



生物多样性 ›› 2012, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (6): 693-702. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.10062 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2012.10062
向妮1,2, 肖炎农2, 段灿星1, 王晓鸣1, 朱振东1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2012-03-02
接受日期:2012-07-16
出版日期:2012-11-20
发布日期:2013-01-04
通讯作者:
朱振东
作者简介:* E-mail: zhuzd115@caas.net.cn基金资助:
Ni Xiang1,2, Yannong Xiao2, Canxing Duan1, Xiaoming Wang1, Zhendong Zhu1,*( )
)
Received:2012-03-02
Accepted:2012-07-16
Online:2012-11-20
Published:2013-01-04
Contact:
Zhendong Zhu
摘要:
由茄镰孢豌豆专化型(Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi, Fsp)引起的根腐病是豌豆(Pisum sativum)最重要的病害之一。研究不同地理来源Fsp的遗传多样性, 对了解该菌的遗传背景及防治病害具有重要意义。本研究从血红丛赤壳交配群VI(Nectria haematococca MPVI)全基因组序列中筛选SSR位点, 选取107个SSR位点设计引物, 获得24对多态性引物。用24对多态性引物对不同地理来源的96个Fsp分离物进行遗传多样性分析, 结果表明, 24对引物共扩增出132个等位基因, 变异范围为3-15, 平均为5.5。基因多样性指数范围为0.4855-0.8264, 平均为0.7038。供试的96个Fsp分离物可分为93个基因型。聚类分析表明, 在相似性系数为0.8时, 96个Fsp分离物被划分为10个组群。Fsp分离物的地理来源或致病性与SSR聚类结果无关。分子方差分析(AMOVA)结果表明, Fsp遗传变异主要存在于群体内, 地理条件和生态区环境对Fsp遗传分化有显著影响。
向妮, 肖炎农, 段灿星, 王晓鸣, 朱振东 (2012) 利用SSR标记分析茄镰孢豌豆专化型的遗传多样性. 生物多样性, 20, 693-702. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.10062.
Ni Xiang, Yannong Xiao, Canxing Duan, Xiaoming Wang, Zhendong Zhu (2012) Genetic diversity in Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi based on SSR markers. Biodiversity Science, 20, 693-702. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.10062.
| 来源 Location | 数量 Amount | 分离物 Isolates |
|---|---|---|
| 安徽 Anhui | 17 | AH-1a、AH-2、AH-3、AH-4、AH-5、AH-6、AH-7、AH-8、AH-9、AH-10、AH-11、AH-12、AH-13、AH-14b、AH-15a、AH-16、AH-17 |
| 北京 Beijing | 13 | BJ-1、BJ-2、BJ-3、BJ-4、BJ-5、BJ-6、BJ-7、BJ-8、BJ-9、BJ-10、BJ-11、BJ-12、BJ-13 |
| 福建 Fujian | 4 | FJ-1b、FJ-2a、FJ-3b、FJ-4a |
| 甘肃 Gansu | 20 | LZ-1、LZ-2、LZ-3b、LZ-4、LZ-5、LZ-6、DX-1、DX-2、DX-3、DX-4a、DX-5、DX-6、DX-7、DX-8、DX-9、DX-10、DX-11、DX-12、DX-13、DX-14 |
| 河北 Hebei | 10 | ZB-1、ZB-2、ZB-3、ZB-4、ZB-5、ZB-6、ZB-7、ZB-8、ZB-9、ZB-10 |
| 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 7 | NM-1、NM-2、NM-3、NM-4b、NM-5、NM-6b、NM-7 |
| 吉林 Jilin | 1 | BC-1a |
| 宁夏 Ningxia | 12 | SB-1、SB-2、SB-3、SB-4、SB-5、SB-6、SB-7、SB-8、XB-1、XB-2、PC-1、PC-2 |
| 青海 Qinghai | 5 | QH-1、QH-2、QH-3b、QH-4b、QH-5b |
| 四川 Sichuan | 3 | SC-1、SC-2、SC-3 |
| 云南 Yunnan | 4 | YN-1a、YN-2a、YN-3、YN-4 |
表1 用于本研究的96个茄镰孢豌豆专化型分离物
Table 1 Ninety-six isolates of Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi used in this study
| 来源 Location | 数量 Amount | 分离物 Isolates |
|---|---|---|
| 安徽 Anhui | 17 | AH-1a、AH-2、AH-3、AH-4、AH-5、AH-6、AH-7、AH-8、AH-9、AH-10、AH-11、AH-12、AH-13、AH-14b、AH-15a、AH-16、AH-17 |
| 北京 Beijing | 13 | BJ-1、BJ-2、BJ-3、BJ-4、BJ-5、BJ-6、BJ-7、BJ-8、BJ-9、BJ-10、BJ-11、BJ-12、BJ-13 |
| 福建 Fujian | 4 | FJ-1b、FJ-2a、FJ-3b、FJ-4a |
| 甘肃 Gansu | 20 | LZ-1、LZ-2、LZ-3b、LZ-4、LZ-5、LZ-6、DX-1、DX-2、DX-3、DX-4a、DX-5、DX-6、DX-7、DX-8、DX-9、DX-10、DX-11、DX-12、DX-13、DX-14 |
| 河北 Hebei | 10 | ZB-1、ZB-2、ZB-3、ZB-4、ZB-5、ZB-6、ZB-7、ZB-8、ZB-9、ZB-10 |
| 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 7 | NM-1、NM-2、NM-3、NM-4b、NM-5、NM-6b、NM-7 |
| 吉林 Jilin | 1 | BC-1a |
| 宁夏 Ningxia | 12 | SB-1、SB-2、SB-3、SB-4、SB-5、SB-6、SB-7、SB-8、XB-1、XB-2、PC-1、PC-2 |
| 青海 Qinghai | 5 | QH-1、QH-2、QH-3b、QH-4b、QH-5b |
| 四川 Sichuan | 3 | SC-1、SC-2、SC-3 |
| 云南 Yunnan | 4 | YN-1a、YN-2a、YN-3、YN-4 |
| 位点a Locusa | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5'-3') | 重复基元 Repeat motif | 基因组位置b Location in the genome b | 期望大小 Expected size (bp) | 片段大小 Allele size range (bp) | 退火温度 Annealing tem- perature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fsp1.7 | F: TGTTCCCATAGTCCGATTCCG | (AC)17 | Contig 1: 3457867-3458072 | 206 | 180-220 | 54 |
| R: GCCGCTTGACTTGCTAACCA | ||||||
| Fsp1.10 | F: CGATTCGTTCTTCCCAACACC | (TCT)14 | Contig 1/: 709046-709225 | 180 | 147-242 | 54 |
| R: AAACCTGCCTCAAGCCCTGA | ||||||
| Fsp1.17 | F: AATCCCATTGTTTCGGTGCG | (GT)21 | Contig 1/: 245108-245324 | 217 | 165-217 | 54 |
| R: CCGTTGAGGAATAGAGAGGCA | ||||||
| Fsp2.2 | F: GCTTTGGGTCCAGGTATTACG | (AC)11 | Contig 15/: 2408632-2409004 | 373 | 600-622 | 54 |
| R: TTCTCTCTCTCCCGTCACCA | ||||||
| Fsp2.3 | F: TGCTCCTACACCTCCGTCTC | (TG)12 | Contig 15: 1878221-1878425 | 205 | 160-209 | 54 |
| R: CACGTTTTATCTGCCTTGCTG | ||||||
| Fsp2.4 | F: GATGATTGTGCTGGTAGCCTG | (TTTC)8 | Contig 15: 802092-802323 | 232 | 195-238 | 54 |
| R: CGCTTGACGCCATAATTGAG | ||||||
| Fsp3.1 | F: AACAAGGAGGGTGACGGGAT | (AC)13 | Contig 2/: 1062296-1062559 | 264 | 210-290 | 54 |
| R: AGTGACAAATAGGGAGGTGGG | ||||||
| Fsp3.6 | F: CTTGCCCAAACGCATTGAAG | (TG)16 | Contig 2/: 2066491-2066782 | 292 | 260-320 | 54 |
| R: ACTAACACACACCCAGCCTC | ||||||
| Fsp3.7 | F: CCATTTCCATTCCACCTCACC | (AGC)9 | Contig 2/: 1170545-1170752 | 208 | 180-217 | 52 |
| R: CAGTCTGCTGTTATGAAGGGC | ||||||
| Fsp4.2 | F: TTGACCTCTGCACACCATCAG | (AC)15 | Contig 3/: 2330520-2330703 | 184 | 160-200 | 54 |
| R: CTCACTCTCGGCTCTCGTTAT | ||||||
| Fsp4.4 | F: CGGTCACAGGCAAAGCAAT | (TG)15 | Contig 3/: 2288923-2289149 | 227 | 190-250 | 54 |
| R: GGGATAGAGCAAGCAGCGTT | ||||||
| Fsp4.7 | F: ACACACACACAGGCACAAG | (AC)10 | Contig 4/: 1510008-1510245 | 238 | 201-260 | 54 |
| R: TGAGTAAGGTAGGCTGGGTCT | ||||||
| Fsp5.3 | F: TACACTCCCGTTCCTGGCTA | (TC)15 | Contig 4/: 161679-161833 | 155 | 90-147 | 54 |
| R: CCAAATCTCAACCGTCGTGG | ||||||
| Fsp5.4 | F: TGAATCTGACTGTGGCTGGAG | (TG)11 | Contig 4/: 330399-330579 | 181 | 160-210 | 54 |
| R: ATGGTTCGCCTTGGCTCTGA | ||||||
| Fsp5.8 | F: CAGTTAGGTTCCACTCCAGGT | (ACT)14 | Contig 4/: 216245-216574 | 330 | 260-375 | 54 |
| R: TGGGCGGTCATTGTGTAGGT | ||||||
| Fsp6.3 | F: AGCACGAGGAACGAGTCTA | (AC)15 | Contig 18/: 1864740-1864874 | 135 | 110-150 | 52 |
| R: CGCTACTTGTTTGTGTCCG | ||||||
| Fsp6.7 | F: TGACCGAGAACTGAAGCCA | (TTC)9 | Contig 18/: 2280272-2280530 | 259 | 250-350 | 52 |
| R: GACGACGAAACCTTTGAAGAG | ||||||
| Fsp7.3 | F: CTCTCATTATGTAGCGACGAC | (TCG)10 | Contig 7/: 808299-808470 | 173 | 150-250 | 52 |
| R: TCGATACCCCTGAGTTCTGTG | ||||||
| Fsp9.6 | F: GCATCCAATGTCTTTCCCAAT | (TG)17 | Contig 5/: 189772--190021 | 250 | 230-275 | 52 |
| R: GACTCGATATTCATCAACACCA | ||||||
| Fsp9.8 | F: TTGGTTTCCCTGCCTTGT | (TG)20 | Contig 5/: 1802083-1802348 | 266 | 240-300 | 52 |
| R: TGTTGGGTCATCTTGGTTTC | ||||||
| Fsp9.9 | F: ACGCCACTCTTCCATACTCAG | (AAC)15 | Contig 5/: 764399-764632 | 234 | 200-280 | 54 |
| R: GTTGACGGTCTTGTGGCATAC | ||||||
| Fsp9.10 | F: TCAACAACACCAACCACCTG | (AGC)9 | Contig 5/: 509965-510211 | 247 | 200-300 | 54 |
| R: TTCGTCCGAGTCGCCTTCTA | ||||||
| Fsp9.15 | F: GCTTGTGCTGGAGTTGACCT | (GAAT)8 | Contig 5/: 168328-168492 | 165 | 123-155 | 52 |
| R: CAGGAGCATAGGAGGAATAC | ||||||
| Fsp10.2 | F: CGAGAAAGGTGAGGAAGGGA | (GGA)8 | Contig 11/: 258852-259033 | 182 | 175-200 | 52 |
| R: TATCTGTGAGGTGTGGCGA |
表2 24个茄镰孢豌豆专化型多态性SSR位点
Table 2 Twenty-four polymorphic SSR loci in Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi isolates
| 位点a Locusa | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5'-3') | 重复基元 Repeat motif | 基因组位置b Location in the genome b | 期望大小 Expected size (bp) | 片段大小 Allele size range (bp) | 退火温度 Annealing tem- perature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fsp1.7 | F: TGTTCCCATAGTCCGATTCCG | (AC)17 | Contig 1: 3457867-3458072 | 206 | 180-220 | 54 |
| R: GCCGCTTGACTTGCTAACCA | ||||||
| Fsp1.10 | F: CGATTCGTTCTTCCCAACACC | (TCT)14 | Contig 1/: 709046-709225 | 180 | 147-242 | 54 |
| R: AAACCTGCCTCAAGCCCTGA | ||||||
| Fsp1.17 | F: AATCCCATTGTTTCGGTGCG | (GT)21 | Contig 1/: 245108-245324 | 217 | 165-217 | 54 |
| R: CCGTTGAGGAATAGAGAGGCA | ||||||
| Fsp2.2 | F: GCTTTGGGTCCAGGTATTACG | (AC)11 | Contig 15/: 2408632-2409004 | 373 | 600-622 | 54 |
| R: TTCTCTCTCTCCCGTCACCA | ||||||
| Fsp2.3 | F: TGCTCCTACACCTCCGTCTC | (TG)12 | Contig 15: 1878221-1878425 | 205 | 160-209 | 54 |
| R: CACGTTTTATCTGCCTTGCTG | ||||||
| Fsp2.4 | F: GATGATTGTGCTGGTAGCCTG | (TTTC)8 | Contig 15: 802092-802323 | 232 | 195-238 | 54 |
| R: CGCTTGACGCCATAATTGAG | ||||||
| Fsp3.1 | F: AACAAGGAGGGTGACGGGAT | (AC)13 | Contig 2/: 1062296-1062559 | 264 | 210-290 | 54 |
| R: AGTGACAAATAGGGAGGTGGG | ||||||
| Fsp3.6 | F: CTTGCCCAAACGCATTGAAG | (TG)16 | Contig 2/: 2066491-2066782 | 292 | 260-320 | 54 |
| R: ACTAACACACACCCAGCCTC | ||||||
| Fsp3.7 | F: CCATTTCCATTCCACCTCACC | (AGC)9 | Contig 2/: 1170545-1170752 | 208 | 180-217 | 52 |
| R: CAGTCTGCTGTTATGAAGGGC | ||||||
| Fsp4.2 | F: TTGACCTCTGCACACCATCAG | (AC)15 | Contig 3/: 2330520-2330703 | 184 | 160-200 | 54 |
| R: CTCACTCTCGGCTCTCGTTAT | ||||||
| Fsp4.4 | F: CGGTCACAGGCAAAGCAAT | (TG)15 | Contig 3/: 2288923-2289149 | 227 | 190-250 | 54 |
| R: GGGATAGAGCAAGCAGCGTT | ||||||
| Fsp4.7 | F: ACACACACACAGGCACAAG | (AC)10 | Contig 4/: 1510008-1510245 | 238 | 201-260 | 54 |
| R: TGAGTAAGGTAGGCTGGGTCT | ||||||
| Fsp5.3 | F: TACACTCCCGTTCCTGGCTA | (TC)15 | Contig 4/: 161679-161833 | 155 | 90-147 | 54 |
| R: CCAAATCTCAACCGTCGTGG | ||||||
| Fsp5.4 | F: TGAATCTGACTGTGGCTGGAG | (TG)11 | Contig 4/: 330399-330579 | 181 | 160-210 | 54 |
| R: ATGGTTCGCCTTGGCTCTGA | ||||||
| Fsp5.8 | F: CAGTTAGGTTCCACTCCAGGT | (ACT)14 | Contig 4/: 216245-216574 | 330 | 260-375 | 54 |
| R: TGGGCGGTCATTGTGTAGGT | ||||||
| Fsp6.3 | F: AGCACGAGGAACGAGTCTA | (AC)15 | Contig 18/: 1864740-1864874 | 135 | 110-150 | 52 |
| R: CGCTACTTGTTTGTGTCCG | ||||||
| Fsp6.7 | F: TGACCGAGAACTGAAGCCA | (TTC)9 | Contig 18/: 2280272-2280530 | 259 | 250-350 | 52 |
| R: GACGACGAAACCTTTGAAGAG | ||||||
| Fsp7.3 | F: CTCTCATTATGTAGCGACGAC | (TCG)10 | Contig 7/: 808299-808470 | 173 | 150-250 | 52 |
| R: TCGATACCCCTGAGTTCTGTG | ||||||
| Fsp9.6 | F: GCATCCAATGTCTTTCCCAAT | (TG)17 | Contig 5/: 189772--190021 | 250 | 230-275 | 52 |
| R: GACTCGATATTCATCAACACCA | ||||||
| Fsp9.8 | F: TTGGTTTCCCTGCCTTGT | (TG)20 | Contig 5/: 1802083-1802348 | 266 | 240-300 | 52 |
| R: TGTTGGGTCATCTTGGTTTC | ||||||
| Fsp9.9 | F: ACGCCACTCTTCCATACTCAG | (AAC)15 | Contig 5/: 764399-764632 | 234 | 200-280 | 54 |
| R: GTTGACGGTCTTGTGGCATAC | ||||||
| Fsp9.10 | F: TCAACAACACCAACCACCTG | (AGC)9 | Contig 5/: 509965-510211 | 247 | 200-300 | 54 |
| R: TTCGTCCGAGTCGCCTTCTA | ||||||
| Fsp9.15 | F: GCTTGTGCTGGAGTTGACCT | (GAAT)8 | Contig 5/: 168328-168492 | 165 | 123-155 | 52 |
| R: CAGGAGCATAGGAGGAATAC | ||||||
| Fsp10.2 | F: CGAGAAAGGTGAGGAAGGGA | (GGA)8 | Contig 11/: 258852-259033 | 182 | 175-200 | 52 |
| R: TATCTGTGAGGTGTGGCGA |
| SSR位点 SSR locus | 观测等位基因数 Observed number of alleles (Na) | 有效等位基因数 Effective number of alleles (Ne) | 基因多样性指数 Gene diversity index (H) | Shannon指数 Shannon index (I) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fsp1.7 | 5 | 2.8447 | 0.6485 | 1.2162 |
| Fsp1.10 | 15 | 4.0502 | 0.7531 | 1.9836 |
| Fsp1.17 | 5 | 3.6560 | 0.7265 | 1.4019 |
| Fsp2.2 | 6 | 4.8578 | 0.7941 | 1.6700 |
| Fsp2.3 | 5 | 3.3457 | 0.7011 | 1.3637 |
| Fsp2.4 | 5 | 2.1525 | 0.5354 | 0.9979 |
| Fsp3.1 | 4 | 2.3027 | 0.5657 | 1.0762 |
| Fsp3.6 | 3 | 2.7466 | 0.6359 | 1.0521 |
| Fsp3.7 | 5 | 4.4211 | 0.7738 | 1.5415 |
| Fsp4.2 | 4 | 1.9438 | 0.4855 | 0.8826 |
| Fsp4.4 | 4 | 3.5333 | 0.7170 | 1.3187 |
| Fsp4.7 | 4 | 2.5645 | 0.6101 | 1.0413 |
| Fsp5.3 | 6 | 4.3986 | 0.7727 | 1.5779 |
| Fsp5.4 | 5 | 4.2793 | 0.7663 | 1.5211 |
| Fsp5.8 | 6 | 5.1658 | 0.8064 | 1.7170 |
| Fsp6.3 | 4 | 2.5908 | 0.6140 | 1.1040 |
| Fsp6.7 | 7 | 5.2721 | 0.8103 | 1.7429 |
| Fsp7.3 | 5 | 2.7909 | 0.6417 | 1.2545 |
| Fsp9.6 | 5 | 4.0180 | 0.7511 | 1.4874 |
| Fsp9.8 | 4 | 3.1232 | 0.6798 | 1.2192 |
| Fsp9.9 | 8 | 5.7601 | 0.8264 | 1.8905 |
| Fsp9.10 | 7 | 5.3629 | 0.8135 | 1.7745 |
| Fsp9.15 | 4 | 3.1419 | 0.6817 | 1.2351 |
| Fsp10.2 | 6 | 4.5338 | 0.7794 | 1.6062 |
| 平均 Mean | 5.5 | 3.7023 | 0.7038 | 1.4031 |
表3 24个SSR位点在96个茄镰孢豌豆专化型分离物中的等位基因频率及其他多样性指数
Table 3 Allelic frequencies and other diversity indices of 24 SSR loci in 96 isolates of Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi
| SSR位点 SSR locus | 观测等位基因数 Observed number of alleles (Na) | 有效等位基因数 Effective number of alleles (Ne) | 基因多样性指数 Gene diversity index (H) | Shannon指数 Shannon index (I) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fsp1.7 | 5 | 2.8447 | 0.6485 | 1.2162 |
| Fsp1.10 | 15 | 4.0502 | 0.7531 | 1.9836 |
| Fsp1.17 | 5 | 3.6560 | 0.7265 | 1.4019 |
| Fsp2.2 | 6 | 4.8578 | 0.7941 | 1.6700 |
| Fsp2.3 | 5 | 3.3457 | 0.7011 | 1.3637 |
| Fsp2.4 | 5 | 2.1525 | 0.5354 | 0.9979 |
| Fsp3.1 | 4 | 2.3027 | 0.5657 | 1.0762 |
| Fsp3.6 | 3 | 2.7466 | 0.6359 | 1.0521 |
| Fsp3.7 | 5 | 4.4211 | 0.7738 | 1.5415 |
| Fsp4.2 | 4 | 1.9438 | 0.4855 | 0.8826 |
| Fsp4.4 | 4 | 3.5333 | 0.7170 | 1.3187 |
| Fsp4.7 | 4 | 2.5645 | 0.6101 | 1.0413 |
| Fsp5.3 | 6 | 4.3986 | 0.7727 | 1.5779 |
| Fsp5.4 | 5 | 4.2793 | 0.7663 | 1.5211 |
| Fsp5.8 | 6 | 5.1658 | 0.8064 | 1.7170 |
| Fsp6.3 | 4 | 2.5908 | 0.6140 | 1.1040 |
| Fsp6.7 | 7 | 5.2721 | 0.8103 | 1.7429 |
| Fsp7.3 | 5 | 2.7909 | 0.6417 | 1.2545 |
| Fsp9.6 | 5 | 4.0180 | 0.7511 | 1.4874 |
| Fsp9.8 | 4 | 3.1232 | 0.6798 | 1.2192 |
| Fsp9.9 | 8 | 5.7601 | 0.8264 | 1.8905 |
| Fsp9.10 | 7 | 5.3629 | 0.8135 | 1.7745 |
| Fsp9.15 | 4 | 3.1419 | 0.6817 | 1.2351 |
| Fsp10.2 | 6 | 4.5338 | 0.7794 | 1.6062 |
| 平均 Mean | 5.5 | 3.7023 | 0.7038 | 1.4031 |
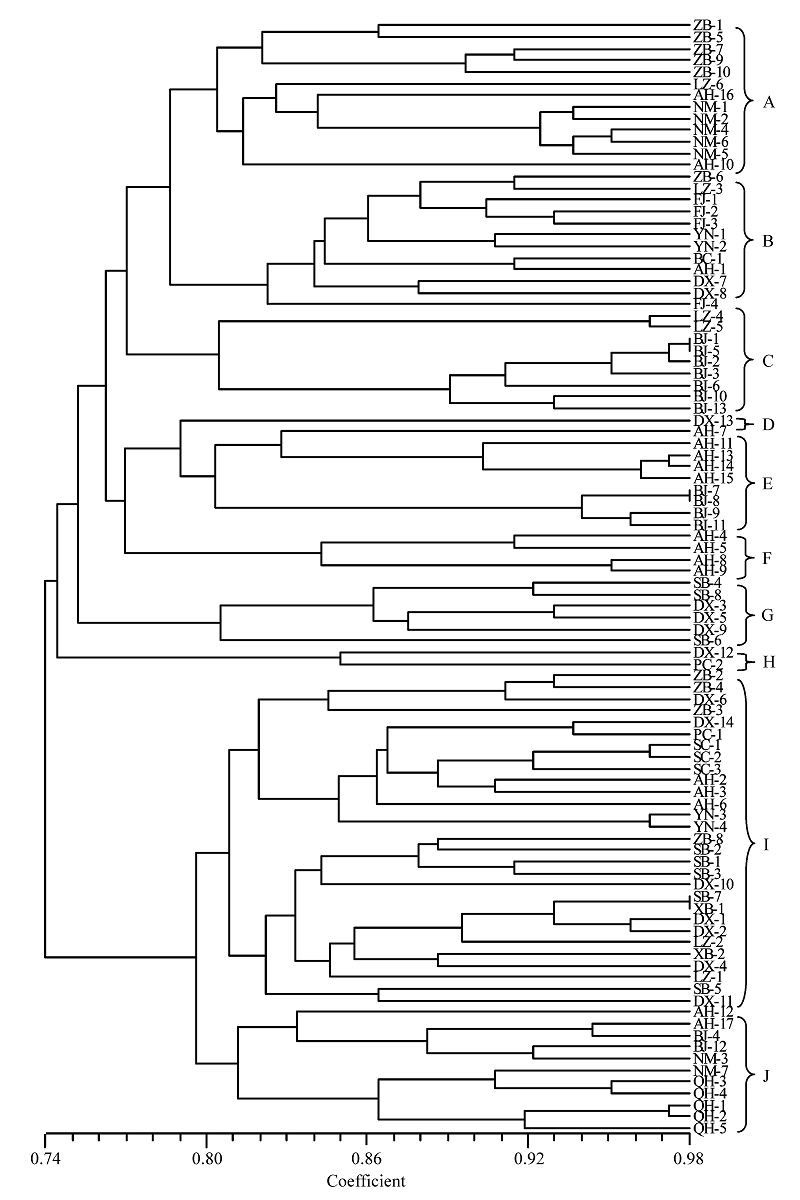
图1 基于遗传相似性系数构建的96个茄镰孢豌豆专化型分离物的UPGMA聚类图(A-J分别代表不同的基因型组, 分离物代号同表1)
Fig. 1 A UPGMA dendrogram of 96 isolates of Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi based on genetic similarity. A-J indicate different genotype clusters, and isolate codes see Table 1.
| 群体 Population | 菌株数 No. of isolates | 观测等位基因数 Observed number of alleles (Na) | 有效等位基因数 Effective number of alleles (Ne) | 基因多样性指数 Gene diversity Index (H) | Shannon指数 Shannon index (I) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 河北 Hebei | 10 | 2.8750 | 2.5377 | 0.5925 | 0.9599 |
| 宁夏 Ningxia | 12 | 3.3750 | 2.5005 | 0.5593 | 0.9905 |
| 甘肃 Gansu | 20 | 3.9583 | 2.9460 | 0.6353 | 1.1590 |
| 安徽 Anhui | 17 | 3.8750 | 2.7750 | 0.6040 | 1.1058 |
| 北京 Beijing | 13 | 2.8750 | 2.2937 | 0.5262 | 0.8820 |
| 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 7 | 2.1250 | 1.7474 | 0.4007 | 0.6140 |
| 青海 Qinghai | 5 | 1.5000 | 1.3867 | 0.2144 | 0.3091 |
表4 7个茄镰孢豌豆专化型群体遗传多样性分析
Table 4 Genetic diversity in seven populations of Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi
| 群体 Population | 菌株数 No. of isolates | 观测等位基因数 Observed number of alleles (Na) | 有效等位基因数 Effective number of alleles (Ne) | 基因多样性指数 Gene diversity Index (H) | Shannon指数 Shannon index (I) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 河北 Hebei | 10 | 2.8750 | 2.5377 | 0.5925 | 0.9599 |
| 宁夏 Ningxia | 12 | 3.3750 | 2.5005 | 0.5593 | 0.9905 |
| 甘肃 Gansu | 20 | 3.9583 | 2.9460 | 0.6353 | 1.1590 |
| 安徽 Anhui | 17 | 3.8750 | 2.7750 | 0.6040 | 1.1058 |
| 北京 Beijing | 13 | 2.8750 | 2.2937 | 0.5262 | 0.8820 |
| 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 7 | 2.1250 | 1.7474 | 0.4007 | 0.6140 |
| 青海 Qinghai | 5 | 1.5000 | 1.3867 | 0.2144 | 0.3091 |
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 平方和 Sum of squares | 方差分量 Variance component | 变异率 Percentage of variation (%) | FST | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群体间 Among populations | 6 | 134.733 | 1.25595 | 13.86 | 0.13865 | <0.001 |
| 群体内 Within population | 77 | 600.814 | 7.80278 | 86.14 | - | <0.001 |
| 合计 Total | 83 | 735.548 | 9.05873 | 100 | - | - |
表5 基于SSR标记的7个不同地理来源茄镰孢豌豆专化型群体遗传变异分析(AMOVA)
Table 5 AMOVA analysis of genetic variation in seven Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi populations from different geographical regions based on SSR markers
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 平方和 Sum of squares | 方差分量 Variance component | 变异率 Percentage of variation (%) | FST | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群体间 Among populations | 6 | 134.733 | 1.25595 | 13.86 | 0.13865 | <0.001 |
| 群体内 Within population | 77 | 600.814 | 7.80278 | 86.14 | - | <0.001 |
| 合计 Total | 83 | 735.548 | 9.05873 | 100 | - | - |
| 群体 Population | 河北 Hebei | 宁夏 Ningxia | 甘肃 Gansu | 安徽 Anhui | 北京 Beijing | 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 青海Qinghai |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 河北 Heibei | **** | 0.6780 | 0.7550 | 0.6943 | 0.5416 | 0.5859 | 0.5435 |
| 宁夏 Ningxia | 0.3886 | **** | 0.8536 | 0.6432 | 0.4899 | 0.4528 | 0.6226 |
| 甘肃 Gansu | 0.2810 | 0.1583 | **** | 0.7515 | 0.5628 | 0.5260 | 0.5931 |
| 安徽 Anhui | 0.3648 | 0.4413 | 0.2857 | **** | 0.5917 | 0.5285 | 0.4808 |
| 北京 Beijing | 0.6133 | 0.7135 | 0.5748 | 0.5248 | **** | 0.6442 | 0.4073 |
| 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 0.5346 | 0.7922 | 0.6425 | 0.6377 | 0.4398 | **** | 0.4802 |
| 青海 Qinghai | 0.6097 | 0.4738 | 0.5224 | 0.7324 | 0.8983 | 0.7336 | **** |
表6 7个茄镰孢豌豆专化型群体间遗传相似性系数(对角线上方)及遗传距离(对角线下方)
Table 6 Genetic similarity coefficient (above diagonal) and genetic distance (below diagonal) among seven populations of Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi
| 群体 Population | 河北 Hebei | 宁夏 Ningxia | 甘肃 Gansu | 安徽 Anhui | 北京 Beijing | 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 青海Qinghai |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 河北 Heibei | **** | 0.6780 | 0.7550 | 0.6943 | 0.5416 | 0.5859 | 0.5435 |
| 宁夏 Ningxia | 0.3886 | **** | 0.8536 | 0.6432 | 0.4899 | 0.4528 | 0.6226 |
| 甘肃 Gansu | 0.2810 | 0.1583 | **** | 0.7515 | 0.5628 | 0.5260 | 0.5931 |
| 安徽 Anhui | 0.3648 | 0.4413 | 0.2857 | **** | 0.5917 | 0.5285 | 0.4808 |
| 北京 Beijing | 0.6133 | 0.7135 | 0.5748 | 0.5248 | **** | 0.6442 | 0.4073 |
| 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 0.5346 | 0.7922 | 0.6425 | 0.6377 | 0.4398 | **** | 0.4802 |
| 青海 Qinghai | 0.6097 | 0.4738 | 0.5224 | 0.7324 | 0.8983 | 0.7336 | **** |
| [1] | Alves-Santos FM, Benito EP, Eslava AP, Díaz-Mínguez JM (1999) Genetic diversity of Fusarium oxysporum strains from common bean fields in Spain. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65, 3335-3340. |
| [2] | Chen QH (陈庆河), Weng QY (翁启勇), He YX (何玉仙), Zhao J (赵健) (2004) Pathogens and pathogenicity of root disease of peas in Fujian Province. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences (福建农业学报), 19, 28-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Chen XM, Line RF, Leung H (1993) Relationship between virulence variation and DNA polymorphism in Puccinia striiformis. Phytopathology, 83, 1489-1497. |
| [4] |
Coleman JJ, Rounsley SD, Rodriguez-Carres M, Kuo A, Wasmann CC, Grimwood J, Schmutz J, Taga M, White GJ, Zhou SG, Schwartz DC, Freitag M, Ma LJ, Danchin EGJ, Henrissat B, Coutinho PM, Nelson DR, Straney D, Napoli CA, Barker BM, Gribskov M, Rep M, Kroken S, Molnàr I, Rensing C, Kennell JC, Zamora J, Farman ML, Selker EU, Salamov A, Shapiro H, Shapiro J, Lindquist E, Lamers C, Grigoriev IV, Geiser DM, Covert SF, Temporini E, VanEtten HD (2009) The genome of Nectria haematococca: contribution of supernumerary chromosomes to gene expansion. PLoS Genetics, 5, e1000618.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] | Diao ZM (刁治民) (1996) Studies on the species and pathogenicity of root disease of peas in Qinghai province. Journal of Microbiology (微生物学杂志), 16(1), 31-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] | Etebu E, Osborn AM (2010) Molecular quantification of the pea footrot disease pathogen (Nectria haematococca) in agricultural soils. Phytoparasitica, 38, 447-454. |
| [7] | Etebu E, Osborn AM (2011) Pea footrot disease depends on the combination of pathogenicity genes in Nectria haematococca. Asian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 3, 156-161. |
| [8] |
Excoffier L, Laval S, Schneider G (2005) Arlequin ver. 3.0: an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evolutionary Bioinformatics Online, 1, 47-50.
URL PMID |
| [9] | Feng J, Hwang R, Chang KF, Conner RL, Hwang SF, Strelkov SE, Gossen BD, McLaren DL, Xue AG (2011) Identification of microsatellite markers linked to quantitative trait loci controlling resistance to Fusarium root rot in field pea. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 91, 199-204. |
| [10] | Feng J, Hwang R, Chang KF, Hwang SF, Strelkov SE, Gossen BD, Conner RL, Turnbu GD (2010) Genetic variation in Fusarium avenaceum causing root rot on field pea. Plant Pathology, 59, 845-852. |
| [11] | Fiers M, Edel-Hermann V, Héraud C, Gautheron N, Chatot C, Le Hingrat Y, Bouchek-Mechiche K, Steinberg C (2011) Genetic diversity of Rhizoctonia solani associated with potato tubers in France. Mycologia, 103, 1230-1244. |
| [12] |
Graham PH, Vance CP (2003) Legumes: importance and constraints to greater use. Plant Physiology, 131, 872-877.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] | Han YN, Liu XG, Benny U, Kistler HC, VanEtten HD (2001) Genes determining pathogenicity to pea are clustered on a supernumerary chromosome in the fungal plant pathogen Nectria haematococca. The Plant Journal, 25, 305-314. |
| [14] | Hasanzade F, Rastegar MF, Jafarpour B, Kermani M (2008) Identification of Fusarium solani f. sp. Pisi: the cause of root rot in chickpea and assessment of its genetic diversity using AFLP in Northeast Iran. Research Journal of Biological Sciences, 3, 737-741. |
| [15] | Hill AL, Reeves PA, Larson RL, Fenwick AL, Hanson LE, Panell L (2011) Genetic variability among isolates of Fusarium oxysporum from sugar beet. Plant Pathology, 60, 496-505. |
| [16] | Infantino A, Kharrat M, Riccioni L, Coyne CJ, McPhee KE, Grünwald NJ (2006) Screening techniques and sources of resistance to root diseases in cool season food legumes. Euphytica, 147, 201-221. |
| [17] | Kalendar R, Lee D, Schulman AH (2009) FastPCR software for PCR primer and probe design and repeat search. Genes, Genomes and Genomics, 3, 1-14. |
| [18] |
Kimura M, Crow JF (1964) The number of alleles that can be maintained in a finite population. Genetics, 49, 725-738.
URL PMID |
| [19] | Lewontin RC (1972) The apportionment of human diversity. Evolutionary Biology, 6, 381-398. |
| [20] |
McDonald BA (1997) The population genetics of fungi: tools and techniques. Phytopathology, 87, 448-453.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] |
McDonald BA, Lindem C (2002) Pathogen population genetics, evolutionary potential, and durable resistance. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 40, 349-379.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] | Mwang’ombe AW, Kipsumbai PK, Kiprop EK, Olubayo FM, Ochieng JW (2008) Analysis of Kenyan isolates of Fusarium solani f. sp. phaseoli from common bean using colony characteristics, pathogenicity and microsatellite DNA. African Journal of Biotechnology, 7, 1662-1671. |
| [23] | Nei M (1972) Genetic distance between populations. The American Naturalist, 106, 283-292. |
| [24] | Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 76, 5269-5273. |
| [25] | Ren X (任旭), Zhu ZD (朱振东), Li HJ (李洪杰), Duan CX (段灿星), Wang XM (王晓鸣) (2012) SSR marker development and analysis of genetic diversity of Fusarium verticillioides isolated from maize in China. Scientia Agricultura Sinica (中国农业科学), 45, 52-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] |
Rep M, Kistler HC (2010) The genomic organization of plant pathogenicity in Fusarium species. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 13, 420-426.
URL PMID |
| [27] | Rohlf FJ (1997) NTSYSpc Version 2.1. Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System. Exeter Software, Setauket, New York. |
| [28] | Rush CM, Kraft JM (1986) Effects of inoculum density and placement on Fusarium root rot of peas. Phytopathology, 76, 1325-1329. |
| [29] | Skovgaard K, Bødker L, Rosendahl S (2002) Population structure and pathogenicity of members of the Fusarium oxysporum complex isolated from soil and root necrosis of pea (Pisum sativum L.). FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 42, 367-374. |
| [30] | Tang DZ (唐德志), He SQ (何苏琴), Li YQ (李玉奇), Zhu RS (朱润身) (1993) Studies on the species and pathogenicity of root disease of peas in Gansu Province. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica (西北农业学报), (2), 37-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] |
Temporini ED, VanEtten HD (2002) Distribution of the pea pathogenicity (PEP) genes in the fungus Nectria haematococca mating population VI. Current Genetics, 41, 107-114.
URL PMID |
| [32] | VanEtten HD (1978) Identification of additional habitats of Nectria haematococca mating population. VI. Phytopathology, 68, 1552-1556. |
| [33] |
VanEtten HD, Funnel-Baerg D, Wasmann C, McCluskey K (1994) Location of pathogenicity genes on dispensable chromosomes in Nectria haematococca MPVI. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 65, 263-267.
URL PMID |
| [34] | VanEtten HD, Matthews PS, Tegtmeier KJ, Dietert MF, Stein JI (1980) The association of pisatin tolerance and demethylation with virulence on pea in Nectria haematococca. Physiological Plant Pathology, 16, 257-268. |
| [35] | Wang KC (王宽仓), Zhang ZS (张宗山), Chen JN (陈渐宁), Fan ZQ (樊仲庆), Niu BS (牛宝山), Zhao M (赵明), Xie CJ (谢成君) (1995) Studies on occurrence regulation and the integrated prevention and control techniques of Fusarium root rot of pea. Ningxia Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology (宁夏农林科技), (5), 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [36] | Wang MC (王梅春), Lian RF (连荣芳), Mo JP (墨金萍), Wang SH (王思慧) (2008) Research of the pea root rot and resistant breeding in Gansu Province. Rain Fed Crops (杂粮作物), 28, 272-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [37] | Wu KJ (伍克俊), Xie ZT (谢正团), Li XJ (李秀君) (1992) Study on the pathogens of root rot of pea in the central region of Gansu Province. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University (甘肃农业大学学报), 27, 225-231. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [38] | Xiang N (向妮), Duan CX (段灿星), Xiao YN (肖炎农), Wang XM (王晓鸣), Zhu ZD (朱振东) (2012) Identification of the pathogen causing Fusarium root rot of pea and diversity of pathogenicity genes. Scientia Agricultura Sinica (中国农业科学), 45, 2838-2847. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [39] | Xu JJ (徐静静), Lin Y (蔺宇), Zhu ZD (朱振东) (2008) Development and applications of SSR markers in plant pathogen. Plant Protection (植物保护), 34, 14-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [40] | Yu TF (俞大绂) (1955) A preliminary list of Fusaria in China. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica (植物病理学报), 1(1), 1-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [41] | Zong XX (宗绪晓), Guan JP (关建平), Wang SM (王述民), Liu QC (刘庆昌) (2008) Genetic diversity among Chinese pea (Pisum sativum L.) landraces revealed by SSR markers. Acta Agronomica Sinica (作物学报), 34, 1330-1338. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 翁茁先, 黄佳琼, 张仕豪, 余锴纯, 钟福生, 黄勋和, 张彬. 利用线粒体COI基因揭示中国乌骨鸡遗传多样性和群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(6): 667-676. |
| [2] | 盛芳, 陈淑英, 田嘉, 李鹏, 秦雪, 罗淑萍, 李疆. 新疆准噶尔山楂不同居群的遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(5): 518-530. |
| [3] | 于少帅, 徐启聪, 林彩丽, 王圣洁, 田国忠. 植原体遗传多样性研究现状与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(2): 205-215. |
| [4] | 徐刚标, 梁艳, 蒋燚, 刘雄盛, 胡尚力, 肖玉菲, 郝博搏. 伯乐树种群遗传多样性及遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(6): 723-731. |
| [5] | 陈碧云, 胡琼, Christina Dixelius, 李国庆, 伍晓明. 利用SRAP分析核盘菌遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(5): 509-515. |
| [6] | 王长忠, 李忠, 梁宏伟, 呼光富, 吴勤超, 邹桂伟, 罗相忠. 长江下游地区4个克氏原螯虾群体的遗传多样性分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(5): 518-523. |
| [7] | 王峥峰, 葛学军. 不仅仅是遗传多样性: 植物保护遗传学进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(4): 330-339. |
| [8] | 凌英会, 成月娇, 王艳萍, 关伟军, 韩建林, 傅宝玲, 赵倩君, 何晓红, 浦亚斌, 马月辉. 应用微卫星标记分析23个中国地方马种的遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(3): 240-247. |
| [9] | 梁宏伟, 李忠, 罗相忠, 王长忠, 呼光富, 邹桂伟, 杨永铨. 基于微卫星标记的5个尼罗罗非鱼品系的遗传多样性分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(1): 82-87. |
| [10] | 丁艳来, 赵团结, 盖钧镒. 中国野生大豆的遗传多样性和生态特异性分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2008, 16(2): 133-142. |
| [11] | 陆雪莹, 张道远, 马文宝. 准噶尔无叶豆片断化居群的遗传变异及克隆多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(3): 282-291. |
| [12] | 罗永发, 王志刚, 李加琪, 张桂香, 陈瑶生, 梁勇, 于福清, 宋卫涛, 张自富. 采用微卫星标记分析13个中外牛品种的遗传变异和品种间的遗传关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2006, 14(6): 498-507. |
| [13] | 夏颖哲, 盛岩, 陈宜瑜. 利用线粒体DNA控制区序列分析细鳞鲑种群的遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2006, 14(1): 48-54. |
| [14] | 潘丽芹, 季华, 陈龙清. 荷叶铁线蕨自然居群的遗传多样性研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2005, 13(2): 122-129. |
| [15] | 王希龙, 欧江涛, 黄礼光, 郭春华, 钟金城, 李小成, 王峰, 郑心力. 海南五指山猪遗传多样性的微卫星分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2005, 13(1): 20-26. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()