



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 23160. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023160 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023160
• 研究报告: 遗传多样性 • 下一篇
何艺玥1, 刘玉莹1, 张富斌3,4, 秦强3,4, 曾燏1,4, 吕振宇1, 杨坤1,2,4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-22
接受日期:2023-10-18
出版日期:2023-11-20
发布日期:2023-11-29
通讯作者:
* E-mail: 作者简介:# 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Yiyue He1, Yuying Liu1, Fubin Zhang3,4, Qiang Qin3,4, Yu Zeng1,4, Zhenyu Lü1, Kun Yang1,2,4,*( )
)
Received:2023-05-22
Accepted:2023-10-18
Online:2023-11-20
Published:2023-11-29
Contact:
* E-mail: About author:# Co-first authors
摘要:
随着嘉陵江航道渠化工程建设逐步完成, 由此造成的嘉陵江水生生境破碎化、鱼类资源衰退等问题日益凸显。在这种情形下, 鱼类的遗传多样性是否受到影响, 是非常令人关心的问题。2018年7-12月于嘉陵江干流朝天区(CT)、苍溪县(CX)、蓬安县(PA)、合川区(HC) 4个区域采集蛇鮈(Saurogobio dabryi)样本113尾, 以线粒体控制区序列和微卫星位点为分子标记, 研究梯级水利工程背景下蛇鮈种群的遗传多样性与遗传结构。结果显示: 在遗传多样性分析中, 无论是线粒体数据还是微卫星标记, 下游江段HC种群的遗传多样性参数(PIC = 0.543, π = 0.0264, Hd = 0.940)均显著高于中上游江段CT、CX和PA种群, 推测这种现象可能与HC种群地处于长江干流交汇口有关; 相反处于上游江段的CT种群的遗传多样性和单倍型数量均较高, 推测可能与近期种群扩张有关; 在种群结构分析中, CT、CX和PA处于同一分支, HC种群成为独立一支, 单倍型网络图和系统发育分析显示同样结果, 推测与水利工程导致的地理隔离与开闸放水形成向下的基因流向有关。
何艺玥, 刘玉莹, 张富斌, 秦强, 曾燏, 吕振宇, 杨坤 (2023) 梯级水利工程背景下的嘉陵江干流蛇鮈群体遗传多样性和遗传结构. 生物多样性, 31, 23160. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023160.
Yiyue He, Yuying Liu, Fubin Zhang, Qiang Qin, Yu Zeng, Zhenyu Lü, Kun Yang (2023) Genetic diversity and population structure of Saurogobio dabryi under cascade water conservancy projects in the Jialing River. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23160. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023160.
| 种群 Populations | 样本数(尾) Sample size | 体长 Body length (mm) | 湿重 Wet weight (g) | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 朝天区 CT | 27 | 100.12 ± 26.81 | 15.71 ± 10.27 | 32.65° N | 105.89° E |
| 苍溪县 CX | 28 | 132.04 ± 11.15 | 27.75 ± 6.47 | 31.74° N | 105.96° E |
| 蓬安县 PA | 30 | 109.95 ± 16.58 | 25.43 ± 33.82 | 31.04° N | 106.40° E |
| 合川区 HC | 28 | 114.84 ± 11.07 | 17.42 ± 4.40 | 29.98° N | 106.29° E |
表1 嘉陵江4个蛇鮈种群的样本信息
Table 1 Sample information of four Saurogobio dabryi populations. CT, Chaotian; CX, Cangxi; PA, Peng’an; HC, Hechuan.
| 种群 Populations | 样本数(尾) Sample size | 体长 Body length (mm) | 湿重 Wet weight (g) | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 朝天区 CT | 27 | 100.12 ± 26.81 | 15.71 ± 10.27 | 32.65° N | 105.89° E |
| 苍溪县 CX | 28 | 132.04 ± 11.15 | 27.75 ± 6.47 | 31.74° N | 105.96° E |
| 蓬安县 PA | 30 | 109.95 ± 16.58 | 25.43 ± 33.82 | 31.04° N | 106.40° E |
| 合川区 HC | 28 | 114.84 ± 11.07 | 17.42 ± 4.40 | 29.98° N | 106.29° E |
| 位点 Loci | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5'-3') | 重复单元 Repeat motif | 片段大小 Size range (bp) | 退火温度 Tm (℃) | 参考来源 Reference source | 登录号 Accession number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD01 | GCTCCATTCCCAACCTATAACACAT GCCTTGATGAACGGTTATGTATG | (ACAT)10 | 98 | 61 | sdF5010 | KX250317 |
| SD02 | GTGGCTCCTTCCCTTTCACAGAGCA GATTGTACATGTGGCTCAAG | (GCA)9 | 116 | 62 | sdF6400 | KX25347 |
| SD03 | ATGACAAAGGAAAACCACGAGAAA TGCAGATACAGCGCATCACTTTAG | (AAAC)16 | 132 | 62 | sdF5261 | KX250326 |
| SD04 | CACAGACGAGGATTCCAGTCGACA TGCAGTCCCTTACCTGTTCTC | (GAG)5 | 154 | 65 | sdF6273 | KX250343 |
| SD05 | TCCGTTGTTTAGGCTACTGATCAAA TGAGATGACATGACGATAGCTGTG | (GATA)17 | 155 | 63 | sdF6479 | KX250350 |
| SD07 | ACACTACTCGTCTGCCGCAAACAA TGCAGATTGTTTCAAAGCAG | (AAAT)2 | 111 | 53 | sdF7209 | KX250353 |
| SD08 | AACTGTAGGGCACGACAAATTGAT AGTCTAAACCCGTCTGCAAGAATG | (AGAC)18 | 232 | 56 | sdF5145 | KX250320 |
| SD09 | TCTCAGATGACGTTGAGCATATTGA CATTCATCTGGGCTCACTAAAACA | (ATCT)15 | 151 | 57 | sdF5163 | KX250321 |
| SD10 | TTTCTGTACTTGTTAGTTTGGGGTC AGATCAATTAAATGCATCATTGCTGA | (TTTC)6 | 156 | 56 | sdF5351 | KX250333 |
| SD11 | CGTCTAGTGCTGAAGGAGGTGAGT TCTCAGCCTGGAACACAGAGAGAT | (ACTC)25 | 123 | 62 | sdF6476 | KX25329 |
表2 蛇鮈微卫星位点引物序列和特征
Table 2 Primer sequences and characteristics of microsatellite loci of Saurogobio dabryi
| 位点 Loci | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5'-3') | 重复单元 Repeat motif | 片段大小 Size range (bp) | 退火温度 Tm (℃) | 参考来源 Reference source | 登录号 Accession number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD01 | GCTCCATTCCCAACCTATAACACAT GCCTTGATGAACGGTTATGTATG | (ACAT)10 | 98 | 61 | sdF5010 | KX250317 |
| SD02 | GTGGCTCCTTCCCTTTCACAGAGCA GATTGTACATGTGGCTCAAG | (GCA)9 | 116 | 62 | sdF6400 | KX25347 |
| SD03 | ATGACAAAGGAAAACCACGAGAAA TGCAGATACAGCGCATCACTTTAG | (AAAC)16 | 132 | 62 | sdF5261 | KX250326 |
| SD04 | CACAGACGAGGATTCCAGTCGACA TGCAGTCCCTTACCTGTTCTC | (GAG)5 | 154 | 65 | sdF6273 | KX250343 |
| SD05 | TCCGTTGTTTAGGCTACTGATCAAA TGAGATGACATGACGATAGCTGTG | (GATA)17 | 155 | 63 | sdF6479 | KX250350 |
| SD07 | ACACTACTCGTCTGCCGCAAACAA TGCAGATTGTTTCAAAGCAG | (AAAT)2 | 111 | 53 | sdF7209 | KX250353 |
| SD08 | AACTGTAGGGCACGACAAATTGAT AGTCTAAACCCGTCTGCAAGAATG | (AGAC)18 | 232 | 56 | sdF5145 | KX250320 |
| SD09 | TCTCAGATGACGTTGAGCATATTGA CATTCATCTGGGCTCACTAAAACA | (ATCT)15 | 151 | 57 | sdF5163 | KX250321 |
| SD10 | TTTCTGTACTTGTTAGTTTGGGGTC AGATCAATTAAATGCATCATTGCTGA | (TTTC)6 | 156 | 56 | sdF5351 | KX250333 |
| SD11 | CGTCTAGTGCTGAAGGAGGTGAGT TCTCAGCCTGGAACACAGAGAGAT | (ACTC)25 | 123 | 62 | sdF6476 | KX25329 |
| 种群 Populations | mtDNA线粒体控制区 mtDNA control region | 微卫星位点 Microsatellite loci | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | H | Hd | π | n | k | A | Ai | Ho | He | PIC | Fis | |
| 朝天区 CT | 27 | 18 | 0.929 | 0.0180 | 94 | 16.328 | 4.500 | 4.500 | 0.493 | 0.433 | 0.391 | -0.139 |
| 苍溪县 CX | 28 | 10 | 0.877 | 0.0100 | 43 | 9.050 | 4.600 | 5.711 | 0.273 | 0.378 | 0.302 | 0.152 |
| 蓬安县 PA | 30 | 14 | 0.875 | 0.0120 | 89 | 10.863 | 6.400 | 6.169 | 0.357 | 0.490 | 0.443 | 0.275 |
| 合川区 HC | 28 | 17 | 0.940 | 0.0264 | 129 | 23.818 | 8.700 | 8.319 | 0.483 | 0.579 | 0.543 | 0.150 |
| 总计 Total | 113 | 39 | 0.894 | 0.0348 | 203 | 12.654 | 12 | 5.923 | 0.302 | 0.438 | 0.531 | 0.145 |
表3 嘉陵江干流蛇鮈4个种群mtDNA控制区和微卫星位点遗传多样性参数
Table 3 Genetic variability of Saurogobio dabryi populations based on mtDNA control region and microsatellite loci. CT, Chaotian; CX, Cangxi; PA, Peng’an; HC, Hechuan.
| 种群 Populations | mtDNA线粒体控制区 mtDNA control region | 微卫星位点 Microsatellite loci | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | H | Hd | π | n | k | A | Ai | Ho | He | PIC | Fis | |
| 朝天区 CT | 27 | 18 | 0.929 | 0.0180 | 94 | 16.328 | 4.500 | 4.500 | 0.493 | 0.433 | 0.391 | -0.139 |
| 苍溪县 CX | 28 | 10 | 0.877 | 0.0100 | 43 | 9.050 | 4.600 | 5.711 | 0.273 | 0.378 | 0.302 | 0.152 |
| 蓬安县 PA | 30 | 14 | 0.875 | 0.0120 | 89 | 10.863 | 6.400 | 6.169 | 0.357 | 0.490 | 0.443 | 0.275 |
| 合川区 HC | 28 | 17 | 0.940 | 0.0264 | 129 | 23.818 | 8.700 | 8.319 | 0.483 | 0.579 | 0.543 | 0.150 |
| 总计 Total | 113 | 39 | 0.894 | 0.0348 | 203 | 12.654 | 12 | 5.923 | 0.302 | 0.438 | 0.531 | 0.145 |
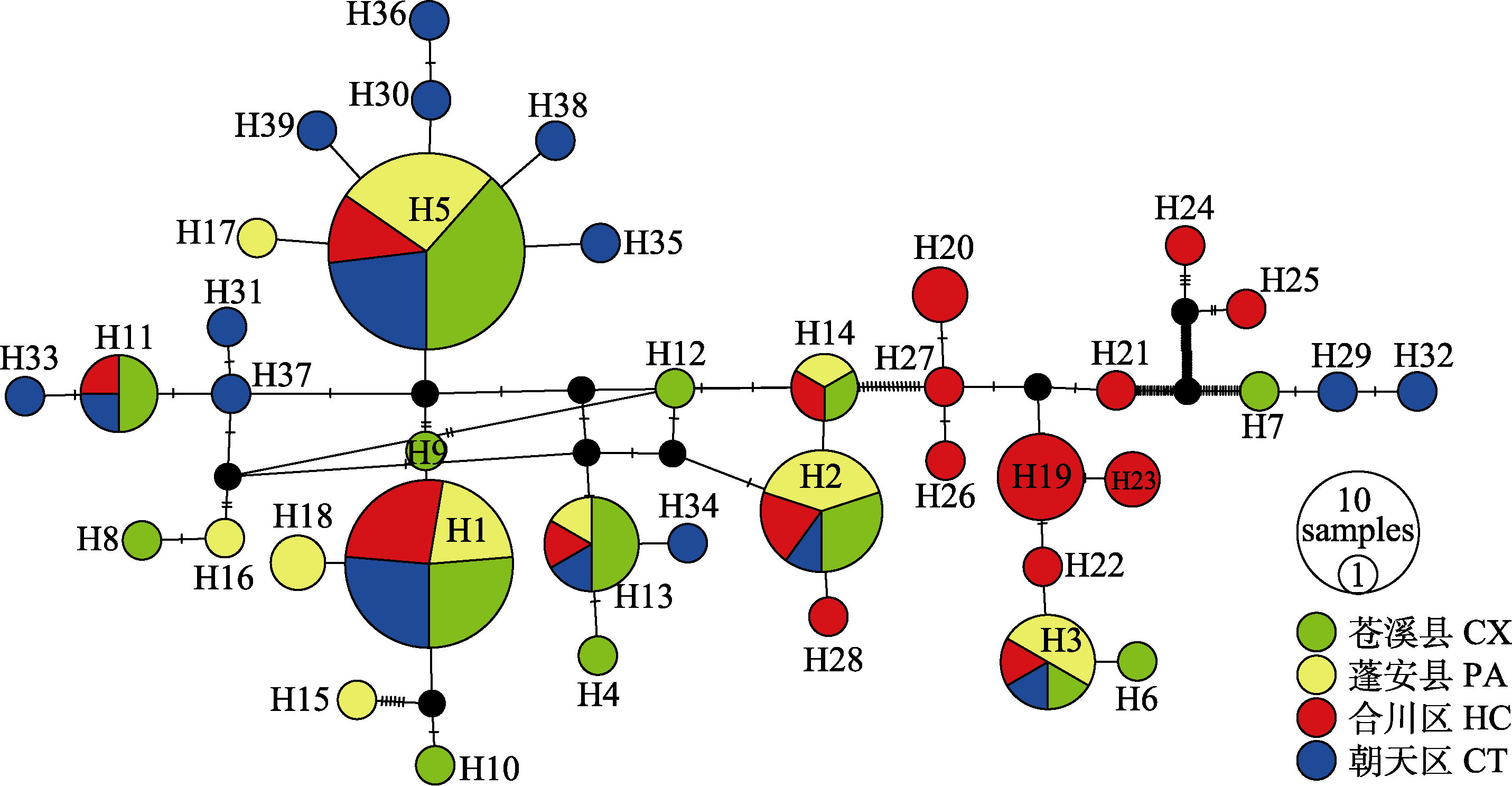
图2 嘉陵江4个蛇鮈种群的39个单倍型网络关系图。CT: 朝天; CX: 苍溪; PA: 蓬安; HC: 合川。
Fig. 2 Haplotype network for 39 haplotypes of four Saurogobio dabryi populations in Jialing River based on the median-joining algorithm. CT, Chaotian; CX, Cangxi; PA, Peng’an; HC, Hechuan.
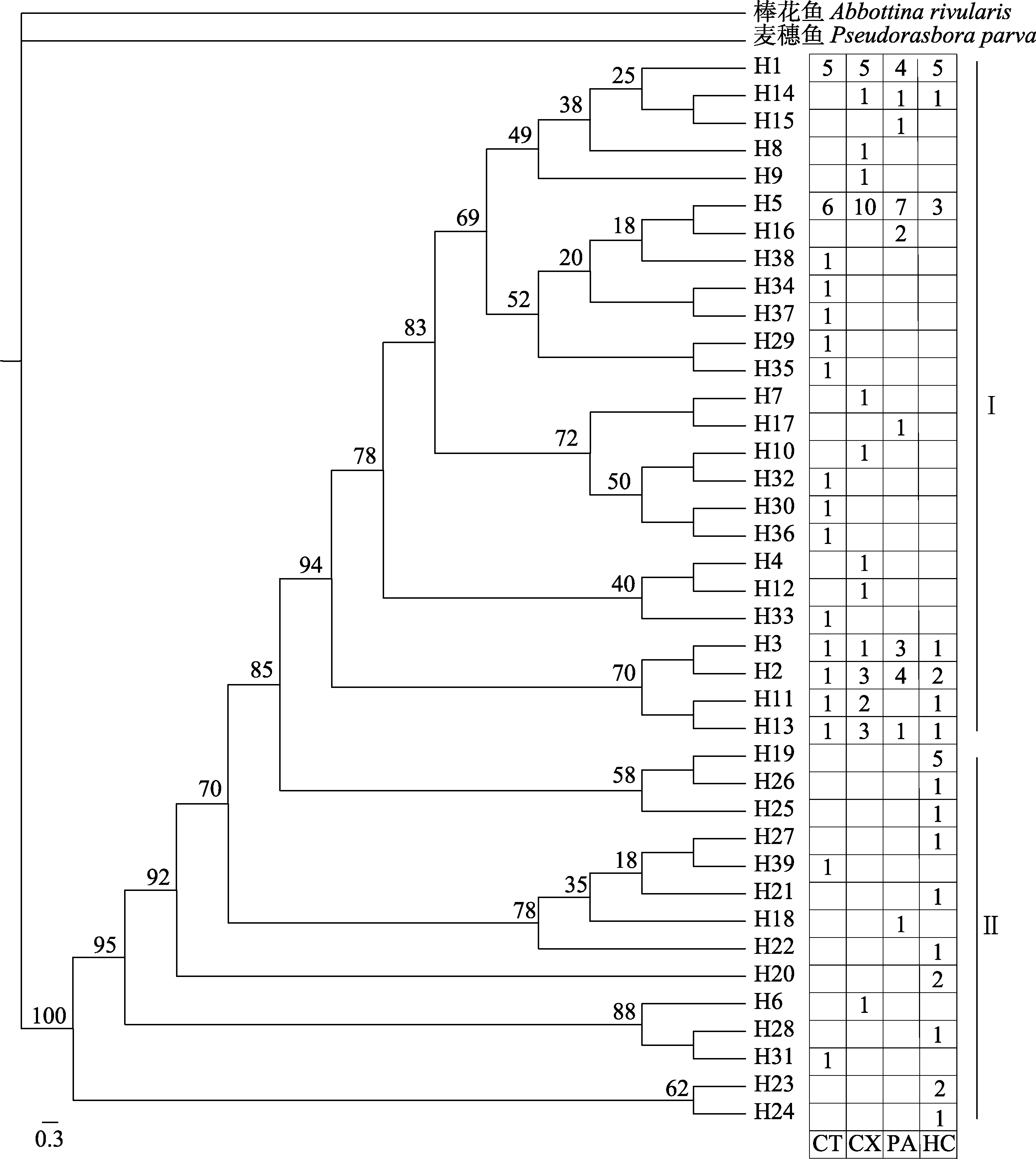
图3 蛇鮈mtDNA控制区单倍型系统发育树。节点数字为贝叶斯后验概率。CT: 朝天; CX: 苍溪; PA: 蓬安; HC: 合川。
Fig. 3 Molecular phylogenetic tree of Saurogobio dabryi derived from the mitochondrial control region. The number of each branch correspond to the Bayesian posterior probability. CT, Chaotian; CX, Cangxi; PA, Peng’an; HC, Hechuan.
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 总方差 Total variance | 变异比率 Variation ratio (%) | 固定系数 Fixed parameter | 概率 Probability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 组间 Intergroup | 2 | 733.641 | 69.38 | 0.02561 | 0.00027 ± 0.01111 |
| 组内种群间 Intragroup inter-population | 1 | 81.944 | 12.85 | 0.10621 | 0.00047 ± 0.01031 |
| 种群内个体间 Among individuals within a population | 110 | 102.266 | 22.23 | 0.12853 | 0.00000 ± 0.00000 |
| 合计 Total | 113 | 917.851 |
表4 4个蛇鮈种群的分子方差分析
Table 4 The AMOVA analysis of the four Saurogobio dabryi populations
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 总方差 Total variance | 变异比率 Variation ratio (%) | 固定系数 Fixed parameter | 概率 Probability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 组间 Intergroup | 2 | 733.641 | 69.38 | 0.02561 | 0.00027 ± 0.01111 |
| 组内种群间 Intragroup inter-population | 1 | 81.944 | 12.85 | 0.10621 | 0.00047 ± 0.01031 |
| 种群内个体间 Among individuals within a population | 110 | 102.266 | 22.23 | 0.12853 | 0.00000 ± 0.00000 |
| 合计 Total | 113 | 917.851 |
| 种群 Population | CT | CX | PA | HC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 朝天区 CT | 0.18921* | 0.01396** | 0.21069* | |
| 苍溪县 CX | 0.00028 | 0.03035* | 0.16243** | |
| 蓬安县 PA | 0.01624 | 0.01993 | 0.14526** | |
| 合川区 HC | 0.12140** | 0.13835* | 0.15537* |
表5 基于微卫星位点(对角线上)和mtDNA控制区(对角线下)的4个蛇鮈种群间的遗传分化系数Fst
Table 5 Pairwise genetic differentiation (Fst) of Saurogobio dabryi populations based on microsatellite loci (above the diagonal) and mtDNA control region (below the diagonal). CT, Chaotian; CX, Cangxi; PA, Peng’an; HC, Hechuan.
| 种群 Population | CT | CX | PA | HC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 朝天区 CT | 0.18921* | 0.01396** | 0.21069* | |
| 苍溪县 CX | 0.00028 | 0.03035* | 0.16243** | |
| 蓬安县 PA | 0.01624 | 0.01993 | 0.14526** | |
| 合川区 HC | 0.12140** | 0.13835* | 0.15537* |
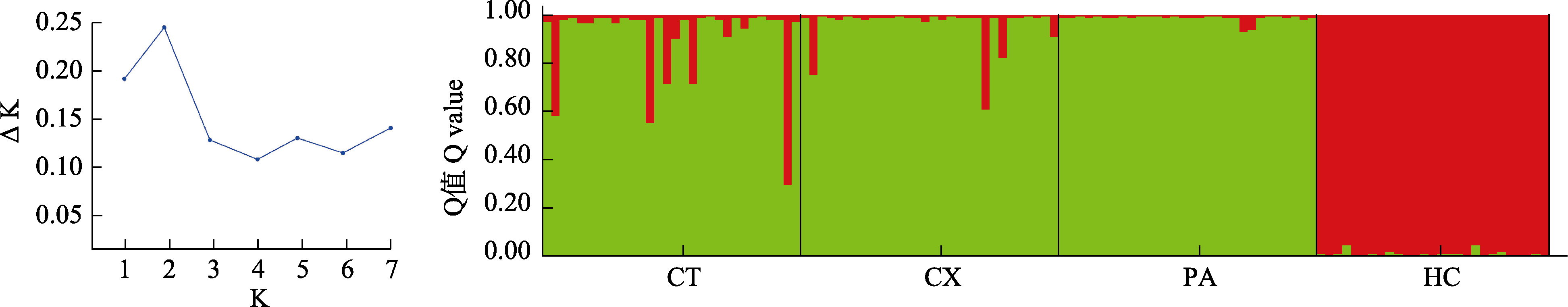
图4 4个蛇鮈种群的遗传结构图(K = 2时)。CT: 朝天; CX: 苍溪; PA: 蓬安; HC: 合川; K: 分组数量。
Fig. 4 Genetic structure of four Saurogobio dabryi populations based on K = 2. CT, Chaotian; CX, Cangxi; PA, Peng’an; HC, Hechuan. K, Number of subgroups. ΔK = mean(|L"(K)|) / sd(L(K)).
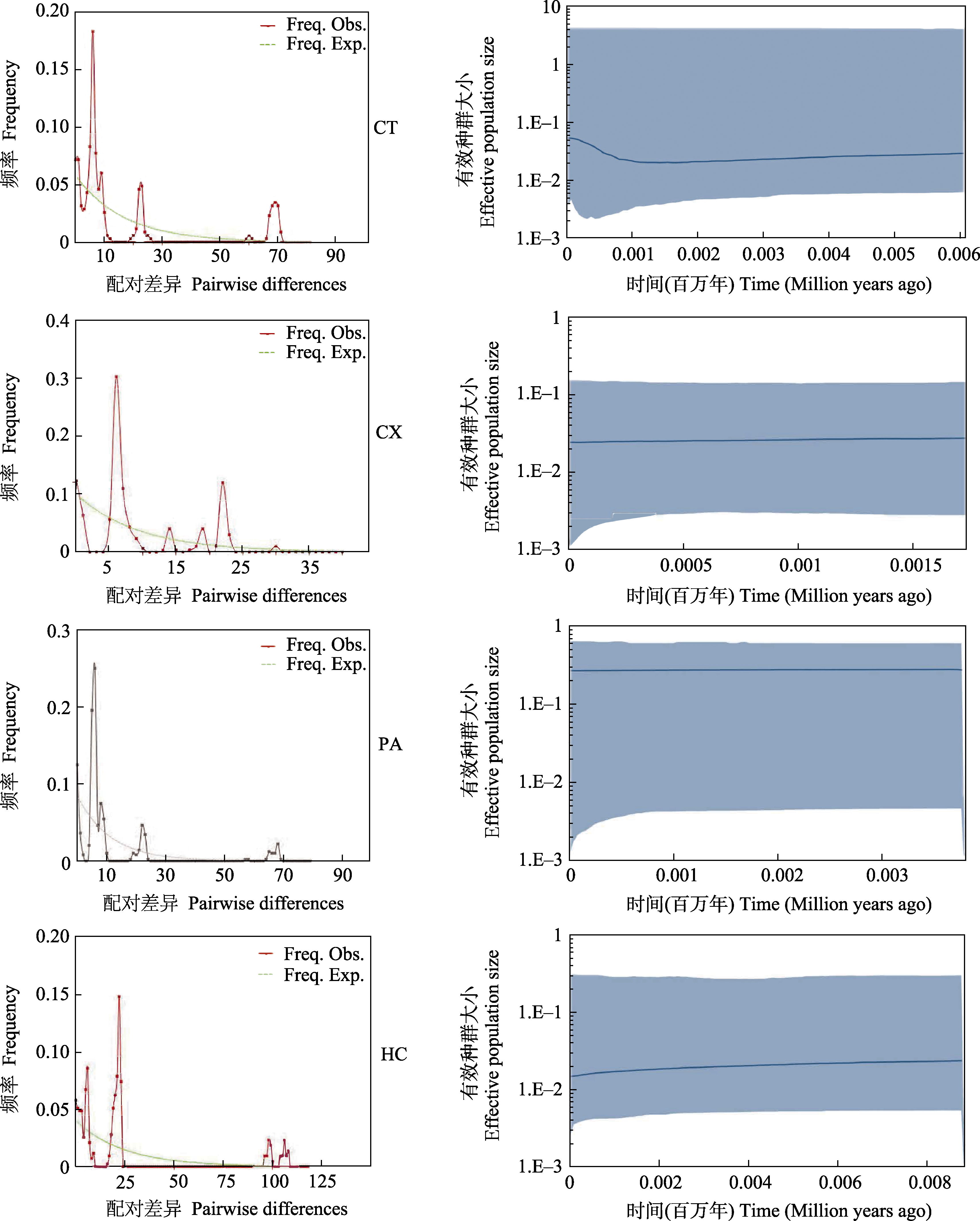
图5 错配分布和基于Bayesian skyline plot分析的4个蛇鮈种群的历史动态趋势。Freq. Obs.: 观测值; Freq. Exp.: 期望值。
Fig. 5 Mismatch distributions and Bayesian skyline plot of mitochondrial lineages of four Saurogobio dabryi populations. Freq. Obs., Observed value; Freq. Exp., Expected value.
| 种群 Population | Afd | P(The/d) | P(OHe) | P(OHd) | 种群 Population | Afd | P(The/d) | P(OHe) | P(OHd) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 朝天区 CT | L-shaped | 0.64063 | 0.72656 | 0.01031 | 蓬安县 PA | L-shaped | 0.03711 | 0.98633 | 0.19855 |
| 苍溪县 CX | L-shaped | 0.01367 | 0.99512 | 0.30684 | 合川区 HC | L-shaped | 0.00977 | 0.99658 | 0.20488 |
表6 基于微卫星位点的蛇鮈种群瓶颈检测
Table 6 Bottleneck tests for microsatellite loci applied in Saurogobio dabryi populations
| 种群 Population | Afd | P(The/d) | P(OHe) | P(OHd) | 种群 Population | Afd | P(The/d) | P(OHe) | P(OHd) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 朝天区 CT | L-shaped | 0.64063 | 0.72656 | 0.01031 | 蓬安县 PA | L-shaped | 0.03711 | 0.98633 | 0.19855 |
| 苍溪县 CX | L-shaped | 0.01367 | 0.99512 | 0.30684 | 合川区 HC | L-shaped | 0.00977 | 0.99658 | 0.20488 |
| [1] |
Blanchet S, Rey O, Etienne R, Lek S, Loot G (2010) Species-specific responses to landscape fragmentation: Implications for management strategies. Evolutionary Applications, 3, 291-304.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Bouckaert R, Heled J, Kühnert D, Vaughan T, Wu CH, Xie D, Suchard MA, Rambaut A, Drummond AJ (2014) BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Computational Biology, 10, e1003537. |
| [3] |
Bu QT, Li X, Zhu R, Chu L, Yan YZ (2017) Low-head dams driving the homogenization of local habitat and fish assemblages in upland streams of the Qingyi River. Biodiversity Science, 25, 830-839. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[卜倩婷, 李献, 朱仁, 储玲, 严云志 (2017) 低头坝驱动山区溪流局域栖息地和鱼类群落的同质化. 生物多样性, 25, 830-839.]
DOI |
|
| [4] | Chen K, Luo MY, Zhang CK, Zhang DC, Xu WC (2007) Countermeasures to multistage navigable electricity project’s impaction on the Jialing River (Nanchong) to ecological environment. Journal of China West Normal University (Natural Sciences), 28, 195-199. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谌柯, 罗明云, 张崇昆, 张道川, 许武成 (2007) 嘉陵江干流(南充段)梯级航电开发对生态环境的影响和对策研究. 西华师范大学学报(自然科学版), 28, 195-199.] | |
| [5] | Chen YY (1998) Fauna Sinica·Osteichthyes·Cypriniformes (Ⅱ). Science Press, Beijing.. (in Chinese) |
| [陈宜瑜 (1998) 中国动物志·硬骨鱼纲·鲤形目(中卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [6] |
Cole TL, Hammer MP, Unmack PJ, Teske PR, Brauer CJ, Adams M, Beheregaray LB (2016) Range-wide fragmentation in a threatened fish associated with post-European settlement modification in the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia. Conservation Genetics, 17, 1377-1391.
DOI |
| [7] |
de Brito MTFM, Leila SAT, da Silva Pinto D (2018) Seroepidemiology of arbovirus in communities living under the influence of the lake of a hydroelectric dam in Brazil. Cadernos Saúde Coletiva, 26, 1-6.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin (version 3.0): An integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evolutionary Bioinformatics, 1, 47-50. |
| [9] |
Faulks LK, Kerezsy A, Unmack PJ, Johnson JB, Hughes JM (2017) Going, going, gone? Loss of genetic diversity in two critically endangered Australian freshwater fishes, Scaturiginichthys vermeilipinnis and Chlamydogobius squamigenus, from Great Artesian Basin springs at Edgbaston, Queensland, Australia. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 27, 39-50.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Goldstein DB, Ruiz Linares A, Cavalli-Sforza LL, Feldman MW (1995) Genetic absolute dating based on microsatellites and the origin of modern humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 92, 6723-6727. |
| [11] |
Gouskov A, Reyes M, Wirthner-Bitterlin L, Vorburger C (2016) Fish population genetic structure shaped by hydroelectric power plants in the upper Rhine Catchment. Evolutionary Applications, 9, 394-408.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | He P, Jiang ZB, Yu SD, Hu J (2003) Water pollution evaluation under present condition and its control measures in Jialing River of Nanchong Section. Sichuan Journal of Environment, 22(3), 35-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [何平, 蒋祖斌, 余世东, 胡健 (2003) 嘉陵江南充段水污染现状评价及防治对策. 四川环境, 22(3), 35-37.] | |
| [13] | He XF, Song ZB, Xie EY (1996) The breeding habits and embryonic development of longnose gudgeon (Saurogobio dabryi Bleeker). Journal of China West Normal University (Natural Sciences), 21, 276-281. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [何学福, 宋昭彬, 谢恩义 (1996) 蛇鮈的产卵习性及胚胎发育. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 21, 276-281.] | |
| [14] |
Heilveil JS, Stockwell CA (2017) Genetic signatures of translocations and habitat fragmentation for two evolutionarily significant units of a protected fish species. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 100, 631-638.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Hou FX (2013) The Genetic Diversity and Population Structure Analysis of Schizopygopsis chengi and Schizopygopsis malacanthus. PhD dissertation, Sichuan University, Chengdu. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [侯飞侠 (2013) 大渡裸裂尻鱼和软刺裸裂尻鱼的遗传多样性及种群结构研究. 博士学位论文, 四川大学, 成都.] | |
| [16] | Jiang GF, He XF (2008) Status of fish resources in the lower reaches of the Jialing River. Freshwater Fisheries, 38(2), 3-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蒋国福, 何学福 (2008) 嘉陵江下游鱼类资源现状调查. 淡水渔业, 38(2), 3-7.] | |
| [17] |
Kalinowski ST, Taper ML, Marshall TC (2007) Revising how the computer program CERVUS accommodates genotyping error increases success in paternity assignment. Molecular Ecology, 16, 1099-1106.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Khaire D, Atkulwar A, Farah S, Baig M (2017) Mitochondrial DNA analyses revealed low genetic diversity in the endangered Indian wild ass Equus hemionus khur. Mitochondrial DNA: Part A, 28, 681-686.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33, 1870-1874.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Leigh JW, Bryant D (2015) Popart: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 6, 1110-1116.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Liu HG, Yang Z, Tang HY, Gong Y, Wan L (2017) Microsatellite development and characterization for Saurogobio dabryi Bleeker, 1871 in a Yangtze River- connected Lake, China. Journal of Genetics, 96, e1-e4. |
| [22] |
Liu HZ, Tzeng CS, Teng HY (2002) Sequence variations in the mitochondrial DNA control region and their implications for the phylogeny of the Cypriniformes. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 80, 569-581.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Liu XL, Sun J, Han JQ, Wang YN, Tan JD (2019) Genetic variation of Rattus losea populations in island habitats. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 6898-6907. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘小丽, 孙佼, 韩金巧, 王艳妮, 谭江东 (2019) 岛屿生境下黄毛鼠种群的遗传变异. 生态学报, 39, 6898-6907.] | |
| [24] | Liu YY, Zeng Y, Xiong XQ, Lü ZY, Hu Y, Jiang ZM, Cheng L, Yu DL (2019) Difference and adaptation of reproductive biological characteristics of Saurogobio dabryi in Jialing River cascade water conservancy project. Freshwater Fisheries, 49(2), 3-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘玉莹, 曾燏, 熊小琴, 吕振宇, 胡月, 蒋朝明, 程磊, 俞丹莉 (2019) 嘉陵江梯级水利工程开发下不同江段蛇鮈的繁殖生物学特性差异及适应. 淡水渔业, 49(2), 3-8.] | |
| [25] |
Pavlova A, Beheregaray LB, Coleman R, Gilligan D, Harrisson KA, Ingram BA, Kearns J, Lamb AM, Lintermans M, Lyon J, Nguyen TTT, Sasaki M, Tonkin Z, Yen JDL, Sunnucks P (2017) Severe consequences of habitat fragmentation on genetic diversity of an endangered Australian freshwater fish: A call for assisted gene flow. Evolutionary Applications, 10, 531-550.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | Posada D (2009) Selection of models of DNA evolution with jModelTest. Bioinformatics for DNA Sequence Analysis, 93-112. |
| [27] | Ren LP (2012) The Study of Muli-scale Health Evaluation of the Cascade Hydropower Development on the Jialing River in Sichuan. PhD dissertation, Chongqing University, Chongqing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [任丽平 (2012) 嘉陵江(四川段)梯级开发的多尺度健康评价研究. 博士学位论文, 重庆大学, 重庆.] | |
| [28] |
Rogers AR, Harpending H (1992) Population growth makes waves in the distribution of pairwise genetic differences. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 9, 552-569.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics, 19, 1572-1574.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Rozas J, Ferrer-Mata A, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Guirao-Rico S, Librado P, Ramos-Onsins SE, Sánchez-Gracia A (2017) DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 34, 3299-3302.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Schneider S, Excoffier L (1999) Estimation of past demographic parameters from the distribution of pairwise differences when the mutation rates vary among sites: Application to human mitochondrial DNA. Genetics, 152, 1079-1089.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Sungirai M, Baron S, van der Merwe NA, Moyo DZ, De Clercq P, Maritz-Olivier C, Madder M (2018) Population structure and genetic diversity of Rhipicephalus microplus in Zimbabwe. Acta Tropica, 180, 42-46.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Tao JP, Gong YT, Tan XC, Yang Z, Chang JB (2012) Spatiotemporal patterns of the fish assemblages downstream of the Gezhouba Dam on the Yangtze River. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 42, 677-688. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陶江平, 龚昱田, 谭细畅, 杨志, 常剑波 (2012) 长江葛洲坝坝下江段鱼类群落变化的时空特征. 中国科学: 生命科学, 42, 677-688.] | |
| [34] | Tian HW, Duan XB, Wang DQ, Liu SP, Chen DQ (2013) Sequence variability of cytochrome b and genetic structure of Leptobotia elongata in the Upper Yangtze River. Freshwater Fisheries, 43, 13-18, 28. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [田辉伍, 段辛斌, 汪登强, 刘绍平, 陈大庆 (2013) 长江上游长薄鳅Cytb基因的序列变异与遗传结构分析. 淡水渔业, 43, 13-18, 28.] | |
| [35] | Turan C, Gurlek M, Erguden D, Yaglioglu D, Uyan A, Reyhaniye AN, Ozbalcilar B, Ozturk B, Erdogan ZA, Ivanova P, Soldo A (2015) Population genetic analysis of Atlantic bonito Sarda sarda (Bloch, 1793) using sequence analysis of mtDNA D-loop region. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 45, 231-237. |
| [36] |
Van Oosterhout C, Hutchinson WF, Wills DPM, Shipley P (2004) Micro-checker: Software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Molecular Ecology Notes, 4, 535-538.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Wang T, Du YY, Yang ZY, Zhang YP, Lou ZY, Jiao WL (2017) Population genetic structure of Schizopygopsis kialingensis inferred from mitochondrial D-loop sequences. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 7741-7749. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王太, 杜岩岩, 杨濯羽, 张艳萍, 娄忠玉, 焦文龙 (2017) 基于线粒体控制区的嘉陵裸裂尻鱼种群遗传结构分析. 生态学报, 37, 7741-7749.] | |
| [38] | Yang JQ, Hu XL, Tang WQ, Lin HD (2008) mtDNA control region sequence variation and genetic diversity of Coilia nasus in Yangtze River Estuary and its adjacent waters. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 43, 8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨金权, 胡雪莲, 唐文乔, 林弘都 (2008) 长江口邻近水域刀鲚的线粒体控制区序列变异与遗传多样性. 动物学杂志, 43, 8-15.] | |
| [39] | Zeng Y, Chen YB, Li ZJ (2014) Utilization and protection status of fish resources in Jialing River. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 20, 60-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曾燏, 陈永柏, 李钟杰 (2014) 嘉陵江鱼类资源利用与保护现状. 天津农业科学, 20, 60-62.] | |
| [40] | Zhang F, Zhang BW, Tang WQ, Liu J, Wu JH, Tang B (2018) Analysis of genetic diversity and population dynamics of the narrow-ridged finless porpoise in the Yangtze River Estuary. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 27, 656-665. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张枫, 张保卫, 唐文乔, 刘健, 吴建辉, 唐斌 (2018) 长江口江豚的遗传多样性现状及种群动态. 上海海洋大学学报, 27, 656-665.] | |
| [41] | Zhang FT, Tan DQ (2010) Genetic diversity in population of largemouth bronze gudgeon (Coreius guichenoti Sauvage et Dabry) from Yangtze River determined by microsatellite DNA analysis. Genes & Genetic Systems, 85, 351-357. |
| [42] |
Zhou Y, Lei Y, Lu Y, Song ZB (2018) Population genetics of a Chinese endemic, Gymnocypris potanini Herzenstein, threatened by population isolation: Conflicting patterns between microsatellites and mitochondrial DNA. Hydrobiologia, 819, 145-159.
DOI |
| [1] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [2] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [3] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [4] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [5] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [6] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [7] | 孙维悦, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 莫日根高娃, 杜夏瑾, 刘保东, 严岳鸿. 基于保护基因组学揭示荷叶铁线蕨的濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [8] | 陶克涛, 白东义, 图格琴, 赵若阳, 安塔娜, 铁木齐尔·阿尔腾齐米克, 宝音德力格尔, 哈斯, 芒来, 韩海格. 基于基因组SNPs对东亚家马不同群体遗传多样性的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [9] | 崔静, 徐明芳, 章群, 李瑶, 曾晓舒, 李莎. 基于3种线粒体标记探讨中日沿海角木叶鲽遗传多样性差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21485-. |
| [10] | 孙军, 宋煜尧, 施义锋, 翟键, 燕文卓. 近十年中国海洋生物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22526-. |
| [11] | 栗冬梅, 杨卫红, 李庆多, 韩茜, 宋秀平, 潘虹, 冯云. 巴尔通体在滇西南蝙蝠中高度流行并具有丰富的遗传变异特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1245-1255. |
| [12] | 姚志, 郭军, 金晨钟, 刘勇波. 中国纳入一级保护的极小种群野生植物濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 394-408. |
| [13] | 叶俊伟, 田斌. 中国西南地区重要木本油料植物扁核木的遗传结构及成因[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1629-1637. |
| [14] | 向登高, 李跃飞, 李新辉, 陈蔚涛, 马秀慧. 多基因联合揭示海南鲌的遗传结构与遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1505-1512. |
| [15] | 苏金源, 燕语, 李冲, 李丹, 杜芳. 通过遗传多样性探讨极小种群野生植物的致濒机理及保护策略: 以裸子植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(3): 376-384. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn