



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 23443. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023443 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023443
所属专题: 数据论文
池玉杰1,*( )(
)( ), 张心甜1(
), 张心甜1( ), 田志炫1(
), 田志炫1( ), 关成帅1(
), 关成帅1( ), 谷新治1,2(
), 谷新治1,2( ), 刘智会3(
), 刘智会3( ), 王占斌1, 王金杰1
), 王占斌1, 王金杰1
收稿日期:2023-11-20
接受日期:2024-02-01
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-03-28
通讯作者:
* E-mail: 基金资助:
Yujie Chi1,*( )(
)( ), Xintian Zhang1(
), Xintian Zhang1( ), Zhixuan Tian1(
), Zhixuan Tian1( ), Chengshuai Guan1(
), Chengshuai Guan1( ), Xinzhi Gu1,2(
), Xinzhi Gu1,2( ), Zhihui Liu3(
), Zhihui Liu3( ), Zhanbin Wang1, Jinjie Wang1
), Zhanbin Wang1, Jinjie Wang1
Received:2023-11-20
Accepted:2024-02-01
Online:2024-04-20
Published:2024-03-28
Contact:
* E-mail: 摘要:
对不同地理区域的菌物进行系统的编目和分类研究是生物多样性研究的核心内容。白粉菌是一类植物专性寄生病原真菌, 广泛分布在世界各地, 能引起多种植物的白粉病。为了全面了解中国东北与东北亚其他地区白粉菌的物种多样性和寄主多样性, 本文通过文献收集、数据分析, 并结合作者2022-2023年野外调查结果, 按照最新的分类系统, 整理出中国东北和东北亚其他各国和地区的白粉菌物种名录、寄主名录和地理分布信息。通过整理分析发现, 中国东北地区有白粉菌142种和17变种, 隶属于1科5族、10个有性属和1个无性属, 分布在572种(含37变种)寄主植物上, 隶属64科243属; 日本有白粉菌258种和46变种, 隶属于1科5族, 12个有性属和2个无性属, 分布在1,171种(含163变种)寄主植物上, 隶属108科449属; 韩国有白粉菌150种和15变种, 隶属于1科5族, 11个有性属和1个无性属, 分布在515种(含53变种)寄主植物上, 隶属79科255属; 俄罗斯远东地区有白粉菌89种和22变种, 隶属于1科5族, 8个有性属和2个无性属。中国东北地区、日本、韩国和俄罗斯远东地区共有的白粉菌种类有50个, 归属于8个共有的有性属(布氏白粉菌属(Blumeria)、单囊壳属(Podosphaera)、叉钩丝壳属(Sawadaea)、白粉菌属(Erysiphe)、高氏白粉菌属(Golovinomyces)、新白粉菌属(Neoërysiphe)、内丝白粉菌属(Leveillula)和球针壳属(Phyllactinia)), 它们分布在相同或相近的寄主植物上。日本和韩国的白粉菌共有种最多(136种)。中国东北地区、日本和韩国白粉菌的特有种分别为28种、116种和17种。东北亚地区白粉菌的寄主植物总共有1,760种(含263个变种), 隶属112科541属。虽然东北亚地区约占全球陆地面积的8%, 但是该地区共有318种和53变种白粉菌, 占全球已知白粉菌总数的40.33%。因此, 东北亚地区属于白粉菌多样性研究的重点地区与区系单元。研究结果为建立东北亚地区白粉菌多样性与区系研究格局、系统发育关系、寄主多样性概貌等提供了白粉菌物种和寄主物种的数据支持。
池玉杰, 张心甜, 田志炫, 关成帅, 谷新治, 刘智会, 王占斌, 王金杰 (2024) 东北亚地区白粉菌的物种多样性与寄主物种多样性. 生物多样性, 32, 23443. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023443.
Yujie Chi, Xintian Zhang, Zhixuan Tian, Chengshuai Guan, Xinzhi Gu, Zhihui Liu, Zhanbin Wang, Jinjie Wang (2024) Species diversity of powdery mildew fungi (Erysiphaceae) and their host plants in Northeast Asia. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23443. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023443.
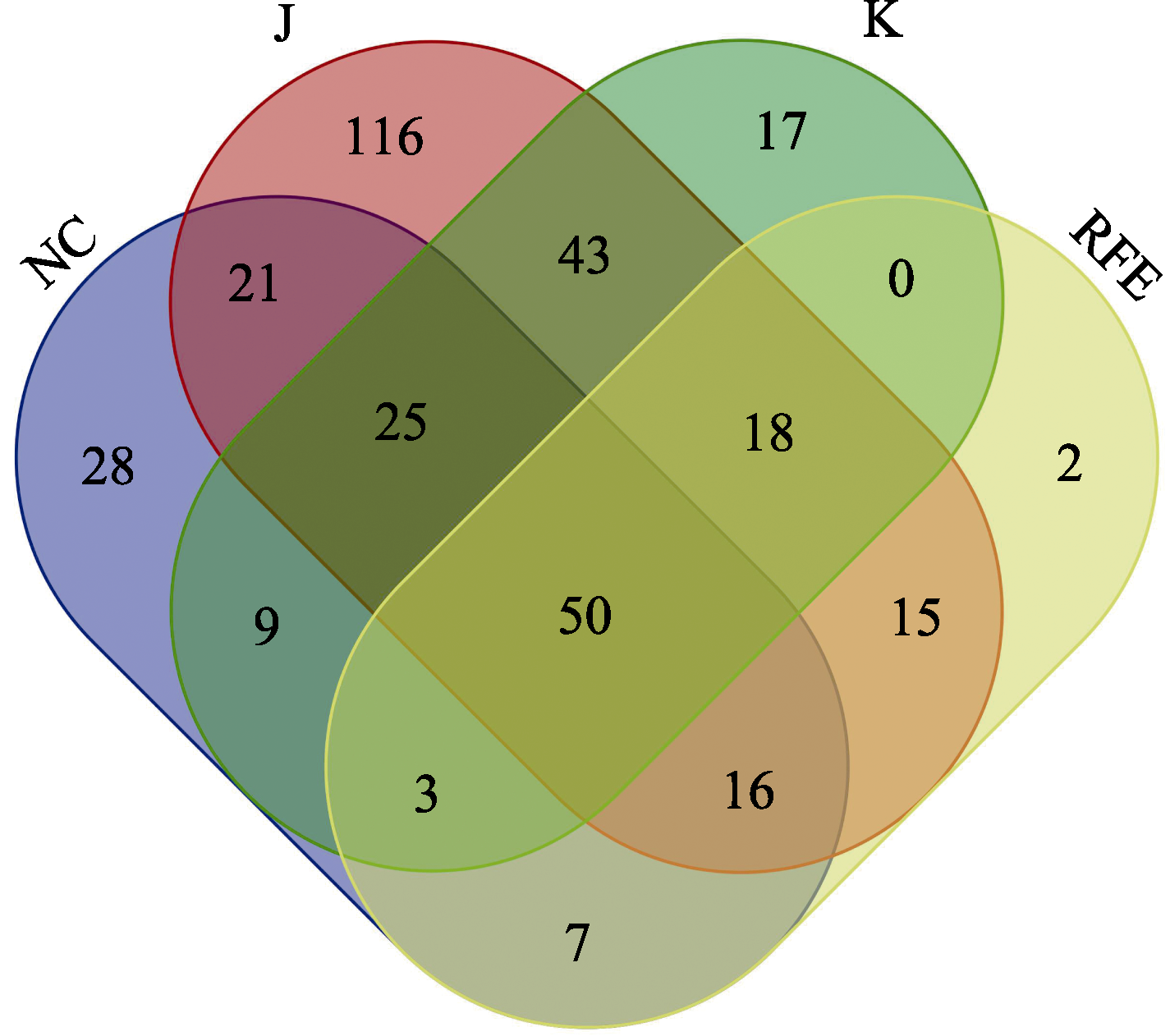
图3 中国东北地区(NC)、日本(J)、韩国(K)、俄罗斯远东地区(RFE)白粉菌的共有种和特有种
Fig. 3 Common and endemic species of powdery mildews among Northeast China (NC), Japan (J), Republic of Korea (K), and Russian Far East (RFE)
| 地区Areas | 种和变种数 Number of species and varieties | 与东北亚共有种 Common species with Northeast Asia | 相似性系数 Similarity coefficient (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 中国内蒙古 Nei Mongol, China 中国西南地区 Southwest China | 123 175 | 116 114 | 46.96 41.76 |
表1 东北亚与其他地区白粉菌区系比较
Table 1 Comparison of powdery mildew mycobiota between Northeast Asia and other areas
| 地区Areas | 种和变种数 Number of species and varieties | 与东北亚共有种 Common species with Northeast Asia | 相似性系数 Similarity coefficient (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 中国内蒙古 Nei Mongol, China 中国西南地区 Southwest China | 123 175 | 116 114 | 46.96 41.76 |
| [1] | Ajitomi A, Takushi T, Sato Y, Arasaki C, Ooshiro A (2020) First report of powdery mildew of mango caused by Erysiphe quercicola in Japan. Journal of General Plant Pathology, 86, 316-321. |
| [2] | Amano K (1986) Host Range and Geographical Distribution of Powdery Mildew Fungi. Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo. |
| [3] | Bai LC (2015) Studies on Taxonomy, Phylogeny and Flora of Powdery Mildews (Erysiphales) in the Qinling Mts. PhD dissertation, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, Shaanxi. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [白露超 (2015) 秦岭林区白粉菌分类、分子系统学研究及区系分析. 博士学位论文, 西北农林科技大学, 陕西杨凌.] | |
| [4] |
Bradshaw M, Braun U, Wang S, Liu SY, Feng J, Shin HD, Choi YJ, Takamatsu S, Bulgakov TS, Tobin PC (2020) Phylogeny and taxonomy of powdery mildew on Viburnum species. Mycologia, 112, 616-632.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Braun U (1987) A monograph of the Erysiphales (powdery mildews). Beiheft zur Nova Hedwigia, 89, 1-700. |
| [6] | Braun U (1999) Some critical notes on the classification and generic concept of the Erysiphaceae. Schlechtendalia, 3, 49-55. |
| [7] | Braun U (2011) The current systematics and taxonomy of the powdery mildews (Erysiphales): An overview. Mycoscience, 52, 210-212. |
| [8] | Braun U, Cook RTA (2012) Taxonomic Manual of the Erysiphales (Powdery Mildews). CBS Biodiversity Series No. 11. CBS-KNAW Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht. |
| [9] | Braun U, Takamatsu S (2000) Phylogeny of Erysiphe, Microsphaera, Uncinula (Erysipheae) and Cystotheca, Podosphaera, Sphaerotheca (Cystotheceae) inferred from rDNA ITS sequences-some taxonomic consequences. Schlechtendalia, 4, 1-33. |
| [10] | Cho SE, Choi IY, Hong SH, Lee YH, Shin HD (2017a) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe begoniicola on Begonia in Korea. Plant Disease, 101, 1681. |
| [11] | Cho SE, Lee SH, Lee SK, Seo ST, Shin HD (2017b) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe quercicola on Quercus mongolica in Korea. Plant Disease, 101, 1324. |
| [12] | Cho SE, Lee SH, Lee SK, Seo ST, Shin HD (2018a) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe quercicola on Quercus robur in Korea. Plant Disease, 102, 1455. |
| [13] | Cho SE, Lee SH, Lee SK, Seo ST, Shin HD (2018b) Identification of Erysiphe izuensis on Rhododendron yedoense f. poukhanense in Korea based on morphological and molecular characteristics. Korean Journal of Mycology, 46, 69-74. |
| [14] | Cho SE, Lee SH, Lee SY, Lee CK, Shin HD (2016a) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe hedwigii on Viburnum awabuki in Korea. Plant Disease, 100, 2533. |
| [15] | Cho SE, Lee SK, Lee SH, Lee CK, Shin HD (2014a) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe elevata on Catalpa bignonioides in Korea. Plant Disease, 98, 856. |
| [16] | Cho SE, Park JH, Hong SH, Choi IY, Shin HD (2014b) First report of powdery mildew caused by Golovinomyces biocellatus on Agastache rugosa in Korea. Plant Disease, 98, 1278. |
| [17] | Cho SE, Park JH, Hong SH, Choi IY, Shin HD (2015a) First report of powdery mildew caused by Golovinomyces biocellatus on Meehania urticifolia in Korea. Plant Disease, 99, 892. |
| [18] | Cho SE, Park JH, Hong SH, Park MJ, Shin HD (2015b) First report of powdery mildew caused by Neoerysiphe galeopsidis on Lamium amplexicaule in Korea. Plant Disease, 99, 1179. |
| [19] | Cho SE, Park JH, Hong SH, Shin HD (2013) First report of powdery mildew caused by Golovinomyces asterum var. solidaginis on invasive weed Solidago gigantea in Korea. Plant Disease, 97, 1120. |
| [20] | Cho SE, Park JH, Lee SK, Lee SH, Lee CK, Shin HD (2014c) First report of powdery mildew caused by Phyllactinia actinidiae on hardy kiwi in Korea. Plant Disease, 98, 1436. |
| [21] | Cho SE, Park MJ, Han KS, Choi IY, Shin HD (2016b) First confirmed report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe aquilegiae var. aquilegiae on Aquilegia buergeriana var. oxysepala in Korea. Plant Disease, 100, 2333. |
| [22] | Cho SE, Park MJ, Kim JY, Shin HD (2012) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe sedi on Kalanchoe blossfeldiana in Korea. Plant Disease, 96, 1701. |
| [23] | Cho SE, Takamatsu S, Meeboon J, Shin HD (2014d) Erysiphe magnoliicola, a new powdery mildew on Magnolia. Mycotaxon, 129, 153-161. |
| [24] | Cho SE, Zhao TT, Choi IY, Choi YJ, Shin HD (2016c) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe trifoliorum on Indigofera amblyantha in Korea. Plant Disease, 100, 1954. |
| [25] | Cho SE, Zhao TT, Lee SH, Lee SY, Shin HD (2017c) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe aucubae on Aucuba japonica in Korea. Plant Disease, 101, 1033. |
| [26] | Choi IY, Abasova L, Choi JH, Choi BK, Shin HD (2023a) Morphology and molecular phylogeny of Erysiphe japonica var. japonica found on Quercus aliena in Korea. Forest Pathology, 53, e12819. |
| [27] | Choi IY, Abasova L, Choi JH, Park JH, Shin HD (2023b) Erysiphe lonicerigena sp. nov., a powdery mildew species found on Lonicera harae. Mycobiology, 51, 67-71. |
| [28] | Choi IY, Abasova L, Choi JH, Shin HD (2022a) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe lonicerae on Lonicera periclymenum in Korea. Journal of Plant Pathology, 104, 1153. |
| [29] | Choi IY, Choi CH, Cho SE, Park JH, Shin HD (2016a) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe limonii on perennial hybrid statice in Korea. Plant Disease, 100, 652. |
| [30] | Choi IY, Choi JH, Abasova L, Shin HD (2023c) First report of powdery mildew caused by Golovinomyces ambrosiae on Solanum carolinense in Korea. Plant Disease, 107, 2245. |
| [31] | Choi IY, Choi YJ, Shin HD (2020) First report of powdery mildew caused by Podosphaera xanthii on Cucurbita maxima in Korea. Journal of Plant Pathology, 102, 599. |
| [32] | Choi IY, Hong SH, Lee YH, Shin HD (2021a) First report of powdery mildew caused by Podosphaera erigerontis- canadensis on Conyza sumatrensis in Korea. Journal of Plant Pathology, 103, 381. |
| [33] | Choi IY, Kang CH, Song YJ, Cho SE, Shin HD (2016b) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe buhrii on Gypsophila oldhamiana in Korea. Plant Disease, 100, 2164. |
| [34] | Choi IY, Kim BS, Cho SE, Park JH, Shin HD (2014) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe buhrii on Gypsophila paniculata in Korea. Plant Disease, 98, 1013. |
| [35] | Choi IY, Kim JH, Kim KM, Cho SE, Shin HD (2016c) First report of powdery mildew caused by Neoerysiphe galeopsidis on Stachys affinis in Korea. Plant Disease, 100, 218. |
| [36] | Choi IY, Lee CK, Shin HD (2022b) First report of powdery mildew caused by Podosphaera astericola on Kalimeris incisa in Korea. Journal of Plant Pathology, 104, 401. |
| [37] | Choi IY, Nam EY, Cho SE, Park JH, Shin HD (2015) First report of powdery mildew caused by Podosphaera tridactyla on sweet cherry in Korea. Plant Disease, 99, 1648. |
| [38] | Choi IY, Park JH, Jung BN, Shin HD (2021b) First report of powdery mildew caused by Podosphaera sibirica on Veronicastrum sibiricum in Korea. Journal of Plant Pathology, 103, 705. |
| [39] | Choi JK, Kim BS, Choi IY, Cho SE, Shin HD (2014a) First report of powdery mildew caused by Golovinomyces artemisiae on Artemisia annua in Korea. Plant Disease, 98, 1010. |
| [40] | Choi JK, Kim BS, Hong SH, Cho SE, Shin HD (2014b) First report of powdery mildew caused by Golovinomyces sonchicola on Ixeris chinensis in Korea. Plant Disease, 98, 999. |
| [41] | Choi YJ, Choi BK, Choi IY, Shin HD (2021) Erysiphe magnifica causes powdery mildew on Magnolia compressa. Forest Pathology, 51, e12706. |
| [42] | Darsaraei H, Khodaparast SA, Takamatsu S, Abbasi M, Asgari B, Sajedi S, Götz M, Liu SY, Feng J, Bradshaw M, Bulgakov T, Braun U (2021) Phylogeny and taxonomy of the Erysiphe adunca complex (Erysiphaceae, Helotiales) on poplars and willows. Mycological Progress, 20, 517-537. |
| [43] | Dong L, Ou Y, Meng QL (2020) Investigation on tomato powdery mildew in Chaoyang City of Liaoning Province. Horticulture & Seed, 40, 12-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [董莉, 欧勇, 孟庆林 (2020) 辽宁朝阳地区番茄白粉病发生调查研究. 园艺与种苗, 40, 12-13.] | |
| [44] | Feng J, Liu SY, Braun U, Takamatsu S, Bradshaw M, Khodaparast SA, Bulgakov TS, Guan GX, Zhao FY, Tang SR (2022) Discovery of a cryptic species, Erysiphe salicina sp. nov., and reconstruction of the phylogeny of powdery mildews on Populus and Salix spp. Mycological Progress, 21, 54. |
| [45] | Frantzeskakis L, Németh MZ, Barsoum M, Kusch S, Kiss L, Takamatsu S, Panstruga R (2019) The Parauncinula polyspora draft genome provides insights into patterns of gene erosion and genome expansion in powdery mildew fungi. mBio, 10, e01692-19. |
| [46] |
Heluta V, Takamatsu S, Harada M, Voytyuk S (2010) Molecular phylogeny and taxonomy of Eurasian Neoerysiphe species infecting Asteraceae and Geranium. Persoonia, 24, 81-92.
DOI PMID |
| [47] | Heluta VP (1988) Filogeneticheskie vzaimosvyazi mezhdu rodami erizifal’ nykh gribov i nekotorye voprosy sistematika poryadka Erysiphales. Biologicheskii Zhurnal Armenii, 41, 351-358. |
| [48] | Homma Y (1937) Erysiphaceae of Japan. Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture, Hokkaido University, 38, 183-461. |
| [49] | Hong SH, Choi YJ, Cho SE, Zhao TT, Shin HD (2016) First report of powdery mildew caused by Golovinomyces asterum var. solidaginis on Solidago altissima in Korea. Plant Disease, 100, 1245. |
| [50] | Hong SH, Lee YH, Choi YJ, Shin HD (2019a) First report of powdery mildew caused by Neoerysiphe galeopsidis on Lamium purpureum in Korea. Plant Disease, 103, 1769. |
| [51] | Hong SH, Lee YH, Choi YJ, Shin HD (2019b) First report of powdery mildew caused by Neoerysiphe nevoi on Hypochaeris radicata in Korea. Plant Disease, 103, 369. |
| [52] | Hong SH, Lee YH, Choi YJ, Shin HD (2020) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe trifoliorum on Trifolium hybridum in Korea. Plant Disease, 104, 3056. |
| [53] | Hsiao HY, Ariyawansa HA, Hsu CC, Wang CJ, Shen YM (2022) New records of powdery mildews from Taiwan: Erysiphe ipomoeae comb. nov., E. aff. betae on buckwheat, and E. neolycopersici comb. nov. on Cardiospermum halicacabum. Diversity, 14, 204. |
| [54] | Jiang WT, Liu SY, Wang LL, Yang LL (2013) New record species of Erysiphales in Jilin Province. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 35, 24-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姜文涛, 刘淑艳, 王丽兰, 杨丽丽 (2013) 吉林省白粉菌新记录种. 吉林农业大学学报, 35, 24-26.] | |
| [55] | Katumoto K (1973) Notes on the genera Lanomyces Gäum. and Cystotheca Berk. et Curt. Reports of the Tottori Mycological Institute, 10, 437-446. |
| [56] | Kim CS, Kim HJ, Choi IY, Cho SE, Zhao TT, Shin HD (2018) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe hyperici on Hypericum ascyron in Korea. Plant Disease, 102, 680. |
| [57] | Kim KH, Lee SK, Shin HD (2008) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe lonicerae var. lonicerae on Lonicera sempervirens in Korea. Plant Pathology, 57, 374. |
| [58] | Kiss L, Vaghefi N, Bransgrove K, Dearnaley JDW, Takamatsu S, Tan YP, Marston C, Liu SY, Jin DN, Adorada DL, Bailey J, Daly A, Dirchwolf PM, Jones L, Nguyen TD, Edwards J, Ho W, Kelly L, Mintoff SJL, Morrison J, Németh MZ, Perkins S, Shivas RG, Smith R, Stuart K, Southwell R, Turaganivalu U, Váczy KZ, Van Blommestein A, Wright D, Young A, Braun U (2020) Australia: A continent without native powdery mildews? the first comprehensive catalog indicates recent introductions and multiple host range expansion events, and leads to the re-discovery of Salmonomyces as a new lineage of the Erysiphales. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 1571. |
| [59] | Kwon JH, Choi OH, Shin HD, Kim JW (2012) First report of powdery mildew caused by Podosphaera fusca on Trichosanthes kirilowii var. japonica in Korea. The Plant Pathology Journal, 28, 116. |
| [60] | Kwon JH, Jee HJ, Kim J (2015) Characterization of powdery mildew caused by Podosphaera fusca infecting Melothria japonica (Thunb.) Maxim. Journal of Agriculture & Life Science, 49, 47-56. |
| [61] | La YJ, Cho SE, Shin HD (2013) First report of powdery mildew of Platanus occidentalis caused by Erysiphe platani in Korea. Plant Disease, 97, 843. |
| [62] | La YJ, Lee SK, Shin CH, Cho SE, Shin HD (2014) First report of powdery mildew caused by Cystotheca wrightii on Quercus glauca in Korea. Plant Disease, 98, 850. |
| [63] | Lee HB (2013) First report of Oidium anamorph of Erysiphe hypophylla causing powdery mildew on leafy Lespedeza (Lespedeza cyrtobotrya) in Korea. Plant Disease, 97, 287. |
| [64] | Lee HB, Kim CJ, Mun HY, Hong JP, Glawe DA (2009) First report of powdery mildew on trident maple caused by Sawadaea nankinensis in Korea. Plant Disease, 93, 1348. |
| [65] | Lee HB, Kim CJ, Mun HY, Lee KH (2011) First report of Erysiphe quercicola causing powdery mildew on ubame oak in Korea. Plant Disease, 95, 77. |
| [66] | Lee HB, Lee HW, Mun HY (2013) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe platani on Sycamore (Platanus occidentalis) in South Korea. Plant Disease, 97, 841. |
| [67] | Lee HB, Nguyen TTT (2019a) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe palczewskii on Robinia pseudoacacia in Korea. Plant Disease, 103, 1428. |
| [68] | Lee HB, Nguyen TTT (2019b) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe salmonii on Fraxinus rhynchophylla in Korea. Plant Disease, 103, 769. |
| [69] | Lee HB, Nguyen TTT (2020) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe lespedezae on Kummerowia striata in Korea. Plant Disease, 104, 1548-1549. |
| [70] | Lee HB, Nguyen TTT (2021) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe viciae-unijugae on Vicia sativa subsp. nigra in Korea. Plant Disease, 105, 493. |
| [71] | Lee SH, Lee CK, Cho SE, Park JH, Shin HD (2016) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe lonicerae var. lonicerae on Lonicera japonica in Korea. Plant Disease, 100, 856. |
| [72] | Li Y, Li Y, Shi J, Yang XD (1992) Erysiphales from Jilin Province III. Microsphaera genus of Erysiphaceae. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 14(2), 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李亚, 李玉, 时杰, 杨信东 (1992) 吉林省白粉菌III. 叉丝壳属Microsphaera Lév. 吉林农业大学学报, 14(2), 1-4.] | |
| [73] | Li Y, Li Y, Shi J, Yang XD (1995) Erysiphales from Jilin Province IV. Phyllactinia Lév, Sawadaia Miyabe, Podosphaera Kunze, Uncinula Lév. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 17(3), 29-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李玉, 李亚, 时杰, 杨信东 (1995) 吉林省白粉菌IV. 球针壳属Phyllactinia Lév, 叉钩丝壳属 Sawadaia Miyabe, 叉丝单囊壳属Podosphaera Kunze, 钩丝壳属Uncinula Lév. 吉林农业大学学报, 17(3), 29-32.] | |
| [74] | Li Y, Shi J, Li Y, Yang XD (1990) Erysiphales from Jilin Province I. The genus of Erysiphe. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 12(4), 6-16, 102. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李玉, 时杰, 李亚, 杨信东 (1990) 吉林省白粉菌I. 白粉菌属Erysiphe. 吉林农业大学学报, 12(4), 6-16, 102.] | |
| [75] | Liu SY, Wang LL, Jiang WT, Li Y (2011) First report of powdery mildew on Euphorbia pekinensis caused by Podosphaera euphorbiae-helioscopiae in China. Plant Disease, 95, 1314. |
| [76] | Liu SY, Wang LL, Jiang WT, Li Y (2012) New recorded species of Erysiphales for Northeastern China. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 34, 376-380. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘淑艳, 王丽兰, 姜文涛, 李玉 (2012) 中国东北地区白粉菌新记录种. 吉林农业大学学报, 34, 376-380.] | |
| [77] | Liu TZ (1998) Investigation of powdery mildew on trees and their pathogenic identification in South Chifeng. Forest Pest and Disease, (1), 15-18, 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘铁志 (1998) 赤峰南部林木白粉病调查及其病原鉴定. 森林病虫通讯, (1), 15-18, 39.] | |
| [78] | Liu TZ (2010) The Erysiphaceae of Inner Mongolia. Inner Mongolia Science and Technology Press, Chifeng, Inner Mongolia. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘铁志 (2010) 内蒙古白粉菌志. 内蒙古科学技术出版社, 内蒙古赤峰.] | |
| [79] | Liu TZ (2011) Flora diversity of powdery mildews in Inner Mongolia. Journal of Fungal Research, 9(1), 15-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘铁志 (2011) 内蒙古白粉菌区系多样性. 菌物研究, 9(1), 15-20.] | |
| [80] | Liu TZ (2022) Erysiphaceae of Inner Mongolia: Supplement and revision. Journal of Fungal Research, 20(1), 6-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘铁志 (2022) 《内蒙古白粉菌志》增补与修订. 菌物研究, 20(1), 6-22.] | |
| [81] | Liu TZ, Qin XC, Wang YC (2002a) Erysiphales of the Chifeng regions of NeiMongol: Arthrocladiella, Blumeria, Sphaerotheca. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis NeiMongol, 33(1), 57-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘铁志, 秦晓春, 王迎春 (2002a) 内蒙古赤峰地区的白粉菌I——节丝壳属、布氏白粉菌属和单囊壳属. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 33(1), 57-61.] | |
| [82] | Liu TZ, Qin XC, Wang YC (2002b) Erysiphe of the Chifeng regions of NeiMongol. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis NeiMongol, 33(2), 177-181. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘铁志, 秦晓春, 王迎春 (2002b) 内蒙古赤峰地区的白粉菌II——白粉菌属. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 33(2), 177-181.] | |
| [83] | Liu TZ, Wang YC (2004) Erysiphales of the Chifeng regions of Nei Mongol: Microsphaera and Podosphaera. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis NeiMongol, 35(2), 234-237. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘铁志, 王迎春 (2004) 内蒙古赤峰地区的白粉菌IV——叉丝壳属和叉丝单囊壳属. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 35(2), 234-237.] | |
| [84] | Liu TZ, Wang YC, Xia H (2004) Erysiphales of the Chifeng regions of Nei Mongol III: Leveillula, Phyllactinia, Sawadaea and Uncinula. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis NeiMongol, 35, 115-118. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘铁志, 王迎春, 夏红 (2004) 内蒙古赤峰地区的白粉菌III——内丝白粉菌属、球针壳属、叉钩丝壳属和钩丝壳属. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 35, 115-118.] | |
| [85] | Liu W, Liu SY, Li Y, Jiang WT (2009) The identification of the pathogen causing tomato powdery mildew. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 39(1), 11-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘微, 刘淑艳, 李玉, 姜文涛 (2009) 番茄白粉病的病原菌鉴定. 植物病理学报, 39(1), 11-15.] | |
| [86] | Marmolejo J, Siahaan SAS, Takamatsu S, Braun U (2018) Three new records of powdery mildews found in Mexico with one genus and one new species proposed. Mycoscience, 59, 1-7. |
| [87] |
Meeboon J, Okamoto J, Takamatsu S (2021) Two new records of powdery mildews (Erysiphaceae) from Japan: Erysiphe actinidiicola sp. nov. and Erysiphe sp. on Limonium tetragonum. Mycoscience, 62, 198-204.
DOI PMID |
| [88] | Meeboon J, Siahaan SAS, Fujioka K, Takamatsu S (2017) Molecular phylogeny and taxonomy of Parauncinula (Erysiphales) and two new species P. polyspora and P. uncinata. Mycoscience, 58, 361-368. |
| [89] | Meeboon J, Siahaan SAS, Takamatsu S (2015) Notes on powdery mildews (Erysiphales) in Japan. IV. Phyllactinia, Parauncinula and Sawadaea. Mycoscience, 56, 590-596. |
| [90] | Meeboon J, Takamatsu S (2015a) Notes on powdery mildews (Erysiphales) in Japan. I. Erysiphe sect. Erysiphe. Mycoscience, 56, 257-266. |
| [91] | Meeboon J, Takamatsu S (2015b) Notes on powdery mildews (Erysiphales) in Japan. II. Erysiphe sect. Microsphaera. Mycoscience, 56, 230-236. |
| [92] | Meeboon J, Takamatsu S (2015c) Notes on powdery mildews (Erysiphales) in Japan. III. Golovinomyces and Podosphaera. Mycoscience, 56, 243-251. |
| [93] | Meeboon J, Takamatsu S (2015d) Erysiphe takamatsui, a powdery mildew of lotus: Rediscovery of teleomorph after 40 years, morphology and phylogeny. Mycoscience, 56, 159-167. |
| [94] | Meeboon J, Takamatsu S (2015e) Erysiphe viburni-plicati and Podosphaera photiniae, two new species of Erysiphales (Ascomycota) from Japan. Mycoscience, 56, 14-23. |
| [95] | Men XY, Liu SY, Jiang WT, Li Y (2014) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe macleayae on Torenia fournieri in China. Plant Disease, 98, 1277. |
| [96] | Park JH, Choi YJ, Choi IY, Shin HD (2023) First report of powdery mildew caused by Golovinomyces ambrosiae on Leucanthemum vulgare in Korea. Plant Disease, 107, 963. |
| [97] | Park MJ, Cho SE, Park JH, Lee SK, Shin HD (2012a) First report of powdery mildew caused by Oidium hortensiae on Mophead Hydrangea in Korea. Plant Disease, 96, 1072. |
| [98] | Park MJ, Cho SE, Wolcan S, Shin HD (2012b) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe betae on the invasive weed Dysphania ambrosioides in Korea. Plant Disease, 96, 592. |
| [99] | Qi PK, Bai JK, Zhu GX (1966) Fungal Diseases of Cultivated Plants in Jilin Province. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [戚佩坤, 白金凯, 朱桂香 (1966) 吉林省栽培植物真菌病害志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [100] |
Qian HY, Yu JP, Shen XL, Ding P, Li S (2019) Diversity and composition of birds in the Qianjiangyuan National Park pilot. Biodiversity Science, 27, 76-80. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[钱海源, 余建平, 申小莉, 丁平, 李晟 (2019) 钱江源国家公园体制试点区鸟类多样性与区系组成. 生物多样性, 27, 76-80.]
DOI |
|
| [101] | Qiu PL, Liu SY, Bradshaw M, Rooney-Latham S, Takamatsu S, Bulgakov TS, Tang SR, Feng J, Jin DN, Aroge T, Li Y, Wang LL, Braun U (2020) Multi-locus phylogeny and taxonomy of an unresolved, heterogeneous species complex within the genus Golovinomyces (Ascomycota, Erysiphales), including G. ambrosiae, G. circumfusus and G. spadiceus. BMC Microbiology, 20, 51. |
| [102] | Qiu PL, Tang SR, Guan GX, Li Y, Takamatsu S, Liu SY (2019) Revisiting a poorly known powdery mildew species: Morphology and molecular phylogeny of Erysiphe longissima. Mycoscience, 60, 250-254. |
| [103] | Qu L, Qin ZW (2007) Research progress of pathogen and resistance of cucumber powdery mildew. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 38, 835-841. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曲丽, 秦智伟 (2007) 黄瓜白粉病病原菌及抗病性研究进展. 东北农业大学学报, 38, 835-841.] | |
| [104] | Sato Y, Eto S (2014) Powdery mildews and their host plants in Japan. Bulletin of Toyama Prefectural University, 24, 26-65. (in Japanese) |
| [105] | Shi J, Li Y, Li Y, Yang XD (1991) Erysiphales from Jilin Province II. Sphaerotheca genus of Erysiphaceae. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 13(4), 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [时洁, 李玉, 李亚, 杨信东 (1991) 吉林省白粉菌II. 单囊壳属Sphaerotheca Lév. 吉林农业大学学报, 13(4), 1-6.] | |
| [106] | Shin HD (2000) Erysiphaceae of Korea. National Institute of Agricultural Science and Technology, Suwon. |
| [107] | Shin HD, Meeboon J, Takamatsu S, Adhikari MK, Braun U (2019) Phylogeny and taxonomy of Pseudoidium pedaliacearum. Mycological Progress, 18, 237-246. |
| [108] | Shin HD, Park MJ (2011) Sawadaea koelreuteriae comb, nov., a powdery mildew of Koelreuteria paniculata. Journal of Microbiology, 49, 862-866. |
| [109] | Siahaan SAS, Sakamoto H, Shinoda T, Takamatsu S (2018a) Geographic and temporal distributions of four genotypes found in Erysiphe gracilis var. gracilis, a powdery mildew of evergreen oaks (Erysiphales). Mycoscience, 59, 110-118. |
| [110] | Siahaan SAS, Sakamoto H, Shinoda T, Takamatsu S (2018b) Morphophylogenetic study revealed that Erysiphe gracilis (powdery mildew of evergreen oaks, Erysiphales) is a species complex consisting of six different species. Mycoscience, 59, 124-136. |
| [111] | Siahaan SAS, Takamatsu S (2016) Erysiphe aucubae sp. nov., a new powdery mildew species on Aucuba japonica from Japan. Mycoscience, 57, 251-254. |
| [112] | Takamatsu S (2004) Phylogeny and evolution of the powdery mildew fungi (Erysiphales, Ascomycota) inferred from nuclear ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycoscience, 45, 147-157. |
| [113] | Takamatsu S (2012) Overview of revised systematics of the powdery mildews (Ascomycota: Erysiphales) in the new monograph published in 2012. Bulletin of the Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University, 38, 1-73. (in Japanese) |
| [114] | Takamatsu S, Cho SE, Meeboon J, Shin HD (2013) Revisiting Erysiphe magnoliae with morphological and molecular data. Sydowia, 65, 13-20. |
| [115] | Takamatsu S, Masuya H, Divarangkoon R, Nomura Y (2008) Erysiphe fimbriata sp. nov.: A powdery mildew fungus found on Carpinus laxiflora. Mycoscience, 49, 185-191. |
| [116] | Takamatsu S, Siahaan SAS, Shinoda T (2015) Erysiphe kissiana sp. nov.: First finding of sect. Californiomyces in Japan. Mycoscience, 56, 512-515. |
| [117] | Tang S, Liu S (2023) First report of powdery mildew caused by Podosphaera fuliginea on Veronica spicata in China. Plant Disease, 107, 584. |
| [118] | Tang SR, Guan GX, Liu SY (2018) Advances on the taxonomy of Erysiphales in China. Journal of Fungal Research, 16, 138-149. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [唐淑荣, 管观秀, 刘淑艳 (2018) 中国白粉菌目分类学研究现状. 菌物研究, 16, 138-149.] | |
| [119] | Wang LL, Liu SY, Jiang WT, Li Y (2011) New varieties record to Jilin Province and new host of Erysiphe sect. Microsphaera. Journal of Fungal Research, 9, 65-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王丽兰, 刘淑艳, 姜文涛, 李玉 (2011) 吉林省白粉菌属叉丝壳组新记录变种与新寄主. 菌物研究, 9, 65-68.] | |
| [120] |
Wang X, Zhang FL, Zhang J (2017) Biodiversity information resources. I. Species distribution, catalogue, phylogeny, and life history traits. Biodiversity Science, 25, 1223-1238. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [王昕, 张凤麟, 张健 (2017) 生物多样性信息资源. I. 物种分布、编目、系统发育与生活史性状. 生物多样性, 25, 1223-1238.] | |
| [121] | Wang YY, Chen LJ, Duan YX, Lv GZ (2004) Powdery mildew occurred in greenhouse tomatoes in Shenyang area. Plant Protection, 30(5), 91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王媛媛, 陈立杰, 段玉玺, 吕国忠 (2004) 沈阳地区温室番茄发生白粉病. 植物保护, 30(5), 91.] | |
| [122] | Wu ZY, Zhou ZK, Li DZ, Peng H, Sun H (2003) The areal-types of the world families of seed plants. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 25, 245-257. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴征镒, 周浙昆, 李德铢, 彭华, 孙航 (2003) 世界种子植物科的分布区类型系统. 云南植物研究, 25, 245-257.] | |
| [123] | Wu ZY, Zhou ZK, Sun H, Li DZ, Peng H (2006) The Areal-types of Seed Plants and Their Origin and Differentiation. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [吴征镒, 周浙昆, 孙航, 李德铢, 彭华 (2006) 种子植物分布区类型及其起源和分化. 云南科学技术出版社, 昆明.] | |
| [124] | Zhao HH, Xing HH, Liang C, Yang XY, Cho SE, Shin HD (2014) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe cruciferarum on Chinese cabbage in China. Plant Disease, 98, 421. |
| [125] | Zhao YZ, Zhao LQ, Cao R (2020) Flora IntraMongolica, Vol. 3. Inner Mongolia People’s Publishing House, Hohhot. (in Chinese) |
| [赵一之, 赵利清, 曹瑞 (2020) 内蒙古植物志(第三卷). 内蒙古人民出版社, 呼和浩特.] | |
| [126] | Zheng RY, Yu YN (1987) Flora Fungorum Sinicorum, Vol. 1 (Erysiphales). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑儒永, 余永年 (1987) 中国真菌志·第一卷(白粉菌目). 科学出版社, 北京.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [5] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [6] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [7] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [8] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [9] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [10] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [11] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [12] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [13] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [14] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [15] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()