



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 23166. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023166 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023166
收稿日期:2023-05-25
接受日期:2023-07-31
出版日期:2023-09-20
发布日期:2023-08-14
通讯作者:
*E-mail: lidongmei@icdc.cn
基金资助:Received:2023-05-25
Accepted:2023-07-31
Online:2023-09-20
Published:2023-08-14
Contact:
*E-mail: lidongmei@icdc.cn
摘要:
巴尔通体是一群全球广泛分布的细菌, 部分种类能引起多种人兽共患病, 宿主包括食肉类、反刍类、啮齿类、灵长类以及海洋中鲸类等哺乳动物。近年来, 世界各地陆续报道蝙蝠能够携带巴尔通体。为了解全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行情况, 本文系统检索汇总了自2005年以来世界各地对蝙蝠巴尔通体的研究, 较为详细地描述了巴尔通体在蝙蝠这一大类群中的感染状况、宿主分布及遗传进化关系等信息。分析发现, 在31个国家和地区的106种蝙蝠体内检测到巴尔通体, 表明蝙蝠是巴尔通体重要的动物宿主。通过对蝙蝠巴尔通体柠檬酸合酶基因(citrate synthase gene, gltA)序列构建系统发育树, 发现绝大多数蝙蝠巴尔通体与其他宿主来源的巴尔通体亲缘关系较远, 构成蝙蝠巴尔通体独立的类群, 初步揭示这一类巴尔通体具有宿主特异性特征, 提示巴尔通体可能与宿主蝙蝠存在协同进化关系。
李庆多, 栗冬梅 (2023) 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析. 生物多样性, 31, 23166. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023166.
Qingduo Li, Dongmei Li (2023) Analysis for the prevalence of global bat-borne Bartonella. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23166. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023166.
| 洲和国家(参考文献) Continents and countries studied (References) | 感染巴尔通体的蝙蝠 Bats infected with Bartonellae | 感染率 Infection rates (%) | 调查方法(目标基因) Investigation methods (target genes) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非洲 Africa | 南非 South Africa (Dietrich et al, | 韦氏颈囊果蝠 Epomophorus wahlbergi 长翼蝠 Miniopterus natalensis 埃及果蝠 Rousettus aegyptiacus | 15.5 | PCR (gltA) | ||||
| 斯威士兰 Swaziland (Dietrich et al, | 非洲凹脸蝠 Nycteris thebaica | 2.7 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 尼日利亚 Nigeria (Kamani et al, | 黄毛果蝠 Eidolon helvum Epomophorus sp. Micropterus sp. 埃及果蝠 Rousettus aegyptiacus 菊头蝠属一种 Rhinolophus sp. | 12.4-15.5 | 分离培养 Isolation & culture, PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 赞比亚 Zambia (Qiu et al, | 埃及果蝠 Rousettus aegyptiacus Hipposideros vittatus | 16.7 | 分离培养 Isolation & culture, PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 马达加斯加 Madagascar (Brook et al, | Eidolon dupreanum | 23.6 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 肯尼亚 Kenya (Kosoy et al, | 南鞘尾蝠 Coleura afra 黄毛果蝠 Eidolon helvum 康氏蹄蝠 Hipposideros commersoni 长翼蝠属一种 Miniopterus sp. 埃及果蝠 Rousettus aegyptiacus 波斯叶鼻蝠 Triaenops persicus | 32.0 | 分离培养 Isolation & culture, PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 欧洲 Europe | 芬兰 Finland (Veikkolainen et al, | 水鼠耳蝠 Myotis daubentonii 圆形叶口蝠 Desmodus rotundus 北棕蝠 Eptesicus nilssonii | 33.3-37.1 | PCR (gltA, rpoB) | ||||
| 英国 Britain (Concannon et al, | 翼蝠属一种 Pipistrellus sp. | 8.3 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 法国 France (Stuckey et al, | 水鼠耳蝠 Myotis daubentonii 须鼠耳蝠 Myotis mystacinus 褐山蝠 Nyctalus noctula 纳氏伏翼蝠 Pipistrellus nathusii | 10.1 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 意大利 Italy (Szentiványi et al, | 普通长翼蝠 Miniopterus schreibersii | 25.0 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 匈牙利 Hungary (Szentiványi et al, | 普通长翼蝠 Miniopterus schreibersii | 33.3 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 波兰 Poland (Szubert-Kruszyńska et al, | 大鼠耳蝠 Myotis myotis | 25.4 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 西班牙 Spain (Stuckey et al, | 未鉴定 Unidentified | 3.8 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 亚洲 Asia | 马来西亚 Malaysia (Hou et al, | 小狐蝠 Pteropus hypomelanus | 6.7 | 分离培养 Isolation & culture, PCR (gltA) | ||||
| 日本 Japan (Nabeshima et al, | 亚洲长翼蝠 Miniopterus fuliginosus 北棕蝠 Eptesicus nilssonii | 24.0-26.0 | 分离培养 Isolation & culture, PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 中国 China (Han et al, | 普通长翼蝠 Miniopterus schreibersii 毛腿鼠耳蝠 Myotis fimbriatus 北京鼠耳蝠 Myotis pequinius 大足鼠耳蝠 Myotis ricketti 小菊头蝠 Rhinolophus pusillus 马铁菊头蝠 Rhinolophus ferrumequinum 中菊头蝠 Rhinolophus affinis 棕果蝠 Rousettus leschenaultii 小鼠耳蝠 Myotis davidii 郝氏鼠耳蝠 Myotis adversus | 10.3-56.4 | PCR (gltA), qPCR (ssrA) | |||||
| 越南 Vietnam (Anh et al, | 大蹄蝠 Hipposideros armiger Hipposideros larvatui 印度假吸血蝠 Megaderma lyra 马来假吸血蝠 Megaderma spasma 泰国无尾果蝠 Megaerops niphanae 大角菊头蝠 Rhinolophus acuminatus Rhinolophus chaseli 中华菊头蝠 Rhinolophus sinicus | 35.0 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 泰国 Thailand (Mckee et al, | 无尾长鼻蝠 Anoura geoffroyi 中蹄蝠 Hipposideros larvatus 黑髯墓蝠 Taphozous melanopogon 圆形叶口蝠 Desmodus rotundus 大耳蹄蝠 Hipposideros fulvus 大蹄蝠 Hipposideros armiger Craseonycteris thonglongyai Rhinolophus coelophyllus Hipposideros kunzi Hipposideros gentilis 喜山鼠耳蝠 Myotis muricola 小蹄蝠 Hipposideros cineraceus 马来假吸血蝠 Megaderma spasma 马来菊头蝠 Rhinolophus malayanus 皮氏菊头蝠 Rhinolophus pearsonii 高颅鼠耳蝠 Myotis siligorensis | 25.5-36.6 | 分离培养 Isolation & culture, PCR (gltA, 16S rRNA gene) | |||||
| 格鲁吉亚 Georgia (Bai et al, | 棕蝠 Eptesicus serotinus 普通长翼蝠 Miniopterus schreibersii 尖耳鼠耳蝠 Myotis blythii 佐氏鼠耳蝠 Myotis emarginatus Pipistrellus pygmaeus 地中海菊头蝠 Rhinolophus euryale 马铁菊头蝠 Rhinolophus ferrumequinum | 35.3-49.5 | PCR (ITS (16S-23S internal transcribed spacer locus), gltA) | |||||
| 美洲 America | 美国 United States of America (Lilley et al, | 灰鼠耳蝠 Myotis grisescens 小棕蝠 Myotis lucifugus | 9.8 | PCR (gltA) | ||||
| 圣基茨和尼维斯 Saint Kitts and Nevis (Reeves et al, | 牙买加果蝠 Artibeus jamaicensis Artibeus fimbriatus 艾氏短尾叶鼻蝠 Carollia castanea | 36.9 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 哥斯达黎加 Costa Rica (Judson et al, et al, | Micronycteris microtus Myotis keaysei Chaerephon plicatus Artibeus obscurus 大食果蝠 Artibeus lituratus Platyrrhinus vittatus Vampyressa thyone 昭短尾叶鼻蝠 Carollia perspicillata 毛足黄肩蝠 Sturnira mordax 苍白矛吻蝠 Phyllostomus discolor 美洲林蝠 Ardops nichollsi 黄肩蝠 Sturnira lilium | 10.7-33.3 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 危地马拉 Guatemala (Bai, | 中美果蝠 Artibeus toltecus 昭短尾叶鼻蝠 Carollia perspicillata 圆形叶口蝠 Desmodus rotundus 鼩形长舌蝠 Glossophaga soricina 美洲大耳蝠 Micronycteris microtis 苍白矛吻蝠 Phyllostomus discolor 裸背蝠 Pteronotus davyi 黄肩蝠 Sturnira lilium | 33.1-39.3 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 墨西哥 Mexico (Chomel et al, | 牙买加果蝠 Artibeus jamaicensis 襞兜翼蝠 Balantiopteryx plicata 圆形叶口蝠 Desmodus rotundus 红斑裸背蝠 Pteronotus parnellii 黄肩蝠属一种 Sturnira sp. | 22.7 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 秘鲁 Peru (Bai et al, | Artibeus obscurus 扁吻美洲果蝠 Artibeus planirostris 短尾叶鼻蝠 Carollia brevicauda 昭短尾叶鼻蝠 Carollia perspicillata 圆形叶口蝠 Desmodus rotundus 鼩形长舌蝠 Glossophaga soricina 鼠耳蝠属一种 Myotis sp. 苍白矛吻蝠 Phyllostomus discolor 矛吻蝠 Phyllostomus hastatus | 24.1-67.3 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 黄肩蝠 Sturnira lilium Vampyriscus bidens | ||||||||
| 法属圭亚那 French Guiana (Davoust et al, | 垂耳真蝠 Eumops auripendulus Noctilio albiventris 红斑裸背蝠 Pteronotus parnellii | 13.6 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 伯利兹 Belize (Becker et al, | 圆形叶口蝠 Desmodus rotundus | 45.0 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 巴西 Brazil (Ikeda et al, | 昭短尾叶鼻蝠 Carollia perspicillata 牙买加果蝠 Artibeus jamaicensis 小叶吻蝠 Rhinophylla pumilio 狭叶蝠 Brachyphylla cavernarum 毛腿吸血蝠 Diphylla ecaudata 黄肩蝠 Sturnira lilium 大蹄蝠 Hipposideros armiger 大食果蝠 Artibeus lituratus 苍白矛吻蝠 Phyllostomus discolor 扁吻美洲果蝠 Artibeus planirostris Platyrrhinus lineatus Natalus espiritosantensis 鼩形长舌蝠 Glossophaga soricina Carollia sowelii 圆形叶口蝠 Desmodus rotundus | 4.3-24.5 | PCR (gltA, nuoG (NADH dehydrogenase gamma subunit gene)), qPCR (ITS) | |||||
| 阿根廷 Argentina (Cicuttin et al, | 巴西犬吻蝠 Tadarida brasiliensis | 4.9 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 波多黎各 Puerto Rico (Olival et al, | 牙买加果蝠 Artibeus jamaicensis 狭叶蝠 Brachyphylla cavernarum 牙买加长舌蝠 Monophyllus redmani | 17.6 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 智利 Chile (Müller et al, | 智利鼠耳蝠 Myotis chiloensis Histiotus montanus Histiotus macrotus 巴西犬吻蝠 Tadarida brasiliensis | 38.1 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
表1 全球蝙蝠感染巴尔通体的地理、宿主、感染率和调查方法信息
Table 1 Information on the geography, hosts, prevalence and survey methods of the worldwide Bartonella infection in bats
| 洲和国家(参考文献) Continents and countries studied (References) | 感染巴尔通体的蝙蝠 Bats infected with Bartonellae | 感染率 Infection rates (%) | 调查方法(目标基因) Investigation methods (target genes) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非洲 Africa | 南非 South Africa (Dietrich et al, | 韦氏颈囊果蝠 Epomophorus wahlbergi 长翼蝠 Miniopterus natalensis 埃及果蝠 Rousettus aegyptiacus | 15.5 | PCR (gltA) | ||||
| 斯威士兰 Swaziland (Dietrich et al, | 非洲凹脸蝠 Nycteris thebaica | 2.7 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 尼日利亚 Nigeria (Kamani et al, | 黄毛果蝠 Eidolon helvum Epomophorus sp. Micropterus sp. 埃及果蝠 Rousettus aegyptiacus 菊头蝠属一种 Rhinolophus sp. | 12.4-15.5 | 分离培养 Isolation & culture, PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 赞比亚 Zambia (Qiu et al, | 埃及果蝠 Rousettus aegyptiacus Hipposideros vittatus | 16.7 | 分离培养 Isolation & culture, PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 马达加斯加 Madagascar (Brook et al, | Eidolon dupreanum | 23.6 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 肯尼亚 Kenya (Kosoy et al, | 南鞘尾蝠 Coleura afra 黄毛果蝠 Eidolon helvum 康氏蹄蝠 Hipposideros commersoni 长翼蝠属一种 Miniopterus sp. 埃及果蝠 Rousettus aegyptiacus 波斯叶鼻蝠 Triaenops persicus | 32.0 | 分离培养 Isolation & culture, PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 欧洲 Europe | 芬兰 Finland (Veikkolainen et al, | 水鼠耳蝠 Myotis daubentonii 圆形叶口蝠 Desmodus rotundus 北棕蝠 Eptesicus nilssonii | 33.3-37.1 | PCR (gltA, rpoB) | ||||
| 英国 Britain (Concannon et al, | 翼蝠属一种 Pipistrellus sp. | 8.3 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 法国 France (Stuckey et al, | 水鼠耳蝠 Myotis daubentonii 须鼠耳蝠 Myotis mystacinus 褐山蝠 Nyctalus noctula 纳氏伏翼蝠 Pipistrellus nathusii | 10.1 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 意大利 Italy (Szentiványi et al, | 普通长翼蝠 Miniopterus schreibersii | 25.0 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 匈牙利 Hungary (Szentiványi et al, | 普通长翼蝠 Miniopterus schreibersii | 33.3 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 波兰 Poland (Szubert-Kruszyńska et al, | 大鼠耳蝠 Myotis myotis | 25.4 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 西班牙 Spain (Stuckey et al, | 未鉴定 Unidentified | 3.8 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 亚洲 Asia | 马来西亚 Malaysia (Hou et al, | 小狐蝠 Pteropus hypomelanus | 6.7 | 分离培养 Isolation & culture, PCR (gltA) | ||||
| 日本 Japan (Nabeshima et al, | 亚洲长翼蝠 Miniopterus fuliginosus 北棕蝠 Eptesicus nilssonii | 24.0-26.0 | 分离培养 Isolation & culture, PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 中国 China (Han et al, | 普通长翼蝠 Miniopterus schreibersii 毛腿鼠耳蝠 Myotis fimbriatus 北京鼠耳蝠 Myotis pequinius 大足鼠耳蝠 Myotis ricketti 小菊头蝠 Rhinolophus pusillus 马铁菊头蝠 Rhinolophus ferrumequinum 中菊头蝠 Rhinolophus affinis 棕果蝠 Rousettus leschenaultii 小鼠耳蝠 Myotis davidii 郝氏鼠耳蝠 Myotis adversus | 10.3-56.4 | PCR (gltA), qPCR (ssrA) | |||||
| 越南 Vietnam (Anh et al, | 大蹄蝠 Hipposideros armiger Hipposideros larvatui 印度假吸血蝠 Megaderma lyra 马来假吸血蝠 Megaderma spasma 泰国无尾果蝠 Megaerops niphanae 大角菊头蝠 Rhinolophus acuminatus Rhinolophus chaseli 中华菊头蝠 Rhinolophus sinicus | 35.0 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 泰国 Thailand (Mckee et al, | 无尾长鼻蝠 Anoura geoffroyi 中蹄蝠 Hipposideros larvatus 黑髯墓蝠 Taphozous melanopogon 圆形叶口蝠 Desmodus rotundus 大耳蹄蝠 Hipposideros fulvus 大蹄蝠 Hipposideros armiger Craseonycteris thonglongyai Rhinolophus coelophyllus Hipposideros kunzi Hipposideros gentilis 喜山鼠耳蝠 Myotis muricola 小蹄蝠 Hipposideros cineraceus 马来假吸血蝠 Megaderma spasma 马来菊头蝠 Rhinolophus malayanus 皮氏菊头蝠 Rhinolophus pearsonii 高颅鼠耳蝠 Myotis siligorensis | 25.5-36.6 | 分离培养 Isolation & culture, PCR (gltA, 16S rRNA gene) | |||||
| 格鲁吉亚 Georgia (Bai et al, | 棕蝠 Eptesicus serotinus 普通长翼蝠 Miniopterus schreibersii 尖耳鼠耳蝠 Myotis blythii 佐氏鼠耳蝠 Myotis emarginatus Pipistrellus pygmaeus 地中海菊头蝠 Rhinolophus euryale 马铁菊头蝠 Rhinolophus ferrumequinum | 35.3-49.5 | PCR (ITS (16S-23S internal transcribed spacer locus), gltA) | |||||
| 美洲 America | 美国 United States of America (Lilley et al, | 灰鼠耳蝠 Myotis grisescens 小棕蝠 Myotis lucifugus | 9.8 | PCR (gltA) | ||||
| 圣基茨和尼维斯 Saint Kitts and Nevis (Reeves et al, | 牙买加果蝠 Artibeus jamaicensis Artibeus fimbriatus 艾氏短尾叶鼻蝠 Carollia castanea | 36.9 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 哥斯达黎加 Costa Rica (Judson et al, et al, | Micronycteris microtus Myotis keaysei Chaerephon plicatus Artibeus obscurus 大食果蝠 Artibeus lituratus Platyrrhinus vittatus Vampyressa thyone 昭短尾叶鼻蝠 Carollia perspicillata 毛足黄肩蝠 Sturnira mordax 苍白矛吻蝠 Phyllostomus discolor 美洲林蝠 Ardops nichollsi 黄肩蝠 Sturnira lilium | 10.7-33.3 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 危地马拉 Guatemala (Bai, | 中美果蝠 Artibeus toltecus 昭短尾叶鼻蝠 Carollia perspicillata 圆形叶口蝠 Desmodus rotundus 鼩形长舌蝠 Glossophaga soricina 美洲大耳蝠 Micronycteris microtis 苍白矛吻蝠 Phyllostomus discolor 裸背蝠 Pteronotus davyi 黄肩蝠 Sturnira lilium | 33.1-39.3 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 墨西哥 Mexico (Chomel et al, | 牙买加果蝠 Artibeus jamaicensis 襞兜翼蝠 Balantiopteryx plicata 圆形叶口蝠 Desmodus rotundus 红斑裸背蝠 Pteronotus parnellii 黄肩蝠属一种 Sturnira sp. | 22.7 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 秘鲁 Peru (Bai et al, | Artibeus obscurus 扁吻美洲果蝠 Artibeus planirostris 短尾叶鼻蝠 Carollia brevicauda 昭短尾叶鼻蝠 Carollia perspicillata 圆形叶口蝠 Desmodus rotundus 鼩形长舌蝠 Glossophaga soricina 鼠耳蝠属一种 Myotis sp. 苍白矛吻蝠 Phyllostomus discolor 矛吻蝠 Phyllostomus hastatus | 24.1-67.3 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 黄肩蝠 Sturnira lilium Vampyriscus bidens | ||||||||
| 法属圭亚那 French Guiana (Davoust et al, | 垂耳真蝠 Eumops auripendulus Noctilio albiventris 红斑裸背蝠 Pteronotus parnellii | 13.6 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 伯利兹 Belize (Becker et al, | 圆形叶口蝠 Desmodus rotundus | 45.0 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 巴西 Brazil (Ikeda et al, | 昭短尾叶鼻蝠 Carollia perspicillata 牙买加果蝠 Artibeus jamaicensis 小叶吻蝠 Rhinophylla pumilio 狭叶蝠 Brachyphylla cavernarum 毛腿吸血蝠 Diphylla ecaudata 黄肩蝠 Sturnira lilium 大蹄蝠 Hipposideros armiger 大食果蝠 Artibeus lituratus 苍白矛吻蝠 Phyllostomus discolor 扁吻美洲果蝠 Artibeus planirostris Platyrrhinus lineatus Natalus espiritosantensis 鼩形长舌蝠 Glossophaga soricina Carollia sowelii 圆形叶口蝠 Desmodus rotundus | 4.3-24.5 | PCR (gltA, nuoG (NADH dehydrogenase gamma subunit gene)), qPCR (ITS) | |||||
| 阿根廷 Argentina (Cicuttin et al, | 巴西犬吻蝠 Tadarida brasiliensis | 4.9 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 波多黎各 Puerto Rico (Olival et al, | 牙买加果蝠 Artibeus jamaicensis 狭叶蝠 Brachyphylla cavernarum 牙买加长舌蝠 Monophyllus redmani | 17.6 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
| 智利 Chile (Müller et al, | 智利鼠耳蝠 Myotis chiloensis Histiotus montanus Histiotus macrotus 巴西犬吻蝠 Tadarida brasiliensis | 38.1 | PCR (gltA) | |||||
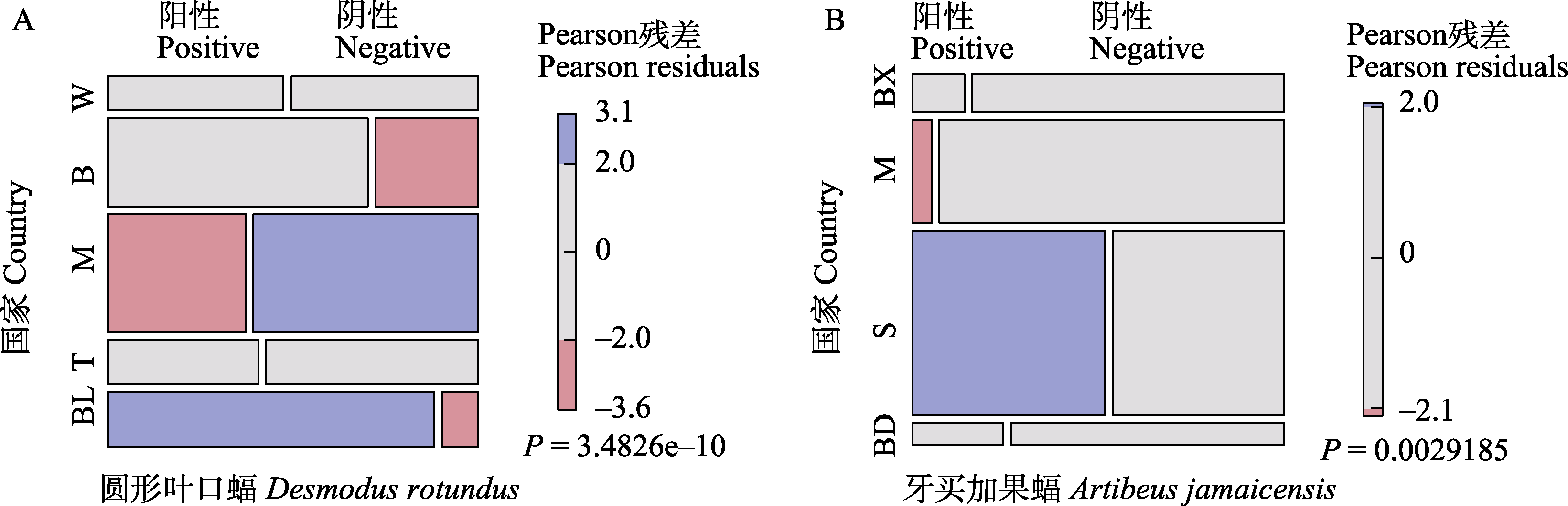
图1 圆形叶口蝠(A)和牙买加果蝠(B)在不同国家/地区巴尔通体感染情况分布差异。W: 危地马拉; B: 秘鲁; M: 墨西哥; T: 泰国; BL: 伯利兹; BX: 巴西; S: 圣基茨岛; BD: 波多黎各。
Fig. 1 Distribution differences of Bartonella infections of Desmodus rotundus and Artibeus jamaicensis in the different countries and regions. W, Guatemala; B, Peru; M, Mexico; T, Thailand; BL, Belize; BX, Brazil; S, Saint Kitts; BD, Puerto Rico.
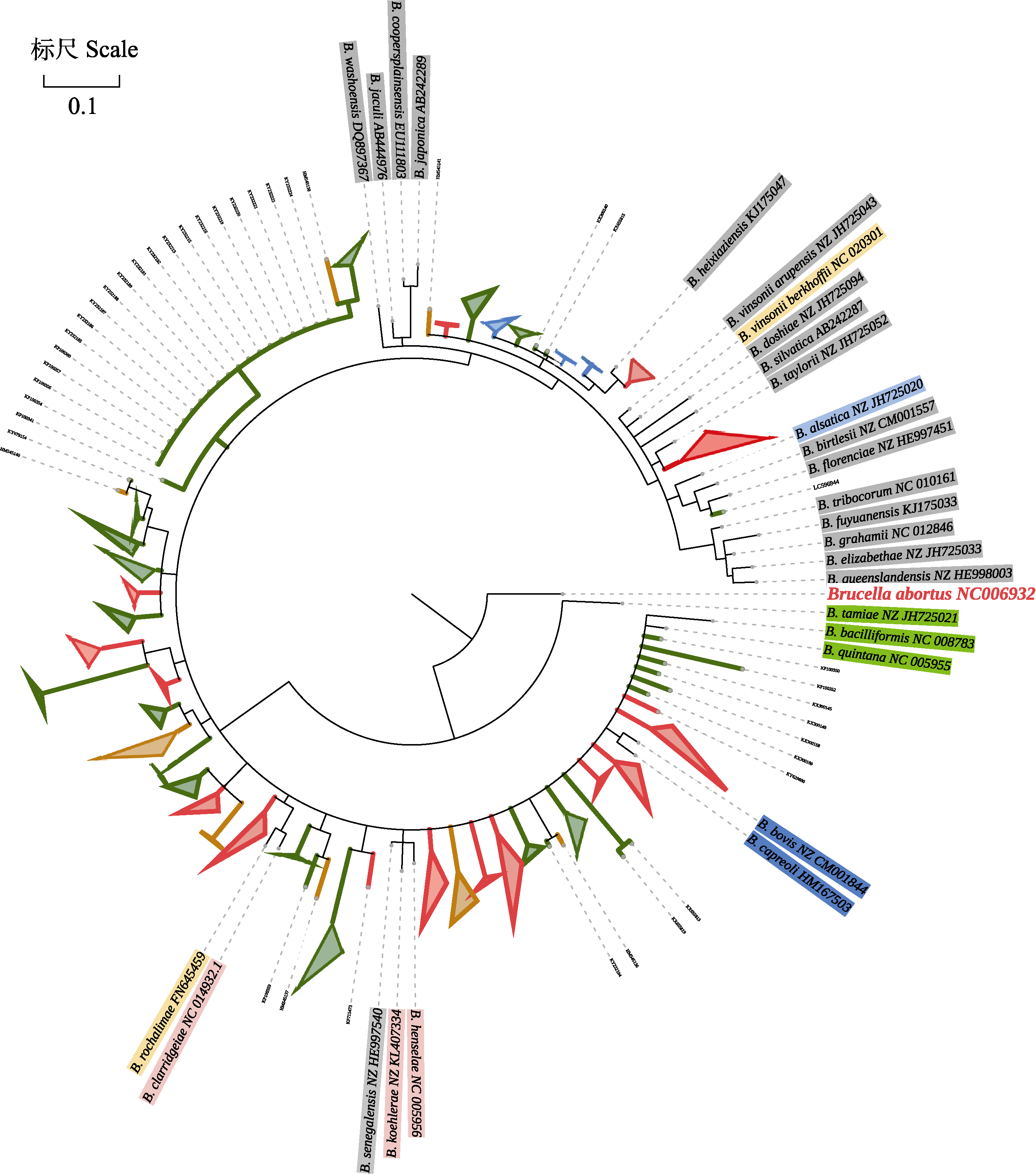
图2 蝙蝠巴尔通体gltA 362 bp序列片段构建的贝叶斯系统发育树。将此树中已知参考巴尔通体叶名称标注背景颜色, 代表宿主来源。绿色: 人; 蓝色: 鹿; 粉色: 猫; 灰色: 鼠; 黄色: 犬; 淡蓝色: 兔。所有蝙蝠巴尔通体的叶名称无背景颜色标注, 标注其分支颜色代表地理来源。绿色: 亚洲; 棕黄色: 非洲; 蓝色: 欧洲; 红色: 美洲。外群为布鲁氏菌。
Fig. 2 The Bayesian phylogenetic tree constructed based on 362 bp of the gltA sequences from the bat-borne Bartonella. The leaf names of known reference Bartonella in this phylogenetic tree were labeled with background colors representing host origins. Green, Human; Blue, Deer; Pink, Cat; Gray, Rodent; Yellow, Dog; Light blue, Rabbit. All leaf names of bat-borne Bartonella without background color labels labeled branch color representing geographical origins. Green, Asia; Brown-yellow, Africa; Blue, Europe; Red, America. The outgroup is Brucella abortus NC006932.
| [1] |
André MR, Gutiérrez R, Ikeda P, Amaral RB, Sousa KCM, Nachum-Biala Y, Lima L, Teixeira MMG, Machado RZ, Harrus S (2019) Genetic diversity of Bartonella spp. in vampire bats from Brazil. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 66, 2329-2341.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Anh PH, Van Cuong N, Son NT, Tue NT, Kosoy M, Woolhouse MEJ, Baker S, Bryant JE, Thwaites G, Carrique-Mas JJ, Rabaa MA (2015) Diversity of Bartonella spp. in bats, southern Vietnam. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 21, 1266-1267.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Bai Y (2011) Bartonella spp. in bats, Guatemala. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 17, 1269-1272.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Bai Y, Gómez J, Kosoy MY, Recuenco S, Osikowicz LM, Rupprecht C, Gilbert AT (2012) Prevalence and diversity of Bartonella spp. in bats in Peru. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 87, 518-523.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Bai Y, Osinubi MOV, Osikowicz L, McKee C, Vora NM, Rizzo MR, Recuenco S, Davis L, Niezgoda M, Ehimiyein AM, Kia GSN, Oyemakinde A, Adeniyi OS, Gbadegesin YH, Saliman OA, Ogunniyi A, Ogunkoya AB, Kosoy MY (2018) Human exposure to novel Bartonella species from contact with fruit bats. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 24, 2317-2323.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Bai Y, Urushadze L, Osikowicz L, McKee C, Kuzmin I, Kandaurov A, Babuadze G, Natradze I, Imnadze P, Kosoy M (2017) Molecular survey of bacterial zoonotic agents in bats from the country of Georgia (Caucasus). PLoS ONE, 12, e171175. |
| [7] | Becker DJ, Bergner LM, Bentz AB, Orton RJ, Altizer S, Streicker DG (2018) Genetic diversity, infection prevalence, and possible transmission routes of Bartonella spp. in vampire bats. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 12, e0006786. |
| [8] | Breitschwerdt EB (2017) Bartonellosis, One Health and all creatures great and small. Veterinary Dermatology, 28, 96-e21. |
| [9] | Brook CE, Bai Y, Dobson AP, Osikowicz LM, Ranaivoson HC, Zhu QY, Kosoy MY, Dittmar K (2015) Bartonella spp. in fruit bats and blood-feeding ectoparasites in Madagascar. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 9, e0003532. |
| [10] |
Chomel BB, Obregón-Morales C, Olave-Leyva JI, Aréchiga-Ceballos N, Stuckey MJ, Moreno-Sandoval H, Aguilar-Setién A, Salas-Rojas M, Galvez-Romero G (2017) Bartonella infection in hematophagous, insectivorous, and phytophagous bat populations of central Mexico and the Yucatan Peninsula. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 97, 413-422.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Cicuttin GL, De Salvo MN, La Rosa I, Dohmen FEG (2017) Neorickettsia risticii, Rickettsia sp. and Bartonella sp. in Tadarida brasiliensis bats from Buenos Aires, Argentina. Comparative Immunology, Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 52, 1-5.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Concannon R, Wynn-Owen K, Simpson VR, Birtles RJ (2005) Molecular characterization of haemoparasites infecting bats (Microchiroptera) in Cornwall, UK. Parasitology, 131, 489-496.
PMID |
| [13] |
Davoust B, Marié JL, Dahmani M, Berenger JM, Bompar JM, Blanchet D, Cheuret M, Raoult D, Mediannikov O (2016) Evidence of Bartonella spp. in blood and ticks (Ornithodoros hasei) of bats, in French Guiana. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 16, 516-519.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Dietrich M, Tjale MA, Weyer J, Kearney T, Seamark ECJ, Nel LH, Monadjem A, Markotter W (2016) Diversity of Bartonella and Rickettsia spp. in bats and their blood-feeding ectoparasites from South Africa and Swaziland. PLoS ONE, 11, e0152077.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Ferreira MS, Guterres A, Rozental T, Novaes RLM, Vilar EM, Oliveira RC, Fernandes J, Forneas D, Junior AA, Brandão ML, Cordeiro JLP, Del Valle Alvarez MR, Althoff SL, Moratelli R, Cordeiro-Estrela P, Silva RCD, Lemos ERS (2018) Coxiella and Bartonella spp. in bats (Chiroptera) captured in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest biome. BMC Veterinary Research, 14, 279.
DOI |
| [16] |
Gonçalves-Oliveira J, Rozental T, Guterres A, Teixeira BR, Elise Andrade-Silva B, da Costa-Neto SF, Furtado MC, Moratelli R, D’Andrea PS, Lemos ERS (2020) Investigation of Bartonella spp. in Brazilian mammals with emphasis on rodents and bats from the Atlantic Forest. International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife, 13, 80-89.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Han HJ, Li ZM, Li X, Liu JX, Peng QM, Wang R, Gu XL, Jiang Y, Zhou CM, Li D, Xiao X, Yu XJ (2022) Bats and their ectoparasites (Nycteribiidae and Spinturnicidae) carry diverse novel Bartonella genotypes, China. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 69, e845-e858. |
| [18] | Han HJ, Wen HL, Zhao L, Liu JW, Luo LM, Zhou CM, Qin XR, Zhu YL, Zheng XX, Yu XJ (2017) Novel Bartonella species in insectivorous bats, northern China. PLoS ONE, 12, e0167915. |
| [19] |
Hou SL, Koh FX, Nuryana I, Sitam FT, Tay ST (2018) Molecular detection of Bartonella spp. in Malaysian small flying foxes (Pteropus hypomelanus). Tropical Biomedicine, 35, 293-299.
PMID |
| [20] |
Ikeda P, Marinho Torres J, Perles L, Lourenço EC, Herrera HM, de Oliveira CE, Zacarias Machado R, André MR (2020) Intra- and inter-host assessment of Bartonella diversity with focus on non-hematophagous bats and associated ectoparasites from Brazil. Microorganisms, 8, 1822.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Ikeda P, Seki MC, Carrasco AOT, Rudiak LV, Miranda JMD, Gonçalves SMM, Hoppe EGL, Albuquerque ACA, Teixeira MMG, Passos CE, Werther K, Machado RZ, André MR (2017) Evidence and molecular characterization of Bartonella spp. and hemoplasmas in neotropical bats in Brazil. Epidemiology and Infection, 145, 2038-2052.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Judson SD, Frank HK, Hadly EA (2015) Bartonellae are prevalent and diverse in Costa Rican bats and bat flies. Zoonoses and Public Health, 62, 609-617.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Kaiser PO, Riess T, O’Rourke F, Linke D, Kempf VAJ (2011) Bartonella spp.: Throwing light on uncommon human infections. International Journal of Medical Microbiology, 301, 7-15.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Kamani J, Baneth G, Mitchell M, Mumcuoglu KY, Gutiérrez R, Harrus S (2014) Bartonella species in bats (Chiroptera) and bat flies (Nycteribiidae) from Nigeria, West Africa. Vector Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 14, 625-632.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Kosoy M, Bai Y, Lynch T, Kuzmin IV, Niezgoda M, Franka R, Agwanda B, Breiman RF, Rupprecht CE (2010) Bartonella spp. in bats, Kenya. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 16, 1875-1881.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Li DM, Yang WH, Li QD, Han X, Song XP, Pan H, Feng Y (2021) High prevalence and genetic variation of Bartonella species inhabiting the bats in southwestern Yunnan. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1245-1255. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [栗冬梅, 杨卫红, 李庆多, 韩茜, 宋秀平, 潘虹, 冯云 (2021) 巴尔通体在滇西南蝙蝠中高度流行并具有丰富的遗传变异特征. 生物多样性, 29, 1245-1255.] | |
| [27] |
Lilley TM, Veikkolainen V, Pulliainen AT (2015) Molecular detection of Candidatus Bartonella hemsundetiensis in bats. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 15, 706-708.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Lilley TM, Wilson CA, Bernard RF, Willcox EV, Vesterinen EJ, Webber QM, Kurpiers L, Prokkola JM, Ejotre I, Kurta A, Field KA, Reeder DM, Pulliainen AT (2017) Molecular detection of Candidatus Bartonella mayotimonensis in north American bats. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 17, 243-246.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Lin J, Hsu Y, Chomel BB, Lin L, Pei J, Wu S, Chang C (2012) Identification of novel Bartonella spp. in bats and evidence of Asian gray shrew as a new potential reservoir of Bartonella. Veterinary Microbiology, 156, 119-126.
DOI URL |
| [30] | McKee CD, Kosoy MY, Bai Y, Osikowicz LM, Franka R, Gilbert AT, Boonmar S, Rupprecht CE, Peruski LF (2017) Diversity and phylogenetic relationships among Bartonella strains from Thai bats. PLoS ONE, 12, e0181696. |
| [31] |
Mitchell MM, Vicente-Santos A, Rodríguez-Herrera B, Corrales-Aguilar E, Gillespie TR (2022) Genetic diversity of Bartonella spp. in cave-dwelling bats and bat flies, Costa Rica, 2018. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 28, 488-491.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Mühldorfer K (2013) Bats and bacterial pathogens: A review. Zoonoses and Public Health, 60, 93-103.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Müller A, Sepúlveda P, Di Cataldo S, Cevidanes A, Lisón F, Millán J (2020) Molecular investigation of zoonotic intracellular bacteria in Chilean bats. Comparative Immunology, Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 73, 101541.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Nabeshima K, Sato S, Brinkerhoff RJ, Amano M, Kabeya H, Itou T, Maruyama S (2023) Prevalence and genetic diversity of Bartonella spp. in northern bats (Eptesicus nilssonii) and their blood-sucking ectoparasites in Hokkaido, Japan. Microbial Ecology, 85, 298-306.
DOI |
| [35] |
Nabeshima K, Sato S, Kabeya H, Kato C, Suzuki K, Maruyama S (2020) Isolation and genetic properties of Bartonella in eastern bent-wing bats (Miniopterus fuliginosus) in Japan. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 83, 104354.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Noguchi H, Battistini TS (1926) Etiology of Oroya fever: I. Cultivation of Bartonella bacilliformis. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 43, 851-864.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Olival KJ, Dittmar K, Bai Y, Rostal MK, Lei BR, Daszak P, Kosoy M (2015) Bartonella spp. in a Puerto Rican bat community. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 51, 274-278.
DOI PMID |
| [38] | Oren A, Garrity GM (2021) Valid publication of the names of forty-two phyla of prokaryotes. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 71, 005056. |
| [39] |
Parte AC, Sardà Carbasse J, Meier-Kolthoff JP, Reimer LC, Göker M (2020) List of Prokaryotic names with standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) moves to the DSMZ. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 70, 5607-5612.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Poofery J, Narapakdeesakul D, Riana E, Arnuphapprasert A, Nugraheni YR, Ngamprasertwong T, Wangthongchaicharoen M, Soisook P, Bhodhibundit P, Kaewthamasorn M (2022) Molecular identification and genetic diversity of Bartonella spp. in 24 bat species from Thailand. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 69, e717-e733. |
| [41] |
Qiu YJ, Kajihara M, Nakao R, Mulenga E, Harima H, Hang’ombe BM, Eto Y, Changula K, Mwizabi D, Sawa H, Higashi H, Mweene A, Takada A, Simuunza M, Sugimoto C (2020) Isolation of Candidatus Bartonella rousetti and other bat-associated Bartonellae from bats and their flies in Zambia. Pathogens, 9, 469.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Reeves WK, Beck J, Orlova MV, Daly JL, Pippin K, Revan F, Loftis AD (2016) Ecology of bats, their ectoparasites, and associated pathogens on Saint Kitts Island. Journal of Medical Entomology, 53, 1218-1225.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
Stuckey MJ, Boulouis HJ, Cliquet F, Picard-Meyer E, Servat A, Aréchiga-Ceballos N, Echevarría JE, Chomel BB (2017) Potentially zoonotic Bartonella in bats from France and Spain. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 23, 539-541.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Szentiványi T, Markotter W, Dietrich M, Clément L, Ançay L, Brun L, Genzoni E, Kearney T, Seamark E, Estók P, Christe P, Glaizot O (2020) Host conservation through their parasites: Molecular surveillance of vector-borne microorganisms in bats using ectoparasitic bat flies. Parasite, 27, 72.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
Szubert-Kruszyńska A, Stańczak J, Cieniuch S, Podsiadły E, Postawa T, Michalik J (2019) Bartonella and Rickettsia infections in Haematophagous Spinturnix myoti mites (Acari: Mesostigmata) and their bat host, Myotis myotis (Yangochiroptera: Vespertilionidae), from Poland. Microbial Ecology, 77, 759-768.
DOI PMID |
| [46] | Urushadze L, Bai Y, Osikowicz L, McKee C, Sidamonidze K, Putkaradze D, Imnadze P, Kandaurov A, Kuzmin I, Kosoy M (2017) Prevalence, diversity, and host associations of Bartonella strains in bats from Georgia (Caucasus). PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 11, e0005428. |
| [47] |
Veikkolainen V, Vesterinen EJ, Lilley TM, Pulliainen AT (2014) Bats as reservoir hosts of human bacterial pathogen, Bartonella mayotimonensis. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 20, 960-967.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Wray AK, Olival KJ, Morán D, Lopez MR, Alvarez D, Navarrete-Macias I, Liang E, Simmons NB, Lipkin WI, Daszak P, Anthony SJ (2016) Viral diversity, prey preference, and Bartonella prevalence in Desmodus rotundus in Guatemala. Ecohealth, 13, 761-774.
PMID |
| [1] | 廖雅晴, 黄泽锋, 王晓云, 张礼标, 吴毅, 余文华. 广东省翼手目物种名录更新及分子条形码数据库[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24584-. |
| [2] | 仝淼, 王欢, 张文双, 王超, 宋建潇. 重金属污染土壤中细菌抗生素抗性基因分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [3] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [4] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [5] | 耿江天, 王菲, 赵华斌. 城市化对中国蝙蝠影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24109-. |
| [6] | 刘莹莹, 龚立新, 曾皓, 冯江, 董永军, 王磊, 江廷磊. 被动声学监测在蝙蝠研究中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24233-. |
| [7] | 段晓敏, 李佳佳, 李靖宇, 李艳楠, 袁存霞, 王英娜, 刘建利. 腾格里沙漠东南缘藓结皮植物-土壤连续体不同粒径土壤微生物群落多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23131-. |
| [8] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [9] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [10] | 张雅丽, 张丙昌, 赵康, 李凯凯, 刘燕晋. 毛乌素沙地不同类型生物结皮细菌群落差异及其驱动因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23027-. |
| [11] | 吴春玲, 罗竹慧, 李意德, 许涵, 陈德祥, 丁琼. 热带山地雨林木本豆科和樟科植物叶内生细菌群落: 物种与功能群多样性及驱动因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23146-. |
| [12] | 朱晓华, 高程, 王聪, 赵鹏. 尿素对土壤细菌与真菌多样性影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22636-. |
| [13] | 毛莹儿, 周秀梅, 王楠, 李秀秀, 尤育克, 白尚斌. 毛竹扩张对杉木林土壤细菌群落的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22659-. |
| [14] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [15] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()
