



生物多样性 ›› 2009, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (5): 518-523. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09017 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2009.09017
王长忠1,2, 李忠1, 梁宏伟1, 呼光富1,2, 吴勤超1,2, 邹桂伟1,2,*( ), 罗相忠1
), 罗相忠1
收稿日期:2009-01-14
接受日期:2009-06-11
出版日期:2009-09-20
发布日期:2009-09-20
通讯作者:
邹桂伟
作者简介:*E-mail: zougw@yfi.ac.cn基金资助:
Changzhong Wang1,2, Zhong Li1, Hongwei Liang1, Guangfu Hu1,2, Qinchao Wu1,2, Guiwei Zou1,2,*( ), Xiangzhong Luo1
), Xiangzhong Luo1
Received:2009-01-14
Accepted:2009-06-11
Online:2009-09-20
Published:2009-09-20
Contact:
Guiwei Zou
摘要:
为了对长江下游地区克氏原螯虾(Procambarus clarkii)群体的遗传多样性状况进行本底调查, 本文利用17对微卫星引物对南京(NJ)、盱眙(XY)、合肥(HF)、南昌(NC)4个克氏原螯虾地理群体进行了遗传多样性研究。结果表明, 4个地理群体的平均观测杂合度为0.4322-0.4826、平均期望杂合度为0.4024-0.6121、平均多态信息含量为0.3408-0.5624, 4个克氏原螯虾群体的遗传多样性处于中等水平, 其中南京群体遗传多样性最高, 合肥群体最低; 4个克氏原螯虾群体的基因流为1.3729-5.9161, 遗传分化指数为0.0405-0.1540, 群体间基因流水平较高, 群体间遗传分化程度较小。聚类结果显示4个群体可分为2支: 南京、南昌、盱眙三个群体聚为一支, 合肥群体独自成一支。以上结果将为克氏原螯虾遗传育种、资源保护和利用提供一定的理论依据。
王长忠, 李忠, 梁宏伟, 呼光富, 吴勤超, 邹桂伟, 罗相忠 (2009) 长江下游地区4个克氏原螯虾群体的遗传多样性分析. 生物多样性, 17, 518-523. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09017.
Changzhong Wang, Zhong Li, Hongwei Liang, Guangfu Hu, Qinchao Wu, Guiwei Zou, Xiangzhong Luo (2009) Genetic diversity in fourProcambarus clarkii populations in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Biodiversity Science, 17, 518-523. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09017.
| 座位 Locus | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequence(5′→3′) | 退火温度 Annealing temperature (℃) | 重复类型 SSR motif | 片段大小 Allele size (bp) | 等位基因No. of alleles | 登录号 GenBank accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PclG02 | F:CTCCCCATGCACTCTGGCTCTGT R:TGGCGAATTTTGCCTGTTTCTGTC | 66 | (GATA)3GAGAA(GATA)5 | 216-224 | 3 | AF290919 |
| PclG03 | F:CTCTCCACCAGTCATTTCTT R:AAGCTTACAATAAATATAGATAGAC | 52 | (TCTA)20 | 216-420 | 4 | AF290920 |
| PclG04 | F:TATATCAGTCAATCTGTCCAG R:TCAGTAAGTAGATTGATAGAAGG | 54 | (TCTA)3…(TCTA)2…(TCTA)29… (TCTA)2 | 170-290 | 4 | AF290921 |
| PclG07 | F:CCTCCCACCAGGGTTATCTATTCA R:GTGGGTGTGGCGCTCTTGTT | 63 | (TCTA)8 | 100-160 | 4 | AF290922 |
| PclG08 | F:ACGATAAATGGATAGATGGATGAA R:CCGGGTCTGTCTGTCTGTCA | 62 | (GATA)16 | 148-220 | 5 | AF290923 |
| PclG09 | F:TATGCACCTTTACCTGAAT R:TGTTGGTGTGGTCATCA | 60 | (TCTA)14 | 80-160 | 4 | AF290924 |
| PclG10 | F:TGCTCACGCAAACTTGTATTCAGT R:CAATGGTCCTTGATTTGGTGTTCT | 54 | (TAGA)2TA(TAGA)16 | 90-176 | 3 | AF290925 |
| PclG13 | F:CTCTCCTGGCGCTGTTATTTAGC R:TGAAGAGGCAGAGTGAGGATTCTC | 62 | (TCTA)12 | 130-150 | 2 | AF290926 |
| PclG15 | F:GGCGTGACGCCAACGTGTCTT R:GGCTGGCCACTTTGTTAGCCTGAG | 70 | (TATC)2TGTC(TATC)17TATT(TATC)3 | 150-185 | 3 | AF290927 |
| PclG16 | F:CTCGGAATGTCCACCTGAGA R:TCATTATGGATTTTGTCAATCTAT | 54 | (TCTA)18TCTC(TATC)3 | 80-160 | 4 | AF290928 |
| PclG17 | F:GTCGGGAACCTATTTACAGTGTAT R:AAGAGCGAAGAAAGAGATAAAGAT | 57 | (TCTA)14 | 156-190 | 4 | AF290929 |
| PclG27 | F:AATCTTAAGATCATGAAAAAGGTA R:TTTAAGGAACGTATAAGAAAAGAC | 57 | (TATC)4CATC(TATC)8 | 80-150 | 6 | AF290932 |
| PclG28 | F:CTCGGCGAGTTTACTGAAAT R:AGAAGAAAGGGATATAAGGTAAAG | 60 | (GATA)22(GA)5 | 210-270 | 3 | AF290933 |
| PclG29 | F:GAAAGTCATGGGTGTAGGTGTAAC R:TTTTTGGGCTATGTGACGAG | 65 | (TATC)9 | 95-165 | 3 | AF290934 |
| PclG33 | F:TTCGAGGCGTTGCTGATTGTAAGT R:CAAGGAAGCGTATAGCCGGAGTCT | 68 | (GT)21 | 120-180 | 5 | AF290936 |
| PclG37 | F:TAAATAAGTGGCGTGTAAGACGAG R:TAACTAAGCCAGGGTGGTCTCCAG | 66 | (CA)4CG(CA)15CG (CA)23 | 80-180 | 7 | AF290939 |
| PclG48 | F:CTGTTGGTGATTTCCGTCAATTTT R:AGATTCAACGCTGTGTTCCTGATC | 66 | (CA)12 | 146-190 | 2 | AF290941 |
表1 17个微卫星位点引物序列及退火温度
Table 1 Primer sequence and annealing temperature for 17 microsatellite loci
| 座位 Locus | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequence(5′→3′) | 退火温度 Annealing temperature (℃) | 重复类型 SSR motif | 片段大小 Allele size (bp) | 等位基因No. of alleles | 登录号 GenBank accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PclG02 | F:CTCCCCATGCACTCTGGCTCTGT R:TGGCGAATTTTGCCTGTTTCTGTC | 66 | (GATA)3GAGAA(GATA)5 | 216-224 | 3 | AF290919 |
| PclG03 | F:CTCTCCACCAGTCATTTCTT R:AAGCTTACAATAAATATAGATAGAC | 52 | (TCTA)20 | 216-420 | 4 | AF290920 |
| PclG04 | F:TATATCAGTCAATCTGTCCAG R:TCAGTAAGTAGATTGATAGAAGG | 54 | (TCTA)3…(TCTA)2…(TCTA)29… (TCTA)2 | 170-290 | 4 | AF290921 |
| PclG07 | F:CCTCCCACCAGGGTTATCTATTCA R:GTGGGTGTGGCGCTCTTGTT | 63 | (TCTA)8 | 100-160 | 4 | AF290922 |
| PclG08 | F:ACGATAAATGGATAGATGGATGAA R:CCGGGTCTGTCTGTCTGTCA | 62 | (GATA)16 | 148-220 | 5 | AF290923 |
| PclG09 | F:TATGCACCTTTACCTGAAT R:TGTTGGTGTGGTCATCA | 60 | (TCTA)14 | 80-160 | 4 | AF290924 |
| PclG10 | F:TGCTCACGCAAACTTGTATTCAGT R:CAATGGTCCTTGATTTGGTGTTCT | 54 | (TAGA)2TA(TAGA)16 | 90-176 | 3 | AF290925 |
| PclG13 | F:CTCTCCTGGCGCTGTTATTTAGC R:TGAAGAGGCAGAGTGAGGATTCTC | 62 | (TCTA)12 | 130-150 | 2 | AF290926 |
| PclG15 | F:GGCGTGACGCCAACGTGTCTT R:GGCTGGCCACTTTGTTAGCCTGAG | 70 | (TATC)2TGTC(TATC)17TATT(TATC)3 | 150-185 | 3 | AF290927 |
| PclG16 | F:CTCGGAATGTCCACCTGAGA R:TCATTATGGATTTTGTCAATCTAT | 54 | (TCTA)18TCTC(TATC)3 | 80-160 | 4 | AF290928 |
| PclG17 | F:GTCGGGAACCTATTTACAGTGTAT R:AAGAGCGAAGAAAGAGATAAAGAT | 57 | (TCTA)14 | 156-190 | 4 | AF290929 |
| PclG27 | F:AATCTTAAGATCATGAAAAAGGTA R:TTTAAGGAACGTATAAGAAAAGAC | 57 | (TATC)4CATC(TATC)8 | 80-150 | 6 | AF290932 |
| PclG28 | F:CTCGGCGAGTTTACTGAAAT R:AGAAGAAAGGGATATAAGGTAAAG | 60 | (GATA)22(GA)5 | 210-270 | 3 | AF290933 |
| PclG29 | F:GAAAGTCATGGGTGTAGGTGTAAC R:TTTTTGGGCTATGTGACGAG | 65 | (TATC)9 | 95-165 | 3 | AF290934 |
| PclG33 | F:TTCGAGGCGTTGCTGATTGTAAGT R:CAAGGAAGCGTATAGCCGGAGTCT | 68 | (GT)21 | 120-180 | 5 | AF290936 |
| PclG37 | F:TAAATAAGTGGCGTGTAAGACGAG R:TAACTAAGCCAGGGTGGTCTCCAG | 66 | (CA)4CG(CA)15CG (CA)23 | 80-180 | 7 | AF290939 |
| PclG48 | F:CTGTTGGTGATTTCCGTCAATTTT R:AGATTCAACGCTGTGTTCCTGATC | 66 | (CA)12 | 146-190 | 2 | AF290941 |
| 座位 Locus | 南京群体 Nanjing population | 盱眙群体 Xuyi population | 合肥群体 Hefei population | 南昌群体 Nanchang population | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIC | 观测杂合度 Ho | 期望杂合度 He | 平衡偏离指数 D | PIC | 观测杂合度 Ho | 期望杂合度 He | 平衡偏离指数 D | PIC | 观测杂合度 Ho | 期望杂合度 He | 平衡偏离指数 D | PIC | 观测杂合度 Ho | 期望杂合度 He | 平衡偏离指数 D | ||||
| PclG02 | 0.4446 | 0.4894 | 0.5067 | -0.0341 | 0.4296 | 0.4783 | 0.5380 | -0.1110 | 0.1693 | 0.1250 | 0.1886 | -0.3372 | 0.5226 | 0.6250 | 0.6116 | 0.0219 | |||
| PclG03 | 0.5127 | 0.4103 | 0.6051 | -0.3219 | 0.5677 | 0.6222 | 0.6492 | -0.0416 | 0.3705 | 0.5111 | 0.4966 | 0.0292 | 0.4087 | 0.5000 | 0.5290 | -0.0548 | |||
| PclG04 | 0.6663 | 0.3542 | 0.7265 | -0.5125 | 0.3018 | 0.2292 | 0.3537 | -0.3520 | 0.4868 | 0.5208 | 0.5524 | -0.0572 | 0.3680 | 0.4583 | 0.4912 | -0.0670 | |||
| PclG07 | 0.5020 | 0.4894 | 0.5546 | -0.1176 | 0.4536 | 0.3750 | 0.5570 | -0.3268 | 0.4346 | 0.3750 | 0.4974 | -0.2461 | 0.4039 | 0.4583 | 0.5068 | -0.0957 | |||
| PclG08 | 0.6980 | 0.3409 | 0.7531 | -0.5473 | 0.5592 | 0.4583 | 0.6397 | -0.2836 | 0.4093 | 0.5000 | 0.5267 | -0.0507 | 0.4101 | 0.3542 | 0.4721 | -0.2497 | |||
| PclG09 | 0.6377 | 0.2500 | 0.7017 | -0.6437 | 0.3775 | 0.1707 | 0.4279 | -0.6011 | 0.4356 | 0.5814 | 0.5453 | 0.0662 | 0.5279 | 0.1591 | 0.6142 | -0.7410 | |||
| PclG10 | 0.4331 | 0.3864 | 0.5421 | -0.2872 | 0.3664 | 0.0811 | 0.4498 | -0.8197 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.2454 | 0.2045 | 0.2652 | -0.2289 | |||
| PclG13 | 0.3660 | 0.3542 | 0.4875 | -0.2734 | 0.3225 | 0.3958 | 0.4086 | -0.0313 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.3444 | 0.3617 | 0.4468 | -0.1905 | |||
| PclG15 | 0.6289 | 0.2292 | 0.2623 | -0.1262 | 0.3263 | 0.4130 | 0.3641 | 0.1343 | 0.5916 | 0.7234 | 0.6728 | 0.0752 | 0.0976 | 0.1042 | 0.1011 | 0.0307 | |||
| PclG16 | 0.6800 | 0.6170 | 0.7369 | -0.1627 | 0.5934 | 0.5778 | 0.6504 | -0.1116 | 0.4485 | 0.4643 | 0.5292 | -0.1226 | 0.6629 | 0.6250 | 0.7230 | -0.1356 | |||
| PclG17 | 0.5867 | 0.4583 | 0.6607 | -0.3063 | 0.4836 | 0.3750 | 0.5401 | -0.3057 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.5642 | 0.6458 | 0.6465 | -0.0011 | |||
| PclG27 | 0.6902 | 0.5909 | 0.7450 | -0.2069 | 0.6812 | 0.7391 | 0.7360 | 0.0042 | 0.3045 | 0.4255 | 0.3672 | 0.1588 | 0.6853 | 0.6809 | 0.7380 | -0.0774 | |||
| PclG28 | 0.5517 | 0.2045 | 0.6335 | -0.6772 | 0.4092 | 0.1087 | 0.4909 | -0.7786 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.3733 | 0.3750 | 0.5018 | -0.2527 | |||
| PclG29 | 0.4904 | 0.3830 | 0.5726 | -0.3311 | 0.4366 | 0.6522 | 0.5162 | 0.2635 | 0.5558 | 0.5870 | 0.6362 | -0.0773 | 0.3884 | 0.3043 | 0.5115 | -0.4051 | |||
| PclG33 | 0.5800 | 1.0000 | 0.6536 | 0.5300 | 0.6700 | 1.0000 | 0.7550 | 0.3245 | 0.5862 | 1.0000 | 0.6577 | 0.5205 | 0.7290 | 1.0000 | 0.7746 | 0.2910 | |||
| PclG37 | 0.7231 | 1.0000 | 0.7703 | 0.2982 | 0.6837 | 1.0000 | 0.7389 | 0.3534 | 0.6470 | 1.0000 | 0.7076 | 0.4132 | 0.5673 | 1.0000 | 0.6436 | 0.5538 | |||
| PclG48 | 0.3686 | 0.4318 | 0.4929 | -0.1240 | 0.2490 | 0.3125 | 0.2945 | 0.0611 | 0.3533 | 0.5333 | 0.4634 | 0.1508 | 0.3629 | 0.3478 | 0.4816 | -0.2778 | |||
表2 4个克氏原螯虾群体在17个微卫星位点上的多态信息含量(PIC)、观测杂合度(Ho)、期望杂合度(He)和Hardy-Weinberg平衡偏离指数统计
Table 2 Polymorphism information content (PIC), observed heterozygosity (Ho), expected heterozygosity (He) and Hardy-Weinberg departure value (D) of 17 microsatellite loci in four Procambarus clarkii populations
| 座位 Locus | 南京群体 Nanjing population | 盱眙群体 Xuyi population | 合肥群体 Hefei population | 南昌群体 Nanchang population | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIC | 观测杂合度 Ho | 期望杂合度 He | 平衡偏离指数 D | PIC | 观测杂合度 Ho | 期望杂合度 He | 平衡偏离指数 D | PIC | 观测杂合度 Ho | 期望杂合度 He | 平衡偏离指数 D | PIC | 观测杂合度 Ho | 期望杂合度 He | 平衡偏离指数 D | ||||
| PclG02 | 0.4446 | 0.4894 | 0.5067 | -0.0341 | 0.4296 | 0.4783 | 0.5380 | -0.1110 | 0.1693 | 0.1250 | 0.1886 | -0.3372 | 0.5226 | 0.6250 | 0.6116 | 0.0219 | |||
| PclG03 | 0.5127 | 0.4103 | 0.6051 | -0.3219 | 0.5677 | 0.6222 | 0.6492 | -0.0416 | 0.3705 | 0.5111 | 0.4966 | 0.0292 | 0.4087 | 0.5000 | 0.5290 | -0.0548 | |||
| PclG04 | 0.6663 | 0.3542 | 0.7265 | -0.5125 | 0.3018 | 0.2292 | 0.3537 | -0.3520 | 0.4868 | 0.5208 | 0.5524 | -0.0572 | 0.3680 | 0.4583 | 0.4912 | -0.0670 | |||
| PclG07 | 0.5020 | 0.4894 | 0.5546 | -0.1176 | 0.4536 | 0.3750 | 0.5570 | -0.3268 | 0.4346 | 0.3750 | 0.4974 | -0.2461 | 0.4039 | 0.4583 | 0.5068 | -0.0957 | |||
| PclG08 | 0.6980 | 0.3409 | 0.7531 | -0.5473 | 0.5592 | 0.4583 | 0.6397 | -0.2836 | 0.4093 | 0.5000 | 0.5267 | -0.0507 | 0.4101 | 0.3542 | 0.4721 | -0.2497 | |||
| PclG09 | 0.6377 | 0.2500 | 0.7017 | -0.6437 | 0.3775 | 0.1707 | 0.4279 | -0.6011 | 0.4356 | 0.5814 | 0.5453 | 0.0662 | 0.5279 | 0.1591 | 0.6142 | -0.7410 | |||
| PclG10 | 0.4331 | 0.3864 | 0.5421 | -0.2872 | 0.3664 | 0.0811 | 0.4498 | -0.8197 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.2454 | 0.2045 | 0.2652 | -0.2289 | |||
| PclG13 | 0.3660 | 0.3542 | 0.4875 | -0.2734 | 0.3225 | 0.3958 | 0.4086 | -0.0313 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.3444 | 0.3617 | 0.4468 | -0.1905 | |||
| PclG15 | 0.6289 | 0.2292 | 0.2623 | -0.1262 | 0.3263 | 0.4130 | 0.3641 | 0.1343 | 0.5916 | 0.7234 | 0.6728 | 0.0752 | 0.0976 | 0.1042 | 0.1011 | 0.0307 | |||
| PclG16 | 0.6800 | 0.6170 | 0.7369 | -0.1627 | 0.5934 | 0.5778 | 0.6504 | -0.1116 | 0.4485 | 0.4643 | 0.5292 | -0.1226 | 0.6629 | 0.6250 | 0.7230 | -0.1356 | |||
| PclG17 | 0.5867 | 0.4583 | 0.6607 | -0.3063 | 0.4836 | 0.3750 | 0.5401 | -0.3057 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.5642 | 0.6458 | 0.6465 | -0.0011 | |||
| PclG27 | 0.6902 | 0.5909 | 0.7450 | -0.2069 | 0.6812 | 0.7391 | 0.7360 | 0.0042 | 0.3045 | 0.4255 | 0.3672 | 0.1588 | 0.6853 | 0.6809 | 0.7380 | -0.0774 | |||
| PclG28 | 0.5517 | 0.2045 | 0.6335 | -0.6772 | 0.4092 | 0.1087 | 0.4909 | -0.7786 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.3733 | 0.3750 | 0.5018 | -0.2527 | |||
| PclG29 | 0.4904 | 0.3830 | 0.5726 | -0.3311 | 0.4366 | 0.6522 | 0.5162 | 0.2635 | 0.5558 | 0.5870 | 0.6362 | -0.0773 | 0.3884 | 0.3043 | 0.5115 | -0.4051 | |||
| PclG33 | 0.5800 | 1.0000 | 0.6536 | 0.5300 | 0.6700 | 1.0000 | 0.7550 | 0.3245 | 0.5862 | 1.0000 | 0.6577 | 0.5205 | 0.7290 | 1.0000 | 0.7746 | 0.2910 | |||
| PclG37 | 0.7231 | 1.0000 | 0.7703 | 0.2982 | 0.6837 | 1.0000 | 0.7389 | 0.3534 | 0.6470 | 1.0000 | 0.7076 | 0.4132 | 0.5673 | 1.0000 | 0.6436 | 0.5538 | |||
| PclG48 | 0.3686 | 0.4318 | 0.4929 | -0.1240 | 0.2490 | 0.3125 | 0.2945 | 0.0611 | 0.3533 | 0.5333 | 0.4634 | 0.1508 | 0.3629 | 0.3478 | 0.4816 | -0.2778 | |||
| 群体 Population | 代号 Code | 平均等位 基因数 Mean Na | 平均有效 等位基因数 Mean Ne | 平均多态 信息含量 Mean PIC | 平均观测 杂合度 Mean Ho | 平均期望 杂合度 Mean He |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 南京群体 Nanjing population | NJ | 3.7647 | 2.7778 | 0.5624 | 0.4700 | 0.6121 |
| 盱眙群体 Xuyi population | XY | 3.4706 | 2.3455 | 0.4654 | 0.4699 | 0.5359 |
| 合肥群体 Hefei population | HF | 2.5294 | 1.9415 | 0.3408 | 0.4322 | 0.4024 |
| 南昌群体 Nanchang population | NC | 3.2941 | 2.3656 | 0.4507 | 0.4826 | 0.5329 |
| 平均 Mean | 3.2647 | 3.3576 | 0.4548 | 0.4637 | 0.5208 | |
表3 4个克氏原螯虾群体在17个微卫星位点上的平均等位基因数(Na)、平均有效等位基因数(Ne)、平均多态信息含量(PIC)、平均观测杂合度(Ho)和平均期望杂合度(He)
Table 3 The mean number of alleles (Na), mean number of effective alleles (Ne), mean polymorphism information content (PIC), mean observed heterozygosity (Ho) and mean expected heterozygosity (He) of 17 microsatellite loci in four Procambarus clarkii populations
| 群体 Population | 代号 Code | 平均等位 基因数 Mean Na | 平均有效 等位基因数 Mean Ne | 平均多态 信息含量 Mean PIC | 平均观测 杂合度 Mean Ho | 平均期望 杂合度 Mean He |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 南京群体 Nanjing population | NJ | 3.7647 | 2.7778 | 0.5624 | 0.4700 | 0.6121 |
| 盱眙群体 Xuyi population | XY | 3.4706 | 2.3455 | 0.4654 | 0.4699 | 0.5359 |
| 合肥群体 Hefei population | HF | 2.5294 | 1.9415 | 0.3408 | 0.4322 | 0.4024 |
| 南昌群体 Nanchang population | NC | 3.2941 | 2.3656 | 0.4507 | 0.4826 | 0.5329 |
| 平均 Mean | 3.2647 | 3.3576 | 0.4548 | 0.4637 | 0.5208 | |
| 群体 Population | 南京 Nanjing | 盱眙 Xuyi | 合肥Hefei | 南昌Nanchang |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 南京 Nanjing | **** | 0.8475 | 0.7871 | 0.8997 |
| 盱眙 Xuyi | 0.1655 | **** | 0.6898 | 0.8309 |
| 合肥 Hefei | 0.2394 | 0.3714 | **** | 0.8239 |
| 南昌 Nanchang | 0.1057 | 0.1852 | 0.1937 | **** |
表4 4个克氏原螯虾群体的遗传相似性系数(对角线上)及遗传距离(对角线下)
Table 4 Genetic similarity index (above the diagonal) and genetic distance (below the diagonal) in four Procambarus clarkii populations
| 群体 Population | 南京 Nanjing | 盱眙 Xuyi | 合肥Hefei | 南昌Nanchang |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 南京 Nanjing | **** | 0.8475 | 0.7871 | 0.8997 |
| 盱眙 Xuyi | 0.1655 | **** | 0.6898 | 0.8309 |
| 合肥 Hefei | 0.2394 | 0.3714 | **** | 0.8239 |
| 南昌 Nanchang | 0.1057 | 0.1852 | 0.1937 | **** |
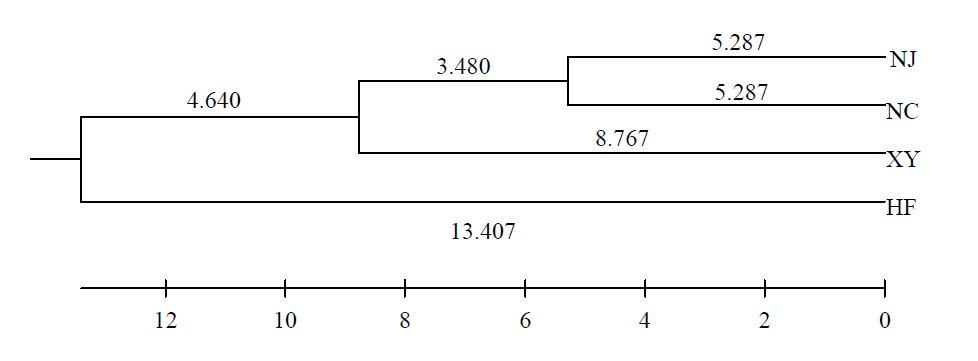
图1 基于Nei’s遗传距离构建的4个克氏原螯虾群体的UPGMA聚类图。群体代号同表3。
Fig. 1 A UPGMA dendrogram of four Procambarus clarkii populations based on Nei’s genetic distance. Population codes see Table 3.
| [1] | Barbaresi S, Fani R, Gherardi F, Mengoni A, Souty-Grosset C (2003) Genetic variability in European populations of an invasive American crayfish: preliminary results. Biological Invasions, 5,269-274. |
| [2] | Barbaresi S, Fani R, Gherardi F, Mengoni A, Souty-Grosset C (2007) Genetics and invasion biology in fresh waters: a pilot study of Procambarus clarkii in Europe. Biological Invaders in Inland Waters: Profiles, Distribution, and Threats, 4,381-400. |
| [3] |
Belfiore NM, May B (2000) Variable microsatellite loci in red swamp crayfish, Procambarus clarkii, and their characterization in other crayfish taxa. Molecular Ecology, 9,2231-2233.
URL PMID |
| [4] |
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 32,314-331.
URL PMID |
| [5] | Huner JV (1988) Procambarus in North America and elsewhere. In: Freshwater Crayfish: Biology, Management and Exploitation (eds Holdich DM, Lowery RS), pp.239-261. Croom Helm,London & Sydney and Timber Press, Portland. |
| [6] | Lu CY (鲁翠云), Jin WK (金万昆), Sun XW (孙效文), Li DY (李大宇), Zhu XD (朱晓东), Ma HT (马海涛), Yu DM (于东梅), Yang JX (杨建新) (2008) Effects of sample size on various genetic structure parameter in cultured population genetic study. Journal of Fisheries of China (水产学报), 32,674-683. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] |
Rozas J, Hernandez M, Cabrera VM, Prevosti A (1990) Colonization of America by Drosophila subobscura: effect of the founder event on the mitochondrial DNA polymorphism. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 7,103-109.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] | Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York. |
| [9] | Shen JR (沈嘉瑞) (1976) Shrimps and crabs in China (中国的虾蟹). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [10] | Stepine CA, Taylor CD, Dabrowska KA (2002) Genetic variability and phylogeographical patterns of a nonindigenous species invasion: a comparison of exotic vs. native zebra and quagga mussel populations. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 15,314-328. |
| [11] | Wang WM (王卫民) (1999) The exploitation and utilization of red swamp crayfish in China. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica (水生生物学报), 23,375-381. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] |
Yue GH, Wang GL, Zhu BQ, Wang CM, Zhu ZY, Lo LC (2008) Discovery of four natural clones in a crayfish species Procambarus clarkii. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 4,279-282.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [2] | 牛晓锋, 王晓梅, 张研, 赵志鹏, 樊恩源. 鲟鱼分子鉴定方法的整合应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 22034-. |
| [3] | 叶俊伟, 田斌. 中国西南地区重要木本油料植物扁核木的遗传结构及成因[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1629-1637. |
| [4] | 李潮,金锦锦,罗锦桢,王春晖,王俊杰,赵俊. 唐鱼养殖种群与广州附近4个野生种群的遗传关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(4): 474-484. |
| [5] | 翁茁先, 黄佳琼, 张仕豪, 余锴纯, 钟福生, 黄勋和, 张彬. 利用线粒体COI基因揭示中国乌骨鸡遗传多样性和群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(6): 667-676. |
| [6] | 武星彤, 陈璐, 王敏求, 张原, 林雪莹, 李鑫玉, 周宏, 文亚峰. 丹霞梧桐群体遗传结构及其遗传分化[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(11): 1168-1179. |
| [7] | 盛芳, 陈淑英, 田嘉, 李鹏, 秦雪, 罗淑萍, 李疆. 新疆准噶尔山楂不同居群的遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(5): 518-530. |
| [8] | 于少帅, 徐启聪, 林彩丽, 王圣洁, 田国忠. 植原体遗传多样性研究现状与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(2): 205-215. |
| [9] | 薛建华, 姜莉, 马晓林, 邴艳红, 赵思晨, 马克平. 莲品种DNA指纹图谱的构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(1): 3-11. |
| [10] | 何长欢, 周玉, 王利繁, 张立. 尚勇保护区亚洲象种群数量评估和遗传多样性分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(2): 202-209. |
| [11] | 熊敏, 田双, 张志荣, 范邓妹, 张志勇. 华木莲居群遗传结构与保护单元[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(4): 476-484. |
| [12] | 王德元, 彭婕, 陈雅静, 吕国胜, 张小平, 邵剑文. 毛茛叶报春的遗传多样性及遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(5): 601-609. |
| [13] | 文亚峰, KentaroUchiyama, 韩文军, SaneyoshiUeno, 谢伟东, 徐刚标, YoshihikoTsumura. 微卫星标记中的无效等位基因[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(1): 117-126. |
| [14] | 向妮, 肖炎农, 段灿星, 王晓鸣, 朱振东. 利用SSR标记分析茄镰孢豌豆专化型的遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2012, 20(6): 693-702. |
| [15] | 王霞, 王静, 蒋敬虎, 康明. 观光木片断化居群的遗传多样性和交配系统[J]. 生物多样性, 2012, 20(6): 676-684. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()