



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 23439. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023439 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023439
刘荆州1,#, 钱易鑫2,#, 张燕雪丹1,*( ), 崔凤1,*(
), 崔凤1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-11-20
接受日期:2024-03-23
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-04-07
通讯作者:
* E-mail: 作者简介:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
Jingzhou Liu1,#, Yixin Qian2,#, Yanxuedan Zhang1,*( ), Feng Cui1,*(
), Feng Cui1,*( )
)
Received:2023-11-20
Accepted:2024-03-23
Online:2024-04-20
Published:2024-04-07
Contact:
* E-mail: About author:#Co-first authors
摘要:
旗舰物种范式是借助代表性物种的公共影响力实现生物多样性保护的一种策略。尽管这一策略在国际上已成为提升公众环保意识和筹措保护资金的重要手段, 但国内学界关注度不够, 限制了其发展。因此, 有必要对国际研究进行梳理, 启发国内采取相关策略。本文利用潜在迪利克雷分布(latent Dirichlet allocation, LDA)的主题模型, 选取英文学术期刊上发表的旗舰物种范式相关文献, 聚合为旗舰物种范式的理论研究、旗舰物种项目的案例研究、问卷访谈揭示的公众态度及其影响因素、旗舰物种范式的场景落地问题、旗舰物种范式的负面效应和旗舰物种范式的优化策略等6个主题并进行综述。综述发现: (1)旗舰物种范式存在动物福利问题、天花板效应、“诺亚方舟”问题与未经本土化的保护主义4个负面效应; (2)对应上述问题存在本土化、降干扰、去偏见与跨界传播4个发展方向; (3)旗舰物种范式存在围绕旗舰物种定义与本质属性的冲突。本文进一步讨论了旗舰物种的定义、遴选及其局限性的争论3个重大问题, 提出了明确范式的实现形式、多主体协同参与、优化旗舰物种遴选与项目安排、加强本土创新与国际合作等建议。
刘荆州, 钱易鑫, 张燕雪丹, 崔凤 (2024) 基于潜在迪利克雷分布(LDA)模型的旗舰物种范式研究进展与启示. 生物多样性, 32, 23439. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023439.
Jingzhou Liu, Yixin Qian, Yanxuedan Zhang, Feng Cui (2024) Research progress and implications of flagship species paradigms based on latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) model. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23439. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023439.
| 主题编码 Topic coding | 出现频次前10的主题词概率分布 Probability distribution of the top 10 topic words with the highest frequency |
|---|---|
| 主题1 Topic 1 | 0.019 * “species” + 0.016 * “conservation” + 0.006 * “animal” + 0.006 * “management” + 0.006 * “public” + 0.005 * “people” + 0.004 * “nature” + 0.004 * “conflict” + 0.004 * “local” + 0.004 * “flagship” |
| 主题2 Topic 2 | 0.032 * “species” + 0.019 * “conservation” + 0.008 * “flagship” + 0.007 * “public” + 0.005 * “study” + 0.005 * “animal” + 0.005 * “wildlife” + 0.005 * “charismatic” + 0.005 * “group” + 0.004 * “benefit” |
| 主题3 Topic 3 | 0.020 * “conservation” + 0.019 * “species” + 0.010 * “flagship” + 0.006 * “area” + 0.005 * “wildlife” + 0.005 * “tourism” + 0.004 * “protected” + 0.004 * “awareness” + 0.004 * “biodiversity” + 0.004 * “used” |
| 主题4 Topic 4 | 0.017 * “species” + 0.016 * “conservation” + 0.011 * “biodiversity” + 0.007 * “area” + 0.005 * “habitat” + 0.005 * “management” + 0.004 * “study” + 0.004 * “information” + 0.004 * “public” + 0.004 * “flagship” |
| 主题5 Topic 5 | 0.033 * “species” + 0.019 * “conservation” + 0.007 * “wildlife” + 0.006 * “area” + 0.006 * “study” + 0.005* “flagship” + 0.005 * “biodiversity” + 0.005 * “result” + 0.004 * “public” + 0.004 * “management” |
| 主题6 Topic 6 | 0.018 * “conservation” + 0.012 * “wildlife” + 0.012 * “species” + 0.007 * “people” + 0.006 * “management” + 0.006 * “attitude” + 0.006 * “flagship” + 0.005 * “towards” + 0.005 * “conflict” + 0.005 * “public” |
表1 基于潜在迪利克雷分布(LDA)模型的旗舰物种范式文献“主题-词组”分布表。引号用以强调特定关键术语或词语、星号表示术语在对应主题中的权重、加号用于连接同一主题下不同术语及其对应的概率。
Table 1 “Topic-Phrase” distribution table of flagship species paradigm literature based on latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) model. Quotation marks are used to emphasise specific key terms or words, asterisks indicate the weight of a term in the corresponding topic, and plus signs are used to link different terms and their corresponding probabilities under the same topic.
| 主题编码 Topic coding | 出现频次前10的主题词概率分布 Probability distribution of the top 10 topic words with the highest frequency |
|---|---|
| 主题1 Topic 1 | 0.019 * “species” + 0.016 * “conservation” + 0.006 * “animal” + 0.006 * “management” + 0.006 * “public” + 0.005 * “people” + 0.004 * “nature” + 0.004 * “conflict” + 0.004 * “local” + 0.004 * “flagship” |
| 主题2 Topic 2 | 0.032 * “species” + 0.019 * “conservation” + 0.008 * “flagship” + 0.007 * “public” + 0.005 * “study” + 0.005 * “animal” + 0.005 * “wildlife” + 0.005 * “charismatic” + 0.005 * “group” + 0.004 * “benefit” |
| 主题3 Topic 3 | 0.020 * “conservation” + 0.019 * “species” + 0.010 * “flagship” + 0.006 * “area” + 0.005 * “wildlife” + 0.005 * “tourism” + 0.004 * “protected” + 0.004 * “awareness” + 0.004 * “biodiversity” + 0.004 * “used” |
| 主题4 Topic 4 | 0.017 * “species” + 0.016 * “conservation” + 0.011 * “biodiversity” + 0.007 * “area” + 0.005 * “habitat” + 0.005 * “management” + 0.004 * “study” + 0.004 * “information” + 0.004 * “public” + 0.004 * “flagship” |
| 主题5 Topic 5 | 0.033 * “species” + 0.019 * “conservation” + 0.007 * “wildlife” + 0.006 * “area” + 0.006 * “study” + 0.005* “flagship” + 0.005 * “biodiversity” + 0.005 * “result” + 0.004 * “public” + 0.004 * “management” |
| 主题6 Topic 6 | 0.018 * “conservation” + 0.012 * “wildlife” + 0.012 * “species” + 0.007 * “people” + 0.006 * “management” + 0.006 * “attitude” + 0.006 * “flagship” + 0.005 * “towards” + 0.005 * “conflict” + 0.005 * “public” |
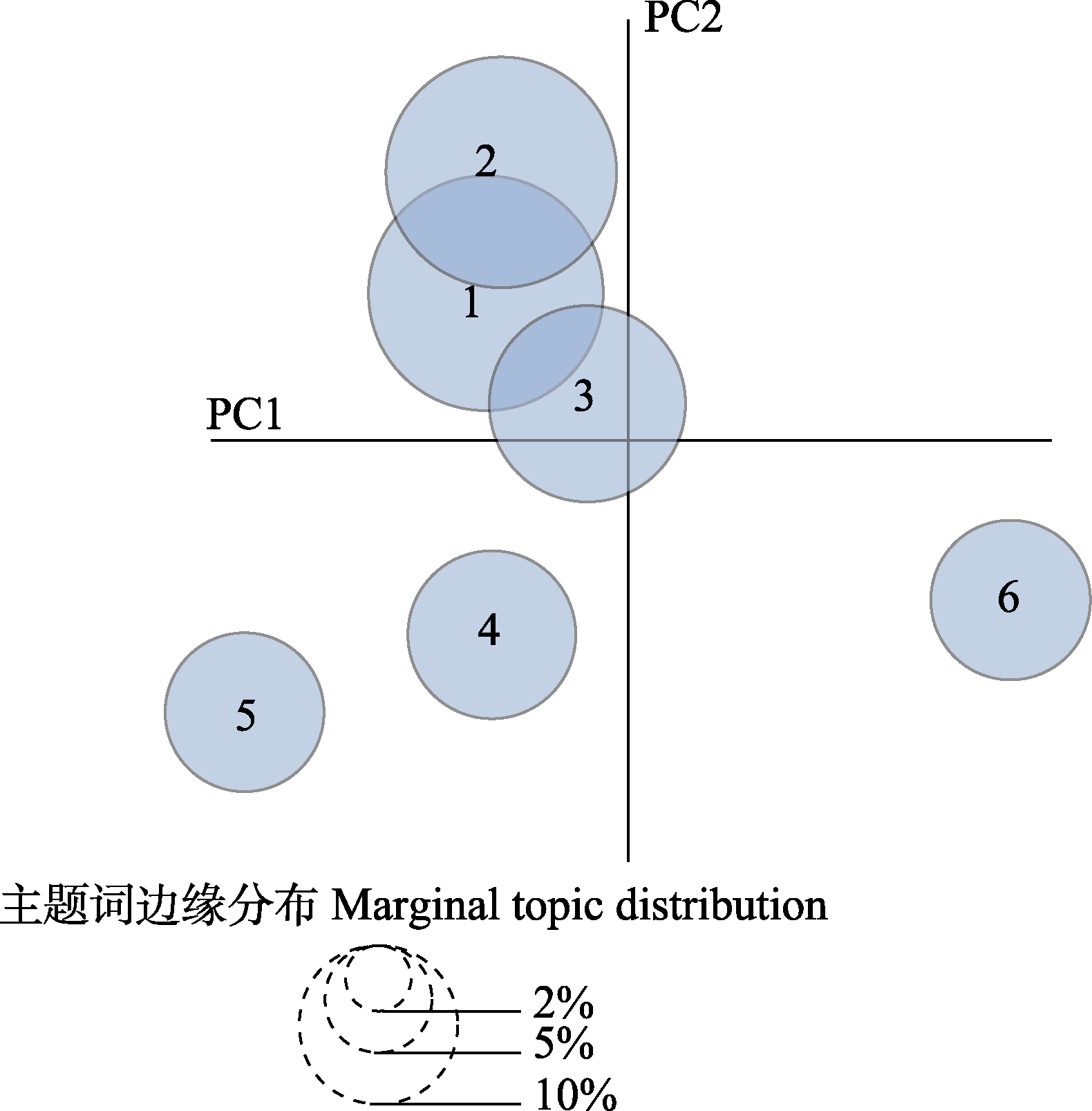
图2 基于潜在迪利克雷分布(LDA)模型的旗舰物种范式文献主题间距离图。1-6分别表示6个主题。百分比对应圆的面积表示图中各主题对应的文献占总样本文献的百分比大小。
Fig. 2 The distance between topics of flagship species paradigm literature based on latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) model. 1-6 represent the 6 themes respectively. The area of the circle corresponding to the percentage indicates the size of the literature corresponding to each theme in the graph as a percentage of the total sample literature.
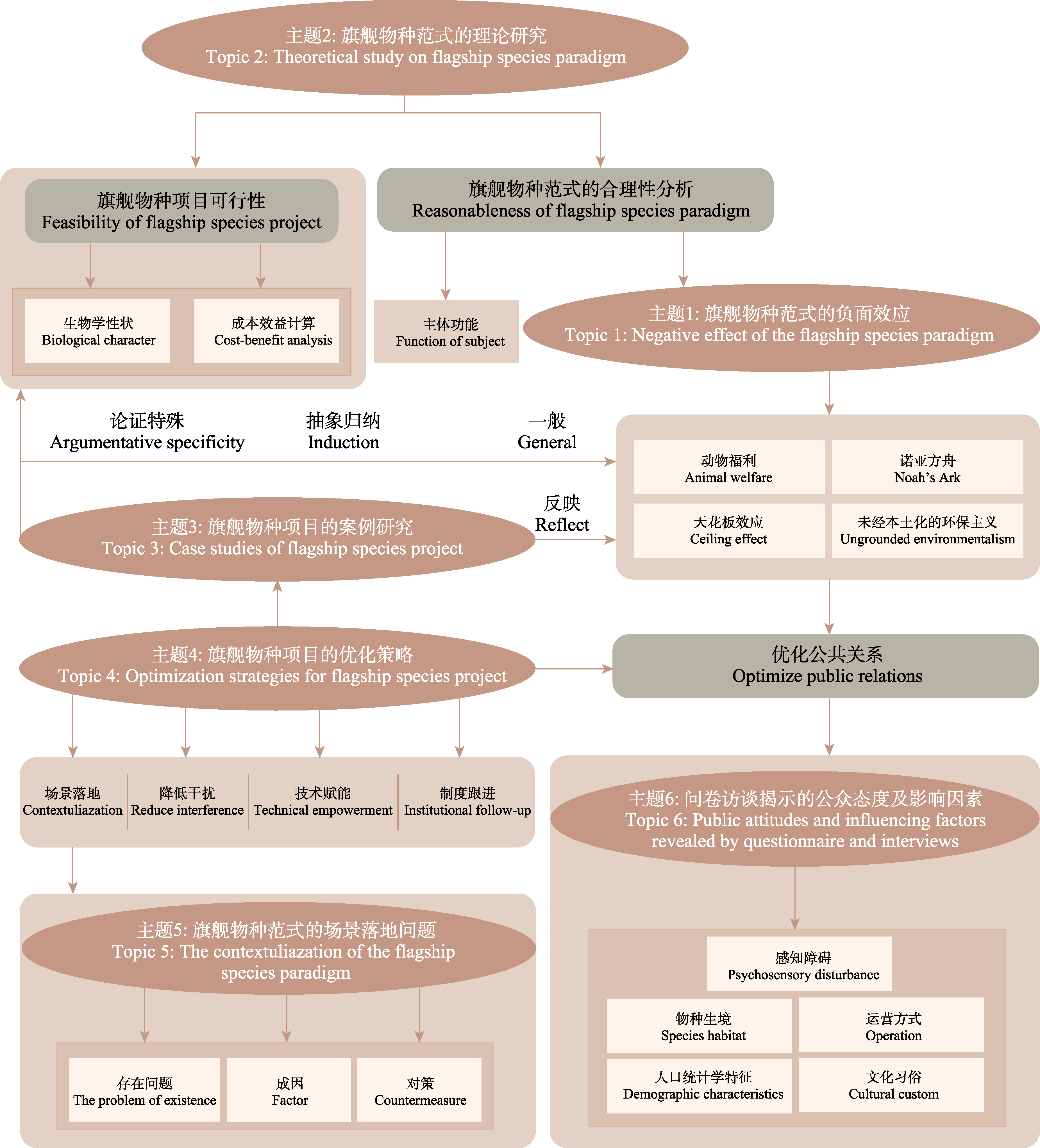
图3 基于潜在迪利克雷分布(LDA)模型的旗舰物种范式文献主题逻辑框架图
Fig. 3 The topic logic framework of the flagship species paradigm literature based on latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) model
| [1] |
Allendorf TD, Aung M, Songer M (2012) Using residents’ perceptions to improve park-people relationships in Chatthin Wildlife Sanctuary, Myanmar. Journal of Environmental Management, 99, 36-43.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Arpin I, Cosson A (2018) What the ecosystem approach does to conservation practices. Biological Conservation, 219, 153-160. |
| [3] | Barbato D, Benocci A, Guasconi M, Manganelli G (2021) Light and shade of citizen science for less charismatic invertebrate groups: Quality assessment of iNaturalist nonmarine mollusc observations in central Italy. Journal of Molluscan Studies, 87, eyab033. |
| [4] | Barua M (2011) Mobilizing metaphors: The popular use of keystone, flagship and umbrella species concepts. Biodiversity and Conservation, 20, 1427-1440. |
| [5] | Batel A, Basta J, Mackelworth P (2014) Valuing visitor willingness to pay for marine conservation—The case of the proposed Cres-Lošinj Marine Protected Area, Croatia. Ocean & Coastal Management, 95, 72-80. |
| [6] | Begum A, Sarker S, Uzzaman MS, Shamsuzzaman MM, Islam MM (2020) Marine megafauna in the northern Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh: Status, threats and conservation needs. Ocean & Coastal Management, 192, 105228. |
| [7] | Bele A, Chakradeo U (2021) Public perception of biodiversity: A literature review of its role in urban green spaces. Journal of Landscape Ecology, 14, 1-28. |
| [8] | Blei DM, Ng A, Jordan MI (2001) Latent Dirichlet allocation. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 3, 993-1022. |
| [9] | Brandon S (2021) Selling extinction: The social media(tion) of global cheetah conservation. Geoforum, 127, 189-197. |
| [10] | Brook SM, Dudley N, Mahood SP, Polet G, Williams AC, Duckworth JW, Van Ngoc T, Long B (2014) Lessons learned from the loss of a flagship: The extinction of the Javan rhinoceros Rhinoceros sondaicus annamiticus from Vietnam. Biological Conservation, 174, 21-29. |
| [11] | Buckley R, Mossaz A (2018) Private conservation funding from wildlife tourism enterprises in sub-Saharan Africa: Conservation marketing beliefs and practices. Biological Conservation, 218, 57-63. |
| [12] | Caro TM, Girling S (2010) Conservation by Proxy: Indicator, Umbrella, Keystone, Flagship, and Other Surrogate Species. Island Press, Washington, DC. |
| [13] | Caro TM, O’Doherty G (1999) On the use of surrogate species in conservation biology. Conservation Biology, 13, 805-814. |
| [14] | Chakrabarti A, Chase LS, Strong AM, Swallow SK (2019) Making markets for private provision of ecosystem services: The Bobolink Project. Ecosystem Services, 37, 100936. |
| [15] | Clark D, Artelle K, Darimont C, Housty W, Tallio C, Neasloss D, Schmidt A, Wiget A, Turner N (2021) Grizzly and polar bears as nonconsumptive cultural keystone species. FACETS, 6, 379-393. |
| [16] | Collins C, McKeown S, O’Riordan R (2023) A comprehensive investigation of negative visitor behaviour in the zoo setting and captive animals’ behavioural response. Heliyon, 9, e16879. |
| [17] | Courchamp F, Jaric I, Albert C, Meinard Y, Ripple WJ, Chapron G (2018) The paradoxical extinction of the most charismatic animals. PLoS Biology, 16, e2003997. |
| [18] | Craigie ID, Pressey RL (2022) Fine-grained data and models of protected-area management costs reveal cryptic effects of budget shortfalls. Biological Conservation, 272, 109589. |
| [19] | Cranswick AS, Constantine R, Hendriks H, Carroll EL (2022) Social media and citizen science records are important for the management of rarely sighted whales. Ocean & Coastal Management, 226, 106271. |
| [20] | Curtin P, Papworth S (2018) Increased information and marketing to specific individuals could shift conservation support to less popular species. Marine Policy, 88, 101-107. |
| [21] | Danley B, Sandorf ED, Campbell D (2021) Putting your best fish forward: Investigating distance decay and relative preferences for fish conservation. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 108, 102475. |
| [22] | Davis EO, Willemsen M, Dang V, O’Connor D, Glikman JA (2020) An updated analysis of the consumption of tiger products in urban Vietnam. Global Ecology and Conservation, 22, e00960. |
| [23] |
de Silva S, Srinivasan K (2019) Revisiting social natures: People-elephant conflict and coexistence in Sri Lanka. Geoforum, 102, 182-190.
DOI |
| [24] | Delibes-Mateos M (2015) Conservation conflicts involving mammals in Europe. Therya, 6, 123-137. |
| [25] | Doak DF, Bakker VJ, Goldstein BE, Hale B (2014) What is the future of conservation? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 29, 77-81. |
| [26] | Doubleday KF (2017) Nonlinear liminality: Human-animal relations on preserving the world’s most famous tigress. Geoforum, 81, 32-44. |
| [27] | Douglas LR, Alie K (2014) High-value natural resources: Linking wildlife conservation to international conflict, insecurity, and development concerns. Biological Conservation, 171, 270-277. |
| [28] | Doussard C (2023) Perceptions and representations of biodiversity in Lausanne, Switzerland: Acknowledging the importance of residential environments. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 86, 128004. |
| [29] | Drijfhout M, Kendal D, Green P (2022) Mind the gap: Comparing expert and public opinions on managing overabundant koalas. Journal of Environmental Management, 308, 114621. |
| [30] | Ducarme F, Luque GF (2013) What are “charismatic species” for conservation biologists? BioSciences Master Reviews, 10, 1-8. |
| [31] | Engel MT, Vaske JJ, Bath AJ (2021) Seal hunting in Newfoundland from the perspective of local people. Marine Policy, 128, 104491. |
| [32] | Freeman S, Taff BD, Miller ZD, Benfield JA, Newman P (2021) Acceptability factors for wildlife approach in park and protected area settings. Journal of Environmental Management, 286, 112276. |
| [33] | Frontuto V, Dalmazzone S, Vallino E, Giaccaria S (2017) Earmarking conservation: Further inquiry on scope effects in stated preference methods applied to nature-based tourism. Tourism Management, 60, 130-139. |
| [34] | Garnett ST, Ainsworth GB, Zander KK (2018) Are we choosing the right flagships? The bird species and traits Australians find most attractive. PLoS ONE, 13, e0199253. |
| [35] |
Gerber LR, Costello C, Gaines SD (2014) Conservation markets for wildlife management with case studies from whaling. Ecological Applications, 24, 4-14.
PMID |
| [36] | Griffiths TL, Steyvers M (2004) Finding scientific topics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 101, 5228-5235. |
| [37] |
Hannigan TR, Haans RFJ, Vakili K, Tchalian H, Glaser VL, Wang MS, Kaplan S, Jennings PD (2019) Topic modeling in management research: Rendering new theory from textual data. Academy of Management Annals, 13, 586-632.
DOI |
| [38] | Heighton SP, Gaubert P (2021) A timely systematic review on pangolin research, commercialization, and popularization to identify knowledge gaps and produce conservation guidelines. Biological Conservation, 256, 109042. |
| [39] | Heywood VH, Watson RT (1995) Global Biodiversity Assessment. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [40] | Hunter M, Westgate MJ, Barton PS, Calhoun AJ, Pierson JC, Tulloch AI, Beger M, Branquinho C, Caro T, Gross JE, Heino J, Lane P, Longo C, Martin K, McDowell WH, Mellin C, Salo HH, Lindenmayer DB (2016) Two roles for ecological surrogacy: Indicator surrogates and management surrogates. Ecological Indicators, 63, 121-125. |
| [41] | Ishihara H, Pascual U, Hodge I (2017) Dancing with storks: The role of power relations in payments for ecosystem services. Ecological Economics, 139, 45-54. |
| [42] |
Iwasaki JM, Hogendoorn K (2021) How protection of honey bees can help and hinder bee conservation. Current Opinion in Insect Science, 46, 112-118.
DOI PMID |
| [43] | Jefferson RL, Bailey I, Laffoley DD, Richards JP, Attrill MJ (2014) Public perceptions of the UK marine environment. Marine Policy, 43, 327-337. |
| [44] | Kajaria S, Sekar N, Sharma S (2022) Charisma failure: Understanding differences in support for conservation of Asian elephants compared to tigers and African elephants. Biological Conservation, 276, 109745. |
| [45] | Kansky R, Kidd M, Fischer J (2021) Understanding drivers of human tolerance towards mammals in a mixed-use transfrontier conservation area in southern Africa. Biological Conservation, 254, 108947. |
| [46] | Katuwal HB, Zhang MX, Baral HS, Sharma HP, Quan RC (2021) Assessment of farmers’ knowledge and perceptions towards farmland birds show the need of conservation interventions. Global Ecology and Conservation, 27, e01563. |
| [47] | Kelemen D, Brown SA, Pizza L (2023) Don’t bug me!: The role of names, functions, and feelings in shaping children’s and adults’ conservation attitudes about unappealing species. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 87, 101990. |
| [48] | Lavín FV, Gelcich S, Lerdón XP, Bustos FM (2016) The role of information in changing tourists behavioral preferences at the Humboldt penguin reserve in northern Chile. Ocean & Coastal Management, 125, 63-69. |
| [49] | Lévesque A, Gagné L, Dupras J (2022) Expressing citizen preferences on endangered wildlife for building socially appealing species recovery policies: A stated preference experiment in Quebec, Canada. Journal for Nature Conservation, 69, 126255. |
| [50] |
Li WP, Bao H, Zhang MH (2017) Habitat analysis and design of potential ecological corridors for Amur tiger in Northeastern China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 37, 317-326. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [李维平, 包衡, 张明海(2017) 中国东北虎栖息地分析与潜在生态廊道构建. 兽类学报, 37, 317-326.] | |
| [51] | Lindsey P, Baghai M, Bigurube G, Cunliffe S, Dickman A, Fitzgerald K, Flyman M, Gandiwa P, Kumchedwa B, Madope A, Morjan M, Parker A, Steiner K, Tumenta P, Uiseb K, Robson A (2021) Attracting investment for Africa’s protected areas by creating enabling environments for collaborative management partnerships. Biological Conservation, 255, 108979. |
| [52] | Liordos V, Kontsiotis VJ, Kokoris S, Pimenidou M (2018) The two faces of Janus, or the dual mode of public attitudes towards snakes. Science of the Total Environment, 621, 670-678. |
| [53] | Lodi L, Tardin RH (2018) Citizen science contributes to the understanding of the occurrence and distribution of cetaceans in southeastern Brazil—A case study. Ocean & Coastal Management, 158,45-55. |
| [54] | Lundberg P, Veríssimo D, Vainio A, Arponen A (2020) Preferences for different flagship types in fundraising for nature conservation. Biological Conservation, 250, 108738. |
| [55] | MacDonald C, Gallagher AJ, Barnett A, Brunnschweiler J, Shiffman DS, Hammerschlag N (2017) Conservation potential of apex predator tourism. Biological Conservation, 215, 132-141. |
| [56] | Mangachena JR, Geerts S, Pickering CM (2023) Spatial and temporal patterns in wildlife tourism encounters and how people feel about them based on social media data from South Africa. Journal of Outdoor Recreation and Tourism, 44, 100642. |
| [57] | Mangachena JR, Pickering CM (2021) Implications of social media discourse for managing national parks in South Africa. Journal of Environmental Management, 285, 112159. |
| [58] | Mann JB, Ballantyne R, Packer J (2020) The role of aquariums and zoos in encouraging visitor conservation action. Encyclopedia of the World’s Biomes, 5, 380-389. |
| [59] | Mannocci L, Villon S, Chaumont M, Guellati N, Mouquet N, Iovan C, Vigliola L, Mouillot D (2022) Leveraging social media and deep learning to detect rare megafauna in video surveys. Conservation Biology, 36, e13798. |
| [60] | McGregor J (2005) Crocodile crimes: People versus wildlife and the politics of postcolonial conservation on Lake Kariba, Zimbabwe. Geoforum, 36, 353-369. |
| [61] | McIntosh D, Wright PA (2017) Emotional processing as an important part of the wildlife viewing experience. Journal of Outdoor Recreation and Tourism, 18, 1-9. |
| [62] | Mekonnen A, Fashing PJ, Chapman CA, Venkataraman VV, Stenseth NC (2022) The value of flagship and umbrella species for restoration and sustainable development: Bale monkeys and bamboo forest in Ethiopia. Journal for Nature Conservation, 65, 126117. |
| [63] | Miller K, Johnstone K, Antos M (2015) Grassland conservation and the plains-wanderer: A small brown bird makes an effective local flagship. Conservation and Society, 13, 407. |
| [64] | Monsarrat S, Kerley GIH (2018) Charismatic species of the past: Biases in reporting of large mammals in historical written sources. Biological Conservation, 223, 68-75. |
| [65] | Monti F, Duriez O, Dominici JM, Sforzi A, Robert A, Fusani L, Grémillet D (2018) The price of success: Integrative long- term study reveals ecotourism impacts on a flagship species at a UNESCO site. Animal Conservation, 21, 448-458. |
| [66] | Morse-Jones S, Bateman IJ, Kontoleon A, Ferrini S, Burgess ND, Burgess ND, Turner RK (2012) Stated preferences for tropical wildlife conservation amongst distant beneficiaries: Charisma, endemism, scope and substitution effects. Ecological Economics, 78, 9-18. |
| [67] | Nekaris KAI, Arnell AP, Svensson MS (2015) Selecting a conservation surrogate species for small fragmented habitats using ecological niche modelling. Animals, 5, 27-40. |
| [68] | Ninon FV, Esteban Brenes-Mora, Dans AJ, Estrada N, Cabrera V, García MJ, Martínez W, Poot C, Reyna-Hurtado R, Rivero M, Jordan CA (2022) Ecology and Conservation of the Baird’s Tapir in Mesoamerica. Imperiled: The Encyclopedia of Conservation, 1, 144-145. |
| [69] | Obour R, Domokana S, Ankomah PK, Larson T (2019) Accessibility to elephants as tourism flagship species: The case of more national park. African Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 1, 18-32. |
| [70] | Parker BG, Jacobsen KS, Vucetich JA, Dickman AJ, Loveridge AJ, MacDonald DW (2022) Towards equitable conservation: Social capital, fear and livestock loss shape perceived benefit from a protected area. Journal of Environmental Management, 319, 115676. |
| [71] | Pearce K, Serfass T (2014) Assessing the potential of the river otter to promote aquatic conservation in the greater Yellowstone ecosystem: A unique approach for developing a long-term aquatic flagship. The UW National Parks Service Research Station Annual Reports, 37, 108-113. |
| [72] | Penn J, Hu WY (2023) Benefit-cost analysis of becoming certified pollinator friendly. Journal of Environmental Management, 326, 116679. |
| [73] | Pumphrey A, Meletis ZA (2023) Roadside bear viewing in Kananaskis Country: Visitor perceptions of bear Jams and related management strategies. Journal of Outdoor Recreation and Tourism, 43, 100657. |
| [74] | Rao A, Saksena S (2021) Wildlife tourism and local communities: Evidence from India. Annals of Tourism Research Empirical Insights, 2, 100016. |
| [75] | Ripple WJ, Chapron G, López-Bao JV, Durant SM, MacDonald DW, Lindsey PA, Bennett EL, Beschta RL, Bruskotter JT, Campos-Arceiz A, Corlett RT, Darimont CT, Dickman AJ, Dirzo R, Dublin HT, Estes JA, Everatt KT, Galetti M, Goswami VR, Hayward MW, Hedges S, Hoffmann M, Hunter LTB, Kerley GIH, Letnic M, Levi T, Maisels F, Morrison JC, Nelson MP, Newsome TM, Painter L, Pringle RM, Sandom CJ, Terborgh J, Treves A, Van Valkenburgh B, Vucetich JA, Wirsing AJ, Wallach AD, Wolf C, Woodroffe R, Young H, Zhang L (2016) Saving the world’s terrestrial megafauna. Bioscience, 66, 807-812. |
| [76] | Röder M, Both A, Hinneburg A (2015) Exploring the space of topic coherence measures. In:Proceedings of the Eighth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. ACM, Shanghai. |
| [77] | Root-Bernstein M, Bennett M (2017) Mapping opportunities for environmental education in a defaunated landscape. Perspectives in Ecology and Conservation, 15, 119-123. |
| [78] | Rosenthal J, Booth R, Carolan N, Clarke O, Curnew J, Hammond C, Jenkins J, McGee E, Moody B, Roman J, Rossi K, Schaefer K, Stanley M, Ward E, Weber L (2022) The impact of recreational activities on species at risk in Canada. Journal of Outdoor Recreation and Tourism, 40, 100567. |
| [79] | Rosenthal MF, Gertler M, Hamilton AD, Prasad S, Andrade MCB (2017) Taxonomic bias in animal behaviour publications. Animal Behaviour, 127, 83-89. |
| [80] | Runge CA, Withey JC, Naugle DE, Fargione JE, Helmstedt KJ, Larsen AE, Martinuzzi S, Tack JD (2019) Single species conservation as an umbrella for management of landscape threats. PLoS ONE, 14, e0209619. |
| [81] | Sampson L, Riley JV, Carpenter AI (2020) Applying IUCN reintroduction guidelines: An effective medium for raising public support prior to conducting a reintroduction project. Journal for Nature Conservation, 58, 125914. |
| [82] | Sarma UK, Barpujari I (2023) Realizing a rights-based approach to resettlement from protected areas: Lessons from Satpura Tiger Reserve, Madhya Pradesh (India). Land Use Policy, 125, 106494. |
| [83] |
Sarta A, Durand R, Vergne JP (2021) Organizational adaptation. Journal of Management, 47, 43-75.
DOI PMID |
| [84] | Schlagloth R, Dr FS, Golding B, Thomson H (2018) Why is it important to use flagship species in community education? The koala as a Case Study. Animal Studies Journal, 7, 127-148. |
| [85] | Schönfelder ML, Bogner FX (2017) Individual perception of bees: Between perceived danger and willingness to protect. PLoS ONE, 12, e0180168. |
| [86] | Sehra KK, MacMillan DC (2021) Wildlife-friendly food requires a multi-stakeholder approach to deliver landscape- scale biodiversity conservation in the Satoyama landscape of Japan. Journal of Environmental Management, 297, 113275. |
| [87] | Senigaglia V, New L, Hughes M (2020) Close encounters of the dolphin kind: Contrasting tourist support for feeding based interactions with concern for dolphin welfare. Tourism Management, 77, 104007. |
| [88] | Senzaki M, Yamaura Y, Shoji Y, Kubo T, Nakamura F (2017) Citizens promote the conservation of flagship species more than ecosystem services in wetland restoration. Biological Conservation, 214, 1-5. |
| [89] | Sharma S, Kreye MM (2022) Social value of bird conservation on private forest lands in Pennsylvania, USA. Ecological Economics, 196, 107426. |
| [90] |
Shreedhar G, Mourato S (2019) Experimental evidence on the impact of biodiversity conservation videos on charitable donations. Ecological Economics, 158, 180-193.
DOI |
| [91] | Shumway N, Seabrook L, McAlpine C, Ward P (2014) A mismatch of community attitudes and actions: A study of koalas. Landscape and Urban Planning, 126, 42-52. |
| [92] |
Sibarani MC, Di Marco M, Rondinini C, Kark S (2019) Measuring the surrogacy potential of charismatic megafauna species across taxonomic, phylogenetic and functional diversity on a megadiverse island. Journal of Applied Ecology, 56, 1220-1231.
DOI |
| [93] | Surrey KC, Hawley CR, Davis ON, Clements JL, Bernat I, Gerber LR (2022) Refining the ecosystems services model: Integrating animal behavior into ecotourism management. Imperiled: The Encyclopedia of Conservation, 3, 28-36. |
| [94] | Sutcliffe SR, Barnes ML (2018) The role of shark ecotourism in conservation behaviour: Evidence from Hawaii. Marine Policy, 97, 27-33. |
| [95] | Tan ASL, de la Torre JA, Wong EP, Thuppil V, Campos-Arceiz A (2020) Factors affecting urban and rural tolerance towards conflict-prone endangered megafauna in Peninsular Malaysia. Global Ecology and Conservation, 23, e01179. |
| [96] | Thompson BS (2022) Ecotourism anywhere? The lure of ecotourism and the need to scrutinize the potential competitiveness of ecotourism developments. Tourism Management, 92, 104568. |
| [97] | Thompson BS, Rog SM (2019) Beyond ecosystem services: Using charismatic megafauna as flagship species for mangrove forest conservation. Environmental Science & Policy, 102, 9-17. |
| [98] | Tiller R, Arenas F, Galdies C, Leitão F, Malej A, Romera BM, Solidoro C, Stojanov R, Turk V, Guerra R (2019) Who cares about ocean acidification in the Plasticene? Ocean & Coastal Management, 174, 170-180. |
| [99] | Treves A, Jones SM (2010) Strategic tradeoffs for wildlife-friendly eco-labels. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 8, 491-498. |
| [100] | Turvey ST, Fernández-Secades C, Nuñez-Miño JM, Hart T, Martinez P, Brocca JL, Young RP (2014) Is local ecological knowledge a useful conservation tool for small mammals in a Caribbean multicultural landscape? Biological Conservation, 169, 189-197. |
| [101] | Veríssimo D, Fraser I, Groombridge J, Bristol R, MacMillan DC (2009) Birds as tourism flagship species: A case study of tropical islands. Animal Conservation, 12, 549-558. |
| [102] | Verissimo D, MacMillan DC, Smith RJ (2011) Toward a systematic approach for identifying conservation flagships. Conservation Letters, 4, 1-8. |
| [103] | Vũ AN (2023) Demand reduction campaigns for the illegal wildlife trade in authoritarian Vietnam: Ungrounded environmentalism. World Development, 164, 106150. |
| [104] | Weckel M, Wincorn A (2016) Urban conservation: The northeastern coyote as a flagship species. Landscape and Urban Planning, 150, 10-15. |
| [105] | Wright AJ, Veríssimo D, Pilfold K, Parsons ECM, Ventre K, Cousins J, Jefferson R, Koldewey H, Llewellyn F, McKinley E (2015) Competitive outreach in the 21st century: Why we need conservation marketing. Ocean & Coastal Management, 115, 41-48. |
| [106] | Wu Y, Xie L, Huang S, Li P, Yuan Z, Liu W (2018) Using social media to strengthen public awareness of wildlife conservation. Ocean & Coastal Management, 153, 76-83. |
| [107] | Wunder S (2015) Revisiting the concept of payments for environmental services. Ecological Economics, 117, 234-243. |
| [108] | Wünscher T, Engel S, Wunder S (2008) Spatial targeting of payments for environmental services: A tool for boosting conservation benefits. Ecological Economics, 65, 822-833. |
| [109] | Xiang ZF, Yu Y, Yang M, Yang JY, Niao MY, Li M (2011) Does flagship species tourism benefit conservation? A case study of the golden snub-nosed monkey in Shennongjia National Nature Reserve. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56, 2553-2558. |
| [110] |
Xu WX, Xu F, Ma W, Wang MY, Wang JC, Yang WK (2022) Proposing a quantitative selection method for determining flagship species based on an analytic hierarchy process. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21536. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [徐文轩, 徐峰, 马伟, 汪沐阳, 王建成, 杨维康 (2022) 基于层次分析法的旗舰物种遴选方法. 生物多样性, 30, 21536.] | |
| [111] | Yeh FC, Lin L, Zhang T, Green RM, Martin F, Shi H (2021) Advancing sea turtle conservation in the South China Sea via U.S.-China diplomacy. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 40, e13643. |
| [112] | Zhuang HF, Zhang C, Jin XL, Ge AX, Chen MH, Ye J, Qiao HL, Xiong P, Zhang XF, Chen JZ, Luan XF, Wang W (2022) A flagship species-based approach to efficient, cost- effective biodiversity conservation in the Qinling Mountains, China. Journal of Environmental Management, 305, 114388. |
| [1] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [2] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [3] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [4] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [5] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| [6] | 周志华, 金效华, 罗颖, 李迪强, 岳建兵, 刘芳, 何拓, 李希, 董晖, 罗鹏. 中国林草部门落实《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》的机制、成效分析及建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24487-. |
| [7] | 刘立, 臧明月, 马月, 万雅琼, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 刘燕. 央地协同推动国家生物多样性战略和行动计划执行的措施、进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24532-. |
| [8] | 宋阳, 柳军, 何少林, 徐薇, 程琛, 刘博, 余绩庆. 我国能源企业生物多样性保护主流化管理路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24345-. |
| [9] | 耿江天, 王菲, 赵华斌. 城市化对中国蝙蝠影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24109-. |
| [10] | 苏荣菲, 陈睿山, 俞霖琳, 吴婧彬, 康燕. 基于红外相机调查的上海市长宁区社区生境花园生物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24068-. |
| [11] | 蔡颖莉, 朱洪革, 李家欣. 中国生物多样性保护政策演进、主要措施与发展趋势[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23386-. |
| [12] | 鄢德奎. 中国生物多样性保护政策的共同要素、不足和优化建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23293-. |
| [13] | 陈越, 毛子昆, 王绪高. 基于生态独特性的β多样性研究进展与未来展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24199-. |
| [14] | 张梓欣, 张承云, 郝泽周, 何凯莹, 黄泳桥, 肖治术. 陆地生物声学数据采集设备的进展及展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24265-. |
| [15] | 刘莹莹, 龚立新, 曾皓, 冯江, 董永军, 王磊, 江廷磊. 被动声学监测在蝙蝠研究中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24233-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()