



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 22391. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022391 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022391
• 研究报告: 遗传多样性 • 下一篇
熊飞1,2, 刘红艳1,2,*( ), 翟东东1,2, 段辛斌3,*(
), 翟东东1,2, 段辛斌3,*( ), 田辉伍3, 陈大庆3
), 田辉伍3, 陈大庆3
收稿日期:2022-07-09
接受日期:2022-11-14
出版日期:2023-04-20
发布日期:2023-04-20
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 基金资助:
Fei Xiong1,2, Hongyan Liu1,2,*( ), Dongdong Zhai1,2, Xinbin Duan3,*(
), Dongdong Zhai1,2, Xinbin Duan3,*( ), Huiwu Tian3, Daqing Chen3
), Huiwu Tian3, Daqing Chen3
Received:2022-07-09
Accepted:2022-11-14
Online:2023-04-20
Published:2023-04-20
Contact:
*E-mail: 摘要:
利用基因组重测序的方法获取高通量SNP标记, 分析了长江上游三峡大坝-白鹤滩大坝之间8个不同江段(太平溪、巴南、合川、岷江口、宜宾、邵女坪、桧溪、冯家坪)共136尾瓦氏黄颡鱼(Pelteobagrus vachelli)的遗传多样性和遗传分化水平, 阐明了长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构。结果显示: (1)三峡库区太平溪群体和巴南群体具有较高的SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism)数量和核苷酸多样性指数, 遗传来源丰富, 其遗传多样性高于其他群体; 上游的岷江口、宜宾、邵女坪和冯家坪群体遗传来源单一。(2)瓦氏黄颡鱼存在3个不同的遗传分支, 且不同遗传分支之间存在较大的遗传分化。(3)群体SNP数量和核苷酸多样性指数与河流坡降呈显著负相关, 群体遗传分化指数与地理距离和隔离时间无显著相关性。研究结果表明, 在三峡大坝-白鹤滩大坝江段, 瓦氏黄颡鱼上游群体具有更低的遗传多样性, 更易发生遗传漂变作用, 在鱼类遗传多样性保护中需要特别关注; 瓦氏黄颡鱼存在3种显著的遗传结构, 应视为3个不同遗传单元进行种质资源管理。
熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆 (2023) 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构. 生物多样性, 31, 22391. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022391.
Fei Xiong, Hongyan Liu, Dongdong Zhai, Xinbin Duan, Huiwu Tian, Daqing Chen (2023) Population genetic structure of Pelteobagrus vachelli in the upper Yangtze River based on genome re-sequencing. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22391. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022391.
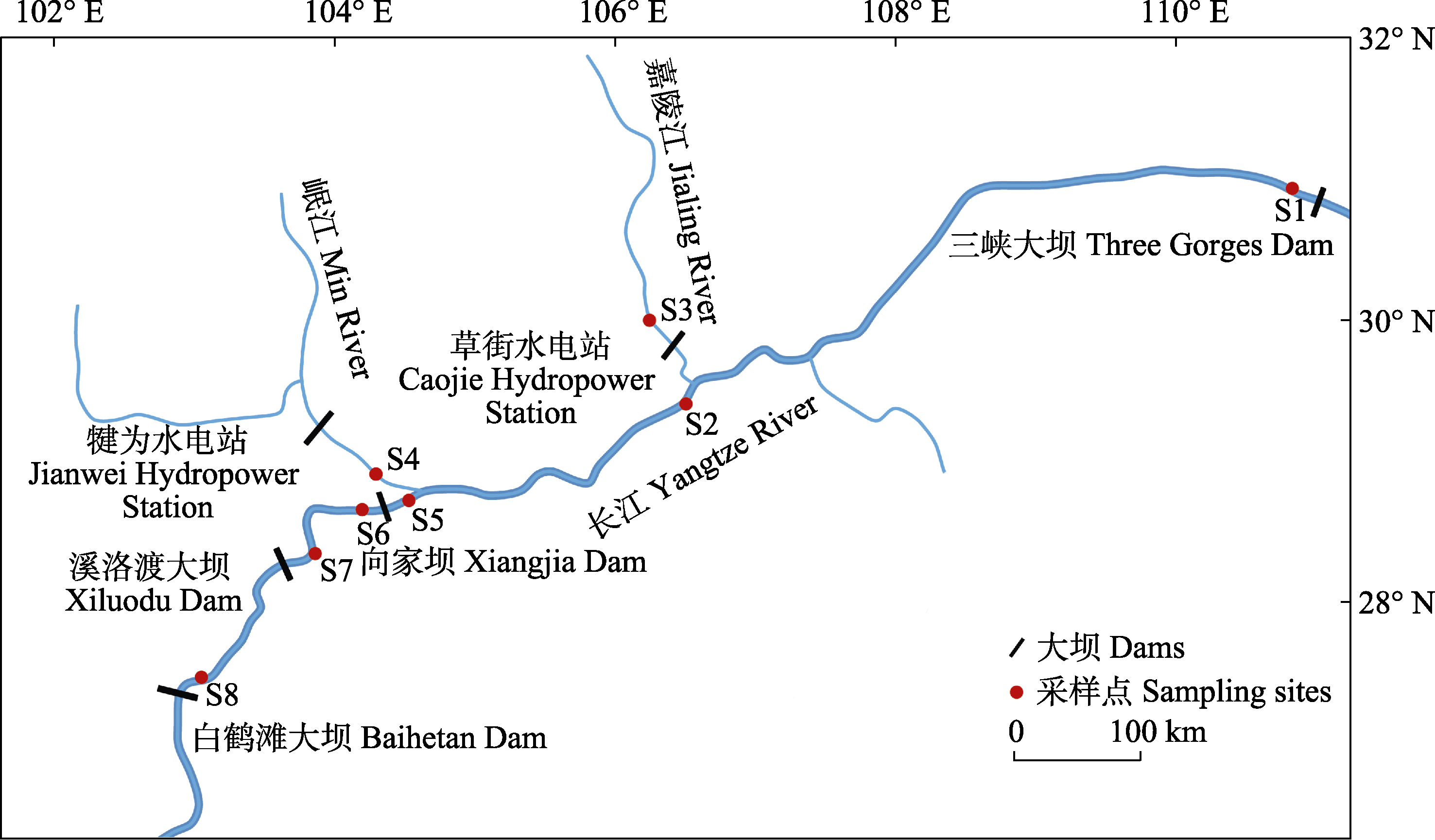
图1 长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼的样点分布。S1: 太平溪(TP); S2: 巴南(BN); S3: 合川(HC); S4: 岷江口(MJ); S5: 宜宾(YB); S6: 邵女坪(SN); S7: 桧溪(HX); S8: 冯家坪(FJ)。
Fig. 1 Sampling sites of Pelteobagrus vachelli in the upper reaches of Yangtze River. S1, Taipingxi (TP); S2, Banan (BN); S3, Hechuan (HC); S4, Minjiangkou (MJ); S5, Yibin (YB); S6, Shaonüping (SN); S7, Huixi (HX); S8, Fengjiaping (FJ).
| 群体 Population | 采样时间 Sampling time | 样本数 No. of sample | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 坡降 Channel slope (m/km) | 生境类型 Habitat type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 太平溪 TP | 2019.8 | 14 | 110 | 0.12 | 水库 Reservoir |
| 巴南 BN | 2019.8 | 25 | 160 | 0.20 | 回水区 Backwater area |
| 合川 HC | 2019.9 | 4 | 187 | 1.85 | 水库 Reservoir |
| 岷江口 MJ | 2019.10 | 25 | 257 | 2.26 | 河流 River |
| 宜宾 YB | 2019.10 | 6 | 253 | 0.70 | 河流 River |
| 邵女坪 SN | 2019.10 | 12 | 296 | 0.90 | 水库 Reservoir |
| 桧溪 HX | 2019.10 | 25 | 356 | 1.40 | 河流 River |
| 冯家坪 FJ | 2019.10 | 25 | 578 | 1.50 | 河流 River |
表1 瓦氏黄颡鱼8个群体的样点信息。样点缩写见图1。
Table 1 Sampling information in eight populations of Pelteobagrus vachelli. Site abbreviations are shown in Fig. 1.
| 群体 Population | 采样时间 Sampling time | 样本数 No. of sample | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 坡降 Channel slope (m/km) | 生境类型 Habitat type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 太平溪 TP | 2019.8 | 14 | 110 | 0.12 | 水库 Reservoir |
| 巴南 BN | 2019.8 | 25 | 160 | 0.20 | 回水区 Backwater area |
| 合川 HC | 2019.9 | 4 | 187 | 1.85 | 水库 Reservoir |
| 岷江口 MJ | 2019.10 | 25 | 257 | 2.26 | 河流 River |
| 宜宾 YB | 2019.10 | 6 | 253 | 0.70 | 河流 River |
| 邵女坪 SN | 2019.10 | 12 | 296 | 0.90 | 水库 Reservoir |
| 桧溪 HX | 2019.10 | 25 | 356 | 1.40 | 河流 River |
| 冯家坪 FJ | 2019.10 | 25 | 578 | 1.50 | 河流 River |
| 群体 Population | 样本数 No. of sample | Clean data (Gb) | Q30 (%) | 测序深度Sequencing depth | 序列比对率 Sequence mapped (%) | 基因组覆盖度Coverage of genomic reference (%) | SNP数目 Number of SNP | 核苷酸多样性指数Nucleotide diversity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 太平溪 TP | 14 | 145.22 | 93.11 | 9.54 | 54.31 | 72.92 | 4,172,876 | 2.44 × 10?3 |
| 巴南 BN | 25 | 236.41 | 92.82 | 8.71 | 53.43 | 71.68 | 3,543,176 | 2.81 × 10?3 |
| 合川 HC | 4 | 35.77 | 92.81 | 8.38 | 49.94 | 66.28 | 534,504 | 8.59 × 10?4 |
| 岷江口 MJ | 25 | 217.32 | 92.73 | 8.25 | 50.68 | 66.39 | 419,733 | 5.60 × 10?4 |
| 宜宾 YB | 6 | 50.16 | 91.87 | 7.44 | 48.50 | 67.36 | 563,968 | 6.76 × 10?4 |
| 邵女坪 SN | 12 | 128.29 | 92.79 | 9.37 | 49.09 | 69.64 | 457,603 | 5.75 × 10?4 |
| 桧溪 HX | 25 | 258.76 | 92.79 | 9.20 | 49.22 | 68.87 | 597,465 | 6.60 × 10?4 |
| 冯家坪 FJ | 25 | 273.27 | 92.78 | 9.57 | 49.06 | 69.73 | 441,092 | 5.84 × 10?4 |
| 总体 Total | 136 | 1,345.21 | 92.78 | 8.95 | 50.73 | 69.43 | 7,341,959 | 1.19 × 10?3 |
表2 瓦氏黄颡鱼8个群体重测序数据及群体遗传多样性参数
Table 2 The genome re-sequencing data and genetic diversity parameters in eight populations of Pelteobagrus vachelli
| 群体 Population | 样本数 No. of sample | Clean data (Gb) | Q30 (%) | 测序深度Sequencing depth | 序列比对率 Sequence mapped (%) | 基因组覆盖度Coverage of genomic reference (%) | SNP数目 Number of SNP | 核苷酸多样性指数Nucleotide diversity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 太平溪 TP | 14 | 145.22 | 93.11 | 9.54 | 54.31 | 72.92 | 4,172,876 | 2.44 × 10?3 |
| 巴南 BN | 25 | 236.41 | 92.82 | 8.71 | 53.43 | 71.68 | 3,543,176 | 2.81 × 10?3 |
| 合川 HC | 4 | 35.77 | 92.81 | 8.38 | 49.94 | 66.28 | 534,504 | 8.59 × 10?4 |
| 岷江口 MJ | 25 | 217.32 | 92.73 | 8.25 | 50.68 | 66.39 | 419,733 | 5.60 × 10?4 |
| 宜宾 YB | 6 | 50.16 | 91.87 | 7.44 | 48.50 | 67.36 | 563,968 | 6.76 × 10?4 |
| 邵女坪 SN | 12 | 128.29 | 92.79 | 9.37 | 49.09 | 69.64 | 457,603 | 5.75 × 10?4 |
| 桧溪 HX | 25 | 258.76 | 92.79 | 9.20 | 49.22 | 68.87 | 597,465 | 6.60 × 10?4 |
| 冯家坪 FJ | 25 | 273.27 | 92.78 | 9.57 | 49.06 | 69.73 | 441,092 | 5.84 × 10?4 |
| 总体 Total | 136 | 1,345.21 | 92.78 | 8.95 | 50.73 | 69.43 | 7,341,959 | 1.19 × 10?3 |
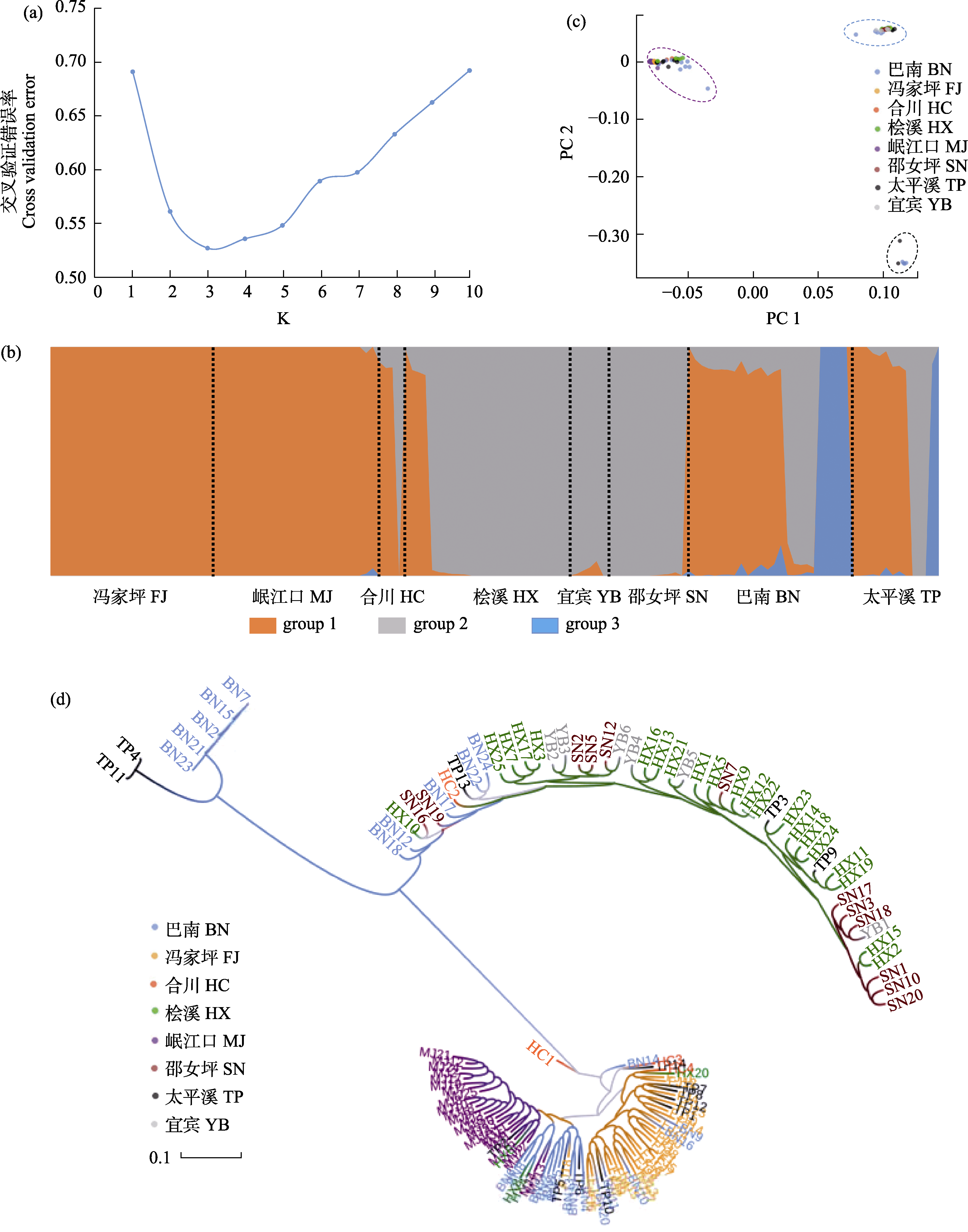
图2 基于SNP标记分析8个瓦氏黄颡鱼群体的遗传结构。(a)由交叉验证错误率确定的最优分组数; (b) K = 3时, 所有个体的分组情况; (c) PCA聚类情况; (d) ML聚类树。样点缩写见图1。
Fig. 2 Genetic structure based on SNP markers in eight populations of Pelteobagrus vaclerii. (a) The optimal number of clusters determined by cross-validated error rate valley. (b) Population structure (K = 3) of all individuals. (c) PCA plot of every individual. (d) ML phylogenetic tree. Site abbreviations are shown in Fig. 1.
| 群体 Population | 太平溪 TP | 巴南 BN | 合川 HC | 岷江口 MJ | 宜宾 YB | 邵女坪 SN | 桧溪 HX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巴南 BN | 0.050 | ||||||
| 合川 HC | ?0.109 | ?0.039 | |||||
| 岷江口 MJ | 0.112 | 0.143 | 0.075 | ||||
| 宜宾 YB | ?0.020 | 0.043 | 0.152 | 0.233 | |||
| 邵女坪 SN | 0.068 | 0.112 | 0.192 | 0.235 | 0.000 | ||
| 桧溪 HX | 0.126 | 0.154 | 0.079 | 0.179 | ?0.008 | 0.002 | |
| 冯家坪 FJ | 0.125 | 0.152 | 0.092 | 0.016 | 0.261 | 0.257 | 0.193 |
表3 长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼两两群体之间的遗传分化指数
Table 3 Genetic differentiation between the pairwise populations of Pelteobagrus vaclerii in the upper Yangtze River
| 群体 Population | 太平溪 TP | 巴南 BN | 合川 HC | 岷江口 MJ | 宜宾 YB | 邵女坪 SN | 桧溪 HX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巴南 BN | 0.050 | ||||||
| 合川 HC | ?0.109 | ?0.039 | |||||
| 岷江口 MJ | 0.112 | 0.143 | 0.075 | ||||
| 宜宾 YB | ?0.020 | 0.043 | 0.152 | 0.233 | |||
| 邵女坪 SN | 0.068 | 0.112 | 0.192 | 0.235 | 0.000 | ||
| 桧溪 HX | 0.126 | 0.154 | 0.079 | 0.179 | ?0.008 | 0.002 | |
| 冯家坪 FJ | 0.125 | 0.152 | 0.092 | 0.016 | 0.261 | 0.257 | 0.193 |
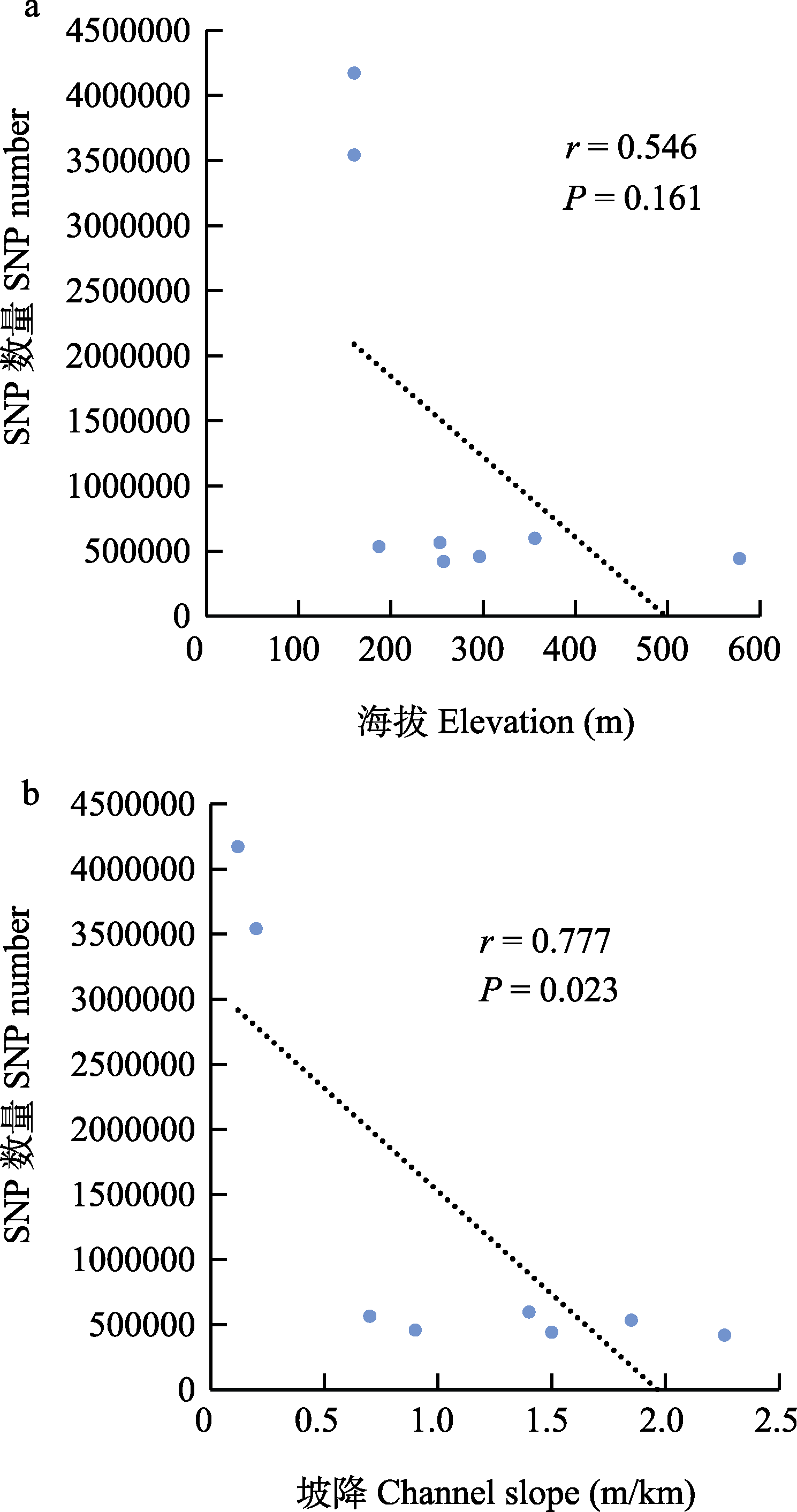
图4 瓦氏黄颡鱼SNP数量与河道海拔(a)和坡降(b)的相关性分析。P < 0.05表示显著相关。
Fig. 4 Correlation analysis of the SNP numbers with elevation (a) and channel slope (b). P < 0.05 indicates significant correlation.
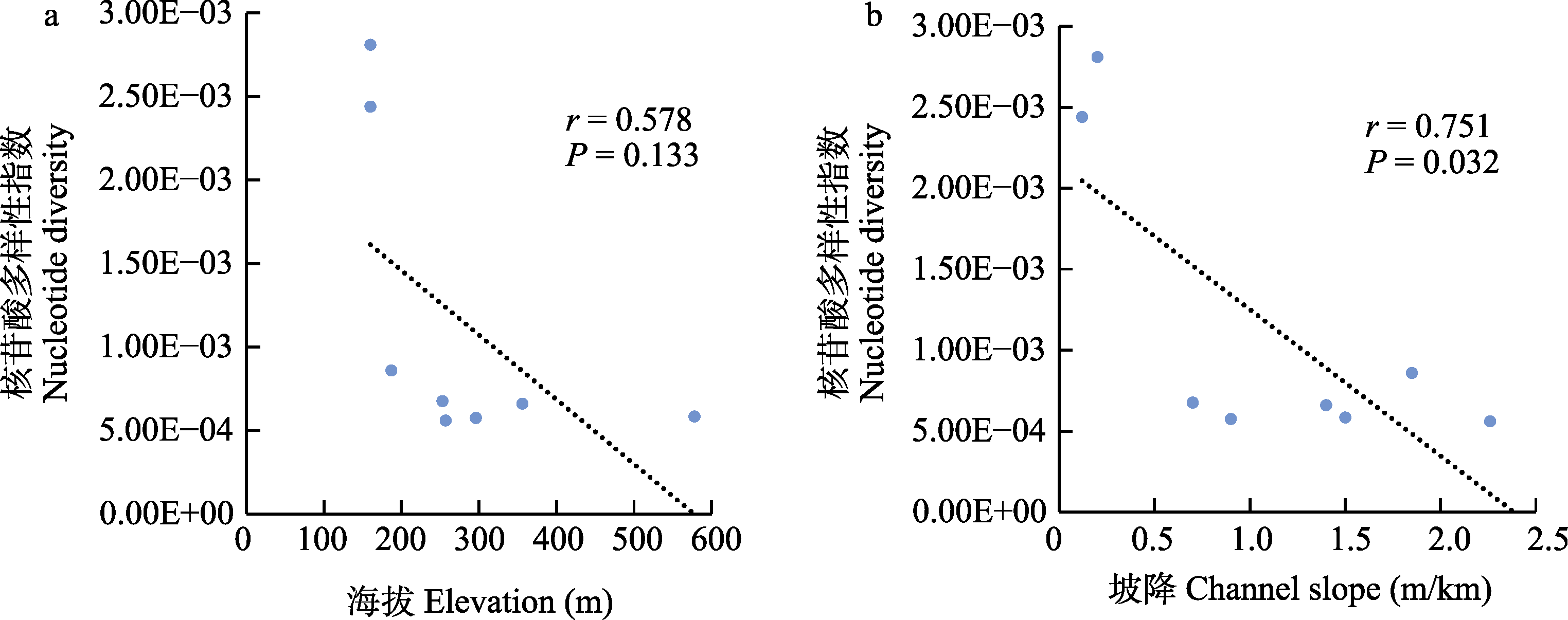
图5 瓦氏黄颡鱼核苷酸多样性指数与海拔(a)和坡降(b)的相关性分析。P < 0.05表示显著相关。
Fig. 5 Correlation analysis of nucleotide diversity with elevation (a) and channel slope (b). P < 0.05 indicates significant correlation.
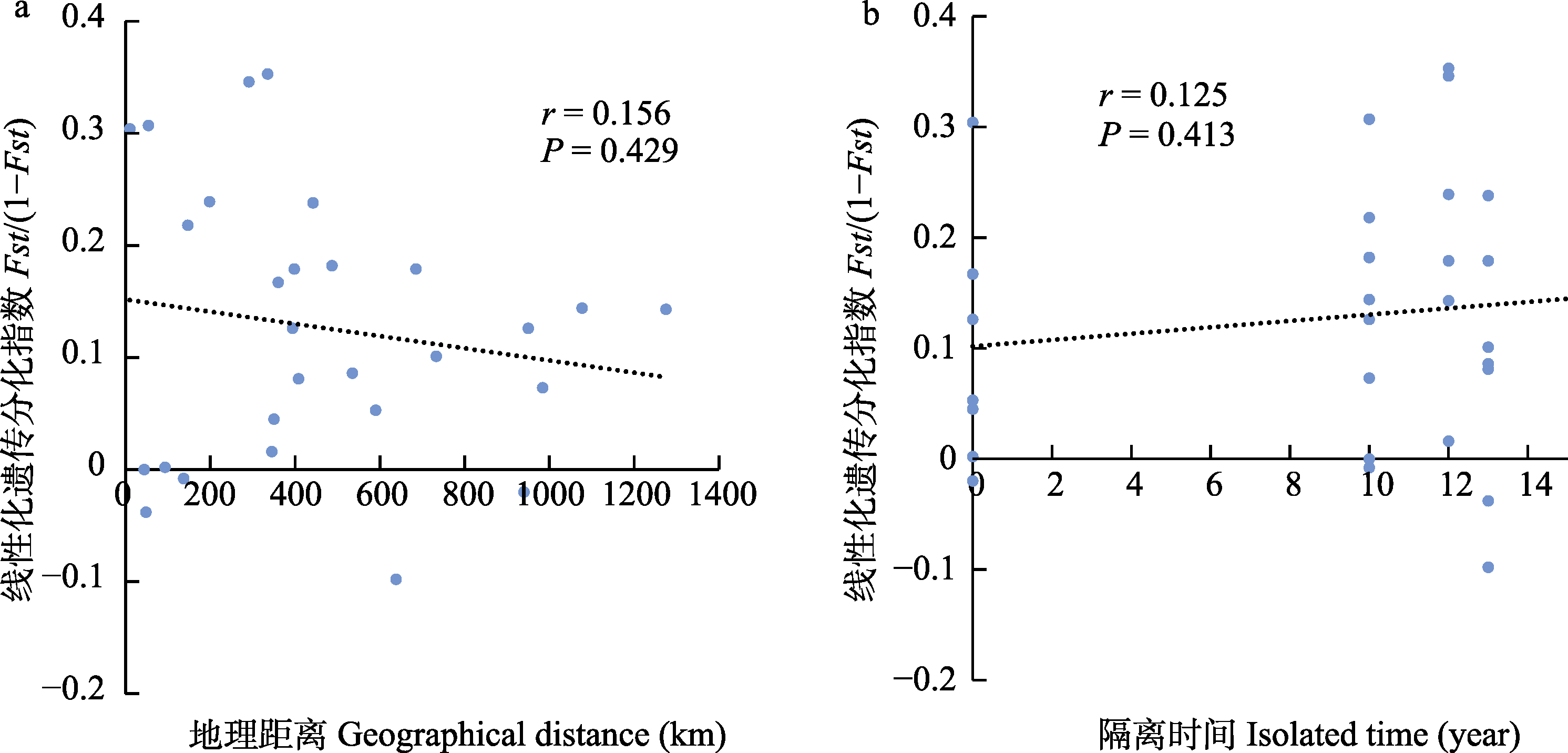
图6 遗传分化(a)与地理距离(b)和隔离时间的Mantel检验。Fst: 遗传分化指数。
Fig. 6 Mantel test of genetic differentiation with geographical distance and isolated time. Fst, Index of genetic differentiation.
| [1] |
Alexander DH, Novembre J, Lange K (2009) Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Research, 19, 1655-1664.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Chen DQ, Liu SP, Duan XB, Xiong F (2002) A preliminary study of the fisheries biology of main commercial fishes in the middle and upper reaches of the Yangtze River. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 26, 618-622. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈大庆, 刘绍平, 段辛斌, 熊飞 (2002) 长江中上游主要经济鱼类的渔业生物学特征. 水生生物学报, 26, 618-622.] | |
| [3] |
Cheng F, Li W, Castello L, Murphy BR, Xie SG (2015) Potential effects of dam cascade on fish: Lessons from the Yangtze River. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 25, 569-585.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Cheng F, Li W, Wu QJ, Hallerman E, Xie SG (2013) Microsatellite DNA variation among samples of bronze gudgeon, Coreius heterodon, in the mainstem of the Yangtze River, China. Ichthyological Research, 60, 165-171.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Cook DR, Sullivan SMP (2018) Associations between riffle development and aquatic biota following low head dam removal. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 339.
DOI |
| [6] |
Danecek P, Auton A, Abecasis G, Albers CA, Banks E, DePristo MA, Handsaker RE, Lunter G, Marth GT, Sherry ST, McVean G, Durbin R (2011) The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics, 27, 2156-2158.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Deiner K, Garza JC, Coey R, Girman DJ (2007) Population structure and genetic diversity of trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) above and below natural and man-made barriers in the Russian River, California. Conservation Genetics, 8, 437-454.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Ding RH (1994) The Fishes of Sichuan. Sichuan Science & Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [ 丁瑞华 (1994) 四川鱼类志. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [9] |
Dixon P (2003) Vegan, a package of R functions for community ecology. Journal of Vegetation Science, 14, 927-930.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Gong GR, Dan C, Xiao SJ, Guo WJ, Huang PP, Xiong Y, Wu JJ, He Y, Zhang JC, Li XH, Chen NS, Gui JF, Mei J (2018) Chromosomal-level assembly of yellow catfish genome using third-generation DNA sequencing and Hi-C analysis. GigaScience, 7, giy120. |
| [11] |
Kang JL, Ma XH, He SP (2017) Population genetics analysis of the Nujiang catfish Creteuchiloglanis macropterus through a genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphisms resource generated by RAD-seq. Scientific Reports, 7, 2813.
DOI |
| [12] |
Kanno Y, Vokoun JC, Letcher BH (2011) Fine-scale population structure and riverscape genetics of brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) distributed continuously along headwater channel networks. Molecular Ecology, 20, 3711-3729.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with bowtie 2. Nature Methods, 9, 357-359.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R, Proc GPD (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinfor- matics, 25, 2078-2079. |
| [15] |
Liu D, Li X, Song Z (2020) No decline of genetic diversity in elongate loach (Leptobotia elongata) with a tendency to form population structure in the upper Yangtze River. Global Ecology and Conservation, 23, e01072.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Liu HY, Xiong F, Duan XB, Tian HW, Liu SP, Chen DQ (2017) Low population differentiation revealed in the highly threatened elongate loach (Leptobotia elongata Bleeker), a species endemic to the fragmented upper reaches of the Yangtze River. Biochemical Systematics & Ecology, 70, 22-28. |
| [17] | Lü H, Tian HW, Duan XB, Chen DQ, Shen SY, Liu SP (2018) The larval resources of fishes spawning drifting eggs in the lower reaches of the Minjiang River. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 27(1), 88-96. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吕浩, 田辉伍, 段辛斌, 陈大庆, 申绍祎, 刘绍平 (2018) 岷江下游干流段鱼类资源现状及其多样性分析. 长江流域资源与环境, 27(1), 88-96.] | |
| [18] | McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenk AO, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly M, DePristo MA (2010) The genome analysis toolkit: A mapreduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Resources, 20, 1297-1303. |
| [19] |
Nakajima N, Hirota SK, Matsuo A, Suyama Y, Nakamura F (2020) Genetic structure and population demography of white-spotted charr in the upstream watershed of a large dam. Water, 12, 2406.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA, Reich D (2006) Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nature Genetics, 38, 904-909.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MAR, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, Bakker PIWD, Daly MJ, Sham PC (2007) PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 81, 559-575.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Song J, Chang LJ, Wang D (2016) Multi-locus genomic analysis reveals the genetic diversity and population structure of the rock carp (Procypris rabaudi) in the upper Yangtze River. Biochemical Systematics & Ecology, 66, 86-93. |
| [23] |
Stamatakis A (2014) RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics, 30, 1312-1313.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Vera-Escalona I, Habit E, Ruzzante DE (2015) Echoes of a distant time: Effects of historical processes on contemporary genetic patterns in Galaxias platei in Patagonia. Molecular Ecology, 24, 4112-4128.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Wang ZW, Wu QJ, Zhou JF, Ye YZ (2004) Geographic distribution of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco and Pelteobagrus vachelli in the Yangtze River based on mitochondrial DNA markers. Biochemical Genetics, 42, 391-400.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Xiong F, Liu HY, Duan XB, Liu SP, Chen DQ (2015) Present status of fishery resources in Yibin section of the Upper Yangtze River. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 37(11), 43-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 熊飞, 刘红艳, 段辛斌, 刘绍平, 陈大庆 (2015) 长江上游宜宾江段渔业资源现状研究. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 37(11), 43-50.] | |
| [27] |
Xu SY, Song N, Zhao LL, Cai SS, Han ZQ, Gao TX (2017) Genomic evidence for local adaptation in the ovoviviparous marine fish Sebastiscus marmoratus with a background of population homogeneity. Scientific Reports, 7, 1562.
DOI |
| [28] | Yang JY (1994) The reproductive biology of Pelteobagrus vachelli in the Jialing River. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Natural Science), 19, 639-645. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨家云 (1994) 嘉陵江瓦氏黄颡鱼的繁殖生物学. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 19, 639-645.] | |
| [29] | Yao WZ (2018) Habitat and restoration of fluvial fish which producing sticky eggs: A case study in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. In:Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on Modern Marine Ranching and the Fisheries Resources and Environment Committee of the Chinese Aquatic Society, pp. 100. China Aquatic Society Marine Ranching Research Association, Dalian. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 姚维志 (2018) 河流产粘性卵鱼类生境及修复——以长江上游为例. 见: 第二届现代化海洋牧场国际学术研讨会、中国水产学会渔业资源与环境专业委员会2018年学术年会论文集, pp.100. 中国水产学会海洋牧场研究会, 大连.] | |
| [30] |
Zhai DD, Zhang Z, Zhang FT, Liu HZ, Cao WX, Gao X (2019) Genetic diversity and population structure of a cyprinid fish (Ancherythroculter nigrocauda) in a highly fragmented river. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 35, 701-708.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Zhang LW, Tian HW, Chen DQ, Liu SP, Duan XB, Wang DQ (2020) Genetic diversity and structure of Glyptothorax sinensis in upper Yangtze River. Freshwater Fisheries, 50, 3-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张力文, 田辉伍, 陈大庆, 刘绍平, 段辛斌, 汪登强 (2020) 长江上游中华纹胸鮡遗传多样性及遗传结构研究. 淡水渔业, 50, 3-11.] |
| [1] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [2] | 姚祥坦, 张心怡, 陈阳, 袁晔, 程旺大, 王天瑞, 邱英雄. 基于基因组重测序揭示栽培欧菱遗传多样性及‘南湖菱’的起源驯化历史[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24212-. |
| [3] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [4] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [5] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [6] | 景昭阳, 程可光, 舒恒, 马永鹏, 刘平丽. 全基因组重测序方法在濒危植物保护中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22679-. |
| [7] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [8] | 何艺玥, 刘玉莹, 张富斌, 秦强, 曾燏, 吕振宇, 杨坤. 梯级水利工程背景下的嘉陵江干流蛇鮈群体遗传多样性和遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [9] | 罗瑞, 陈娅, 张汉马. 芸薹属植物全基因组重测序研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(10): 23237-. |
| [10] | 孙维悦, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 莫日根高娃, 杜夏瑾, 刘保东, 严岳鸿. 基于保护基因组学揭示荷叶铁线蕨的濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [11] | 陶克涛, 白东义, 图格琴, 赵若阳, 安塔娜, 铁木齐尔·阿尔腾齐米克, 宝音德力格尔, 哈斯, 芒来, 韩海格. 基于基因组SNPs对东亚家马不同群体遗传多样性的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [12] | 崔静, 徐明芳, 章群, 李瑶, 曾晓舒, 李莎. 基于3种线粒体标记探讨中日沿海角木叶鲽遗传多样性差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21485-. |
| [13] | 孙军, 宋煜尧, 施义锋, 翟键, 燕文卓. 近十年中国海洋生物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22526-. |
| [14] | 栗冬梅, 杨卫红, 李庆多, 韩茜, 宋秀平, 潘虹, 冯云. 巴尔通体在滇西南蝙蝠中高度流行并具有丰富的遗传变异特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1245-1255. |
| [15] | 姚志, 郭军, 金晨钟, 刘勇波. 中国纳入一级保护的极小种群野生植物濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 394-408. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn