



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 388-399. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019007 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019007
江焕1, 张辉1, 龙文兴1,*( ), 方燕山2, 符明期2, 朱孔新3
), 方燕山2, 符明期2, 朱孔新3
收稿日期:2019-01-08
接受日期:2019-03-11
出版日期:2019-04-20
发布日期:2019-06-05
通讯作者:
龙文兴
基金资助:
Huan Jiang1, Hui Zhang1, Wenxing Long1,*( ), Yanshan Fang2, Mingqi Fu2, Kongxin Zhu3
), Yanshan Fang2, Mingqi Fu2, Kongxin Zhu3
Received:2019-01-08
Accepted:2019-03-11
Online:2019-04-20
Published:2019-06-05
Contact:
Wenxing Long
摘要:
金钟藤(Decalobanthus boisianus)是林业有害植物, 其暴发生长和扩散对森林生态系统造成了严重破坏。本文以海南岛48个金钟藤典型分布群落为研究对象, 用方差比率法和贡献定律法探究群落的稳定性; 用χ 2统计量、联结系数(AC)、共同出现百分率(PC)、Ochiai指数和Dice指数分析金钟藤与伴生物种的种间联结关系; 用生态位宽度、生态位相似性系数和生态位重叠指数研究群落中各物种的生态位特征, 以期为金钟藤生物防治的植物物种筛选提供借鉴。结果表明: (1)金钟藤所在48个群落共有156种伴生植物, 其中大戟科、茜草科、桑科、无患子科和樟科植物占优势; (2)群落中优势物种呈正联结关系, 植物种类累积倒数百分比与累积相对频度交点坐标为(44.53, 55.47), 远离稳定交点坐标(20, 80), 说明群落处于不稳定状态; (3)金钟藤与芳槁润楠(Machilus suaveolens)、黄椿木姜子(Litsea variabilis)、岭南山竹子(Garcinia oblongifolia)、显脉杜英(Elaeocarpus dubius)、鸭脚木(Schefflera octophylla)和银柴(Aporusa dioica)都紧密关联, 说明金钟藤与这些物种的资源利用方式较相似; (4)金钟藤的生态位宽度最大, 与伴生物种间的生态位重叠度较高, 但伴生物种间的生态位重叠度较低。金钟藤的入侵导致群落处于不稳定状态, 并与伴生物种间存在激烈的竞争关系。因此, 建议在金钟藤已入侵的群落中大量栽种芳槁润楠、黄椿木姜子、显脉杜英、鸭脚木和银柴, 以遏制其蔓延; 大量栽种翻白叶树(Pterospermum heterophyllum)、海南菜豆树(Radermachera hainanensis)、九节(Psychotria rubra)和肉实树(Sarcosperma laurinum)用于金钟藤入侵群落的植被恢复。
江焕, 张辉, 龙文兴, 方燕山, 符明期, 朱孔新 (2019) 金钟藤入侵群落的种间联结及生态位特征. 生物多样性, 27, 388-399. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019007.
Huan Jiang, Hui Zhang, Wenxing Long, Yanshan Fang, Mingqi Fu, Kongxin Zhu (2019) Interspecific associations and niche characteristics of communities invaded by Decalobanthus boisianus. Biodiversity Science, 27, 388-399. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019007.
| 序号 No. | 种名 Species | 相对频度 Relative frequency (%) | 相对密度 Relative density (%) | 相对显著度 Relative prominence (%) | 重要值 Importance value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 金钟藤 Decalobanthus boisianus | 4.53 | 14.88 | 2.21 | 7.21 |
| 2 | 鸭脚木 Schefflera octophylla | 1.89 | 4.27 | 3.89 | 3.35 |
| 3 | 水锦树 Wendlandia uvariifolia | 1.42 | 2.22 | 1.32 | 1.65 |
| 4 | 黄椿木姜子 Litsea variabilis | 1.89 | 2.09 | 0.72 | 1.57 |
| 5 | 假苹婆 Sterculia lanceolata | 1.79 | 2.09 | 0.56 | 1.48 |
| 6 | 假柿木姜子 Litsea monopetala | 1.13 | 1.41 | 1.63 | 1.39 |
| 7 | 倒吊笔 Wrightia pubescens | 1.32 | 1.58 | 1.24 | 1.38 |
| 8 | 芳槁润楠 Machilus suaveolens | 1.61 | 1.21 | 1.28 | 1.37 |
| 9 | 翻白叶树 Pterospermum heterophyllum | 0.94 | 1.31 | 1.76 | 1.34 |
| 10 | 肉实树 Sarcosperma laurinum | 1.32 | 1.25 | 1.11 | 1.23 |
| 11 | 岭南山竹子 Garcinia oblongifolia | 1.42 | 1.25 | 0.99 | 1.22 |
| 12 | 楝叶吴茱萸 Evodia glabrifolia | 1.04 | 0.64 | 1.87 | 1.18 |
| 13 | 九节 Psychotria rubra | 1.23 | 2.05 | 0.13 | 1.14 |
| 14 | 银柴 Aporusa dioica | 1.61 | 1.31 | 0.43 | 1.11 |
| 15 | 显脉杜英 Elaeocarpus dubius | 1.42 | 0.71 | 1.1 | 1.07 |
| 16 | 海南菜豆树 Radermachera hainanensis | 1.13 | 0.98 | 1.04 | 1.05 |
| 17 | 白楸 Mallotus paniculatus | 1.23 | 0.81 | 1.08 | 1.04 |
表1 金钟藤群落优势种的相对频度、相对密度、相对显著度及重要值
Table 1 Relative frequency, relative density, relative prominence and importance value of dominant plant species in Decalobanthus boisianus community
| 序号 No. | 种名 Species | 相对频度 Relative frequency (%) | 相对密度 Relative density (%) | 相对显著度 Relative prominence (%) | 重要值 Importance value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 金钟藤 Decalobanthus boisianus | 4.53 | 14.88 | 2.21 | 7.21 |
| 2 | 鸭脚木 Schefflera octophylla | 1.89 | 4.27 | 3.89 | 3.35 |
| 3 | 水锦树 Wendlandia uvariifolia | 1.42 | 2.22 | 1.32 | 1.65 |
| 4 | 黄椿木姜子 Litsea variabilis | 1.89 | 2.09 | 0.72 | 1.57 |
| 5 | 假苹婆 Sterculia lanceolata | 1.79 | 2.09 | 0.56 | 1.48 |
| 6 | 假柿木姜子 Litsea monopetala | 1.13 | 1.41 | 1.63 | 1.39 |
| 7 | 倒吊笔 Wrightia pubescens | 1.32 | 1.58 | 1.24 | 1.38 |
| 8 | 芳槁润楠 Machilus suaveolens | 1.61 | 1.21 | 1.28 | 1.37 |
| 9 | 翻白叶树 Pterospermum heterophyllum | 0.94 | 1.31 | 1.76 | 1.34 |
| 10 | 肉实树 Sarcosperma laurinum | 1.32 | 1.25 | 1.11 | 1.23 |
| 11 | 岭南山竹子 Garcinia oblongifolia | 1.42 | 1.25 | 0.99 | 1.22 |
| 12 | 楝叶吴茱萸 Evodia glabrifolia | 1.04 | 0.64 | 1.87 | 1.18 |
| 13 | 九节 Psychotria rubra | 1.23 | 2.05 | 0.13 | 1.14 |
| 14 | 银柴 Aporusa dioica | 1.61 | 1.31 | 0.43 | 1.11 |
| 15 | 显脉杜英 Elaeocarpus dubius | 1.42 | 0.71 | 1.1 | 1.07 |
| 16 | 海南菜豆树 Radermachera hainanensis | 1.13 | 0.98 | 1.04 | 1.05 |
| 17 | 白楸 Mallotus paniculatus | 1.23 | 0.81 | 1.08 | 1.04 |
| 编号 No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0.39 | |||||||||||||||
| 3 | -0.09 | 0.15 | ||||||||||||||
| 4 | 0.26 | 0.83 | 0.33 | |||||||||||||
| 5 | -0.26 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||
| 6 | -0.21 | 1.26 | 0.94 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |||||||||||
| 7 | -0.16 | 0.68 | 0.02 | 5.15 | 0.01 | 2.39 | ||||||||||
| 8 | 0.32 | 1.29 | 0.03 | 1.54 | 0.01 | 2.46 | 0.22 | |||||||||
| 9 | -0.09 | 2.02 | 0.11 | 3.19 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 1.19 | 0.03 | ||||||||
| 10 | -0.16 | 3.48 | 0.49 | 0.95 | 0.05 | 1.46 | 4.88 | 0.02 | 0.01 | |||||||
| 11 | 0.39 | 0.73 | 2.55 | 0.70 | 0.11 | 1.26 | 0.13 | 1.40 | 4.11 | 0.01 | ||||||
| 12 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.62 | 0.99 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.32 | 0.67 | |||||
| 13 | -0.21 | 1.26 | 0.13 | 6.29 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.90 | 0.61 | 0.75 | 0.00 | 0.40 | 1.22 | ||||
| 14 | 0.16 | 4.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 2.80 | 0.06 | 0.35 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 4.03 | 0.13 | 0.12 | |||
| 15 | 0.21 | 1.26 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.66 | 0.06 | 0.96 | 0.75 | 0.00 | 8.30 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.90 | ||
| 16 | -0.16 | 0.68 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 1.69 | 0.06 | 1.43 | 0.22 | 2.92 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 2.39 | 0.35 | 0.06 | |
| 17 | -0.12 | 0.45 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.68 | 0.37 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.49 | 0.59 | 0.27 | 0.01 | 1.46 | 0.98 | 0.00 | 0.15 |
表2 金钟藤群落优势种间χ2统计量检验
Table 2 χ2 correlation test of dominant plant species in Decalobanthus boisianus community
| 编号 No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0.39 | |||||||||||||||
| 3 | -0.09 | 0.15 | ||||||||||||||
| 4 | 0.26 | 0.83 | 0.33 | |||||||||||||
| 5 | -0.26 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||
| 6 | -0.21 | 1.26 | 0.94 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |||||||||||
| 7 | -0.16 | 0.68 | 0.02 | 5.15 | 0.01 | 2.39 | ||||||||||
| 8 | 0.32 | 1.29 | 0.03 | 1.54 | 0.01 | 2.46 | 0.22 | |||||||||
| 9 | -0.09 | 2.02 | 0.11 | 3.19 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 1.19 | 0.03 | ||||||||
| 10 | -0.16 | 3.48 | 0.49 | 0.95 | 0.05 | 1.46 | 4.88 | 0.02 | 0.01 | |||||||
| 11 | 0.39 | 0.73 | 2.55 | 0.70 | 0.11 | 1.26 | 0.13 | 1.40 | 4.11 | 0.01 | ||||||
| 12 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.62 | 0.99 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.32 | 0.67 | |||||
| 13 | -0.21 | 1.26 | 0.13 | 6.29 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.90 | 0.61 | 0.75 | 0.00 | 0.40 | 1.22 | ||||
| 14 | 0.16 | 4.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 2.80 | 0.06 | 0.35 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 4.03 | 0.13 | 0.12 | |||
| 15 | 0.21 | 1.26 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.66 | 0.06 | 0.96 | 0.75 | 0.00 | 8.30 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.90 | ||
| 16 | -0.16 | 0.68 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 1.69 | 0.06 | 1.43 | 0.22 | 2.92 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 2.39 | 0.35 | 0.06 | |
| 17 | -0.12 | 0.45 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.68 | 0.37 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.49 | 0.59 | 0.27 | 0.01 | 1.46 | 0.98 | 0.00 | 0.15 |
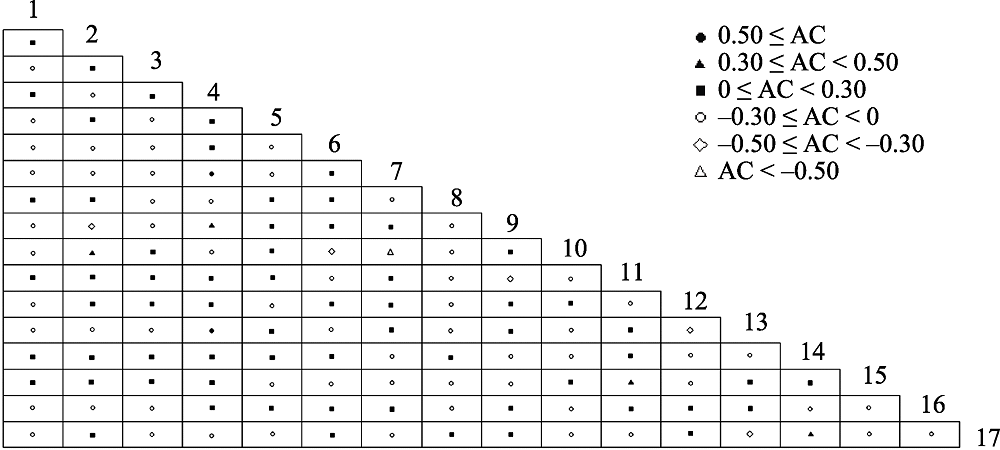
图1 金钟藤群落主要优势种种间联结系数(AC)半矩阵图。物种编号含义见表1。
Fig. 1 Semi-matrix diagram of association coefficients (AC) of dominant plant species in Decalobanthus boisianus community. Species codes are the same as in Table 1.
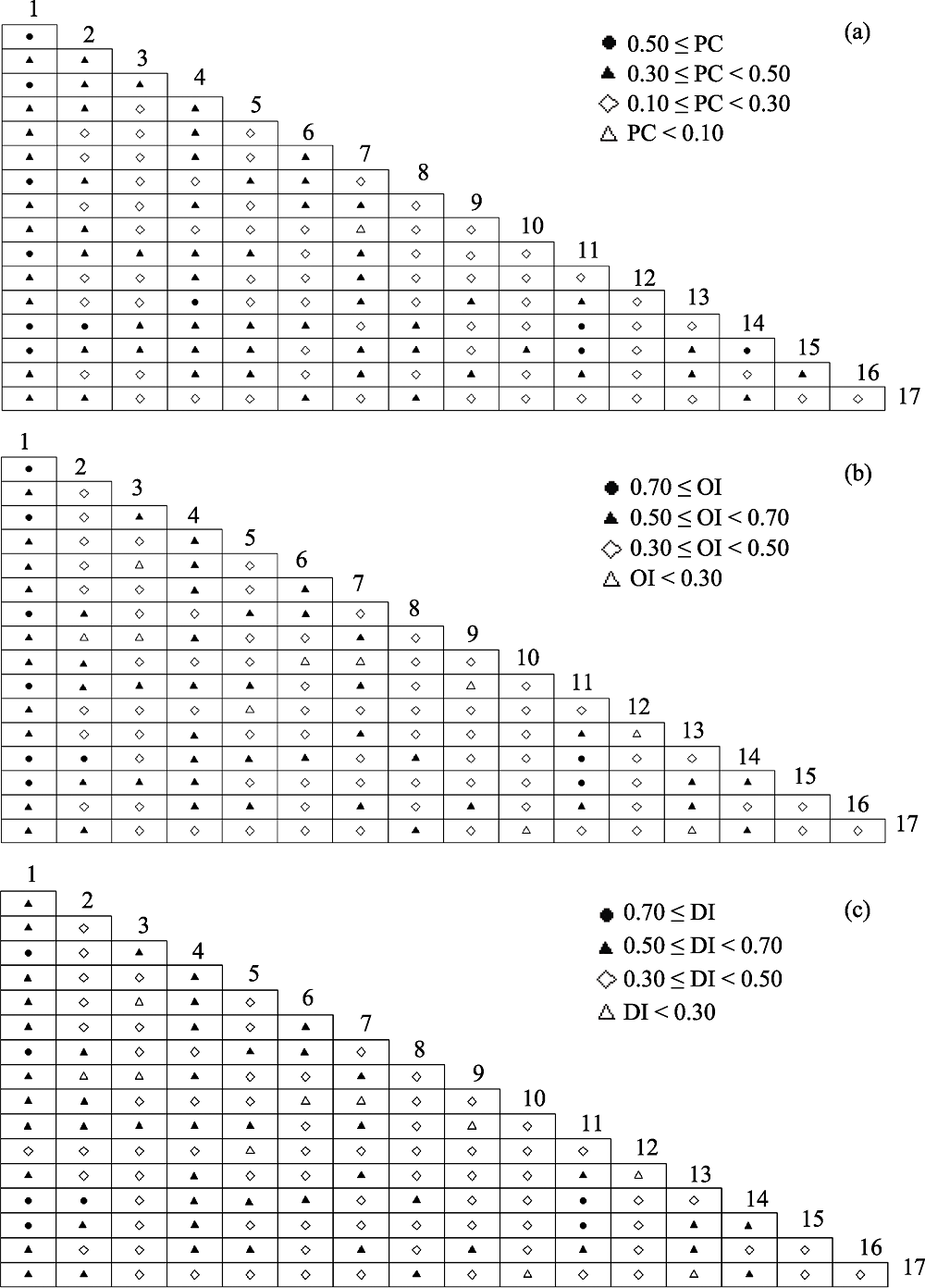
图2 金钟藤群落主要优势种共同出现百分率(PC)、Ochiai指数(OI)和Dice指数(DI)半矩阵图。物种编号含义见表1。
Fig. 2 Semi-matrix diagram of co-occurence rate (PC), Ochiai index (OI), and Dice index (DI) of dominant species in Decalobanthus boisianus community. Species codes are the same as in Table 1.
| 编号 No. | 生态位 宽度Niche width | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.83 | - | 0.42 | 0.32 | 0.51 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 0.52 | 0.36 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.32 | 0.40 | 0.54 | 0.51 | 0.37 | 0.39 |
| 2 | 2.82 | 0.54 | - | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.52 | 0.09 | 0.41 | 0.27 | 0.33 | 0.17 | 0.42 | 0.28 | 0.19 | 0.31 |
| 3 | 2.58 | 0.45 | 0.34 | - | 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.23 | 0.16 |
| 4 | 3.04 | 0.64 | 0.25 | 0.33 | - | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.38 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 0.18 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.50 | 0.34 | 0.29 | 0.37 | 0.25 |
| 5 | 2.61 | 0.45 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.29 | - | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.25 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.15 |
| 6 | 2.69 | 0.41 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.27 | 0.17 | - | 0.25 | 0.34 | 0.20 | 0.14 | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.19 | 0.34 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.24 |
| 7 | 2.47 | 0.35 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.42 | 0.24 | 0.11 | - | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.09 | 0.24 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.22 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 0.26 |
| 8 | 3.07 | 0.63 | 0.68 | 0.42 | 0.25 | 0.11 | 0.28 | 0.11 | - | 0.24 | 0.40 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.40 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.30 |
| 9 | 2.55 | 0.51 | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.27 | - | 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.22 | 0.45 | 0.16 | 0.27 | 0.46 | 0.28 |
| 10 | 2.68 | 0.54 | 0.56 | 0.26 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.58 | 0.20 | - | 0.23 | 0.33 | 0.17 | 0.24 | 0.34 | 0.22 | 0.14 |
| 11 | 2.78 | 0.37 | 0.17 | 0.35 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.23 | - | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.36 | 0.49 | 0.22 | 0.24 |
| 12 | 2.57 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.39 | 0.31 | 0.11 | 0.54 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.13 | - | 0.12 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.23 |
| 13 | 2.67 | 0.50 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.56 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.23 | 0.61 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.12 | - | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.46 | 0.17 |
| 14 | 3.10 | 0.62 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 0.37 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.20 | 0.43 | 0.14 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.37 | 0.13 | - | 0.46 | 0.29 | 0.34 |
| 15 | 3.09 | 0.56 | 0.28 | 0.38 | 0.28 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.31 | 0.38 | 0.56 | 0.35 | 0.16 | 0.43 | - | 0.36 | 0.33 |
| 16 | 2.76 | 0.51 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.47 | 0.38 | 0.19 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.55 | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.22 | 0.53 | 0.34 | 0.43 | - | 0.29 |
| 17 | 2.69 | 0.46 | 0.28 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.36 | 0.28 | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.17 | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.37 | - |
表3 金钟藤群落主要优势种间的生态位相似性比例(对角线上)和生态位重叠指数(对角线下)
Table 3 Niche similarity (above the diagonal) and niche overlap (below the diagonal) of dominant plant species in Decalobanthus boisianus community
| 编号 No. | 生态位 宽度Niche width | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.83 | - | 0.42 | 0.32 | 0.51 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 0.52 | 0.36 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.32 | 0.40 | 0.54 | 0.51 | 0.37 | 0.39 |
| 2 | 2.82 | 0.54 | - | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.52 | 0.09 | 0.41 | 0.27 | 0.33 | 0.17 | 0.42 | 0.28 | 0.19 | 0.31 |
| 3 | 2.58 | 0.45 | 0.34 | - | 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.23 | 0.16 |
| 4 | 3.04 | 0.64 | 0.25 | 0.33 | - | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.38 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 0.18 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.50 | 0.34 | 0.29 | 0.37 | 0.25 |
| 5 | 2.61 | 0.45 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.29 | - | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.25 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.15 |
| 6 | 2.69 | 0.41 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.27 | 0.17 | - | 0.25 | 0.34 | 0.20 | 0.14 | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.19 | 0.34 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.24 |
| 7 | 2.47 | 0.35 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.42 | 0.24 | 0.11 | - | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.09 | 0.24 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.22 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 0.26 |
| 8 | 3.07 | 0.63 | 0.68 | 0.42 | 0.25 | 0.11 | 0.28 | 0.11 | - | 0.24 | 0.40 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.40 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.30 |
| 9 | 2.55 | 0.51 | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.27 | - | 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.22 | 0.45 | 0.16 | 0.27 | 0.46 | 0.28 |
| 10 | 2.68 | 0.54 | 0.56 | 0.26 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.58 | 0.20 | - | 0.23 | 0.33 | 0.17 | 0.24 | 0.34 | 0.22 | 0.14 |
| 11 | 2.78 | 0.37 | 0.17 | 0.35 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.23 | - | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.36 | 0.49 | 0.22 | 0.24 |
| 12 | 2.57 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.39 | 0.31 | 0.11 | 0.54 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.13 | - | 0.12 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.23 |
| 13 | 2.67 | 0.50 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.56 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.23 | 0.61 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.12 | - | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.46 | 0.17 |
| 14 | 3.10 | 0.62 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 0.37 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.20 | 0.43 | 0.14 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.37 | 0.13 | - | 0.46 | 0.29 | 0.34 |
| 15 | 3.09 | 0.56 | 0.28 | 0.38 | 0.28 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.31 | 0.38 | 0.56 | 0.35 | 0.16 | 0.43 | - | 0.36 | 0.33 |
| 16 | 2.76 | 0.51 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.47 | 0.38 | 0.19 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.55 | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.22 | 0.53 | 0.34 | 0.43 | - | 0.29 |
| 17 | 2.69 | 0.46 | 0.28 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.36 | 0.28 | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.17 | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.37 | - |
| [1] |
Callaway RM, Maron J (2006) What have exotic plant invasions taught us over the past 20 years. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 21, 369-374.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Cárdenas RE, Valencia R, Kraft NJB, Argoti A, Dangles O, Swenson N (2014) Plant traits predict inter- and intraspecific variation in susceptibility to herbivory in a hyperdiverse neotropical rain forest tree community. Journal of Ecology, 102, 939-952.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Chai ZZ, Wang DX, Zhang LN, Zhang Y, Huang QP, Wu H (2012) Niche characteristics of main plant populations in natural Pinus tabulaeformis communities in Qinling Mountains, Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 31, 1917-1923. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 柴宗政, 王得祥, 张丽楠, 张洋, 黄青平, 吴昊 (2012) 秦岭山地天然油松群落主要植物种群生态位特征. 生态学杂志, 31, 1917-1923.] | |
| [4] | Chen YK, Yang XB, Li DH, Nong SQ, Lü XB, Lü JJ, Yang M, Li XC (2011) Interspecific associations among dominant plant populations in Keteleeria hainanensis communities in Bawangling, Hainan Island. Plant Science Journal, 29, 278-287. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈玉凯, 杨小波, 李东海, 农寿千, 吕晓波, 吕洁杰, 杨民, 李小成 (2011) 海南霸王岭海南油杉群落优势种群的种间联结性研究. 植物科学学报, 29, 278-287.] | |
| [5] | Chen T, Liu WL, Zhang CB, Wang J (2012) Effects of Solidago canadensis invasion on dynamics of native plant communities and their mechanisms. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 36, 253-261. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈彤, 刘文莉, 张崇邦, 王江 (2012) 加拿大一枝黄花入侵对本土植物群落动态的影响及其机制. 植物生态学报, 36, 253-261. ] | |
| [6] | Fang F, Hu YK, Zhang W, Gong YM, Liu YY, Yang XJ (2012) Numerical analysis of inter-specific relationships in alpine steppe community in Bayanbulak. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 1898-1906. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 房飞, 胡玉昆, 张伟, 公延明, 柳妍妍, 杨秀娟 (2012) 高寒草原植物群落种间关系的数量分析. 生态学报, 32, 1898-1906.] | |
| [7] | Finch D (2012) Climate Change in Grasslands, Shrublands and Deserts of the Interior American West: A Review and Needs Assessment. USDA Forest Service Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fort Collins. |
| [8] | Gao RM, Shi XD, Guo YD (2012) Community stability evaluation of riparian forest of the upper reaches of Wenyuhe in Shanxi, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 36, 491-503. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 高润梅, 石晓东, 郭跃东 (2012) 山西文峪河上游河岸林群落稳定性评价. 植物生态学报, 36, 491-503.] | |
| [9] |
Gleason HA (1926) The individualistic concept of the plant association. Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club, 53, 7-26.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Godron M (1972) Some aspects of heterogeneity in grasslands of Cantal. Statistical Ecology, 3, 397-415. |
| [11] | Greig-Smith P (1983) Quantitative Plant Ecology, 3rd edn. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford. |
| [12] | Guo LJ (2011) Impacts to the interspecies association and stability of native community invaded by an exotic plant Conyza sumatrensis. Subtropical Plant Science, 40(2), 18-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭连金 (2011) 苏门白酒草对乡土植物群落种间联结性及稳定性的影响. 亚热带植物科学, 40(2), 18-23.] | |
| [13] | Guo LJ, Wang T (2009) Impact of invasion of exotic plant Alternanthera philoxeroides on interspecies association and stability of native plant community. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 17, 851-856. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭连金, 王涛 (2009) 空心莲子草入侵对乡土植物群落种间联结性及稳定性的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 17, 851-856.] | |
| [14] | Guo YX, Hu YN, Kong LT, Wang DX, Yang GH (2011) Interspecific association and correlation of main plant species in subalpine meadow of Zibai Mountain. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 30, 1775-1780. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭垚鑫, 胡有宁, 孔令童, 王得祥, 杨改河 (2011) 紫柏山亚高山草甸群落的种间关联和相关分析. 生态学杂志, 30, 1775-1780.] | |
| [15] | Hao JF, Li Y, Qi JQ, Pei ZL, Huang YJ, Jiang Q, Chen Y (2016) Effects of anthropogenic disturbances on the species diversity and niche of the dominant populations in a Castanopsis fargesii secondary forest community in Bifengxia, Sichuan. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 7678-7688. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郝建锋, 李艳, 齐锦秋, 裴曾莉, 黄雨佳, 蒋倩, 陈亚 (2016) 人为干扰对碧峰峡栲树次生林群落物种多样性及其优势种群生态位的影响. 生态学报, 36, 7678-7688.] | |
| [16] | Hong SS, Miao CC, Fang BJ, Hu RY, Ding BY (2008) On species diversity, niche breath and interspecies association in communities invaded by Spermacoce latifolia Zhejiang Province. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 26, 501-508. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 洪思思, 缪崇崇, 方本基, 胡仁勇, 丁炳扬 (2008) 浙江省阔叶丰花草入侵群落物种多样性、生态位及种间联结研究. 武汉植物学研究, 26, 501-508.] | |
| [17] | Hu XC, Gao HH (2008) General situation and protection of tropical natural forests in Hainan Island. Modern Agriculture Science and Technology, ( 22), 76-77. (in Chinese) |
| [ 胡小婵, 高宏华 (2008) 海南岛热带天然林概况及其保护. 现代农业科技, ( 22), 76-77.] | |
| [18] |
Huang QQ, Shen YD, Li XX, Fan ZW, Li MG, Cheng HT (2013) Native expanding Merremia boisiana is not more allelopathic than its non-expanding congener M. vitifolia in the expanded range in Hainan. American Journal of Plant Sciences, 4, 774-779.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Huang QQ, Shen YD, Fan ZW, Li XX, Song X, Cheng HT, Hou YP (2013) Effects of soil from different forest types in Wuzhi Mountain on the seedling growth of Merremia boisiana. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 22, 95-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄乔乔, 沈奕德, 范志伟, 李晓霞, 宋鑫, 程汉亭, 侯玉平 (2013) 五指山不同林型土壤对金钟藤幼苗生长的影响. 生态环境学报, 22, 95-99.] | |
| [20] | Huang XT, Wang SX, Huang BJ, Yin H, Cui KF, Zhao W, Fan YG, Gu DF (2015) Analyses of community stability and inter-specific associations between the rare plant Phyllitis scolopendrium and its associated species. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 80-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄祥童, 王绍先, 黄炳军, 尹航, 崔凯峰, 赵伟, 范宇光, 顾德峰 (2015) 珍稀植物对开蕨与其伴生物种的联结性及群落稳定性. 生态学报, 35, 80-90.] | |
| [21] |
Hubalek Z (1982) Coeffident of association and similarity based on binary data: An evaluation. Biological Reviews, 57, 669-689.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Hutchinson GE (1957) Concluding remarks: Cold spring harbor symposium of quantitative biology. Quantitative Biology, 22, 415-427.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Kang B, Liu SR, Zhang GJ, Chang JG, Wen YG, Ma JM, Hao WF (2006) Carbon accumulation and distribution in Pinus massoniana and Cunninghamia lanceolata mixed forest ecosystem in Daqingshan, Guangxi of China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26, 1320-1329. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 康冰, 刘世荣, 张广军, 常建国, 温远光, 马姜明, 郝文芳 (2006) 广西大青山南亚热带马尾松、杉木混交林生态系统碳素积累和分配特征. 生态学报, 26, 1320-1329.] | |
| [24] | Levins R (1968) Evolution in Changing Environments: Some Theoretical Explorations. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [25] | Li JM, Xie F, Chen CJ, Zhang SY, Xiao RH, Zhao DZ (2001) Interspecific association of dominant species in Betula luminifera natural forest communities of Shaowu, Fujian Province. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 12, 168-170. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李建民, 谢芳, 陈存及, 张思玉, 肖日红, 赵大洲 (2001) 光皮桦天然林群落优势种群的种间联结性研究. 应用生态学报, 12, 168-170.] | |
| [26] | Li L, Xu ZF, Wei X, Cao HL, Su J, Ye WH (2008) Physiological compare Merremia boisiana with Pueraria lobata under drought stress and rewatering conditions. Guihaia, 28, 806-810. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李玲, 徐志防, 韦霄, 曹洪麟, 粟娟, 叶万辉 (2008) 金钟藤和葛藤在干旱与复水条件下的生理比较. 广西植物, 28, 806-810.] | |
| [27] | Li SF, Liu WD, Su JR, Zhang ZJ (2011) Niches and interspecific associations of dominant tree populations at different restoration stages of monsoonal broad-leaved evergreen forest. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 30, 508-515. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李帅锋, 刘万德, 苏建荣, 张志钧 (2011) 季风常绿阔叶林不同恢复阶段乔木优势种群生态位和种间联结. 生态学杂志, 30, 508-515.] | |
| [28] | Li XX, Huang QQ, Fan ZW, Shen YD, Cheng HT, Liu LZ (2014) Chemical compositions and allelopathic potential of volatile oil from Merremia boisiana. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 35, 1643-1647. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李晓霞, 黄乔乔, 范志伟, 沈奕德, 程汉亭, 刘丽珍 (2014) 金钟藤叶挥发油化学成分分析及其化感潜力研究. 热带作物学报, 35, 1643-1647.] | |
| [29] | Li YF, Tie J, Zhang GP, Guo H (2014) Niche characteristics of an artificial Pinus tabuliformis forest in Manghe National Nature Reserve of Shanxi. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33, 2905-2912. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李燕芬, 铁军, 张桂萍, 郭华 (2014) 山西蟒河国家级自然保护区人工油松林生态位特征. 生态学杂志, 33, 2905-2912.] | |
| [30] | Liang WS, Fang TS, Yu HB, Wang Z (2012) Risk analysis of Merremia boisiana in China. Guangdong Forestry Science and Technology, 26(3), 42-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 梁玮莎, 方天松, 余海滨, 王忠 (2012) 金钟藤在中国的风险性分析. 广东林业科技, 26(3), 42-45.] | |
| [31] | Liu H, Du RW, Wang Y, Chen YL, Wu YK, Yuan L (2017) Effects of Eupatorium adenophorum on interspecific association and the stability of companion species in Liangshan Prefecture of Sichuan Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 5031-5038. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘海, 杜如万, 王勇, 陈玉蓝, 吴叶宽, 袁玲 (2017) 紫茎泽兰对四川省凉山州共生植物种间联结性及稳定性的影响. 生态学报, 37, 5031-5038.] | |
| [32] | Liu W, Cao W (2011) Niche characteristics of main plant species in spruce-fir forests in Changbai Mountains. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 30, 1766-1774. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘巍, 曹伟 (2011) 长白山云冷杉群落主要种群生态位特征. 生态学杂志, 30, 1766-1774.] | |
| [33] | Liu YH, Zhao HX (2000) Advances in theory of disturbance and species diversity preservation. Journal of Beijing Normal University, 22(4), 101-105. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘艳红, 赵惠勋 (2000) 干扰与物种多样性维持理论研究进展. 北京林业大学学报, 22(4), 101-105.] | |
| [34] | Liu YH, Gao H, Zhang LH, Chen LP, Zhao NX, Gao YB (2010) Comparative analysis of inter-specific association within the Stipa grandis-S. krylovii community in typical steppe of Inner Mongolia, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 34, 1016-1024. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘珏宏, 高慧, 张丽红, 陈丽萍, 赵念席, 高玉葆 (2010) 内蒙古锡林郭勒草原大针茅-克氏针茅群落的种间关联特征分析. 植物生态学报, 34, 1016-1024.] | |
| [35] | Pan G, Zhang HP, Pan D (2017) Interspecific associations of dominant plant populations in a mid-subtropical Choerospondias axillaris forest. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36, 892-901. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 潘高, 张合平, 潘登 (2017) 中亚热带南酸枣林优势种群的种间联结性. 生态学杂志, 36, 892-901.] | |
| [36] | Peng SL, Zhou HC, Guo SC, Huang ZL (1999) Studies on the changes in interspecific association of zonal vegetation in Dinghushan. Acta Botanica Sinica, 41, 1239-1244. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 彭少麟, 周厚诚, 郭少聪, 黄忠良 (1999) 鼎湖山地带性植被种间联结变化研究. 植物学报, 41, 1239-1244.] | |
| [37] | Pianka ER (1973) The structure of lizzard communities. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 89, 1561-1565. |
| [38] |
Pimentel D, Lach L, Zuniga R, Morrison D (2000) Environmental and economic costs of nonindigenous species in the United States. BioScience, 50, 53-65.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Rosenthal G (2003) Selecting target species to evaluate the success of wet grassland restoration. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 98, 227-246.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Roxburgh SH, Chesson P (1998) A new method for detecting species associations with spatially autocorrelated data. Ecology, 79, 2180-2192.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Schluter D (1984) A variance test for detecting species associations, with some example applications. Ecology, 65, 998-1005.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Schoener TW (1974) Resource partitioning in ecological communities. Science, 185, 27-39.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Shi ZM, Cheng RM, Liu SR (1999) Niche characteristics of plant populations in deciduous broad-leaved forest in Baotianman. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 10, 265-269. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 史作民, 程瑞梅, 刘世荣 (1999) 宝天曼落叶阔叶林种群生态位特征. 应用生态学报, 10, 265-269.] | |
| [44] | Tang JM, Ai XR, Yi YM, Li L, Xu HM, Song YL (2012) Niche dynamics during restoration process for the dominant tree species in montane mixed evergreen and deciduous broadleaved forests at Mulinzi of southwest Hubei. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 6334-6342. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 汤景明, 艾训儒, 易咏梅, 李玲, 徐红梅, 宋亚丽 (2012) 鄂西南木林子常绿落叶阔叶混交林恢复过程中优势树种生态位动态. 生态学报, 32, 6334-6342.] | |
| [45] | Thevathasan NV, Gordon AM (2004) Ecology of tree intercropping systems in the north temperate region: Experiences from southern Ontario, Canada. Agroforestry Systems, 61, 257-268. |
| [46] | Tie J, Li YF, Wang X, Bai FL, Cui FT, Jin S (2015) Species diversity of forest community in Macaca mulatta habitat in Lishan National Nature Reserve, Shanxi. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34, 3009-3015. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 铁军, 李燕芬, 王霞, 白凤麟, 崔方天, 金山 (2015) 山西历山国家级自然保护区猕猴栖息地森林群落物种多样性. 生态学杂志, 34, 3009-3015.] | |
| [47] | Tong GJ, Chen MR, Yu HB (2005) Preliminary report on the damage of Merremia boisiana. Forest Pest and Disease, 24(3), 17-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 童国建, 陈沐荣, 余海滨 (2005) 金钟藤的危害性初报. 中国森林病虫, 24(3), 17-18.] | |
| [48] |
Walker BH (1995) Conserving biological diversity through ecosystem resilience. Conservation Biology, 9, 747-752.
DOI URL |
| [49] | Wang BS, Li MG, Liao WB (2005) Geographical distribution of Merremia boisiana. Ecology and Environment, 14, 451-454. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王伯荪, 李鸣光, 廖文波 (2005) 金钟藤的地理分布. 生态环境, 14, 451-454.] | |
| [50] | Wang BS, Peng SL (1985) Studies on the measuring techniques of interspecific association of lower-subtropical evergreen-broadleaved forests. I. The exploration and the revision on the measuring formulas of interspecific association. Acta Phytoecologica et Geobotanica Sinica, 9, 32-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王伯荪, 彭少麟 (1985) 南亚热带常绿阔叶林种间联结测定技术研究. I. 种间联结测式的探讨与修正. 植物生态学与地植物学丛刊, 9, 32-43.] | |
| [51] | Wang BS, Peng SL, Li DJ, Zhou T (2009) Research progress on Merremia boisiana. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 28, 2360-2365. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王伯荪, 彭少麟, 李代江, 周婷 (2009) 金钟藤研究述评. 生态学杂志, 28, 2360-2365.] | |
| [52] | Wang BS, Qiu HX, Liao WB, Li MG, Ding MY, Peng SL (2007) Revision and additional notes on Merremia boisiana and M. boisiana var. fulvopilosa (Convolvulaceae). Guihaia, 27, 527-536. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王伯荪, 丘华兴, 廖文波, 李鸣光, 丁明艳, 彭少麟 (2007) 金钟藤分类考证及补充描述. 广西植物, 27, 527-536.] | |
| [53] | Wu HF, Song LJ, Du F, Hao WF (2017) Niche of main populations and environmental interpretation in grassland of Loess Plateau hilly region, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28, 3494-3504. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴会峰, 宋丽娟, 杜峰, 郝文芳 (2017) 黄土丘陵区草地主要种群生态位及其环境解释. 应用生态学报, 28, 3494-3504.] | |
| [54] | Wu LF, Liang YQ, Chen K, Li ZC, Cao HL (2007) Damage and prevention of Merremia boisiana in Hainan Province, China. Guangdong Forestry Science and Technology, 23(1), 83-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴林芳, 梁永勤, 陈康, 李忠超, 曹洪麟 (2007) 金钟藤在海南的危害与防治. 广东林业科技, 23(1), 83-86.] | |
| [55] | Xin XJ, Yang YB, Wang G, Ren ZW, Chu CJ, Zhang RY (2011) Niche dynamics of plant community succession and grassland quality index on zokor mounds. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 30, 700-706. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 辛小娟, 杨莹博, 王刚, 任正炜, 储诚进, 张仁懿 (2011) 鼢鼠土丘植物群落演替生态位动态及草地质量指数. 生态学杂志, 30, 700-706.] | |
| [56] | Xu MH, Liu M, Zhai DT, Liu T (2016) A review of contents and methods used to analyze various aspects of plant interspecific associations. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 8224-8233. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐满厚, 刘敏, 翟大彤, 刘彤 (2016) 植物种间联结研究内容与方法评述. 生态学报, 36, 8224-8233.] | |
| [57] | Ye QP, Zhang WH, Yu SC, Xue WY (2018) Interspecific association of the main tree populations of the Quercus acutissima community in the Qiaoshan forest area. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 3165-3174. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 叶权平, 张文辉, 于世川, 薛文艳 (2018) 桥山林区麻栎群落主要乔木种群的种间联结性. 生态学报, 38, 3165-3174.] | |
| [58] | Zhang JY, Zhao HL, Zhang TH, Zhao XY (2003) Niche dynamics of main populations of plants communities in the restoring succession process in Horqin Sandy Land. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 23, 2741-2746. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张继义, 赵哈林, 张铜会, 赵学勇 (2003) 科尔沁沙地植物群落恢复演替系列种群生态位动态特征. 生态学报, 23, 2741-2746.] | |
| [59] | Zhao CL, Zhang F, Pang CH, Wang HM, Fan X (2013) Interspecific association of dominant species of Amaranthus retroflexus L. community. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 33, 454-460. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵彩莉, 张峰, 庞春花, 王慧敏, 范晓 (2013) 反枝苋群落优势种的种间关联性分析. 植物研究, 33, 454-460.] | |
| [60] | Zheng YR (2000) Comparison of methods for studying stability of forest community. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 36(5), 28-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 郑元润 (2000) 森林群落稳定性研究方法初探. 林业科学, 36(5), 28-32.]
DOI |
|
| [61] | Zhou XY, Wang BS, Li MG, Zan QJ (2000) An analysis of interspecific associations in secondary succession forest communities in Heishiding Natural Reserve, Guangdong Province. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 24, 332-339. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 周先叶, 王伯荪, 李鸣光, 昝启杰 (2000) 广东黑石顶自然保护区森林次生演替过程中群落的种间联结性分析. 植物生态学报, 24, 332-339.] |
| [1] | 龚翠凤, 韦伟, 罗概, 韩一敏, 吴鹏程, 何梦楠, 闵清悦, 付强, 陈鹏. 大熊猫国家公园崇州片区有蹄类动物空间分布及共存关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24260-. |
| [2] | 卢佳玉, 石小亿, 多立安, 王天明, 李治霖. 基于红外相机技术的天津城市地栖哺乳动物昼夜活动节律评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23369-. |
| [3] | 曲锐, 左振君, 王有鑫, 张良键, 吴志刚, 乔秀娟, 王忠. 基于元素组的生物地球化学生态位及其在不同生态系统中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23378-. |
| [4] | 吕晓波, 李东海, 杨小波, 张孟文. 红树林群落通过淹水时间及海水盐度的生态位分化实现物种共存[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23302-. |
| [5] | 杜聪聪, 冯学宇, 陈志林. 桥头堡效应中气候生态位差异的缩小促进了红火蚁的入侵[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24276-. |
| [6] | 原雪姣, 张渊媛, 张衍亮, 胡璐祎, 桑卫国, 杨峥, 陈颀. 基于飞机草历史分布数据拟合的物种分布模型及其预测能力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24288-. |
| [7] | 谢将剑, 沈忱, 张飞宇, 肖治术. 融合音频及生态位信息的跨地域鸟类物种识别方法[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24259-. |
| [8] | 韩丽霞, 王永健, 刘宣. 外来物种入侵与本土物种分布区扩张的异同[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23396-. |
| [9] | 刘志发, 王新财, 龚粤宁, 陈道剑, 张强. 基于红外相机监测的广东南岭国家级自然保护区鸟兽多样性及其垂直分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22689-. |
| [10] | 公欣桐, 陈飞, 高欢欢, 习新强. 两种果蝇成虫与幼虫期的竞争及其对二者共存的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22603-. |
| [11] | 赵坤明, 陈圣宾, 杨锡福. 基于红外相机技术调查四川都江堰破碎化森林鸟兽多样性及优势种活动节律[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22529-. |
| [12] | 彭步青, 陶玲, 李靖, 范荣辉, 陈顺德, 付长坤, 王琼, 唐刻意. 基于DNA宏条形码研究四川老君山国家级自然保护区6种同域共存小型哺乳动物的食性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22474-. |
| [13] | 付树森, 宋普庆, 李渊, 李袁源, 张然, 张琥顺, 王芮, 林龙山. 白令海与楚科奇海鱼类营养级与营养生态位[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22521-. |
| [14] | 李婷婷, 朱锡红, 吴光年, 宋虓, 徐爱春. 镇海棘螈产卵场微生境选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(1): 22293-. |
| [15] | 陈敏豪, 张超, 王嘉栋, 湛振杰, 陈君帜, 栾晓峰. 北美水貂和欧亚水獭在东北地区的分布与生态位重叠[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(1): 22289-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn