



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 22474. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022474 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022474
彭步青, 陶玲, 李靖, 范荣辉, 陈顺德, 付长坤, 王琼, 唐刻意*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-18
接受日期:2022-11-24
出版日期:2023-04-20
发布日期:2023-04-20
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 基金资助:
Buqing Peng, Ling Tao, Jing Li, Ronghui Fan, Shunde Chen, Changkun Fu, Qiong Wang, Keyi Tang*( )
)
Received:2022-08-18
Accepted:2022-11-24
Online:2023-04-20
Published:2023-04-20
Contact:
*E-mail: 摘要:
揭示物种共存的发生和维持机制对于群落生态学理论的发展具有重要意义, 同时也是生物多样性和保护生物学研究的热点之一。生态位分化是同域分布物种实现共存的重要原因之一。为了解同域分布的多种小型哺乳动物的共存机制, 本研究采用DNA宏条形码技术对四川老君山国家级自然保护区内的6种小型哺乳动物胃内容物进行分子食性分析, 解析其夏季食物组成特征, 并计算和比较种间食物的多样性、生态位宽度和重叠指数。结果表明: (1)鳞翅目(相对丰度: 3.76%-42.33%)和双翅目(2.59%-62.63%)是6种小型哺乳动物的主要动物性食物, 禾本目(0.02%-45.33%)和豆目(0.19%-38.95%)为其主要植物性食物。6种小型哺乳动物取食主要动植物性食物的相对丰度存在种间差异。(2)黄胸鼠(Rattus tanezumi)和淡灰黑齿鼩鼱(Blarinella griselda)的属水平动物性食物显著重叠(Ojk = 0.63); 其余物种间的营养生态位存在一定程度重叠, 但在主要食物的构成和组成比例上存在明显差异; (3) 6种小型哺乳动物的动物性食物α多样性存在明显种间差异, 而植物性食物α多样性在6种小型哺乳动物之间差异不显著, 其中社鼠(Niviventer confucianus)食物多样性最高, 其动植物营养生态位宽度(8.2-11.1)均高于其余物种。以上结果表明6种小型哺乳动物的食物组成存在一定程度重叠, 但在主要食物上出现分离, 它们可能通过对主要食物摄食种类和比例的分化来减少竞争, 实现长期共存。本研究为揭示四川老君山地区多种小型哺乳动物物种多样性的维持机制提供理论依据, 也为该地区鼠形动物的生态管理提供参考。考虑到本研究在样本量和时间尺度上的局限性, 未来基于营养生态位对多种小型哺乳动物进行同域共存机制研究时建议适当增加取样的时空跨度, 更多的样本量能更好地反映种间关系。
彭步青, 陶玲, 李靖, 范荣辉, 陈顺德, 付长坤, 王琼, 唐刻意 (2023) 基于DNA宏条形码研究四川老君山国家级自然保护区6种同域共存小型哺乳动物的食性. 生物多样性, 31, 22474. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022474.
Buqing Peng, Ling Tao, Jing Li, Ronghui Fan, Shunde Chen, Changkun Fu, Qiong Wang, Keyi Tang (2023) DNA metabarcoding dietary analysis of six sympatric small mammals at the Laojunshan National Nature Reserve, Sichuan Province. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22474. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022474.
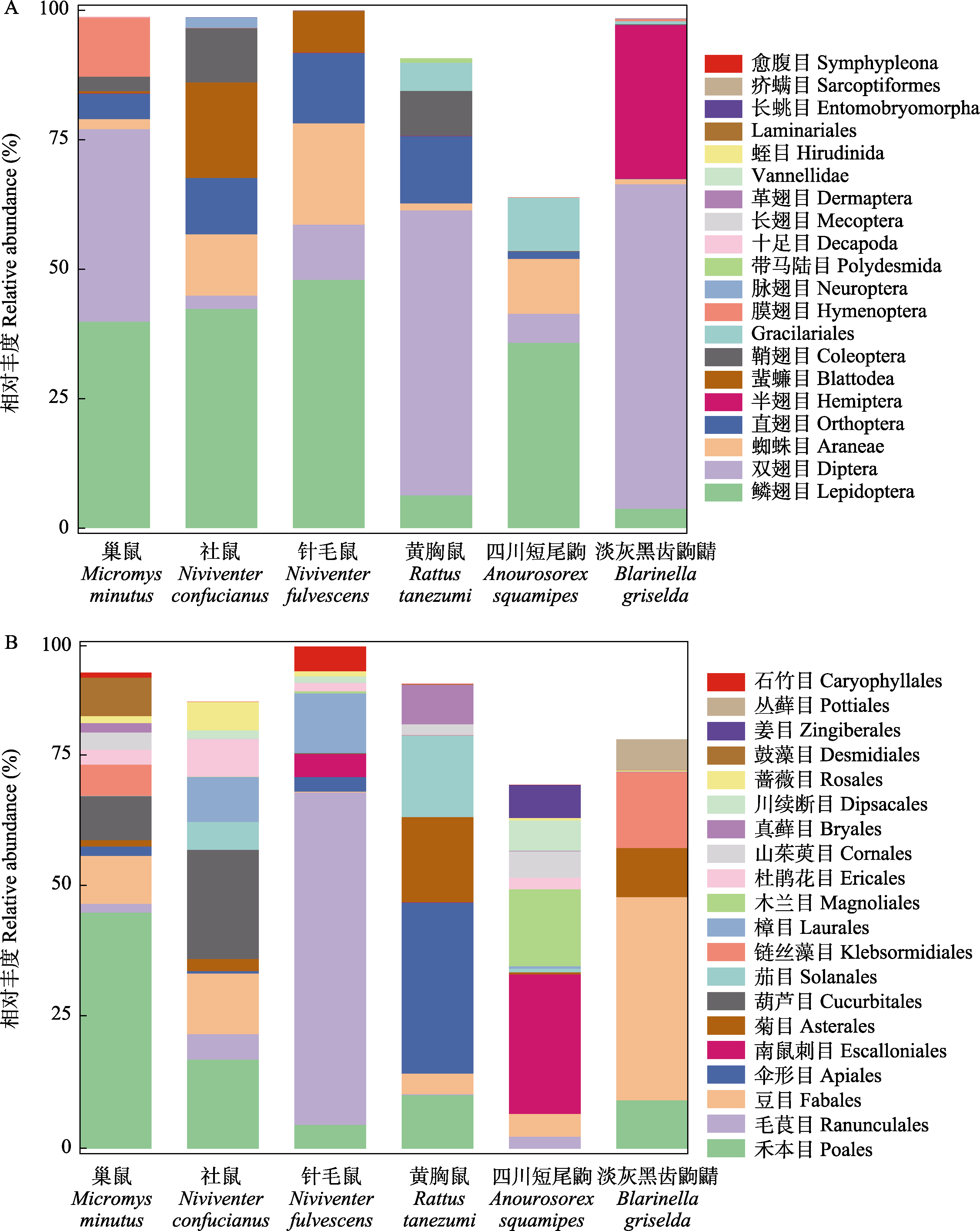
图1 6种小型哺乳动物目水平排名前20的动物性食物(A)和植物性食物(B)的相对丰度
Fig. 1 Relative abundance of top 20 animal- (A) and plant-derived (B) food items at the order level in the six small mammals
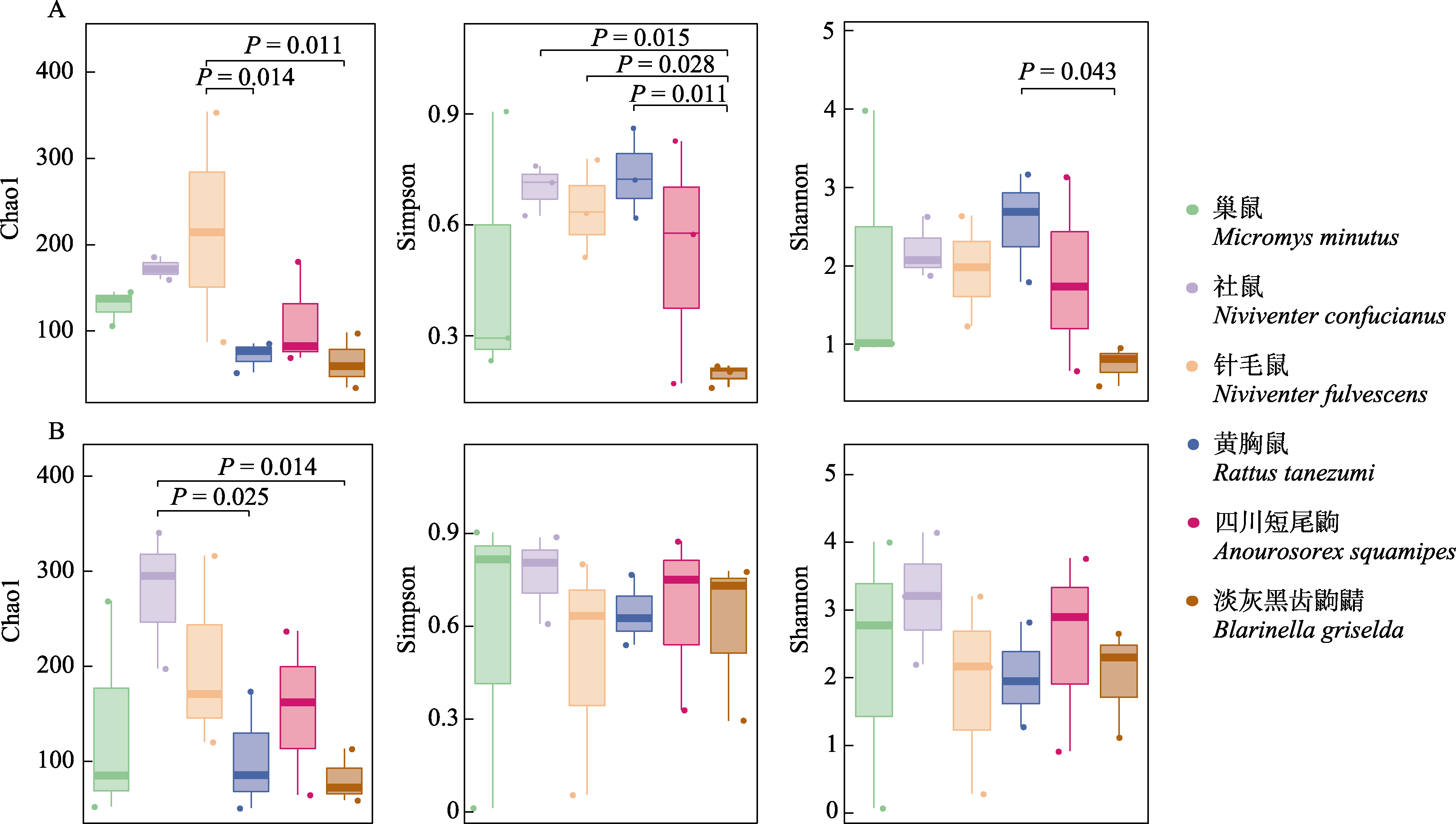
图2 6种小型哺乳动物动物性食物(A)和植物性食物(B)的α多样性指数的分组箱线图
Fig. 2 Box-and-whisker plots for α diversity of animal- (A) and plant-derived (B) food items of six small mammals
| 动物性食物 Animal-derived food | 植物性食物 Plant-derived food | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 属水平 Genus level | 科水平 Family level | 属水平 Genus level | 科水平 Family level | |
| 巢鼠 Micromys minutus | 5.4882 | 5.4409 | 6.9642 | 4.7517 |
| 社鼠 Niviventer confucianus | 8.6485 | 8.2191 | 11.0998 | 8.6986 |
| 针毛鼠 Niviventer fulvescens | 8.1913 | 6.4274 | 2.5601 | 2.5435 |
| 黄胸鼠 Rattus tanezumi | 6.1445 | 6.1359 | 5.5751 | 5.5339 |
| 四川短尾鼩 Anourosorex squamipes | 4.0286 | 4.0239 | 5.8556 | 5.8525 |
| 淡灰黑齿鼩鼱 Blarinella griselda | 3.7137 | 3.7118 | 4.5893 | 4.5681 |
表1 6种小型哺乳动物的营养生态位宽度
Table 1 Trophic niche breadth of the six small mammals
| 动物性食物 Animal-derived food | 植物性食物 Plant-derived food | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 属水平 Genus level | 科水平 Family level | 属水平 Genus level | 科水平 Family level | |
| 巢鼠 Micromys minutus | 5.4882 | 5.4409 | 6.9642 | 4.7517 |
| 社鼠 Niviventer confucianus | 8.6485 | 8.2191 | 11.0998 | 8.6986 |
| 针毛鼠 Niviventer fulvescens | 8.1913 | 6.4274 | 2.5601 | 2.5435 |
| 黄胸鼠 Rattus tanezumi | 6.1445 | 6.1359 | 5.5751 | 5.5339 |
| 四川短尾鼩 Anourosorex squamipes | 4.0286 | 4.0239 | 5.8556 | 5.8525 |
| 淡灰黑齿鼩鼱 Blarinella griselda | 3.7137 | 3.7118 | 4.5893 | 4.5681 |
| 巢鼠 Micromys minutus | 社鼠 Niviventer confucianus | 针毛鼠 Niviventer fulvescens | 黄胸鼠 Rattus tanezumi | 四川短尾鼩 Anourosorex squamipes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 社鼠 Niviventer confucianus | 0.04/0.34 | ||||
| 针毛鼠 Niviventer fulvescens | 0.07/0.09 | 0.31/0.22 | |||
| 黄胸鼠 Rattus tanezumi | 0.08/0.12 | 0.08/0.24 | 0.14/0.01 | ||
| 四川短尾鼩 Anourosorex squamipes | 0.01/0.06 | 0.40/0.26 | 0.35/0.12 | 0.21/0.12 | |
| 淡灰黑齿鼩鼱 Blarinella griselda | 0.04/0.23 | 0.01/0.48 | 0.02/0.01 | 0.63/0.24 | 0.03/0.31 |
表2 6种小型哺乳动物属水平的动物性(斜线左)和植物性(斜线右)食物营养生态位重叠指数
Table 2 Trophic niche overlap index of the animal- (the left side of the slash) and plant-derived (the right side of the slash) food items at the genus level in the six small mammals
| 巢鼠 Micromys minutus | 社鼠 Niviventer confucianus | 针毛鼠 Niviventer fulvescens | 黄胸鼠 Rattus tanezumi | 四川短尾鼩 Anourosorex squamipes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 社鼠 Niviventer confucianus | 0.04/0.34 | ||||
| 针毛鼠 Niviventer fulvescens | 0.07/0.09 | 0.31/0.22 | |||
| 黄胸鼠 Rattus tanezumi | 0.08/0.12 | 0.08/0.24 | 0.14/0.01 | ||
| 四川短尾鼩 Anourosorex squamipes | 0.01/0.06 | 0.40/0.26 | 0.35/0.12 | 0.21/0.12 | |
| 淡灰黑齿鼩鼱 Blarinella griselda | 0.04/0.23 | 0.01/0.48 | 0.02/0.01 | 0.63/0.24 | 0.03/0.31 |
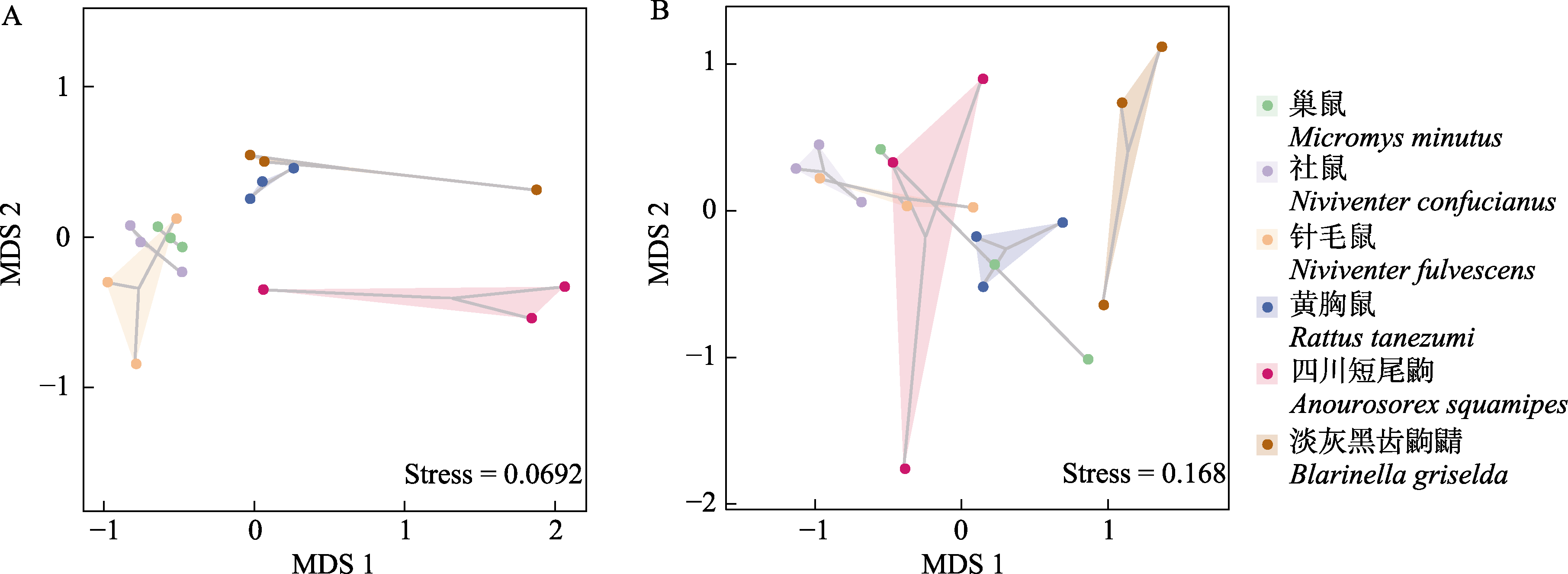
图3 基于Jaccard distance矩阵的6种小型哺乳动物的动物性食物(A)和植物性食物(B)的NMDS图
Fig. 3 The NMDS of animal- (A) and plant-derived (B) food items of six small mammals based on Jaccard distance
| [1] |
Akrim F, Mahmood T, Max T, Nadeem MS, Qasim S, Andleeb S (2018) Assessment of bias in morphological identification of carnivore scats confirmed with molecular scatology in north-eastern Himalayan region of Pakistan. PeerJ, 6, e5262.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Berry TE, Osterrieder SK, Murray DC, Coghlan ML, Richardson AJ, Grealy AK, Stat M, Bejder L, Bunce M (2017) DNA metabarcoding for diet analysis and biodiversity: A case study using the endangered Australian sea lion (Neophoca cinerea). Ecology and Evolution, 7, 5435-5453.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Biffi M, Laffaille P, Jabiol J, André A, Gillet F, Lamothe S, Michaux JR, Buisson L (2017) Comparison of diet and prey selectivity of the Pyrenean desman and the Eurasian water shrew using next-generation sequencing methods. Mammalian Biology, 87, 176-184.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Burgar JM, Murray DC, Craig MD, Haile J, Houston J, Stokes V, Bunce M (2014) Who’s for dinner? High-throughput sequencing reveals bat dietary differentiation in a biodiversity hotspot where prey taxonomy is largely undescribed. Molecular Ecology, 23, 3605-3617.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Calhoun JB (1941) Distribution and food habits of mammals in the vicinity of the Reelfoot Lake Biological Station. Journal of the Tennessee Academy of Science, 16, 177-185. |
| [6] |
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Huntley J, Fierer N, Owens SM, Betley J, Fraser L, Bauer M, Gormley N, Gilbert JA, Smith G, Knight R (2012) Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. The ISME Journal, 6, 1621-1624.
DOI |
| [7] | Chen WW, Zhong J, Liu SX, Xiong GM, Chen FQ, Xie ZQ, Jiang GH, Zhou YB (2014) Variations in food habit and viscera organ morphology of four rodents in Shennongjia, central China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 3620-3628. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈文文, 钟杰, 刘三峡, 熊高明, 陈芳清, 谢宗强, 江广华, 周友兵 (2014) 神农架地区4种啮齿类食性及脏器形态差异比较. 生态学报, 34, 3620-3628.] | |
| [8] |
Churchfield JS (1979) A note on the diet of the European Water shrew, Neomys fodiens bicolor. Journal of Zoology, 188, 294-296.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Churchfield S, Rychlik L (2006) Diets and coexistence in Neomys and Sorex shrews in Białowieża forest, eastern Poland. Journal of Zoology, 269, 381-390.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Churchfield S, Sheftel BI (1994) Food niche overlap and ecological separation in a multi-species community of shrews in the Siberian taiga. Journal of Zoology, 234, 105-124.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Clare EL, Symondson WOC, Broders H, Fabianek F, Fraser EE, MacKenzie A, Boughen A, Hamilton R, Willis CKR, Martinez-Nuñez F, Menzies AK, Norquay KJO, Brigham M, Poissant J, Rintoul J, Barclay RMR, Reimer JP (2014) The diet of Myotis lucifugus across Canada: Assessing foraging quality and diet variability. Molecular Ecology, 23, 3816-3832. |
| [12] |
Cooke SB, Crowley BE (2018) Deciphering the isotopic niches of now-extinct Hispaniolan rodents. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, 38, e1510414.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Crozier WW (1985) Observations on the food and feeding of the angler-fish, Lophim piscatorius L., in the northern Irish Sea. Journal of Fish Biology, 27, 655-665.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
De León LF, Podos J, Gardezi T, Herrel A, Hendry AP (2014) Darwin’s finches and their diet niches: The sympatric coexistence of imperfect generalists. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 27, 1093-1104.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Deagle BE, Thomas AC, McInnes JC, Clarke LJ, Vesterinen EJ, Clare EL, Kartzinel TR, Eveson JP (2019) Counting with DNA in metabarcoding studies: How should we convert sequence reads to dietary data? Molecular Ecology, 28, 391-406.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Deng Z (1991) Harm of rodents to human health. Chinese Journal of Public Health, 7, 131-134. (in Chinese) |
| [ 邓址 (1991) 啮齿动物对人类健康的危害. 中国公共卫生, 7, 131-134.] | |
| [17] |
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nature Methods, 10, 996-998.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Fu YQ, Wen LY, Dai B, Chen BP, Zhang ZW (2016) Winter habitat characteristics of Sichuan partridge (Arborophila rufipectus). Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35, 3012-3016. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 付义强, 文陇英, 戴波, 陈本平, 张正旺 (2016) 四川山鹧鸪冬季栖息地特征. 生态学杂志, 35, 3012-3016.] | |
| [19] |
Grinnell J (1917) The niche-relationships of the California thrasher. The Auk, 34, 427-433.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Guo YP, Zhang H, Zhao XG, Luo HL, Zhang YJ (2021) Applications of DNA metabarcoding in diet identification of herbivores. Biotechnology Bulletin, 37, 252-260. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 郭艳萍, 张浩, 赵新钢, 罗海玲, 张英俊 (2021) DNA宏条形码技术在食草动物食性研究中的应用. 生物技术通报, 37, 252-260.]
DOI |
|
| [21] |
Hardin G (1960) The competitive exclusion principle. Science, 131, 1292-1297.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
He K, Li Y, Brandley MC, Lin L, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Jiang X (2010) A multi-locus phylogeny of Nectogalini shrews and influences of the paleoclimate on speciation and evolution. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 56, 734-746.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Hoffman J, Sylvester T, Lyons E (2012) Diet and ectoparasites of the southern short-tailed shrew (Blarina carolinensis) in Louisiana. Western North American Naturalist, 72, 586-590.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Hofreiter M, Poinar HN, Spaulding WG, Bauer K, Martin PS, Possnert G, Pääbo S (2000) A molecular analysis of ground sloth diet through the last glaciation. Molecular Ecology, 9, 1975-1984.
PMID |
| [25] |
Hou JJ, Li L, Wang YF, Wang WJ, Zhan HY, Dai NH, Lu P (2021) Influences of submerged plant collapse on diet composition, breadth, and overlap among four crane species at Poyang Lake, China. Frontiers in Zoology, 18, 1-17.
DOI |
| [26] |
Huisman J, Weissing FJ (1999) Biodiversity of plankton by species oscillations and chaos. Nature, 402, 407-410.
DOI |
| [27] | Jow J, Hartman GD, Hein R (1994) Food and ectoparasites of the southern short-tailed shrew, Blarina carolinensis (Mammalia: Soricidae), from South Carolina. Brimleyana, 21, 97-105. |
| [28] |
Jusino MA, Banik MT, Palmer JM, Wray AK, Xiao L, Pelton E, Barber JR, Kawahara AY, Gratton C, Peery MZ, Lindner DL (2019) An improved method for utilizing high-throughput amplicon sequencing to determine the diets of insectivorous animals. Molecular Ecology Resources, 19, 176-190.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Kartzinel TR, Chen PA, Coverdale TC, Erickson DL, Kress WJ, Kuzmina ML, Rubenstein DI, Wang W, Pringle RM (2015) DNA metabarcoding illuminates dietary niche partitioning by African large herbivores. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 8019-8024. |
| [30] | Krebs CJ (1999) Ecological Methodology. Addison Wesley Longman, Menlo Park. |
| [31] |
Krüger F, Clare EL, Greif S, Siemers BM, Symondson WC, Sommer RS (2014) An integrative approach to detect subtle trophic niche differentiation in the sympatric trawling bat species Myotis dasycneme and Myotis daubentonii. Molecular Ecology, 23, 3657-3671.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | Ladine T, Munoz A (2010) Food habits of the southern short-tailed shrew (Blarina carolinensis) in East Texas. Texas Journal of Science, 62, 153-156. |
| [33] | Levins R (1968) Evolution in Changing Environment. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [34] | Li TB (2020) Analysis of feeding habits of forest rodents in Wangwu Mountain area of Jiyuan City. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, (20), 83-85, 88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李天保 (2020) 济源市王屋山地区林栖鼠类食性分析. 现代农业科技, (20), 83-85, 88.] | |
| [35] | Li XM, Li SJ, He JF (1989) Preliminary observation on feeding habits and activities of Rattus norvegicus and Rattus flavipectus. Chinese Journal of Vector Biology and Control, (4), 209. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李新民, 李书建, 贺金方 (1989) 对褐家鼠、黄胸鼠食性及活动规律的初步观察. 中国鼠类防制杂志, (4), 209.] | |
| [36] |
Liao WB, Fuller RA, Hu JC, Li C (2008) Habitat use by endangered Sichuan partridges Arborophila rufipectus during the breeding season. Acta Ornithologica, 43, 179-184.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Liao WB, Li C, Hu JC, Lu X (2007) Habitat utilization of the Sichuan hill partridge (Arborophila rufipectus) in the non-breeding period in Laojunshan Nature Reserve. Zoological Research, 28, 172-178. |
| [38] | Liu G, Ning Y, Xia XF, Gong MH (2018) The application of high-throughput sequencing technologies to wildlife diet analysis. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 3347-3356. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘刚, 宁宇, 夏晓飞, 龚明昊 (2018) 高通量测序技术在野生动物食性分析中的应用. 生态学报, 38, 3347-3356.] | |
| [39] | Liu ZS, Wang XM, Teng LW, Cao LR (2007) Food habits of blue sheep, Pseudois nayaur in the Helan Mountains, China. Folia Zoologica, 56, 13-22. |
| [40] |
Lu Q, Hu Q, Shi XG, Jin SL, Li S, Yao M (2019) Metabarcoding diet analysis of snow leopards (Panthera uncia) in Wolong National Nature Reserve, Sichuan Province. Biodiversity Science, 27, 960-969. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 陆琪, 胡强, 施小刚, 金森龙, 李晟, 姚蒙 (2019) 基于分子宏条形码分析四川卧龙国家级自然保护区雪豹的食性. 生物多样性, 27, 960-969.]
DOI |
|
| [41] |
MacArthur RH, Pianka ER (1966) On optimal use of a patchy environment. The American Naturalist, 100, 603-609.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Marshal JP, Bleich VC, Andrew NG, Bighorn S, Andrew N (2008) Evidence for interspecific competition between feral ass Equus asinus and mountain sheep Ovis canadensis in a desert environment. Wildlife Biology, 14, 228-236.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Pianka ER (1973) The structure of lizard communities. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 4, 53-74.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Pompanon F, Deagle BE, Symondson WOC, Brown DS, Jarman SN, Taberlet P (2012) Who is eating what: Diet assessment using next generation sequencing. Molecular Ecology, 21, 1931-1950.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
Porter LM (2001) Dietary differences among sympatric Callitrichinae in northern Bolivia: Callimico goeldii, Saguinus fuscicollis and S. labiatus. International Journal of Primatology, 22, 961-992.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Razgour O, Clare EL, Zeale MRK, Hanmer J, Schnell IB, Rasmussen M, Gilbert TP, Jones G (2011) High-throughput sequencing offers insight into mechanisms of resource partitioning in cryptic bat species. Ecology and Evolution, 1, 556-570.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Rognes T, Flouri T, Nichols B, Quince C, Mahé F (2016) Vsearch: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ, 4, e2584.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Rutrough A, Widick IV, Bean WT (2019) Reconstruction of the historical range alters niche estimates in an endangered rodent. Ecography, 42, 1742-1751.
DOI |
| [49] |
Shao XN, Lu Q, Xiong MY, Bu HL, Shi XY, Wang DJ, Zhao JD, Li S, Yao M (2021) Prey partitioning and livestock consumption in the world’s richest large carnivore assemblage. Current Biology, 31, 4887-4897.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Shao XN, Song DZ, Huang QW, Li S, Yao M (2019) Fast surveys and molecular diet analysis of carnivores based on fecal DNA and metabarcoding. Biodiversity Science, 27, 543-556. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 邵昕宁, 宋大昭, 黄巧雯, 李晟, 姚蒙 (2019) 基于粪便DNA及宏条形码技术的食肉动物快速调查及食性分析. 生物多样性, 27, 543-556.]
DOI |
|
| [51] |
Shutt JD, Nicholls JA, Trivedi UH, Burgess MD, Stone GN, Hadfield JD, Phillimore AB (2020) Gradients in richness and turnover of a forest passerine’s diet prior to breeding: A mixed model approach applied to faecal metabarcoding data. Molecular Ecology, 29, 1199-1213.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
Sommer U (1999) Competition and coexistence. Nature, 402, 366-367.
DOI |
| [53] |
Sullins DS, Haukos DA, Craine JM, Lautenbach JM, Robinson SG, Lautenbach JD, Kraft JD, Plumb RT, Reitz JH, Sandercock BK, Fierer N (2018) Identifying the diet of a declining prairie grouse using DNA metabarcoding. The Auk, 135, 583-608.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Taberlet P, Coissac E, Pompanon F, Brochmann C, Willerslev E (2012) Towards next-generation biodiversity assessment using DNA metabarcoding. Molecular Ecology, 21, 2045-2050.
DOI PMID |
| [55] |
Tang KY, Xie F, Liu HY, Pu YT, Chen D, Qin BX, Fu CK, Wang Q, Chen SD, Guo KJ (2021) DNA metabarcoding provides insights into seasonal diet variations in Chinese mole shrew (Anourosorex squamipes) with potential implications for evaluating crop impacts. Ecology and Evolution, 11, 376-389.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Udvardy MFD (1959) Notes on the ecological concepts of habitat, biotope and niche. Ecology, 40, 725-788.
DOI URL |
| [57] | Wang C, Su HJ, Hu CS, Shi L, Zhang MM (2020) Spatial distribution of sympatric Rhinopithecus brelichi and Macaca thibetana in Fanjingshan National Nature Reserve, Guizhou, China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 40, 193-200. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王丞, 粟海军, 胡灿实, 石磊, 张明明 (2020) 梵净山保护区同域分布黔金丝猴与藏酋猴的空间分布初探. 兽类学报, 40, 193-200.] | |
| [58] | Wang DL, Li XC, Pan DF, De KJ (2016) The ecological significance and controlling of rodent outbreaks in the Qinghai-Tibetan Grasslands. Journal of Southwest University for Nationalities (Natural Science Edition), 42, 237-245. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王德利, 李心诚, 潘多峰, 德科加 (2016) 青藏高原草地鼠害的生态释义及控制. 西南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 42, 237-245.] | |
| [59] | Wang GL (2004) Causes and control countermeasures of forest rodent damage in Bailongjiang forest area. Journal of Gansu Forestry Science and Technology, 29(4), 74-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王贵来 (2004) 白龙江林区森林鼠害发生原因及防治对策. 甘肃林业科技, 29(4), 74-75.] | |
| [60] | Wang GM, Zhou QQ, Zhong WQ (1996) Trophic niches of four species of common small mammals in Inner Mongolia grassland and their relationships. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 16, 71-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王桂明, 周庆强, 钟文勤 (1996) 内蒙古典型草原4种常见小哺乳动物的营养生态位及相互关系. 生态学报, 16, 71-76.] | |
| [61] | Wang MC, Han CX, Hu ZL, Chen XD, Yang XJ (1997) A study on Gansu Zokor’s feeding rhythm and its food preference to different beits. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis, 25(2), 46-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王明春, 韩崇选, 胡忠朗, 陈孝达, 杨学军 (1997) 甘肃鼢鼠取食节律及对不同饵料喜食性的研究. 西北农业大学学报, 25(2), 46-50.] | |
| [62] | Wang XQ, Wang GH, Qiao F, Gao QK, Heong KL, Zhu ZR, Cheng JA (2017) Progress on high-throughput sequencing and its applications in food web analysis. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 2530-2539. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王雪芹, 王光华, 乔飞, 高其康, Heong KL, 祝增荣, 程家安 (2017) 高通量测序及其在食物网解析中的应用进展. 生态学报, 37, 2530-2539.] | |
| [63] |
Whitaker J (2006) Food of the southern short-tailed shrew (Blarina carolinensis) on Cumberland Island, Georgia. Southeastern Naturalist, 5, 361-366.
DOI URL |
| [64] | Wickham H (2009) ggplot2:Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Springer-Verlag, New York. |
| [65] | Xi LYZ, Luo G, Ran JH, Feng SL, Chen JW, Chen BP (2020) Habitat use and change of Arborophila rufiperctus during the breeding season in the Laojunshan National Nature Reserve, Sichuan. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 39, 258-265. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 西丽媛子, 罗概, 冉江洪, 冯盛林, 陈建武, 陈本平 (2020) 四川老君山国家级自然保护区四川山鹧鸪繁殖期的生境利用及其变化研究. 四川动物, 39, 258-265.] | |
| [66] | Yang CW, Ma JZ, Jin JL, Liu Z (2008) Research on autumn time niche of five rodents in forests ecosystem. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 43(2), 64-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨春文, 马建章, 金建丽, 刘铸 (2008) 森林生态系统中5种啮齿动物秋季时间生态位. 动物学杂志, 43(2), 64-69.] | |
| [67] |
Yang YZ, Zhan AB, Cao L, Meng FJ, Xu WB (2016) Selection of a marker gene to construct a reference library for wetland plants, and the application of metabarcoding to analyze the diet of wintering herbivorous waterbirds. PeerJ, 4, e2345.
DOI URL |
| [68] | Yin BF, Huai HY, Zhang YL, Zhou L, Wei WH (2007) Trophic niches of Pantholops hodgsoni, Procapra picticaudata and Equus kiang in Kekexili Region. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 18, 766-770. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 殷宝法, 淮虎银, 张镱锂, 周乐, 魏万红 (2007) 可可西里地区藏羚羊、藏原羚和藏野驴的营养生态位. 应用生态学报, 18, 766-770.] | |
| [69] | Yong ZY, Guo C, Zhang MW, Wang Y, Li B (2011) Significance and methodology of rodent’s food habit research: A review. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 30, 2637-2645. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 雍仲禹, 郭聪, 张美文, 王勇, 李波 (2011) 啮齿动物食性研究的意义及方法评述. 生态学杂志, 30, 2637-2645.] | |
| [70] | Zhang CJ, Wang XY, Yao BH, Wang C, Kang YK, Zhang Q, Su JH (2021) Diet composition and trophic niche characteristics of three rodents in Gannan meadow. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 29, 1484-1490. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 张彩军, 王小燕, 姚宝辉, 王缠, 康宇坤, 张倩, 苏军虎 (2021) 甘南草原3种啮齿动物的食性及其营养生态位特征. 草地学报, 29, 1484-1490.]
DOI |
|
| [71] | Zhang YY, Dong JY, Sun X, Zhang XM (2022) Bibliometric analysis of food habit research based on DNA molecular biology. Fisheries Science, 41, 160-172. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张宇洋, 董建宇, 孙昕, 张秀梅 (2022) 基于DNA分子生物学食性研究领域的文献计量分析. 水产科学, 41, 160-172.] | |
| [72] | Zhao G (2021) A review of rodent feeding methods. Biological Chemical Engineering, 7(5), 163-165. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵耕 (2021) 啮齿动物食性研究方法. 生物化工, 7(5), 163-165.] | |
| [73] | Zhong LQ (2020) Feeding and Nutrition Strategy and Feeding Habitat Evaluation of Red Deer and Sika Deer Distributed in the Same Domain. PhD dissertation, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 钟林强 (2020) 同域分布马鹿与梅花鹿采食和营养策略及采食生境评价. 博士学位论文, 东北林业大学, 哈尔滨.] |
| [1] | 贺加贝, 柯可, 孙海明, 胡丽萍, 赵晓伟, 王文豪, 赵强. 基于DNA宏条形码技术分析香螺食性[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24403-. |
| [2] | 王淏林, 张怀胜, 朱建强, 陈中义, 柯雨琳, 杨涛, 陈卉. 麋鹿食物组成及其分析方法研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23057-. |
| [3] | 董志远, 陈琳琳, 张乃鹏, 陈莉, 孙德斌, 倪艳梅, 李宝泉. 基于环境DNA宏条形码技术研究黄河三角洲典型潮沟系统鱼类多样性及其对水文连通性的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23073-. |
| [4] | 湛振杰, 张超, 陈敏豪, 王嘉栋, 富爱华, 范雨薇, 栾晓峰. 基于DNA宏条形码技术的大兴安岭北部欧亚水獭冬季食性分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22586-. |
| [5] | 付树森, 宋普庆, 李渊, 李袁源, 张然, 张琥顺, 王芮, 林龙山. 白令海与楚科奇海鱼类营养级与营养生态位[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22521-. |
| [6] | 沈梅, 郭宁宁, 罗遵兰, 郭晓晨, 孙光, 肖能文. 基于eDNA metabarcoding探究北京市主要河流鱼类分布及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22240-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()