



生物多样性 ›› 2013, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (6): 723-731. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.09117 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2013.09117
徐刚标1,*( ), 梁艳1, 蒋燚2, 刘雄盛1, 胡尚力1, 肖玉菲1, 郝博搏1
), 梁艳1, 蒋燚2, 刘雄盛1, 胡尚力1, 肖玉菲1, 郝博搏1
收稿日期:2013-05-13
接受日期:2013-09-10
出版日期:2013-11-20
发布日期:2013-12-02
通讯作者:
徐刚标
基金资助:
Gangbiao Xu1,*( ), Yan Liang1, Yan Jiang2, Xiongsheng Liu1, Shangli Hu1, Yufei Xiao1, Bobo Hao1
), Yan Liang1, Yan Jiang2, Xiongsheng Liu1, Shangli Hu1, Yufei Xiao1, Bobo Hao1
Received:2013-05-13
Accepted:2013-09-10
Online:2013-11-20
Published:2013-12-02
Contact:
Xu Gangbiao
摘要:
了解种内遗传变异信息是制定种群遗传多样性保护策略的前提。伯乐树(Bretschneidera sinensis)是古老的单科属孑遗植物, 被列为国家一级保护植物。为了揭示伯乐树天然种群的遗传多样性和遗传结构, 采用7条ISSR引物分析了采自湖南、江西、广东、广西和贵州5个省区15个天然种群的219株个体的样本。结果显示, 伯乐树遗传多样性水平较高, 物种和种群水平上的多态位点百分率(PPB)分别为74.42%和38.06%, Shannon’s表型多样性指数(I)分别为0.3630和0.2081, Nei’s基因多样性指数(He)分别为0.2397和0.1405。种群间遗传分化显著, 基于表型多样性指数和分子方差分析揭示的伯乐树天然种群间遗传分化系数分别为FST = 0.4267、GST = 0.2973。UPGMA聚类表明, 参试的15个天然种群可分为2大组群; Mantel检测发现, 种群间遗传距离与其地理距离存在显著相关性(r = 0.3096, P = 0.008)。基于上述研究结果, 我们认为, 伯乐树濒危原因不是种群遗传进化潜力小, 而是由于生境破坏严重, 以及自身繁殖能力低、适应性差、竞争力弱等生物学特征导致的。建议优先保护遗传多样性较为丰富的阳明山、莽山、乳阳、八面山种群, 并对种群近交衰退开展相应的监测工作。
徐刚标, 梁艳, 蒋燚, 刘雄盛, 胡尚力, 肖玉菲, 郝博搏 (2013) 伯乐树种群遗传多样性及遗传结构. 生物多样性, 21, 723-731. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.09117.
Gangbiao Xu,Yan Liang,Yan Jiang,Xiongsheng Liu,Shangli Hu,Yufei Xiao,Bobo Hao (2013) Genetic diversity and population structure of Bretschneidera sinensis, an endangered species. Biodiversity Science, 21, 723-731. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.09117.
| 种群 Population | 位置 Location | 经纬度 Latitude and longitude | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 株数 Sample size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YMS | 湖南阳明山省级自然保护区 Yangmingshan Provincial Nature Reserve, Hunan | 26º07′ N, 111º50′ E | 1,390 | 22 |
| MS | 湖南莽山国家级自然保护区 Mangshan National Nature Reserve, Hunan | 24º58′ N, 112º51′ E | 1,230 | 23 |
| SHS | 湖南舜皇山国家级自然保护区 Shunhuangshan National Nature Reserve, Hunan | 26º35′ N, 110º00′ E | 950 | 22 |
| BMS | 湖南八面山国家级自然保护区 Bamianshan National Nature Reserve, Hunan | 26º10′ N, 113º39′ E | 1,020 | 15 |
| HS | 湖南黄桑国家级自然保护区 Huangsang National Nature Reserve, Hunan | 26º38′ N, 110º55′ E | 1,180 | 16 |
| LP | 贵州黎平国家森林公园 Liping National Forest Park, Guizhou | 25º42′ N, 109º13′ E | 500 | 14 |
| DY | 广西大瑶山国家级自然保护区 Dayaoshan National Nature Reserve, Guangxi | 24º14′ N, 110º12′ E | 920 | 11 |
| MRS | 广西猫儿山国家级自然保护区 Maoershan National Nature Reserve, Guangxi | 24º25′ N, 111º29′ E | 800 | 10 |
| HP | 广西花坪国家级自然保护区 Huaping National Nature Reserve, Guangxi | 25º18′ N, 110º53′ E | 1,070 | 5 |
| TX | 广东田心省级自然保护区 Tianxin Provincial Nature Reserve, Guangdong | 25°01′ N, 112°30′ E | 970 | 15 |
| DDS | 广东南岭国家级自然保护区大东山管理处 Dadongshan Administration Bureau of the Nanling National Nature Reserve, Guangdong | 24°38′ N, 113°12′ E | 950 | 16 |
| RY | 广东南岭国家级自然保护区乳阳管理处 Rurang Administration Bureau of the Nanling National Nature Reserve, Guangdong | 24°45′ N, 112°53′ E | 1,000 | 21 |
| JGS | 江西井冈山国家级自然保护区 Jinggangshan National Nature Reserve, Jiangxi | 26°26′ N, 114°15′ E | 450 | 14 |
| NKS | 广东南昆山省级自然保护区 Nankunshan Provincial Nature Reserve, Guangdong | 23°40′ N, 113°50′ E | 600 | 10 |
| JLS | 江西九连山国家级自然保护区 Jiulianshan National Nature Reserve, Jiangxi | 24°33′ N, 114°28′ E | 580 | 5 |
表1 伯乐树种群采样信息及样本量
Table 1 Sample locations and sample size of Bretschneidera sinensis populations
| 种群 Population | 位置 Location | 经纬度 Latitude and longitude | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 株数 Sample size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YMS | 湖南阳明山省级自然保护区 Yangmingshan Provincial Nature Reserve, Hunan | 26º07′ N, 111º50′ E | 1,390 | 22 |
| MS | 湖南莽山国家级自然保护区 Mangshan National Nature Reserve, Hunan | 24º58′ N, 112º51′ E | 1,230 | 23 |
| SHS | 湖南舜皇山国家级自然保护区 Shunhuangshan National Nature Reserve, Hunan | 26º35′ N, 110º00′ E | 950 | 22 |
| BMS | 湖南八面山国家级自然保护区 Bamianshan National Nature Reserve, Hunan | 26º10′ N, 113º39′ E | 1,020 | 15 |
| HS | 湖南黄桑国家级自然保护区 Huangsang National Nature Reserve, Hunan | 26º38′ N, 110º55′ E | 1,180 | 16 |
| LP | 贵州黎平国家森林公园 Liping National Forest Park, Guizhou | 25º42′ N, 109º13′ E | 500 | 14 |
| DY | 广西大瑶山国家级自然保护区 Dayaoshan National Nature Reserve, Guangxi | 24º14′ N, 110º12′ E | 920 | 11 |
| MRS | 广西猫儿山国家级自然保护区 Maoershan National Nature Reserve, Guangxi | 24º25′ N, 111º29′ E | 800 | 10 |
| HP | 广西花坪国家级自然保护区 Huaping National Nature Reserve, Guangxi | 25º18′ N, 110º53′ E | 1,070 | 5 |
| TX | 广东田心省级自然保护区 Tianxin Provincial Nature Reserve, Guangdong | 25°01′ N, 112°30′ E | 970 | 15 |
| DDS | 广东南岭国家级自然保护区大东山管理处 Dadongshan Administration Bureau of the Nanling National Nature Reserve, Guangdong | 24°38′ N, 113°12′ E | 950 | 16 |
| RY | 广东南岭国家级自然保护区乳阳管理处 Rurang Administration Bureau of the Nanling National Nature Reserve, Guangdong | 24°45′ N, 112°53′ E | 1,000 | 21 |
| JGS | 江西井冈山国家级自然保护区 Jinggangshan National Nature Reserve, Jiangxi | 26°26′ N, 114°15′ E | 450 | 14 |
| NKS | 广东南昆山省级自然保护区 Nankunshan Provincial Nature Reserve, Guangdong | 23°40′ N, 113°50′ E | 600 | 10 |
| JLS | 江西九连山国家级自然保护区 Jiulianshan National Nature Reserve, Jiangxi | 24°33′ N, 114°28′ E | 580 | 5 |
| 引物 Primer code | 序列(5′ to 3′) Sequence (5′ to 3′) | 退火温度 Annealing temperature (℃) | 总条带数 Scored bands | 多态条带数 No. of polymorphic bands | 多态条带百分比 % of polymorphic bands |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBC824 | (TC)8G | 51 | 11 | 6 | 54.54 |
| UBC825 | (AC)8T | 52 | 13 | 12 | 92.30 |
| UBC834 | (AG)8YT | 53 | 12 | 11 | 91.66 |
| UBC836 | (AG)8YA | 52 | 11 | 8 | 72.72 |
| UBC843 | (CT)8RA | 53 | 8 | 4 | 50.00 |
| UBC844 | (CT)8RC | 52 | 16 | 12 | 75.00 |
| UBC872 | (GATA)4 | 40 | 15 | 11 | 73.33 |
| 平均 Mean | 12 | 9 | 72.80 | ||
| 物种 Species level | 86 | 64 | 74.42 |
表2 ISSR-PCR引物及扩增结果
Table 2 Primers and their amplification polymorphism of amplified bands
| 引物 Primer code | 序列(5′ to 3′) Sequence (5′ to 3′) | 退火温度 Annealing temperature (℃) | 总条带数 Scored bands | 多态条带数 No. of polymorphic bands | 多态条带百分比 % of polymorphic bands |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBC824 | (TC)8G | 51 | 11 | 6 | 54.54 |
| UBC825 | (AC)8T | 52 | 13 | 12 | 92.30 |
| UBC834 | (AG)8YT | 53 | 12 | 11 | 91.66 |
| UBC836 | (AG)8YA | 52 | 11 | 8 | 72.72 |
| UBC843 | (CT)8RA | 53 | 8 | 4 | 50.00 |
| UBC844 | (CT)8RC | 52 | 16 | 12 | 75.00 |
| UBC872 | (GATA)4 | 40 | 15 | 11 | 73.33 |
| 平均 Mean | 12 | 9 | 72.80 | ||
| 物种 Species level | 86 | 64 | 74.42 |
| 种群 Population | Shannon表型多样性指数 Shannon's phenotypic diversity index | I | PPB (%) | He | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBC824 | UBC825 | UBC834 | UBC836 | UBC843 | UBC844 | UBC872 | ||||
| 阳明山 YMS | 0.1411 | 0.5048 | 0.3045 | 0.3181 | 0.2545 | 0.3374 | 0.2520 | 0.3079 | 53.49 | 0.2057 |
| 莽山 MS | 0.0955 | 0.5595 | 0.2976 | 0.2004 | 0.0700 | 0.3008 | 0.1728 | 0.2566 | 45.35 | 0.1742 |
| 舜皇山 SHS | 0.0843 | 0.4068 | 0.3353 | 0.1152 | 0.2191 | 0.2371 | 0.2288 | 0.2382 | 43.02 | 0.1608 |
| 八面山 BMS | 0.1678 | 0.2706 | 0.3439 | 0.2200 | 0.1838 | 0.3210 | 0.2119 | 0.2522 | 46.51 | 0.1698 |
| 黄桑 HS | 0.2377 | 0.2266 | 0.2901 | 0.1870 | 0.1258 | 0.1903 | 0.2378 | 0.2176 | 38.37 | 0.1486 |
| 黎平 LP | 0.1241 | 0.2029 | 0.3086 | 0.2841 | 0.1512 | 0.2671 | 0.0860 | 0.2047 | 37.21 | 0.1373 |
| 大瑶山 DY | 0.1699 | 0.1481 | 0.0908 | 0.1573 | 0.0522 | 0.1815 | 0.1051 | 0.1339 | 26.74 | 0.0881 |
| 猫儿山 MRS | 0.0625 | 0.1420 | 0.0919 | 0.1948 | 0.0920 | 0.1922 | 0.0940 | 0.1279 | 26.74 | 0.0834 |
| 花坪 HP | 0.1110 | 0.1518 | 0.0562 | 0.0792 | 0.1527 | 0.0955 | 0.0581 | 0.0972 | 18.60 | 0.0644 |
| 田心 TX | 0.1752 | 0.2798 | 0.2685 | 0.2125 | 0.1202 | 0.3412 | 0.1671 | 0.2331 | 41.86 | 0.1578 |
| 大东山 DDS | 0.2163 | 0.2111 | 0.2097 | 0.2226 | 0.1111 | 0.3094 | 0.1819 | 0.2170 | 39.53 | 0.1466 |
| 乳阳 RY | 0.2650 | 0.2446 | 0.2693 | 0.2859 | 0.1311 | 0.2660 | 0.1468 | 0.2323 | 45.35 | 0.1538 |
| 井冈山 JGS | 0.2127 | 0.1014 | 0.2787 | 0.2018 | 0.0539 | 0.2452 | 0.1651 | 0.1867 | 36.05 | 0.1255 |
| 南昆山 NKS | 0.0856 | 0.3194 | 0.1156 | 0.2362 | 0.1973 | 0.3532 | 0.2950 | 0.2411 | 41.86 | 0.1641 |
| 九连山 JLS | 0.0600 | 0.2047 | 0.1377 | 0.3304 | 0.1644 | 0.1567 | 0.2223 | 0.1833 | 30.23 | 0.1269 |
| 平均 Mean | 0.1472 | 0.2650 | 0.2266 | 0.2134 | 0.1386 | 0.2522 | 0.1750 | 0.2081 | 38.06 | 0.1405 |
| 物种 Species level | 0.2622 | 0.4607 | 0.3942 | 0.3190 | 0.2279 | 0.4369 | 0.3528 | 0.3630 | 74.42 | 0.2397 |
表3 伯乐树15个种群的遗传多样性参数的估算
Table 3 Estimates of genetic diversity within 15 Bretschneidera sinensis populations
| 种群 Population | Shannon表型多样性指数 Shannon's phenotypic diversity index | I | PPB (%) | He | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBC824 | UBC825 | UBC834 | UBC836 | UBC843 | UBC844 | UBC872 | ||||
| 阳明山 YMS | 0.1411 | 0.5048 | 0.3045 | 0.3181 | 0.2545 | 0.3374 | 0.2520 | 0.3079 | 53.49 | 0.2057 |
| 莽山 MS | 0.0955 | 0.5595 | 0.2976 | 0.2004 | 0.0700 | 0.3008 | 0.1728 | 0.2566 | 45.35 | 0.1742 |
| 舜皇山 SHS | 0.0843 | 0.4068 | 0.3353 | 0.1152 | 0.2191 | 0.2371 | 0.2288 | 0.2382 | 43.02 | 0.1608 |
| 八面山 BMS | 0.1678 | 0.2706 | 0.3439 | 0.2200 | 0.1838 | 0.3210 | 0.2119 | 0.2522 | 46.51 | 0.1698 |
| 黄桑 HS | 0.2377 | 0.2266 | 0.2901 | 0.1870 | 0.1258 | 0.1903 | 0.2378 | 0.2176 | 38.37 | 0.1486 |
| 黎平 LP | 0.1241 | 0.2029 | 0.3086 | 0.2841 | 0.1512 | 0.2671 | 0.0860 | 0.2047 | 37.21 | 0.1373 |
| 大瑶山 DY | 0.1699 | 0.1481 | 0.0908 | 0.1573 | 0.0522 | 0.1815 | 0.1051 | 0.1339 | 26.74 | 0.0881 |
| 猫儿山 MRS | 0.0625 | 0.1420 | 0.0919 | 0.1948 | 0.0920 | 0.1922 | 0.0940 | 0.1279 | 26.74 | 0.0834 |
| 花坪 HP | 0.1110 | 0.1518 | 0.0562 | 0.0792 | 0.1527 | 0.0955 | 0.0581 | 0.0972 | 18.60 | 0.0644 |
| 田心 TX | 0.1752 | 0.2798 | 0.2685 | 0.2125 | 0.1202 | 0.3412 | 0.1671 | 0.2331 | 41.86 | 0.1578 |
| 大东山 DDS | 0.2163 | 0.2111 | 0.2097 | 0.2226 | 0.1111 | 0.3094 | 0.1819 | 0.2170 | 39.53 | 0.1466 |
| 乳阳 RY | 0.2650 | 0.2446 | 0.2693 | 0.2859 | 0.1311 | 0.2660 | 0.1468 | 0.2323 | 45.35 | 0.1538 |
| 井冈山 JGS | 0.2127 | 0.1014 | 0.2787 | 0.2018 | 0.0539 | 0.2452 | 0.1651 | 0.1867 | 36.05 | 0.1255 |
| 南昆山 NKS | 0.0856 | 0.3194 | 0.1156 | 0.2362 | 0.1973 | 0.3532 | 0.2950 | 0.2411 | 41.86 | 0.1641 |
| 九连山 JLS | 0.0600 | 0.2047 | 0.1377 | 0.3304 | 0.1644 | 0.1567 | 0.2223 | 0.1833 | 30.23 | 0.1269 |
| 平均 Mean | 0.1472 | 0.2650 | 0.2266 | 0.2134 | 0.1386 | 0.2522 | 0.1750 | 0.2081 | 38.06 | 0.1405 |
| 物种 Species level | 0.2622 | 0.4607 | 0.3942 | 0.3190 | 0.2279 | 0.4369 | 0.3528 | 0.3630 | 74.42 | 0.2397 |
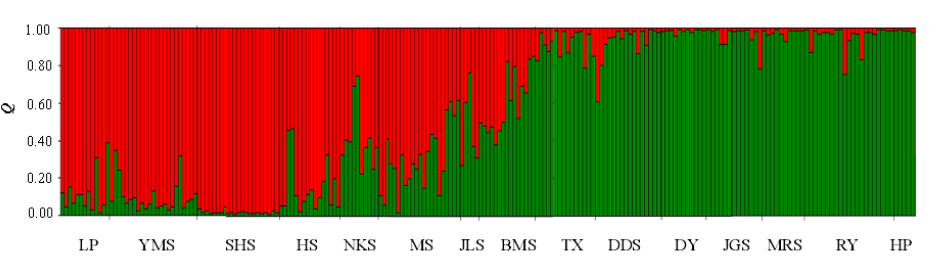
图1 伯乐树15个种群219株个体的遗传结构(Q值为个体归属各组群的比例。种群代号见表1)
Fig. 1 Genetic structure of 219 individuals from 15 Bretschneidera sinensis populations. The Q value is the proportion of each individual belonging to each population genetic cluster. Population codes see Table 1.
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 均方和 Sum of squares | 方差组分 Variance components | 变异百分比 % of variation | 遗传分化系数(GST) Genetic differentiation index | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种群间 Among populations | 14 | 685.9610 | 2.9145 | 29.73 | 0.2973 | <0.001 |
| 种群内 Within populations | 204 | 1,405.0889 | 6.8877 | 70.27 | <0.001 | |
| 总和 Total | 218 | 2,091.0501 | 9.8022 |
表4 伯乐树天然种群的分子方差分析
Table 4 Analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) of 15 natural populations of Bretschneidera sinensis
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 均方和 Sum of squares | 方差组分 Variance components | 变异百分比 % of variation | 遗传分化系数(GST) Genetic differentiation index | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种群间 Among populations | 14 | 685.9610 | 2.9145 | 29.73 | 0.2973 | <0.001 |
| 种群内 Within populations | 204 | 1,405.0889 | 6.8877 | 70.27 | <0.001 | |
| 总和 Total | 218 | 2,091.0501 | 9.8022 |
| 种群 Population | 黎平 LP | 阳明山YMS | 莽山 MS | 舜皇山SHS | 田心 TX | 大东山DDS | 八面山BMS | 大瑶山DY | 井冈山JGS | 猫儿山MRS | 黄桑 HS | 乳阳 RY | 花坪 HP | 南昆山NKS | 九连山JLS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黎平 LP | 292 | 397 | 194 | 416 | 443 | 480 | 240 | 507 | 127 | 106 | 342 | 138 | 554 | 574 | |
| 阳明山 YMS | 0.3157 | 152 | 100 | 126 | 210 | 198 | 289 | 228 | 160 | 189 | 170 | 200 | 331 | 312 | |
| 莽山 MS | 0.2752 | 0.2443 | 240 | 55 | 47 | 155 | 291 | 223 | 275 | 325 | 40 | 267 | 180 | 170 | |
| 舜皇山 SHS | 0.3674 | 0.2600 | 0.3593 | 204 | 289 | 283 | 267 | 308 | 92 | 95 | 250 | 150 | 413 | 398 | |
| 田心 TX | 0.3787 | 0.2611 | 0.2713 | 0.3231 | 75 | 167 | 270 | 235 | 236 | 300 | 75 | 245 | 195 | 204 | |
| 大东山 DDS | 0.3793 | 0.2683 | 0.2219 | 0.3751 | 0.3922 | 162 | 321 | 228 | 322 | 364 | 29 | 315 | 124 | 135 | |
| 八面山 BMS | 0.3439 | 0.1488 | 0.2457 | 0.3004 | 0.1349 | 0.1030 | 435 | 66 | 341 | 370 | 154 | 378 | 261 | 165 | |
| 大瑶山 DY | 0.4976 | 0.3949 | 0.3849 | 0.4525 | 0.2516 | 0.2201 | 0.2881 | 483 | 194 | 274 | 312 | 135 | 377 | 450 | |
| 井冈山 JGS | 0.4056 | 0.3065 | 0.2841 | 0.4081 | 0.1065 | 0.1145 | 0.1686 | 0.2216 | 380 | 401 | 212 | 422 | 319 | 215 | |
| 猫儿山 MRS | 0.4460 | 0.3387 | 0.3608 | 0.4204 | 0.2200 | 0.2251 | 0.2681 | 0.0563 | 0.1429 | 79 | 284 | 56 | 422 | 425 | |
| 黄桑 HS | 0.4253 | 0.2805 | 0.3683 | 0.2019 | 0.3109 | 0.3125 | 0.2562 | 0.4188 | 0.3995 | 0.3762 | 356 | 119 | 488 | 473 | |
| 乳阳 RY | 0.3940 | 0.3149 | 0.3098 | 0.3833 | 0.0716 | 0.0922 | 0.2160 | 0.2572 | 0.1176 | 0.2027 | 0.3423 | 291 | 175 | 116 | |
| 花坪 HP | 0.4857 | 0.3426 | 0.3938 | 0.4311 | 0.2046 | 0.2309 | 0.2798 | 0.1641 | 0.1762 | 0.0741 | 0.3836 | 0.1680 | 419 | 440 | |
| 南昆山 NKS | 0.3319 | 0.2463 | 0.2092 | 0.3185 | 0.1825 | 0.1652 | 0.1899 | 0.3955 | 0.3146 | 0.3802 | 0.3385 | 0.2765 | 0.3885 | 136 | |
| 九连山 JLS | 0.3441 | 0.2508 | 0.2588 | 0.3268 | 0.1940 | 0.2088 | 0.2469 | 0.4163 | 0.3212 | 0.3721 | 0.3661 | 0.2954 | 0.4030 | 0.0391 |
表5 伯乐树天然种群间遗传分化系数(ΦST)估算值(对角线下方)与地理距离(km, 对角线上方)的相关性
Table 5 Pairwise estimated values of genetic differentiation coefficient (ΦST) (below diagonal) and geographic distance (km, above diagonal) among natural populations of Bretschneidera sinensis
| 种群 Population | 黎平 LP | 阳明山YMS | 莽山 MS | 舜皇山SHS | 田心 TX | 大东山DDS | 八面山BMS | 大瑶山DY | 井冈山JGS | 猫儿山MRS | 黄桑 HS | 乳阳 RY | 花坪 HP | 南昆山NKS | 九连山JLS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黎平 LP | 292 | 397 | 194 | 416 | 443 | 480 | 240 | 507 | 127 | 106 | 342 | 138 | 554 | 574 | |
| 阳明山 YMS | 0.3157 | 152 | 100 | 126 | 210 | 198 | 289 | 228 | 160 | 189 | 170 | 200 | 331 | 312 | |
| 莽山 MS | 0.2752 | 0.2443 | 240 | 55 | 47 | 155 | 291 | 223 | 275 | 325 | 40 | 267 | 180 | 170 | |
| 舜皇山 SHS | 0.3674 | 0.2600 | 0.3593 | 204 | 289 | 283 | 267 | 308 | 92 | 95 | 250 | 150 | 413 | 398 | |
| 田心 TX | 0.3787 | 0.2611 | 0.2713 | 0.3231 | 75 | 167 | 270 | 235 | 236 | 300 | 75 | 245 | 195 | 204 | |
| 大东山 DDS | 0.3793 | 0.2683 | 0.2219 | 0.3751 | 0.3922 | 162 | 321 | 228 | 322 | 364 | 29 | 315 | 124 | 135 | |
| 八面山 BMS | 0.3439 | 0.1488 | 0.2457 | 0.3004 | 0.1349 | 0.1030 | 435 | 66 | 341 | 370 | 154 | 378 | 261 | 165 | |
| 大瑶山 DY | 0.4976 | 0.3949 | 0.3849 | 0.4525 | 0.2516 | 0.2201 | 0.2881 | 483 | 194 | 274 | 312 | 135 | 377 | 450 | |
| 井冈山 JGS | 0.4056 | 0.3065 | 0.2841 | 0.4081 | 0.1065 | 0.1145 | 0.1686 | 0.2216 | 380 | 401 | 212 | 422 | 319 | 215 | |
| 猫儿山 MRS | 0.4460 | 0.3387 | 0.3608 | 0.4204 | 0.2200 | 0.2251 | 0.2681 | 0.0563 | 0.1429 | 79 | 284 | 56 | 422 | 425 | |
| 黄桑 HS | 0.4253 | 0.2805 | 0.3683 | 0.2019 | 0.3109 | 0.3125 | 0.2562 | 0.4188 | 0.3995 | 0.3762 | 356 | 119 | 488 | 473 | |
| 乳阳 RY | 0.3940 | 0.3149 | 0.3098 | 0.3833 | 0.0716 | 0.0922 | 0.2160 | 0.2572 | 0.1176 | 0.2027 | 0.3423 | 291 | 175 | 116 | |
| 花坪 HP | 0.4857 | 0.3426 | 0.3938 | 0.4311 | 0.2046 | 0.2309 | 0.2798 | 0.1641 | 0.1762 | 0.0741 | 0.3836 | 0.1680 | 419 | 440 | |
| 南昆山 NKS | 0.3319 | 0.2463 | 0.2092 | 0.3185 | 0.1825 | 0.1652 | 0.1899 | 0.3955 | 0.3146 | 0.3802 | 0.3385 | 0.2765 | 0.3885 | 136 | |
| 九连山 JLS | 0.3441 | 0.2508 | 0.2588 | 0.3268 | 0.1940 | 0.2088 | 0.2469 | 0.4163 | 0.3212 | 0.3721 | 0.3661 | 0.2954 | 0.4030 | 0.0391 |
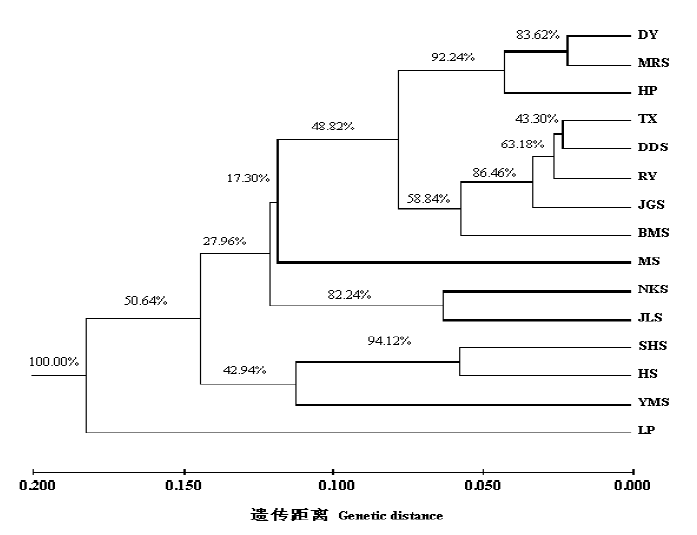
图2 基于Nei’s遗传距离的15个伯乐树种群的UPGMA聚类(种群代号见表1)
Fig. 2 Dendrogram of UPGMA illustrating the genetic relationships among 15 populations of Bretschneidera sinensis based on Nei’s distance calculated. Population codes see Table 1.
| 1 | Banerjee S, Das M, Mir RR, Kujdu A, Topdar N, Sarkar D, Sinha MK, Balyan HS, Gupta PK (2012) Assessment of genetic diversity and population structure in a selected germplasm collection of 292 Jute genotypes by microsatellite (SSR) markers.Molecular Plant Breeding, 3(2), 11-26. |
| 2 | Chen J (陈娇), Wang XR (王小蓉), Tang HR (汤浩茹), Chen T (陈涛), Huang XJ (黄晓姣), Liang QB (梁勤彪) (2013) Assessment of genetic diversity and population genetic structure in wild Chinese cherry from Sichuan Province using SSR markers.Acta Horticulturae Sinica(园艺学报), 40, 333-340. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 3 | Chen T (陈涛), Chang HT (张宏达) (1994) The floristic geography of Nanling Mountain Range, China. I. Floristic composition and characteristics.Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany(热带亚热带植物学报), 2, 10-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 4 | Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study.Molecular Ecology, 14, 2611-2620. |
| 5 | Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2006) Arlequin (version 3. 1): an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis.Evolutionary Bioinformatics Online, 1, 47-50. |
| 6 | Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2007) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: dominant markers and null alleles.Molecular Ecology Notes, 7, 574-578. |
| 7 | Fu LK (傅立国), Jin JM (金鉴明) (1992) China Plant Red Data Book: Rare and Endangered Plants, Volume 1 (中国植物红皮书——稀有濒危植物, 第一册), pp. 194-195. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 8 | Glémin S, Bazin E, Cliarleswortli D (2006) Impact of mating systems on patterns of sequence polymorphism in flowering plants.Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 273, 3011-3019. |
| 9 | Guan BC, Song GR, Ge G (2012) Sixteen microsatellite markers developed from Bretschneidera sinensis.Conservation Genetics Resources, 4, 473-475. |
| 10 | He JS (何敬胜), Li ZZ (李作洲), Huang HW (黄宏文) (2005) Allozymic genetic diversity in Manglietia patungensis, an endangered species, and its conservation strategies.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 13, 27-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 11 | Liang Y (梁艳), Xu GB (徐刚标), Zhang HP (张合平), Wu XQ (吴雪琴), Shen XB (申响保), Wang AY (王爱云) (2012) Genetic diversity of natural and planted populations of Bretschneidera sinensis from Nanling region.Scientia Silvae Sinicae(林业科学), 48(12), 45-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 12 | Nei M (1987) Molecular Evolutionary Genetics, pp. 187-192. Columbia University Press, New York. |
| 13 | Nybom H (2004) Comparison of different nuclear DNA markers for estimating intraspecific genetic diversity in plants.Molecular Ecology, 13, 1143-1156. |
| 14 | Nybom H, Bartish IV (2000) Effects of life history traits and sampling strategies on genetic diversity estimates obtained with RAPD markers in plants.Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 3, 93-114. |
| 15 | Peng SS (彭沙沙), Huang HH (黄华宏), Tong ZK (童再康), Zhou HJ (周厚君), Shi J (时剑), Yu GM (余国民), Luo WJ (骆文坚) (2011) Genetic diversity of endangered plant Bretschneidera sinensis.Journal of Plant Genetic Resources(植物遗传资源学报), 12, 362-367. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 16 | Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data.Genetics, 155, 945-959. |
| 17 | Qiao Q (乔琦), Chen HF (陈红锋), Xing FW (邢福武) (2009) Seed category and storage of Bretschneidera sinensis, a rare endemic plant in China.Seed(种子), 28(12), 25-27. |
| 18 | Qiao Q (乔琦), Xing FW (邢福武), Chen HF (陈红锋), Wang MN (王美娜) (2011a) Research progress and direction in Bretschneidera sinensis, a rare endemic plant in China.China Wild Plant Resources(中国野生植物资源), 30(3), 4-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 19 | Qiao Q (乔琦), Qin XS (秦新生), Xing FW (邢福武), Chen HF (陈红锋), Liu DM (刘东明) (2011b) Death causes and conservation strategies of the annual regenerated seedlings of a rare plant,Bretschneidera sinensis. Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 31, 4709-4716. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 20 | Qiao Q, Chen HF, Xing FW, Wang FG, Zhong WC, Wen XY, Hou XG (2012) Pollination ecology of Bretschneidera sinensis (Hemsley), a rare and endangered tree in China.Pakistan Journal of Botany, 44, 1897-1903. |
| 21 | Schnabel A, Nason JD, Hamrick JL (1998) Understanding the population genetic structure of Gleditsia triacanthos L.: seed dispersal and variation in female reproductive success.Molecular Ecology, 7, 819-832. |
| 22 | Sork VL, Smouse PE (2006) Genetic analysis of landscape connectivity in tree populations.Landscape Ecology, 21, 821-836. |
| 23 | Souza GB, Souza VA, Lima PS (2013) Molecular characteri- zation of Platonia insignis Mart. (‘‘Bacurizeiro’’) using inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers.Molecular Biology Reports, 40, 3835-3845. |
| 24 | State Forestry Administration and the Ministry of Agriculture, P. R. C. (国家林业局和农业部) (1999) List of Wild Plants Under State Protection (First Batch) (国家重点保护野生植物名录(第一批)). Decree No. 4. (in Chinese) |
| 25 | Tu Q (涂蔷), Wu T (吴涛), Zhao LC (赵良成), Liu YC (刘羽成), Liu RL (刘仁林), Zhang ZX (张志翔) (2012) Features of leaf appendages of Bretschneidera sinensis in different development stages.Plant Diversity and Resources(植物资源与分类学报), 34, 248-256. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 26 | Wang L (王蕾), Shi S (施诗), Liao WB (廖文波), Chen CQ (陈春泉), Li Z (李贞) (2013) Rare and endangered plants in Mount Jinggangshan region.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 21, 163-169. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 27 | Wang MN (王美娜), Qiao Q (乔琦), Zhang RJ (张荣京), Hu PW (胡普炜), Yang G (杨国), Chen HF (陈红锋) (2011) Studies on the community feature comparison and phylogeography of relic plant Bretschneidera sinensis in Nankun and Daling Mountains, Guangdong Province.Guihaia(广西植物), 31, 789-794. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 28 | Wang S (汪松), Xie Y (解焱) (2004) China Species Red List: Vol. I. (中国物种红色名录 (第一卷)). Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 29 | Wang ZF (王峥峰), Ge XJ (葛学军) (2009) Not only genetic diversity: advances in plant conservation genetics.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 17, 330-339. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 30 | Wright S (1965) The interpretation of population structure by F-statistics with special regard to systems of mating.Evolution, 19, 395-420. |
| 31 | Xing FW (邢福武) (2005) Rare and Endangered Plants in China (中国的珍稀濒危植物). Hunan Education Press, Changsha. (in Chinese) |
| 32 | Yeh FC, Yang RC, Boyle T (2000) POPGENE version 1. 32, Microsoft Window-based Freeware for Population Genetic Analysis. University of Alberta, Edmonton. |
| 33 | Yoon MY, Moe KT, Kim KY, Rho Y, Kim S, Kim KT, won MK, Chung JW, Park YJ (2012) Genetic diversity and population structure analysis of strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) using SSR markers.Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 15(2), 1-16. |
| 34 | Zhang DY (张大勇), Jiang XH (姜新华) (2001) Mating system evolution, resource allocation, and genetic diversity in plants.Acta Phytoecologica Sinica(植物生态学报), 25, 130-143. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 35 | Zhang JH (张俊红), Huang HH (黄华宏), Tong ZK (童再康), Cheng LJ (程龙军), Liang YL (梁跃龙), Chen YL (陈奕良) (2010) Genetic diversity in six natural populations of Betula luminifera from southern China.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 18, 233-240. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 姚志, 郭军, 金晨钟, 刘勇波. 中国纳入一级保护的极小种群野生植物濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 394-408. |
| [2] | 傅洪拓, 乔慧, 姚建华, 龚永生, 吴滟, 蒋速飞, 熊贻伟. 基于SRAP分子标记的海南沼虾种群遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(2): 145-149. |
| [3] | 潘丽芹, 季华, 陈龙清. 荷叶铁线蕨自然居群的遗传多样性研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2005, 13(2): 122-129. |
| [4] | 罗晓莹, 唐光大, 许涵, 庄雪影, 郑文经, 曾明. 山茶科3种中国特有濒危植物的遗传多样性研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2005, 13(2): 112-121. |
| [5] | 何敬胜, 李作洲, 黄宏文. 濒危物种巴东木莲的等位酶遗传多样性及其保护策略[J]. 生物多样性, 2005, 13(1): 27-35. |
| [6] | 周伟. 云南湿地生态系统鱼类物种濒危机制初探[J]. 生物多样性, 2000, 08(2): 163-168. |
| [7] | 王建波, 陈家宽, 利容千, 何国庆. 长喙毛茛泽泻的生活史特征及濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 1998, 06(3): 167-171. |
| [8] | 林金星, 胡玉熹, 王献溥, 魏令波. 中国特有植物长苞铁杉的生物学特性及其保护[J]. 生物多样性, 1995, 03(3): 147-152. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()