



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 23184. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023184 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023184
收稿日期:2023-06-04
接受日期:2023-08-29
出版日期:2023-09-20
发布日期:2023-10-12
通讯作者:
*E-mail: huanghw@scbg.ac.cn
基金资助:
Chen Feng1, Jie Zhang1, Hongwen Huang1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2023-06-04
Accepted:2023-08-29
Online:2023-09-20
Published:2023-10-12
Contact:
*E-mail: huanghw@scbg.ac.cn
摘要:
本文系统地梳理了植物就地保护和迁地保护存在的问题, 尤其是因气候变化等原因导致就地保护存在的不确定性、迁地保护居群遗传多样性丧失、遗传漂变导致的一系列遗传风险等, 进而提出了植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)的概念及方法。并地保护是依据植物居群间的基因流动态规律进行保护物种的迁地保育设计, 其核心是受保护物种通过居群间花粉传播的基因流连接自然居群与迁地保护居群。并地保护就是在自然保护区等就地保护区域内或周边花粉可传播范围内, 建立植物迁地保育圃, 使迁地保护居群与自然居群之间维持基因交流, 即: 将迁地保护小居群融入自然大居群的基因池并有效维持物种的适应性进化潜能。深入的“一种一策”的花粉流检测和保育圃设计是该方法成功的关键。并地保护与其他植物保护途径相互补充, 对实现生物多样性保护具有重要意义。
冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文 (2023) 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation). 生物多样性, 31, 23184. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023184.
Chen Feng, Jie Zhang, Hongwen Huang (2023) Parallel situ conservation: A new plant conservation strategy to integrate in situ and ex situ conservation of plants. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23184. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023184.
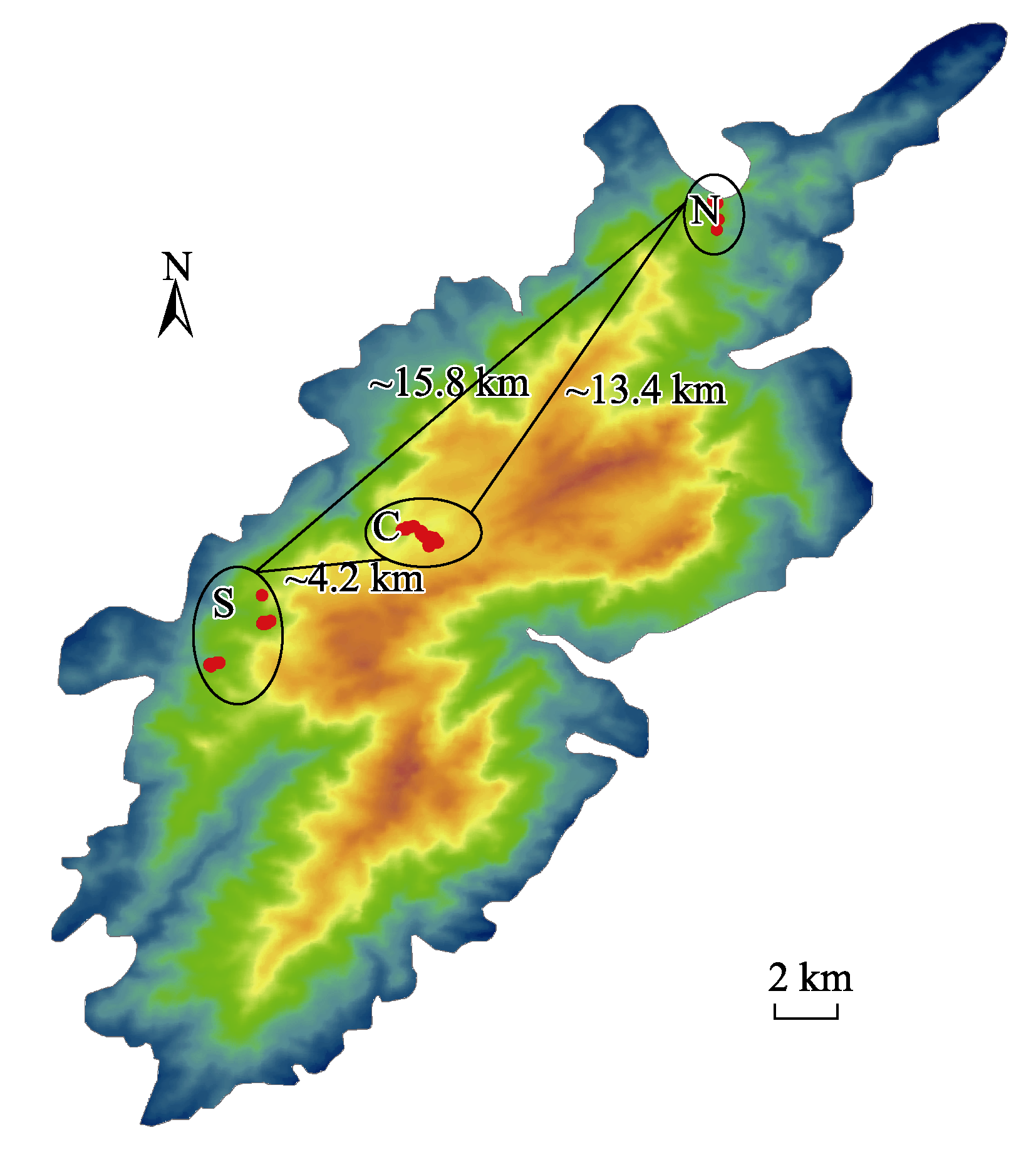
图1 江西省庐山国家级自然保护区的小叶青冈取样分布图。数字表示各居群间的平均水平距离。N: 北部居群; C: 中部居群; S: 南部居群。
Fig. 1 Geographic information of Quercus myrsinifolia sampling in Mount Lushan National Nature Reserve. Horizontal distances among populations are labeled between each population pairs. N, North population; C, Central population; S, South population.
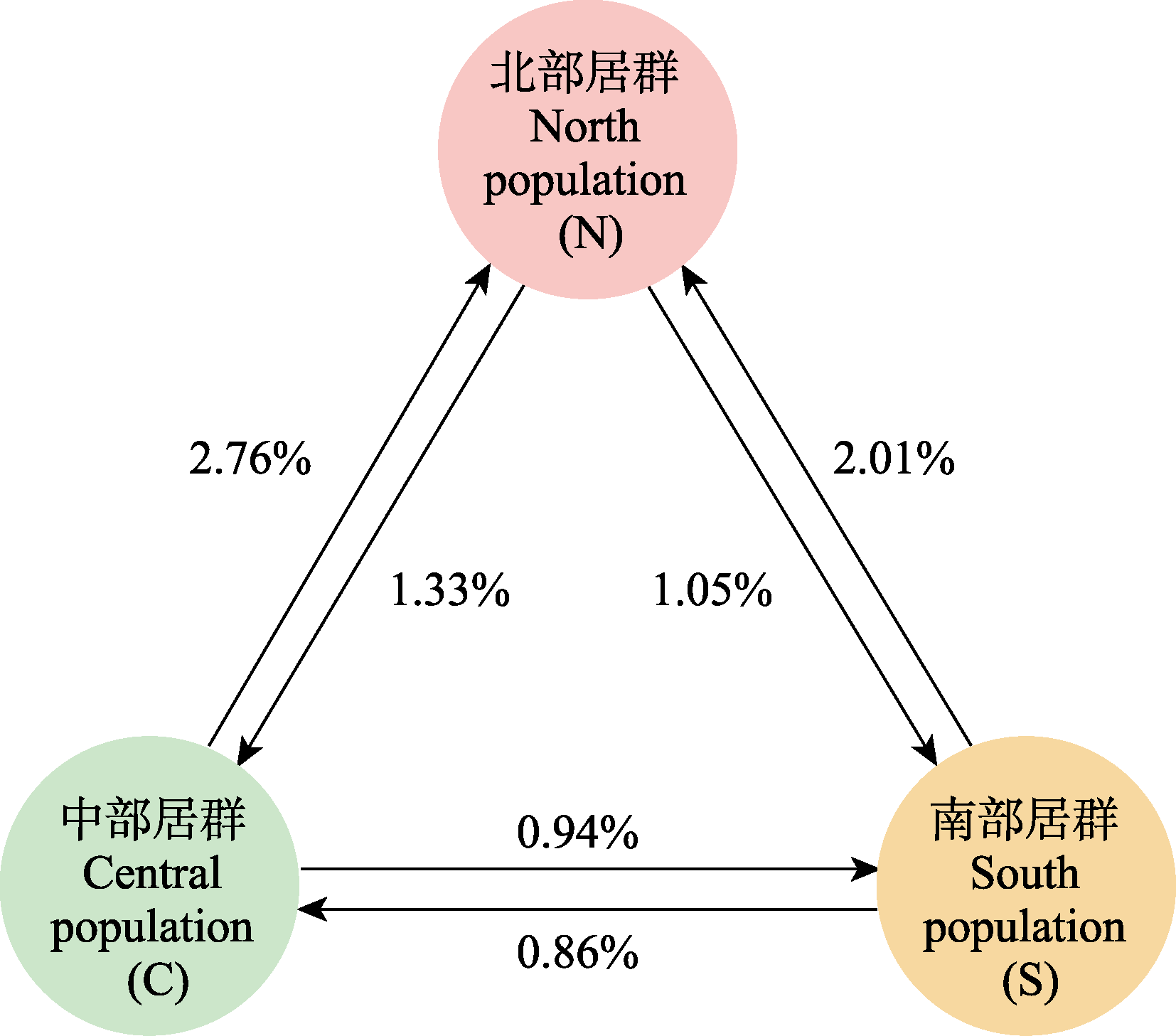
图2 江西省庐山国家级自然保护区不同小叶青冈居群间的杂交率。箭头表示花粉传播方向, 数字表示该花粉传播方向造成的杂交率。
Fig. 2 Rate of hybridization among different Quercus myrsinifolia populations in Mount Lushan National Nature Reserve. Arrows and numbers indicate the pollen dispersal and hybridization rates.
| 保护策略 Conservation strategy | 保护对象 Conservation target | 保护单元 Conservation unit | 方法和依据 Method and justification | 多样性保护 Diversity conservation | 存在的主要问题 Main limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 就地保护 In situ conservation | 生态系统 Ecosystem | 群落 Community | 原生态自然过程 Natural process | α、β、γ多样性 α, β, γ diversity | 生境消失, 气候变迁 Habitat loss, climate changes |
| 迁地保护 Ex situ conservation | 珍稀濒危类群 Rare and endangered plants | 个体或小居群 Individuals or small population | 自然栖息地以外管护 Outside habitats and controlled care | α多样性 α diversity | 遗传多样性丧失 Genetic diversity loss |
| 近地保护 Near situ conservation | 珍稀濒危类群 Rare and endangered | 个体或小居群 Individuals or small population | 相似的气候与环境 Similar climate and environment | α多样性 α diversity | 遗传多样性丧失, 外在风险脆弱性 Genetic diversity loss, vulnerability to local threats |
| 微保护区 Micro-reserves | 片断化生态系统 Fragmented ecosystem | 群落 Community | 城市生态系统 Urban ecosystem | α和β多样性 α, β diversity | 边缘效应, 片断化 Edge effects, fragmentation |
| 间地保护 Inter situ conservation | 珍稀濒危类群 Rare and endangered plants | 个体或小居群 Individuals or small population | 临时措施至新栖息地 Temporary measures until new habitats found | α多样性 α diversity | 遗传多样性丧失 Genetic diversity loss |
| 森林基因库 Forest gene bank | 森林树种种质 Germplasm of forest trees | 遗传材料 Genetic materials | 天然种子库 Natural seed banks | 遗传多样性 Genetic diversity | 遗传代表性不足 Limited genetic representation |
| 并地保护 Parallel situ conservation | 珍稀濒危类群 Rare and endangered plants | 居群或物种 Population or species | 基因流及居群遗传学原理 Gene flow and population genetics | α和β多样性 α, β diversity | 受环境和自然居群因素限制 Restricted by environment and natural populations availability |
表1 野生濒危植物保护策略和方法的比较
Table 1 Comparison of strategies and methods for the conservation of endangered wild plants
| 保护策略 Conservation strategy | 保护对象 Conservation target | 保护单元 Conservation unit | 方法和依据 Method and justification | 多样性保护 Diversity conservation | 存在的主要问题 Main limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 就地保护 In situ conservation | 生态系统 Ecosystem | 群落 Community | 原生态自然过程 Natural process | α、β、γ多样性 α, β, γ diversity | 生境消失, 气候变迁 Habitat loss, climate changes |
| 迁地保护 Ex situ conservation | 珍稀濒危类群 Rare and endangered plants | 个体或小居群 Individuals or small population | 自然栖息地以外管护 Outside habitats and controlled care | α多样性 α diversity | 遗传多样性丧失 Genetic diversity loss |
| 近地保护 Near situ conservation | 珍稀濒危类群 Rare and endangered | 个体或小居群 Individuals or small population | 相似的气候与环境 Similar climate and environment | α多样性 α diversity | 遗传多样性丧失, 外在风险脆弱性 Genetic diversity loss, vulnerability to local threats |
| 微保护区 Micro-reserves | 片断化生态系统 Fragmented ecosystem | 群落 Community | 城市生态系统 Urban ecosystem | α和β多样性 α, β diversity | 边缘效应, 片断化 Edge effects, fragmentation |
| 间地保护 Inter situ conservation | 珍稀濒危类群 Rare and endangered plants | 个体或小居群 Individuals or small population | 临时措施至新栖息地 Temporary measures until new habitats found | α多样性 α diversity | 遗传多样性丧失 Genetic diversity loss |
| 森林基因库 Forest gene bank | 森林树种种质 Germplasm of forest trees | 遗传材料 Genetic materials | 天然种子库 Natural seed banks | 遗传多样性 Genetic diversity | 遗传代表性不足 Limited genetic representation |
| 并地保护 Parallel situ conservation | 珍稀濒危类群 Rare and endangered plants | 居群或物种 Population or species | 基因流及居群遗传学原理 Gene flow and population genetics | α和β多样性 α, β diversity | 受环境和自然居群因素限制 Restricted by environment and natural populations availability |
| [1] | Antonelli A, Fry C, Smith RJ, Simmonds MSJ, Twyford AD (2020) State of the World’s Plants and Fungi 2020. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Richmond. |
| [2] |
Avise JC (2010) Perspective: Conservation genetics enters the genomics era. Conservation Genetics, 11, 665-669.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Ayres DR, Garcia-Rossi D, Davis HG, Strong DR (1999) Extent and degree of hybridization between exotic (Spartina alterniflora) and native (S. foliosa) cordgrass (Poaceae) in California, USA determined by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPDs). Molecular Ecology, 8, 1179-1186.
PMID |
| [4] |
Ayres DR, Zaremba K, Strong DR (2004) Extinction of a common native species by hybridization with an invasive congener. Weed Technology, 18, 1288-1291.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Bryant EH, Reed DH (1999) Fitness decline under relaxed selection in captive populations. Conservation Biology, 13, 1487-1496.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Buchholz K (2023) Number of Threatened Species is Rising. https://www.statista.com/chart/17122/number-of-threatened-species-red-list. (accessed on 2023-04-11) |
| [7] |
Burney DA, Burney LP (2007) Paleoecology and “inter-situ” restoration on Kauai, Hawaii. Frontiers in Ecology and Environment, 5, 483-490.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Culley TM, Weller SG, Sakai AK (2002) The evolution of wind pollination in angiosperms. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 17, 361-369.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Ekblom R, Galindo J (2011) Applications of next generation sequencing in molecular ecology of non-model organisms. Heredity, 107, 1-15.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Ellstrand NC, Elam DR (1993) Population genetic consequences of small population size: Implications for plant conservation. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 24, 217-242.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Enßlin A, Tschope O, Burkart M, Joshi J (2015) Fitness decline and adaptation to novel environments in ex situ plant collections: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Biological Conservation, 192, 394-401.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Haroldson MA, Schwartz CC, Kendall KC, Gunther KA, Moody DS, Frey K, Paetkau D (2010) Genetic analysis of individual origins supports isolation of grizzly bears in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem. Ursus, 21, 1-13.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Huang HW (2018) The Principle and Practice of Ex Situ Plant Conservation. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [黄宏文 (2018) 植物迁地保护原理与实践. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [14] |
Huang HW, Duan ZY, Liao JP, Zhang Z (2015) Impact of plant introduction or domestication on the recent 500 years of civilization and scientific research value of plant living collections. Chinese Bulletin Botany, 50, 280-294. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[黄宏文, 段子渊, 廖景平, 张征 (2015) 植物引种驯化对近500年人类文明史的影响及其科学意义. 植物学报, 50, 280-294.]
DOI |
|
| [15] |
Huang HW, Liao JP (2022) On China’s national botanical gardens: Building a comprehensive system of ex situ conservation of national botanical gardens with task oriented disciplines. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22220. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[黄宏文, 廖景平 (2022) 论我国国家植物园体系建设: 以任务带学科构建国家植物园迁地保护综合体系. 生物多样性, 30, 22220.]
DOI |
|
| [16] |
Huang HW, Raven PH, Wang L, Liao JP, Zhan Q (2023) China: The role of botanical gardens in conservation. The Innovation, 4, 100433.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Huang SX, Li RT, Luo WH, Zhou TJ, Tang WX, Wang Y (2001) Variation in characteristics of rare and threatened plants after ex-situ conservation. Biodiversity Science, 9, 359-365. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [黄仕训, 李瑞棠, 骆文华, 周太久, 唐文秀, 王燕 (2001) 石山稀有濒危植物在迁地保护后的性状变异. 生物多样性, 9, 359-365.] | |
| [18] | Humphreys AM, Govaerts R, Ficinski SZ, Lughadha EN, Vorontsova MS (2019) Global dataset shows geography and life form predict modern plant extinction and rediscovery. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 3, 1043-1047. |
| [19] | Hurka H (1994) Conservation genetics and the role of botanical gardens. In: Conservation Genetics (eds Loeschcke V, Jain SK, Tomiuk J), pp. 371-380. Birkhauser Verlag, Basel. |
| [20] | Husband BC, Campbell LG (2004) Population responses to novel environments:Implications for ex situ plant conservation. In: Ex Situ Plant Conservation: Supporting Species Survival in the Wild (eds Guerrant EO, Havens K, Maunder M), pp. 231-285. Island Press, Washington. |
| [21] | IPBES (2019) Global Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. IPBES Secretariat, Bonn. |
| [22] | Kang M, Ye QG, Huang HW (2005) Genetic risks in plant ex situ conservation. Hereditas, 27, 160-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [康明, 叶其刚, 黄宏文 (2005) 植物迁地保护中的遗传风险. 遗传, 27, 160-166.] | |
| [23] |
Krauss SL, Phillips RD, Karron JD, Johnson SD, Roberts DG, Hopper SD (2017) Novel consequences of bird pollination for plant mating. Trends in Plant Science, 22, 395-410.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Laguna E, Deltoro VI, Pèrez-Botella J, Pèrez-Rovira P, Serra LI, Olivares A, Fabregat C (2004) The role of small reserves in plant conservation in a region of high diversity in eastern Spain. Biological Conservation, 119, 421-426.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Lee GJ, Regier HA, Rapport DJ (1982) Ten ecosystem approaches to the planning and management of the Great Lakes. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 8, 505-519.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Li JS, Luo JW, Wang W, Zhu YP, Luo ZL (2015) Green Book of China’s Nature Reserves:A Progress Report of National Nature Reserves. China Environmental Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李俊生, 罗建武, 王伟, 朱彦鹏, 罗遵兰 (2015) 中国自然保护区绿皮书——国家级自然保护区发展报告. 中国环境出版社, 北京.] | |
| [27] |
Li QM, Xu ZF, He TH (2002) Ex situ genetic conservation of endangered Vatica guangxiensis (Dipterocarpaceae) in China. Biological Conservation, 106, 151-156.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Ma JZ, Rong K, Cheng K (2012) Research and practice on biodiversity in situ conservation in China: Progress and prospect. Biodiversity Science, 20, 551-558. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[马建章, 戎可, 程鲲 (2012) 中国生物多样性就地保护的研究与实践. 生物多样性, 20, 551-558.]
DOI |
|
| [29] |
Markert JA, Champlin DM, Gutjahr-Gobell R, Grear JS, Kuhn A, McGreevy TJ Jr, Roth A, Bagley MJ, Nacci DE (2010) Population genetic diversity and fitness in multiple environments. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 10, 205.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Miller CR, Waits LP (2003) The history of effective population size and genetic diversity in the Yellowstone grizzly (Ursus arctos): Implications for conservation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 100, 4334-4339. |
| [31] |
Newman D, Pilson D (1997) Increased probability of extinction due to decreased genetic effective population size: Experimental population of Clarkia pulchella. Evolution, 51, 354-362.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Ollerton J, Winfree R, Tarrant S (2011) How many flowering plants are pollinated by animals. Oikos, 120, 321-326.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Pasquet RS, Peltier A, Hufford MB, Oudin E, Saulnier J, Paul L, Knudsen JT, Herren HR, Gepts P (2008) Long-distance pollen flow assessment through evaluation of pollinator foraging range suggests transgene escape distances. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 105, 13456-13461. |
| [34] |
Pitman NCA, Jorgensen PM (2002) Estimating the size of the world’s threatened flora. Science, 298, 989.
PMID |
| [35] | Roberson EB, Frances A, Havens K, Maschinski J, Meyer A, Ott L (2020) Fund plant conservation to solve biodiversity crisis. Science, 367, 258-258. |
| [36] |
Rogers C, Levetin E (1998) Evidence of long-distance transport of mountain cedar pollen into Tulsa, Oklahoma. International Journal of Biometeorology, 42, 65-72.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Schoen DJ, Brown ADH (2001) The conservation of wild plant species in seed banks. BioScience, 51, 960-966.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Schröder R, Prasse R (2013) Cultivation and hybridization alter the germination behavior of native plants used in revegetation and restoration. Restoration Ecology, 21, 1-8.
DOI URL |
| [39] | Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity SCBD (2020) Global Biodiversity Outlook 5. Montreal, Canada. |
| [40] |
Seehausen O (2004) Hybridization and adaptive radiation. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 19, 198-207.
DOI URL |
| [41] | Shepherd G (2004) The Ecosystem Approach: Five Steps to Implementation. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland & Cambridge, UK. |
| [42] | Spielman D, Brook BW, Frankham R (2004) Most species are not driven to extinction before genetic factors impact them. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 101, 15261-15264. |
| [43] |
Strong DR, Ayres DR (2013) Ecological and evolutionary misadventures of Spartina. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 44, 389-410.
DOI URL |
| [44] | Sun WB (2013) Conserving Plant Species with Extremely Small Populations (PSESP) in Yunnan:Practice and Exploration. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [孙卫邦 (2013) 云南省极小种群野生植物保护实践与探索. 云南科技出版社, 昆明.] | |
| [45] |
Todesco M, Pascual MA, Owens GL, Ostevik KL, Moyers BT, Hübner S, Heredia SM, Hahn MA, Caseys C, Bock DG, Rieseberg LH (2016) Hybridization and extinction. Evolutionary Applications, 9, 892-908.
DOI PMID |
| [46] | Uma Shaanker R, Ganeshaiah KN (1997) Mapping genetic diversity of Phyllanthus emblica: Forest gene banks as a new approach for in situ conservation of genetic resources. Current Science, 73, 163-168. |
| [47] | Uma Shaanker R, Ganeshaiah KN, Nageswara Rao M, Ravikanth G (2001) A new approach to conservation of genetic resources of forest trees:Promise and processes. In: Forest Genetic Resources: Status, Threats and Conservation Strategies (eds Uma Shaanker R, Ganeshaiah KN, Bawa KS), pp. 263-271. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co., New Delhi. |
| [48] | Uma Shaanker R, Ganeshaiah KN, Nageswara Rao M, Ravikanth G (2002) Forest gene banks—A new integrated approach for the conservation of forest tree genetic resources. In: Managing Plant Genetic Resources (eds Engels JMM, Brown AHD, Jackson MT), pp. 229-235. CABI Publishing, Nosworthy. |
| [49] | UNEP (2021) Making Peace with Nature: A Scientific Blueprint to Tackle the Climate, Biodiversity and Pollution Emergencies. Nairobi. https://www.unep.org/resources/making-peace-nature. (accessed on 2023-04-11) |
| [50] | Volis S (2017) Complementarities of two existing intermediate conservation approaches. Plant Diversity, 11, 379-382. |
| [51] |
Volis S, Blecher M (2010) Quasi in situ: A bridge between ex situ and in situ conservation of plants. Biodiversity Conservation, 19, 2441-2454.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Wang CJ, Wan JZ, Zhang GM, Zhang ZX, Zhang J (2016) Protected areas may not effectively support conservation of endangered forest plants under climate change. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75, 466.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Wessinger CA (2021) From pollen dispersal to plant diversification: Genetic consequences of pollination mode. New Phytologist, 229, 3125-3132.
DOI PMID |
| [54] |
Wu YM, Shen XL, Tong L, Lei FW, Mu XY, Zhang ZX (2021) Impact of past and future climate change on the potential distribution of an endangered montane shrub Lonicera oblata and its conservation implications. Forests, 12, 125.
DOI URL |
| [55] | Xia X, Zhang HN, Guo C, Qian ZD, Gao J, Xu WG, Zhou DQ, Jiang MK (2018) Evaluation of in-situ conservation of mammals in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 3712-3717. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [夏欣, 张昊楠, 郭辰, 钱者东, 高军, 徐网谷, 周大庆, 蒋明康 (2018) 我国哺乳动物就地保护状况评估. 生态学报, 38, 3712-3717.] | |
| [56] | Xu ZF (1998) Principle and Methodology of Ex Situ Conservation for Rare and Endangered Plants. Yunnan Science & Technology Press, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [许再富 (1998) 稀有濒危植物迁地保护的原理与方法. 云南科技出版社, 昆明.] | |
| [57] | Xu ZF, Gao JY, Li BG, Zhou HF (2012) Comparative study on conservative efficiency of national protected plants between “Off Site” and “Near Site” Conservation. The Botanical Gardens of China, (15), 6-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [许再富, 高江云, 李保贵, 周慧芳 (2012) 国家重点保护植物“迁地”与“近地”保护有效性的比较研究. 中国植物园, (15), 6-15.] | |
| [58] | Xu ZF, Huang JY, Hu HB, Zhou HF, Meng LZ (2009) A commentary on plant ex situ conservation and its researches in China nearly thirty years. Guihaia, 28, 764-774. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [许再富, 黄加元, 胡华斌, 周慧芳, 孟令曾 (2009) 我国近30年来植物迁地保护及其研究的综述. 广西植物, 28, 764-774.] | |
| [59] |
Yesuf GU, Brown KA, Walford NS, Rakotoarisoa SE, Rufino MC (2021) Predicting range shifts for critically endangered plants: Is habitat connectivity irrelevant or necessary? Biological Conservation, 256, 109033.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Yi H, Wang J, Wang J, Rausher M, Kang M (2022) Genomic insights into inter- and intraspecific mating system shifts in Primulina. Molecular Ecology, 31, 5699-5713.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Zhang JJ, Ye QG, Yao XH, Huang HW (2010) Spontaneous interspecific hybridization and patterns of pollen dispersal in ex situ populations of a tree species (Sinojackia xylocapa) that is extinct in the wild. Conservation Biology, 24, 246-255.
DOI URL |
| [62] | Zhu HY, Kang M, Ye QG, Huang HW (2005) Allozymic genetic diversity in Eurycorymbus caraleriei (Levl.) Rehd. et Hand.-Mazz., an endemic and dioecious tree in China. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 23, 310-318. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱红艳, 康明, 叶其刚, 黄宏文 (2005) 雌雄异株稀有植物伞花木(Eurycorymbus cavaleriei)自然居群的等位酶遗传多样性研究. 武汉植物研究, 23, 310-318.] |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn