翼甲藻类以及原多甲藻类, 活体休眠包囊密度介于0.73-44.3 cysts/g DW。其中塔玛亚历山大藻复合种(Alexandrium tamarense species complex)、网状原角藻(Protoceratium reticulatum)、具刺膝沟藻(Gonyaulax spinifera)等有毒有害甲藻的包囊在取样的5艘船舶中均有发现。此外还发现了多种中国近海未报道的甲藻包囊种类, 其中一种经过分子手段确定为异常亚历山大藻(Alexandrium insuetum)包囊, 萌发和培养实验表明该种包囊能够在中国近海萌发并增殖, 有潜在的入侵风险和暴发赤潮的可能性。
张家真, 高春蕾, 李艳, 孙萍, 王宗灵 (2020) 江阴港口外来船舶压载舱沉积物中甲藻包囊种类及组成. 生物多样性, 28, 144-154. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019253.
Jiazhen Zhang, Chunlei Gao, Yan Li, Ping Sun, Zongling Wang (2020) Species composition of dinoflagellates cysts in ballast tank sediments of foreign ships berthed in Jiangyin Port. Biodiversity Science, 28, 144-154. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019253.
| 船号 Ship number | 压载水替换港口(按时间顺序排列) Port for replace of ballast water (in order of time) |
|---|---|
| 1号 Number 1 | 巴尔的摩港→伊塔瓜伊港→乍浦港→吉朗港→波特兰港→阿德莱德港→昂山港 Baltimore→Itaguai→Zhapu→Geelong→Portland→Adelaide→Onsan |
| 2号 Number 2 | 美国→巴拿马→蔚山港 USA→Panama→Ulsan |
| 3号 Number 3 | 富查伊拉港→吉赞港→拉文纳港→瑞山港→新加坡→台中港→太仓港→蔚山港 Fujairah→Jizan→Ravenna→Daesan→Singapore→Taichung→Taicang→Ulsan |
| 4号 Number 4 | 圣洛伦索港→格拉德斯通港 Arslo→Auglt |
| 5号 Number 5 | 大阪港→宁波港 Osaka→Ningbo |
表1 江阴港口外来船舶压载水替换地点
Table 1 Location of ballast water exchange sites of foreign ships berthed in Jiangyin Port
| 船号 Ship number | 压载水替换港口(按时间顺序排列) Port for replace of ballast water (in order of time) |
|---|---|
| 1号 Number 1 | 巴尔的摩港→伊塔瓜伊港→乍浦港→吉朗港→波特兰港→阿德莱德港→昂山港 Baltimore→Itaguai→Zhapu→Geelong→Portland→Adelaide→Onsan |
| 2号 Number 2 | 美国→巴拿马→蔚山港 USA→Panama→Ulsan |
| 3号 Number 3 | 富查伊拉港→吉赞港→拉文纳港→瑞山港→新加坡→台中港→太仓港→蔚山港 Fujairah→Jizan→Ravenna→Daesan→Singapore→Taichung→Taicang→Ulsan |
| 4号 Number 4 | 圣洛伦索港→格拉德斯通港 Arslo→Auglt |
| 5号 Number 5 | 大阪港→宁波港 Osaka→Ningbo |
| 引物 Primer | 序列 Sequence (5′-3′) | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|
| ITS-F | CCTCGTAACAAGGHTCCGTAGGT | |
| ITS-R | CAGATGCTTAARTTCAGCRGG | |
| LSU-F | ACCCGCTGAATTTAAGCATA | |
| LSU-R | CCTTGGTCCGTGTTTCAAGA |
表2 PCR扩增引物及其序列
Table 2 Primers used for amplification and sequencing
| 引物 Primer | 序列 Sequence (5′-3′) | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|
| ITS-F | CCTCGTAACAAGGHTCCGTAGGT | |
| ITS-R | CAGATGCTTAARTTCAGCRGG | |
| LSU-F | ACCCGCTGAATTTAAGCATA | |
| LSU-R | CCTTGGTCCGTGTTTCAAGA |
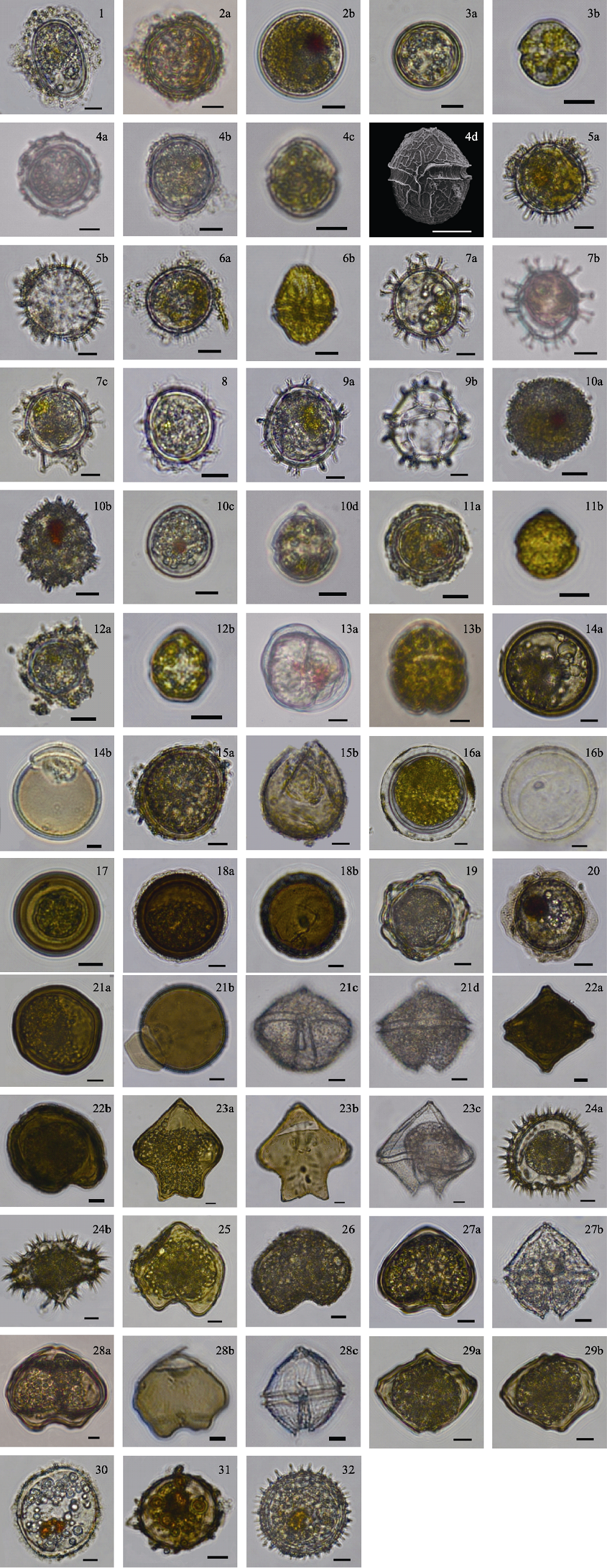
图1 江阴港船舶压载舱沉积物中的甲藻包囊及萌发细胞。(1)塔玛亚历山大藻复合种包囊; (2a-b)相关亚历山大藻包囊; (3a)安德森亚历山大藻包囊, (3b)游动细胞; (4a-b)异常亚历山大藻包囊, (4c-d)游动细胞; (5a-b)多边舌甲藻包囊; (6a)网状原角藻包囊, (6b)游动细胞; (7a-c)具刺膝沟藻包囊; (8)膝沟藻未定种1包囊; (9a-b)膝沟藻未定种2包囊; (10a-c)锥状斯氏藻包囊, (10d)游动细胞; (11a)异常斯氏藻包囊, (11b)游动细胞; (12a)东海斯氏藻包囊, (12b)游动细胞; (13a)无纹环沟藻包囊, (13b)游动细胞; (14a-b)翼藻类未定种1包囊; (15a-b)翼藻类未定种2包囊; (16a-b)墨西哥易碎藻包囊; (17)褐色原多甲藻包囊; (18a-b)安倍原多甲藻包囊; (19)美国原多甲藻包囊; (20)菱形原多甲藻包囊; (21a-b)穿刺原多甲藻包囊, (21c-d)游动细胞; (22a-b)双尖原多甲藻; (23a-b)宽刺原多甲藻包囊, (23c)游动细胞; (24a-b)锥形原多甲藻包囊; (25)长形原多甲藻包囊; (26)窄角原多甲藻包囊; (27a)玛丽雷伯原多甲藻包囊, (27b)游动细胞; (28a-b)原多甲藻未定种1包囊, (28c)游动细胞; (29a-b)原多甲藻未定种2包囊; (30)未定种1; (31)未定种2; (32)未定种3。标尺: 10 μm。
Fig. 1 Dinoflagellate cysts and germinated cells in sediments of ballast tanks in Jiangyin Port. (1) Alexandrium tamarense species complex cyst; (2a-b) Alexandrium affine cyst; (3a) Alexandrium andersonii cyst, (3b) A. andersonii motile cell; (4a-b) Alexandrium insuetum cyst, (4c-d) A. insuetum motile cell; (5a-b) Lingulodinium polyedrum cyst; (6a) Protoceratium reticulatum cyst, (6b) P. reticulatum motile cell; (7a-c) Gonyaulax spinifera cyst; (8) Gonyaulax sp. 1 cyst; (9a-b) Gonyaulax sp. 2 cyst; (10a-c) Scrippsiella acuminata cyst, (10d) S. acuminata motile cell; (11a) Scrippsiella enormis cyst, (11b) S. enormis motile cell; (12a) Scrippsiella donghaiensis cyst, (12b) S. donghaiensis motile cell; (13a) Gyrodinium instriatum cyst, (13b) G. instriatum motile cell; (14a-b) Diplopsalid group type 1 cyst; (15a-b) Diplopsalid group type 2 cyst; (16a-b) Fragilidium mexicanum cyst; (17) Protoperidinium avellana cyst; (18a-b) Protoperidinium abei cyst; (19) Protoperidinium americanum cyst; (20) Protoperidinium rhombiforme cyst; (21a-b) Protoperidinium punctulatum cyst, (21c-d) P. punctulatum motile cell; (22a-b) Protoperidinium biconicum cyst; (23a-b) Protoperidinium latissinum cyst, (23c) P. latissinum motile cell; (24a-b) Protoperidinium conicum cyst; (25) Protoperidinium oblongum cyst; (26) Protoperidinium claudicans cyst; (27a) Protoperidinium marielebourae cyst, (27b) P. marielebourae motile cell; (28a-b) Protoperidinium sp. 1 cyst, (28c) Protoperidinium sp. 1 motile cell; (29a-b) Protoperidinium sp. 2 cyst; (30) Unknown species 1; (31) Unknown species 2; (32) Unknown species 3. Scale bars: 10 μm.
| 种名 Species | 基因 Gene | GeneBank序列号 Accession number | GeneBank比对序列 Alignment sequence | 相似度 Similarity (%) | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 异常亚历山大藻 Alexandrium insuetum | ITS | MN197893 | JF521630 | 99.81 | |
| 锥状斯氏藻 Scrippsiella acuminata | ITS | MN197899 | HQ729493 | 99.54 | |
| 锥状斯氏藻 S. acuminata | ITS | MN197902 | HM483396 | 90.36 | |
| 锥状斯氏藻 S. acuminata | ITS | MN200945 | HM483396 | 99.15 | |
| 无纹环沟藻 Gymrdinium instriatum | ITS | MN209264 | GU477607 | 99.68 | Wang et al, 未发表 |
| 网状原角藻 Protoceratium reticulatum | ITS | MN203677 | JQ638939 | 98.60 | |
| 安德森亚历山大藻 A. andersonii | LSU | MN197869 | KF034855 | 100 | |
| 异常斯氏藻 S. enormis | LSU | MN197911 | KT804917 | 100 | |
| 东海斯氏藻 S. donghaiensis | LSU | MN197912 | JN982374 | 100 | |
| 墨西哥易碎藻 Fragilidium mexicanum | LSU | MN203623 | KY624505 | 99.52 | |
| 宽刺原多甲藻 Protoperidinium latissinum | LSU | MN209392 | KM591209 | 91.40 |
表3 分子序列及比对序列相关信息
Table 3 Related information of molecular sequence and alignment sequence
| 种名 Species | 基因 Gene | GeneBank序列号 Accession number | GeneBank比对序列 Alignment sequence | 相似度 Similarity (%) | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 异常亚历山大藻 Alexandrium insuetum | ITS | MN197893 | JF521630 | 99.81 | |
| 锥状斯氏藻 Scrippsiella acuminata | ITS | MN197899 | HQ729493 | 99.54 | |
| 锥状斯氏藻 S. acuminata | ITS | MN197902 | HM483396 | 90.36 | |
| 锥状斯氏藻 S. acuminata | ITS | MN200945 | HM483396 | 99.15 | |
| 无纹环沟藻 Gymrdinium instriatum | ITS | MN209264 | GU477607 | 99.68 | Wang et al, 未发表 |
| 网状原角藻 Protoceratium reticulatum | ITS | MN203677 | JQ638939 | 98.60 | |
| 安德森亚历山大藻 A. andersonii | LSU | MN197869 | KF034855 | 100 | |
| 异常斯氏藻 S. enormis | LSU | MN197911 | KT804917 | 100 | |
| 东海斯氏藻 S. donghaiensis | LSU | MN197912 | JN982374 | 100 | |
| 墨西哥易碎藻 Fragilidium mexicanum | LSU | MN203623 | KY624505 | 99.52 | |
| 宽刺原多甲藻 Protoperidinium latissinum | LSU | MN209392 | KM591209 | 91.40 |
| 种类 Species | 1号船 Ship number 1 | 2号船 Ship number 2 | 3号船 Ship number 3 | 4号船 Ship number 4 | 5号船 Ship number 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 膝沟藻类 Gonyaulacoid group | |||||
| 塔玛亚历山大藻复合种 Alexandrium tamarense species complex | ++ | + | + | + | ++ |
| 相关亚历山大藻 Alexandrium affine | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ |
| 安德森亚历山大藻 Alexandrium andersonii | ++ | + | + | ||
| 异常亚历山大藻 Alexandrium insuetum | + | ||||
| 多边舌甲藻 Lingulodinium polyedrum | + | + | + | ||
| 网状原角藻 Protoceratium reticulatum | + | + | + | ++ | + |
| 具刺膝沟藻 Gonyaulax spinifera | + | + | + | ++ | + |
| 膝沟藻未定种1 Gonyaulax sp. 1 | ++ | + | |||
| 膝沟藻未定种2 Gonyaulax sp. 2 | + | + | + | ||
| 钙甲藻类 Calcoidinellid group | |||||
| 锥状斯氏藻 Scrippsiella acuminata | ++ | + | ++ | + | +++ |
| 异常斯氏藻 Scrippsiella enormis | + | ||||
| 东海斯氏藻 Scrippsiella donghaiensis | ++ | + | + | ||
| 裸甲藻类 Gymnodinioid group | |||||
| 无纹环沟藻 Gyrodinium instriatum | ++ | + | |||
| 翼甲藻类 Diplopsalid group | |||||
| 翼藻类未定种1 Diplopsalid group type 1 | + | + | + | ||
| 翼藻类未定种2 Diplopsalid group type 2 | ++ | + | + | + | |
| 墨西哥易碎藻 Fragilidium mexicanum | + | + | + | ||
| 原多甲藻类 Protoperidinioid group | |||||
| 褐色原多甲藻 Protoperidinium avellana | + | + | + | + | + |
| 安倍原多甲藻 Protoperidinium abei | + | + | |||
| 美国原多甲藻 Protoperidinium americanum | + | + | |||
| 菱形原多甲藻 Protoperidinium rhombiforme | + | ||||
| 穿刺原多甲藻 Protoperidinium punctulatum | + | + | + | ||
| 双尖原多甲藻 Protoperidinium biconicum | + | ||||
| 宽刺原多甲藻 Protoperidinium latissinum | + | + | |||
| 锥形原多甲藻 Protoperidinium conicum | + | ||||
| 长形原多甲藻 Protoperidinium oblongum | + | + | ++ | + | |
| 窄角原多甲藻 Protoperidinium claudicans | + | + | |||
| 玛丽雷伯原多甲藻 Protoperidinium marielebourae | + | ||||
| 原多甲藻未定种1 Protoperidinium sp. 1 | + | + | |||
| 原多甲藻未定种2 Protoperidinium sp. 2 | + | + | |||
| 未定种 Unidentified | |||||
| 未定种1 Unknown species 1 | + | + | |||
| 未定种2 Unknown species 2 | +++ | ||||
| 未定种3 Unknown species 3 | + |
表4 不同船只压载舱沉积物中甲藻包囊的物种组成及密度
Table 4 Composition and density of dinoflagellate cysts in the sediments from ballast tanks of different ship
| 种类 Species | 1号船 Ship number 1 | 2号船 Ship number 2 | 3号船 Ship number 3 | 4号船 Ship number 4 | 5号船 Ship number 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 膝沟藻类 Gonyaulacoid group | |||||
| 塔玛亚历山大藻复合种 Alexandrium tamarense species complex | ++ | + | + | + | ++ |
| 相关亚历山大藻 Alexandrium affine | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ |
| 安德森亚历山大藻 Alexandrium andersonii | ++ | + | + | ||
| 异常亚历山大藻 Alexandrium insuetum | + | ||||
| 多边舌甲藻 Lingulodinium polyedrum | + | + | + | ||
| 网状原角藻 Protoceratium reticulatum | + | + | + | ++ | + |
| 具刺膝沟藻 Gonyaulax spinifera | + | + | + | ++ | + |
| 膝沟藻未定种1 Gonyaulax sp. 1 | ++ | + | |||
| 膝沟藻未定种2 Gonyaulax sp. 2 | + | + | + | ||
| 钙甲藻类 Calcoidinellid group | |||||
| 锥状斯氏藻 Scrippsiella acuminata | ++ | + | ++ | + | +++ |
| 异常斯氏藻 Scrippsiella enormis | + | ||||
| 东海斯氏藻 Scrippsiella donghaiensis | ++ | + | + | ||
| 裸甲藻类 Gymnodinioid group | |||||
| 无纹环沟藻 Gyrodinium instriatum | ++ | + | |||
| 翼甲藻类 Diplopsalid group | |||||
| 翼藻类未定种1 Diplopsalid group type 1 | + | + | + | ||
| 翼藻类未定种2 Diplopsalid group type 2 | ++ | + | + | + | |
| 墨西哥易碎藻 Fragilidium mexicanum | + | + | + | ||
| 原多甲藻类 Protoperidinioid group | |||||
| 褐色原多甲藻 Protoperidinium avellana | + | + | + | + | + |
| 安倍原多甲藻 Protoperidinium abei | + | + | |||
| 美国原多甲藻 Protoperidinium americanum | + | + | |||
| 菱形原多甲藻 Protoperidinium rhombiforme | + | ||||
| 穿刺原多甲藻 Protoperidinium punctulatum | + | + | + | ||
| 双尖原多甲藻 Protoperidinium biconicum | + | ||||
| 宽刺原多甲藻 Protoperidinium latissinum | + | + | |||
| 锥形原多甲藻 Protoperidinium conicum | + | ||||
| 长形原多甲藻 Protoperidinium oblongum | + | + | ++ | + | |
| 窄角原多甲藻 Protoperidinium claudicans | + | + | |||
| 玛丽雷伯原多甲藻 Protoperidinium marielebourae | + | ||||
| 原多甲藻未定种1 Protoperidinium sp. 1 | + | + | |||
| 原多甲藻未定种2 Protoperidinium sp. 2 | + | + | |||
| 未定种 Unidentified | |||||
| 未定种1 Unknown species 1 | + | + | |||
| 未定种2 Unknown species 2 | +++ | ||||
| 未定种3 Unknown species 3 | + |
| [1] | Adachi M, Sake Y, Ishida Y (1996) Analysis of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) species using sequences of the 5.8S ribosomal DNA and internal transcribed spacer regions. Journal of Phycology, 32, 424-432. |
| [2] | Bailey SA (2015) An overview of thirty years of research on ballast water as a vector for aquatic invasive species to freshwater and marine environments. Aquatic Ecosystem Health and Management, 18, 261-268. |
| [3] | Bolch CJS (1997) The use of polytungstate for the separation and concentration of living dinoflagellate cysts from marine sediments. Phycologia, 36, 472-478. |
| [4] | Bolch CJS (2001) PCR protocols for genetic identification of dinoflagellates directly from single cysts and plankton cells. Phycologia, 40, 162-167. |
| [5] | Casas-Monroy O, Roy S, Rochon A (2013) Dinoflagellate cysts in ballast sediments: Differences between Canada’s east coast, west coast and the Great Lakes. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 23, 254-276. |
| [6] |
Coats DW, Kim S, Bachvaroff TR, Handy SM, Delwiche CF (2010) Tintinnophagus acutus n. g. n. sp. (Phylum Dinoflagellata), an ectoparasite of the ciliate Tintinnopsis cylindrica Daday 1887, and its relationship to Duboscquodinium collini Grassé 1952. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 57, 468-482.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] | Dai XF, Lu DD, Wang CS, Xia P, Huang L, Wang CD, Wang HX, Huang HY, He PX (2012) Analysis of the population structure of dinoflagellate cysts in the sediment of ballast tank of four cargo boats at Zhoushan Port. Journal of Marine Sciences, 30(1), 11-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴鑫烽, 陆斗定, 王春生, 夏平, 黄雷, 王彩典, 王红霞, 黄海燕, 何飘霞 (2012) 舟山港4艘商船压舱箱沉积物中甲藻包囊种群结构的分析. 海洋学研究, 30(1), 11-18.] | |
| [8] | Dang K (2015) Current situation and implementation recommendations of ships ballast water management convention. China Ocean Shipping, 21(2), 62-63. (in Chinese) |
| [ 党坤 (2015) 船舶压载水管理公约现状及履约建议. 中国远洋航务, 21(2), 62-63.] | |
| [9] | Fahnenstiel G, Hong Y, Millie D, Doblin M, Johengen T, Reid D (2009) Marine dinoflagellate cysts in the ballast tank sediments of ships entering the Laurentian Great Lakes. Transport Engineering in Australia, 30, 1035-1038. |
| [10] | Gao YC, Dong YH, Li HT, Zhan AB (2016) Research progress on identification of harmful dinoflagellate cysts: A review. Journal of Biosafety, 25, 238-254. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 高养春, 董燕红, 李海涛, 战爱斌 (2016) 有害甲藻包囊的分类鉴定研究进展. 生物安全学报, 25, 238-254.] | |
| [11] |
Gao YC, Fang YH, Dong YH, Li HT, Pu CL, Zhan AB (2017) An improved method for the molecular identification of single dinoflagellate cysts. PeerJ, 5, e3224.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] | Gu HF (2007) Resting Cysts, Life Cycle and Phylogenetic Analysis of Typical Algae from Southeastern China Sea. PhD dissertation, Ocean University of China, Qingdao. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 顾海峰 (2007) 中国东南沿海典型藻类的休眠体、生活史和系统发育. 博士学位论文, 中国海洋大学, 青岛.] | |
| [13] | Gu HF, Liu TT, Lan DZ (2011) Progress of dinoflagellate cyst research in the China seas. Biodiversity Science, 19, 779-786. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 顾海峰, 刘婷婷, 蓝东兆 (2011) 中国沿海甲藻包囊研究进展. 生物多样性, 19, 779-786.] | |
| [14] | Gu HF, Liu TT, Mertens K (2015) Cyst-theca relationship and phylogenetic positions of Protoperidinium (Peridiniales, Dinophyceae) species of the sections Conica and Tabulata, with description of Protoperidinium shanghaiense sp. nov. Phycologia, 54, 49-66. |
| [15] | Gu HF, Luo ZH, Liu TT, Lan DZ (2013a) Morphology and phylogeny of Scrippsiella enormis sp. nov. and S. cf. spinifera (Peridiniales, Dinophyceae) from the China Sea. Phycologia, 52, 182-190. |
| [16] | Gu HF, Zeng N, Liu TT, Yang WD, Muller A, Krock B (2013b) Morphology, toxicity, and phylogeny of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) species along the coast of China. Harmful Algae, 27, 68-81. |
| [17] |
Hallegraeff GM (1998) Transport of toxic dinoflagellates via ships’ ballast water: Bioeconomic risk assessment and efficacy of possible ballast water management strategies. Marine Ecology Progress, 168, 297-309.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Hallegraeff GM, Bolch CJ (1991) Transport of toxic dinoflagellate cysts via ships’ ballast water. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 22, 27-30. |
| [19] | Hamer JP, McCollin TA, Lucas IAN (2000) Dinoflagellate cysts in ballast tank sediments: Between tank variability. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40, 731-733. |
| [20] | Hamer JP, Lucas IAN, McCollin TA (2001) Harmful dinoflagellate resting cysts in ships’ ballast tank sediments: Potential for introduction into English and Welsh waters. Phycologia, 40, 246-255. |
| [21] |
Herrera-Sepúlveda A, Hernandez-Saavedra NY, Medlin LK, West N (2012) Capillary electrophoresis finger print technique (CE-SSCP): An alternative tool for the monitoring activities of HAB species in Baja California Sur Costal. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 6863-6871.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] | Huang HY, Lu DD (2009) Recent progress in the study of dinoflagellate cyst. Journal of Marine Sciences, 27(3), 85-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄海燕, 陆斗定 (2009) 甲藻包囊研究进展. 海洋学研究, 27(3), 85-92.] | |
| [23] |
Kim S, Park MG (2017) Feeding characteristics and molecular phylogeny of the thecate mixotrophic dinoflagellate, Fragilidium mexicanum. Harmful Algae, 63, 154-163.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] | Lan DZ, Gu HF (2014) Dinoflagellate Cysts Along the Coast of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 蓝东兆, 顾海峰 (2015) 中国近海甲藻包囊. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [25] | Li WC, Sun J, Song SQ, Lei ZW, Jia JT, Wang D (2006a) Phytoplankton community in Yantai Harbor, Yantai anchorage and entry ship’s ballast water, China. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 28(4), 70-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李伟才, 孙军, 宋书群, 雷质文, 贾俊涛, 王丹 (2006a) 烟台港和邻近锚地及其入境船舶压舱水中的浮游植物. 海洋湖沼通报, 28(4), 70-77.] | |
| [26] | Li WC, Sun J, Wang D, Jia JT, Lei ZW, Wang XD (2006b) The characteristics of phytoplankton assemblage in Rizhao Harbor, Rizhao anchorage ground and entry ship’s ballast water, China. Marine Sciences, 30(12), 52-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李伟才, 孙军, 王丹, 贾俊涛, 雷质文, 王小冬 (2006b) 日照港和邻近锚地及其入境船舶压舱水中浮游植物群集结构的特征. 海洋科学, 30(12), 52-57.] | |
| [27] | Luo ZH, Mertens KN, Bagheri S, Aydin H, Takano Y, Matsuoka K, Mccarthy F, Gu HF (2016) Cyst-theca relationship and phylogenetic positions of Scrippsiella plana sp. nov. and S. spinifera (Peridiniales, Dinophyceae). European Journal of Phycology, 51, 188-202. |
| [28] | Orr RJS, Stüken A, Rundberget T, Eikrem W, Jakobsen KS (2011) Improved phylogenetic resolution of toxic and non-toxic Alexandrium strains using a concatenated rDNA approach. Harmful Algae, 10, 676-688. |
| [29] | Rochon A, Lewis J, Ellegaard M, Harding IC (2009) The Gonyaulax spinifera (Dinophyceae) “complex”: Perpetuating the paradox? Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 155, 52-60. |
| [30] |
Scholin CA, Herzog M, Sogin M, Anderson DM (1994) Identification of group and strain-specific genetic markers for globally distributed Alexandrium (Dinophyceae). II. Sequence analysis of a fragment of the LSU rRNA gene. Journal of Phycology, 30, 999-1011.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Shin HH, Baek SH, Li Z, Han MS, Oh SJ, Youn SH, Kim YS, Kim D, Lim WA (2014) Resting cysts, and effects of temperature and salinity on the growth of vegetative cells of the potentially harmful species Alexandrium insuetum Balech (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae, 39, 175-184.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Spatharis S, Danielidis DB, Tsirtsis G (2007) Recurrent Pseudo-nitzschia calliantha (Bacillariophyceae) and Alexandrium insuetum (Dinophyceae) winter blooms induced by agricultural runoff. Harmful Algae, 6, 811-822.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Su YP, Xue C, You XJ, Zhong YP, Gu HF (2016) Research on the distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in the surface sediments of the XiPi Reservoir in the Jiulong River. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 1728-1736. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 苏玉萍, 薛铖, 游雪静, 钟燕平, 顾海峰 (2016) 九龙江西陂库区沉积物甲藻包囊的分布. 生态学报, 36, 1728-1736.] | |
| [34] | Tang YZ, Hu ZX, Deng YY (2016) Characteristical life history (resting cyst) provides a mechanism for recurrence and geographic expansion of harmful algal blooms of dinoflagellates: A review. Studia Marina Sinica, 17, 132-154. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 唐赢中, 胡章喜, 邓蕴彦 (2016) 休眠孢囊作为甲藻有害藻华年际频发和地理扩散一种关键机制的研究进展. 海洋科学集刊, 17, 132-154.] | |
| [35] |
Williams SL, Davidson IC, Pasari JR, Ashton GV, Carlton JT, Crafton RE, Fontana RE, Grosholz ED, Miller AW, Rulz GM, Zabin CJ (2013) Managing multiple vectors for marine invasions in an increasingly connected world. BioScience, 63, 952-966.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Yang SM, Li RX, Dong SS (2014) Dinoflagellates in the China’s Seas II (Gonyaulacales). China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 杨世民, 李瑞香, 董树刚 (2014) 中国海域甲藻Ⅱ(膝沟藻目). 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| [37] | Yuki K, Yoshimatsu S (1990) New record of Alexandrium insuetum Balech (Dinophyceae) from Japan with some supplementary observations on thecal morphology. Bulletin of Plankton Society of Japan, 36, 121-126. |
| [38] | Zhou J, Liu B, Li CL, Wang ZH, Jiang N, Su XR, Li TW (2012) Study on diversity of phytoplankton in ballast water from Ningbo Port. Biotechnology Bulletin, 28(9), 197-201. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 周君, 刘兵, 李春丽, 王中华, 姜南, 苏秀榕, 李太武 (2012) 宁波港压载水浮游植物多样性的研究. 生物技术通报, 28(9), 197-201.] | |
| [39] | Zinssmeister C, Soehner S, Facher E, Kirsch M, Meier KJS, Gottschling M (2011) Catch me if you can: The taxonomic identity of Scrippsiella trochoidea (F. Stein) A.R.Loebl. (Thoracosphaeraceae, Dinophyceae). Systematics and Biodiversity, 9, 145-157. |
| [40] |
Zinssmeister C, Soehner S, Kirsch M, Facher E, Meier KJS, Keupp H, Gottschling M (2012) Same but different: Two novel bicarinate species of extant calcareous dinophytes (Thoracosphaeraceae, Peridiniales) from the Mediterranean Sea. Journal of Phycology, 48, 1107-1118.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 原雪姣, 张渊媛, 张衍亮, 胡璐祎, 桑卫国, 杨峥, 陈颀. 基于飞机草历史分布数据拟合的物种分布模型及其预测能力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24288-. |
| [2] | 杜聪聪, 冯学宇, 陈志林. 桥头堡效应中气候生态位差异的缩小促进了红火蚁的入侵[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24276-. |
| [3] | 韩丽霞, 王永健, 刘宣. 外来物种入侵与本土物种分布区扩张的异同[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23396-. |
| [4] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [5] | 魏博, 刘林山, 谷昌军, 于海彬, 张镱锂, 张炳华, 崔伯豪, 宫殿清, 土艳丽. 紫茎泽兰在中国的气候生态位稳定且其分布范围仍有进一步扩展的趋势[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 21443-. |
| [6] | 刘艳杰, 黄伟, 杨强, 郑玉龙, 黎绍鹏, 吴昊, 鞠瑞亭, 孙燕, 丁建清. 近十年植物入侵生态学重要研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22438-. |
| [7] | 严靖, 闫小玲, 李惠茹, 杜诚, 马金双. 华东地区归化植物的组成特征、引入时间及时空分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 428-438. |
| [8] | 何维明. 生物入侵的影响是否准确可知?[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(2): 253-255. |
| [9] | 殷万东, 吴明可, 田宝良, 于宏伟, 王麒云, 丁建清. 生物入侵对黄河流域生态系统的影响及对策[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(12): 1533-1545. |
| [10] | 李晗溪, 黄雪娜, 李世国, 战爱斌. 基于环境DNA-宏条形码技术的水生生态系统入侵生物的早期监测与预警[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(5): 491-504. |
| [11] | 余文生, 郭耀霖, 江佳佳, 孙可可, 鞠瑞亭. 土著昆虫素毒蛾在本地植物芦苇与入侵植物互花米草上的生活史[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(4): 433-438. |
| [12] | 李雪晴, 孙赫英, 何德奎, 陈毅峰. 澜沧江-湄公河中上游淡水鱼类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(10): 1090-1100. |
| [13] | 孙士国, 卢斌, 卢新民, 黄双全. 入侵植物的繁殖策略以及对本土植物繁殖的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(5): 457-467. |
| [14] | 高宇, 林光辉. 典型红树林生态系统藻类多样性及其在生态过程中的作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(11): 1223-1235. |
| [15] | 孙燕, 周忠实, 王瑞, HeinzMüller-Schärer. 气候变化预计会减少东亚地区豚草的生物防治效果**[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(12): 1285-1294. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn