



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 23294. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023294 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023294
刘啸林1,2, 吴友贵3,*( ), 张敏华1,2,*(
), 张敏华1,2,*( ), 陈小荣3, 朱志成3, 陈定云3, 董舒1,2, 李步杭4, 丁炳扬5, 刘宇1,2
), 陈小荣3, 朱志成3, 陈定云3, 董舒1,2, 李步杭4, 丁炳扬5, 刘宇1,2
收稿日期:2023-08-15
接受日期:2024-01-14
出版日期:2024-02-20
发布日期:2024-03-01
通讯作者:
E-mail: 基金资助:
Xiaolin Liu1,2, Yougui Wu3,*( ), Minhua Zhang1,2,*(
), Minhua Zhang1,2,*( ), Xiaorong Chen3, Zhicheng Zhu3, Dingyun Chen3, Shu Dong1,2, Buhang Li4, Bingyang Ding5, Yu Liu1,2
), Xiaorong Chen3, Zhicheng Zhu3, Dingyun Chen3, Shu Dong1,2, Buhang Li4, Bingyang Ding5, Yu Liu1,2
Received:2023-08-15
Accepted:2024-01-14
Online:2024-02-20
Published:2024-03-01
Contact:
E-mail: 摘要:
百山祖常绿林是亚热带中高海拔地区保存较好的森林类型, 群落结构复杂。本研究以百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地(简称百山祖样地)为平台, 对样地内胸径(DBH) ≥ 1 cm的所有木本植物进行调查和统计, 分析了其物种组成、区系特征、径级结构和空间分布格局。结果表明: 样地内DBH ≥ 1 cm的木本植物独立个体有210,556株, 分属43科85属163种。热带分布的科(20个)多于温带分布的科(17个), 但在属水平上以温带性质为主(温带分布的属为47个, 热带分布的属为33个)。常绿树种有90种, 占总树种数的55.21%。样地内稀有种和偶见种分别占所有物种数的35.58%和25.77%。重要值 ≥ 1%的物种共有25个, 分别占样地总个体数和总胸高断面积的85.84%和91.18%。重要值最大的3个物种分别是鹿角杜鹃(Rhododendron latoucheae)、黄山松(Pinus taiwanensis)和杉木(Cunninghamia lanceolata)。样地内所有个体的平均胸径为5.26 cm, 整体径级分布呈倒“J”型, 小径级个体较多, 群落更新良好。样地内优势种在1-100 m尺度上呈聚集分布, 且不同优势种表现出不同的生境偏好。本文可为后续开展亚热带中高海拔地带常绿林群落构建及生物多样性维持机制的研究提供科学基础。
刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇 (2024) 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征. 生物多样性, 32, 23294. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023294.
Xiaolin Liu, Yougui Wu, Minhua Zhang, Xiaorong Chen, Zhicheng Zhu, Dingyun Chen, Shu Dong, Buhang Li, Bingyang Ding, Yu Liu (2024) Community composition and structure of a 25-ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical forest in Baishanzu, Zhejiang Province. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23294. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023294.
| 物种名 Species name | 相对密度 Relative density | 相对胸高断面积 Relative basal area | 相对频度 Relative frequency | 重要值 Importance value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鹿角杜鹃 Rhododendron latoucheae | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 9.17 |
| 黄山松 Pinus taiwanensis | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 9.01 |
| 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 6.38 |
| 木荷 Schima superba | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 5.78 |
| 微毛柃 Eurya hebeclados | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 5.49 |
| 尖连蕊茶 Camellia cuspidata | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 4.04 |
| 多脉青冈 Quercus multinervis | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 3.75 |
| 窄基红褐柃 Eurya rubiginosa var. attenuata | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 3.74 |
| 光叶水青冈 Fagus lucida | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 2.81 |
| 云锦杜鹃 Rhododendron fortunei | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 2.58 |
| 短尾柯 Lithocarpus brevicaudatus | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 2.34 |
| 石灰花楸 Sorbus folgneri | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 2.21 |
| 厚叶红淡比 Cleyera pachyphylla | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 2.09 |
| 翅柃 Eurya alata | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 2.01 |
| 硬壳柯 Lithocarpus hancei | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 1.94 |
| 褐叶青冈 Quercus stewardiana | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.77 |
| 交让木 Daphniphyllum macropodum | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.62 |
| 水丝梨 Sycopsis sinensis | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.56 |
| 香冬青 Ilex suaveolens | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.54 |
| 光亮山矾 Symplocos lucida | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.44 |
| 显脉冬青 Ilex editicostata | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.21 |
| 浙闽新木姜子 Neolitsea aurata var. undulatula | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 1.16 |
| 马银花 Rhododendron ovatum | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 1.07 |
| 中华石楠 Photinia beauverdiana | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.05 |
| 大萼杨桐 Adinandra glischroloma var. macrosepala | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 1.02 |
| 其他 Others | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.47 | 23.20 |
| 合计 Total | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
表1 浙江百山祖25 ha森林动态监测样地的优势木本植物种类组成
Table 1 Dominant species composition of woody plants in Baishanzu 25-ha forest dynamics plot in Zhejiang Province
| 物种名 Species name | 相对密度 Relative density | 相对胸高断面积 Relative basal area | 相对频度 Relative frequency | 重要值 Importance value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鹿角杜鹃 Rhododendron latoucheae | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 9.17 |
| 黄山松 Pinus taiwanensis | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 9.01 |
| 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 6.38 |
| 木荷 Schima superba | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 5.78 |
| 微毛柃 Eurya hebeclados | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 5.49 |
| 尖连蕊茶 Camellia cuspidata | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 4.04 |
| 多脉青冈 Quercus multinervis | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 3.75 |
| 窄基红褐柃 Eurya rubiginosa var. attenuata | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 3.74 |
| 光叶水青冈 Fagus lucida | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 2.81 |
| 云锦杜鹃 Rhododendron fortunei | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 2.58 |
| 短尾柯 Lithocarpus brevicaudatus | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 2.34 |
| 石灰花楸 Sorbus folgneri | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 2.21 |
| 厚叶红淡比 Cleyera pachyphylla | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 2.09 |
| 翅柃 Eurya alata | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 2.01 |
| 硬壳柯 Lithocarpus hancei | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 1.94 |
| 褐叶青冈 Quercus stewardiana | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.77 |
| 交让木 Daphniphyllum macropodum | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.62 |
| 水丝梨 Sycopsis sinensis | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.56 |
| 香冬青 Ilex suaveolens | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.54 |
| 光亮山矾 Symplocos lucida | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.44 |
| 显脉冬青 Ilex editicostata | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.21 |
| 浙闽新木姜子 Neolitsea aurata var. undulatula | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 1.16 |
| 马银花 Rhododendron ovatum | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 1.07 |
| 中华石楠 Photinia beauverdiana | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.05 |
| 大萼杨桐 Adinandra glischroloma var. macrosepala | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 1.02 |
| 其他 Others | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.47 | 23.20 |
| 合计 Total | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| 分布区类型 Distribution area types | 科数 No. of families | 属数 No. of genera | 物种数 No. of species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 世界分布 Cosmopolitan | 6 | 1 | 1 |
| 2. 泛热带分布 Pantropic | 10 | 14 | 38 |
| 3. 热带亚洲和热带美洲间断分布 Tropical Asia and Tropical America disjuncted | 5 | 5 | 12 |
| 4. 旧世界热带分布 Old World Tropical | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 5. 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布 Tropical Asia to Tropical Australasia | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 6. 热带亚洲至热带非洲分布 Tropical Asia to Tropical Africa | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 7. 热带亚洲分布 Tropical Asia | 2 | 9 | 14 |
| 热带成分(分布型2-7) Tropical elements (2-7) | 20 | 33 | 70 |
| 8. 北温带分布 North Temperate | 12 | 17 | 49 |
| 9. 东亚和北美洲间断分布 East Asia and North America disjuncted | 4 | 17 | 25 |
| 10. 旧世界温带 Old World Temperate | 0 | 3 | 4 |
| 12. 地中海区、西亚至中亚分布 Mediterranean, West Asia to Central Asia | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 14. 东亚分布 East Asia | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 温带成分(分布型8-14) Temperate elements (8-14) | 17 | 47 | 88 |
| 15. 中国特有分布 Endemic to China | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| 总计 Total | 43 | 85 | 163 |
表2 浙江百山祖25 ha森林动态监测样地木本植物科、属、种的区系类型统计
Table 2 The areal-types of families, genera and species of woody plants in Baishanzu 25-ha forest dynamics plot in Zhejiang Province
| 分布区类型 Distribution area types | 科数 No. of families | 属数 No. of genera | 物种数 No. of species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 世界分布 Cosmopolitan | 6 | 1 | 1 |
| 2. 泛热带分布 Pantropic | 10 | 14 | 38 |
| 3. 热带亚洲和热带美洲间断分布 Tropical Asia and Tropical America disjuncted | 5 | 5 | 12 |
| 4. 旧世界热带分布 Old World Tropical | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 5. 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布 Tropical Asia to Tropical Australasia | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 6. 热带亚洲至热带非洲分布 Tropical Asia to Tropical Africa | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 7. 热带亚洲分布 Tropical Asia | 2 | 9 | 14 |
| 热带成分(分布型2-7) Tropical elements (2-7) | 20 | 33 | 70 |
| 8. 北温带分布 North Temperate | 12 | 17 | 49 |
| 9. 东亚和北美洲间断分布 East Asia and North America disjuncted | 4 | 17 | 25 |
| 10. 旧世界温带 Old World Temperate | 0 | 3 | 4 |
| 12. 地中海区、西亚至中亚分布 Mediterranean, West Asia to Central Asia | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 14. 东亚分布 East Asia | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 温带成分(分布型8-14) Temperate elements (8-14) | 17 | 47 | 88 |
| 15. 中国特有分布 Endemic to China | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| 总计 Total | 43 | 85 | 163 |
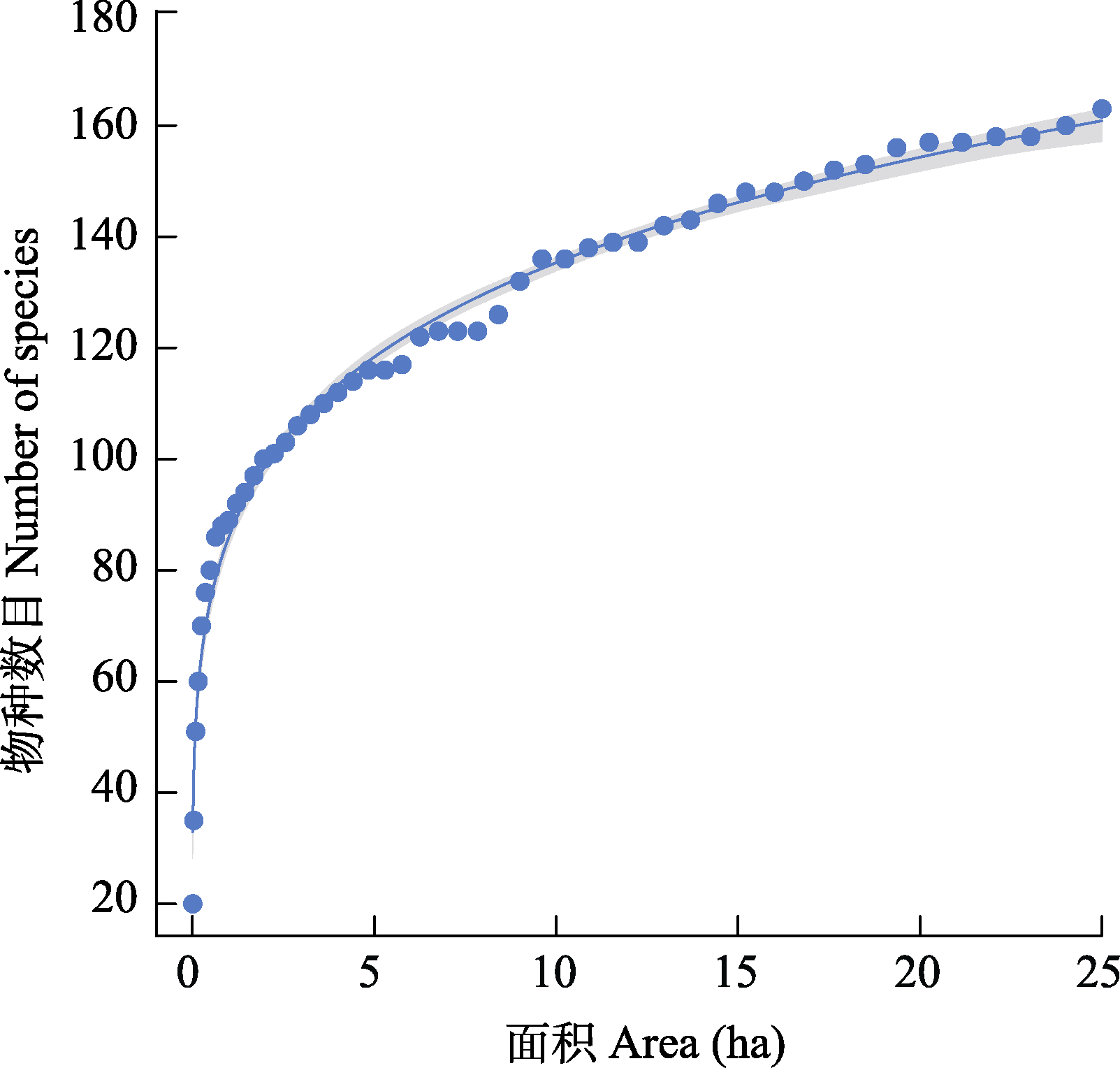
图2 浙江百山祖25 ha森林动态监测样地木本植物的种-面积曲线。阴影表示95%的置信区间。
Fig. 2 Species-area relationship curve of woody plants in Baishanzu 25-ha forest dynamics plot in Zhejiang Province. The shadow is the 95% confidence interval.
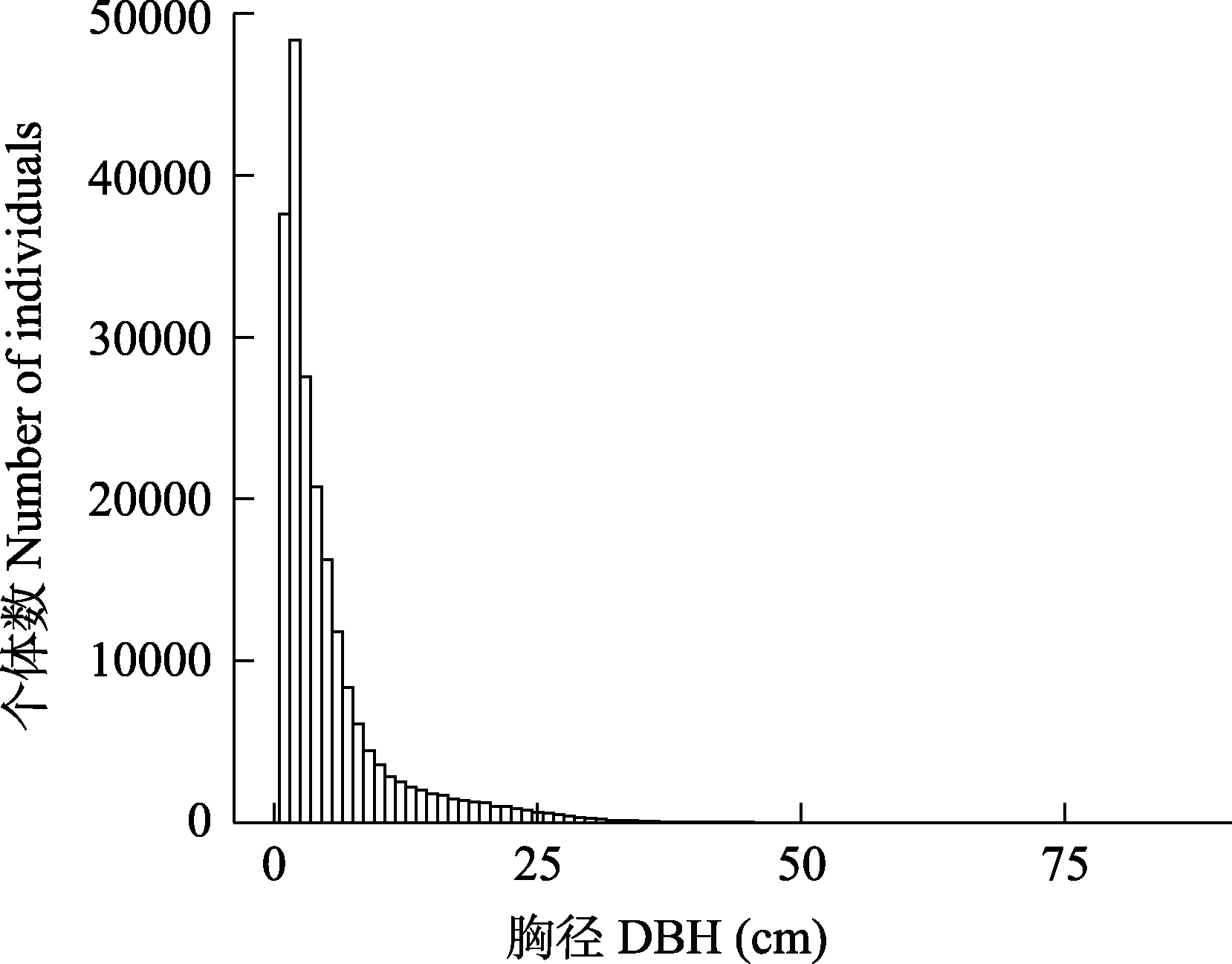
图3 浙江百山祖25 ha森林动态监测样地木本植物总体径级分布
Fig. 3 DBH-class distribution for overall woody plant species in Baishanzu 25-ha forest dynamics plot in Zhejiang Province
| 胸径 DBH (cm) | 植株数 No. of stems | 科数 No. of families | 属数 No. of genera | 物种数 No. of species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥ 1.0 | 210,556 | 43 | 85 | 163 |
| ≥ 5.0 | 68,191 | 35 | 74 | 133 |
| ≥ 10.0 | 27,770 | 35 | 71 | 114 |
| ≥ 15.0 | 15,512 | 34 | 65 | 93 |
| ≥ 20.0 | 8,131 | 27 | 52 | 73 |
| ≥ 40.0 | 228 | 9 | 13 | 15 |
表3 浙江百山祖25 ha森林动态监测样地木本植物不同胸径的植株数和科属种数
Table 3 Number of woody plant species, genera, families, and stems with different DBH in Baishanzu 25-ha forest dynamics plot in Zhejiang Province
| 胸径 DBH (cm) | 植株数 No. of stems | 科数 No. of families | 属数 No. of genera | 物种数 No. of species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥ 1.0 | 210,556 | 43 | 85 | 163 |
| ≥ 5.0 | 68,191 | 35 | 74 | 133 |
| ≥ 10.0 | 27,770 | 35 | 71 | 114 |
| ≥ 15.0 | 15,512 | 34 | 65 | 93 |
| ≥ 20.0 | 8,131 | 27 | 52 | 73 |
| ≥ 40.0 | 228 | 9 | 13 | 15 |
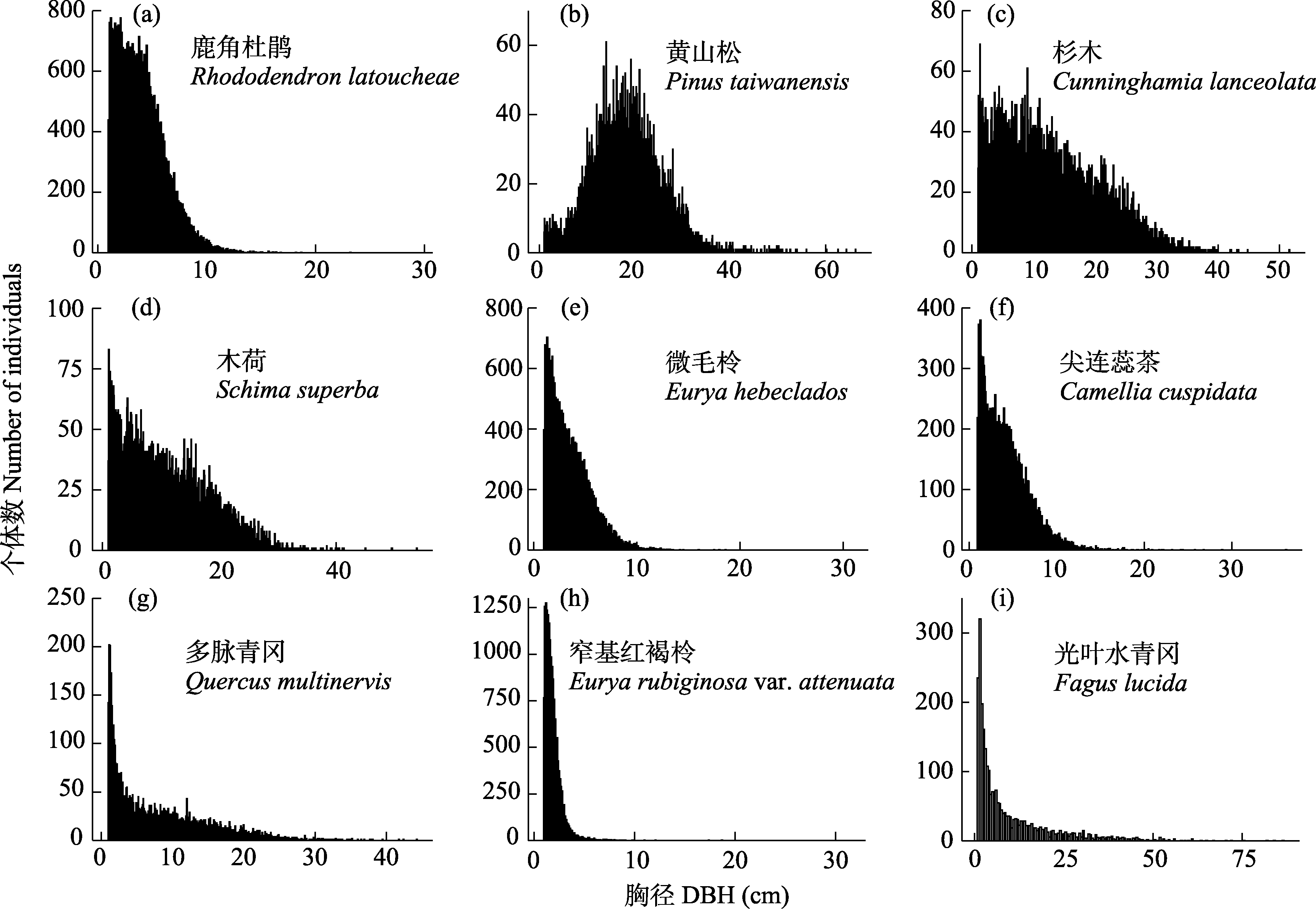
图4 浙江百山祖25 ha森林动态监测样地9个优势种木本植物的径级分布
Fig. 4 DBH-class distribution for nine dominant woody plant species in Baishanzu 25-ha forest dynamics plot in Zhejiang Province
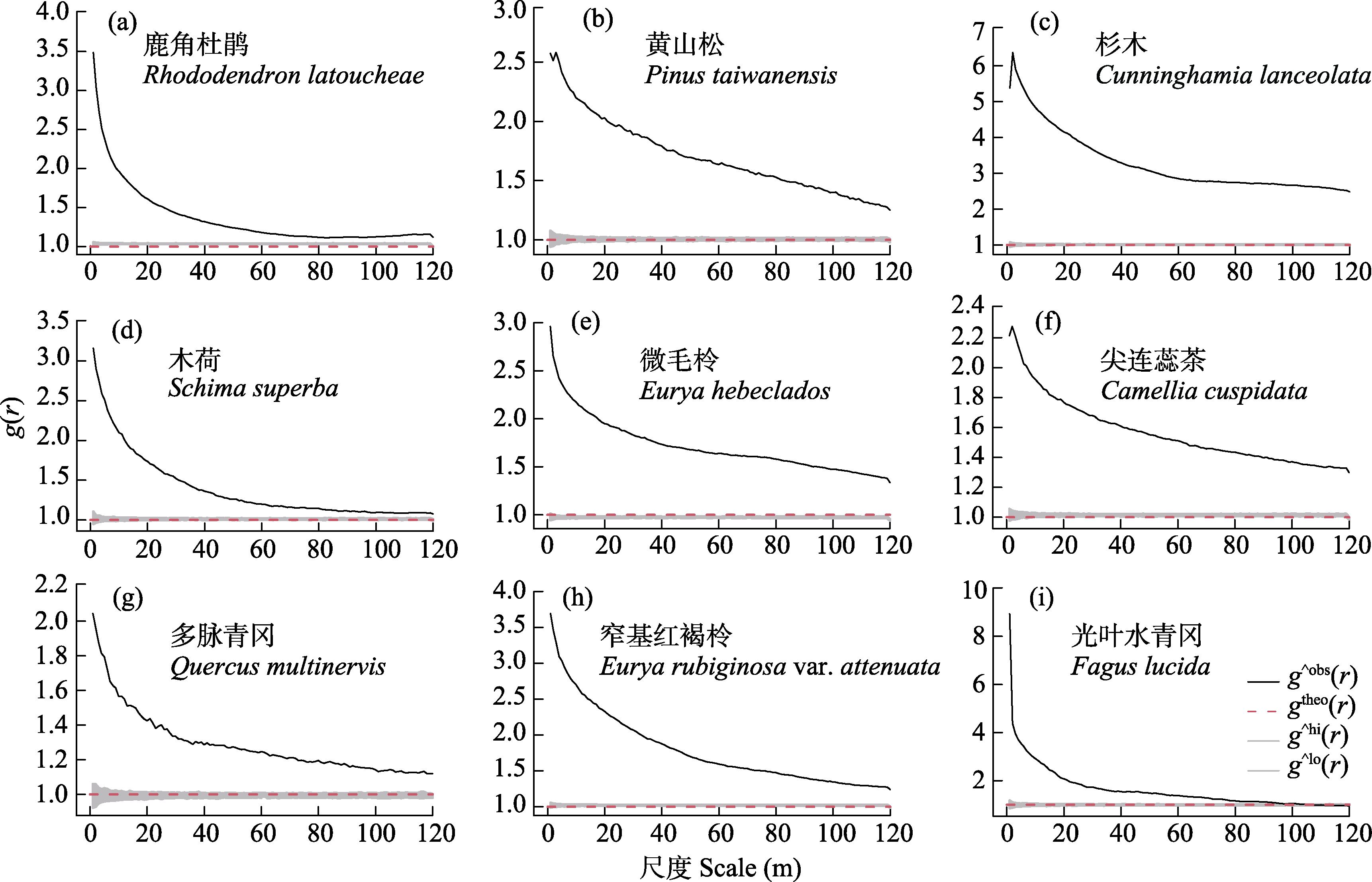
图5 浙江百山祖25 ha森林动态监测样地9个优势种在完全随机模型下的空间分布。g^obs(r): g(r)的观测值; g^theo(r): g(r)的理论值; g^hi(r): g(r)的99%置信区间上界; g^lo(r): g(r)的99%置信区间下界。
Fig. 5 Spatial distribution pattern of nine dominant woody plant species under complete spatial randomness null model Baishanzu 25-ha forest dynamics plot in Zhejiang Province. g^obs(r), Observed value of g(r); g^theo(r), Theoretical value of g(r); g^hi(r), Upper bound of 99% confidence interval for g(r); g^lo(r), Lower bound of 99% confidence interval for g(r).
| [1] | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and a Comparison with Other Plots. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. |
| [2] |
Connor EF, McCoy ED (1979) The statistics and biology of the species-area relationship. The American Naturalist, 113, 791-833.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Chen DL, Gu SS, Ding BY, Luo ZR (2015) Population structure and distribution pattern of Schima superba in Baishanzu. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry Science and Technology, 35(1), 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈德良, 顾莎莎, 丁炳扬, 骆争荣 (2015) 百山祖木荷的种群结构与分布格局. 浙江林业科技, 35(1), 1-7.] | |
| [4] | Chen XR, Li L, Xia JT, Yang X, Wang W, Ding BY (2012) Population structure and distribution of Fagus lucida in the Baishanzu forest. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 29, 647-654. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈小荣, 李乐, 夏家天, 杨旭, 王伟, 丁炳扬 (2012) 百山祖亮叶水青冈种群结构和分布格局. 浙江农林大学学报, 29, 647-654.] | |
| [5] |
Dai D, Xing H, Yang JR, Liu YJ, Cai HM, Liu Y (2021) Advances in mechanisms of rare species maintenance and plant-soil feedback in plant communities. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1687-1699. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[戴冬, 邢华, 杨佳绒, 刘雅静, 蔡焕满, 刘宇 (2021) 植物群落稀有种维持机制与土壤反馈的研究进展. 生物多样性, 29, 1687-1699.]
DOI |
|
| [6] | Ding BY, Chen DL, Luo ZR, Chen XR, Hu RY, Ye ZL (2013) Zhejiang Baishanzu Forest Dynamics Plot:Tree Species and Their Distribution Patterns. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [丁炳扬, 陈德良, 骆争荣, 陈小荣, 胡仁勇, 叶珍林 (2013) 浙江百山祖森林动态样地: 树种及其分布格局. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [7] | Ding SY, Song YC (2004) Research advances in vegetation dynamic of evergreen broad-leaved forest. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24, 1769-1779. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [丁圣彦, 宋永昌 (2004) 常绿阔叶林植被动态研究进展. 生态学报, 24, 1769-1779.] | |
| [8] |
Huang YX, Xu X, Zhang LX, Song Y, Luo ZR (2016) Ten-years period of grass and small woody plant dynamics in a 5-ha evergreen forest plot in Baishanzu, Zhejiang Province. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1353-1363. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[黄云霞, 徐萱, 张莉芗, 宋玥, 骆争荣 (2016) 百山祖常绿阔叶林灌草层物种组成和分布的10年动态. 生物多样性, 24, 1353-1363.]
DOI |
|
| [9] | Hubbell SP, Foster RB (1986) Commonness and rarity in a neotropical forest:Implications for tropical tree conservation. In: Conservation Biology: Science of Scarcity and Diversity (ed. Soulé ME), pp. 205-231. Sinauer Press, Sunderland. |
| [10] | Jin XF, Ding BY, Zheng CZ, Ye ZL, Chen XR (2004) The floristic analysis of seed plants in Baishanzu Nature Reserve from Zhejiang Province. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 26, 605-618. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [金孝锋, 丁炳扬, 郑朝宗, 叶珍林, 陈小荣 (2004) 浙江百山祖自然保护区种子植物区系分析. 云南植物研究, 26, 605-618.] | |
| [11] |
Kong FH, Chen XR, Zhang MH, Liu Y, Jiang S, Chisholm RA, He FL (2023) Pioneer tree species accumulate higher neighbourhood diversity than late-successional species in a subtropical forest. Forest Ecology and Management, 531, 120740.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Linares-Palomino R, Ponce Alvarez SI (2005) Tree community patterns in seasonally dry tropical forests in the Cerros de Amotape Cordillera, Tumbes, Peru. Forest Ecology and Management, 209, 261-272.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Luo ZR, Mi XC, Chen XR, Ye ZL, Ding BY (2012) Density dependence is not very prevalent in a heterogeneous subtropical forest. Oikos, 121, 1239-1250.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Ma KP (2008) Large scale permanent plots: Important platform for long term research on biodiversity in forest ecosystem. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32, 237. (in Chinese) |
|
[马克平 (2008) 大型固定样地: 森林生物多样性定位研究的平台. 植物生态学报, 32, 237.]
DOI |
|
| [15] | Ma KP (2011) Assessing progress of biodiversity conservation with monitoring approach. Biodiveristy Science, 19, 125-126. (in Chinese) |
|
[马克平 (2011) 监测是评估生物多样性保护进展的有效途径. 生物多样性, 19, 125-126.]
DOI |
|
| [16] | Ma KP, Mi XC, Zhu L, Du XJ, Xu XH, Liu YN, Feng G, Cao M, Lin LX, Jiang MX, Dang HS, Hao ZQ, Jin GZ, Li XK, Ni HW, Sang WG, Tian SY, Wang XH, Xu K, Ye WH, Yu MJ, Zeng FP (2019) Chinese Forest Biodiversity Monitoring Networks:Biodiversity Science Synthesis Platform. In: Change and Its Effects of Ecosystems in China (ed. Fu BJ), pp. 251-278. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平, 米湘成, 朱丽, 杜晓军, 徐学红, 刘忆南, 冯刚, 曹敏, 林露湘, 江明喜, 党海山, 郝占庆, 金光泽, 李先琨, 倪宏伟, 桑卫国, 田松岩, 王希华, 许琨, 叶万辉, 于明坚, 曾馥平 (2019) 中国森林生物多样性监测网络:生物多样性科学综合研究平台. 见: 中国生态系统变化及效应(傅伯杰主编), 251-278页. 高等教育出版社: 北京(傅伯杰主编).] | |
| [17] |
Matthews TJ, Triantis KA, Whittaker RJ, Guilhaumon F (2019) sars: An R package for fitting, evaluating and comparing species-area relationship models. Ecography, 42, 1446-1455.
DOI |
| [18] |
Mi XC, Guo J, Hao ZQ, Xie ZQ, Guo K, Ma KP (2016) Chinese forest biodiversity monitoring: Scientific foundations and strategic planning. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1203-1219. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[米湘成, 郭静, 郝占庆, 谢宗强, 郭柯, 马克平 (2016) 中国森林生物多样性监测: 科学基础与执行计划. 生物多样性, 24, 1203-1219.]
DOI |
|
| [19] |
Mi XC, Wang XG, Shen GC, Liu XB, Song XY, Qiao XJ, Feng G, Yang J, Mao ZK, Xu XH, Ma KP (2022) Chinese Forest Biodiversity Monitoring Network (CForBio): Twenty years of exploring community assembly mechanisms and prospects for future research. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22504. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[米湘成, 王绪高, 沈国春, 刘徐兵, 宋晓阳, 乔秀娟, 冯刚, 杨洁, 毛子昆, 徐学红, 马克平 (2022) 中国森林生物多样性监测网络: 二十年群落构建机制探索的回顾与展望. 生物多样性, 30, 22504.]
DOI |
|
| [20] | Pan X, Zhou RF, Gu SS, Xia JT, Wang DD, Ding BY (2013) Structure and distribution pattern of Cyclobalanopsis multinervis population in an evergreen broad-leaved forest in Baishanzu. Subtropical Plant Science, 42, 227-232. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[潘霞, 周荣飞, 顾莎莎, 夏家天, 王丹丹, 丁炳扬 (2013) 百山祖北坡常绿阔叶林多脉青冈种群结构和分布格局. 亚热带植物科学, 42, 227-232.]
DOI |
|
| [21] | R Core Team (2022) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/. (accessed on 2023-09-15) |
| [22] |
Shen GC, He FL, Waagepetersen R, Sun IF, Hao ZQ, Chen ZS, Yu MJ (2013) Quantifying effects of habitat heterogeneity and other clustering processes on spatial distributions of tree species. Ecology, 94, 2436-2443.
PMID |
| [23] | Song YC, Chen XY, Wang XH (2005) Studies on evergreen broad-leaved forests of China: A retrospect and prospect. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), 119(1), 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋永昌, 陈小勇, 王希华 (2005) 中国常绿阔叶林研究的回顾与展望. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), 119(1), 1-8.] | |
| [24] | Song YC, Wang XH, Yan ER (2013) Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest in China: Classification, Ecology, Conservation. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [宋永昌, 王希华, 闫恩荣 (2013) 中国常绿阔叶林: 分类·生态·保育. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [25] |
Song YC, Yan ER, Song K (2015) Synthetic comparison of eight dynamics plots in evergreen broadleaf forests, China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 139-148. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[宋永昌, 阎恩荣, 宋坤 (2015) 中国常绿阔叶林8大动态监测样地植被的综合比较. 生物多样性, 23, 139-148.]
DOI |
|
| [26] |
Tjørve E (2003) Shapes and functions of species-area curves: A review of possible models. Journal of Biogeography, 30, 827-835.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Wang W, Luo ZR, Zhou RF, Xu DM, Ai JG, Ding BY (2011) Habitat associations of woody plant species in Baishanzu subtropical broad-leaved evergreen forest. Biodiversity Science, 19, 134-142. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[王伟, 骆争荣, 周荣飞, 许大明, 哀建国, 丁炳扬 (2011) 百山祖常绿阔叶林木本植物的生境相关性分析. 生物多样性, 19, 134-142.]
DOI |
|
| [28] |
Wiegand T, Moloney KA (2004) Rings, circles, and null-models for point pattern analysis in ecology. Oikos, 104, 209-229.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Wu ZY (1980) Vegetation of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [吴征镒 (1980) 中国植被. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [30] | Wu ZY, Sun H, Zhou ZK, Li DZ, Peng H (2011) Floristics of Seed Plants from China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [吴征镒, 孙航, 周浙昆, 李德铢, 彭华 (2011) 中国种子植物区系地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [31] | Wu ZY, Zhou ZK, Li DZ, Peng H, Sun H (2003) The areal-types of the world families of seed plants. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 25, 245-257. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴征镒, 周浙昆, 李德铢, 彭华, 孙航 (2003) 世界种子植物科的分布区类型系统. 云南植物研究, 25, 245-257.] | |
| [32] | Wu YG, Ye ZL, Zhou RF, Yang H, Luo ZR (2016) Niche of dominant species populations in an evergreen broad-leaved forest in Baishanzu. Guihaia, 36, 186-192. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴友贵, 叶珍林, 周荣飞, 杨辉, 骆争荣 (2016) 百山祖常绿阔叶林优势种群的生态位. 广西植物, 36, 186-192.] | |
| [33] |
Xie FL, Zhou Q, Shi H, Shu X, Zhang KR, Li T, Feng SY, Zhang QF, Dang HS (2019) Species composition and community characteristics of a 25 ha forest dynamics plot in deciduous broad-leaved forest, Qinling Mountains, north-central China. Biodiversity Science, 27, 439-448. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[谢峰淋, 周全, 史航, 舒枭, 张克荣, 李涛, 冯水园, 张全发, 党海山 (2019) 秦岭落叶阔叶林25 ha森林动态监测样地物种组成与群落特征. 生物多样性, 27, 439-448.]
DOI |
|
| [34] | Xiong XH, Gao M, Wu QL, Fang T, Ding BY (2014) Canonical correspondence analysis on relationships between herbage distribution and environmental factors in the Xingangshan Subtropical Forest Biodiversity Monitoring Site A, Jiangxi Province. China Ecological Science, 33, 474-479. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [熊先华, 高末, 吴庆玲, 方腾, 丁炳扬 (2014) 江西新岗山亚热带森林生物多样性监测样地A草本植物分布与环境关系的典范对应分析. 生态科学, 33, 474-479.] | |
| [35] | Xu M, Luo ZR, Yu MJ, Ding BY, Wu YG (2007) Floristic composition and community structure of mid-montane evergreen broad-leaved forest in north slope of Baishanzu Mountain. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences), 33, 450-457. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐敏, 骆争荣, 于明坚, 丁炳扬, 吴友贵 (2007) 百山祖北坡中山常绿阔叶林的物种组成和群落结构. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 33, 450-457.] | |
| [36] |
Yang QS, Ma ZP, Xie YB, Zhang ZG, Wang ZH, Liu HM, Li P, Zhang N, Wang DL, Yang HB, Fang XF, Yan ER, Wang XH (2011) Community structure and species composition of an evergreen broad-leaved forest in Tiantong’s 20 ha dynamic plot, Zhejiang Province, eastern China. Biodiversity Science, 19, 215-223. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[杨庆松, 马遵平, 谢玉彬, 张志国, 王樟华, 刘何铭, 李萍, 张娜, 王达力, 杨海波, 方晓峰, 阎恩荣, 王希华 (2011) 浙江天童20 ha常绿阔叶林动态监测样地的群落特征. 生物多样性, 19, 215-223.]
DOI |
|
| [37] | Ye WH, Cao HL, Huang ZL, Lian JY, Wang ZG, Li L, Wei SG, Wang ZM (2008) Community structure of a 20 hm2 lower subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest plot in Dinghushan, China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32, 274-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[叶万辉, 曹洪麟, 黄忠良, 练琚愉, 王志高, 李林, 魏识广, 王章明 (2008) 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林20公顷样地群落特征研究. 植物生态学报, 32, 274-286.]
DOI |
|
| [38] | Yu JH, Yao FP, Chen XR, Zhou RF, Cheng QB, Ding BY (2003) An introduction to main vegetation types in the Baishanzu National Nature Reserve. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 11, 93-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [余久华, 姚丰平, 陈小荣, 周荣飞, 程秋波, 丁炳扬 (2003) 百山祖自然保护区主要植被类型概述. 热带亚热带植物学报, 11, 93-98.] | |
| [39] |
Zhu Y, Mi XC, Ma KP (2009) A mechanism of plant species coexistence: The negative density-dependent hypothesis. Biodiversity Science, 17, 594-604. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[祝燕, 米湘成, 马克平 (2009) 植物群落物种共存机制: 负密度制约假说. 生物多样性, 17, 594-604.]
DOI |
|
| [40] | Zhu Y, Zhao GF, Zhang LW, Shen GC, Mi XC, Ren HB, Yu MJ, Chen JH, Chen SW, Fang T, Ma KP (2008) Community composition and structure of Gutianshan forest dynamics plot in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest, East China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32, 262-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[祝燕, 赵谷风, 张俪文, 沈国春, 米湘成, 任海保, 于明坚, 陈建华, 陈声文, 方腾, 马克平 (2008) 古田山中亚热带常绿阔叶林动态监测样地——群落组成与结构. 植物生态学报, 32, 262-273.]
DOI |
| [1] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [2] | 仝淼, 王欢, 张文双, 王超, 宋建潇. 重金属污染土壤中细菌抗生素抗性基因分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [3] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [4] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [5] | 时永强, 栾青杉, 单秀娟, 韦超, 赵永松, 孙策策, 金显仕. 长岛南部海域浮游动物多样性周年变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [6] | 倪艳梅, 陈莉, 董志远, 孙德斌, 李宝泉, 王绪敏, 陈琳琳. 黄河三角洲湿地生态修复区大型底栖动物群落结构与生态健康评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [7] | 魏嘉欣, 姜治国, 杨林森, 熊欢欢, 金胶胶, 罗方林, 李杰华, 吴浩, 徐耀粘, 乔秀娟, 魏新增, 姚辉, 余辉亮, 杨敬元, 江明喜. 湖北神农架中亚热带山地落叶阔叶林25 ha动态监测样地群落物种组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [8] | 吴芳芳, 刘娜, 何春梅, 原作强, 郝占庆, 尹秋龙. 秦岭山地木本植物群落结构及多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [9] | 单航, 雷祖培, 郑方东, 韦博良, 仲磊, 于明坚. 2013-2023年浙江乌岩岭次生常绿阔叶林群落动态变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24372-. |
| [10] | 冯嘉谊, 练琚愉, 冯瑜莙, 张东旭, 曹洪麟, 叶万辉. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林群落垂直分层对群落结构及功能的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| [11] | 王兴煜, 孟京辉, 任思远, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林群落生物多样性与地上生物量的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24230-. |
| [12] | 杜晴晴, 任思远, Nicole Tsz Shun Yuan, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林幼树及成树生产力的影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24284-. |
| [13] | 黄骏涵, 余梵冬, 王裕祥, 黄哲, 张铭斯, 房苗, 舒璐, 徐猛, 韦慧, 汪学杰, 顾党恩, 罗思. 花地河中下游外来鱼类入侵现状及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24249-. |
| [14] | 张楚然, 李生发, 李逢昌, 唐志忠, 刘辉燕, 王丽红, 顾荣, 邓云, 张志明, 林露湘. 云南鸡足山亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地木本植物生境关联与群落数量分类[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23393-. |
| [15] | 杨舒涵, 王贺, 陈磊, 廖蓥飞, 严光, 伍一宁, 邹红菲. 松嫩平原异质生境对土壤线虫群落特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23295-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn