



生物多样性 ›› 2012, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (4): 443-450. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.08202 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2012.08202
所属专题: 生物入侵
收稿日期:2011-11-03
接受日期:2012-05-11
出版日期:2012-07-20
发布日期:2012-09-12
通讯作者:
张加勇
作者简介:*E-mail: zhang3599533@163.com基金资助:
Zhe Chen, Jiang Zhang, Hangfei Fu, Zhengzheng Xu, Kunzheng Deng, Jiayong Zhang*( )
)
Received:2011-11-03
Accepted:2012-05-11
Online:2012-07-20
Published:2012-09-12
Contact:
Jiayong Zhang
摘要:
扶桑绵粉蚧(Phenacoccus solenopsis)于2008年首次在广东发现, 到目前为止, 浙江、广西、云南等10多个省市均有其入侵的报道。为探讨入侵中国的扶桑绵粉蚧是否存在两大隐存谱系或姊妹种的复合种, 作者对浙江的该物种进行了调查。在调查过程中, 发现体色浅橘黄色、背部具三对黄色斑点的体色变异型个体, 通过形态特征比较和线粒体COI基因部分序列的分析, 证实该体色变异型粉蚧为扶桑绵粉蚧。同时对中国、巴基斯坦、美国的扶桑绵粉蚧COI基因序列进行碱基差异比较、遗传距离(genetic distance)分析, 发现所扩增的浙江省内6个地点7种不同寄主植物上的25条扶桑绵粉蚧COI基因(694 bp)可以分成3种单倍型, 这3种单倍型与中国海南、中国广州、巴基斯坦和美国加州的扶桑绵粉蚧遗传分歧较小(0-1.0%), 而与美国佛罗里达州的遗传分歧较大(3-3.6%); 但两者遗传距离小于绵粉蚧属内物种之间的遗传距离(13.0-17.2%)。综合形态特征和COI基因数据的分析结果显示, 扶桑绵粉蚧可能没有达到种间分化。基于碱基差异所构建的网络关系图、遗传分歧差异和系统发生关系分析, 扶桑绵粉蚧存在两个进化支系, 至于是否是复合种, 目前尚难作结论, 还有待更多证据。
陈哲, 张姜, 傅杭飞, 许争争, 邓坤正, 张加勇 (2012) 基于形态特征和线粒体COI基因探讨扶桑绵粉蚧物种的有效性并记述一体色变异型扶桑绵粉蚧. 生物多样性, 20, 443-450. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.08202.
Zhe Chen, Jiang Zhang, Hangfei Fu, Zhengzheng Xu, Kunzheng Deng, Jiayong Zhang (2012) On the validity of the species Phenacoccus solenopsis based on morphological and mitochondrial COI data, with the description of a new body color variety. Biodiversity Science, 20, 443-450. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.08202.
| 样品编码 Sample code | 单倍型 Haplotypes | 寄主植物 Host | 采集地点 Collecting location | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 经度 Longitude (E) | 采集时间 Collecting date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDm1-4 | F1 | 木槿 Hibiscus syriacus | 浙江金华婺城区 Wucheng, Jinhua, Zhejiang | 29.1° | 119.7° | 2009.7 |
| PJt1-4 | F1 | 铁苋菜 Acalypha australis | 浙江金华浦江县 Pujiang, Jinhua, Zhejiang | 29.4° | 119.9° | 2010.8 |
| WYq1-3 | F1 | 牵牛花 Pharbitis nil | 浙江金华武义县 Wuyi, Jinhua, Zhejiang | 28.9° | 119.8° | 2011.7 |
| LXy1-2 | F1 | 一年蓬 Erigeron annuus | 浙江金华兰溪市 Lanxi, Jinhua, Zhejiang | 29.2° | 119.5° | 2011.7 |
| LXz1-5 | F1 | 钻形紫菀 Aster subulatus | 浙江金华兰溪市 Lanxi, Jinhua, Zhejiang | 29.2° | 119.5° | 2011.7 |
| HZt1-3 | F1 | 太阳花 Erodium stephanianum | 浙江杭州萧山区 Xiaoshan, Hangzhou, Zhejiang | 30.0° | 120.1° | 2011.8 |
| XYm1-3 | F2 | 木芙蓉 Cottonrose hibiscus | 浙江师范大学校园 Zhejiang Normal University | 29.1° | 119.7° | 2011.8 |
| XYm5 | F3 | 木芙蓉 Cottonrose hibiscus | 浙江师范大学校园 Zhejiang Normal University | 29.1° | 119.7° | 2011.8 |
表1 扶桑绵粉蚧样本采集信息
Table 1 The collection information of Phenacoccus solenopsis
| 样品编码 Sample code | 单倍型 Haplotypes | 寄主植物 Host | 采集地点 Collecting location | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 经度 Longitude (E) | 采集时间 Collecting date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDm1-4 | F1 | 木槿 Hibiscus syriacus | 浙江金华婺城区 Wucheng, Jinhua, Zhejiang | 29.1° | 119.7° | 2009.7 |
| PJt1-4 | F1 | 铁苋菜 Acalypha australis | 浙江金华浦江县 Pujiang, Jinhua, Zhejiang | 29.4° | 119.9° | 2010.8 |
| WYq1-3 | F1 | 牵牛花 Pharbitis nil | 浙江金华武义县 Wuyi, Jinhua, Zhejiang | 28.9° | 119.8° | 2011.7 |
| LXy1-2 | F1 | 一年蓬 Erigeron annuus | 浙江金华兰溪市 Lanxi, Jinhua, Zhejiang | 29.2° | 119.5° | 2011.7 |
| LXz1-5 | F1 | 钻形紫菀 Aster subulatus | 浙江金华兰溪市 Lanxi, Jinhua, Zhejiang | 29.2° | 119.5° | 2011.7 |
| HZt1-3 | F1 | 太阳花 Erodium stephanianum | 浙江杭州萧山区 Xiaoshan, Hangzhou, Zhejiang | 30.0° | 120.1° | 2011.8 |
| XYm1-3 | F2 | 木芙蓉 Cottonrose hibiscus | 浙江师范大学校园 Zhejiang Normal University | 29.1° | 119.7° | 2011.8 |
| XYm5 | F3 | 木芙蓉 Cottonrose hibiscus | 浙江师范大学校园 Zhejiang Normal University | 29.1° | 119.7° | 2011.8 |
| 编号 Code | 单倍型 Haplotypes | 种名 Species | 地理分布 Geo-distribution | 登录号 No. of GenBank Accession | 来源 Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GZ-FJ597914 | F1 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 中国广州 Guangzhou, China | FJ597914 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| SY-GQ398777 | F1 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 中国海南 Hainan, China | GQ398777 | Chu et al., 2009 |
| LS-GQ903580 | F2 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 中国海南 Hainan, China | GQ903580 | Chu et al., 2009 |
| LS-GQ903581 | F4 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 中国海南 Hainan, China | GQ903581 | Chu et al., 2009 |
| B-AB499696 | F5 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 巴基斯坦 Pakistan | AB499696 | Ashfaq et al., 2010 |
| M-EU267208 | F6 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 美国 USA | EU267208 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| M-EU267209 | F6 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 美国 USA | EU267209 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| M-EU267210 | F6 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 美国 USA | EU267210 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| M-EU267211 | F6 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 美国 USA | EU267211 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| M-EU267212 | F7 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 美国 USA | EU267212 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| M-JN112802 | F8 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 美国 USA | JN112802 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| W-EU267195 | _ | Phenacoccus manihoti | 乌干达 Uganda | EU267195 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| W-EU267196 | _ | Phenacoccus manihoti | 乌干达 Uganda | EU267196 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| R-AB439518 | _ | Phenacoccus pergandei | 日本 Japan | AB439518 | Yokogawa & Yahara , 2009 |
| R-AB512120 | _ | Phenacoccus avenae | 日本 Japan | AB512120 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
表2 从GenBank获取的绵粉蚧属线粒体COI基因序列相关信息
Table 2 The information of mtDNA COI sequences of Phenacoocus from GenBank
| 编号 Code | 单倍型 Haplotypes | 种名 Species | 地理分布 Geo-distribution | 登录号 No. of GenBank Accession | 来源 Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GZ-FJ597914 | F1 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 中国广州 Guangzhou, China | FJ597914 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| SY-GQ398777 | F1 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 中国海南 Hainan, China | GQ398777 | Chu et al., 2009 |
| LS-GQ903580 | F2 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 中国海南 Hainan, China | GQ903580 | Chu et al., 2009 |
| LS-GQ903581 | F4 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 中国海南 Hainan, China | GQ903581 | Chu et al., 2009 |
| B-AB499696 | F5 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 巴基斯坦 Pakistan | AB499696 | Ashfaq et al., 2010 |
| M-EU267208 | F6 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 美国 USA | EU267208 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| M-EU267209 | F6 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 美国 USA | EU267209 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| M-EU267210 | F6 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 美国 USA | EU267210 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| M-EU267211 | F6 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 美国 USA | EU267211 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| M-EU267212 | F7 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 美国 USA | EU267212 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| M-JN112802 | F8 | Phenacoccus solenopsis | 美国 USA | JN112802 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| W-EU267195 | _ | Phenacoccus manihoti | 乌干达 Uganda | EU267195 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| W-EU267196 | _ | Phenacoccus manihoti | 乌干达 Uganda | EU267196 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| R-AB439518 | _ | Phenacoccus pergandei | 日本 Japan | AB439518 | Yokogawa & Yahara , 2009 |
| R-AB512120 | _ | Phenacoccus avenae | 日本 Japan | AB512120 | 直接上传 Direct submission |
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F2 | 0.001 | |||||||
| F3 | 0.003 | 0.001 | ||||||
| F4 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.003 | |||||
| F5 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.006 | ||||
| F6 | 0.031 | 0.031 | 0.031 | 0.031 | 0.034 | |||
| F7 | 0.033 | 0.030 | 0.033 | 0.033 | 0.036 | 0.001 | ||
| F8 | 0.010 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.027 | 0.028 |
表3 基于Kimura双参数模型所得扶桑绵粉蚧8个单倍型间COI基因序列遗传距离
Table 3 Genetic distance among eight haplotypes of Phenacoccus solenopsis based on COI sequences using Kimura 2 parameter model
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F2 | 0.001 | |||||||
| F3 | 0.003 | 0.001 | ||||||
| F4 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.003 | |||||
| F5 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.006 | ||||
| F6 | 0.031 | 0.031 | 0.031 | 0.031 | 0.034 | |||
| F7 | 0.033 | 0.030 | 0.033 | 0.033 | 0.036 | 0.001 | ||
| F8 | 0.010 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.027 | 0.028 |
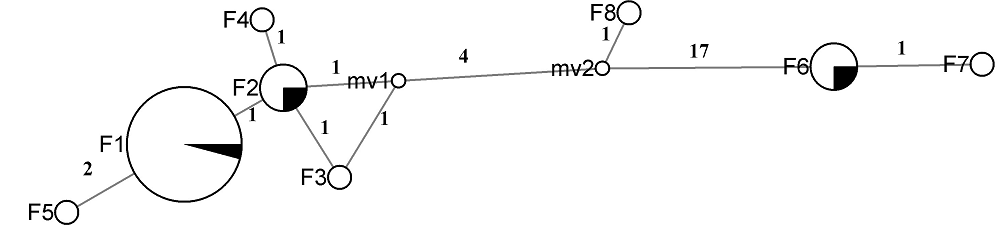
图1 基于Network软件构建的36个扶桑绵粉蚧COI序列网络关系树(圆圈黑色部分表示1条序列所占的比值): F1-8分别表示相应的单倍型, mv1-2表示中间可能的连接点, 单倍型具体信息见表1和表2; 横线上数值表示单倍型之间的碱基数差异。
Fig. 1 Median-Jointing network constructed from 36 COI of Phenacoccus solenopsis. The sector in black within the haplotype circles corresponds to the proportion of one sequence. F1-8 showed the haplotype in Table 1 and 2, mv1-2 showed median vectors, the numbers above line showed the different bases among haplotypes.
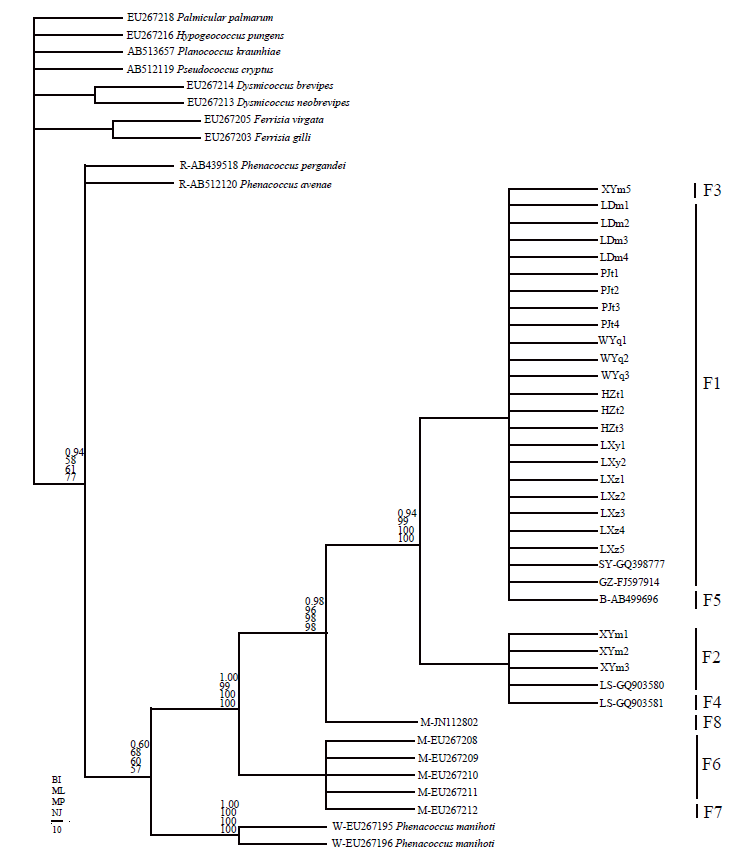
图2 基于COI基因序列构建的扶桑绵粉蚧的系统进化树(BI、ML、MP和NJ所构建的系统发生树拓扑结构一致, 最后选用ML树为框架。各节点的数值, 从上到下分别对应BI、ML、MP和NJ的后验概率或自检验值)
Fig. 2 Phylogenetic tree of Phenacoccus solenopsis based on COI sequences (The toplogy of BI, ML, MP and NJ analysis is largely identical, and hence that of ML analyses was chosen. Numbers above branches specify posterior probabilities from Bayesian inference (BI), bootstrap percentages from maximum parsimony (MP, 1,000 replicates), maximum likelihood (ML, 1,000 replicates) and neighbour joining (NJ, 1,000 replicates) analyses.
| [1] | Ashfaq M, Noor AR, Mansoor S (2010) DNA-based characterization of an invasive mealybug (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) species damaging cotton in Pakistan. Applied Entomology and Zoology, 45, 395-404. |
| [2] |
Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Rohl A (1999) Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 37-48.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] | Barth D, Krenek S, Forin SI, Berendonk TU (2006) Intraspecific genetic variation in nacoccus 原因适应不同的寄主, paramecium .ylaryrevealed by mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase I sequences. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 53, 20-25. |
| [4] | Chen HY (陈华燕), He LF (何嫏芬), Zheng CH (郑春红), Li P (李盼), Yi QH (易晴辉), Xu ZF (许再福) (2011) Survey on the natural enemies of mealybug, Phenacoccus solenopsis Tinsley (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) from Guangdong and Hainan, China. Journal of Environmental Entomology (环境昆虫学报), 33, 269-272. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Chu D, Liu GX, Fu HB, Xu W (2009) Phylogenetic analysis of mt COI reveals the cryptic lineages in Phenacoccus solenopsis complex (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae). Acta Entomologica Sinica, 52, 1261-1265. |
| [6] | Culik MP, Gullan PJ (2005) A new pest of tomato and other records of mealybugs (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) from Espírito Santo, Brazil. Zootaxa, 964, 1-8. |
| [7] | Dong YW (董云伟), Niu CJ (牛翠娟) (2004) Sequence variability of mitochondrial COI region and population genetic structure of rotifer Brachionus calyflorus. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (海洋与湖沼), 35, 473-479. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] |
Frohlich DR, Torres-Jerez I, Bedford ID, Markham PG, Brown JK (1999) A phylogeographical analysis of the Bemisia tabaci species complex based on mitochondrial DNA markers. Molecular Ecology, 8, 1683-1691.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] | Fuchs TW, Stewart JW, Minzenmayer R, Rose M (1991) First record of Phenacoccus solenopsis Tinsley in cultivated cotton in the United States. Southwestern Entomology, 16, 215-221. |
| [10] |
Hebert PDN, Cywinska A, Ball SL, deWaard JR (2003a) Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series B: Biological Sciences, 270, 313-321.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] | Hebert PDN, Ratnasingham S, deWaard JR (2003b) Barcoding animal life: cytochrome coxidase subunit I divergences among closely related species. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series B: Biological Sciences, 270(Suppl. 1), s96-s99. |
| [12] | Huang H (黄华), Niu LM (牛黎明), Han DY (韩冬银), Zhang FP (张方平), Fu YG (符悦冠) (2010) mtDNA COI sequence analysis and phylogenetic studies of Scirtothrips dorsalis hood on different hosts. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops (热带作物学报), 31, 1010-1013. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Huang L (黄玲), Liu H (刘慧), Ou GC (欧高财), Xiao TG (肖铁光), Zhou SW (周社文) (2011) Preliminary studies on biology of Phenacoccus solenopsis Tinsley, a cotton pest. Crop Research (作物研究), 25, 245-248. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] |
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics, 17, 754-755.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] |
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 16, 111-120.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] | Leng HN (冷海楠), Chi DF (迟德富), Xiao F (肖放) (2010) Variation in mtDNA COI sequences of ten geographical populations of Dendrolimus. Journal of Northeast Forestry University (东北林业大学学报), 38, 106-107. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Luo M (罗梅), Bin SY (宾淑英), Dong ZY (董章勇), Lin JT (林进添) (2011) Study on the cotton-endangering invasive pest, Phenacoccus solenopsis. Journal of Anhui Agriculture Science (安徽农业科学), 39, 11517-11519. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Ma J (马骏), Hu XN (胡学难), Peng ZQ (彭正强), Liu HJ (刘海军), Liang F (梁帆), Lu YY (陆永跃) (2011) The potential geographical distribution of Phenacoccus solenopsis Tinsley based on the CLIMEX in China. Plant Quarantine (植物检疫), 25, 5-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Malausa T, Fenis A, Warot S, Germain JF, Ris N, Prado E, Botton M, Vanlerberghe-Masutti F, Sforza R, Cruaud C, Couloux A, Kreiter P (2011) DNA markers to disentangle complexes of cryptic taxa in mealybugs (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae). Journal of Applied Entomology, 135, 142-155. |
| [20] | Muniappan R, Shepard BM, Watson GW, Carner GR, Rauf A, Sartiami D, Hidayat P, Afun JVK, Goergen G, Ziaur Rahman AKM (2009) New records of invasive insects (Hemiptera: Sternorrhyncha) in Southeast Asia and West Africa. Journal of Agricultural and Urban Entomology, 26, 167-174. |
| [21] | Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. BMC Biology, 14, 817-818. |
| [22] | Rani A, Jain S, Gautam RD (2012) Investigation of insecticidal activity of some α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds and their synergistic combination with natural products against Phenacoccus solenopsis Tinsley. Journal of Plant Protection Research, 52, 146-155. |
| [23] |
Rozas J, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Messeguer X, Rozas R (2003) DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics, 19, 2496-2497.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] | Sun F (孙峰), Guan X (关鑫), Lu YY (陆永跃) (2011) Research on individual equivalency of Phenacoccus solenopsis Tinsley based on biomass and its application. China Plant Protection (中国植保导刊), 31, 5-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Swofford DL (2002) PAUP*: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods), version 4.0b10. Sinauer Associates Inc., Sunderland, MA. |
| [26] |
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28, 2731-2739.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] | Tinsley JD (1898) An ants-nest coccid from New Mexico. The Canadian Entomologist, 30, 47-48. |
| [28] | Wang FX (王福祥), Xiong HL (熊红利), Xiang Y (项宇), Liu H (刘慧), Li XN (李潇楠), Feng XD (冯晓东) (2011) Factors and procedures considered in dealing with the new detected pest from the controlling of Solenopsis mealybug. Plant Quarantine (植物检疫), 25(4), 89-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Wang YP, Watson GW, Zhang RZ (2010) The potential distribution of an invasive mealybug Phenacoccus solenopsis and its threat to cotton in Asia. Agricultural and Forest Entomology, 12, 403-416. |
| [30] | Wang YP (王艳平), Wu SA (武三安), Zhang RZ (张润志) (2009) Pest risk analysis of a new invasive pest, Phenacoccus solenopsis, to China. Chinese Bulletin of Entomology (昆虫知识), 46, 101-106. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | Wu SA (武三安), Zhang RZ (张润志) (2009) A new invasive pest, Phenacoccus solenopsis, threatening seriously to cotton production. Chinese Bulletin of Entomology (昆虫知识), 46, 159-162. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] |
Yang B, Cai JL, Cheng XJ (2010) Identification of astigmatid mites using ITS2 and COI regions. Parasitology Research, 108, 497-503.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] |
Yokogawa T, Yahara T (2009) Mitochondrial phylogeny certified PGL (Paternal Genome Loss) is of single origin and haplodiploidy sensu stricto (arrhenotoky) did not evolve from PGL in the scale insects (Hemiptera: Coccoidea). Genes & Genetic Systems, 84, 57-66.
URL PMID |
| [34] |
Zhang C, Zhang DX, Zhu YQ, Yang ZH (2011) Evaluation of a Bayesian coalescent method of species delimitation. Systematic Biology, 60, 747-761.
DOI URL PMID |
| [35] | Zhu YY (朱艺勇), Huang F (黄芳), Lü YB (吕要斌) (2011) Bionomics of mealybug Phenacoccus solenopsis Tinsley (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) on cotton. Acta Entomologica Sinica (昆虫学报), 54, 246-252. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [2] | 杜聪聪, 冯学宇, 陈志林. 桥头堡效应中气候生态位差异的缩小促进了红火蚁的入侵[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24276-. |
| [3] | 原雪姣, 张渊媛, 张衍亮, 胡璐祎, 桑卫国, 杨峥, 陈颀. 基于飞机草历史分布数据拟合的物种分布模型及其预测能力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24288-. |
| [4] | 韩丽霞, 王永健, 刘宣. 外来物种入侵与本土物种分布区扩张的异同[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23396-. |
| [5] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [6] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [7] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [8] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [9] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [10] | 何艺玥, 刘玉莹, 张富斌, 秦强, 曾燏, 吕振宇, 杨坤. 梯级水利工程背景下的嘉陵江干流蛇鮈群体遗传多样性和遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [11] | 魏博, 刘林山, 谷昌军, 于海彬, 张镱锂, 张炳华, 崔伯豪, 宫殿清, 土艳丽. 紫茎泽兰在中国的气候生态位稳定且其分布范围仍有进一步扩展的趋势[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 21443-. |
| [12] | 孙维悦, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 莫日根高娃, 杜夏瑾, 刘保东, 严岳鸿. 基于保护基因组学揭示荷叶铁线蕨的濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [13] | 陶克涛, 白东义, 图格琴, 赵若阳, 安塔娜, 铁木齐尔·阿尔腾齐米克, 宝音德力格尔, 哈斯, 芒来, 韩海格. 基于基因组SNPs对东亚家马不同群体遗传多样性的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [14] | 崔静, 徐明芳, 章群, 李瑶, 曾晓舒, 李莎. 基于3种线粒体标记探讨中日沿海角木叶鲽遗传多样性差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21485-. |
| [15] | 刘艳杰, 黄伟, 杨强, 郑玉龙, 黎绍鹏, 吴昊, 鞠瑞亭, 孙燕, 丁建清. 近十年植物入侵生态学重要研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22438-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()