



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 23303. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023303 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023303
倪艳梅1, 陈莉2, 董志远2, 孙德斌2, 李宝泉2,3( ), 王绪敏1, 陈琳琳2,3,*(
), 王绪敏1, 陈琳琳2,3,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2023-08-29
接受日期:2024-01-14
出版日期:2024-03-20
发布日期:2024-02-27
通讯作者:
*E-mail: llchen@yic.ac.cn
基金资助:
Yanmei Ni1, Li Chen2, Zhiyuan Dong2, Debin Sun2, Baoquan Li2,3( ), Xumin Wang1, Linlin Chen2,3,*(
), Xumin Wang1, Linlin Chen2,3,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-08-29
Accepted:2024-01-14
Online:2024-03-20
Published:2024-02-27
Contact:
*E-mail: llchen@yic.ac.cn
摘要:
黄河三角洲国际重要湿地生物多样性保护工程于2019年动工, 本研究基于修复区内大型底栖动物群落组成特点及其与环境因子的相关关系, 分析大型底栖动物群落恢复特征, 了解该地区的生态系统健康状况, 评估保护工程实施三年后修复区湿地生态系统演替阶段及修复效果。结果表明: 2022年春、夏、秋三季共采集到大型底栖动物16种, 隶属于5门6纲15科, 昆虫纲动物在物种组成中占据优势地位; 大型底栖动物密度和生物多样性指数的时空差异均不显著(P > 0.05); 大型底栖动物生物量存在显著的季节差异, 表现为秋季(2.89 g/m2) > 夏季(1.95 g/m2) > 春季(1.90 g/m2), 秋季与春季和夏季间均存在显著差异(P < 0.05), 空间差异不显著(P > 0.05)。与环境因子的相关性分析结果显示, 蠓科一种(Ceratopogonidae sp.)、石缨虫属一种(Laonome sp.)、椭圆萝卜螺(Radix swinhoei)、尖口圆扁螺(Hippeutis cantori)等物种密度与电导率、盐度、总碳、铵盐和亚硝酸盐等指标显著相关(P < 0.01)。快速生物综合评价指数评定修复区为“亚健康”状态。本研究通过对黄河三角洲湿地修复区大型底栖动物群落特征以及生态健康评价的分析, 为修复区底栖动物群落的演替规律研究提供基础数据和科学依据, 为后续湿地修复工程的实施和管理提供指导和参考, 对于黄河三角洲生物多样性的保护具有重要意义。
倪艳梅, 陈莉, 董志远, 孙德斌, 李宝泉, 王绪敏, 陈琳琳 (2024) 黄河三角洲湿地生态修复区大型底栖动物群落结构与生态健康评价. 生物多样性, 32, 23303. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023303.
Yanmei Ni, Li Chen, Zhiyuan Dong, Debin Sun, Baoquan Li, Xumin Wang, Linlin Chen (2024) Community structure of macrobenthos and ecological health evaluation in the restoration area of the Yellow River Delta wetland. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23303. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023303.
| 物种 Species | 优势度 Dominance (Y) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022.5 | 2022.8 | 2022.10 | |
| 节肢动物门 Arthropoda | |||
| 摇蚊幼虫一种 Chironomidae sp. | 0.475* | 0.738* | 0.757* |
| 蠓科一种 Ceratopogonidae sp. | 0.072* | 0.002 | 0.010 |
| 龙虱科一种 Dytiscidae sp. | 0.005 | 0.026* | |
| 软体动物门 Mollusca | |||
| 椭圆萝卜螺 Radix swinhoei | 0.220* | 0.043* | 0.084* |
| 尖口圆扁螺 Hippeutis cantori | 0.011 | 0.178* | 0.071* |
| 线虫动物门 Nematoda | |||
| 线虫动物一种 Nematoda sp. | 0.111* | 0.009 | |
表1 黄河三角洲湿地修复区大型底栖动物群落优势种组成
Table 1 The dominant species composition of macrobenthic communities in the Yellow River Delta wetland restoration area
| 物种 Species | 优势度 Dominance (Y) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022.5 | 2022.8 | 2022.10 | |
| 节肢动物门 Arthropoda | |||
| 摇蚊幼虫一种 Chironomidae sp. | 0.475* | 0.738* | 0.757* |
| 蠓科一种 Ceratopogonidae sp. | 0.072* | 0.002 | 0.010 |
| 龙虱科一种 Dytiscidae sp. | 0.005 | 0.026* | |
| 软体动物门 Mollusca | |||
| 椭圆萝卜螺 Radix swinhoei | 0.220* | 0.043* | 0.084* |
| 尖口圆扁螺 Hippeutis cantori | 0.011 | 0.178* | 0.071* |
| 线虫动物门 Nematoda | |||
| 线虫动物一种 Nematoda sp. | 0.111* | 0.009 | |
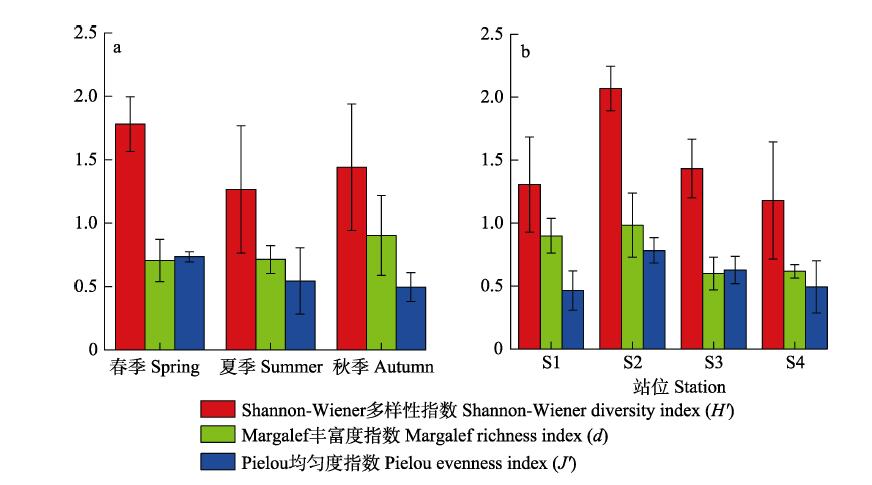
图4 2022年黄河三角洲修复区大型底栖动物群落多样性指数的季节(a)和空间(b)差异
Fig. 4 Seasonal (a) and spatial (b) change of biodiversity index of macrobenthic communities in the restoration area of the Yellow River Delta in 2022
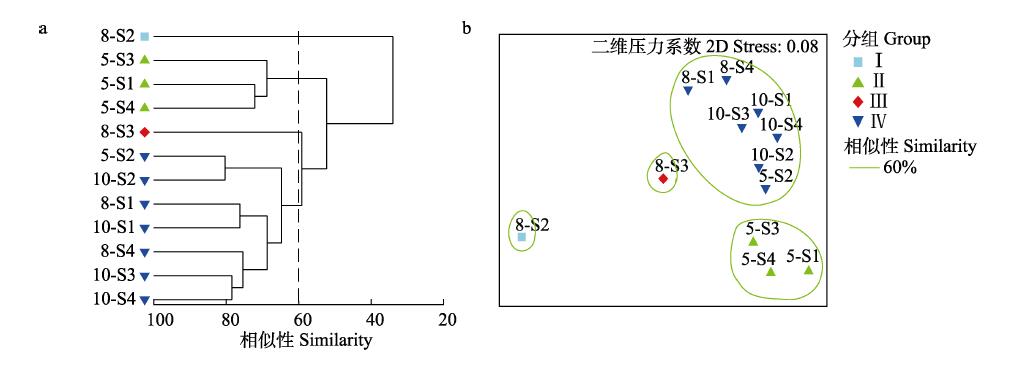
图5 黄河三角洲修复区大型底栖动物群落的聚类分析(a)和多维尺度排序(b)。5-S1: 春季S1站位; 5-S2: 春季S2站位; 5-S3: 春季S3站位; 5-S4: 春季S4站位; 8-S1: 夏季S1站位; 8-S2: 夏季S2站位; 8-S3: 夏季S3站位; 8-S4: 夏季S4站位; 10-S1: 秋季S1站位; 10-S2: 秋季S2站位; 10-S3: 秋季S3站位; 10-S4: 秋季S4站位。
Fig. 5 Cluster analysis (a) and multi-dimensional scaling (b) of macrobenthic communities in the Yellow River Delta restoration area. 5-S1, S1 station in spring; 5-S2, S2 station in spring; 5-S3, S3 station in spring; 5-S4, S4 station in spring; 8-S1, S1 station in summer; 8-S2, S2 station in summer; 8-S3, S3 station in summer; 8-S4, S4 station in summer; 10-S1, S1 station in autumn; 10-S2, S2 station in autumn; 10-S3, S3 station in autumn; 10-S4, S4 station in autumn.
| 物种 Species | 平均相似度 Average similarity (%) | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| II组 Group II (组内相似性69.9% Within-group similarity 69.9%) | |||
| 摇蚊幼虫一种 Chironomidae sp. | 31.90 | 45.64 | 45.64 |
| 椭圆萝卜螺 Radix swinhoei | 18.78 | 26.87 | 72.51 |
| 蠓科一种 Ceratopogonidae sp. | 11.95 | 17.10 | 89.61 |
| 线虫动物一种 Nematoda sp. | 5.09 | 7.28 | 96.89 |
| IV组 Group IV (组内相似性68.81% Within-group similarity 68.81%) | |||
| 摇蚊幼虫一种 Chironomidae sp. | 36.91 | 53.65 | 53.65 |
| 椭圆萝卜螺 Radix swinhoei | 11.73 | 17.05 | 70.69 |
| 尖口圆扁螺 Hippeutis cantori | 10.76 | 15.63 | 86.32 |
| 龙虱科一种 Dytiscidae sp. | 3.64 | 5.29 | 91.62 |
| II组和IV组 Group II and Group IV (组间差异性47.22% 47.22% difference between groups) | |||
| 摇蚊幼虫一种 Chironomidae sp. | 13.03 | 27.59 | 27.59 |
| 尖口圆扁螺 Hippeutis cantori | 8.24 | 17.46 | 45.05 |
| 线虫动物一种 Nematoda sp. | 6.00 | 12.69 | 57.74 |
| 龙虱科一种 Dytiscidae sp. | 3.88 | 8.21 | 65.95 |
| 蠓科一种 Ceratopogonidae sp. | 3.82 | 8.09 | 74.04 |
| 椭圆萝卜螺 Radix swinhoei | 2.63 | 5.56 | 79.60 |
表2 研究区域大型底栖动物群落相似性分析
Table 2 Similarity analysis of macrobenthic communities in the study area
| 物种 Species | 平均相似度 Average similarity (%) | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| II组 Group II (组内相似性69.9% Within-group similarity 69.9%) | |||
| 摇蚊幼虫一种 Chironomidae sp. | 31.90 | 45.64 | 45.64 |
| 椭圆萝卜螺 Radix swinhoei | 18.78 | 26.87 | 72.51 |
| 蠓科一种 Ceratopogonidae sp. | 11.95 | 17.10 | 89.61 |
| 线虫动物一种 Nematoda sp. | 5.09 | 7.28 | 96.89 |
| IV组 Group IV (组内相似性68.81% Within-group similarity 68.81%) | |||
| 摇蚊幼虫一种 Chironomidae sp. | 36.91 | 53.65 | 53.65 |
| 椭圆萝卜螺 Radix swinhoei | 11.73 | 17.05 | 70.69 |
| 尖口圆扁螺 Hippeutis cantori | 10.76 | 15.63 | 86.32 |
| 龙虱科一种 Dytiscidae sp. | 3.64 | 5.29 | 91.62 |
| II组和IV组 Group II and Group IV (组间差异性47.22% 47.22% difference between groups) | |||
| 摇蚊幼虫一种 Chironomidae sp. | 13.03 | 27.59 | 27.59 |
| 尖口圆扁螺 Hippeutis cantori | 8.24 | 17.46 | 45.05 |
| 线虫动物一种 Nematoda sp. | 6.00 | 12.69 | 57.74 |
| 龙虱科一种 Dytiscidae sp. | 3.88 | 8.21 | 65.95 |
| 蠓科一种 Ceratopogonidae sp. | 3.82 | 8.09 | 74.04 |
| 椭圆萝卜螺 Radix swinhoei | 2.63 | 5.56 | 79.60 |
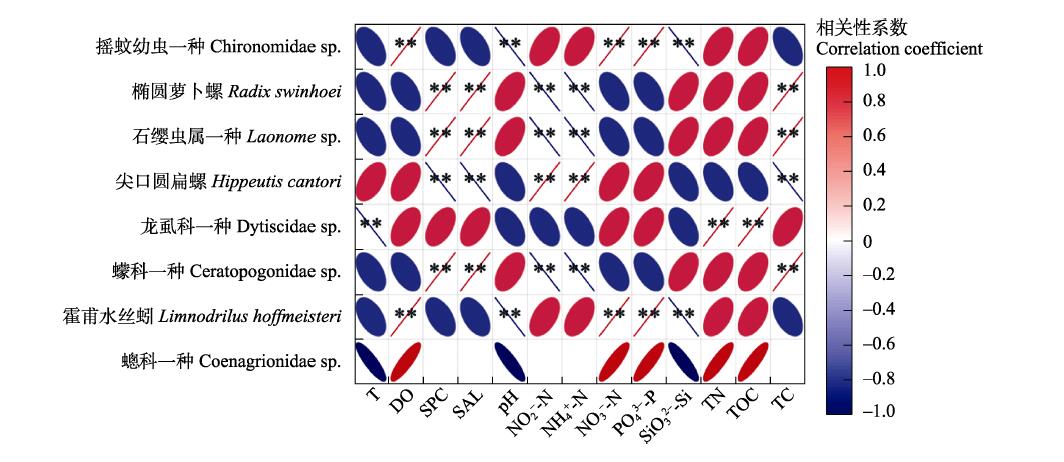
图6 黄河三角洲修复区大型底栖动物类群与环境因子的相关关系。T: 温度; DO: 溶解氧; SPC: 电导率; SAL: 盐度; pH: 酸碱度; NO2--N: 亚硝酸盐; NH4+-N: 铵盐; NO3--N: 硝酸盐; PO43--P: 磷酸盐; SiO32--Si: 硅酸盐; TN: 总氮; TOC: 总有机碳; TC: 总碳。**P < 0.01。
Fig. 6 Correlation between major macrobenthic groups and environmental factors in the Yellow River Delta restoration area. T, Temperature; DO, Dissolved oxygen; SPC, Specific conductance; SAL, Salinity; NO2--N, Nitrite nitrogen; NH4+-N, Ammonium nitrogen; NO3--N, Nitrate; PO43--P, Phosphate; SiO32--Si, Silicate; TN, Total nitrogen; TOC, Total organic carbon; TC, Total carbon. **P < 0.01.
| [1] | Aksnes DL, Wassmann P (1993) Modeling the significance of zooplankton grazing for export production. Limnology and Oceanography, 38, 978-985. |
| [2] | Barbour MT, Stribling JB, Verdonschot PFM (2006) The multihabitat approach of USEPA’s rapid bioassessment protocols: Benthic macroinvertebrates. Limnetica, 25, 839-850. |
| [3] | Boon PI, Allen T, Carr G, Frood D, Harty C, Mcmahon A, Mathews S, Rosengren N, Sinclair S, White M, Yugovic J (2015) Coastal wetlands of Victoria, south-eastern Australia: Providing the inventory and condition information needed for their effective management and conservation. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 25, 454-479. |
| [4] | Buss DF, Vitorino AS (2010) Rapid Bioassessment Protocols using benthic macroinvertebrates in Brazil: Evaluation of taxonomic sufficiency. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 29, 562-571. |
| [5] | Cai LZ, Ma L, Gao Y, Zheng TL, Lin P (2002) Analysis on assessing criterion for polluted situation using species diversity index of marine macrofauna. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 41, 641-646. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蔡立哲, 马丽, 高阳, 郑天凌, 林鹏 (2002) 海洋底栖动物多样性指数污染程度评价标准的分析. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 41, 641-646.] | |
| [6] | Chen BW, Cai LZ, Rao YY, Li WJ, Chen XW, Fu SJ, Peng WQ, Zheng B (2020) Effects of sediment fining on benthic macrofaunal community in subtidal amphioxus habitats in Xiamen. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 51, 494-505. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈丙温, 蔡立哲, 饶义勇, 李文君, 陈昕韡, 傅素晶, 彭文晴, 郑斌 (2020) 底质细化对厦门潮下带文昌鱼栖息地大型底栖动物群落的影响. 海洋与湖沼, 51, 494-505.] | |
| [7] | Chen ZH, Wang Y, Wang Q, Fu J, Pei YS (2021) Restoration of macrozoobenthos community in Baiyangdian Lake based on habit and food web. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 16(5), 136-147. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈泽豪, 王颖, 王乔, 付军, 裴元生 (2021) 基于习性和食物网的白洋淀大型底栖动物群落恢复研究. 生态毒理学报, 16(5), 136-147.] | |
| [8] |
Cuffney TF, Brightbill RA, May JT, Waite IR (2010) Responses of benthic macroinvertebrates to environmental changes associated with urbanization in nine metropolitan areas. Ecological Applications, 20, 1384-1401.
PMID |
| [9] | Duan XH, Wang ZY, Xu MZ (2010) Benthic Macroinvertebrate and Application in the Assessment of Stream Ecology. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 段学花, 王兆印, 徐梦珍 (2010) 底栖动物与河流生态评价. 清华大学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [10] | Geng SW, Qu XD, Zhang Y, Lin KD (2012) Comparison and application of biological indices of macroinvertebrates in river health assessment. Environmental Science, 33, 2281-2287. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 耿世伟, 渠晓东, 张远, 林坤德 (2012) 大型底栖动物生物评价指数比较与应用. 环境科学, 33, 2281-2287.] | |
| [11] | Gu XY, Tao L, You ZJ, Jiao HF, Shi HX, Lou D (2010) The macrobenthic community of the Xiangshan Bay. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 41, 208-213. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 顾晓英, 陶磊, 尤仲杰, 焦海峰, 施慧雄, 楼丹 (2010) 象山港大型底栖动物群落特征. 海洋与湖沼, 41, 208-213.] | |
| [12] | Han M, Zhang XH (2009) Value estimates of the dominant ecosystem services in Yellow River Delta wetland. China Population, Resources and Environment, 19(6), 37-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 韩美, 张晓慧 (2009) 黄河三角洲湿地主导生态服务功能价值估算. 中国人口·资源与环境, 19(6), 37-43.] | |
| [13] | Han QX, Yuan ZY, Chen BJ, Wang YJ, Shi YJ, Liu DY (2014) The community structure and distribution pattern of intertidal macrobenthos in the intertidal zone of Yantai. Marine Sciences, 38(9), 59-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 韩庆喜, 袁泽轶, 陈丙见, 王玉珏, 石雅君, 刘东艳 (2014) 烟台潮间带大型底栖动物群落组成和结构研究. 海洋科学, 38(9), 59-68.] | |
| [14] | Hering D, Moog O, Sandin L, Verdonschot PFM (2004) Overview and application of the AQEM assessment system. Hydrobiologia, 516, 1-20. |
| [15] |
Jia HB, Chai XP, Huang B (2021) Effect of seasonal hypoxia on macrobenthic communities in the Yangtze Estuary from 2016 to 2019. Journal of Marine Sciences, 39(2), 80-88. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [ 贾海波, 柴小平, 黄备 (2021) 2016-2019年长江口海域季节性低氧对大型底栖动物群落的影响. 海洋学研究, 39(2), 80-88.] | |
| [16] | Kagata H, Ohgushi T (2012) Non-additive effects of leaf litter and insect frass mixture on decomposition processes. Ecological Research, 27, 69-75. |
| [17] | Leng LL, Zhang HP, Zhang M, Li TK, Liu XB, Qu XD (2016) Application of the biological monitoring working party (BMWP) score system of macroinvertebrates for river health in Taizi River basin. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 25, 1781-1788. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 冷龙龙, 张海萍, 张敏, 李天科, 刘晓波, 渠晓东 (2016) 大型底栖动物快速评价指数BMWP在太子河流域的应用. 长江流域资源与环境, 25, 1781-1788.] | |
| [18] | Li DF, Gao J, Zhang D (2018) Restoration measures and effect analysis of Yellow River Delta wetland. Science and Technology Innovation Guide, 15(14), 135-136. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李德峰, 高坚, 张冬 (2018) 黄河三角洲湿地恢复措施及效果分析. 科技创新导报, 15(14), 135-136.] | |
| [19] | Li H, Yan BX, Li HY, Xu XJ (2018) Distribution characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in soils of typical saltwater-freshwater interface wetlands of the Yellow River Delta. Wetland Science, 16, 679-683. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李怀, 阎百兴, 李海彦, 徐兴健 (2018) 黄河口典型咸、淡水交互区湿地土壤氮和磷分布特征. 湿地科学, 16, 679-683.] | |
| [20] |
Li M, Yang W, Sun T, Jin YW (2016) Potential ecological risk of heavy metal contamination in sediments and macrobenthos in coastal wetlands induced by freshwater releases: A case study in the Yellow River Delta, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 103, 227-239.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Li SW, Li F, Song XK, Zhang ML (2020) The influence of water-sediment regulation on macrobenthic community structures in the Huanghe River (Yellow River) Estuary during 2012-2016. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 39, 120-128. |
| [22] | Li SZ, Cui BS, Xie T, Zhang SY, Liu WH, Fu SQ (2015) Distribution features of macrobenthic communities in marshes in the Yellow River Delta. Wetland Science, 13, 759-764. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李姗泽, 崔保山, 谢湉, 张树岩, 刘伟华, 付守强 (2015) 黄河三角洲沼泽中大型底栖动物的分布特征. 湿地科学, 13, 759-764.] | |
| [23] | Liang XQ (2004) Fauna Sinica·Invertebrata (Vol. 36): Crustacea•Decapoda•Atyidae. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 梁象秋 (2004) 中国动物志•无脊椎动物(第三十六卷): 甲壳动物亚门•十足目•匙指虾科. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [24] | Liu DD, Wu HT, Lu KL, Yang MY, Guan Q, Zhao WY, Shao LF (2021) Effects of spatial and environmental factors on benthic invertebrate communities in natural and freshwater restored wetlands of the Yellow River Delta. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41, 6893-6903. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘丹丹, 武海涛, 芦康乐, 杨萌尧, 管强, 赵文元, 邵乐夫 (2021) 空间和环境因子对黄河口自然和淡水恢复湿地底栖动物群落的差异影响. 生态学报, 41, 6893-6903.] | |
| [25] |
Liu HY, Zhou ZH, Wang NN, Wang YJ (2022) Wetland ecosystem health assessment in the Yellow River Delta Nature Reserve. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 38(27), 74-78. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 刘宏元, 周志花, 王娜娜, 王艳君 (2022) 黄河三角洲自然保护区湿地生态系统健康评价. 中国农学通报, 38(27), 74-78.]
DOI |
|
| [26] | Liu PJ, Chang HL, Ren D (2010) The role of beetles in Mesozoic non-marine ecosystem in Yanliao District. Journal of Environmental Entomology, 32, 264-274. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘平娟, 常华丽, 任东 (2010) 甲虫在燕辽地区中生代非海相生态系统中的作用. 环境昆虫学报, 32, 264-274.] | |
| [27] | Liu YY (1979) Economic Fauna of China•Freshwater Mollusk. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘月英 (1979) 中国经济动物志•淡水软体动物. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [28] | Lu KL, Wu HT, Xue ZS, Lu XG, Batzer DP (2019) Development of a multi-metric index based on aquatic invertebrates to assess floodplain wetland condition. Hydrobiologia, 827, 141-153. |
| [29] |
Lv WW, Huang YH, Liu ZQ, Yang Y, Fan B, Zhao YL (2016) Application of macrobenthic diversity to estimate ecological health of artificial oyster reef in Yangtze Estuary, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 103, 137-143.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Ma HJ, Li RX, Yuan FY, Shi LY, Guan QW (2013) Stability of Platycladus orientalis mixed forest communities at different successional stages. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 32, 558-562. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马洪婧, 李瑞霞, 袁发银, 史珑燕, 关庆伟 (2013) 不同演替阶段栎树混交林群落稳定性. 生态学杂志, 32, 558-562.] | |
| [31] | Margalef R (1968) Perspectives in Ecological Theory. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [32] | Mawdsley J, Harrison J, Sithole H (2016) Natural history of a South African insect pollinator assemblage (Insecta: Coleoptera, Diptera, Hymenoptera, Lepidoptera): Diagnostic notes, food web analysis and conservation recommendations. Journal of Natural History, 50, 2849-2879. |
| [33] | Morse JC, Bae YJ, Munkhjargal G, Sangpradub N, Tanida K, Vshivkova TS, Wang BX, Yang LF, Yule CM (2007) Freshwater biomonitoring with macroinvertebrates in East Asia. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 5, 33-42. |
| [34] | Niu MX, Wang J, Xu BD (2017) Assessment of the ecosystem health of the Yellow River Estuary based on the pressure-state-response model. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 943-952. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 牛明香, 王俊, 徐宾铎 (2017) 基于PSR的黄河河口区生态系统健康评价. 生态学报, 37, 943-952.] | |
| [35] | Ofenböck T, Moog O, Gerritsen J, Barbour M (2004) A stressor specific multimetric approach for monitoring running waters in Austria using benthic macro-invertebrates. Hydrobiologia, 516, 251-268. |
| [36] | Philippe R, Michel B, Philippe UP, Henri T (translated by Liu W, Wang XT, Huang SF (2015) Systematic Classification, Biology, and Ecology of Freshwater Invertebrates. China Water & Power Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘威, 王旭涛, 黄少峰 (译) (2015) 淡水无脊椎动物系统分类、 生物及生态学. 中国水利水电出版社, 北京.] | |
| [37] |
Pielou EC (1966) Species-diversity and pattern-diversity in the study of ecological succession. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 10, 370-383.
PMID |
| [38] | Qin XH, Huang HQ, Zhang FH, Lei B, Ao L (2023) Health assessment of Liangtan River Basin, a tributary of urbanization at the tail of the Three Gorges Reservoir, based on rapid assessment of macroinvertebrates. Freshwater Fisheries, 53(3), 103-112. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 秦孝辉, 黄河清, 张方辉, 雷波, 敖亮 (2023) 基于大型底栖动物快速评价的三峡库尾城市化支流梁滩河流域健康评估. 淡水渔业, 53(3), 103-112.] | |
| [39] | Qiu WG (2014) Map of Benthic Fauna Monitoring in Liaohe River Basin. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 仇伟光 (2014) 辽河流域底栖动物监测图鉴. 中国环境出版社, 北京.] | |
| [40] | Qu XD, Chen J, Chen HY, Zhang M, Peng WQ, Zhu L, Lei X (2021) Application of rapid bioassessment indices of macroinvertebrates in ecological evaluation of urban streams. Journal of Hydroecology, 42(3), 14-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 渠晓东, 陈军, 陈皓阳, 张敏, 彭文启, 朱磊, 雷璇 (2021) 大型底栖动物快速生物评价指数在城市河流生态评估中的应用. 水生态学杂志, 42(3), 14-22.] | |
| [41] | Shang SQ, Xiang H, Guo W, Yin XW, Xu ZX (2021) Relationship between functional feeding groups of benthic animals and environmental factors. The People’s Yellow River, 43(S1), 77-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 商书芹, 相华, 郭伟, 殷旭旺, 徐宗学 (2021) 底栖动物功能摄食类群与环境因子的关系. 人民黄河, 43(S1), 77-79.] | |
| [42] | Shannon EC, Weaver W (1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana. |
| [43] | Wang BX, Yang LF (2004) A study on tolerance values of benthic macroinvertebrate taxa in Eastern China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24, 2768-2775. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王备新, 杨莲芳 (2004) 我国东部底栖无脊椎动物主要分类单元耐污值. 生态学报, 24, 2768-2775.] | |
| [44] | Wang L (2020) Litter Decomposition and Macroinvertebrates Colonization During Winter in a Stream of the Changbai Mountains. PhD dissertation, Northeast Normal University, Changchun. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王璐 (2020) 长白山溪流冬季凋落物分解与大型底栖动物定殖. 博士学位论文, 东北师范大学, 长春.] | |
| [45] |
Wang Y, Zhang MM, Zhang D, Shen ZY (2016) The influence of sediment particle size on the properties of adsorbed dissolved organic matter in the Yangtze Estuary and its interactions with As/Sb. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 105, 351-358.
DOI PMID |
| [46] | Wu YH, Chen W, Li ZY (2017) Map of Benthic Fauna of the Ashi River. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 伍跃辉, 陈威, 李中宇 (2017) 阿什河底栖动物图谱. 中国环境出版社, 北京.] | |
| [47] | Wu ZS, Cai YJ, Chen YW, Shao XY, Gao JF (2011) Assemblage structure investigation of macrozoobenthos and water quality bioassessment of the main river systems in Taihu Basin. Journal of Lake Sciences, 23, 686-694. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴召仕, 蔡永久, 陈宇炜, 邵晓阳, 高俊峰 (2011) 太湖流域主要河流大型底栖动物群落结构及水质生物学评价. 湖泊科学, 23, 686-694.] | |
| [48] | Wyżga B, Oglęcki P, Hajdukiewicz H, Zawiejska J, Radecki-Pawlik A, Skalski T, Mikuś P (2013) Interpretation of the invertebrate-based BMWP-PL index in a gravel-bed river: Insight from the Polish Carpathians. Hydrobiologia, 712, 71-88. |
| [49] | Xu CY, Pu LJ, Zhu M (2018) Effect of reclamation activity on coastal ecological environment: Progress and perspectives. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 1148-1162. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐彩瑶, 濮励杰, 朱明 (2018) 沿海滩涂围垦对生态环境的影响研究进展. 生态学报, 38, 1148-1162.] | |
| [50] |
Yan J, Xu Y, Sui JX, Li XZ, Wang HF, Zhang BL (2017) Long-term variation of the macrobenthic community and its relationship with environmental factors in the Yangtze River Estuary and its adjacent area. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 123, 339-348.
DOI PMID |
| [51] | Yan RX, Zhu F, Han QG, Huang C, Chen Q, Han QX (2019) Characteristics of macrobenthos community in the intertidal zone of the Yellow River estuary. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 54, 835-844. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 严润玄, 朱峰, 韩庆功, 黄晨, 陈锵, 韩庆喜 (2019) 黄河口潮间带大型底栖动物群落特征. 动物学杂志, 54, 835-844.] | |
| [52] | Yang W, Li M, Sun T, Jin YW (2017) The joint effect of tidal barrier construction and freshwater releases on the macrobenthos community in the northern Yellow River Delta (China). Ocean & Coastal Management, 136, 83-94. |
| [53] | Yuan W, Jin XS, Dai FQ (2010) Influence of hypoxia environment upon macrobenthos. Marine Environmental Science, 29, 293-296. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 袁伟, 金显仕, 戴芳群 (2010) 低氧环境对大型底栖动物的影响. 海洋环境科学, 29, 293-296.] | |
| [54] | Zhang HX, Li XY, Cui BS, Wang Q, Yu HL, Wu X, Xu JM (2023) Effect of wetland ecological restoration project on macrobenthos community in the Yellow River Delta. Environmental Engineering, 41, 222-231. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张晗旭, 李馨宇, 崔保山, 王青, 于海玲, 吴霞, 许佳美 (2023) 黄河三角洲湿地生态修复工程对底栖动物的影响效果研究. 环境工程, 41, 222-231.] | |
| [55] | Zhao SQ, Fan YC, Dai YR, Wang FH, Liang W (2019) Responses of phytoplankton community to abiotic environmental variables with the mitigation of eutrophication: A case study of Donghu Lake, Wuhan City. Journal of Lake Sciences, 31, 1310-1319. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵思琪, 范垚城, 代嫣然, 王飞华, 梁威 (2019) 水体富营养化改善过程中浮游植物群落对非生物环境因子的响应: 以武汉东湖为例. 湖泊科学, 31, 1310-1319.] | |
| [56] | Zhu LM, Xiao WS, Zhou D, Zhang W, Wang LQ, Zhang RL (2019) Macrozoobenthos community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in Dianshan Lake. Journal of Hydroecology, 40(2), 55-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱利明, 肖文胜, 周东, 张玮, 王丽卿, 张瑞雷 (2019) 淀山湖大型底栖动物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系. 水生态学杂志, 40(2), 55-65.] | |
| [57] | Zuo Z, Chen YQ, Cheng BX, Hu W, Zhu XD, Cang JJ, Wang P (2016) Ecological characteristics of macrobenthic communities in SFWs of different hydrophytes and their relationships with environmental factors. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 953-960. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 左倬, 陈煜权, 成必新, 胡伟, 朱雪诞, 仓基俊, 王鹏 (2016) 不同植物配置下人工湿地大型底栖动物群落特征及其与环境因子的关系. 生态学报, 36, 953-960.] |
| [1] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [2] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [3] | 仝淼, 王欢, 张文双, 王超, 宋建潇. 重金属污染土壤中细菌抗生素抗性基因分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [4] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [5] | 宋远昊, 龚吕, 李贲, 胡阳, 李秀珍. 辽河口不同退塘还湿方式对大型底栖动物的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24316-. |
| [6] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [7] | 时永强, 栾青杉, 单秀娟, 韦超, 赵永松, 孙策策, 金显仕. 长岛南部海域浮游动物多样性周年变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [8] | 魏嘉欣, 姜治国, 杨林森, 熊欢欢, 金胶胶, 罗方林, 李杰华, 吴浩, 徐耀粘, 乔秀娟, 魏新增, 姚辉, 余辉亮, 杨敬元, 江明喜. 湖北神农架中亚热带山地落叶阔叶林25 ha动态监测样地群落物种组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [9] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [10] | 吴芳芳, 刘娜, 何春梅, 原作强, 郝占庆, 尹秋龙. 秦岭山地木本植物群落结构及多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [11] | 单航, 雷祖培, 郑方东, 韦博良, 仲磊, 于明坚. 2013-2023年浙江乌岩岭次生常绿阔叶林群落动态变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24372-. |
| [12] | 冯嘉谊, 练琚愉, 冯瑜莙, 张东旭, 曹洪麟, 叶万辉. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林群落垂直分层对群落结构及功能的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| [13] | 王兴煜, 孟京辉, 任思远, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林群落生物多样性与地上生物量的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24230-. |
| [14] | 杜晴晴, 任思远, Nicole Tsz Shun Yuan, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林幼树及成树生产力的影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24284-. |
| [15] | 黄骏涵, 余梵冬, 王裕祥, 黄哲, 张铭斯, 房苗, 舒璐, 徐猛, 韦慧, 汪学杰, 顾党恩, 罗思. 花地河中下游外来鱼类入侵现状及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24249-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()