



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (2): 182-194. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017014 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017014
所属专题: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全
沈泽昊1,*( ), 杨明正1, 冯建孟2, 李新辉3, 彭培好4, 郑智5
), 杨明正1, 冯建孟2, 李新辉3, 彭培好4, 郑智5
收稿日期:2017-01-08
接受日期:2017-02-09
出版日期:2017-02-20
发布日期:2017-03-06
通讯作者:
沈泽昊
基金资助:
Zehao Shen1,*( ), Mingzheng Yang1, Jianmeng Feng2, Xinhui Li3, Peihao Peng4, Zhi Zheng5
), Mingzheng Yang1, Jianmeng Feng2, Xinhui Li3, Peihao Peng4, Zhi Zheng5
Received:2017-01-08
Accepted:2017-02-09
Online:2017-02-20
Published:2017-03-06
Contact:
Shen Zehao
摘要:
高山带是具有极端环境和明确边界的植物分布区, 研究高山植物区系地理对于理解空间彼此隔离的极端高寒环境下植物区系的形成与相互联系具有重要意义。本研究整合了中国境内14座主要山地的高山植物区系数据, 用Jaccard指数测度不同区系之间的相似性, 运用相关分析和Mantel检验方法, 重点分析了中国高山种子植物区系地理成分的构成、不同山地之间的相似性及其环境和空间相关因素。结果表明, 中国山地的高山带分布着物种丰富的种子植物区系, 14座主要山地即包含了65科489属3,670种(含340个种下单位), 主要由北温带分布及其亚型、世界分布、旧世界温带分布和东亚分布及其中国-喜马拉雅分布亚型等成分构成, 缺少中国-日本分布类型, 中国特有属的比例较高(5.2%)。14座山地高山植物区系构成的地理分异显示: 北热带和东亚成分自南向北减少, 而北方温带成分增加; 自西向东古地中海成分减少, 北方温带成分增加, 而东亚成分在中部达到最大值; 在属级地理成分构成上, 北方山地和青藏高原周缘山地构成了区系成分近似的两大群组, 台湾高山植物区系与大陆东部北方高山带的区系联系更密切。地理隔离是高山植物区系分异的首要因素, 高山带的面积大小也影响到其区系成分的构成, 而夏季热量是影响中国高山植物区系地理分异的首要气候因子, 显示全球变暖对未来高山植物区系具有潜在的胁迫作用。
沈泽昊, 杨明正, 冯建孟, 李新辉, 彭培好, 郑智 (2017) 中国高山植物区系地理格局与环境和 空间因素的关系. 生物多样性, 25, 182-194. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017014.
Zehao Shen, Mingzheng Yang, Jianmeng Feng, Xinhui Li, Peihao Peng, Zhi Zheng (2017) Geographic patterns of alpine flora in China in relation to environmental and spatial factors. Biodiversity Science, 25, 182-194. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017014.
| 山名 Mt. name | 省份 Province | 最高峰 Summit (m) | 纬度范围 Latitudinal rang | 树线海拔Alpine Elev. (m) | 林线树种下限 Lower limit (m) | 高山林线树种 Alpine treeline species | 高山带面积 Alpine area (ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 天山 Mt. Tianshan[ | 新疆 Xinjiang | 7,439 | 42°18'-44°15' | 2,800 | 1,800 | 雪岭云杉 Picea schrenkiana | 832,930.0 |
| 阿尔金山 Mt. Arjin[ | 新疆 Xinjiang | 6,973 | 37°55'-39°35' | 3,500 | — | 无 | 3,137.6 |
| 祁连山 Mt. Qilian[ | 青海 Qinghai | 5,808 | 37°16'-39°19' | 3,600 | 2,600 | 祁连圆柏 Sabina przewalskii | 16,345.1 |
| 贺兰山 Mt. Helan[ | 宁夏 Ningxia | 3,556 | 38°07'-39°30' | 3,200 | 2,600 | 青海云杉 P. erassifolia | 755.5 |
| 长白山 Mt. Changbai[ | 吉林 Jilin | 2,750 | 41°42'-42°51' | 2,100 | 1,800 | 岳桦 Betula ermanii | 9,063.4 |
| 五台山 Mt. Wutai[ | 河北 Hebei | 3,061 | 38°50'-39°05' | 2,800 | 2,300 | 华北落叶松 Larix principis-rupprechtii | 923.7 |
| 太白山 Mt. Taibai[ | 陕西 Shaanxi | 3,767 | 33°49'-34°08' | 3,400 | 2,800 | 太白红杉 L. chinensis | 2,678.7 |
| 摩天岭 Mt. Motianling[ | 甘肃 Gansu | 3,837 | 32°39'-32°49' | 3,450 | 2,900 | 秦岭冷杉 Abies chensiensis | 5,698.9 |
| 贡嘎山 Mt. Gongga[ | 四川 Sichuan | 7,556 | 29°20'-30°20' | 3,800 | 2,700 | 峨眉冷杉 A. fabri | 68,413.9 |
| 高黎贡山 Mt. Gaoligong[ | 云南 Yunnan | 5,128 | 24°40'-28°30' | 4,000 | 3,000 | 急尖长苞冷杉 A. georgei var. smithii | 93,695.2 |
| 玉龙雪山 Mt. Yulong[ | 云南 Yunnan | 5,596 | 27°10'-27°15' | 3,900 | 3,200 | 长苞冷杉 A. georgei | 5,628.1 |
| 轿子雪山 Mt. Jiaozi [ | 云南 Yunnan | 4,247 | 26°00'-26°10' | 4,000 | 3,200 | 急尖长苞冷杉 A. georgei var. smithii | 294.3 |
| 台湾山脉 Mts. Taiwan[ | 台湾 Taiwan | 3,998 | 22°36'-24°26' | >3,998 | 3,000 | 台湾冷杉 A. kawakamii | 3,277.2 |
| 珠峰 Mt. Zhumulangma# | 西藏 Tibet | 8,848 | 27°48'-29°19' | 4,300 | 3,600 | 糙皮桦 B. albo-sinensis var. septentrionalis | 231,943.0 |
表1 所分析的14座高山的基本特征
Table 1 The basic characteristics of the 14 mountains studied
| 山名 Mt. name | 省份 Province | 最高峰 Summit (m) | 纬度范围 Latitudinal rang | 树线海拔Alpine Elev. (m) | 林线树种下限 Lower limit (m) | 高山林线树种 Alpine treeline species | 高山带面积 Alpine area (ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 天山 Mt. Tianshan[ | 新疆 Xinjiang | 7,439 | 42°18'-44°15' | 2,800 | 1,800 | 雪岭云杉 Picea schrenkiana | 832,930.0 |
| 阿尔金山 Mt. Arjin[ | 新疆 Xinjiang | 6,973 | 37°55'-39°35' | 3,500 | — | 无 | 3,137.6 |
| 祁连山 Mt. Qilian[ | 青海 Qinghai | 5,808 | 37°16'-39°19' | 3,600 | 2,600 | 祁连圆柏 Sabina przewalskii | 16,345.1 |
| 贺兰山 Mt. Helan[ | 宁夏 Ningxia | 3,556 | 38°07'-39°30' | 3,200 | 2,600 | 青海云杉 P. erassifolia | 755.5 |
| 长白山 Mt. Changbai[ | 吉林 Jilin | 2,750 | 41°42'-42°51' | 2,100 | 1,800 | 岳桦 Betula ermanii | 9,063.4 |
| 五台山 Mt. Wutai[ | 河北 Hebei | 3,061 | 38°50'-39°05' | 2,800 | 2,300 | 华北落叶松 Larix principis-rupprechtii | 923.7 |
| 太白山 Mt. Taibai[ | 陕西 Shaanxi | 3,767 | 33°49'-34°08' | 3,400 | 2,800 | 太白红杉 L. chinensis | 2,678.7 |
| 摩天岭 Mt. Motianling[ | 甘肃 Gansu | 3,837 | 32°39'-32°49' | 3,450 | 2,900 | 秦岭冷杉 Abies chensiensis | 5,698.9 |
| 贡嘎山 Mt. Gongga[ | 四川 Sichuan | 7,556 | 29°20'-30°20' | 3,800 | 2,700 | 峨眉冷杉 A. fabri | 68,413.9 |
| 高黎贡山 Mt. Gaoligong[ | 云南 Yunnan | 5,128 | 24°40'-28°30' | 4,000 | 3,000 | 急尖长苞冷杉 A. georgei var. smithii | 93,695.2 |
| 玉龙雪山 Mt. Yulong[ | 云南 Yunnan | 5,596 | 27°10'-27°15' | 3,900 | 3,200 | 长苞冷杉 A. georgei | 5,628.1 |
| 轿子雪山 Mt. Jiaozi [ | 云南 Yunnan | 4,247 | 26°00'-26°10' | 4,000 | 3,200 | 急尖长苞冷杉 A. georgei var. smithii | 294.3 |
| 台湾山脉 Mts. Taiwan[ | 台湾 Taiwan | 3,998 | 22°36'-24°26' | >3,998 | 3,000 | 台湾冷杉 A. kawakamii | 3,277.2 |
| 珠峰 Mt. Zhumulangma# | 西藏 Tibet | 8,848 | 27°48'-29°19' | 4,300 | 3,600 | 糙皮桦 B. albo-sinensis var. septentrionalis | 231,943.0 |
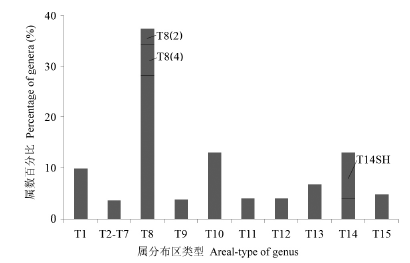
图2 中国14座山地的高山植物区系地理成分构成。T1: 世界分布型; T2-7: 热带分布型; T8-11: 北温带分布型; T12-13: 古地中海分布型; T14: 东亚分布型; T14SH: 中国-喜马拉雅分布型; T15: 中国特有分布型。
Fig. 2 Percentage compositions of alpine flora of 14 main mountains in China. T1, Cosmopolitan; T2-7, Tropic types; T8-11, North temperate types; T12-13, Mediterranean types; T14, East Asia types; T14SH, Sino-Himalayan type; T15, Endemic to China.
| 距离矩阵 Distance matrices | R | P |
|---|---|---|
| 环境距离 Environmental distance | 0.5506 | 0.002 |
| 环境距离|地理距离 Environmental distance | Geographic distance | 0.3543 | 0.008 |
| 形态差异 Physiognomic difference | 0.5455 | 0.002 |
| 形态差异|地理距离 Physiognomic difference | Geographic distance | 0.3532 | 0.017 |
| 最热月最高温差异 MTWM difference | 0.2131 | 0.046 |
| 最热月最高温差异|地理距离 MTWM difference | Geographic distance | 0.2014 | 0.061 |
| 地理距离 Geographic distance | 0.6006 | 0.001 |
| 地理距离|环境差异 Geographic distance | Environmental distance | 0.4401 | 0.004 |
| 地理距离|形态差异 Geographic | Physiognomic distance | 0.4451 | 0.003 |
| 地理距离|最热月最高温差异 Geographic | MTWM distance | 0.5979 | 0.001 |
表2 14座主要山地高山种子植物区系地理成分构成相似性与空间距离、环境差异联系的Mantel检验及偏Mantel检验
Table 2 Mantel tests and partial Mantel tests for the correlations between the similarities of geographic elements composition and spatial distance, environmental distance among the 14 main mountains in China
| 距离矩阵 Distance matrices | R | P |
|---|---|---|
| 环境距离 Environmental distance | 0.5506 | 0.002 |
| 环境距离|地理距离 Environmental distance | Geographic distance | 0.3543 | 0.008 |
| 形态差异 Physiognomic difference | 0.5455 | 0.002 |
| 形态差异|地理距离 Physiognomic difference | Geographic distance | 0.3532 | 0.017 |
| 最热月最高温差异 MTWM difference | 0.2131 | 0.046 |
| 最热月最高温差异|地理距离 MTWM difference | Geographic distance | 0.2014 | 0.061 |
| 地理距离 Geographic distance | 0.6006 | 0.001 |
| 地理距离|环境差异 Geographic distance | Environmental distance | 0.4401 | 0.004 |
| 地理距离|形态差异 Geographic | Physiognomic distance | 0.4451 | 0.003 |
| 地理距离|最热月最高温差异 Geographic | MTWM distance | 0.5979 | 0.001 |
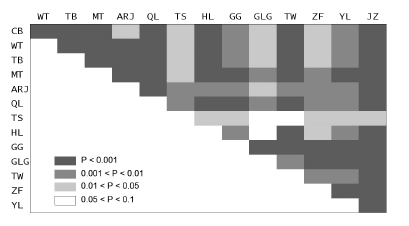
图4 14座山地高山种子植物区系属的地理分布区类型百分比构成的相似性格局
Fig. 4 The similarity patterns of the percentage composition of alpine floristic elements in the 14 main mountains in China
| 1 | Bliss LC (1971) Arctic and alpine plant life cycles. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 2, 405-438. |
| 2 | Cao W, Li JY (2003) Natural Distribution of Plants in Changbai Mountain. Northeast University Press, Shenyang. |
| (in Chinese) [曹伟, 李冀云 (2003) 长白山植物自然分布. 东北大学出版社, 沈阳.] | |
| 3 | Caplat P, Edelaar P, Dudaniec RY, Green AJ, Okamura B, Cote J, Ekroos J, Jonsson PR, Löndahl J, Tesson SVM, Petit EJ (2016) Looking beyond the mountain, dispersal barriers in a changing world. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 14, 261-268. |
| 4 | Chapin III FS, Körner C (1994) Arctic and alpine biodiversity, patterns, causes and ecosystem consequences. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 9, 45-47. |
| 5 | Chen LZ (2014) Geography of Flora and Vegetation in China. Science Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [陈灵芝 (2014) 中国植物区系与植被地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 6 | Chen S, Jiang G, Zhang J, Li Y, Qian H (2011) Species turn- over of amphibians and reptiles in eastern China, disentangling the relative effects of geographic distance and environmental difference. Ecological Research, 26, 949-956. |
| 7 | Chen ZD, Ying JS, Lu AM (2012) Disjunct distribution of seed plants between Southwest China and Taiwan Island of China. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 47, 551-570. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [陈之端, 应俊生, 路安民 (2012) 中国西南地区与台湾种子植物间断分布现象. 植物学报, 47, 551-570.] | |
| 8 | Cui NR, Akefu P (1993) The formation and the basic nature of the flora in the Argion Mountain Natural Reserve, China. Journal of Xinjiang Normal University (Natural Sciences Edition),1, 47-53. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [崔乃然, 彼得·爱克夫 (1993) 中国阿尔金山自然保护区植物区系组成及基本特征. 新疆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 1, 47-53.] | |
| 9 | Cui ZJ, Chen YX, Zhang W, Zhou SZ, Zhou LP, Zhang M, Li CC (2011) Research history, glacial chronology and origins of Quaternary glaciations in China. Quaternary Sciences, 31, 749-764. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [崔之久, 陈艺鑫, 张威, 周尚哲, 周力平, 张梅, 李川川 (2011) 中国第四纪冰期历史、特征及成因探讨. 第四纪研究, 31, 749-764.] | |
| 10 | Farr TG, Kobrick M (2000) Shuttle radar topography mission produces a wealth of data. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 81, 583-585. |
| 11 | Feng JM, Wang XP, Xu CD, Yang YH, Fang JY (2006) Altitudinal patterns of plant species diversity and community structure on Yulong Mountains, Yunnan, China. Journal of Mountain Science, 24, 110-116. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [冯建孟, 王襄平, 徐成东, 杨元合, 方精云 (2006) 玉龙雪山植物物种多样性和群落结构沿海拔梯度的分布格局. 山地学报, 24, 110-116.] | |
| 12 | Han J, Shen ZH, Shi SL, Peng PH (2016) Comparison of plant species diversity and composition in the dry valleys of Yalong River and Dadu River: evaluating the effects of climate, topography and space. Biodiversity Science, 24, 421-430. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [韩杰, 沈泽昊, 石松林, 彭培好 (2016) 雅砻江和大渡河干旱河谷植被物种多样性比较: 气候、地形与空间的影响. 生物多样性, 24, 421-430.] | |
| 13 | Hijmans RJ, Cameron SE, Parra JL, Jones PG, Jarvis A (2005) Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. International Journal of Climatology, 25, 1965-1978. |
| 14 | Keil P, Schweiger O, Kühn I, Kunin WE, Kuussaari M, Settele J, Henle K, Brotons L, Pe’er G, Lengyel S, Moustakas A, Steinicke H, Storch D (2012) Patterns of beta diversity in Europe, the role of climate, land cover and distance across scales. Journal of Biogeography, 39, 1473-1486. |
| 15 | Körner C, Paulsen J (2004) A world-wide study of high altitude treeline temperatures. Journal of Biogeography, 31, 713-732. |
| 16 | Körner C (2003) Alpine Plant Life: Functional Plant Ecology of High Mountain Ecosystems. Springer, Berlin. |
| 17 | Kropf M, Comes HP, Kadereit JW (2006) Long-distance dispersal vs vicariance, the origin and genetic diversity of alpine plants in the Spanish Sierra Nevada. New Phytologist, 172, 169-184. |
| 18 | Li CF, Chytry M, Zelený D, Hsieh CF (2013) Classification of Taiwan forest vegetation. Applied Vegetation Science, 16, 698-719. |
| 19 | Li H, Guo HJ, Dao ZL (2000) Flora of Gaoligong Mountains. Science Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [李恒, 郭辉军, 刀志灵 (2000) 高黎贡山植物. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 20 | Li LP, Yin LK, Tang ZY (2011) Distribution patterns of the species richness of plants and animals in Xinjiang, China. Arid Zone Research, 28, 1-9. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [李利平, 尹林克, 唐志尧 (2011) 新疆野生动植物物种丰富度的分布格局. 干旱区研究, 28, 1-9.] | |
| 21 | Liang CZ (2012) Vegetation of Helan Mountain. Sunshine Press, Yinchuan. |
| (in Chinese) [梁存柱 (2012) 贺兰山植被. 阳光出版社, 银川.] | |
| 22 | López-Pujol J, Zhang FM, Sun HQ, Ying TS, Ge S (2011) Mountains of Southern China as “plant museums” and “plant cradles”, evolutionary and conservation insights. Mountain Research and Development, 31, 261-269. |
| 23 | Lu AM (1999) The Geography of Spermatophytic Families and Genera. Science Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [路安民 (1999) 种子植物科属地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 24 | Luo D, Yue JP, Sun WG, Xu B, Li ZM, Comes HP, Sun H (2016) Evolutionary history of the subnival flora of the Himalaya-Hengduan Mountains, first insights from comparative phylogeography of four perennial herbs. Journal of Biogeography, 43, 31-43. |
| 25 | Luo J, Zheng WL, Pan G, Wang JS (2006) Study on spermatophyte flora of the alpine frigid zone in Shergyla Mountain of Tibet. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 24, 215-219. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [罗建, 郑维列, 潘刚, 王景升 (2006) 色季拉山区高山寒带种子植物区系研究. 武汉植物研究, 24, 215-219.] | |
| 26 | MacArthur RH, Wilson EO(1967) The Theory of Island Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| 27 | Marshall J (1957) The Birds of the Pine-oak Woodland in Southern Arizona and Adjacent Mexico. Pacific Coast Avifauna, 32, 5-125. |
| 28 | Mary E, Diamond JM (1976) Birds on islands in the sky, origin of the montane avifauna of Northern Melanesia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 73, 1765-1769. |
| 29 | Packer JG (1974) Differentiation and dispersal in alpine floras. Arctic and Alpine Research, 6, 117-128. |
| 30 | Peng H, Liu ED (2015) Yunnan Jiaozi Snow Mountain National Nature Reserve. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [彭华, 刘恩德 (2015) 云南轿子雪山国家级自然保护区. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 31 | Qian H, Ricklefs RE (2012) Disentangling the effects of geographic distance and environmental dissimilarity on global patterns of species turnover. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 341-351. |
| 32 | Ren Y (2006) Study and Management of Biodiversity in Taibai Mountain Nature Reserve. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [任毅 (2006) 太白山自然保护区生物多样性研究与管理. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 33 | Russell GJ, Diamond JM, Reed TM, Pimm SL (2006) Breeding birds on small islands, island biogeography or optimal foraging? Journal of Animal Ecology, 75, 324-339. |
| 34 | Sandel B, Arge L, Dalsgaard B (2011) The influence of late Quaternary climate-change velocity on species endemism. Science, 334, 660-664. |
| 35 | Shen ZH, Liu ZL, Wu J (2004) Altitudinal pattern of flora on the eastern slope of Mt. Gongga. Biodiversity Science, 12, 89-98. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [沈泽昊, 刘增力, 伍杰 (2004) 贡嘎山东坡植物区系的垂直分布格局. 生物多样性, 12, 89-98.] | |
| 36 | Shen ZH, Zhang XS (2000) A quantitative analysis on the floristic elements of the Chinese subtropical region and their spatial patterns. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica, 38, 366-380. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [沈泽昊, 张新时 (2000) 中国亚热带地区植物区系地理成分及其空间格局的数量分析. 植物分类学报, 38, 366-380.] | |
| 37 | Shen ZF (1997) Biogeography of Taiwan. I. Some preliminary thinking and studies. Annuals of Taiwan Provincial Museum, 40, 361-450. |
| (in Chinese) [沈中桴 (1997) 台湾的生物地理. 1. 一些初步思考和研究. 台湾省立博物馆年刊, 40, 361-450.] | |
| 38 | Shi YF, Cui ZJ, Su Z (2006) The Quaternary Glaciations and Environmental Variations in China. Hebei Science and Technology Publishing House, Shijiazhuang. |
| (in Chinese) [施雅风, 崔之久, 苏珍 (2006) 中国第四纪冰川与环境变化.河北科学技术出版社, 石家庄.] | |
| 39 | Si X, Pimm SL, Russell GJ, Ding P (2014) Turnover of breeding bird communities on islands in an inundated lake. Journal of Biogeography, 41, 2283-2292. |
| 40 | Sun H (2002) Tethys retreat and Himalayas-Hengduanshan Mountains uplift and their significance on the origin and development of the Sino-Himalayan elements and alpine flora. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 24, 273-288. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [孙航 (2002) 古地中海退却与喜马拉雅-横断山的隆起在中国喜马拉雅成分及高山植物区系的形成与发展上的意义. 云南植物研究, 24, 273-288.] | |
| 41 | Tackenberg O, Stöcklin J (2009) Wind dispersal of alpine plant species, a comparison with lowland species. Journal of Vegetation Science, 19, 109-118. |
| 42 | Tao JR (1992) The Tertiary vegetation and flora and floristic regions in China. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica, 30, 25-43. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [陶君容 (1992) 中国第三纪植被与植物区系历史及分区. 植物分类学报, 30, 25-43.] | |
| 43 | van Zyl JJV (2001) The shuttle radar topography mission (SRTM), a breakthrough in remote sensing of topography. Acta Astronautica, 48, 559-565. |
| 44 | Wang HS (1992) Floristic Geography. Science Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [王荷生 (1992) 植物区系地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 45 | Wang J (2012) Study on the flora of spermatophyte in Xinluhai Nature Reserve of the Queer Mountain. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science, 40, 11020-11021. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [王静 (2012) 雀儿山新路海自然保护区高山种子植物区系研究. 安徽农业科学, 40, 11020-11021.] | |
| 46 | Wang LS, Jia Y, Zhang XC, Qin HN (2015) Overview of higher plant diversity in China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 217-224. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [王利松, 贾渝, 张宪春, 覃海宁 (2015) 中国高等植物多样性. 生物多样性, 23, 217-224.] | |
| 47 | Wang WC (1992) On some distribution patterns and some migration routes found in the eastern Asiatic region. Acta Phytotaxonomic Sinica, 30, 1-24; 30, 97-117. |
| (in English with Chinese abstract) [王文采 (1992) 东亚植物区系的一些分布式样和迁移路线. 植物分类学报, 30, 1-24; 30, 97-117.] | |
| 48 | Wondimu T, Gizaw A, Tusiime FM, Masao CA, Abdi AA, Gussarova G, Popp M, Nemomissa S, Brochmann C (2014) Crossing barriers in an extremely fragmented system, two case studies in the afro-alpine sky island flora. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 300, 415-430. |
| 49 | Wu ZY (1991) The areal-types of Chinese genera of seed plants. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 13(Suppl. IV), 1-139. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [吴征镒 (1991) 中国种子植物属的分布区类型. 云南植物研究, 13(增刊IV), 1-139.] | |
| 50 | Wu ZY, Sun H, Zhou ZK, Li DZ, Peng H (2010) Floristic Geography of Seed Plants in China. Science Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [吴征镒, 孙航, 周浙昆, 李德铢, 彭华 (2010) 中国种子植物区系地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 51 | Wurster CM, Bird MI (2014) Barriers and bridges, early human dispersals in equatorial SE Asia. Geology and Archaeology, Submerged Landscapes of the Continental Shelf (eds Harff J, Bailey G, Lüth F), Special Publications, pp. 411. Geological Society, London. |
| 52 | Yan YH, Zhang XC, Ma KP (2013) Pteridophytes in China: Diversity and Distribution. Science Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [严岳鸿, 张宪春, 马克平 (2013) 中国蕨类植物多样性与地理分布. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 53 | Yang QS, Liu JQ, Wang YK (2008) The Integrated Scientific Investigation Report of Gansu Qilian Mountain National Nature Reserve. Gansu Science and Technology Press, Lanzhou. |
| (in Chinese) [杨全生, 刘建泉, 汪有奎 (2008) 甘肃祁连山国家级自然保护区综合科学考察报告. 甘肃科学技术出版社, 兰州.] | |
| 54 | Ye JF, Chen ZD, Liu B, Qin HN, Yang Y (2012) Disjunct distribution of vascular plants between southwestern area and Taiwan area in China. Biodiversity Science, 20, 482-494. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [叶建飞, 陈之端, 刘冰, 覃海宁, 杨永 (2012) 中国西南与台湾地区维管植物的间断分布格局及形成机制. 生物多样性, 20, 482-494.] | |
| 55 | Ying LX, Liu H, Chiu QA, Chen TY, Chen XY, Luo SJ, Shen ZH (2016) The phylogeography of Fagus hayatae (Fagaceae) in China: genetic isolation among populations. Ecology & Evolution, 6, 2805-2816. |
| 56 | Yu HB, Zhang YL (2013) Advance in phylogeography of alpine plants in the Tibetan Plateau and adjacent region. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 33, 1268-1278. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [于海彬, 张镱锂 (2013) 青藏高原及其周边地区高山植物谱系地理学研究进展. 西北植物学报, 33, 1268-1278.] | |
| 57 | Zhang HD (1980) Origin and development of flora in China. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 1, 89-98. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [张宏达 (1980) 华夏植物区系的起源与发展. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 1, 89-98.] | |
| 58 | Zhang JQ, Meng SY, Allen GA, Wen J, Rao GY (2014) Rapid radiation and dispersal out of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau of an alpine plant lineage Rhodiola (Crassulaceae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 77, 147-158. |
| 59 | Zhang WJ, Lu QY, Liang J, Shen ZH (2010) Altitudinal gradients of species richness and range size of vascular plants in Taiwan, a test of Rapoport’s rule. Biodiversity Science, 18, 312-322. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [张婉君, 卢绮妍, 梁军, 沈泽昊 (2010) 台湾维管束植物物种丰富度和种域宽度的海拔格局及Rapoport法则检验. 生物多样性, 18, 312-322.] | |
| 60 | Zhang XS (1994) The basic ecological geographical types of altitudinal spectrum of mountain vegetation in China. In: Studies of Vegetation Ecology, Memorial of Professor Xueyu Hou, the Famous Ecologist (eds Jiang S, Chen CD), pp. 250-270. Science Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [张新时(1994) 中国山地植被垂直带的基本生态地理类型. 植被生态学研究——纪念著名生态学家侯学煜教授(姜恕, 陈昌笃主编), 250-270页, 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 61 | Zheng Z, Gong DJ, Zhang Q, Zhao HB (2014) Vertical patterns of plant species diversity in the Baishuijiang Nature Reserve, explanation of area, climate and boundary constraint. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25, 3390-3398. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [郑智, 龚大洁, 张乾, 赵海斌 (2014) 白水江自然保护区植物物种多样性的垂直格局、面积、气候、边界限制的解释. 应用生态学报, 25, 3390-3398.] | |
| 62 | Zheng Z (1999) Response of altitudinal belts of vegetation to the late Quaternary climate changes in tropic Asia. Geographic Research, 18, 96-102. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [郑卓 (1999) 亚洲热带山地植被垂直带对晚第四纪气候变化的响应. 地理研究, 18, 96-102.] | |
| 63 | Zhu H (2016) A biogeographical comparison between Yunnan, Southwest China, and Taiwan, Southeast China, with impli- cations for the evolutionary history of the East Asian Flora. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 101, 750-771. |
| [1] | 顾婧婧, 刘宜卓, 苏杨. 基层地方政府在完成《昆蒙框架》中的作用和难点: 基于《联合国气候变化框架公约》任务的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24585-. |
| [2] | 吴琪, 张晓青, 杨雨婷, 周艺博, 马毅, 许大明, 斯幸峰, 王健. 浙江钱江源-百山祖国家公园庆元片区叶附生苔多样性及其时空变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 24010-. |
| [3] | 曹可欣, 王敬雯, 郑国, 武鹏峰, 李英滨, 崔淑艳. 降水格局改变及氮沉降对北方典型草原土壤线虫多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [4] | 杜聪聪, 冯学宇, 陈志林. 桥头堡效应中气候生态位差异的缩小促进了红火蚁的入侵[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24276-. |
| [5] | 原雪姣, 张渊媛, 张衍亮, 胡璐祎, 桑卫国, 杨峥, 陈颀. 基于飞机草历史分布数据拟合的物种分布模型及其预测能力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24288-. |
| [6] | 冯莉. 国际法视野下生物多样性和气候变化的协同治理[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23110-. |
| [7] | 魏庐潞, 徐婷婷, 李媛媛, 艾喆, 马飞. 同质园环境和遗传分化影响锦鸡儿属植物根际土壤固氮菌多样性和群落结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22477-. |
| [8] | 丁炳扬, 金孝锋, 张永华, 李根有, 陈征海, 张方钢. 浙江野生种子植物的分布格局与区系分区[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22515-. |
| [9] | 姚雪, 陈星, 戴尊, 宋坤, 邢诗晨, 曹宏彧, 邹璐, 王健. 采集策略对叶附生苔类植物发现概率及物种多样性的重要性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22685-. |
| [10] | 邵雯雯, 范国祯, 何知舟, 宋志平. 多地同质园实验揭示普通野生稻的表型可塑性与本地适应性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22311-. |
| [11] | 桑佳文, 宋创业, 贾宁霞, 贾元, 刘长成, 乔鲜果, 张琳, 袁伟影, 吴冬秀, 李凌浩, 郭柯. 青藏高原植被调查与制图评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22430-. |
| [12] | 王金洲, 徐靖. “基于自然的解决方案”应对生物多样性丧失和气候变化: 进展、挑战和建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22496-. |
| [13] | 朱华. 地质事件和季风气候影响了云南植物区系和植被的演化[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23262-. |
| [14] | 王晓凤, 饶杰生, 杨涛, 刘文聪, 田希, 陈稀, 刘其明, 徐衍潇, 张秋雨, 张洪强, 张旭, 欧晓昆, 沈泽昊. 云南鸡足山半湿润常绿阔叶林群落木本植物多样性格局与环境解释[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23217-. |
| [15] | 王晓凤, 米湘成, 王希华, 江明喜, 杨涛, 张健, 沈泽昊. 中国中亚热带常绿阔叶林群落木本植物多样性比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23296-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn