



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (8): 940-949. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019342 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019342
所属专题: 昆虫多样性与生态功能; 生物安全
向颖1, 刘素群2, 黄兴龙1, 刘志霄1, 张佑祥1,*( ), 马方舟3,*(
), 马方舟3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-07-18
接受日期:2020-10-08
出版日期:2020-08-20
发布日期:2020-10-19
通讯作者:
张佑祥,马方舟
作者简介:mfz@nies.org基金资助:
Ying Xiang1, Suqun Liu2, Xinglong Huang1, Zhixiao Liu1, Youxiang Zhang1,*( ), Fangzhou Ma3,*(
), Fangzhou Ma3,*( )
)
Received:2020-07-18
Accepted:2020-10-08
Online:2020-08-20
Published:2020-10-19
Contact:
Youxiang Zhang,Fangzhou Ma
摘要:
为了解湖南高望界国家级自然保护区蝶类多样性本底及其影响因素, 2016年5月至2018年10月, 我们采用样线法对保护区内外的6种生境(保护区内4种, 区外2种)开展了20次蝶类多样性调查。共记录蝴蝶个体13,956只, 依照五科分类系统, 隶属5科113属239种, 其中湖南省蝶类新记录17种。区系成分以东洋种为主(139种, 占58.1%), 广布种次之(97种, 占40.6%), 古北种最少(3种, 占1.3%)。对不同生境的蝶类群落多样性指数进行分析后发现, 人为干扰程度和生境异质性共同影响蝶类多样性。不同生境相似性分析结果表明, 蝶类群落的相似度与人为干扰程度和植被类型差异密切相关。3年间, 蝶类多样性指数月度变化基本一致, 蝶类物种数、多样性指数与月均温间呈显著正相关, 与月降水量无相关性。综上, 蝶类多样性受到人为干扰程度和气象因子的影响。为保护蝶类资源, 建议保护好蝶类栖息地, 减少人为干扰。
向颖, 刘素群, 黄兴龙, 刘志霄, 张佑祥, 马方舟 (2020) 湖南高望界国家级自然保护区及其周边蝶类多样性与影响因素. 生物多样性, 28, 940-949. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019342.
Ying Xiang, Suqun Liu, Xinglong Huang, Zhixiao Liu, Youxiang Zhang, Fangzhou Ma (2020) Butterfly diversity and its influencing factors in the Hunan Gaowangjie National Nature Reserve and its surrounding area. Biodiversity Science, 28, 940-949. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019342.
| 科名 Family | 个体数 No. of individuals (%) | 种数 No. of species (%) | 属数 No. of genera (%) | 属种比值 Ratio of genus/species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 凤蝶科 Papilionidae | 2,112 (15.1) | 18 (7.5) | 6 (5.3) | 0.330 |
| 粉蝶科 Pieridae | 3,271 (23.4) | 23 (9.6) | 9 (8.0) | 0.390 |
| 蛱蝶科 Nymphalidae | 4,378 (31.4) | 120 (50.2) | 46 (40.7) | 0.383 |
| 灰蝶科 Lycaenidae | 3,197 (22.9) | 35 (14.7) | 26 (23.0) | 0.743 |
| 弄蝶科 Hesperiidae | 998 (7.2) | 43 (18) | 26 (23.0) | 0.605 |
| 总计 Total | 13,956 (100) | 239 (100) | 113 (100) | 0.473 |
表1 湖南高望界国家级自然保护区及周边蝶类群落中各科的数量
Table 1 Quantitative characteristics of butterfly communities in Hunan Gaowangjie National Nature Reserve and its surrounding area
| 科名 Family | 个体数 No. of individuals (%) | 种数 No. of species (%) | 属数 No. of genera (%) | 属种比值 Ratio of genus/species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 凤蝶科 Papilionidae | 2,112 (15.1) | 18 (7.5) | 6 (5.3) | 0.330 |
| 粉蝶科 Pieridae | 3,271 (23.4) | 23 (9.6) | 9 (8.0) | 0.390 |
| 蛱蝶科 Nymphalidae | 4,378 (31.4) | 120 (50.2) | 46 (40.7) | 0.383 |
| 灰蝶科 Lycaenidae | 3,197 (22.9) | 35 (14.7) | 26 (23.0) | 0.743 |
| 弄蝶科 Hesperiidae | 998 (7.2) | 43 (18) | 26 (23.0) | 0.605 |
| 总计 Total | 13,956 (100) | 239 (100) | 113 (100) | 0.473 |
| 科名 Family | 种数 No. of species | 东洋种 Oriental species (%) | 古北种 Palearctic species (%) | 广布种 Widespread species (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 凤蝶科 Papilionidae | 18 | 8 (3.3) | 0 | 10 (4.2) |
| 粉蝶科 Pieridae | 23 | 10 (4.2) | 2 (0.8) | 11 (4.6) |
| 蛱蝶科 Nymphalidae | 120 | 77 (32.2) | 0 | 43 (18.0) |
| 灰蝶科 Lycaenidae | 35 | 21 (8.8) | 1 (0.4) | 13 (5.4) |
| 弄蝶科 Hesperiidae | 43 | 23 (9.6) | 0 | 20 (8.4) |
| 总计 Total | 239 | 139 (58.1) | 3 (1.3) | 97 (40.6) |
表2 湖南高望界国家级自然保护区及周边的蝶类物种区系组成
Table 2 Fauna components of butterflies in Hunan Gaowangjie National Nature Reserve and its surrounding area
| 科名 Family | 种数 No. of species | 东洋种 Oriental species (%) | 古北种 Palearctic species (%) | 广布种 Widespread species (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 凤蝶科 Papilionidae | 18 | 8 (3.3) | 0 | 10 (4.2) |
| 粉蝶科 Pieridae | 23 | 10 (4.2) | 2 (0.8) | 11 (4.6) |
| 蛱蝶科 Nymphalidae | 120 | 77 (32.2) | 0 | 43 (18.0) |
| 灰蝶科 Lycaenidae | 35 | 21 (8.8) | 1 (0.4) | 13 (5.4) |
| 弄蝶科 Hesperiidae | 43 | 23 (9.6) | 0 | 20 (8.4) |
| 总计 Total | 239 | 139 (58.1) | 3 (1.3) | 97 (40.6) |
| 生境 Habitat | 个体数 No. of individuals | 种数 No. of species | 属数 No. of genera | 多样性指数 Diversity index (H') | 均匀度指数 Evenness index (J) | 物种丰富度 Species richness (R) | 优势度指数 Dominance index (D) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 小河桥 Xiaoheqiao | 2,024 | 110 | 62 | 4.977 | 1.059 | 14.318 | 0.423 |
| 栖凤湖 Qifenghu | 1,723 | 110 | 64 | 4.759 | 1.012 | 14.627 | 0.421 |
| 侯家寨 Houjiazhai | 2,506 | 145 | 78 | 5.683 | 1.142 | 18.399 | 0.187 |
| 麻溪 Maxi | 4,229 | 149 | 82 | 5.454 | 1.090 | 17.725 | 0.205 |
| 焦坪 Jiaoping | 1,673 | 147 | 81 | 5.718 | 1.146 | 19.670 | 0.155 |
| 大溪坪 Daxiping | 1,801 | 143 | 78 | 5.743 | 1.157 | 18.943 | 0.075 |
表3 湖南高望界国家级自然保护区及周边不同生境蝶类的群落多样性指数
Table 3 Diversity indices of butterfly community in different habitats of Hunan Gaowangjie National Nature Reserve and its surrounding area
| 生境 Habitat | 个体数 No. of individuals | 种数 No. of species | 属数 No. of genera | 多样性指数 Diversity index (H') | 均匀度指数 Evenness index (J) | 物种丰富度 Species richness (R) | 优势度指数 Dominance index (D) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 小河桥 Xiaoheqiao | 2,024 | 110 | 62 | 4.977 | 1.059 | 14.318 | 0.423 |
| 栖凤湖 Qifenghu | 1,723 | 110 | 64 | 4.759 | 1.012 | 14.627 | 0.421 |
| 侯家寨 Houjiazhai | 2,506 | 145 | 78 | 5.683 | 1.142 | 18.399 | 0.187 |
| 麻溪 Maxi | 4,229 | 149 | 82 | 5.454 | 1.090 | 17.725 | 0.205 |
| 焦坪 Jiaoping | 1,673 | 147 | 81 | 5.718 | 1.146 | 19.670 | 0.155 |
| 大溪坪 Daxiping | 1,801 | 143 | 78 | 5.743 | 1.157 | 18.943 | 0.075 |
| 小河桥 Xiaoheqiao | 栖凤湖 Qifenghu | 侯家寨 Houjiazhai | 麻溪 Maxi | 焦坪 Jiaoping | 大溪坪 Daxiping | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 小河桥 Xiaoheqiao | 70 | 75 | 90 | 76 | 79 | |
| 栖凤湖 Qifenghu | 0.467 | 75 | 78 | 79 | 73 | |
| 侯家寨 Houjiazhai | 0.417 | 0.417 | 105 | 110 | 98 | |
| 麻溪 Maxi | 0.533 | 0.431 | 0.556 | 110 | 112 | |
| 焦坪 Jiaoping | 0.420 | 0.444 | 0.604 | 0.591 | 101 | |
| 大溪坪 Daxiping | 0.454 | 0.406 | 0.516 | 0.622 | 0.534 |
表4 湖南高望界国家级保护区及周边不同生境蝶类群落的共有种数(对角线上)和相似性系数(对角线下)
Table 4 Number of the shared species (above diagonal) and similarity coefficient (below diagonal) between different habitats in Hunan Gaowangjie National Nature Reserve and its surrounding area
| 小河桥 Xiaoheqiao | 栖凤湖 Qifenghu | 侯家寨 Houjiazhai | 麻溪 Maxi | 焦坪 Jiaoping | 大溪坪 Daxiping | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 小河桥 Xiaoheqiao | 70 | 75 | 90 | 76 | 79 | |
| 栖凤湖 Qifenghu | 0.467 | 75 | 78 | 79 | 73 | |
| 侯家寨 Houjiazhai | 0.417 | 0.417 | 105 | 110 | 98 | |
| 麻溪 Maxi | 0.533 | 0.431 | 0.556 | 110 | 112 | |
| 焦坪 Jiaoping | 0.420 | 0.444 | 0.604 | 0.591 | 101 | |
| 大溪坪 Daxiping | 0.454 | 0.406 | 0.516 | 0.622 | 0.534 |
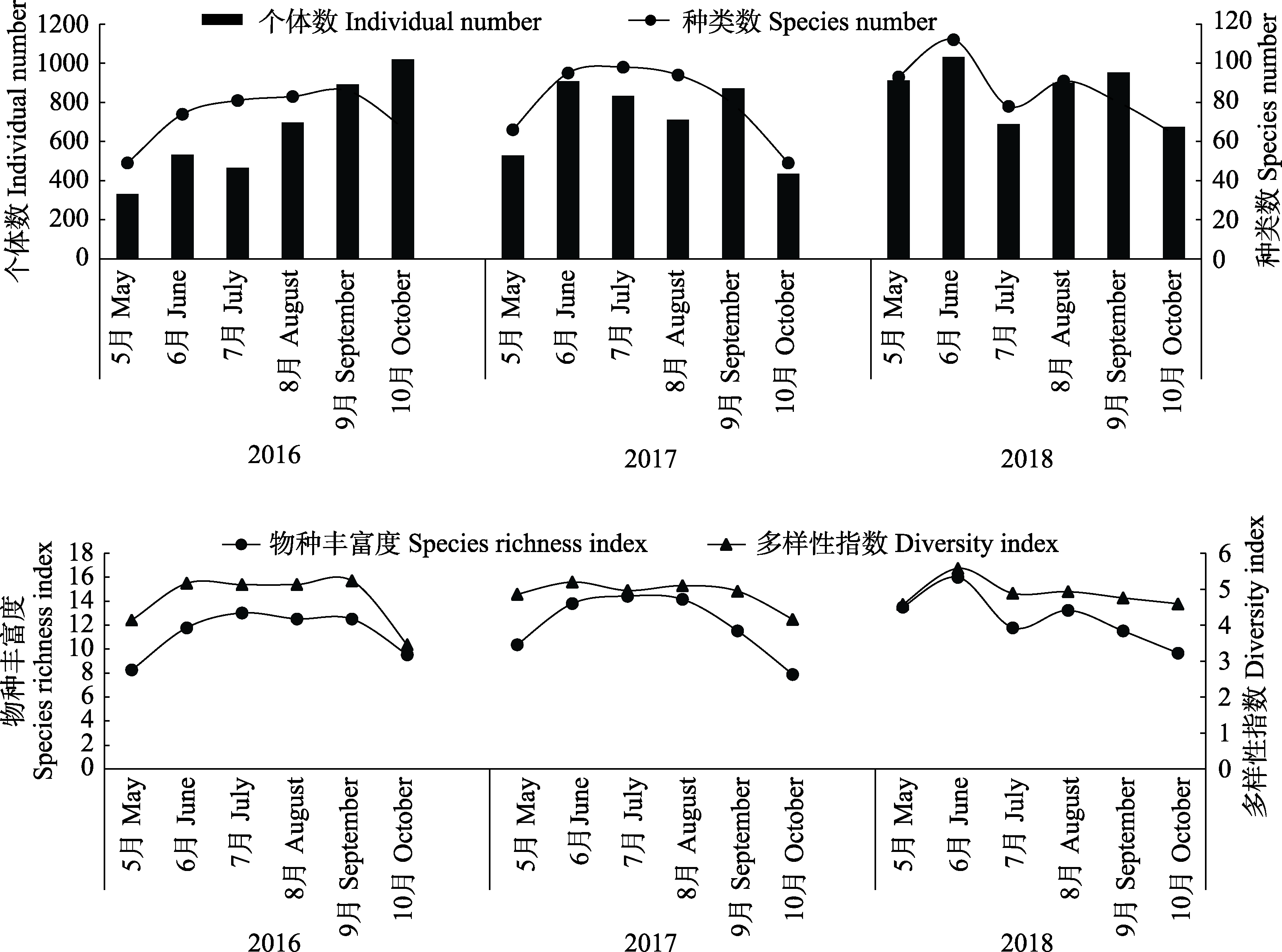
图1 湖南高望界国家级自然保护区及其周边蝶类个体数、种类数、多样性指数及物种丰富度月动态
Fig. 1 Monthly fluctuation of individuals, species, diversity index and species richness index of butterflies in Hunan Gaowangjie National Nature Reserve and its surrounding area from May 2016 to October 2018
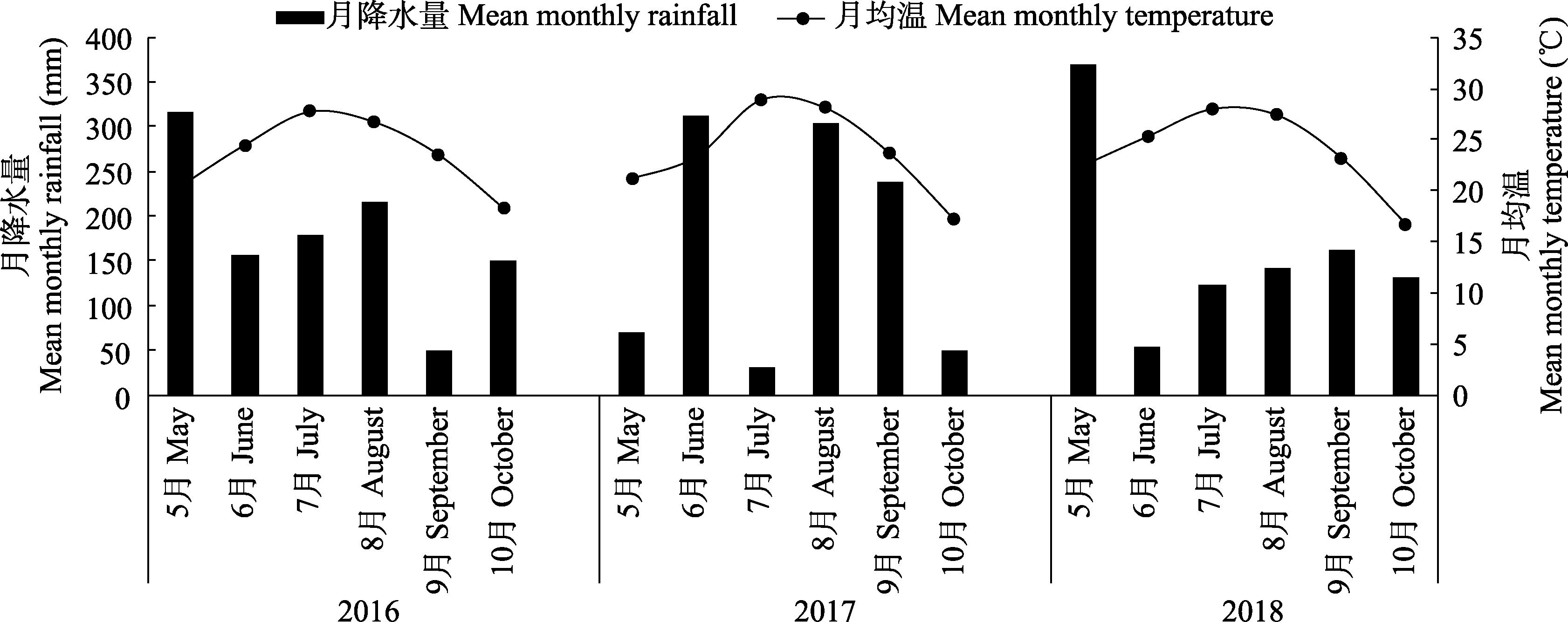
图2 湖南高望界国家级自然保护区及周边月均温和月降水量
Fig. 2 Mean monthly temperature and rainfall in Hunan Gaowangjie National Nature Reserve and its surrounding area from May 2016 to October 2018
| 个体数 No. of individuals | 种数 No. of species | 多样性指数Diversity index (H') | 物种丰富度 Species richness (R) | 均匀度指数 Evenness index (J) | 月均温 Mean monthly temperature | 月降水量 Mean monthly rainfall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 个体数 No. of individuals | 1 | 0.786** | 0.228 | 0.687** | -0.406 | 0.378 | 0.039 |
| 种类数 No. of species | 1 | 0.677** | 0.989** | 0.019 | 0.759** | 0.094 | |
| 多样性指数 Diversity index (H') | 1 | 0.737** | 0.740** | 0.665** | -0.076 | ||
| 物种丰富度 Species richness (R) | 1 | 0.108 | 0.805** | 0.107 | |||
| 均匀度指数 Evenness index (J) | 1 | 0.208 | -0.186 | ||||
| 月均温 Mean monthly temperature | 1 | 0.079 | |||||
| 月降水量 Mean monthly rainfall | 1 |
表5 月气象因子与高望界蝶类群落多样性指数的Pearson相关性分析
Table 5 Pearson correlation analysis between monthly meteorological factors and diversity indices of butterfly community in Hunan Gaowangjie National Nature Reserve and its surrounding area
| 个体数 No. of individuals | 种数 No. of species | 多样性指数Diversity index (H') | 物种丰富度 Species richness (R) | 均匀度指数 Evenness index (J) | 月均温 Mean monthly temperature | 月降水量 Mean monthly rainfall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 个体数 No. of individuals | 1 | 0.786** | 0.228 | 0.687** | -0.406 | 0.378 | 0.039 |
| 种类数 No. of species | 1 | 0.677** | 0.989** | 0.019 | 0.759** | 0.094 | |
| 多样性指数 Diversity index (H') | 1 | 0.737** | 0.740** | 0.665** | -0.076 | ||
| 物种丰富度 Species richness (R) | 1 | 0.108 | 0.805** | 0.107 | |||
| 均匀度指数 Evenness index (J) | 1 | 0.208 | -0.186 | ||||
| 月均温 Mean monthly temperature | 1 | 0.079 | |||||
| 月降水量 Mean monthly rainfall | 1 |
| [1] |
Braga MP, Guimarães PR, Wheat CW, Nylin S, Janz N (2018) Unifying host-associated diversification processes using butterfly-plant networks. Nature Communications, 9, 1-10.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] |
Bried J, Tear T, Shirer R, Zimmerman C, Gifford N, Campbell S, O’Brien K (2014) A framework to integrate habitat monitoring and restoration with endangered insect recovery. Environmental Management, 54, 1385-1398.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] |
Butchart SHM, Walpole M, Collen B, Strien AV, Scharlemann JPW, Almond Rosamunde EA, Baillie JEM, Bomhard B, Brown C, Bruno J, Carpenter KE, Carr GM, Chanson J, Chenery AM, Csirke J, Davidson NC, Dentener F, Foster M, Galli A, Galloway JN, Genovesi P, Gregory RD, Hockings M, Kapos V, Lamarque JF, Leverington F, Loh J, McGeoch MA, McRae L, Minasyan A, Hernández MM, Oldfield TEE, Pauly D, Quader S, Revenga C, Sauer JR, Skolnik B, Spear D, Smith SD, Stuart SN, Symes A, Tierney M, Tyrrell TD, Vié JC, Watson R (2010) Global biodiversity: Indicators of recent declines. Science, 328, 1164-1168.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] | Cai YH, Long ZY, Lin D, Chen JX, Chen MH, Bi QQ, Li XK, Qing N (2015) Influence of habitat fragmentation on butterfly diversity in Dinghu Mountain Nature Reserve. Journal of South China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 47(4), 88-93. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蔡雅虹, 龙志泳, 林东, 陈嘉欣, 陈敏豪, 毕倩琪, 李旭坤, 庆宁 (2015) 生境破碎化对鼎湖山蝶类多样性的影响. 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 474, 88-93.] | |
| [5] | Chang CY, Jia YX, Wang XP (2014) Community structure and diversity of butterfly in Yunwushan National Nature Reserve of Ningxia. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 23(11), 168-172. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 常春燕, 贾彦霞, 王新谱 (2014) 宁夏云雾山国家自然保护区蝶类群落结构与多样性. 西北农业学报, 2311, 168-172.] | |
| [6] | Chen Y, Long JN, Li YC, Yang J (2012) The butterfly bio- diversity in Baiyunshan Nature Reserve. Hunan Forestry Science & Technology, 39(3), 38-40, 49. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈艺, 龙江宁, 李奕成, 杨骏 (2012) 白云山自然保护区蝶类昆虫物种多样性研究. 湖南林业科技, 393, 38-40, 49.] | |
| [7] | Chou I (1994) Monographia Rhopalocerorum Sinensium. Henan Science and Technology Publishing House, Zhengzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 周尧 (1994) 中国蝶类志 河南科学技术出版社, 郑州.] | |
| [8] | Chou I (1998) Classification and Identification of Chinese Butterflies. Henan Science and Technology Publishing House, Zhengzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 周尧 (1998) 中国蝴蝶分类与鉴定 河南科学技术出版社, 郑州.] | |
| [9] | Dan ZC, Bao M, Ma CX, Li LL, Hao HW, Cheng F, Cai XZM, Chen ZN (2018) Community structure and butterfly diversity in different habitat types in the Qinghai Yushu Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 7557-7564. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 旦智措, 鲍敏, 马存新, 李雷雷, 郝会文, 成帆, 才项卓玛, 陈振宁 (2018) 青海玉树高原不同生境类型蝶类群落结构与多样性. 生态学报, 38, 7557-7564.] | |
| [10] |
Dejong R, Vane-Wright RI, Ackery PR (1996) The higher classification of butterflies (Lepidoptera): Problems and prospects. Entomologica Scandinavica, 27, 65-101.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Ding GF, Liu Y, Zeng AP, You LS (2011) Distribution and biogeographical research of butterfly resource in Hunan. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 17(2), 50-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 丁艮凤, 刘洋, 曾爱平, 游兰韶 (2011) 湖南省蝶类资源地理区划分析. 天津农业科学, 172, 50-53.] | |
| [12] |
Espeland M, Breinholt J, Willmott KR, Warren AD, Vila R, Toussaint EFA, Maunsell SC, Aduse-Poku K, Talavera G, Eastwood R, Jarzyna MA, Guralnick R, Lohman DJ, Pierce NE, Kawahara AY (2018) A comprehensive and dated phylogenomic analysis of butterflies. Current Biology, 28, 770-778.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
Fang LJ, Xu HG, Guan JL (2013) History and present status of butterfly monitoring in Europe and related development strategies for China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24, 2691-2698. (in Chinese with English abstract)
URL PMID |
|
[ 房丽君, 徐海根, 关建玲 (2013) 欧洲蝴蝶监测的历史、现状与我国的发展对策. 应用生态学报, 24, 2691-2698.]
PMID |
|
| [14] | Forister ML, McCall AC, Sanders NJ, Fordyce JA, Thorne JH, O’Brien J, Waetjen DP, Shapiro AM (2010) Compounded effects of climate change and habitat alteration shift patterns of butterfly diversity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 107, 2088-2092. |
| [15] |
Franzen M, Schrader J, Sjoberg G (2017) Butterfly diversity and seasonality of Ta Phin mountain area (N. Vietnam, Lao Cai, province). Journal of Insect Conservation, 21, 465-475.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Gao K, Fang LJ, Shang SQ, Zhang YL (2013) Butterfly diversity and faunal characteristics on the south slope of Taibai Mountain, Shaanxi Province of Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24, 1559-1564. (in Chinese with English abstract)
URL PMID |
|
[ 高可, 房丽君, 尚素琴, 张雅林 (2013) 陕西太白山南坡蝶类的多样性及区系特征. 应用生态学报, 24, 1559-1564.]
PMID |
|
| [17] |
Gezon ZJ, Lindborg RJ, Savage A, Daniels JC (2018) Drifting phenologies cause reduced seasonality of butterflies in response to increasing temperatures. Insects, 9(4), 174.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Glawion R (2002) Ecosystems and land use. Physical Geography of Germany, 62, 280-319. |
| [19] | Gu W, Ma L, Liu ZQ, Jiao Y, Wang LD, Zhang C, Sun H, Sun MO (2015) Diversity of butterflies in Liangshui Nature Reserve of Xiao Xing’an Mountains. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 7387-7396. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 顾伟, 马玲, 刘哲强, 焦玥, 王利东, 张琛, 孙虎, 孙美欧 (2015) 小兴安岭凉水自然保护区蝶类多样性. 生态学报, 35, 7387-7396.] | |
| [20] |
Hong XM, Ge XY, Li JL (2018) Butterfly diversity and its influencing factors in Saihanwula Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 26, 590-600. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 洪雪萌, 戈昕宇, 李俊兰 (2018) 赛罕乌拉自然保护区蝶类多样性及其影响因素. 生物多样性, 26, 590-600.] | |
| [21] | Hu BB, Li HH, Liang ZP, Zhao TJ, Ren XB (2010) Diversity and fauna of butterflies in Baxian Mountain State Nature Reserves. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 3226-3238. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡冰冰, 李后魂, 梁之聘, 赵铁建, 任秀柏 (2010) 八仙山自然保护区蝴蝶群落多样性及区系组成. 生态学报, 30, 3226-3238.] | |
| [22] |
Iserhard CA, Romanowski HP, Richter A, Mendonça MS (2017) Monitoring temporal variation to assess changes in the structure of subtropical atlantic forest butterfly communities. Environmental Entomology, 46, 804-813.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] |
Jia YZ, Zhao XH, Meng QF (2010) Effects of temperature and rainfall on composition and diversity of butterflies in broad-leaved and Korean pine mixed forests in the Changbai Mountains, China. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 16, 7-12.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Joubert DML, Pryke JS, Samways MJ (2019) Well-managed grassland heterogeneity promotes butterfly conservation in a corridor network. Journal of Environmental Management, 238, 382-395.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] |
Leingärtner A, Krauss J, Steffan-Dewenter I (2014) Species richness and trait composition of butterfly assemblages change along an altitudinal gradient. Oecologia, 175, 613-623.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | Li CX, Qiao LF, Zhang YC (2006) Characteristic of vegetation of Gaowangjie Nature Reserve in Hunan Province. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science, 34, 1656-1657. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李传霞, 乔丽芳, 张毅川 (2006) 湖南高望界自然保护区植被特点. 安徽农业科学, 34, 1656-1657.] | |
| [27] | Li JX, Dan XQ, Huang Y, Tan HF (2007) Study of vascular plants flora of Gaowangjie Nature Reserve in Hunan Province. Central South Forest Inventory and Planning, 26(4), 52-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李家湘, 但新球, 黄琰, 谭洪福 (2007) 湖南高望界自然保护区维管束植物区系研究. 中南林业调查规划, 264, 52-57.] | |
| [28] | Ma FZ, Xu HG, Chen MM, Tong WJ, Wang CB, Cai L (2018) Progress in construction of China Butterfly Diversity Observation Network (China BON-Butterflies). Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 34, 27-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马方舟, 徐海根, 陈萌萌, 童文君, 王晨彬, 蔡蕾 (2018) 全国蝴蝶多样性观测网络(China BON-Butterflies)建设进展. 生态与农村环境学报, 34, 27-36.] | |
| [29] | Ma KP, Liu CR, Liu YM (1995) Measurement of biotic community diversity. II. β diversity. Chinese Biodiversity, 3, 38-43. (in Chinese) |
| [ 马克平, 刘灿然, 刘玉明 (1995) 生物群落多样性的测度方法. II. β多样性的测度方法. 生物多样性, 3, 38-43.] | |
| [30] | Ma KP, Liu YM (1994) Measurement of biotic community diversity. I. α diversity (Part 2). Chinese Biodiversity, 2, 231-239. (in Chinese) |
| [ 马克平, 刘玉明 (1994) 生物群落多样性的测度方法. I. α多样性的测度方法(下). 生物多样性, 2, 231-239.] | |
| [31] | Ma RL, Ma X, Yang Z, Ma ZX (2012) Community characteristics of butterflies in the Gansu Taitong-Kongtongshan National Nature Reserve. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 49, 1010-1024. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马瑞林, 马雄, 杨镇, 马正学 (2012) 甘肃太统-崆峒山国家自然保护区的蝶类群落特征. 应用昆虫学报, 49, 1010-1024.] | |
| [32] | Mei J, Ran H, Yang TY, Xu QZ (2015) Species diversity of butterflies in Fanjing Mountain National Nature Reserve of Guizhou. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34, 504-509. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 梅杰, 冉辉, 杨天友, 许勤智 (2015) 贵州梵净山国家级自然保护区蝴蝶多样性. 生态学杂志, 34, 504-509.] | |
| [33] |
Pimm SL, Russell GJ, Gittleman JL, Brooks TM (1995) The future of biodiversity. Science, 269, 347-350.
DOI URL PMID |
| [34] |
Rajagopal T, Sekar M, Manimozhi A, Baskar N, Archunan G (2011) Diversity and community structure of butterfly of Arignar Anna Zoological Park, Chennai, Tamil Nadu. Journal of Environmental Biology, 32, 201-207.
URL PMID |
| [35] | Roy DB, Rothery P, Moss D, Pollard E, Thomas JA (2001) Butterfly numbers and weather: Predicting historical trends in abundance and the future effects of climate change. Journal of Animal Ecology, 70, 201-217. |
| [36] |
Rusman R, Atmowidi T, Peggie D (2016) Butterflies (Lepidoptera: Papilionoidea) of Mount Sago, West Sumatra: Diversity and flower preference. Hayati Journal of Biosciences, 23, 132-137.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Shang SQ, Zhang HY, Tian FB, Ru Y, Zhou HL (2017) Diversity of butterfly fauna in Xinglongshan National Nature Reserve of Gansu Province. Pratacultural Science, 34, 1314-1322. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 尚素琴, 张红勇, 田赋斌, 汝阳, 周惠丽 (2017) 甘肃省兴隆山国家级自然保护区蝶类区系组成与多样性. 草业科学, 34, 1314-1322.] | |
| [38] |
Sing KW, Dong H, Wang WZ, Wilson JJ (2016) Can butterflies cope with city life? Butterfly diversity in a young megacity in southern China. Genome, 59, 751-761.
DOI URL PMID |
| [39] |
Thomas JA (2005) Monitoring change in the abundance and distribution of insects using butterflies and other indicator groups. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 360, 339-357.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Weibull AC, Bengtsson J, Nohlgren E (2000) Diversity of butterflies in the agricultural landscape: The role of farming system and landscape heterogeneity. Ecography, 23, 743-750.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Wepprich T, Adrion JR, Ries L, Wiedmann J, Haddad NM (2019) Butterfly abundance declines over 20 years of systematic monitoring in Ohio, USA. PLoS ONE, 14, e0216270.
DOI URL PMID |
| [42] |
Whitworth A, Villacampa J, Brown A, Huarcaya RP, Downie R, MacLeod R (2016) Past human disturbance effects upon biodiversity are greatest in the canopy: A case study on rainforest butterflies. PLoS ONE, 11, e0150520.
DOI URL PMID |
| [43] | Wu CS, Xu YF (2017) Butterflies of China. The Straits Publishing & Distributing Group, Fuzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 武春生, 徐堉峰 (2017) 中国蝴蝶图鉴 海峡出版发行集团, 福州.] | |
| [44] | Wu YH, Gu CB, Li WB, Liu NY, Han DM, Fang J (2016) The influence of urbanization on butterfly diversity in Hefei, Anhui Province. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35, 992-996. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴云鹤, 顾成波, 李文博, 刘乃一, 韩德民, 方杰 (2016) 城市化对合肥蝶类多样性的影响. 生态学杂志, 35, 992-996.] | |
| [45] |
Xu HG, Cao MC, Wu Y, Cai L, Cao Y, Ding H, Cui P, Wu J, Wang Z, Le ZF, Lu XQ, Liu L, Li JQ (2017) Optimized monitoring sites for detection of biodiversity trends in China. Biodiversity and Conservation, 26, 1959-1971.
DOI URL |
| [46] | Xu HG, Ding H, Ouyang ZY, Zhang WG, Cui P, Xu WH, Liu L, Wu J, Lu XQ, Cao MC, Chen L, Le ZF, Wu Y, Lei JC (2016) Assessing China’s progress toward the 2020 Global Biodiversity Targets. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 3847-3858. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐海根, 丁晖, 欧阳志云, 张文国, 崔鹏, 徐卫华, 刘立, 吴军, 卢晓强, 曹铭昌, 陈炼, 乐志芳, 吴翼, 雷军成 (2016) 中国实施2020年全球生物多样性目标的进展. 生态学报, 36, 3847-3858.] | |
| [47] |
Zhang CS, Settele JF, Sun WH, Wiemers M, Zhang YL, Schweiger O (2019) Resource availability drives trait composition of butterfly assemblages. Oecologia, 190, 913-926.
DOI URL PMID |
| [48] | Zhang LW, Zhang HY (2016) Research progress in butterfly as indicators for habitat change. Journal of Biology, 33(3), 88-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张立微, 张红玉 (2016) 蝶类对生境的指示作用研究进展. 生物学杂志, 333, 88-91.] | |
| [49] | Zhang SM, Zhao YX (1996) Geographical Distribution of Agricultural and Forestry Insects in China. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 章士美, 赵泳祥 (1996) 中国农林昆虫地理分布 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [50] | Zhang YJ, Fang LJ (2011) Butterfly diversity in relation to topography: A case study of Dayu Basin. Shaanxi Forest Science and Technology, ( 3), 6-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张宇军, 房丽君 (2011) 蝴蝶多样性与地形相关性研究——以大峪流域为例. 陕西林业科技, ( 3), 6-9.] | |
| [51] | Zhang YX, Yan ZJ, Liu ZX (2011) Faunal characteristics of butterflies in Xiaoxi National Nature Reserve of Hunan, China. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 33, 74-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张佑祥, 阎中军, 刘志霄 (2011) 湖南小溪国家级自然保护区蝶类资源及其区系特征. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 33, 74-79.] | |
| [52] | Zhang ZL, Long JM (2017) Preliminary study on the distribution of Bretschneidera sinensis populations in the Gaowangjie National Nature Reserve of Hunan. Hunan Forestry Science & Technology, 44(5), 88-93. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张自亮, 龙菊美 (2017) 湖南高望界国家级自然保护区钟萼木种群分布原因初探. 湖南林业科技, 445, 88-93.] | |
| [53] | Zhou LY (2019) Study on Effects of Anthropogenic Disturbance on Community Characteristics in Pollinators. PhD dissertation, Henan University, Kaifeng. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 周立垚 (2019) 人为干扰对传粉昆虫群落特征影响研究. 博士学位论文, 河南大学, 开封.] |
| [1] | 刘咏华, 童光蓉, 余航远, 王宁宁, 任海保, 陈磊, 马克平, 米湘成. 钱江源-百山祖国家公园候选区钱江源园区冠层三维结构及光谱特征对人为干扰的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24174-. |
| [2] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [3] | 仝淼, 王欢, 张文双, 王超, 宋建潇. 重金属污染土壤中细菌抗生素抗性基因分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [4] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [5] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [6] | 时永强, 栾青杉, 单秀娟, 韦超, 赵永松, 孙策策, 金显仕. 长岛南部海域浮游动物多样性周年变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [7] | 倪艳梅, 陈莉, 董志远, 孙德斌, 李宝泉, 王绪敏, 陈琳琳. 黄河三角洲湿地生态修复区大型底栖动物群落结构与生态健康评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [8] | 魏嘉欣, 姜治国, 杨林森, 熊欢欢, 金胶胶, 罗方林, 李杰华, 吴浩, 徐耀粘, 乔秀娟, 魏新增, 姚辉, 余辉亮, 杨敬元, 江明喜. 湖北神农架中亚热带山地落叶阔叶林25 ha动态监测样地群落物种组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [9] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [10] | 吴芳芳, 刘娜, 何春梅, 原作强, 郝占庆, 尹秋龙. 秦岭山地木本植物群落结构及多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [11] | 单航, 雷祖培, 郑方东, 韦博良, 仲磊, 于明坚. 2013-2023年浙江乌岩岭次生常绿阔叶林群落动态变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24372-. |
| [12] | 冯嘉谊, 练琚愉, 冯瑜莙, 张东旭, 曹洪麟, 叶万辉. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林群落垂直分层对群落结构及功能的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| [13] | 王兴煜, 孟京辉, 任思远, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林群落生物多样性与地上生物量的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24230-. |
| [14] | 杜晴晴, 任思远, Nicole Tsz Shun Yuan, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林幼树及成树生产力的影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24284-. |
| [15] | 黄骏涵, 余梵冬, 王裕祥, 黄哲, 张铭斯, 房苗, 舒璐, 徐猛, 韦慧, 汪学杰, 顾党恩, 罗思. 花地河中下游外来鱼类入侵现状及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24249-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()