



生物多样性 ›› 2010, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (4): 398-407. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.398 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2010.398
所属专题: 生物入侵
收稿日期:2010-03-02
接受日期:2010-06-13
出版日期:2010-07-20
发布日期:2010-07-20
通讯作者:
周立志
作者简介:*E-mail: zhoulz@ahu.edu.cn基金资助:
Lingliang Cao, Lizhi Zhou( ), Baowei Zhang
), Baowei Zhang
Received:2010-03-02
Accepted:2010-06-13
Online:2010-07-20
Published:2010-07-20
Contact:
Lizhi Zhou
摘要:
克氏原螯虾(Procambarus clarkii)是长江中下游地区较为常见的外来物种, 目前已经扩散到安徽境内的主要水系。我们采集了安徽境内长江、淮河和新安江三大流域的4个地区9个地点的182个样本, 利用9对微卫星分子标记, 通过PCR扩增和微卫星分型, 分析了其种群遗传多样性水平和遗传结构, 构建了地方种群的遗传距离格局。结果表明本研究区域克氏原螯虾种群遗传多样性处于较高水平, 总的期望杂合度(HE)和观测杂合度(HO)分别为0.78和0.36。望江种群遗传多样性最高(期望杂合度为0.76), 肥西种群遗传多样性最低(期望杂合度为0.56)。克氏原螯虾种群显示了极强的杂合子缺失, 人为捕捞可能是造成其种群私有等位基因数目较多和杂合子缺失的主要原因。地方种群分化系数(Fst)与地理距离呈显著正相关(r= 0.33, P< 0.05), 望江种群和城东湖种群存在明显的跳跃性扩散(jump dispersal)。因此, 水系间的交流是种群扩散的主要途径, 人为贸易促使克氏原螯虾种群在不同地区的交流, 对其种群扩散也有一定的作用。
曹玲亮, 周立志, 张保卫 (2010) 安徽三大水系入侵物种克氏原螯虾的种群遗传格局. 生物多样性, 18, 398-407. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.398.
Lingliang Cao, Lizhi Zhou, Baowei Zhang (2010) Genetic patterns of an invasive Procambarus clarkii population in the three river basins of Anhui Province. Biodiversity Science, 18, 398-407. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.398.
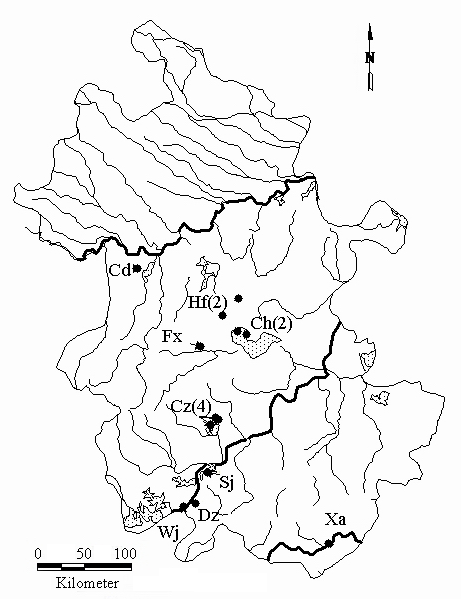
图1 克氏原螯虾样本采集点。样本编号对应的地方种群见表1, 括号中的数字表示取样次数。
Fig. 1 Geographical distribution of the nine Procambarus clarkii populations in the study. The abbreviated codes refer to local populations in Table 1. The numbers in parentheses indicate sampling times.
| 地方种群 Local populations | 编号 Code | 采集点 Sampling site | 样本量 Sample size | 期望杂合度 HE | 观测杂合度 HO | 平均等位 基因数 MNA | 私有等位基因数 Np |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 淮河 Huaihe River | |||||||
| 城东湖 Chengdong Lake | Cd | 霍邱黄泊渡 Huangbodu, Huoqiu | 24 | 0.72 | 0.31 | 6.62 | 5 |
| 江淮之间 Between Yangtze River and Huaihe River | |||||||
| 巢湖 Chaohu Lake | Ch | 义城 Yicheng | 7 | 0.65 | 0.24 | 4.89 | 5 |
| 长临河口 Changlin River Mouths | 3 | 0 | |||||
| 肥西 Feixi | Fx | 柿树岗 Stream in Shishugang | 12 | 0.56 | 0.39 | 4.44 | 3 |
| 合肥 Hefei | Hf | 董铺水库 Dongpu Reservoir | 6 | 0.57 | 0.33 | 4.75 | 2 |
| 三十头支流 Stream in Sanshitou | 9 | 1 | |||||
| 长江 Yangtze River | |||||||
| 菜子湖 Caizi Lake | Czh | 王湾咀 Wangwanzui | 7 | 0.67 | 0.47 | 9.89 | 4 |
| 杨湾 Yangwan | 3 | 0 | |||||
| 肖店 Xiaodian | 21 | 6 | |||||
| 双店 Shuangdian | 12 | 3 | |||||
| 升金湖 Shengjin Lake | Sj | 升金湖 Shenjin Lake | 13 | 0.71 | 0.56 | 6.33 | 5 |
| 东至 Dongzhi | Dz | 香口乡 Stream in Xiangkou | 21 | 0.74 | 0.33 | 7.55 | 9 |
| 望江 Wangjiang | Wj | 华阳河 Huayang River | 20 | 0.76 | 0.17 | 7.44 | 18 |
| 新安江 Xin'anjiang River | |||||||
| 新安江 Xin'anjiang River | Xa | 屯光镇 Tunguang | 24 | 0.64 | 0.39 | 6.00 | 3 |
| 总计 Total | 182 | 0.67 | 0.35 | - | - | ||
表1 克氏原螯虾样本数量分布和遗传变异
Table 1 Sample size, study sites and genetic diversity of the Procambarus clarkii populations
| 地方种群 Local populations | 编号 Code | 采集点 Sampling site | 样本量 Sample size | 期望杂合度 HE | 观测杂合度 HO | 平均等位 基因数 MNA | 私有等位基因数 Np |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 淮河 Huaihe River | |||||||
| 城东湖 Chengdong Lake | Cd | 霍邱黄泊渡 Huangbodu, Huoqiu | 24 | 0.72 | 0.31 | 6.62 | 5 |
| 江淮之间 Between Yangtze River and Huaihe River | |||||||
| 巢湖 Chaohu Lake | Ch | 义城 Yicheng | 7 | 0.65 | 0.24 | 4.89 | 5 |
| 长临河口 Changlin River Mouths | 3 | 0 | |||||
| 肥西 Feixi | Fx | 柿树岗 Stream in Shishugang | 12 | 0.56 | 0.39 | 4.44 | 3 |
| 合肥 Hefei | Hf | 董铺水库 Dongpu Reservoir | 6 | 0.57 | 0.33 | 4.75 | 2 |
| 三十头支流 Stream in Sanshitou | 9 | 1 | |||||
| 长江 Yangtze River | |||||||
| 菜子湖 Caizi Lake | Czh | 王湾咀 Wangwanzui | 7 | 0.67 | 0.47 | 9.89 | 4 |
| 杨湾 Yangwan | 3 | 0 | |||||
| 肖店 Xiaodian | 21 | 6 | |||||
| 双店 Shuangdian | 12 | 3 | |||||
| 升金湖 Shengjin Lake | Sj | 升金湖 Shenjin Lake | 13 | 0.71 | 0.56 | 6.33 | 5 |
| 东至 Dongzhi | Dz | 香口乡 Stream in Xiangkou | 21 | 0.74 | 0.33 | 7.55 | 9 |
| 望江 Wangjiang | Wj | 华阳河 Huayang River | 20 | 0.76 | 0.17 | 7.44 | 18 |
| 新安江 Xin'anjiang River | |||||||
| 新安江 Xin'anjiang River | Xa | 屯光镇 Tunguang | 24 | 0.64 | 0.39 | 6.00 | 3 |
| 总计 Total | 182 | 0.67 | 0.35 | - | - | ||
| 位点 Loci | 重复单元Repeat unit | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5'-3') | 退火温度 Annealing temperature (°C) | 长度 Size range (bp) | 登录号 Accession no. | Na | HE | HO | PIC | Fis | Fit | Fst |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PclG33 | (GT)21 | F: FAM-TTCGAGGCGTTGCTGATTGTAAGT R: CAAGGAAGCGTATAGCCGGAGTCT | 56 | 120-180 | AF290936 | 23 | 0.83 | 0.46 | 0.81 | 0.50 | 0.56 | 0.110 |
| PCL29 | (GA)27 | F: HEX-CACTCAAGCCTGCCCTCACTC R: GTCTCTTCCTCCCCCATTCTCAC | 56 | 170-214 | EF564126 | 14 | 0.87 | 0.44 | 0.85 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.108 |
| PCL47 | (TG)13 | F: TAMRA-ACTCTGCCCATTGTTTCTCGG R: AGCCCTTGGACCCCGCCTATC | 56 | 324-344 | EF564128 | 10 | 0.79 | 0.82 | 0.75 | 0.57 | 0.62 | 0.110 |
| PCL33 | (TG)30 | F: FAM-ACTCCTGTCCCATTTCACTAC R: ACAACTAACTGCAACTCATTCTA | 56 | 132-158 | EF564127 | 24 | 0.81 | 0.43 | 0.78 | 0.49 | 0.54 | 0.100 |
| PCL28 | (CA)29 | F: HEX-CCTACCAGAGAACCCAAAACAGAA R: GTCAGCCTCCACCACATCACTT | 56 | 229-239 | EF564125 | 23 | 0.82 | 0.35 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.56 | 0.111 |
| PCL17 | (TC)17 | F: TAMRA-TTCACTACCGCCCACAGGATG R: TAGGCACCGCACTTATTAGACCAG | 56 | 370-422 | EF564122 | 18 | 0.71 | 0.10 | 0.69 | 0.45 | 0.51 | 0.111 |
| PclG48 | (CA)12 | F: FAM-CTGTTGGTGATTTCCGTCAATTTT R: AGATTCAACGCTGTGTTCCTGATC | 56 | 146-190 | AF290941 | 22 | 0.81 | 0.24 | 0.79 | 0.47 | 0.53 | 0.108 |
| PCL02 | (TG)30 | F: HEX-GAAGACGGGACACCACGAG R: ATCAAATCAAACGAAGCAAGAAAG | 56 | 245-271 | EF564119 | 24 | 0.86 | 0.23 | 0.84 | 0.46 | 0.52 | 0.113 |
| PCL50 | (GA)12 | F: TAMRA-AAGCGCTGAAATGCACAAACAAGA R: CAAGCCCCGAGGTCAAAGGTC | 56 | 424-525 | EF564129 | 19 | 0.53 | 0.17 | 0.51 | 0.48 | 0.53 | 0.105 |
表2 克氏原螯虾9个微卫星位点的引物序列、遗传差异、多态信息含量和F-统计检验
Table 2 Primer sequence, genetic differentiation, polymorphism information content and Wright’ F-statistics at nine microsatellite loci of Procambarus clarkii
| 位点 Loci | 重复单元Repeat unit | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5'-3') | 退火温度 Annealing temperature (°C) | 长度 Size range (bp) | 登录号 Accession no. | Na | HE | HO | PIC | Fis | Fit | Fst |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PclG33 | (GT)21 | F: FAM-TTCGAGGCGTTGCTGATTGTAAGT R: CAAGGAAGCGTATAGCCGGAGTCT | 56 | 120-180 | AF290936 | 23 | 0.83 | 0.46 | 0.81 | 0.50 | 0.56 | 0.110 |
| PCL29 | (GA)27 | F: HEX-CACTCAAGCCTGCCCTCACTC R: GTCTCTTCCTCCCCCATTCTCAC | 56 | 170-214 | EF564126 | 14 | 0.87 | 0.44 | 0.85 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.108 |
| PCL47 | (TG)13 | F: TAMRA-ACTCTGCCCATTGTTTCTCGG R: AGCCCTTGGACCCCGCCTATC | 56 | 324-344 | EF564128 | 10 | 0.79 | 0.82 | 0.75 | 0.57 | 0.62 | 0.110 |
| PCL33 | (TG)30 | F: FAM-ACTCCTGTCCCATTTCACTAC R: ACAACTAACTGCAACTCATTCTA | 56 | 132-158 | EF564127 | 24 | 0.81 | 0.43 | 0.78 | 0.49 | 0.54 | 0.100 |
| PCL28 | (CA)29 | F: HEX-CCTACCAGAGAACCCAAAACAGAA R: GTCAGCCTCCACCACATCACTT | 56 | 229-239 | EF564125 | 23 | 0.82 | 0.35 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.56 | 0.111 |
| PCL17 | (TC)17 | F: TAMRA-TTCACTACCGCCCACAGGATG R: TAGGCACCGCACTTATTAGACCAG | 56 | 370-422 | EF564122 | 18 | 0.71 | 0.10 | 0.69 | 0.45 | 0.51 | 0.111 |
| PclG48 | (CA)12 | F: FAM-CTGTTGGTGATTTCCGTCAATTTT R: AGATTCAACGCTGTGTTCCTGATC | 56 | 146-190 | AF290941 | 22 | 0.81 | 0.24 | 0.79 | 0.47 | 0.53 | 0.108 |
| PCL02 | (TG)30 | F: HEX-GAAGACGGGACACCACGAG R: ATCAAATCAAACGAAGCAAGAAAG | 56 | 245-271 | EF564119 | 24 | 0.86 | 0.23 | 0.84 | 0.46 | 0.52 | 0.113 |
| PCL50 | (GA)12 | F: TAMRA-AAGCGCTGAAATGCACAAACAAGA R: CAAGCCCCGAGGTCAAAGGTC | 56 | 424-525 | EF564129 | 19 | 0.53 | 0.17 | 0.51 | 0.48 | 0.53 | 0.105 |

图2 以邻接法构建的克氏原螯虾个体的系统树。样本编号对应的地方种群见表1。
Fig. 2 A neighbor-joining tree of Procambarus clarkii based on the microsatellite data. The abbreviated codes refer to local populations in Table 1.
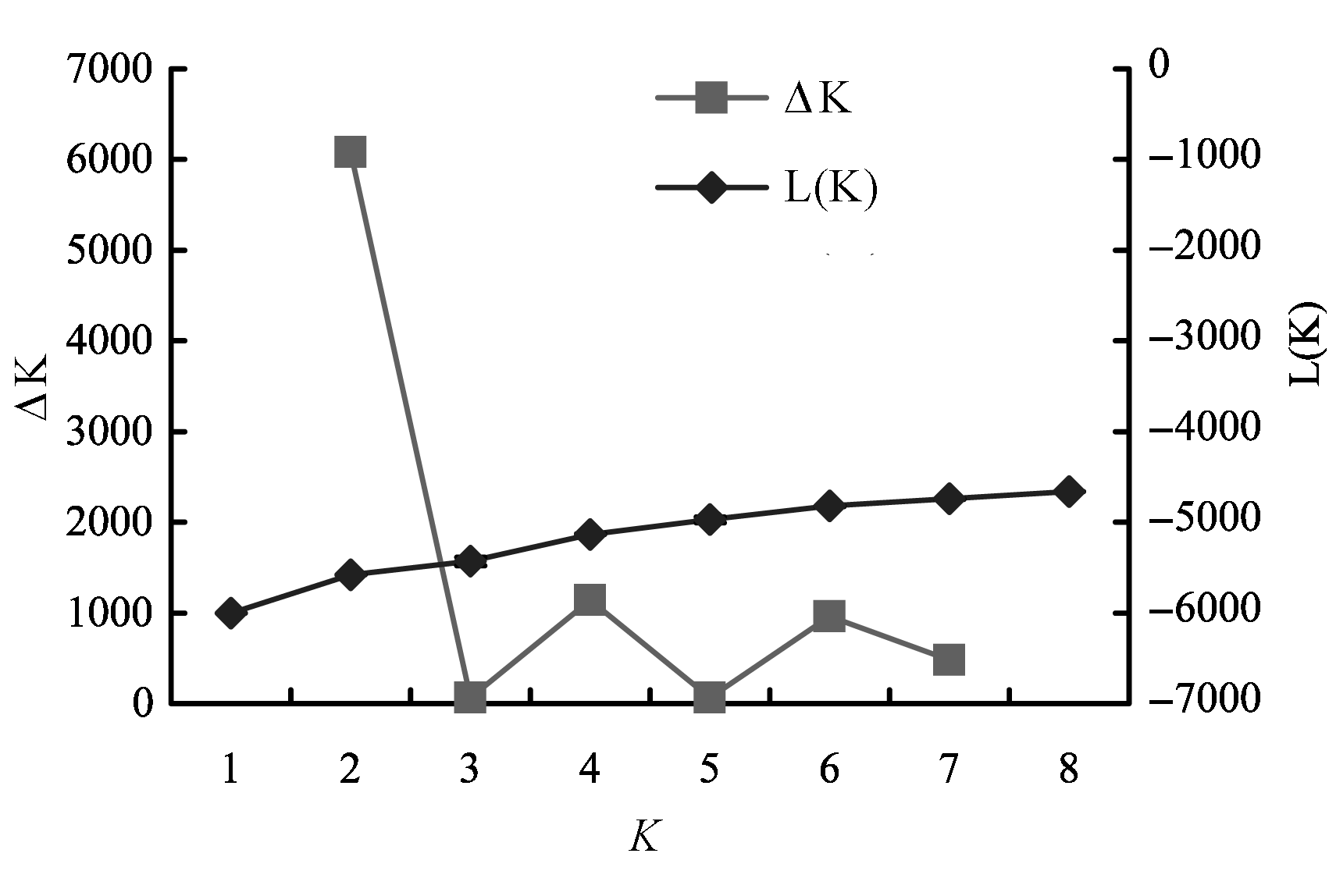
图3 用Structure获得的平均可能性和ΔK评估(利用Structure软件7次重复计算ΔK的平均值)
Fig. 3 Plot of mean likelihood values (averaged across 7 runs) and estimate of ΔK for each possible value of K using the data obtained from Structure software
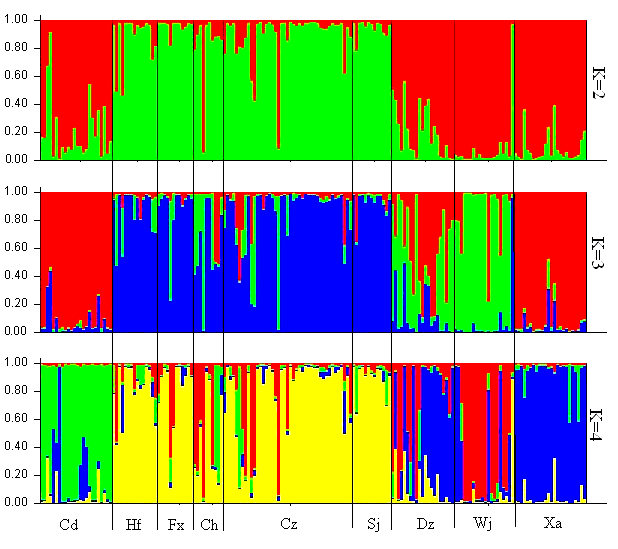
图4 利用Structure构建的9个地方种群结构(显示当潜在亚种群等于2、3和4时种群的聚类关系)。纵坐标表示各种群中的单个个体占种群祖先成分的比例。
Fig. 4 Structure bar plots of Procambarus clarkii from nine local populations. The assignment results show K = 2, 3 and 4, respectively. Each vertical bar represents one individual, and sampling location codes (see Table 1) are indicated along the X-axis. Y-coordinate denotes the proportion of ancestry components in an individual in relation to other population.
| Ch | Czh | Fx | Sj | Dz | Wj | Hf | Xa | Cd | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ch | 4.00 | 1.56 | 4.08 | 2.59 | 1.63 | 2.86 | 1.52 | 3.13 | |
| Czh | 0.06 | 1.67 | 9.49 | 2.52 | 1.62 | 5.75 | 1.38 | 1.92 | |
| Fx | 0.14 | 0.13 | 2.89 | 1.23 | 2.00 | 1.71 | 0.86 | 1.27 | |
| Sj | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 2.72 | 2.58 | 3.97 | 1.27 | 2.03 | |
| Dz | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 2.66 | 1.54 | 2.72 | 2.26 | |
| Wj | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 1.80 | 1.92 | 2.41 | |
| Hf | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 1.11 | 1.57 | |
| Xa | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 1.69 | |
| Cd | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.13 |
表3 9个克氏原螯虾种群基因流(对角线上)和遗传分化系数(Fst) (对角线下)。种群代号见表1。
Table 3 Gene flow (above diagonal) and genetic diversity (Fst) (below diagonal) in nine Procambarus clarkii populations. Population codes see Table 1.
| Ch | Czh | Fx | Sj | Dz | Wj | Hf | Xa | Cd | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ch | 4.00 | 1.56 | 4.08 | 2.59 | 1.63 | 2.86 | 1.52 | 3.13 | |
| Czh | 0.06 | 1.67 | 9.49 | 2.52 | 1.62 | 5.75 | 1.38 | 1.92 | |
| Fx | 0.14 | 0.13 | 2.89 | 1.23 | 2.00 | 1.71 | 0.86 | 1.27 | |
| Sj | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 2.72 | 2.58 | 3.97 | 1.27 | 2.03 | |
| Dz | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 2.66 | 1.54 | 2.72 | 2.26 | |
| Wj | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 1.80 | 1.92 | 2.41 | |
| Hf | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 1.11 | 1.57 | |
| Xa | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 1.69 | |
| Cd | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.13 |
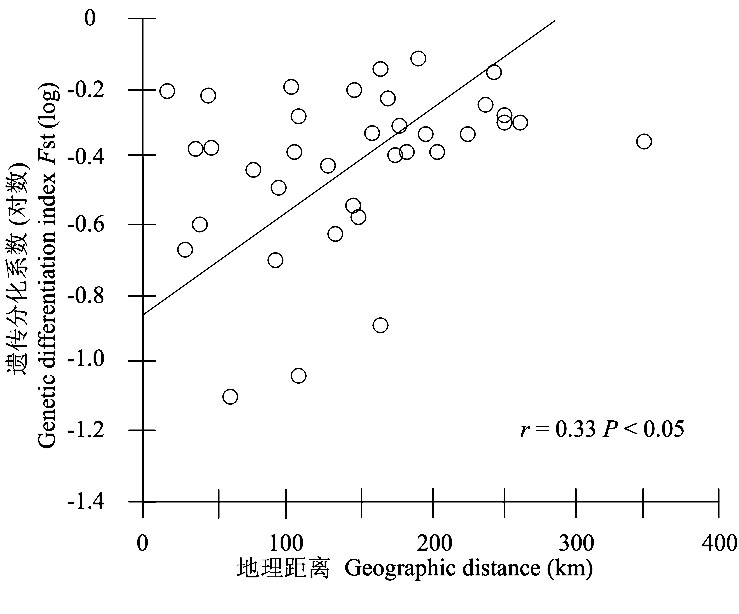
图5 利用IBDWS构建的地理距离和遗传分化系数Fst(log)线性关系(遗传分化和地理距离存在显著正相关r = 0.33, P < 0.05)
Fig. 5 Relationships between geographical distance and population genetic differentiation index (log) of nine sample sites using IBDWS. A Mantel Test indicated a significant correlation (r= 0.33, P< 0.05)
| [1] | Barbaresi S, Fani R, Gherardi F, Mengoni A, Souty-Grosset C (2003) Genetic variability of European populations of an invasive American crayfish: preliminary results. Biological Invasions, 5,269-274. |
| [2] | Barbaresi S, Gherardi F, Mengoni A, Souty-Grosset C (2007) Genetics and invasion biology in fresh waters:a pilot study of Procambarus clarkii in Europe. In: Biological Invaders in Inland Waters: Profile, Distribution and Threats (ed. Gherardi F), pp.381-400. Springer, Dordrecht. |
| [3] |
Belfiore NM, May B (2000) Variable microsatellite loci in red swamp crayfish, Procambarus clarkii, and their characterization in other crayfish taxa. Molecular Ecology, 9,2231-2234.
URL PMID |
| [4] | Berg DJ, Garton DW, Macisaac HJ, Panov VE, Telesh IV (2002) Changes in genetic structure of North American Bythotrephes populations following invasion from Lake Ladoga, Russia. Freshwater Biology, 47,275-282. |
| [5] |
Castric V, Bernatchez L, Belkhir K, Bonhomme F (2002) Heterozygote deficiencies in small lacustrine populations of brook charr Salvelinus fontinalis Mitchill (Pices, Salmonidae): a test of alternative hypotheses. Heredity, 89,27-35.
URL PMID |
| [6] | Chen YF (陈毅峰), Yan YZ (严云志) (2005) Evolutionary biology of invasions. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica (水生生物学报), 29,220-224. (in Chinese) |
| [7] | Chu D (褚栋), Zhang YJ (张友军), Wan FH (万方浩) (2007) Application of molecular marker techniques in invasion ecology. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 18,1383-1387. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] |
DeAssis JB, DeLaat DM, Peixoto MGCD, Bergmann JAG, Fonseca CG, Carvalho MRS (2009) Genetic diversity and population structure in Brazilian Mangalarga Marchador horses. Genetics and Molecular Research, 8,1519-1524.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] |
Facon B, Pointier JP, Glaubrecht M, Poux C, Jarne P, David P (2003) A molecular phylogeography approach to biological invasions of the New World by parthenogenetic Thiarid snails. Molecular Ecology, 12,3027-3039.
URL PMID |
| [10] |
Friar EA, Ladoux TA, Roalson EH, Robichaux RH (2000) Microsatellite analysis of a population crash and bottleneck in the Mauna Kea silverword, Argyroxiphium sandwicense ssp. sandwicense (Asteraceae), and its implications for reintroduction. Molecular Ecology, 9,2027-2034.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] | Gaffney PM, Scott TM, Koehn RK, Diehl WJ (1990) Interrelationships of heterozygosity, growth rate heterozygote deficiencies in the coot clam, Mutinia lateralis. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 124,687-699. |
| [12] | Geiger W, Alcorlo P, Baltanas A, Montes C (2005) Impact of an introduced Crustacean on the trophic webs of Mediterranean wetlands. Biological Invasions, 7,49-73. |
| [13] | Gherardi F (2006) Crayfish invading Europe: the case study of Procambarus clarkii. Marine and Freshwater Behaviour and Physiology, 39,175-191. |
| [14] | Gherardi F, Silvia B (2000) Invasive crayfish: activity patterns of Procambarus clarkii in the rice fields of the Lower Guadalquivir (Spain). Archiv für Hydrobiologie, 150,153-168. (in Spanish with English abstract). |
| [15] | Gregorius HR (1980) The probability of losing an allele when diploid genotype are sampled. Biometrics, 36,632-652. |
| [16] | Guo XM (郭晓鸣), Zhu SQ (朱松泉) (1997) A preliminary study on the larval development of the crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Acta Zoologica Sinica (动物学报), 43,372-381. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Hassan M, Bonhomme F (2005) No reduction in neutral variability of mitochondrial and nuclear genes for a Lessepsian migrant, Upeneus moluccensis. Journal of Fish Biology, 66,865-870. |
| [18] | Hedrick PW (1984) Population Biology: The Evolution and Ecology of Populations. Jones and Bartlett Publishers, Boston. |
| [19] |
Herborg LM, Weetman D, Oosterhout C, Hänfling B (2007) Genetic population structure and contemporary dispersal patterns of a recent European invader, the Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Molecular Ecology, 16,231-242.
URL PMID |
| [20] | Hernández L, Maeda-Martínez AM, Ruiz-Campos G, Rodríguez-Almaraz G, Alonzo-Rojo F, Sainz JC (2007) Geographic expansion of the invasive red crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) (Crustacea: Decapoda) in Mexico. Biological Invasions, 10,977-984. |
| [21] | Huner (1988) Procambarus in North America and elsewhere. In: Freshwater Crayfish: Biology, Management and Exploitation (eds Holdich DM, Lowery RS), pp.239-261. Timber Press, London. |
| [22] |
Jensen JL, Bohonak AJ, Kelley ST (2005) Isolation by distance, web service. BMC Genetics, 6,13.
URL PMID |
| [23] |
Kerby JL, Riley SPD, Kats LB, Wilson P (2005) Barriers and flow as limiting factors in the spread of an invasive crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) in southern California streams. Biological Conservation, 126,402-409.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Kitamoto N, Honjo M, Ueno S, Takenaka A, Tsumura Y, Washitani I, Ohsawa R (2005) Spatial genetic structure among and within populations of Primula sieboldii growing beside separate streams. Molecular Ecology, 14,149-157.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] |
Kolbe JJ, Glor RE, Schettino LR, Lara AC, Larson A, Losos JB (2004) Genetic variation increases during the biological invasion of a Cuban lizard. Nature, 431,177-181.
URL PMID |
| [26] |
Kolbe JJ, Larson A, Losos JB, Queiroz K (2008) Admixture determines genetic diversity and population differentiation in the biological invasion of a lizard species. Biology Letters, 4,434-437.
URL PMID |
| [27] |
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K (2008) MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 9,299-306.
URL PMID |
| [28] | Lee CE (2002) Evolutionary genetics of invasive species. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 17,386-391. |
| [29] | Li CC (1995) Population Genetics. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago and London. |
| [30] | Li LP (李浪平), Lü JL (吕建林), Gong SY (龚世园), Shu XY (舒新亚), Gong LJ (龚珞军) (2006) Studies on the morphology of Procambarus clarkii. Reservoir Fisheries (水利渔业), 26(3),40-42. (in Chinese) |
| [31] | Li SC (李顺才), Xu XY (徐兴友), Du LQ (杜利强), Yin XL (尹秀玲), Meng XD (孟宪东), Xie JY (解敬瑶) (2005) Investigation on and analysis of alien invasions in Chinese farming industry. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin (中国农学通报), 21(6),156-159. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Li ZY (李振宇), Xie Y (解焱) (2002) Invasive Alien Species in China (中国外来入侵种). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [33] |
Manel S, Schwartz MK, Gordon L, Pierre T (2003) Landscape genetics: combining landscape ecology and population genetics. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 18,189-197.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Manning AD, Lindenmayer DB, Nix HA (2004) Continua and umwelt: novel perspectives on viewing landscapes. Oikos, 104,621-628. |
| [35] | Maria JC, Rebelo R (2007) Colonization of freshwater habitats by an introduced crayfish, Procambarus clarkii, in Southwest Iberian Peninsula. Hydrobiologia, 575,191-201. |
| [36] |
Morrison LJ, Tweedie A, Black A, Pinchbeck GL, Christley RM, Schoenefeld A, Hertz-Fowler C, MacLeod A, Turner CM, Tait A (2009) Discovery of mating in the major African livestock pathogen Trypanosoma congolense. PLoS ONE, 4,e5564.
URL PMID |
| [37] | Park SDE (2001) Trypanotolerance in West African Cattle and the Population Genetic Effects of Selection. PhD dissertation of University of Dublin, Dublin. |
| [38] | Parker IM, Simberloff D, Lonsdale WM, Goodell K, Wonham M, Kareiva PM, Williamson MH, Holle BV, Moyle PB, Byers JE, Goldwasser L (1999) Impact: toward a framework for understanding the ecological effects of invaders. Biological Invasions, 1,3-19. |
| [39] |
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics, 155,945-959.
URL PMID |
| [40] | Raymond M, Rousset F (1995) GENEPOP (version 1.2): population genetics software for exact tests and ecumenicism. Journal of Heredity, 86,248-249. |
| [41] |
Rousset F (2008) GENEPOP' 007: a complete re-implemen- tation of the GENEPOP software for Windows and Linux. Molecular Ecology Resources, 8,103-106.
DOI URL PMID |
| [42] |
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 4,406-425.
URL PMID |
| [43] | Sakai AK, Allendorf FW, Holt JS, Lodge DM, Molofsky J, With KA, Baughman S, Cabin RJ, Cohen JE, Ellstrand NC, McCauley DE, O'Neil P, Parker IM, Thompson JN, Weller SG (2001) The population biology of invasive species. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 32,305-332. |
| [44] | Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York. |
| [45] |
Serrano M, Calvo JH, Martínez M, Marcos-Carcavilla A, Cuevas J, González C, Jurado JJ, de Tejada PD (2009) Microsatellite based genetic diversity and population structure of the endangered Spanish Guadarrama goat breed. BMC Genetics, 10,61.
URL PMID |
| [46] | Shi GR (史刚荣), Ma CC (马成仓) (2006) Biological characteristics of alien plants successful invasion. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 17,727-732. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [47] |
Simberloff D (2005) The politics of assessing risk for biological invasions: the USA as a case study. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 20,216-222.
URL PMID |
| [48] | Sjogren P, Wyoni PI (1994) Conservation genetics and detection of rare alleles in finite populations. Conservation Biology, 8,267-270. |
| [49] |
Sork VL, Nason J, Campbell DR, Fernandez JF (1999) Landscape approaches to historical and contemporary gene flow in plants. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 14,219-224.
URL PMID |
| [50] | Stepien CA, Taylor CD, Dabrowska KA (2002) Genetic variability and phylogeographical patterns of a nonindigenous species invasion: a comparison of exotic vs. native zebra and quagga mussel populations. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 15,314-328. |
| [51] | Suarez AV, Holway DA, Case TJ (2001) Patterns of spread in biological invasions dominated by long-distance jump dispersal: insights from Argentine ants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 98,1095-1100. |
| [52] | Tiunov AV, Cindy H, Andrew H, Tamara VP (2006) Invasion patterns of Lumbricidae into the previously earthworm-free areas of northeastern Europe and the western Great Lakes region of North America. Biological Invasions, 8,1223-1234. |
| [53] |
Tsutsui ND, Suarez AV, Holway DA, Case TJ (2001) Relationships among native and introduced populations of the Argentine ant, Linepithema humile and the source of introduced populations. Molecular Ecology, 10,2151-2161.
URL PMID |
| [54] |
Valles-Jimenez R, Cruz P, Perez-Enriquez R (2005) Population genetic structure of pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) from Mexico to Panama microsatellite DNA variation. Marine Biotechnology, 6,475-484.
URL PMID |
| [55] |
Villanelli F, Gherardi F (1998) Breeding in the crayfish, Austropotamobius pallipes: mating patterns, mate choice and intermale competition. Freshwater Biology, 40,305-315.
DOI URL |
| [56] | Wang CZ (王长忠), Li Z (李忠), Liang HW (梁宏伟), Hu GF (呼光富), Wu QC (吴勤超), Zou GW (邹桂伟), Luo XZ (罗相忠) (2009) Genetic diversity in four Procambarus clarkii populations in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 17,518-523. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [57] | Wu ZJ (武正军), Cai FJ (蔡凤金), Jia YF (贾运锋), Lu JX (鲁建鑫), Jiang YF (蒋勇福), Huang CM (黄乘明) (2008) Predation impact of Procambarus clarkii on Rana limnocharis tadpoles in Guilin area. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 16,150-155. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [58] | Xie Y (解焱), Wang S (汪松) (2001) Review on invasive species in China. In: Protecting the Biodiversity of China (II) (保护我国的生物多样性) (eds Schei P, Xie Y (解焱), Wang S (汪松)), pp.91-96. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [59] | Xu RM (徐汝梅), Ye WH (叶万辉) (2003) Biological Invasion: Theory and Practice (生物入侵: 理论与实践). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [60] | Yan LN (闫路娜), Zhang DX (张德兴) (2004) Effects of sample size on various genetic diversity measures in population genetic study with microsatelite DNA markers. Acta Zoologica Sinica (动物学报), 50,279-290. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [61] |
Yasuda N, Nagai S, Hamaguchi M, Okaji K, Gérard K, Nadaoka K (2009) Gene flow of Acanthaster planci (L.) in relation to ocean currents revealed by microsatellite analysis. Molecular Ecology, 18,1574-1590.
DOI URL PMID |
| [62] | Yue GH, Li JL, Bai ZY, Wang CM, Feng F (2010) Genetic diversity and population structure of the invasive alien red swamp crayfish. Biological Invasions, 12,2697-2706. |
| [63] |
Zalewski A, Piertney SB, Zalewska H, Lambin X (2009) Landscape barriers reduce gene flow in an invasive carnivore: geographical and local genetic structure of American mink in Scotland. Molecular Ecology, 18,1601-1615.
DOI URL PMID |
| [64] |
Zhu ZY, Yue GH (2008) Eleven polymorphic microsatellites isolated from red swamp crayfish, Procambarus clarkii. Molecular Ecology Resources, 8,796-798.
URL PMID |
| [1] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [2] | 邓洪, 钟占友, 寇春妮, 朱书礼, 李跃飞, 夏雨果, 武智, 李捷, 陈蔚涛. 基于线粒体全基因组揭示斑鳠的种群遗传结构与演化历史[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24241-. |
| [3] | 杜聪聪, 冯学宇, 陈志林. 桥头堡效应中气候生态位差异的缩小促进了红火蚁的入侵[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24276-. |
| [4] | 原雪姣, 张渊媛, 张衍亮, 胡璐祎, 桑卫国, 杨峥, 陈颀. 基于飞机草历史分布数据拟合的物种分布模型及其预测能力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24288-. |
| [5] | 韩丽霞, 王永健, 刘宣. 外来物种入侵与本土物种分布区扩张的异同[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23396-. |
| [6] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [7] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [8] | 魏博, 刘林山, 谷昌军, 于海彬, 张镱锂, 张炳华, 崔伯豪, 宫殿清, 土艳丽. 紫茎泽兰在中国的气候生态位稳定且其分布范围仍有进一步扩展的趋势[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 21443-. |
| [9] | 孙维悦, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 莫日根高娃, 杜夏瑾, 刘保东, 严岳鸿. 基于保护基因组学揭示荷叶铁线蕨的濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [10] | 牛晓锋, 王晓梅, 张研, 赵志鹏, 樊恩源. 鲟鱼分子鉴定方法的整合应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 22034-. |
| [11] | 刘艳杰, 黄伟, 杨强, 郑玉龙, 黎绍鹏, 吴昊, 鞠瑞亭, 孙燕, 丁建清. 近十年植物入侵生态学重要研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22438-. |
| [12] | 严靖, 闫小玲, 李惠茹, 杜诚, 马金双. 华东地区归化植物的组成特征、引入时间及时空分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 428-438. |
| [13] | 叶俊伟, 田斌. 中国西南地区重要木本油料植物扁核木的遗传结构及成因[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1629-1637. |
| [14] | 向登高, 李跃飞, 李新辉, 陈蔚涛, 马秀慧. 多基因联合揭示海南鲌的遗传结构与遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1505-1512. |
| [15] | 李潮,金锦锦,罗锦桢,王春晖,王俊杰,赵俊. 唐鱼养殖种群与广州附近4个野生种群的遗传关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(4): 474-484. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()