



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (12): 24372. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024372 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024372
单航1, 雷祖培2, 郑方东2, 韦博良1,2, 仲磊1,2, 于明坚1,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2024-08-18
接受日期:2024-12-11
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2025-01-09
通讯作者:
E-mail: 基金资助:
Hang Shan1, Zupei Lei2, Fangdong Zheng2, Boliang Wei1,2, Lei Zhong1,2, Mingjian Yu1,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-08-18
Accepted:2024-12-11
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2025-01-09
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:摘要: 研究次生常绿阔叶林的动态变化对于理解常绿阔叶林群落的形成和维持具有重要意义。本研究分别于2013年、2018年和2023年对浙江省乌岩岭9 ha亚热带次生常绿阔叶林动态监测样地中胸径(DBH) ≥ 1 cm的木本植物个体进行了3次调查, 以研究次生常绿阔叶林群落动态变化规律。结果表明: (1) 10年间样地内重要值排名前10位的物种未发生变化, 但植物群落的物种多样性和多度显著下降, 个别稀有种消失。(2)小径级个体的比例逐渐减少, 中径级和大径级个体的比例逐渐增加; 不同叶生活型和地形生境中植物个体的比例基本保持稳定。(3)植物的死亡率随着径级的增加而降低, 且在不同地形生境间存在差异。(4)与2013-2018年相比, 2018-2023年植物的死亡率整体有所下降, 植物的补员率急剧下降。以上结果表明优势种对资源的竞争优势促进了乌岩岭次生常绿阔叶林群落的动态变化。本研究结果为次生常绿阔叶林的生态恢复和生物多样性保护策略提供了重要的科学依据。
单航, 雷祖培, 郑方东, 韦博良, 仲磊, 于明坚 (2024) 2013-2023年浙江乌岩岭次生常绿阔叶林群落动态变化. 生物多样性, 32, 24372. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024372.
Hang Shan, Zupei Lei, Fangdong Zheng, Boliang Wei, Lei Zhong, Mingjian Yu (2024) Dynamic changes in the community of a secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest in Wuyanling, Zhejiang Province from 2013 to 2023. Biodiversity Science, 32, 24372. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024372.
| 物种 Species | 生长型 Growth form | 多度 Abundance | 重要值 IV (%) | 重要值排序 Order of IV | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 2018 | 2023 | 2013 | 2018 | 2023 | 2013 | 2018 | 2023 | ||
| 甜槠 Castanopsis eyrei | 乔木 Tree | 1,958 | 1,469 | 1,131 | 6.99 | 6.46 | 5.82 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 褐叶青冈 Cyclobalanopsis stewardiana | 乔木 Tree | 2,557 | 2,272 | 1,986 | 5.73 | 5.76 | 5.76 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 鹿角杜鹃 Rhododendron latoucheae | 小乔木 Small tree | 7,077 | 6,476 | 5,947 | 5.10 | 5.30 | 5.42 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 木荷 Schima superba | 乔木 Tree | 1,786 | 1,557 | 1,450 | 4.89 | 5.07 | 5.28 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 窄基红褐柃 Eurya rubiginosa var. attenuata | 灌木 Shrub | 6,760 | 6,143 | 5,736 | 3.97 | 4.13 | 4.25 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 浙江新木姜子 Neolitsea aurata var. chekiangensis | 小乔木 Small tree | 3,493 | 3,272 | 3,139 | 3.05 | 3.29 | 3.46 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 马银花 Rhododendron ovatum | 小乔木 Small tree | 4,010 | 3,800 | 3,567 | 3.00 | 3.24 | 3.36 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| 尖连蕊茶 Camellia cuspidata | 灌木 Shrub | 4,236 | 4,146 | 3,979 | 2.86 | 3.17 | 3.34 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| 短尾柯 Lithocarpus brevicaudatus | 乔木 Tree | 772 | 683 | 606 | 2.68 | 2.73 | 2.68 | 9 | 10 | 10 |
| 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 乔木 Tree | 1,814 | 1,675 | 1,589 | 2.65 | 2.74 | 2.85 | 10 | 9 | 9 |
表1 2013-2023年乌岩岭9 ha森林动态监测样地重要值前10位物种
Table 1 Top 10 species based on importance value (IV) in the 9 ha Wuyanling forest dynamics plot (2013-2023)
| 物种 Species | 生长型 Growth form | 多度 Abundance | 重要值 IV (%) | 重要值排序 Order of IV | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 2018 | 2023 | 2013 | 2018 | 2023 | 2013 | 2018 | 2023 | ||
| 甜槠 Castanopsis eyrei | 乔木 Tree | 1,958 | 1,469 | 1,131 | 6.99 | 6.46 | 5.82 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 褐叶青冈 Cyclobalanopsis stewardiana | 乔木 Tree | 2,557 | 2,272 | 1,986 | 5.73 | 5.76 | 5.76 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 鹿角杜鹃 Rhododendron latoucheae | 小乔木 Small tree | 7,077 | 6,476 | 5,947 | 5.10 | 5.30 | 5.42 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 木荷 Schima superba | 乔木 Tree | 1,786 | 1,557 | 1,450 | 4.89 | 5.07 | 5.28 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 窄基红褐柃 Eurya rubiginosa var. attenuata | 灌木 Shrub | 6,760 | 6,143 | 5,736 | 3.97 | 4.13 | 4.25 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 浙江新木姜子 Neolitsea aurata var. chekiangensis | 小乔木 Small tree | 3,493 | 3,272 | 3,139 | 3.05 | 3.29 | 3.46 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 马银花 Rhododendron ovatum | 小乔木 Small tree | 4,010 | 3,800 | 3,567 | 3.00 | 3.24 | 3.36 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| 尖连蕊茶 Camellia cuspidata | 灌木 Shrub | 4,236 | 4,146 | 3,979 | 2.86 | 3.17 | 3.34 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| 短尾柯 Lithocarpus brevicaudatus | 乔木 Tree | 772 | 683 | 606 | 2.68 | 2.73 | 2.68 | 9 | 10 | 10 |
| 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 乔木 Tree | 1,814 | 1,675 | 1,589 | 2.65 | 2.74 | 2.85 | 10 | 9 | 9 |
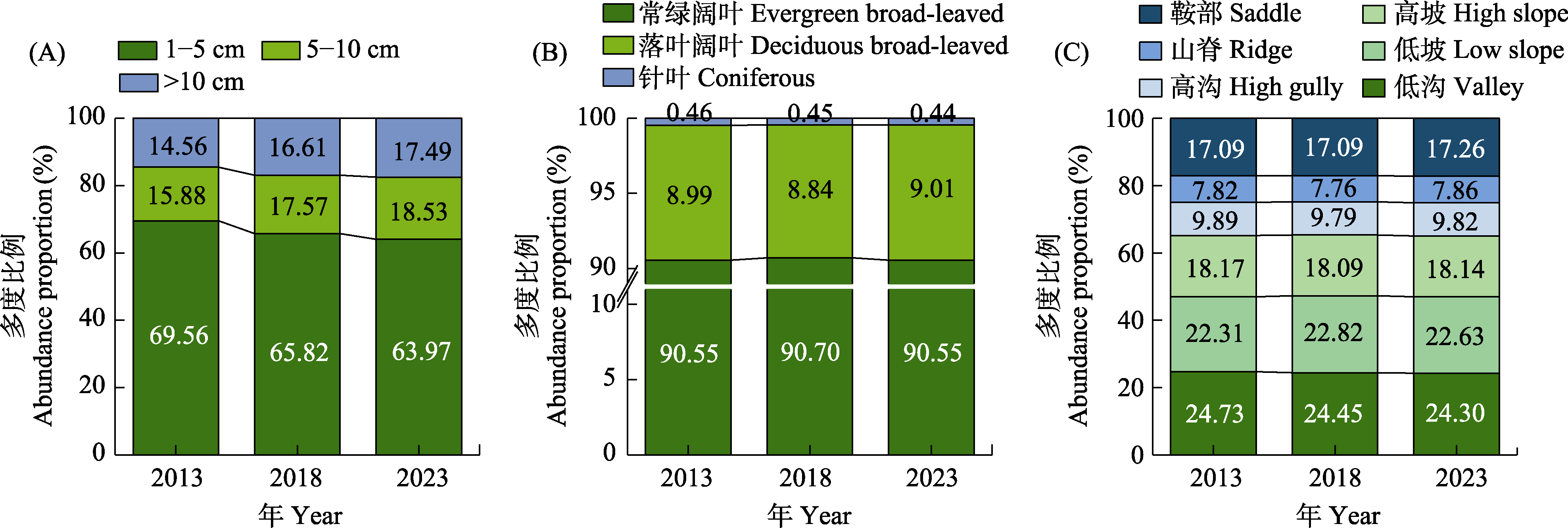
图2 2013年、2018年和2023年不同径级、不同叶生活型和不同地形生境树木的多度比例
Fig. 2 Abundance proportion of trees in different size classes, leaf life forms, and topographic habitat types in 2013, 2018, and 2023
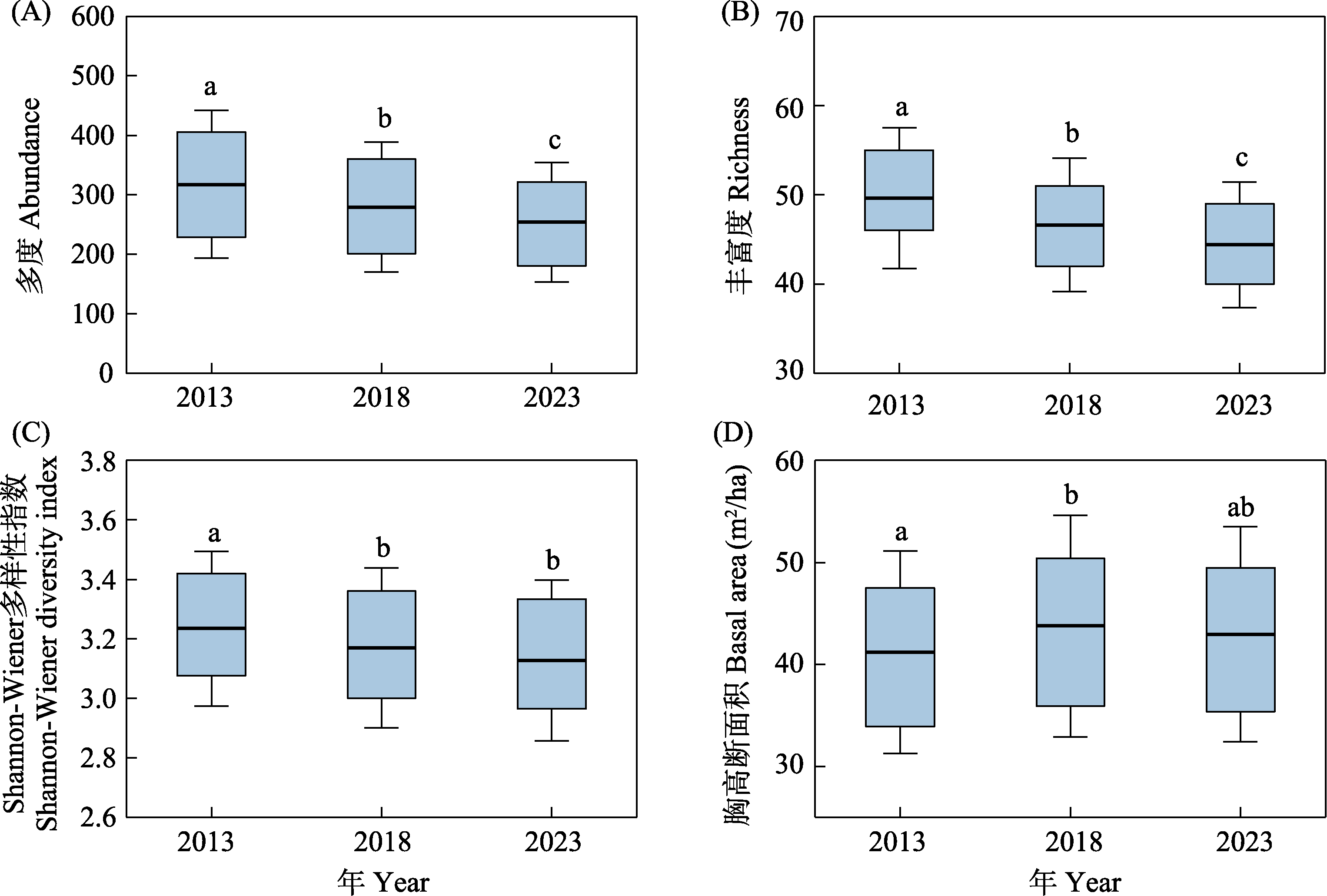
图3 2013年、2018年和2023年群落的多度(A)、丰富度(B)、Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(C)及胸高断面积(D)的比较。箱体代表四分位距, 箱子内的水平线表示均值, 箱形上下方横线分别为上下四分位数加减标准差(SD)。不同字母表示组间差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 3 Comparison of abundance (A), richness (B), Shannon-Wiener diversity index (C), and basal area of communities (D) in 2013, 2018, and 2023. The box represents the quartile range, the horizontal line inside the box represents the mean, and the upper and lower edges represent the upper and lower quartiles plus or minus the standard deviation (SD), respectively. Different letters indicate significant difference (P < 0.05).
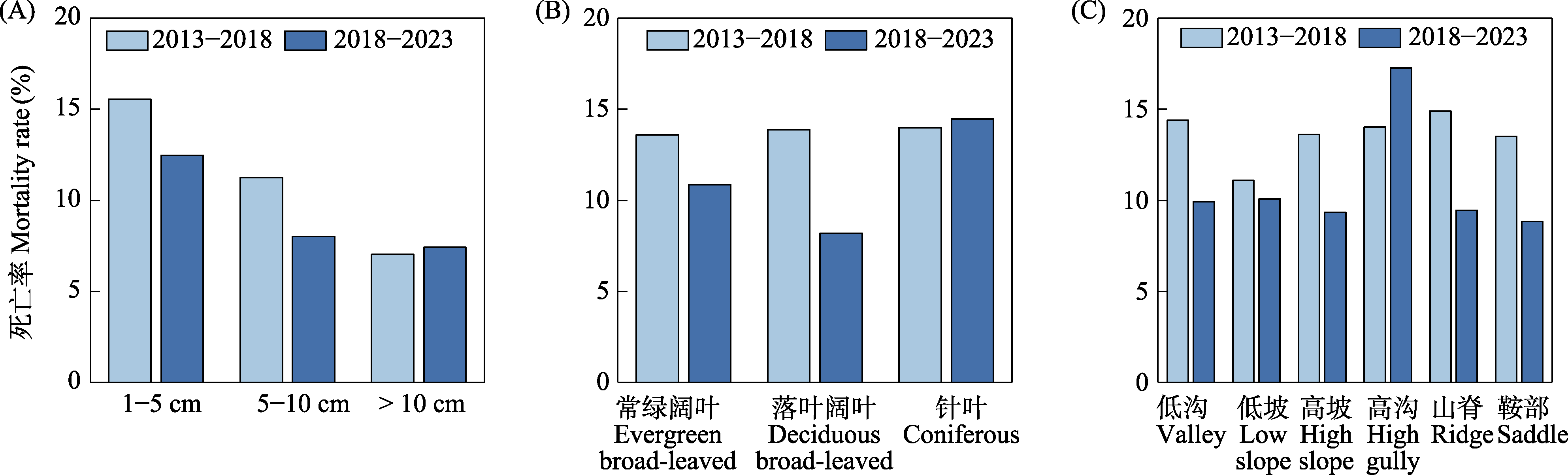
图4 2013年、2018年和2023年不同径级(A)、不同叶生活型(B)和不同地形生境(C)下树木的死亡率
Fig. 4 Mortality rates of trees in different size classes (A), leaf life forms (B), and topographic habitat types (C) in 2013, 2018, and 2023
| 影响因素 Influence factors | β | 标准误 SE | Wald | P | 优势比 Odds ratio | 95%置信区间 95% confidence interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地形生境 Topographic habitat types | ||||||
| 低沟 Valley | 1.000 | |||||
| 低坡 Low slope | 0.105 | 0.034 | 9.444 | 0.002 | 1.111 | 1.039-1.188 |
| 高坡 High slope | -0.085 | 0.036 | 5.547 | 0.019 | 0.918 | 0.856-0.986 |
| 高沟 High gully | 0.023 | 0.037 | 0.379 | 0.538 | 1.023 | 0.952-1.100 |
| 山脊 Ridge | 0.094 | 0.044 | 4.650 | 0.031 | 1.099 | 1.009-1.197 |
| 鞍部 Saddle | 0.155 | 0.046 | 11.186 | 0.001 | 1.167 | 1.066-1.278 |
| 叶生活型 Leaf life forms | ||||||
| 常绿阔叶 Evergreen broad-leaved | 1.000 | |||||
| 落叶阔叶 Deciduous broad-leaved | -0.095 | 0.161 | 0.350 | 0.554 | 0.909 | 0.663-1.247 |
| 针叶 Coniferous | 0.094 | 0.165 | 0.327 | 0.567 | 1.099 | 0.795-1.518 |
| 径级 Size classes | ||||||
| 1-5 cm | 1.000 | |||||
| 5-10 cm | 0.919 | 0.041 | 507.650 | 0.000 | 2.506 | 2.314-2.715 |
| > 10 cm | 0.529 | 0.049 | 118.365 | 0.000 | 1.697 | 1.543-1.867 |
| 常量 Constant | -2.562 | 0.167 | 235.878 | 0.000 | 0.077 | - |
表2 2013-2018年间乌岩岭9 ha森林动态监测样地树木死亡的多因素二元Logistic回归分析
Table 2 Multivariate binary Logistic regression analysis of tree mortality in the 9 ha Wuyanling forest dynamics plot from 2013 to 2018
| 影响因素 Influence factors | β | 标准误 SE | Wald | P | 优势比 Odds ratio | 95%置信区间 95% confidence interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地形生境 Topographic habitat types | ||||||
| 低沟 Valley | 1.000 | |||||
| 低坡 Low slope | 0.105 | 0.034 | 9.444 | 0.002 | 1.111 | 1.039-1.188 |
| 高坡 High slope | -0.085 | 0.036 | 5.547 | 0.019 | 0.918 | 0.856-0.986 |
| 高沟 High gully | 0.023 | 0.037 | 0.379 | 0.538 | 1.023 | 0.952-1.100 |
| 山脊 Ridge | 0.094 | 0.044 | 4.650 | 0.031 | 1.099 | 1.009-1.197 |
| 鞍部 Saddle | 0.155 | 0.046 | 11.186 | 0.001 | 1.167 | 1.066-1.278 |
| 叶生活型 Leaf life forms | ||||||
| 常绿阔叶 Evergreen broad-leaved | 1.000 | |||||
| 落叶阔叶 Deciduous broad-leaved | -0.095 | 0.161 | 0.350 | 0.554 | 0.909 | 0.663-1.247 |
| 针叶 Coniferous | 0.094 | 0.165 | 0.327 | 0.567 | 1.099 | 0.795-1.518 |
| 径级 Size classes | ||||||
| 1-5 cm | 1.000 | |||||
| 5-10 cm | 0.919 | 0.041 | 507.650 | 0.000 | 2.506 | 2.314-2.715 |
| > 10 cm | 0.529 | 0.049 | 118.365 | 0.000 | 1.697 | 1.543-1.867 |
| 常量 Constant | -2.562 | 0.167 | 235.878 | 0.000 | 0.077 | - |
| 影响因素 Influence factors | β | 标准误 SE | Wald | P | 优势比 Odds ratio | 95%置信区间 95% confidence interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地形生境 Topographic habitat types | ||||||
| 低沟 Valley | 1.000 | |||||
| 低坡 Low slope | 0.136 | 0.044 | 9.613 | 0.002 | 1.145 | 1.051-1.248 |
| 高坡 High slope | 0.167 | 0.044 | 14.306 | 0.000 | 1.182 | 1.084-1.289 |
| 高沟 High gully | 0.074 | 0.047 | 2.440 | 0.118 | 1.076 | 0.981-1.181 |
| 山脊 Ridge | 0.112 | 0.056 | 4.050 | 0.044 | 1.118 | 1.003-1.247 |
| 鞍部 Saddle | 0.102 | 0.060 | 2.868 | 0.090 | 1.107 | 0.984-1.245 |
| 叶生活型 Leaf life forms | ||||||
| 常绿阔叶 Evergreen broad-leaved | 1.000 | |||||
| 落叶阔叶 Deciduous broad-leaved | -0.344 | 0.180 | 3.634 | 0.057 | 0.709 | 0.498-1.010 |
| 针叶 Coniferous | -0.505 | 0.187 | 7.323 | 0.007 | 0.603 | 0.418-0.870 |
| 径级 Size classes | ||||||
| 1-5 cm | 1.000 | |||||
| 5-10 cm | 0.448 | 0.042 | 114.210 | 0.000 | 1.565 | 1.442-1.699 |
| > 10 cm | 0.081 | 0.052 | 2.384 | 0.123 | 1.084 | 0.978-1.202 |
| 常量 Constant | -2.313 | 0.186 | 155.001 | 0.000 | 0.099 | - |
表3 2018-2023年间乌岩岭9 ha森林动态监测样地树木死亡的多因素二元Logistic回归分析
Table 3 Multivariate binary Logistic regression analysis of tree mortality in the 9 ha Wuyanling forest dynamics plot from 2018 to 2023
| 影响因素 Influence factors | β | 标准误 SE | Wald | P | 优势比 Odds ratio | 95%置信区间 95% confidence interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地形生境 Topographic habitat types | ||||||
| 低沟 Valley | 1.000 | |||||
| 低坡 Low slope | 0.136 | 0.044 | 9.613 | 0.002 | 1.145 | 1.051-1.248 |
| 高坡 High slope | 0.167 | 0.044 | 14.306 | 0.000 | 1.182 | 1.084-1.289 |
| 高沟 High gully | 0.074 | 0.047 | 2.440 | 0.118 | 1.076 | 0.981-1.181 |
| 山脊 Ridge | 0.112 | 0.056 | 4.050 | 0.044 | 1.118 | 1.003-1.247 |
| 鞍部 Saddle | 0.102 | 0.060 | 2.868 | 0.090 | 1.107 | 0.984-1.245 |
| 叶生活型 Leaf life forms | ||||||
| 常绿阔叶 Evergreen broad-leaved | 1.000 | |||||
| 落叶阔叶 Deciduous broad-leaved | -0.344 | 0.180 | 3.634 | 0.057 | 0.709 | 0.498-1.010 |
| 针叶 Coniferous | -0.505 | 0.187 | 7.323 | 0.007 | 0.603 | 0.418-0.870 |
| 径级 Size classes | ||||||
| 1-5 cm | 1.000 | |||||
| 5-10 cm | 0.448 | 0.042 | 114.210 | 0.000 | 1.565 | 1.442-1.699 |
| > 10 cm | 0.081 | 0.052 | 2.384 | 0.123 | 1.084 | 0.978-1.202 |
| 常量 Constant | -2.313 | 0.186 | 155.001 | 0.000 | 0.099 | - |
| 类别 Category | 补员数量 Recruitment number | 补员率 Recruitment rate (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013-2018 | 2018-2023 | 2013-2018 | 2018-2023 | ||
| 整体 Total | 1,122 | 343 | 1.57 | 0.55 | |
| 叶生活型 Leaf life forms | 常绿阔叶 Evergreen broad-leaved | 1,094 | 328 | 1.69 | 0.58 |
| 落叶阔叶 Deciduous broad-leaved | 26 | 12 | 0.40 | 0.22 | |
| 针叶 Coniferous | 2 | 3 | 0.61 | 1.05 | |
| 地形生境 Topographic habitat types | 低沟 Valley | 259 | 49 | 1.47 | 0.32 |
| 低坡 Low slope | 334 | 42 | 2.10 | 0.29 | |
| 高坡 High slope | 153 | 59 | 1.18 | 0.52 | |
| 高沟 High gully | 80 | 44 | 1.13 | 0.71 | |
| 山脊 Ridge | 120 | 75 | 2.15 | 1.54 | |
| 鞍部 Saddle | 176 | 74 | 1.44 | 0.69 | |
表4 乌岩岭9 ha森林动态监测样地的补员数量和补员率
Table 4 The number and rate of recruitment in the 9 ha Wuyanling forest dynamics plot
| 类别 Category | 补员数量 Recruitment number | 补员率 Recruitment rate (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013-2018 | 2018-2023 | 2013-2018 | 2018-2023 | ||
| 整体 Total | 1,122 | 343 | 1.57 | 0.55 | |
| 叶生活型 Leaf life forms | 常绿阔叶 Evergreen broad-leaved | 1,094 | 328 | 1.69 | 0.58 |
| 落叶阔叶 Deciduous broad-leaved | 26 | 12 | 0.40 | 0.22 | |
| 针叶 Coniferous | 2 | 3 | 0.61 | 1.05 | |
| 地形生境 Topographic habitat types | 低沟 Valley | 259 | 49 | 1.47 | 0.32 |
| 低坡 Low slope | 334 | 42 | 2.10 | 0.29 | |
| 高坡 High slope | 153 | 59 | 1.18 | 0.52 | |
| 高沟 High gully | 80 | 44 | 1.13 | 0.71 | |
| 山脊 Ridge | 120 | 75 | 2.15 | 1.54 | |
| 鞍部 Saddle | 176 | 74 | 1.44 | 0.69 | |
| [1] | Case MJ, Johnson BG, Bartowitz KJ, Hudiburg TW (2021) Forests of the future: Climate change impacts and implications for carbon storage in the Pacific Northwest, USA. Forest Ecology and Management, 482, 118886. |
| [2] | Chen XR, Chen YY, Luo ZR, Ding BY (2013) A 5-year mid-mountain subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest study in Baishanzu, East China. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 30, 821-829. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈小荣, 陈圆圆, 骆争荣, 丁炳扬 (2013) 百山祖中山中亚热带常绿阔叶林群落5年动态特征. 浙江农林大学学报, 30, 821-829.] | |
| [3] | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and a Comparison with Other Plots. Springer, Berlin. |
| [4] | Condit R, Pérez R, Lao S, Aguilar S, Hubbell SP (2017) Demographic trends and climate over 35 years in the Barro Colorado 50 ha plot. Forest Ecosystems, 4, 17. |
| [5] |
Gazol A, Camarero JJ, Sangüesa-Barreda G, Vicente-Serrano SM (2018) Post-drought resilience after forest die-off: Shifts in regeneration, composition, growth and productivity. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9, 1546.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Harms KE, Condit R, Hubbell SP, Foster RB (2001) Habitat associations of trees and shrubs in a 50-ha neotropical forest plot. Journal of Ecology, 89, 947-959. |
| [7] | He H, Pan YZ, Zhu WQ, Liu XL, Zhang Q, Zhu XF (2005) Measurement of terrestrial ecosystem service value in China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 16, 1122-1127. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [何浩, 潘耀忠, 朱文泉, 刘旭拢, 张晴, 朱秀芳 (2005) 中国陆地生态系统服务价值测量. 应用生态学报, 16, 1122-1127.] | |
| [8] | Jin Y, Chen JH, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP, Yu MJ (2015) Impacts of the 2008 ice storm on structure and composition of an evergreen broad-leaved forest community in eastern China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 610-618. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[金毅, 陈建华, 米湘成, 任海保, 马克平, 于明坚 (2015) 古田山24 ha森林动态监测样地常绿阔叶林群落结构和组成动态: 探讨2008年冰雪灾害的影响. 生物多样性, 23, 610-618.]
DOI |
|
| [9] | King DA, Davies SJ, Noor NSM (2006) Growth and mortality are related to adult tree size in a Malaysian mixed dipterocarp forest. Forest Ecology and Management, 223, 152-158. |
| [10] | Kubota Y, Katsuda K, Kikuzawa K (2005) Secondary succession and effects of clear-logging on diversity in the subtropical forests on Okinawa Island, southern Japan. Biodiversity and Conservation, 14, 879-901. |
| [11] | Li YY, Shao MA (2004) The change of plant diversity during natural recovery process of vegetation in Ziwuling area. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24, 252-260. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李裕元, 邵明安 (2004) 子午岭植被自然恢复过程中植物多样性的变化. 生态学报, 24, 252-260.] | |
| [12] | Linares-Palomino R, Alvarez SIP (2005) Tree community patterns in seasonally dry tropical forests in the Cerros de Amotape Cordillera, Tumbes, Peru. Forest Ecology and Management, 209, 261-272. |
| [13] | Liu M, Pietzarka U, Roloff A, Zhang DS (2023) Assessment on the growth sensitivity to drought stress for various tree species growing at diverse habitats—A case study in Saxony, Germany. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 59(11), 12-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘鸣, 乌尔里希·皮特扎卡, 安德烈亚斯·罗洛夫, 张德顺 (2023) 不同生境中多树种生长对干旱胁迫的敏感性评价——以德国萨克森州为例. 林业科学, 59(11), 12-22.] | |
| [14] | Lou MQ, Yin PZ (1987) Relationship between forest vegetation and soil fertility in Wuyanling Nature Reserve, Zhejiang Province, East China. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 18(3), 115-117. (in Chinese) |
| [楼曼青, 殷佩章 (1987) 乌岩岭自然保护区的森林植被与土壤肥力关系. 土壤通报, 18(3), 115-117.] | |
| [15] | Luo Y, Chen HYH (2011) Competition, species interaction and ageing control tree mortality in boreal forests. Journal of Ecology, 99, 1470-1480. |
| [16] |
Ma L, Lian JY, Lin GJ, Cao HL, Huang ZL, Guan DS (2016) Forest dynamics and its driving forces of sub-tropical forest in South China. Scientific Reports, 6, 22561.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Rüger N, Comita LS, Condit R, Purves D, Rosenbaum B, Visser MD, Wright SJ, Wirth C (2018) Beyond the fast-slow continuum: Demographic dimensions structuring a tropical tree community. Ecology Letters, 21, 1075-1084.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Saatchi SS, Houghton RA, Dos Santos Alvalá RC, Soares JV, Yu Y (2007) Distribution of aboveground live biomass in the Amazon basin. Global Change Biology, 13, 816-837. |
| [19] | Seidl R, Turner MG (2022) Post-disturbance reorganization of forest ecosystems in a changing world. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 119, e2202190119. |
| [20] |
Shan WQ, Fang S, Yin J, Ren J, Lin F, Mao ZK, Hao ZQ, Wang XG (2024) Population dynamics and its relationship with functional traits in different succession stages of temperate mixed coniferous broad-leaved forest in Northeast China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 35, 2501-2510. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[单伟强, 房帅, 尹进, 任静, 蔺菲, 毛子昆, 郝占庆, 王绪高 (2024) 东北温带针阔混交林不同演替阶段树木种群动态及其与功能性状的关系. 应用生态学报, 35, 2501-2510.]
DOI |
|
| [21] | Shang KK, Zhang QP, Da LJ, Hara K, Yang YC, Fujihara M, Tomita M, Zhao Y (2014) Effects of natural and artificial disturbance on landscape and forest structure in Tiantong National Forest Park, East China. Landscape and Ecological Engineering, 10, 163-172. |
| [22] | Shannon CE (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. Bell System Technical Journal, 27, 379-423. |
| [23] | Shovon TA, Auge H, Haase J, Nock CA (2024) Positive effects of tree species diversity on productivity switch to negative after severe drought mortality in a temperate forest experiment. Global Change Biology, 30, e17252. |
| [24] | Valencia R, Foster RB, Villa G, Condit R, Svenning JC, Hernández C, Romoleroux K, Losos E, Magård E, Balslev H (2004) Tree species distributions and local habitat variation in the Amazon: Large forest plot in eastern Ecuador. Journal of Ecology, 92, 214-229. |
| [25] | Wang XH, Kent M, Fang XF (2007) Evergreen broad-leaved forest in Eastern China: Its ecology and conservation and the importance of resprouting in forest restoration. Forest Ecology and Management, 245, 76-87. |
| [26] | Wang YH, Mi XC, Chen SW, Li MH, Yu MJ (2011) Regeneration dynamics of major tree species during 2002-2007 in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest in Gutianshan National Nature Reserve in East China. Biodiversity Science, 19, 178-189. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[汪殷华, 米湘成, 陈声文, 李铭红, 于明坚 (2011) 古田山常绿阔叶林主要树种2002-2007年间更新动态. 生物多样性, 19, 178-189.]
DOI |
|
| [27] | Wei BL, Zhong L, Liu JL, Zheng FD, Jin Y, Xie YC, Lei ZP, Shen GC, Yu MJ (2022) Differences in density dependence among tree mycorrhizal types affect tree species diversity and relative growth rates. Plants, 11, 2340. |
| [28] | Wei JX, Jiang ZG, Yang LS, Xiong HH, Jin JJ, Luo FL, Li JH, Wu H, Xu YZ, Qiao XJ, Wei XZ, Yao H, Yu HL, Yang JY, Jiang MX (2024) Community composition and structure in a 25 ha mid-subtropical mountain deciduous broad-leaved forest dynamics plot in Shennongjia, Hubei, China. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23338. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [魏嘉欣, 姜治国, 杨林森, 熊欢欢, 金胶胶, 罗方林, 李杰华, 吴浩, 徐耀粘, 乔秀娟, 魏新增, 姚辉, 余辉亮, 杨敬元, 江明喜 (2024) 湖北神农架中亚热带山地落叶阔叶林25 ha动态监测样地群落物种组成与结构特征. 生物多样性, 32, 23338.] | |
| [29] | Wu ZH, Wang Z, Luan FC, Shu ZF, Li BH (2021) Community composition and floral characteristics of the Chebaling 20 hm2 forest dynamic plot in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest. Forestry and Environmental Science, 37(3), 86-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴智宏, 王梓, 栾福臣, 束祖飞, 李步杭 (2021) 车八岭20 hm2中亚热带常绿阔叶林监测样地群落物种组成和区系特征. 林业与环境科学, 37(3), 86-91.] | |
| [30] | Wu ZY (1980) Vegetation of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [吴征镒 (1980) 中国植被. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [31] |
Xu GX, Shi ZM, Tang JC, Xu H, Yang H, Liu SR, Li YD, Lin MX (2016) Effects of species abundance and size classes on assessing community phylogenetic structure: A case study in Jianfengling tropical montane rainforest. Biodiversity Science, 24, 617-628. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [许格希, 史作民, 唐敬超, 许涵, 杨怀, 刘世荣, 李意德, 林明献 (2016) 物种多度和径级尺度对于评价群落系统发育结构的影响: 以尖峰岭热带山地雨林为例. 生物多样性, 24, 617-628.] | |
| [32] |
Xu XH, Wang WW, Mi XC, Chen L, Ma KP (2023) The Chinese Forest Biodiversity Monitoring Network: 20-year achievements and outlook. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23354. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[徐学红, 王巍伟, 米湘成, 陈磊, 马克平 (2023) 中国森林生物多样性监测网络(CForBio): 二十年进展与展望. 生物多样性, 31, 23354.]
DOI |
|
| [33] |
Xu YJ, Lin DM, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP (2014) Recovery dynamics of secondary forests with different disturbance intensity in the Gutianshan National Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 22, 358-365. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[徐远杰, 林敦梅, 米湘成, 任海保, 马克平 (2014) 古田山不同干扰程度森林的群落恢复动态. 生物多样性, 22, 358-365.]
DOI |
|
| [34] | Yan M, Liu ZP, Subedi MR, Liang LF, Xi WM (2022) The complex impacts of unprecedented drought on forest tree mortality: A case study of dead trees in east Texas, USA. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42, 1034-1046. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [闫明, 刘志萍, Mukti Ram Subedi, 梁林峰, 奚为民 (2022) 特大干旱对树木死亡的影响——以美国德克萨斯州东部森林为例. 生态学报, 42, 1034-1046.] | |
| [35] | Yang J, Zhang GC, Ci XQ, Swenson NG, Cao M, Sha LQ, Li J, Baskin CC, Ferry Slik JW, Lin LX (2014) Functional and phylogenetic assembly in a Chinese tropical tree community across size classes, spatial scales and habitats. Functional Ecology, 28, 520-529. |
| [36] | Yang QS, Ma ZP, Xie YB, Zhang ZG, Wang ZH, Liu HM, Li P, Zhang N, Wang DL, Yang HB, Fang XF, Yan ER, Wang XH (2011) Community structure and species composition of an evergreen broad-leaved forest in Tiantong’s 20 ha dynamic plot, Zhejiang Province, eastern China. Biodiversity Science, 19, 215-223. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨庆松, 马遵平, 谢玉彬, 张志国, 王樟华, 刘何铭, 李萍, 张娜, 王达力, 杨海波, 方晓峰, 阎恩荣, 王希华 (2011) 浙江天童20 ha常绿阔叶林动态监测样地的群落特征. 生物多样性, 19, 215-223.] | |
| [37] |
Zhang TT, Wang X, Ren HB, Yu JP, Jin Y, Qian HY, Song XY, Ma KP, Yu MJ (2019) A comparative study on the community characteristics of secondary and old-growth evergreen broad-leaved forests in Gutianshan, Zhejiang Province. Biodiversity Science, 27, 1069-1080. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张田田, 王璇, 任海保, 余建平, 金毅, 钱海源, 宋小友, 马克平, 于明坚 (2019) 浙江古田山次生与老龄常绿阔叶林群落特征的比较. 生物多样性, 27, 1069-1080.]
DOI |
|
| [38] |
Zhong L, Chang-Yang CH, Lu P, Gu XP, Lei ZP, Cai YB, Zheng FD, Sun IF, Yu MJ (2015) Community structure and species composition of the secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest: The analyses for a 9 ha forest dynamics plot in Wuyanling Nature Reserve, Zhejiang Province, East China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 619-629. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[仲磊, 张杨家豪, 卢品, 顾雪萍, 雷祖培, 蔡延奔, 郑方东, 孙义方, 于明坚 (2015) 次生常绿阔叶林的群落结构与物种组成: 基于浙江乌岩岭9 ha森林动态样地. 生物多样性, 23, 619-629.]
DOI |
|
| [39] | Zhu Y, Zhao GF, Zhang LW, Shen GC, Mi XC, Ren HB, Yu MJ, Chen JH, Chen SW, Fang T, Ma KP (2008) Community composition and structure of Gutianshan forest dynamic plot in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest, east China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32, 262-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[祝燕, 赵谷风, 张俪文, 沈国春, 米湘成, 任海保, 于明坚, 陈建华, 陈声文, 方腾, 马克平 (2008) 古田山中亚热带常绿阔叶林动态监测样地——群落组成与结构. 植物生态学报, 32, 262-273.]
DOI |
|
| [40] |
Zou S, Zhou GY, Zhang QM, Xu S, Xiong X, Xia YJ, Liu SZ, Meng Z, Chu GW (2018) Long-term (1992-2015) dynamics of community composition and structure in a monsoon evergreen broad-leaved forest in Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 42, 442-452. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[邹顺, 周国逸, 张倩媚, 徐姗, 熊鑫, 夏艳菊, 刘世忠, 孟泽, 褚国伟 (2018) 1992-2015年鼎湖山季风常绿阔叶林群落结构动态. 植物生态学报, 42, 442-452.]
DOI |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [3] | 仝淼, 王欢, 张文双, 王超, 宋建潇. 重金属污染土壤中细菌抗生素抗性基因分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [4] | 贾贞妮, 张意岑, 杜彦君, 任海保. 干扰对中亚热带森林群落物种多样性演替动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24078-. |
| [5] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [6] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [7] | 时永强, 栾青杉, 单秀娟, 韦超, 赵永松, 孙策策, 金显仕. 长岛南部海域浮游动物多样性周年变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [8] | 李艳朋, 盘李军, 陈洁, 许涵, 杨立新. 亚热带人工混交林叶功能性状对森林演替的响应规律及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24049-. |
| [9] | 王腾, 李纯厚, 王广华, 赵金发, 石娟, 谢宏宇, 刘永, 刘玉. 西沙群岛七连屿珊瑚礁鱼类的物种组成与演替[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 23481-. |
| [10] | 倪艳梅, 陈莉, 董志远, 孙德斌, 李宝泉, 王绪敏, 陈琳琳. 黄河三角洲湿地生态修复区大型底栖动物群落结构与生态健康评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [11] | 陈瑶琪, 郭晶晶, 蔡国俊, 葛依立, 廖宇, 董正, 符辉. 近七十年(1954-2021)长江中下游湖泊沉水植物群落多样性演变特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23319-. |
| [12] | 魏嘉欣, 姜治国, 杨林森, 熊欢欢, 金胶胶, 罗方林, 李杰华, 吴浩, 徐耀粘, 乔秀娟, 魏新增, 姚辉, 余辉亮, 杨敬元, 江明喜. 湖北神农架中亚热带山地落叶阔叶林25 ha动态监测样地群落物种组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [13] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [14] | 吴芳芳, 刘娜, 何春梅, 原作强, 郝占庆, 尹秋龙. 秦岭山地木本植物群落结构及多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [15] | 徐凯伦, 陈小荣, 张敏华, 于婉婉, 吴素美, 朱志成, 陈定云, 兰荣光, 董舒, 刘宇. 演替和地形共同影响浙江百山祖森林群落的性系统多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24338-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn