



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (8): 1008-1017. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020015 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020015
梁栋栋1, 彭杰1, 高改利3, 洪欣3,*( ), 周守标2,*(
), 周守标2,*( ), 储俊4, 王智5
), 储俊4, 王智5
收稿日期:2020-01-09
接受日期:2020-02-28
出版日期:2020-08-20
发布日期:2020-09-01
通讯作者:
洪欣,周守标
作者简介:hongxin@ahu.edu.cn基金资助:
Dongdong Liang1, Jie Peng1, Gaili Gao3, Xin Hong3,*( ), Shoubiao Zhou2,*(
), Shoubiao Zhou2,*( ), Jun Chu4, Zhi Wang5
), Jun Chu4, Zhi Wang5
Received:2020-01-09
Accepted:2020-02-28
Online:2020-08-20
Published:2020-09-01
Contact:
Xin Hong,Shoubiao Zhou
摘要:
为探讨大别山森林群落的构建和演替机制, 本文基于安徽鹞落坪落叶阔叶林11.56 ha动态监测样地的定位监测资料, 采用最近邻分析和O-ring函数、Monte Carlo拟合和零模型选取的方法, 分析了落叶阔叶林蔷薇科主要树种水榆花楸(Sorbus alnifolia)、山樱花(Cerasus serrulata)和中华石楠(Photinia beauverdiana)不同年龄阶段的空间分布格局及种间关联性。结果表明: (1)在整个样地中3个树种的小树和成年树阶段都为聚集分布, 且随年龄增加聚集性减弱, 在老树阶段转为随机和均匀分布。(2)在0-50 m尺度范围内, 以完全随机模型(complete spatial randomness, CSR)为零假设时, 3个树种整体及小树都在小尺度(≤ 10 m)上呈聚集分布, 成年树与老树多为随机分布。以异质性泊松模型(heterogeneous Poisson, HP)为零假设时, 树种的聚集与生境异质性间呈负相关, 3个树种只在≤ 4 m尺度上出现聚集现象。(3) 3个树种种内各个年龄段之间在较大范围内多为负相关和无显著相关性, 同时各树种及不同年龄段之间受种间竞争和密度制约效应影响在小尺度上(≤ 10 m)多为负相关, 随尺度增加相关性减弱。综合而言, 大别山落叶阔叶林中蔷薇科植物的分布格局整体上多为聚集分布, 随树龄增加聚集性减弱, 在中大尺度上受生境异质性效应的影响显著, 在小尺度上多为负相关, 各树种内部各龄级相互之间也多为负相关。
梁栋栋, 彭杰, 高改利, 洪欣, 周守标, 储俊, 王智 (2020) 鹞落坪落叶阔叶林蔷薇科主要树种的空间分布格局及种间关联性. 生物多样性, 28, 1008-1017. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020015.
Dongdong Liang, Jie Peng, Gaili Gao, Xin Hong, Shoubiao Zhou, Jun Chu, Zhi Wang (2020) Spatial distribution pattern and interspecific correlation analysis of main species of Rosaceae in a deciduous broad-leaved forest in Yaoluoping. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1008-1017. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020015.
| 物种 Species | 个体数量 Number | 相对频度 Relative frequency (%) | 相对优势度 Relative dominance (%) | 相对多度 Relative abundance (%) | 重要值 Importance value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水榆花楸 Sorbus alnifolia | 1,147 | 4.62 | 5.34 | 5.34 | 5.10 |
| 山樱花 Cerasus serrulata | 305 | 1.23 | 1.74 | 1.47 | 1.48 |
| 中华石楠 Photinia beauverdiana | 348 | 1.40 | 0.61 | 1.13 | 1.05 |
| 湖北花楸 Sorbus hupehensis | 122 | 0.49 | 0.97 | 0.85 | 0.77 |
| 短梗稠李 Padus brachypoda | 40 | 0.16 | 0.55 | 0.36 | 0.36 |
| 毛叶石楠 Photinia villosa | 119 | 0.48 | 0.23 | 0.36 | 0.36 |
| 杜梨 Pyrus betulifolia | 61 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.29 |
| 稠李 Padus racemosa | 51 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.24 |
| 短叶中华石楠 Photinia beauverdiana var. brevifolia | 88 | 0.35 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.18 |
| 小叶石楠 Photinia parvifolia | 48 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.16 |
| 石楠 Photinia serrulata | 73 | 0.29 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.16 |
| 湖北海棠 Malus hupehensis | 69 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.15 |
| 三裂绣线菊 Spiraea trilobata | 58 | 0.23 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.11 |
| 细齿稠李 Padus obtusata | 17 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.09 |
| 绣线菊 Spiraea salicifolia | 43 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.09 |
| 麻叶绣线菊 Spiraea cantoniensis | 37 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.07 |
表1 鹞落坪国家级自然保护区内蔷薇科树种重要值
Table 1 Ranking of importance values of Rosaceae species in the Yaoluoping National Nature Reserve
| 物种 Species | 个体数量 Number | 相对频度 Relative frequency (%) | 相对优势度 Relative dominance (%) | 相对多度 Relative abundance (%) | 重要值 Importance value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水榆花楸 Sorbus alnifolia | 1,147 | 4.62 | 5.34 | 5.34 | 5.10 |
| 山樱花 Cerasus serrulata | 305 | 1.23 | 1.74 | 1.47 | 1.48 |
| 中华石楠 Photinia beauverdiana | 348 | 1.40 | 0.61 | 1.13 | 1.05 |
| 湖北花楸 Sorbus hupehensis | 122 | 0.49 | 0.97 | 0.85 | 0.77 |
| 短梗稠李 Padus brachypoda | 40 | 0.16 | 0.55 | 0.36 | 0.36 |
| 毛叶石楠 Photinia villosa | 119 | 0.48 | 0.23 | 0.36 | 0.36 |
| 杜梨 Pyrus betulifolia | 61 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.29 |
| 稠李 Padus racemosa | 51 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.24 |
| 短叶中华石楠 Photinia beauverdiana var. brevifolia | 88 | 0.35 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.18 |
| 小叶石楠 Photinia parvifolia | 48 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.16 |
| 石楠 Photinia serrulata | 73 | 0.29 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.16 |
| 湖北海棠 Malus hupehensis | 69 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.15 |
| 三裂绣线菊 Spiraea trilobata | 58 | 0.23 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.11 |
| 细齿稠李 Padus obtusata | 17 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.09 |
| 绣线菊 Spiraea salicifolia | 43 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.09 |
| 麻叶绣线菊 Spiraea cantoniensis | 37 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.07 |
| 树种 Species | 龄级 Age | 最近邻指数 Nearest neighbor index | Z | 置信水平 Confidence level (P) | 分布类型 Distribution type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水榆花楸 Sorbus alnifolia | 小树 Small tree | 0.76 | -8.68 | 0.00 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered |
| 成年树 Adult tree | 0.68 | -16.61 | 0.68 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered | |
| 老树 Old tree | 0.97 | -0.47 | 0.64 | 随机 Random | |
| 整体 All | 0.63 | -24.09 | 0.00 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered | |
| 山樱花 Cerasus serrulata | 小树 Small tree | 0.76 | -6.15 | 0.00 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered |
| 成年树 Adult tree | 0.81 | -3.72 | 0.00 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered | |
| 老树 Old tree | 1.36 | 3.26 | 0.00 | 均匀 Uniform | |
| 整体 All | 0.79 | -7.17 | 0.00 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered | |
| 中华石楠 Photinia beauverdiana | 小树 Small tree | 0.67 | -8.94 | 0.00 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered |
| 成年树 Adult tree | 0.72 | -5.84 | 0.00 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered | |
| 老树 Old tree | 0.86 | -1.32 | 0.19 | 聚集但不显著 Aggregated but not significant | |
| 整体 All | 0.66 | -12.19 | 0.00 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered |
表2 鹞落坪国家级自然保护区蔷薇科3个主要树种不同龄级最近邻距离分析法结果
Table 2 The nearest neighbor analysis (ANN) result of three main species of Rosaceae in different ages in the Yaoluoping National Nature Reserve
| 树种 Species | 龄级 Age | 最近邻指数 Nearest neighbor index | Z | 置信水平 Confidence level (P) | 分布类型 Distribution type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水榆花楸 Sorbus alnifolia | 小树 Small tree | 0.76 | -8.68 | 0.00 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered |
| 成年树 Adult tree | 0.68 | -16.61 | 0.68 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered | |
| 老树 Old tree | 0.97 | -0.47 | 0.64 | 随机 Random | |
| 整体 All | 0.63 | -24.09 | 0.00 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered | |
| 山樱花 Cerasus serrulata | 小树 Small tree | 0.76 | -6.15 | 0.00 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered |
| 成年树 Adult tree | 0.81 | -3.72 | 0.00 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered | |
| 老树 Old tree | 1.36 | 3.26 | 0.00 | 均匀 Uniform | |
| 整体 All | 0.79 | -7.17 | 0.00 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered | |
| 中华石楠 Photinia beauverdiana | 小树 Small tree | 0.67 | -8.94 | 0.00 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered |
| 成年树 Adult tree | 0.72 | -5.84 | 0.00 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered | |
| 老树 Old tree | 0.86 | -1.32 | 0.19 | 聚集但不显著 Aggregated but not significant | |
| 整体 All | 0.66 | -12.19 | 0.00 | 显著聚集 Significant gathered |
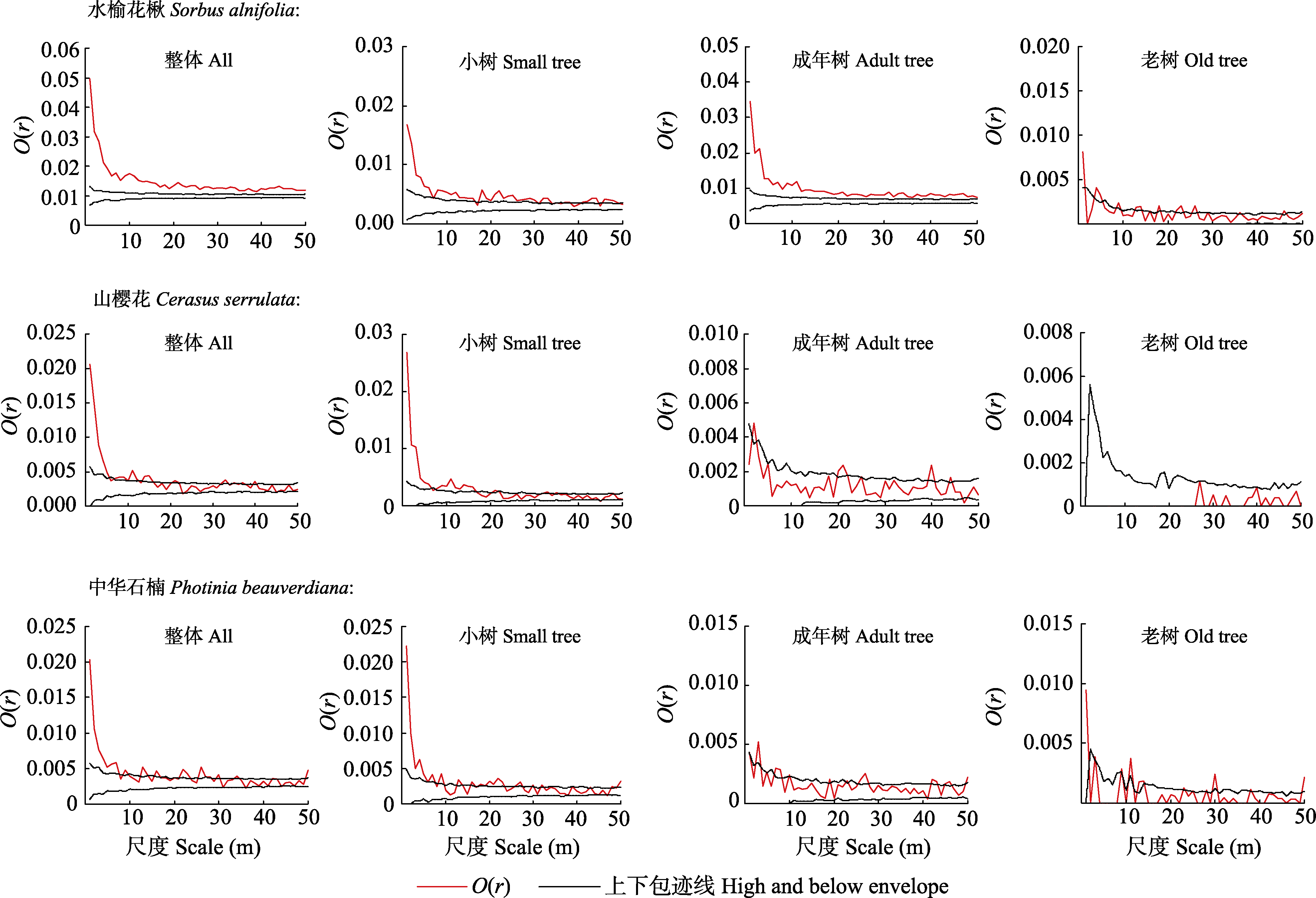
图1 鹞落坪国家级自然保护区蔷薇科3个主要树种不同龄级的空间分布格局(基于完全随机模型CSR)
Fig. 1 Spatial patterns of three main species of Rosaceae in different ages based on complete spatial randomness (CSR) models in the Yaoluoping National Nature Reserve
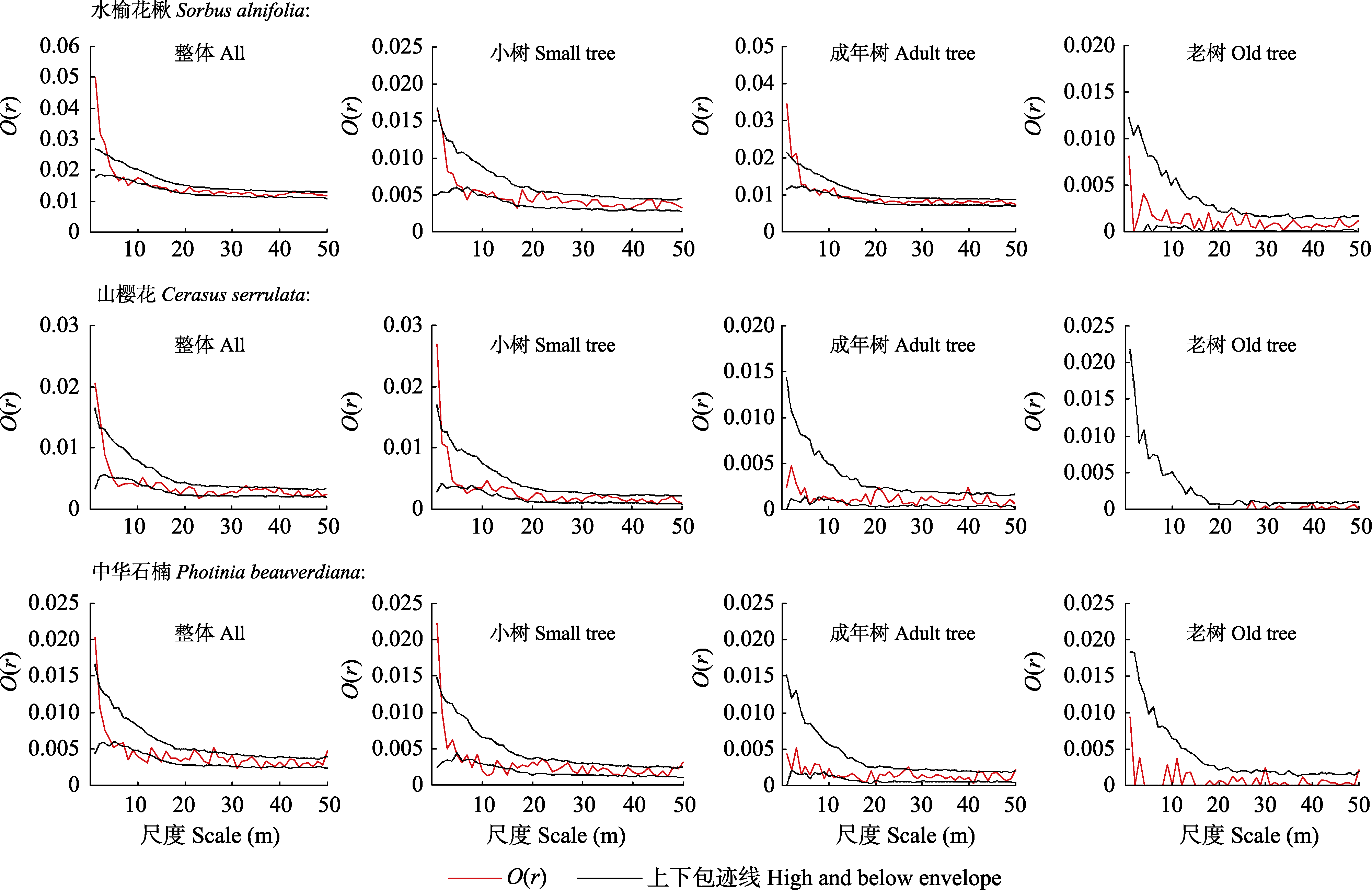
图2 鹞落坪国家级自然保护区蔷薇科3个主要树种不同龄级的空间分布格局(基于异质性泊松模型HP)
Fig. 2 Spatial patterns of three main species of Rosaceae in different ages based on heterogeneous Poisson (HP) models in the Yaoluoping National Nature Reserve
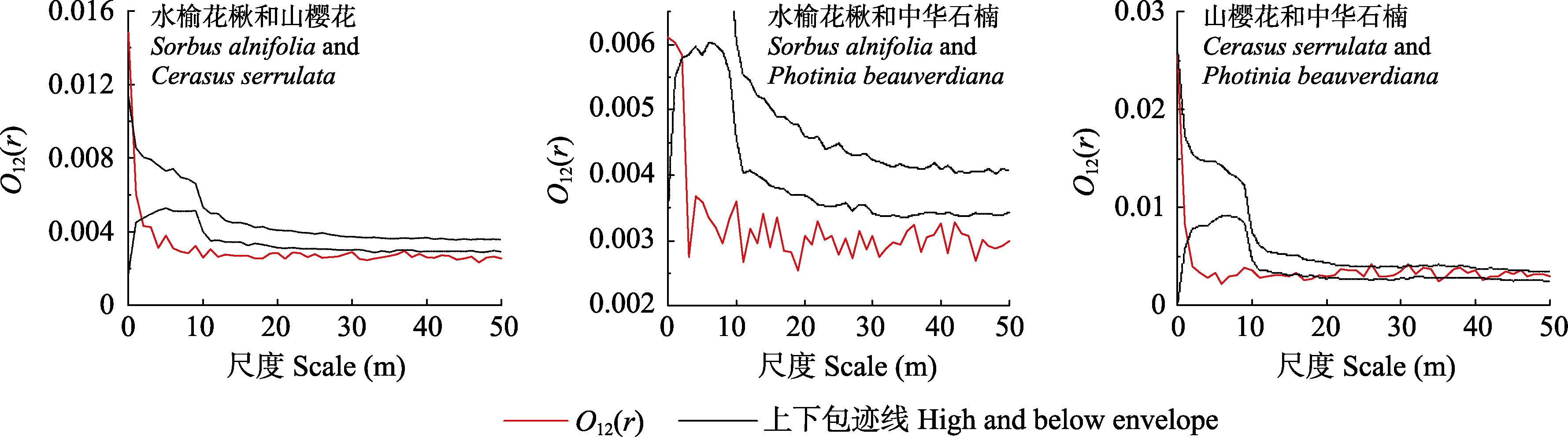
图3 鹞落坪国家级自然保护区蔷薇科3个主要树种整体之间的空间关联性
Fig. 3 Spatial correlation among the three main species of Rosaceae as all in the Yaoluoping National Nature Reserve
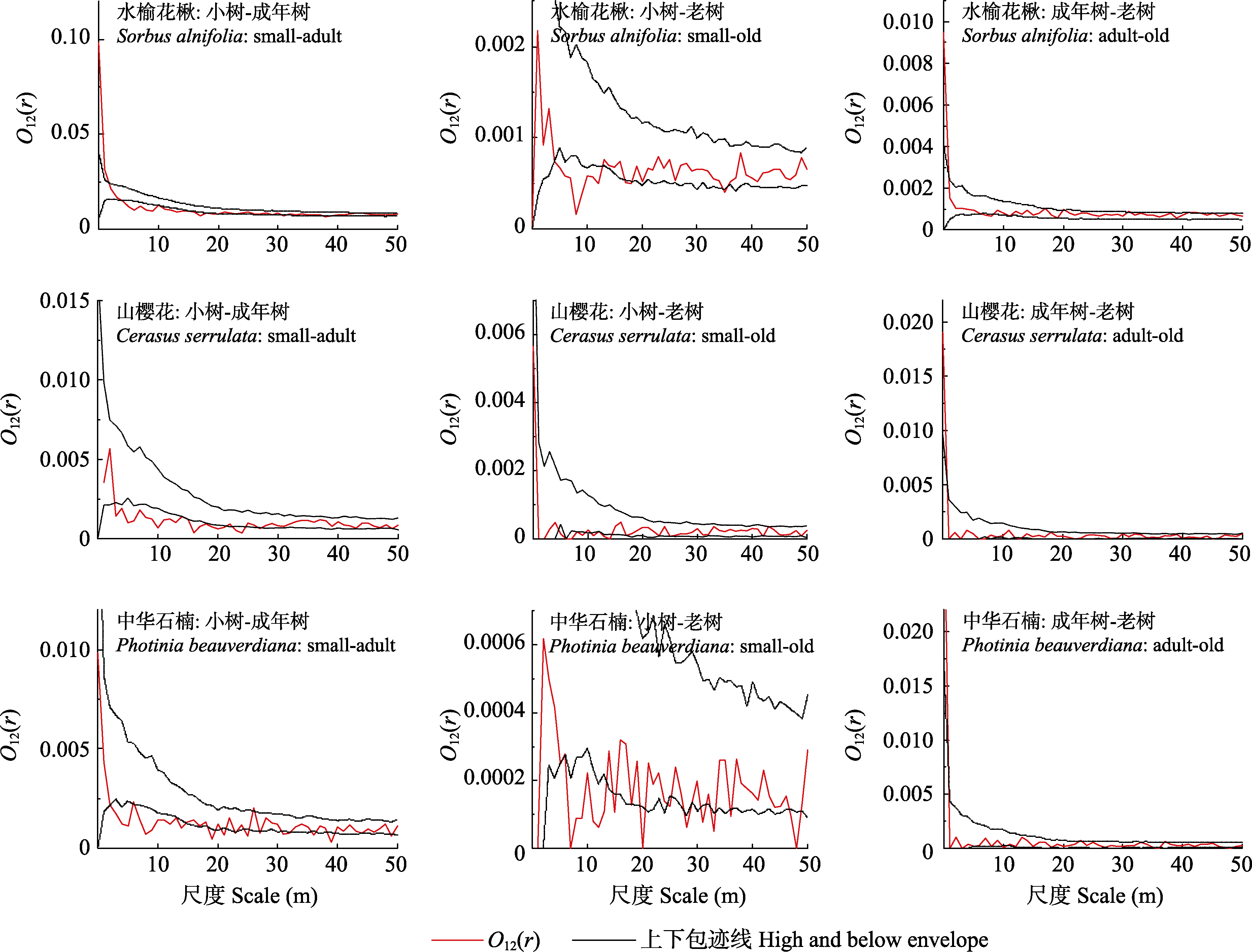
图4 鹞落坪国家级自然保护区蔷薇科3个主要树种不同年龄段之间的空间关联性
Fig. 4 Spatial correlation among different age groups in three main species of Rosaceae in the Yaoluoping National Nature Reserve
| [1] | Chen J, Ai XR, Yao L, Chen SY (2018) Point pattern analysis of two species of Cyclobalanopsis in large plot in Mulinzi Nature Reserve. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 54, 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈俊, 艾训儒, 姚兰, 陈思艺 (2018) 木林子大样地两个青冈属优势种的点格局对比. 林业科学, 54, 1-10.] | |
| [2] | Chen KY, Zhang HR, Lei XD (2018) Spatial pattern of Quercus mongolica in natural secondary forest. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 3462-3470. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈科屹, 张会儒, 雷相东 (2018) 天然次生林蒙古栎种群空间格局. 生态学报, 38, 3462-3470.] | |
| [3] | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots. Springer, Berlin. |
| [4] | Fan J, Zhao XH, Wang JS, Zhang CY, He J, Xia FC (2012) Spatial patterns of dominant species in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest in Jiulian Mountain, Jiangxi Province, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 2729-2737. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 范娟, 赵秀海, 汪金松, 张春雨, 何俊, 夏富才 (2012) 江西九连山亚热带常绿阔叶林优势种空间分布格局. 生态学报, 32, 2729-2737.] | |
| [5] | Getzin S, Wiegand T, Wiegand K, He FL (2008) Heterogeneity influences spatial patterns and demographics in forest stands. Journal of Ecology, 96, 807-820. |
| [6] | Ghorbani M (2013) Cauchy cluster process. Metrika, 76, 697-706. |
| [7] | Grubb PJ (1977) Maintenance of species-richness in plant communities: The importance of the regeneration niche. Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 52, 107-145. |
| [8] | Han YL (1981) Discussion on the spectral base of vertical vegetation belt on the southern slope of Dabie Mountain in Anhui Province. Journal of Anhui Normal University (Natural Science), 2, 110-125. (in Chinese) |
| [ 韩也良 (1981) 对安徽大别山南坡植被垂直带谱基带的讨论. 安徽师大学报(自然科学版), 2, 110-125.] | |
| [9] | Hao WF (2010) Ecological Processes and Mechanisms of the Recovering Succession of Abandoned Farmland in the Hilly and Gully Loess Region of North Shaanxi. PhD dissertation, Northwest A & F University, Yangling. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郝文芳 (2010) 陕北黄土丘陵区撂荒地恢复演替的生态学过程及机理研究. 博士学位论文, 西北农林科技大学, 杨凌.] | |
| [10] |
Harms KE, Wright SJ, Calderon O, Hernandez A, Herre EA (2000) Pervasive density-dependent recruitment enhances seedling diversity in a tropical forest. Nature, 404, 493-495.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] |
Hubbell SP (2006) Neutral theory and the evolution of ecological equivalence. Ecology, 87, 1387-1398.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] | Hu MJ, Hou GL, Zhou NX, Li ZJ, Qi XY, Fang YL (2015) Spatial distribution patterns and multi-scale features of the Lushan forest landscape. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 5294-5305. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡美娟, 侯国林, 周年兴, 李在军, 亓秀云, 方叶林 (2015) 庐山森林景观空间分布格局及多尺度特征. 生态学报, 35, 5294-5305.] | |
| [13] | Li L, Chen JH, Ren HB, Mi XC, Yu MJ, Yang B (2010) Spatial patterns of Castanopsis eyrei and Schima superba in mid-subtropical broad-leaved evergreen forest in Gutianshan National Nature Reserve, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 34, 241-252. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李立, 陈建华, 任海保, 米湘成, 于明坚, 杨波 (2010) 古田山常绿阔叶林优势树种甜槠和木荷的空间格局分析. 植物生态学报, 34, 241-252.] | |
| [14] | Li Z, Zhou ZZ, Wang WG, Shen SB (2008) The floristic analysis of vascular plants in Yaoluoping Nature Reserve from Anhui Province. Journal of Biology, 25, 26-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李珍, 周忠泽, 汪文革, 沈三宝 (2008) 安徽鹞落坪自然保护区维管植物区系分析. 生物学杂志, 25, 26-30.] | |
| [15] | Lin Y, Ren JY, Yue M (2009) Spatial patterns and associations in a birch-fir forest in Mt. Taibai. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 27, 47-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 林玥, 任坚毅, 岳明 (2009) 太白山牛皮桦-巴山冷杉混交林空间格局及关联性研究. 武汉植物学研究, 27, 47-54.] | |
| [16] | Lin Y, Ai XR, Yao L, Huang W, Chen S (2017) Niches of main dominant species of different community types in Mulinzi Nature Reserve. Journal of Natural Resources, 32, 223-234. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 林勇, 艾训儒, 姚兰, 黄伟, 陈斯 (2017) 木林子自然保护区不同群落类型主要优势种群的生态位研究. 自然资源学报, 32, 223-234.] | |
| [17] | Ma F, Wang SZ, Feng JC, Sang WG (2018) Spatial distribution pattern of snag and standing trees in a warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest in Dongling Mountain, Beijing. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 5717-5725. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马芳, 王顺忠, 冯金朝, 桑卫国 (2018) 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林枯立木与活立木空间分布格局. 生态学报, 38, 5717-5725.] | |
| [18] | Queenborough SA, Burslem D, Garwood NC, Valencia R (2007) Habitat niche partitioning by 16 species of Myristicaceae in Amazonian Ecuador. Plant Ecology, 192, 193-207. |
| [19] | Rayburn AP, Schiffers K, Schupp EW (2011) Use of precise spatial data for describing spatial patterns and plant interactions in a diverse Great Basin shrub community. Plant Ecology, 212, 585-594. |
| [20] | Ripley BD (1977) Modelling spatial patterns. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B: Methodological, 39, 172-212. |
| [21] |
Shen ZQ, Hua M, Dan Q, Lu J, Fang JP (2016) Spatial pattern analysis and associations of Quercus aquifolioides population at different growth stages in Southeast Tibet, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27, 387-394. (in Chinese with English abstract)
URL PMID |
|
[ 沈志强, 华敏, 丹曲, 卢杰, 方江平 (2016) 藏东南川滇高山栎种群不同生长阶段的空间格局与关联性. 应用生态学报, 27, 387-394.]
PMID |
|
| [22] | Wang JF (2006) Spatial Analysis. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王劲峰 (2006) 空间分析 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [23] | Wang L, Chang JL, Zhou SB, Wang XY, Zhang JQ, Yan SK, Zhang JM, Chen X, Zhao X, Wang Z (2019) Species diversity and interspecific association of trees in the Yaoluoping National Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 309-319. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王丽, 常锦利, 周守标, 王晓英, 张佳期, 闫少凯, 张金铭, 陈鑫, 赵昕, 王智 (2019) 鹞落坪国家级自然保护区乔木物种多样性与种间联结. 生态学报, 39, 309-319.] | |
| [24] | Wasserstein RL, Lazar NA (2016) The ASA’s statement on p-values: Context, process, and purpose. The American Statistician, 70, 129-133. |
| [25] | Weiler M, Naef F (2003) An experimental tracer study of the role of macropores in infiltration in grassland soils. Hydrological Processes, 17, 477-493. |
| [26] |
Wiegand T, Gunatilleke S, Gunatilleke N, Okuda T (2007) Analyzing the spatial structure of a Sri Lankan tree species with multiple scales of clustering. Ecology, 88, 3088-3102.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] | Wiegand T, Moloney KA (2004) Rings, circles, and null- models for point pattern analysis in ecology. Oikos, 104, 209-229. |
| [28] | Wu CP, Yuan WG, Sheng WX, Huang YJ, Chen QB, Shen AH, Zhu JR, Jiang B (2018) Spatial distribution patterns and associations of tree species in typical natural secondary forest communities in Zhejiang Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 537-549. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴初平, 袁位高, 盛卫星, 黄玉洁, 陈庆标, 沈爱华, 朱锦茹, 江波 (2018) 浙江省典型天然次生林主要树种空间分布格局及其关联性. 生态学报, 38, 537-549.] | |
| [29] |
Yan HB, Ma HJ, Feng F, Liang N, Shi C, Yang XQ, Han YZ (2018) Spatial distribution patterns and associations of typical tree species in different regions. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29, 369-379. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL PMID |
|
[ 闫海冰, 马慧晶, 冯帆, 梁楠, 史婵, 杨秀清, 韩有志 (2018) 不同区域典型树木的空间分布格局及关联性. 应用生态学报, 29, 369-379.]
PMID |
|
| [30] | Yang H, Li YL, Shen L, Kang XG (2014) Spatial distributions and associations of main tree species in a spruce-fir forest in the Changbai Mountains area in northeastern China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 4698-4706. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨华, 李艳丽, 沈林, 亢新刚 (2014) 长白山云冷杉针阔混交林主要树种空间分布及其关联性. 生态学报, 34, 4698-4706.] | |
| [31] | Zhang JY, Cheng KW, Zang RG (2014) The spatial distribution patterns and associations of the principal trees and shrubs in a natural tropical coniferous forest on Hainan Island, China. Biodiversity Science, 22, 129-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张俊艳, 成克武, 臧润国 (2014) 海南岛热带天然针叶林主要树种的空间格局及关联性. 生物多样性, 22, 129-140.] | |
| [32] | Zou DT, Wang QG, Luo A, Wang ZH (2019) Species richness patterns and resource plant conservation assessments of Rosaceae in China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 43, 1-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 邹东廷, 王庆刚, 罗奥, 王志恒 (2019) 中国蔷薇科植物多样性格局及其资源植物保护现状. 植物生态学报, 43, 1-15.] |
| [1] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [2] | 杨俊毅, 关潇, 李俊生, 刘晶晶, 郝颢晶, 王槐睿. 乌江流域生物多样性与生态系统服务的空间格局及相互关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23061-. |
| [3] | 王雅婷, 张定海, 张志山. 古尔班通古特沙漠固定沙丘上白梭梭和梭梭的空间分布及种间关联性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21280-. |
| [4] | 王重阳, 赵联军, 孟世勇. 王朗国家级自然保护区滑坡体兰科植物分布格局及其保护策略[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21313-. |
| [5] | 郝希阳, 贺姹, 楚克林, 申志新, 赵强, 高伟, 潘达, 孙红英. 海南岛淡水蟹类分布格局与多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 605-616. |
| [6] | 王鑫厅, 柴静, 姜超, 邰阳, 迟延艳, 张维华, 刘芳, 李素英. 典型草原大针茅种群空间格局及对长期过度放牧的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(2): 128-134. |
| [7] | 孙远, 胡维刚, 姚树冉, 孙颖, 邓建明. 黄河流域被子植物和陆栖脊椎动物丰富度格局及其影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(12): 1523-1532. |
| [8] | 谢峰淋, 周全, 史航, 舒枭, 张克荣, 李涛, 冯水园, 张全发, 党海山. 秦岭落叶阔叶林25 ha森林动态监测样地物种组成与群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(4): 439-448. |
| [9] | 颜文博,吉晟男,帅凌鹰,赵雷刚,朱大鹏,曾治高. 秦岭南坡陕西洋县辖区哺乳动物物种多样性的空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(2): 177-185. |
| [10] | 胡一鸣, 梁健超, 金崑, 丁志锋, 周智鑫, 胡慧建, 蒋志刚. 喜马拉雅山哺乳动物物种多样性垂直分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(2): 191-201. |
| [11] | 周磊, 万雅琼, 洪欣, 张恒, 钱立富, 王陈成, 孔政, 赵凯, 李佳琦, 张保卫. 利用红外相机技术对安徽省鹞落坪国家级自然保护区大中型兽类及林下鸟类的调查[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(12): 1338-1342. |
| [12] | 农友, 郑路, 贾宏炎, 卢立华, 黄德卫, 黄柏华, 雷丽群. 广西大青山次生林的群落特征及主要乔木种群的空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(3): 321-331. |
| [13] | 姚蓓, 余建平, 刘晓娟, 米湘成, 马克平. 亚热带常绿阔叶林种子性状对木本植物聚集格局的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(2): 157-166. |
| [14] | 任思远, 王婷, 祝燕, 叶永忠, 李聪, 潘娜, 叶永忠. 暖温带-北亚热带过渡带落叶阔叶林群落不同径级系统发育结构的变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(5): 574-582. |
| [15] | 王婷, 任思远, 袁志良, 祝燕, 潘娜, 李鹿鑫, 叶永忠. 密度制约对宝天曼落叶阔叶林锐齿栎死亡前后分布格局的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(4): 449-457. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()