



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 21280. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021280 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021280
收稿日期:2021-07-13
接受日期:2021-11-04
出版日期:2022-03-20
发布日期:2022-01-30
通讯作者:
张定海
作者简介:*E-mail: zhangdh@gsau.edu.cn基金资助:
Yating Wang1, Dinghai Zhang1,*( ), Zhishan Zhang2
), Zhishan Zhang2
Received:2021-07-13
Accepted:2021-11-04
Online:2022-03-20
Published:2022-01-30
Contact:
Dinghai Zhang
摘要:
为了探讨沙漠中固沙灌木种群共存和演替机制, 本文基于古尔班通古特沙漠东南缘固定沙丘上白梭梭(Haloxylon persicum)和梭梭(H. ammodendron)种群的地理位置和生长发育阶段信息(幼株、营养株、生殖株和死株), 采用点格局分析方法(g(r)函数)及Monte-Carlo随机模拟检验和零模型选取的方法, 分析了固沙灌木白梭梭和梭梭种群不同生长发育阶段在0-20 m尺度内的空间分布格局及种间关联性。结果表明: (1)两个种群在研究尺度范围内呈聚集分布, 随着尺度的增大, 其聚集强度逐渐减弱; (2)两个种群整体上呈负关联关系, 尺度越大负关联关系越显著; (3)白梭梭种群生长发育阶段相差越大, 个体间正关联关系越显著; 梭梭种群生长发育阶段越接近, 个体间正关联关系越显著; (4)两个种群中龄级较大的个体(如营养株、生殖株和死株)会对对方种群中龄级较小的幼株产生一定的抑制作用; 同时, 随着两个种群中个体的成长, 双方受到的抑制作用逐渐减弱, 主要表现为正关联和无关联。总体而言, 古尔班通古特沙漠固定沙丘白梭梭和梭梭种群的分布格局整体上为聚集分布, 随龄级增加聚集性减弱, 受生境异质性和扩散限制的影响明显。种间关系多为负相关, 种内不同生长发育阶段之间均为正关联关系。
王雅婷, 张定海, 张志山 (2022) 古尔班通古特沙漠固定沙丘上白梭梭和梭梭的空间分布及种间关联性. 生物多样性, 30, 21280. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021280.
Yating Wang, Dinghai Zhang, Zhishan Zhang (2022) Spatial distribution and interspecific correlation of Haloxylon persicum and H. ammodendron on fixed dunes of the Gurbantunggut Desert, China. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21280. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021280.
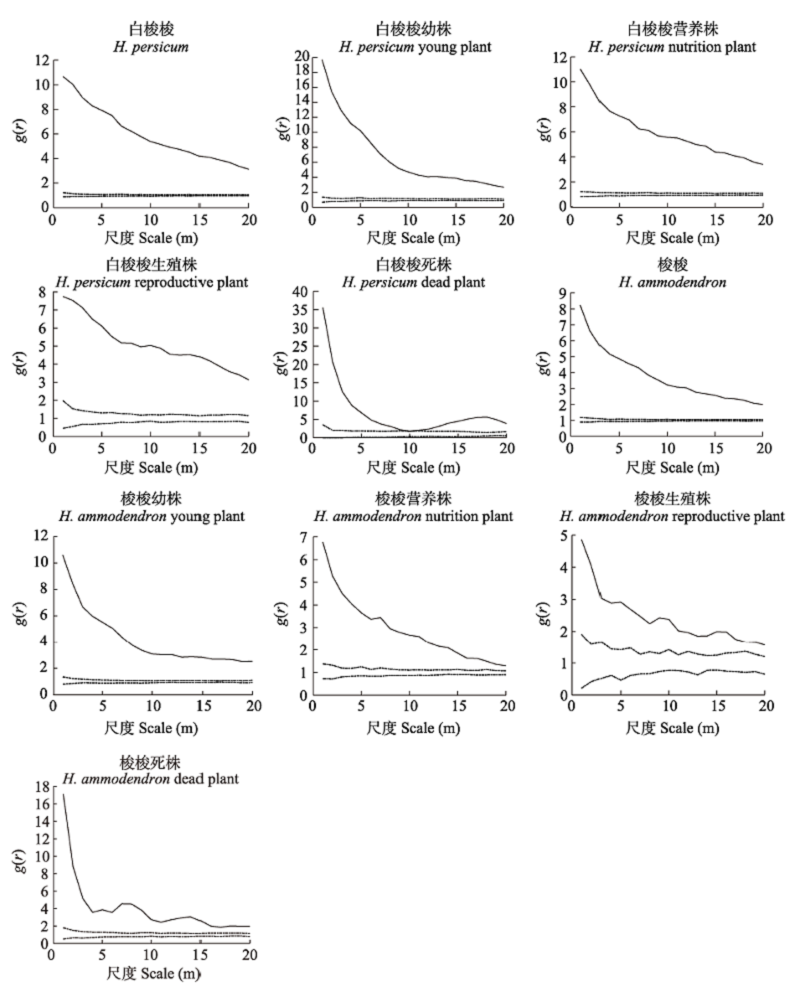
图2 基于完全随机模型(CSR)的白梭梭和梭梭种群及不同生长发育阶段个体的空间格局。虚线为99%置信区间。
Fig. 2 Spatial distribution pattern of Haloxylon persicum and H. ammodendron populations and individuals at different developmental stages based on complete spatial randomness (CSR) models. Dot lines were confidence interval of 99%.
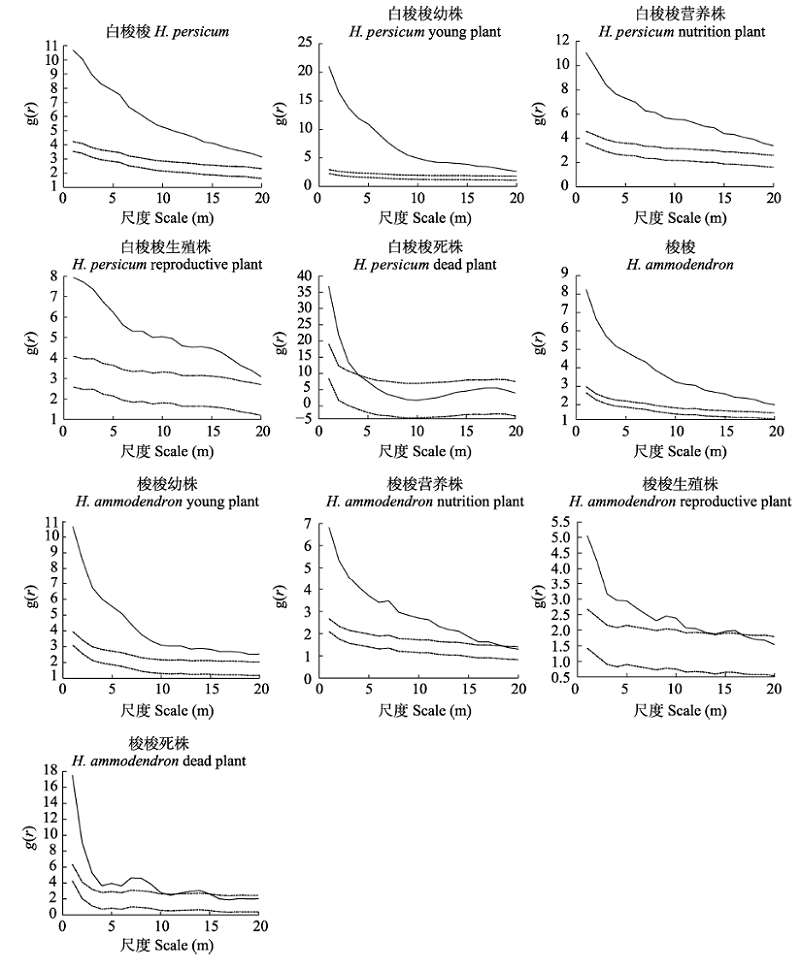
图3 基于异质泊松模型(HP)白梭梭和梭梭种群及不同生长发育阶段个体的空间分布格局。虚线为99%置信区间。
Fig. 3 Spatial distribution pattern of Haloxylon persicum and H. ammodendron populations and individuals at different developmental stages based on heterogeneous Poisson (HP) models. Dot lines were confidence interval of 99%.
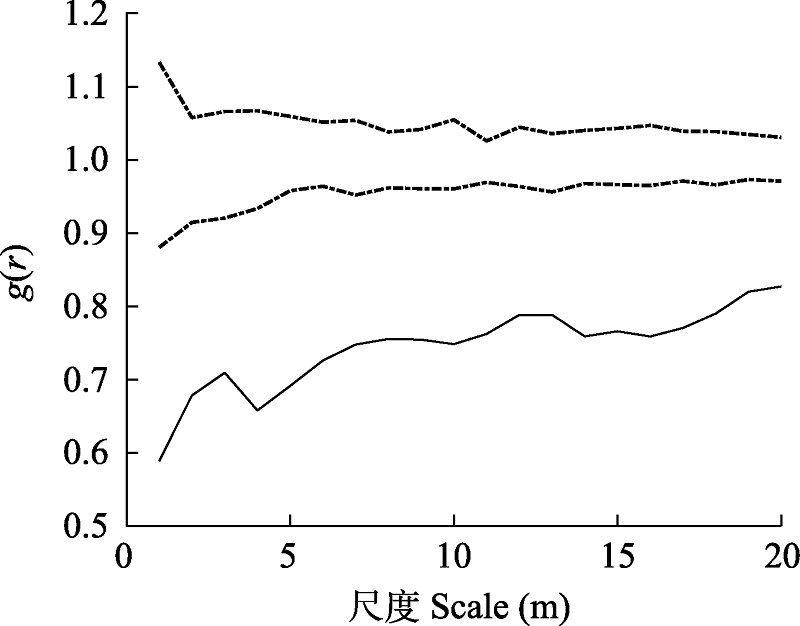
图4 白梭梭和梭梭的种间关联关系。虚线为99%置信区间。
Fig. 4 Interspecific relationship between Haloxylon persicum and H. ammodendron. Dot lines were confidence interval of 99%.
| 白梭梭幼株 H. persicum young plant | 白梭梭营养株 H. persicum nutrition plant | 白梭梭生殖株 H. persicum reproductive plant | 白梭梭死株 H. persicum dead plant | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 梭梭幼株 H. ammodendron young plant | 1 m: / > 1 m: - | > 0 m: - | > 0 m: - | > 0 m: - |
| 梭梭营养株 H. ammodendron nutrition plant | 1-5 m: - 6-7 m: / 8-9 m: + 10-11 m: / > 11 m: + | 1 m: / 2 m: + 3-4 m: / > 4 m: + | 1-2 m: / > 2 m: + | 1 m: - 2-4 m: / 5-6 m: - 7-9 m: / 10-11m: + 12-19 m: / > 19 m: + |
| 梭梭生殖株 H. ammodendron reproductive plant | > 0 m: - | 1 m: / > 1 m: + | 1-4 m: / > 4 m: + | 1-7 m: / 8-9 m: + 10-12 m: / 13-14 m: + 15-16 m: / > 16 m: + |
| 梭梭死株 H. ammodendron dead plant | > 0 m: - | > 0 m: - | > 0 m: - | 1-16 m: - 17-19 m: / > 19 m: - |
表1 白梭梭和梭梭种群不同生长发育阶段之间的空间关联性
Table 1 Spatial correlation between different developmental stages of Haloxylon persicum and H. ammodendron populations
| 白梭梭幼株 H. persicum young plant | 白梭梭营养株 H. persicum nutrition plant | 白梭梭生殖株 H. persicum reproductive plant | 白梭梭死株 H. persicum dead plant | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 梭梭幼株 H. ammodendron young plant | 1 m: / > 1 m: - | > 0 m: - | > 0 m: - | > 0 m: - |
| 梭梭营养株 H. ammodendron nutrition plant | 1-5 m: - 6-7 m: / 8-9 m: + 10-11 m: / > 11 m: + | 1 m: / 2 m: + 3-4 m: / > 4 m: + | 1-2 m: / > 2 m: + | 1 m: - 2-4 m: / 5-6 m: - 7-9 m: / 10-11m: + 12-19 m: / > 19 m: + |
| 梭梭生殖株 H. ammodendron reproductive plant | > 0 m: - | 1 m: / > 1 m: + | 1-4 m: / > 4 m: + | 1-7 m: / 8-9 m: + 10-12 m: / 13-14 m: + 15-16 m: / > 16 m: + |
| 梭梭死株 H. ammodendron dead plant | > 0 m: - | > 0 m: - | > 0 m: - | 1-16 m: - 17-19 m: / > 19 m: - |
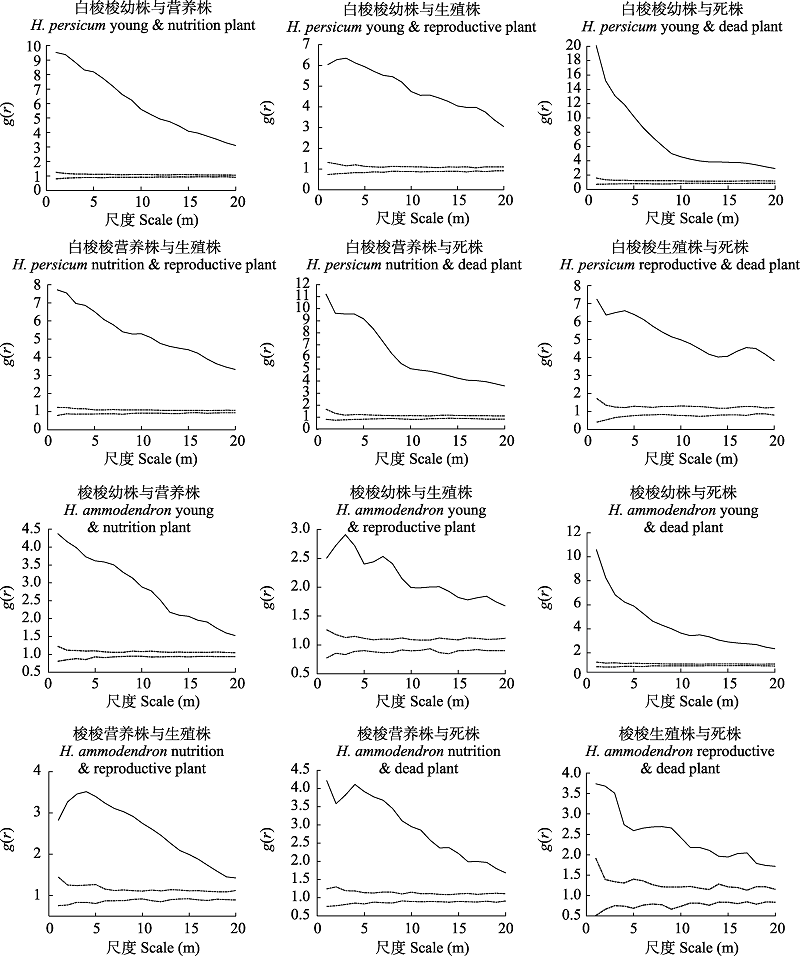
图5 白梭梭和梭梭不同生长发育阶段种内空间关联性。虚线为99%置信区间。
Fig. 5 Intraspecific spatial correlation at different developmental stages of Haloxylon persicum and H. ammodendron. Dot lines were confidence interval of 99%.
| [1] | Baddeley A, Turner R (2005) Spatstat: An R package for analyzing spatial point patterns. Journal of Statistical Software, 12, 1-42. |
| [2] | Baoerhan D, Zhang HF, Zhu YL, Zhang JL (2019) Spatial pattern and influence facotrs of natural regeneration of Haloxylon ammodendron seedlings in Zhungeer Basin. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 48, 134-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 地力夏提•包尔汉, 张绘芳, 朱雅丽, 张景路 (2019) 准格尔盆地梭梭天然更新幼苗空间格局与影响因子. 西部林业科学, 48, 134-138.] | |
| [3] | Cai F (2000) A study on the structure and dynamics of Cyclobalanopsis glauca population at hills around West Lake in Hangzhou. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 36(3), 67-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蔡飞 (2000) 杭州西湖山区青冈种群结构和动态的研究. 林业科学, 36(3), 67-72.] | |
| [4] | Chang J, Pan CD, Shi RF (2006) Analysis on dominant species distribution patterns and relation of Ass. Haloxylon persicum + H. ammodendron. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 29(2), 26-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 常静, 潘存德, 师瑞锋 (2006) 梭梭-白梭梭群落优势种种群分布格局及其种间关系分析. 新疆农业大学学报, 29(2), 26-29.] | |
| [5] |
Chen YN, Wang Q, Li WH, Ruan X (2007) Microbiotic crusts and their interrelations with environmental factors in the Gurbantonggut Desert, western China. Environmental Geology, 52, 691-700.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Feng XL, Liu R, Ma J, Xu Z, Wang YG, Kong L (2021) Photosynthetic characteristics and influencing factors of Haloxylon persicum stems (different diameter classes) in Gurbantonggut Desert. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41, 9784-9795. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 冯晓龙, 刘冉, 马健, 徐柱, 王玉刚, 孔璐 (2021) 古尔班通古特沙漠白梭梭枝干(不同径级)光合及其影响因素. 生态学报, 41, 9784-9795.] | |
| [7] |
Guo YL, Wang B, Xiang WS, Ding T, Lu SH, Huang YS, Huang FZ, Li DX, Li XK (2015) Spatial distribution of tree species in a tropical karst seasonal rainforest in Nonggang, Guangxi, southern China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 183-191. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 郭屹立, 王斌, 向悟生, 丁涛, 陆树华, 黄俞淞, 黄甫昭, 李冬兴, 李先琨 (2015) 广西弄岗北热带喀斯特季节性雨林监测样地种群空间点格局分析. 生物多样性, 23, 183-191.]
DOI |
|
| [8] |
He FL, Duncan RP (2000) Density-dependent effects on tree survival in an old-growth Douglas fir forest. Journal of Ecology, 88, 676-688.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
He FL, Legendre P, LaFrankie JV (1997) Distribution patterns of tree species in a Malaysian tropical rain forest. Journal of Vegetation Science, 8, 105-114.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
He ZL, Xu H, Qin XS, Tang GD, Li YD (2017) Spatial distribution patterns and association of two Apocynaceae plants in the tropical mountain rainforests of Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China. Biodiversity Science, 25, 1065-1074. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 何增丽, 许涵, 秦新生, 唐光大, 李意德 (2017) 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林2种夹竹桃科植物的空间分布格局与关联性. 生物多样性, 25, 1065-1074.]
DOI |
|
| [11] |
Hu EC, Wang XJ, Zhang WJ, Hai L, Zhang L, Zhang SL, Xu PY (2013) Age structure and point pattern of Butula platyphylla in Wulashan Natural Reserve of Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 2867-2876. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 胡尔查, 王晓江, 张文军, 海龙, 张雷, 张胜利, 徐鹏雁 (2013) 乌拉山自然保护区白桦种群的年龄结构和点格局分析. 生态学报, 33, 2867-2876.] | |
| [12] | Hu SZ (1963) Haloxylon ammodendron in the desert of Northwest China. Acta Phytoecologica et Geobotanica Sinica, 1, 80-109. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡式之 (1963) 中国西北地区的梭梭荒漠. 植物生态学与地植物学丛刊, 1, 80-109.] | |
| [13] |
Huang X, Zhu J, Yao L, Ai XR, Wang J, Wu ML, Zhu Q, Chen SL (2020) Structure and spatial distribution pattern of a native Metasequoia glyptostroboides population in Hubei. Biodiversity Science, 28, 463-473. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 黄小, 朱江, 姚兰, 艾训儒, 王进, 吴漫玲, 朱强, 陈绍林 (2020) 水杉原生种群结构及空间分布格局. 生物多样性, 28, 463-473.]
DOI |
|
| [14] |
Huston MA, DeAngelis DL (1994) Competition and coexistence: The effects of resource transport and supply rates. The American Naturalist, 144, 954-977.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Kang JP, Han L (2021) Spatial distribution and association between Populus pruinosa and Tamarix ramosissima population along Tarim River mainstream. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 41(2), 123-132. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 康佳鹏, 韩路 (2021) 塔河源荒漠河岸林灰胡杨与多枝柽柳种群空间格局与空间关联性. 中南林业科技大学学报, 41(2), 123-132.] | |
| [16] |
Lan GY, Getzin S, Wiegand T, Hu YH, Xie GS, Zhu H, Cao M (2012) Spatial distribution and interspecific associations of tree species in a tropical seasonal rain forest of China. PLoS ONE, 7, e46074.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Levin SA (1992) The problem of pattern and scale in ecology. Ecology, 73, 1943-1967.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Li GL, Zhang DH, Zhang ZS, Hu YG, Huang L, Lu LN (2021) Population dynamics of main sand-fixing shrubs in the Gurbantunggut Desert. Journal of Desert Research, 41, 129-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李功麟, 张定海, 张志山, 胡宜刚, 黄磊, 路丽宁 (2021) 古尔班通古特沙漠沙丘主要灌木的种群数量动态. 中国沙漠, 41, 129-137.] | |
| [19] | Li JG, Ning HS, Liu B (2003) Study on character structure and distribution pattern of Haloxylon ammodron. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 26(3), 51-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李建贵, 宁虎森, 刘斌 (2003) 梭梭种群性状结构与空间分布格局的初步研究. 新疆农业大学学报, 26(3), 51-54.] | |
| [20] |
Liang DD, Peng J, Gao GL, Hong X, Zhou SB, Chu J, Wang Z (2020) Spatial distribution pattern and interspecific correlation analysis of main species of Rosaceae in a deciduous broad-leaved forest in Yaoluoping. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1008-1017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 梁栋栋, 彭杰, 高改利, 洪欣, 周守标, 储俊, 王智 (2020) 鹞落坪落叶阔叶林蔷薇科主要树种的空间分布格局及种间关联性. 生物多样性, 28, 1008-1017.] | |
| [21] |
Liang S, Xu H, Lin JY, Li YD, Lin MX (2014) Spatial distribution pattern of the dominant species Gironniera subaequalis in tropical montane rainforest of Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 38, 1273-1282. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 梁爽, 许涵, 林家怡, 李意德, 林明献 (2014) 尖峰岭热带山地雨林优势树种白颜树空间分布格局. 植物生态学报, 38, 1273-1282.] | |
| [22] | Liu HM, Lyu SJ, Liu QQ, Chai XX, Wang M, Wang DH, Nie YQ (2015) Spatial distribution of natural Haloxylon ammodendron forest in relation to topographic undulations in Tamushu. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34, 2415-2423. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘红梅, 吕世杰, 刘清泉, 柴享贤, 王猛, 王德慧, 聂雨芊 (2015) 塔木素天然梭梭林空间分布及其与林地地貌起伏变化的关系. 生态学杂志, 34, 2415-2423.] | |
| [23] | Liu HM, Lyu SJ, Liu QQ, Liu LY, Wang YZ, Ren QN, Zhou Y, Gao Q (2021) Spatial distribution relations of main plant populations in eastern Badain Jaran Desert. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40, 959-967. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘红梅, 吕世杰, 刘青泉, 刘丽英, 王玉芝, 任倩楠, 周瑶, 高启 (2021) 巴丹吉林沙漠东缘主要植物种群空间分布关系. 生态学杂志, 40, 959-967.] | |
| [24] | Liu ZG, Li ZQ (2004) Fine-scale spatial pattern of Artemisia frigida population under different grazing intensities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24, 227-234. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘振国, 李镇清 (2004) 不同放牧强度下冷蒿种群小尺度空间格局. 生态学报, 24, 227-234.] | |
| [25] | MacKay DB (1982) Spatial statistics. Journal of Marketing Research, 19, 279. |
| [26] |
Nong Y, Zheng L, Jia HY, Lu LH, Huang DW, Huang BH, Lei LQ (2015) Community characteristics and spatial distribution of dominant tree species in a secondary forest of Daqing Mountains, southwestern Guangxi, China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 321-331. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 农友, 郑路, 贾宏炎, 卢立华, 黄德卫, 黄柏华, 雷丽群 (2015) 广西大青山次生林的群落特征及主要乔木种群的空间分布格局. 生物多样性, 23, 321-331.]
DOI |
|
| [27] |
Plotkin JB, Potts MD, Leslie N, Manokaran N, LaFrankie J, Ashton PS (2000) Species-area curves, spatial aggregation, and habitat specialization in tropical forests. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 207, 81-99.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Ren YH, Zhou YZ, Hou L, Fang JP, Luo DQ (2021) Spatial distribution patterns of standing trees at different ages in Abies georgei var. smithii forests in Sejila Mountain. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41, 5417-5424. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 任毅华, 周尧治, 侯磊, 方江平, 罗大庆 (2021) 色季拉山急尖长苞冷杉种群不同龄级立木的空间分布格局. 生态学报, 41, 5417-5424.] | |
| [29] |
Ripley BD (1976) The second-order analysis of stationary point processes. Journal of Applied Probability, 13, 255-266.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Shi YF, Zhang ZS, Huang L, Hu YG, Li J, Yang YG (2016) Species composition and population structure of plant communities on semi-fixed dunes of the Gurbantunggut Desert, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27, 1024-1030. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 石亚飞, 张志山, 黄磊, 胡宜刚, 李君, 杨与广 (2016) 古尔班通古特沙漠半固定沙丘植物群落物种组成和种群结构. 应用生态学报, 27, 1024-1030.] | |
| [31] | Song CW, Jiang J, Fan JL, Chen JJ, Quan YW, Wang F (2012) Ecological species groups division based on interspecific association: A case study in the Gurbantunggut Desert, Xinjiang, China. Journal of Desert Research, 32, 77-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 宋春武, 蒋进, 范敬龙, 陈钧杰, 全永威, 王峰 (2012) 从植物种间联结性探讨白梭梭种群生态种组分类--以古尔班通古特沙漠为例. 中国沙漠, 32, 77-85.] | |
| [32] | Song YY, Li YY, Zhang WH (2010) Analysis of spatial pattern and spatial association of Haloxylon ammodendron population in different developmental stages. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 4317-4327. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 宋于洋, 李园园, 张文辉 (2010) 梭梭种群不同发育阶段的空间格局与关联性分析. 生态学报, 30, 4317-4327.] | |
| [33] | Trangmar BB, Yost RS, Uehara AG (1986) Application of geostatistics to spatial studies of soil properties. Advances in Agronomy, 38, 45-94. |
| [34] | Tu HR, Li JF, Liu RH, Liang SC, Lan ZN, Zhang XY, Kang XD, Jiang Y (2019) Spatial distribution patterns and association of Loropetalum chinense population in karst hills of Guilin, Southwest China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30, 2621-2630. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 涂洪润, 李娇凤, 刘润红, 梁士楚, 兰泽南, 章欣仪, 康馨丹, 姜勇 (2019) 桂林岩溶石山檵木种群空间格局及其关联性. 应用生态学报, 30, 2621-2630.] | |
| [35] | Wang CL, Guo QS, Tan DY, Shi ZM, Ma C (2005) Haloxylon ammodendron community patterns in different habitats along southeastern edge of Zhunger Basin. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 16, 1224-1229. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王春玲, 郭泉水, 谭德远, 史作民, 马超 (2005) 准噶尔盆地东南缘不同生境条件下梭梭群落结构特征研究. 应用生态学报, 16, 1224-1229.] | |
| [36] |
Wang L, Sun QW, Hao CY, Tian SN, Zhang SS, Chen YK, Zhang XP (2010) Point pattern analysis of different age-class Taxus chinensis var. mairei individuals in mountainous area of southern Anhui Province. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 21, 272-278. (in Chinese with English abstract)
PMID |
|
[ 王磊, 孙启武, 郝朝运, 田胜尼, 张姗姗, 陈一锟, 张小平 (2010) 皖南山区南方红豆杉种群不同龄级立木的点格局分析. 应用生态学报, 21, 272-278.]
PMID |
|
| [37] | Wang M, Wang J, Meng ZJ, Chai XX, Lü SJ, Wang DH, Wu YG (2016) Spatial heterogeneity of natural Haloxylon ammodendron populations at Ta-MuSu, Badain Jaran Desert, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 4055-4063. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王猛, 汪季, 蒙仲举, 柴享贤, 吕世杰, 王德慧, 乌云嘎 (2016) 巴丹吉林沙漠东缘天然梭梭种群空间分布异质性. 生态学报, 36, 4055-4063.] | |
| [38] |
Wang XT, Hou YL, Liang CZ, Wang W, Liu F (2012) Point pattern analysis based on different null models for detecting spatial patterns. Biodiversity Science, 20, 151-158. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 王鑫厅, 侯亚丽, 梁存柱, 王炜, 刘芳 (2012) 基于不同零模型的点格局分析. 生物多样性, 20, 151-158.]
DOI |
|
| [39] |
Watt AS (1947) Pattern and process in the plant community. Journal of Ecology, 35, 1-22.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Wiegand T, Moloney KA (2004) Rings, circles, and null- models for point pattern analysis in ecology. Oikos, 104, 209-229.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Wright JS (2002) Plant diversity in tropical forests: A review of mechanisms of species coexistence. Oecologia, 130, 1-14.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Xie JB, Peng LZ, Li YM, Li Y (2018) Competitive interactions between two desert shrub seedings towards variation in soil nitrogen and phosphorus content. Arid Land Geography, 41, 83-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谢江波, 彭历芝, 李艳明, 李彦 (2018) 两种梭梭属幼苗在土壤N和P梯度下的竞争能力研究. 干旱区地理, 41, 83-91.] | |
| [43] | Xue WY, Yang B, Zhang WH, Yu SC (2017) Spatial pattern and spatial association of Quercus acutissima at different developmental stages in the Qiaoshan Mountains. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 3375-3384. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 薛文艳, 杨斌, 张文辉, 于世川 (2017) 桥山林区麻栎种群不同发育阶段空间格局及关联性. 生态学报, 37, 3375-3384.] | |
| [44] | Yang HF, Qian YB, Jiang C, Zhao RF (2010) Spatial heterogeneity of soil chemical properties in the South Gurbantonggut Desert. Journal of Desert Research, 30, 319-325. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨海峰, 钱亦兵, 蒋超, 赵锐锋 (2010) 古尔班通古特沙漠南缘主要土壤化学特征的空间异质性. 中国沙漠, 30, 319-325.] | |
| [45] | Yang HX, Zhang JT, Wu B, Li XS, Zhang YY (2006) Point pattern analysis of Artemisia ordosica population in the Mu Us sandy land. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 30, 563-570. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 杨洪晓, 张金屯, 吴波, 李晓松, 张友炎 (2006) 毛乌素沙地油蒿种群点格局分析. 植物生态学报, 30, 563-570.]
DOI |
|
| [46] | Yang XH, Yu CT, Ci LJ (2009) Grid-based spatial pattern of Nitraria tangutorum sand mounds in desert-riverine ecotones. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 45(8), 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨晓晖, 于春堂, 慈龙骏 (2009) 基于栅格数据的沙漠-河岸过渡带白刺沙堆空间格局分析. 林业科学, 45(8), 1-8.] | |
| [47] | You HZ, Liu XL, Miao N, He F, Ma QY (2010) Individual association and scale effect of spatial pattern of Quercus aquifolioides populations along the elevation gradients. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 4004-4011. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 尤海舟, 刘兴良, 缪宁, 何飞, 马钦彦 (2010) 川滇高山栎种群不同海拔空间格局的尺度效应及个体间空间关联. 生态学报, 30, 4004-4011.] | |
| [48] | Yue YM, Li CH, Xu Z, Tang LS (2020) Variation characteristics of canopy nutrients during the rainfall process of Haloxylon ammodendron and Haloxylon persicum in the Gurbantunggut Desert. Arid Zone Research, 37, 1293-1300. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 岳跃蒙, 李晨华, 徐柱, 唐立松 (2020) 古尔班通古特沙漠降雨过程中梭梭与白梭梭冠层养分的变化特征. 干旱区研究, 37, 1293-1300.] | |
| [49] |
Zhang J, Hao ZQ, Song B, Ye J, Li BH, Yao XL (2007) Spatial distribution patterns and associations of Pinus koraiensis and Tilia amurensis in broad-leaved Korean pine mixed forest in Changbai Mountains. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 18, 1681-1687. (in Chinese with English abstract)
PMID |
|
[ 张健, 郝占庆, 宋波, 叶吉, 李步杭, 姚晓琳 (2007) 长白山阔叶红松林中红松与紫椴的空间分布格局及其关联性. 应用生态学报, 18, 1681-1687.]
PMID |
|
| [50] | Zhang JT (1998) Analysis of spatial point pattern for plant species. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 22, 344-349. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张金屯 (1998) 植物种群空间分布的点格局分析. 植物生态学报, 22, 344-349.] | |
| [51] | Zhang JT, Meng DP (2004) Spatial pattern analysis of individuals in different age-classes of Larix principissrupprechtii in Luya Mountain Reserve, Shanxi, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24, 35-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张金屯, 孟东平 (2004) 芦芽山华北落叶松林不同龄级立木的点格局分析. 生态学报, 24, 35-40.] | |
| [52] |
Zhang JY, Cheng KW, Zang RG (2014) The spatial distribution patterns and associations of the principal trees and shrubs in a natural tropical coniferous forest on Hainan Island, China. Biodiversity Science, 22, 129-140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 张俊艳, 成克武, 臧润国 (2014) 海南岛热带天然针叶林主要树种的空间格局及关联性. 生物多样性, 22, 129-140.]
DOI |
|
| [53] | Zhou XY, Wang BS, Li MG, Zan QJ (2000) An analysis of interspecific associations in secondary succession forest communities in Heishiding Natural Reserve, Guangdong Province. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 24, 332-339. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 周先叶, 王伯荪, 李鸣光, 昝启杰 (2000) 广东黑石顶自然保护区森林次生演替过程中群落的种间联结性分析. 植物生态学报, 24, 332-339.] | |
| [54] | Zhu Y, Ma KP (2012) Point pattern analysis and its application in the study of plant spatial distribution pattern. In: Proceedings of the Ninth National Conference on the Conservation and Sustainable Use of Biodiversity in China (eds Chinese National Committee for DIVERSITAS, etc), pp. 319-331. China Meteorological Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 祝燕, 马克平 (2012) 点格局分析及其在植物空间分布格局研究中的应用. 见: 全国生物多样性保护与持续利用研讨会论文集(国际生物多样性计划中国委员会等主编), 319-331页. 气象出版社, 北京.] |
| [1] | 王凤琼, 张心怡, 王鑫厅, 姜超, 侯亚丽, 包道日娜. 羊草草原原生群落羊草种群点格局分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24271-. |
| [2] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [3] | 杨俊毅, 关潇, 李俊生, 刘晶晶, 郝颢晶, 王槐睿. 乌江流域生物多样性与生态系统服务的空间格局及相互关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23061-. |
| [4] | 肖媛媛, 冯薇, 乔艳桂, 张宇清, 秦树高. 固沙灌木林地土壤微生物群落特征对土壤多功能性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22585-. |
| [5] | 徐鹏, 荣晓莹, 刘朝红, 杜芳, 尹本丰, 陶冶, 张元明. 极端干旱对温带荒漠土壤真菌群落和生态网络的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21327-. |
| [6] | 王重阳, 赵联军, 孟世勇. 王朗国家级自然保护区滑坡体兰科植物分布格局及其保护策略[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21313-. |
| [7] | 郝希阳, 贺姹, 楚克林, 申志新, 赵强, 高伟, 潘达, 孙红英. 海南岛淡水蟹类分布格局与多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 605-616. |
| [8] | 梁栋栋, 彭杰, 高改利, 洪欣, 周守标, 储俊, 王智. 鹞落坪落叶阔叶林蔷薇科主要树种的空间分布格局及种间关联性[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(8): 1008-1017. |
| [9] | 孙远, 胡维刚, 姚树冉, 孙颖, 邓建明. 黄河流域被子植物和陆栖脊椎动物丰富度格局及其影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(12): 1523-1532. |
| [10] | 颜文博,吉晟男,帅凌鹰,赵雷刚,朱大鹏,曾治高. 秦岭南坡陕西洋县辖区哺乳动物物种多样性的空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(2): 177-185. |
| [11] | 胡一鸣, 梁健超, 金崑, 丁志锋, 周智鑫, 胡慧建, 蒋志刚. 喜马拉雅山哺乳动物物种多样性垂直分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(2): 191-201. |
| [12] | 农友, 郑路, 贾宏炎, 卢立华, 黄德卫, 黄柏华, 雷丽群. 广西大青山次生林的群落特征及主要乔木种群的空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(3): 321-331. |
| [13] | 姚蓓, 余建平, 刘晓娟, 米湘成, 马克平. 亚热带常绿阔叶林种子性状对木本植物聚集格局的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(2): 157-166. |
| [14] | 高末, 胡仁勇, 陈贤兴, 李伟成, 丁炳扬. 干扰、地形和土壤对温州入侵植物分布的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(4): 424-431. |
| [15] | 蔡永久, 龚志军, 秦伯强. 太湖大型底栖动物群落结构及多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(1): 50-59. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn