



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 22685. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022685 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022685
姚雪1, 陈星1, 戴尊1, 宋坤2,*( ), 邢诗晨1, 曹宏彧1, 邹璐1, 王健1,3,*(
), 邢诗晨1, 曹宏彧1, 邹璐1, 王健1,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-17
接受日期:2023-03-24
出版日期:2023-04-20
发布日期:2023-04-20
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 基金资助:
Xue Yao1, Xing Chen1, Zun Dai1, Kun Song2,*( ), Shichen Xing1, Hongyu Cao1, Lu Zou1, Jian Wang1,3,*(
), Shichen Xing1, Hongyu Cao1, Lu Zou1, Jian Wang1,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-12-17
Accepted:2023-03-24
Online:2023-04-20
Published:2023-04-20
Contact:
*E-mail: 摘要:
叶附生苔类植物主要生长在热带和亚热带常绿阔叶林维管植物叶片的表面, 是苔藓植物中较为复杂的一个类群, 特殊的生理生态特性使其在成为气候变化指示类群方面的潜力很大。为了探究采集者的经验及采样强度是否显著影响叶附生苔的发现概率及物种多样性, 本研究在乌岩岭国家级自然保护区对叶附生苔开展了系统的采集和比较研究, 以期为我国其他地区开展叶附生苔类植物的调查和研究提供经验和方法支持。通过4位具有不同采集经验的采集者在规定的时间(每人每次30 min)和区域(铁炉基至黄家岱)内对叶附生苔进行3次重复采集, 分析不同采集者所采集到的含有叶附生苔的叶片数及所获得的物种多样性之间的差异。结果显示, 4位采集者共采集叶附生苔类植物5科11属36种, 并新增1种首次发现附生于叶片的种类(南溪苔Makinoa crispata)。采集者经验对叶附生苔的发现概率影响不显著, 但对叶附生苔的物种多样性, 尤其是一般种和优势种的多样性具有显著影响, 推测这一差异主要是由采集者不同的采集策略所导致。同时, 本研究结果还表明, 叶附生苔的物种多样性随着采样强度的增加而增加, 4位采集者共同参与的采样结果体现出较高的采样充分性。本研究结果表明即使针对叶附生苔类植物这一类常被认为采集和鉴定非常困难的类群, 如加以必要的采集前的经验培训, 即使是非专业的采集人员也足以开展针对叶附生苔类植物的调查。
姚雪, 陈星, 戴尊, 宋坤, 邢诗晨, 曹宏彧, 邹璐, 王健 (2023) 采集策略对叶附生苔类植物发现概率及物种多样性的重要性. 生物多样性, 31, 22685. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022685.
Xue Yao, Xing Chen, Zun Dai, Kun Song, Shichen Xing, Hongyu Cao, Lu Zou, Jian Wang (2023) Importance of collection strategy on detection probability and species diversity of epiphyllous liverworts. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22685. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022685.
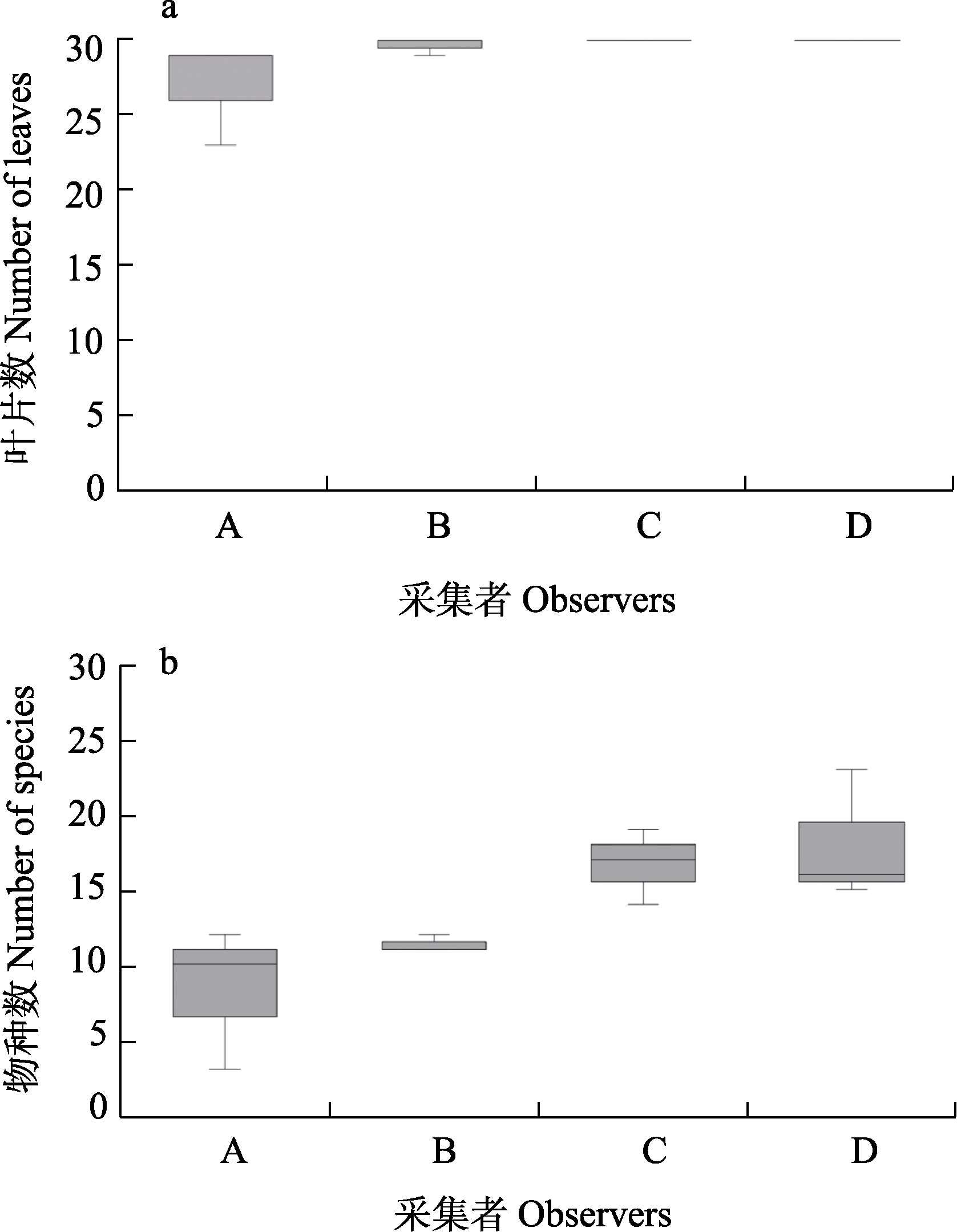
图2 4位采集者所采集的长有叶附生苔类植物的叶片数(a)和采集到的物种数(b)箱型图(箱中实线表示中值, A、B、C、D表示采集经验丰富程度由弱到强)
Fig. 2 Box plot of the number of leaves (a) and species (b) of epiphyllous liverworts collected by four observers (solid line in the box shows the median value, A, B, C, and D indicate the degree of collection experience from weak to strong)
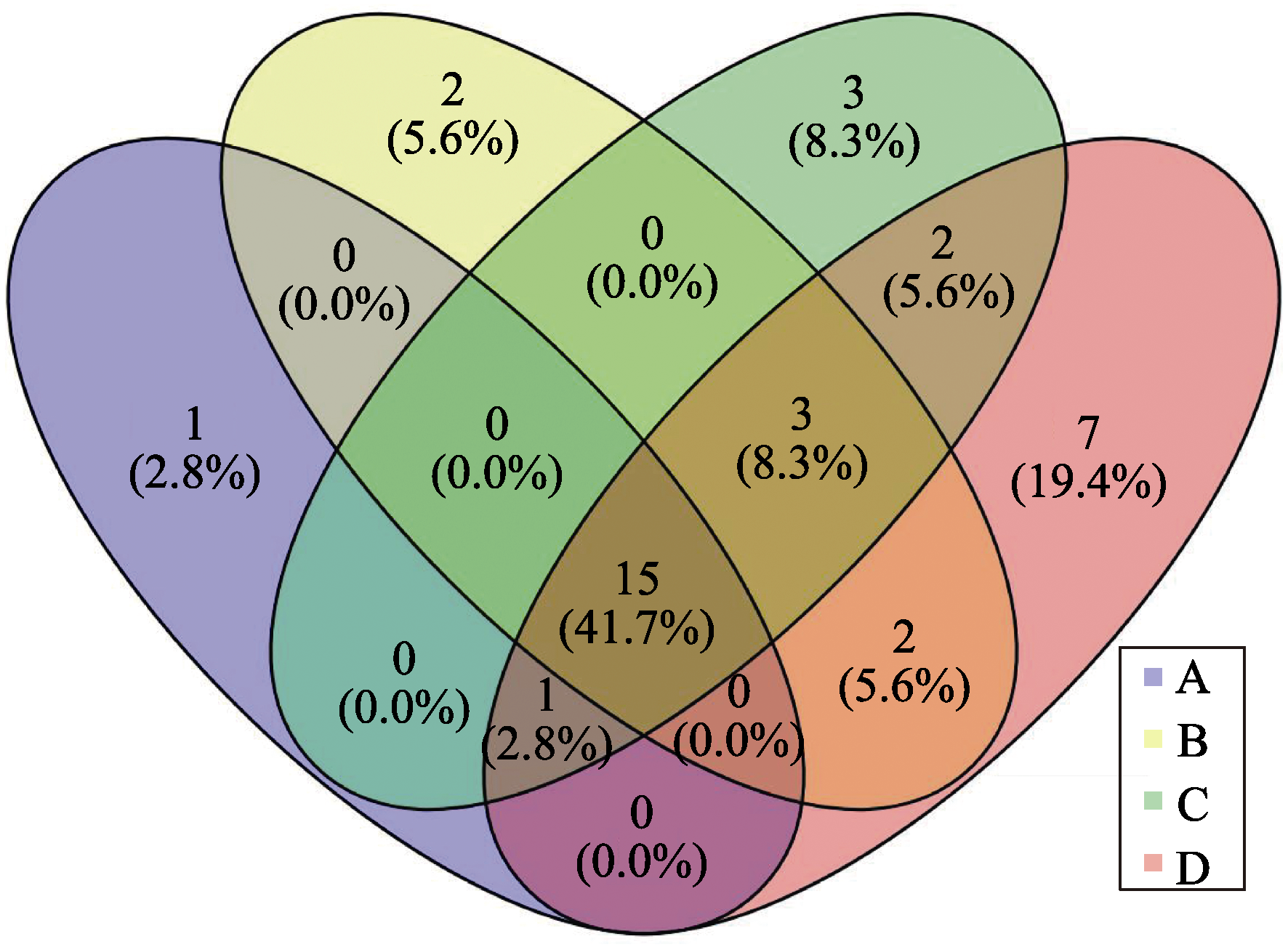
图3 4位采集者采集到的叶附生苔类植物种类的Venn图(A、B、C、D表示采集经验丰富程度由弱到强)
Fig. 3 Venn diagram of collected epiphyllous liverworts among four observers (A, B, C, and D indicate the degree of collection experience from weak to strong)
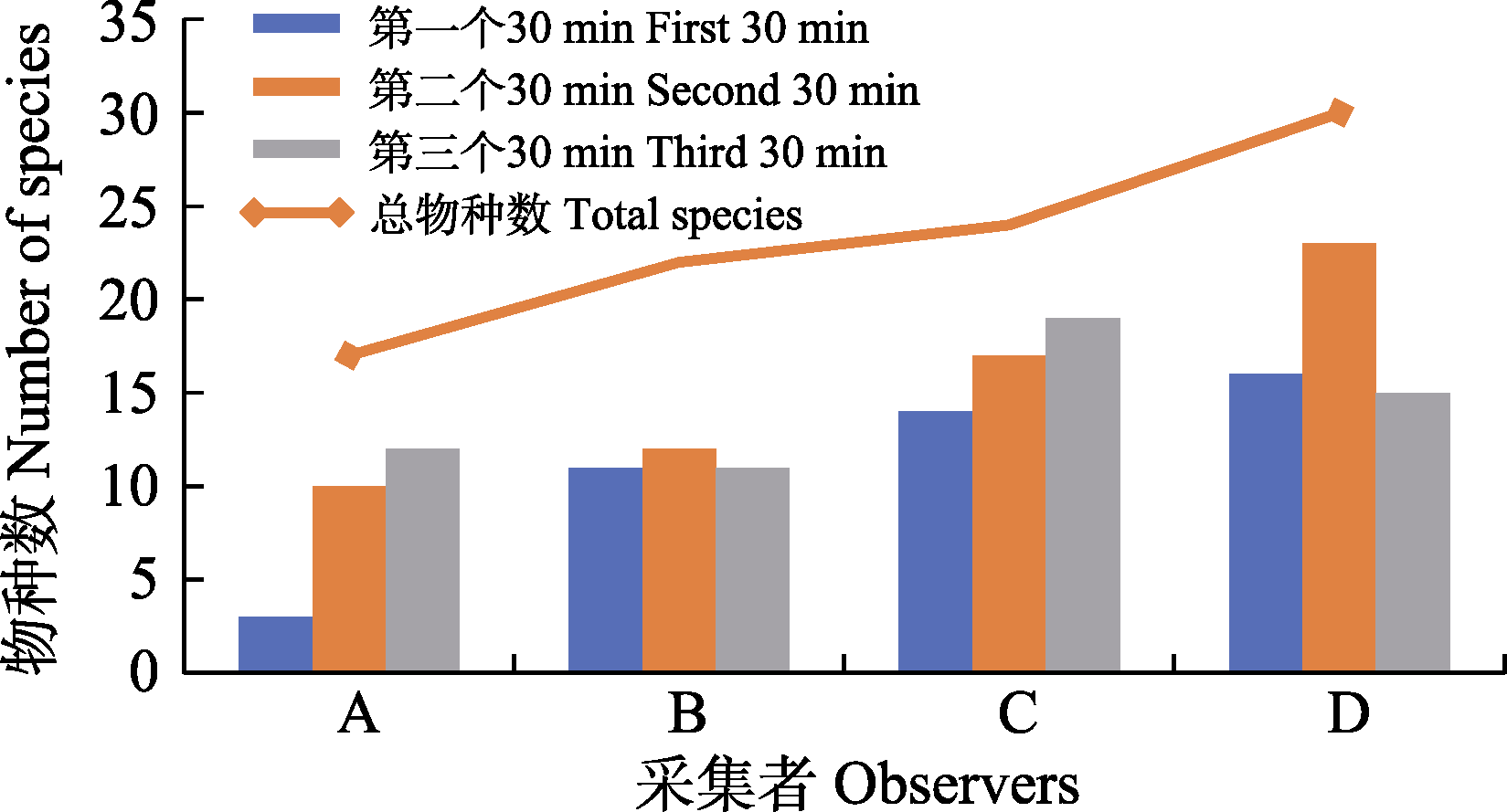
图4 4位采集者3次分别采集到的物种数(A、B、C、D表示采集经验丰富程度由弱到强)
Fig. 4 Species number of epiphyllous liverworts collected by four observers in three sampling efforts (A, B, C, and D indicate the degree of collection experience from weak to strong)
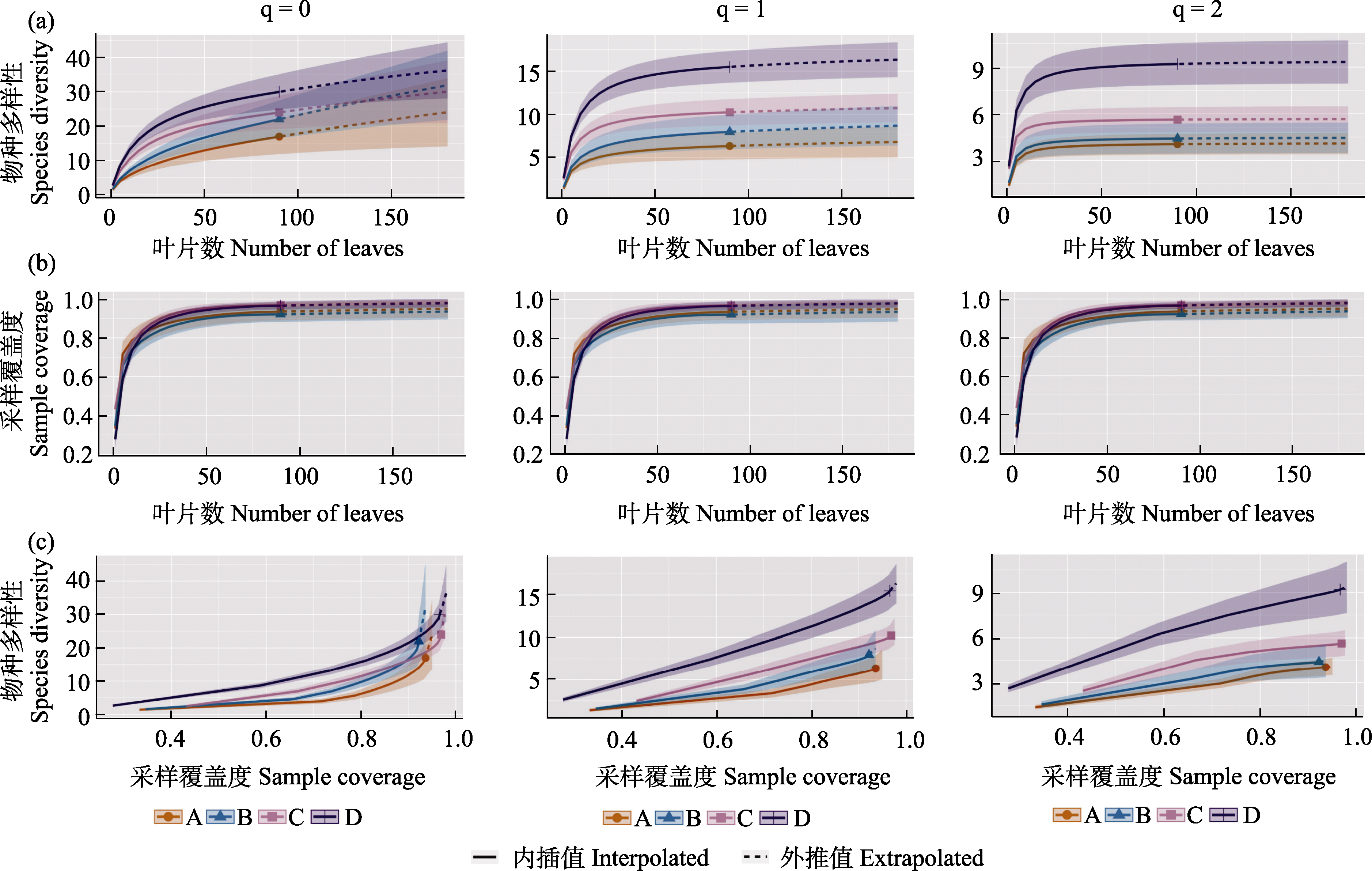
图5 基于叶片数(a)和采样覆盖度(b)的不同位阶下各采集者叶附生苔多样性内插和外推采样曲线、采样充分性曲线(c) (A、B、C、D表示采集经验丰富程度由弱到强)
Fig. 5 The species richness interpolation and extrapolation sampling curve and sampling adequacy curve (c) of epiphyllous liverworts collected by each observer based on the number of leaves (a) and sampling coverage (b) at different rank (A, B, C, and D indicate the degree of collection experience from weak to strong)
| [1] |
Alexander HM, Reed AW, Kettle WD, Slade NA, Bodbyl Roels SA, Collins CD, Salisbury V (2012) Detection and plant monitoring programs: Lessons from an intensive survey of Asclepias meadii with five observers. PLoS ONE, 7, e52762.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Archaux F, Gosselin F, Bergès L, Chevalier R (2006) Effects of sampling time, species richness and observer on the exhaustiveness of plant censuses. Journal of Vegetation Science, 17, 299-306.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Berdugo M, Kéfi S, Soliveres S, Maestre FT (2018) Plant spatial patterns identify alternative ecosystem multifunctionality states in global drylands. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2, 574-576. |
| [4] |
Burnham KP, Overton WS (1978) Estimation of the size of a closed population when capture probabilities vary among animals. Biometrika, 65, 625-633.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Burnham KP, Overton WS (1979) Robust estimation of population size when capture probabilities vary among animals. Ecology, 60, 927-936.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Chao A, Kubota Y, Zelený D, Chiu CH, Li CF, Kusumoto B, Yasuhara M, Thorn S, Wei CL, Costello MJ, Colwell RK (2020) Quantifying sample completeness and comparing diversities among assemblages. Ecological Research, 35, 292-314.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Chen PC, Wu PC (1964) Study on epiphyllous liverworts of China (I). Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica, 9, 213-276. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈邦杰, 吴鹏程 (1964) 中国叶附生苔类植物的研究(一). 植物分类学报, 9, 213-276.] | |
| [8] |
Chen GK, Kéry M, Zhang JL, Ma KP (2009) Factors affecting detection probability in plant distribution studies. Journal of Ecology, 97, 1383-1389.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Chen GK, Kéry M, Plattner M, Ma KP, Gardner B (2013) Imperfect detection is the rule rather than the exception in plant distribution studies. Journal of Ecology, 101,183-191.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Colwell RK (2013) EstimateS: Statistical Estimation of Species Richness and Shared Species from samples. http://viceroy.eeb.uconn.edu/estimates. (accessed on 2021-04-25) |
| [11] |
Dai Z, Chen X, Zhang JH, Zhu MJ, Song K, Xing SC, Tu SW, Zou L, Lei ZP, Li HQ, Wang J (2022) Species diversity of epiphyllous liverworts and host plants in the Wuyanling National Nature Reserve, Zhejiang Province. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21229. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 戴尊, 陈星, 张建行, 朱毛洁, 宋坤, 邢诗晨, 涂淑雯, 邹璐, 雷祖培, 李宏庆, 王健 (2022) 浙江乌岩岭国家级自然保护区叶附生苔类及附主植物多样性. 生物多样性, 30, 21229.]
DOI |
|
| [12] | Du XM, Zheng G, Fang YW, Ji MC (2020) Description on epiphyllous liverworts from Hangzhou West Lake Scenic Area. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences), 46, 484-488. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杜晓孟, 郑钢, 方逸文, 季梦成 (2020) 杭州西湖风景名胜区叶附生苔类植物记述. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 46, 484-488.] | |
| [13] | Gao Q, Cao T (2000) Flora of Yunnan, Vol. 17. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 高谦, 曹同 (2000) 云南植物志(第十七卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [14] |
Gignac LD (2001) Bryophytes as indicators of climate change. The Bryologist, 104, 410-420.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Gradstein SR (1997) The taxonomic diversity of epiphyllous bryophytes. Abstracta Botanica, 21, 15-19. |
| [16] | Gradstein SR, Hietz P, Lücking R, Luecking A, Sipman HJM, Vester H, Wolf JHD, Gardette E (1996) How to sample the epiphytic diversity of tropical rain forests. Ecotropica, 2, 59-72. |
| [17] |
Hill MO (1973) Diversity and evenness: A unifying notation and its consequences. Ecology, 54, 427-432.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Jiang YB, Shao XM (2016) Diversity and distribution pattern of epiphyllous liverworts and its ecological determinants. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 40, 523-532. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 姜炎彬, 邵小明 (2016) 叶附生苔植物物种多样性分布格局及生态成因. 植物生态学报, 40, 523-532.]
DOI |
|
| [19] |
Jiang YB, Wang TJ, Wu YP, Hu RG, Huang K, Shao XM (2018) Past distribution of epiphyllous liverworts in China: The usability of historical data. Ecology and Evolution, 8, 7436-7450.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Nichols JD, Hines JE, Sauer JR, Fallon FW, Fallon JE, Heglund PJ (2000) A double-observer approach for estimating detection probability and abundance from point counts. The Auk, 117, 393-408.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Nilsson IN, Nilsson SG (1985) Experimental estimates of census efficiency and pseudoturnover on islands: Error trend and between-observer variation when recording vascular plants. Journal of Ecology, 73, 65-70.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Patiño J, Vanderpoorten A (2018) Bryophyte biogeography. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 37, 175-209.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Patiño J, Bisang I, Goffinet B, Hedenäs L, McDaniel S, Pressel S, Stech M, Ah-Peng C, Bergamini A, Caners RT, Cargill DC, Cronberg N, Duckett J, Eppley S, Fenton NJ, Fisher K, González-Mancebo J, Hasebe M, Heinrichs J, Hylander K, Ignatov MS, Martínez-Abaigar J, Medina NG, Medina R, Quandt D, Rensing SA, Renzaglia K, Renner M, Ros RM, Schäfer-Verwimp A, Villarreal JC, Vanderpoorten A (2022) Unveiling the nature of a miniature world: A horizon scan of fundamental questions in bryology. Journal of Bryology, 44, 1-34.
DOI URL |
| [24] | R Core Team (2019) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. https://www.r-project.org/. (accessed on 2020-09-01) |
| [25] |
Scott A, Hallam CJ (2003) Assessing species misidentification rates through quality assurance of vegetation monitoring. Plant Ecology, 165, 101-115.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Shu L (2016) Phylogeny and Taxonomy of Leptolejeunea (Lejeuneaceae, Marchantiophyta). PhD dissertation, East China Normal University, Shanghai. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 舒蕾 (2016) 薄鳞苔属(Leptolejeunea)的系统发育和分类研究. 博士学位论文, 华东师范大学, 上海.] | |
| [27] |
Tang X, Gradstein SR, Sun LW, Zhu MJ, Shi RP, Wei QQ, Chen YQ, Zhou XX, Wang J (2018) A contribution to the knowledge of epiphyllous bryophytes in Tianmushan National Nature Reserve (Zhejiang, China), with remarks on climate warming and nature conservation. Lindbergia, 41, 01103.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Toyota M, Koyama H, Asakawa Y (1997) Volatile components of the liverworts Archilejeunea olivacea, Cheilolejeunea imbricata and Leptolejeunea elliptica. Phytochemistry, 44, 1261-1264.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Wang J (2010) Taxonomic Studies on Chinese Lejeuneaceae. PhD dissertation, East China Normal University, Shanghai. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王健 (2010) 中国细鳞苔科植物的分类学研究. 博士学位论文, 华东师范大学, 上海.] | |
| [30] | Wang LS, Jia Y, Zhang XC, Qin HN (2018) Species Catalogue of China (Vol.1) Plants: A Synoptic Checklist (I). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王利松, 贾渝, 张宪春, 覃海宁 (2018) 中国生物物种名录(第一卷)•植物•总名录(上册). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [31] |
Yang WJ, Ma KP, Kreft H (2013) Geographical sampling bias in a large distributional database and its effects on species richness-environment models. Journal of Biogeography, 40, 1415-1426.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Yu Y, Heinrichs J, Zhu RL, Schneider H (2013) Empirical evidence supporting frequent cryptic speciation in epiphyllous liverworts: A case study of the Cololejeunea lanciloba complex. PLoS ONE, 8, e84124.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Zhang J, Nielsen SE, Grainger TN, Kohler M, Chipchar T, Farr DR (2014) Sampling plant diversity and rarity at landscape scales: Importance of sampling time in species detectability. PLoS ONE, 9, e95334.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Zhong L, Zhang YJH, Lu P, Gu XP, Lei ZP, Cai YB, Zheng FD, Sun IF, Yu MJ (2015) Community structure and species composition of the secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest: The analyses for a 9 ha forest dynamics plot in Wuyanling Nature Reserve, Zhejiang Province, East China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 619-629. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 仲磊, 张杨家豪, 卢品, 顾雪萍, 雷祖培, 蔡延奔, 郑方东, 孙义方, 于明坚 (2015) 次生常绿阔叶林的群落结构与物种组成: 基于浙江乌岩岭9 ha森林动态样地. 生物多样性, 23, 619-629.]
DOI |
|
| [35] | Zhu RL (1990) The bryoflora of Wuyanling Nature Reserve in Zhejiang Province, China. Acta Bryolichenologica Asiatica, 2, 25-32. |
| [36] | Zhu RL, Hu RL (1991) A study on the epiphyllous liverworts from Wuyanling of Zhejiang Province. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), (3), 98-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱瑞良, 胡人亮 (1991) 浙江乌岩岭叶附生苔类植物的研究. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (3), 98-103.] | |
| [37] |
Zhu RL, Ma XY, Cao C, Cao ZY (2022) Advances in research on bryophyte diversity in China. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22378. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 朱瑞良, 马晓英, 曹畅, 曹子寅 (2022) 中国苔藓植物多样性研究进展. 生物多样性, 30, 22378.]
DOI |
|
| [38] | Zhu RL, So ML (2001) Epiphyllous Liverworts of China. Nova Hedwigia Beiheft, Berlin. |
| [39] | Zhu RL, So ML, Ye LX (1998) A synopsis of the hepatic flora of Zhejiang, China. Journal of the Hattori Botanical Laboratory, 84, 159-174. |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 顾婧婧, 刘宜卓, 苏杨. 基层地方政府在完成《昆蒙框架》中的作用和难点: 基于《联合国气候变化框架公约》任务的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24585-. |
| [5] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [6] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [7] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [8] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [9] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [10] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [11] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [12] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [13] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [14] | 邝起宇, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [15] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()