



生物多样性 ›› 2009, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (3): 240-247. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08346 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2009.08346
凌英会1,2, 成月娇1,2,3, 王艳萍1,2,3, 关伟军1,2, 韩建林1,2, 傅宝玲1,2, 赵倩君1,2, 何晓红1,2, 浦亚斌1,2, 马月辉1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2008-12-26
接受日期:2009-03-28
出版日期:2009-05-20
发布日期:2009-05-20
通讯作者:
马月辉
作者简介:*E-mail: yuehui.ma@263.net基金资助:
Yinghui Ling1,2, Yuejiao Cheng1,2,3, Yanping Wang1,2,3, Weijun Guan1,2, Jianlin Han1,2, Baoling Fu1,2, Qianjun Zhao1,2, Xiaohong He1,2, Yabin Pu1,2, Yuehui Ma1,2,*( )
)
Received:2008-12-26
Accepted:2009-03-28
Online:2009-05-20
Published:2009-05-20
Contact:
Yuehui Ma
摘要:
为了调查中国马种的群体遗传分化与遗传结构状况, 本研究应用FAO和ISAG推荐的25对微卫星引物, 结合荧光标记PCR分析技术, 对中国23个马群体和1个英纯血马群体进行了分子遗传学研究。结果表明: 中国地方马群体的遗传多样性比较丰富, 23个中国马群体的等位基因数、多态信息含量和遗传杂合度等都高于英国纯血马。根据群体遗传距离构建的系统进化树, 能够清晰地将英纯血马从中国马中独立出来, 同时可将中国马群体分成不同的支, 基本上与其地理分布格局相符。我们用MVSP软件进行群体遗传分化分析可见, 前三个主成分的三维散点图可以明显地把英纯血马从所有群体中独立出来, 并把中国的马群体分成几个相对独立的支。进一步分析第一、二主成分的二维散点图, 可将中国的马群体分化成南方支系、藏马支系、新疆和青海支系、内蒙古支系及东北支系等5个部分。根据Structure软件分析, 推测中国马群体含有5个潜在的支系, 基本上代表了我国现在主要家马来源的基础遗传支系。这些信息可以为我国现有马种类型的划分与马种资源遗传多样性的保护提供科学依据。
凌英会, 成月娇, 王艳萍, 关伟军, 韩建林, 傅宝玲, 赵倩君, 何晓红, 浦亚斌, 马月辉 (2009) 应用微卫星标记分析23个中国地方马种的遗传多样性. 生物多样性, 17, 240-247. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08346.
Yinghui Ling, Yuejiao Cheng, Yanping Wang, Weijun Guan, Jianlin Han, Baoling Fu, Qianjun Zhao, Xiaohong He, Yabin Pu, Yuehui Ma (2009) Genetic diversity of 23 Chinese indigenous horse breeds revealed by microsatellite markers. Biodiversity Science, 17, 240-247. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08346.
| 代码 Code | 品种名称 Breed name | 样本数 Sample size | 来源地 Locality |
|---|---|---|---|
| MG | 蒙古马 Mongolia horse | 50 | 内蒙古呼伦贝尔市 Hulunbeier City, Inner Mongolia |
| XNH | 锡泥河马 Xinihe horse | 50 | 内蒙古呼伦贝尔市 Hulunbeier City, Inner Mongolia |
| SH | 三河马 Sanhe horse | 31 | 内蒙古呼伦贝尔市 Hulunbeier City, Inner Mongolia |
| HH | 黑河马 Heihe horse | 42 | 黑龙江孙吴县 Sunwu County, Heilongjiang |
| ELC | 鄂伦春马 Elunchun horse | 30 | 黑龙江黑河市 Heihe City, Heilongjiang |
| JL | 吉林马 Jilin horse | 52 | 吉林白城市 Baicheng City, Jilin |
| KZK | 哈萨克马 Hazakh horse | 50 | 新疆新源县 Xinyuan County, Xinjiang |
| YQ | 焉耆马 Yanqi horse | 55 | 新疆焉耆县 Yanqi County, Xinjiang |
| YL | 伊犁马 Yili horse | 60 | 新疆伊犁县 Yili County, Xinjiang |
| DT | 大通马 Datong horse | 56 | 青海祁连县 Qilian County, Qinghai |
| CDM | 柴达木马 Cadamu horse | 33 | 青海都兰县 Dulan County, Qinghai |
| HQ | 河曲马 Hequ horse | 24 | 青海河南县 Henan County, Qinghai |
| YSH | 玉树马 Yushu horse | 50 | 青海玉树市 Yushu City, Qinghai |
| TGL | 西藏草地马 Tibet grassland horse | 61 | 西藏浪卡子县 Langkazi County, Tibet |
| TRV | 西藏河谷马 Tibet valley horse | 52 | 西藏江孜县 Jiangzi County, Tibet |
| JC | 建昌马 Jianchang horse | 52 | 四川布拖县 Butuo County, Sichuan |
| LCH | 利川马 Lichuan horse | 38 | 湖北利川市 Lichuan City, Hubei |
| DL | 大理马 Yunnan horse | 30 | 云南剑川县 Jianchuan County, Yunnan |
| WS | 文山马 Wenshan horse | 36 | 云南文山县 Wenshan County, Yunnan |
| GZ | 贵州马 Guizhou horse | 38 | 贵州安顺市 Anshun City, Guizhou |
| BS | 百色马 Baise horse | 60 | 广西百色县 Baise County, Guangxi |
| DBP | 德保矮马 Debao pony | 66 | 广西德保县 Debao County, Guangxi |
| JJ | 晋江马 Jinjiang horse | 60 | 福建晋江县 Jinjiang County, Fujian |
| THB | 英纯血马 Thoroughbred horse | 30 | 英国 UK |
表1 24个马群体名称、代码、来源和采样信息
Table 1 Name, code, sample size and source region of 24 horse populations
| 代码 Code | 品种名称 Breed name | 样本数 Sample size | 来源地 Locality |
|---|---|---|---|
| MG | 蒙古马 Mongolia horse | 50 | 内蒙古呼伦贝尔市 Hulunbeier City, Inner Mongolia |
| XNH | 锡泥河马 Xinihe horse | 50 | 内蒙古呼伦贝尔市 Hulunbeier City, Inner Mongolia |
| SH | 三河马 Sanhe horse | 31 | 内蒙古呼伦贝尔市 Hulunbeier City, Inner Mongolia |
| HH | 黑河马 Heihe horse | 42 | 黑龙江孙吴县 Sunwu County, Heilongjiang |
| ELC | 鄂伦春马 Elunchun horse | 30 | 黑龙江黑河市 Heihe City, Heilongjiang |
| JL | 吉林马 Jilin horse | 52 | 吉林白城市 Baicheng City, Jilin |
| KZK | 哈萨克马 Hazakh horse | 50 | 新疆新源县 Xinyuan County, Xinjiang |
| YQ | 焉耆马 Yanqi horse | 55 | 新疆焉耆县 Yanqi County, Xinjiang |
| YL | 伊犁马 Yili horse | 60 | 新疆伊犁县 Yili County, Xinjiang |
| DT | 大通马 Datong horse | 56 | 青海祁连县 Qilian County, Qinghai |
| CDM | 柴达木马 Cadamu horse | 33 | 青海都兰县 Dulan County, Qinghai |
| HQ | 河曲马 Hequ horse | 24 | 青海河南县 Henan County, Qinghai |
| YSH | 玉树马 Yushu horse | 50 | 青海玉树市 Yushu City, Qinghai |
| TGL | 西藏草地马 Tibet grassland horse | 61 | 西藏浪卡子县 Langkazi County, Tibet |
| TRV | 西藏河谷马 Tibet valley horse | 52 | 西藏江孜县 Jiangzi County, Tibet |
| JC | 建昌马 Jianchang horse | 52 | 四川布拖县 Butuo County, Sichuan |
| LCH | 利川马 Lichuan horse | 38 | 湖北利川市 Lichuan City, Hubei |
| DL | 大理马 Yunnan horse | 30 | 云南剑川县 Jianchuan County, Yunnan |
| WS | 文山马 Wenshan horse | 36 | 云南文山县 Wenshan County, Yunnan |
| GZ | 贵州马 Guizhou horse | 38 | 贵州安顺市 Anshun City, Guizhou |
| BS | 百色马 Baise horse | 60 | 广西百色县 Baise County, Guangxi |
| DBP | 德保矮马 Debao pony | 66 | 广西德保县 Debao County, Guangxi |
| JJ | 晋江马 Jinjiang horse | 60 | 福建晋江县 Jinjiang County, Fujian |
| THB | 英纯血马 Thoroughbred horse | 30 | 英国 UK |
| 代码 Code | 等位基因差异 Allelic diversity | 群体遗传多样性 Genetic diversity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNA | NEA | Pa | Ho | He | AR | PIC | ||
| 蒙古马 MG | 7.48 | 4.16 | 4 | 0.742 | 0.727 | 6.736 | 0.693 | |
| 锡泥河马 XNH | 7.88 | 4.25 | 0 | 0.723 | 0.746 | 7.081 | 0.712 | |
| 三河马 SH | 7.92 | 4.43 | 0 | 0.745 | 0.751 | 7.549 | 0.718 | |
| 黑河马 HH | 7.96 | 4.38 | 2 | 0.752 | 0.747 | 7.248 | 0.715 | |
| 鄂伦春马 ELC | 6.72 | 3.69 | 1 | 0.683 | 0.698 | 6.453 | 0.659 | |
| 吉林马 JL | 7.80 | 4.41 | 1 | 0.743 | 0.745 | 6.969 | 0.713 | |
| 哈萨克马 KZK | 8.36 | 4.81 | 2 | 0.766 | 0.760 | 7.558 | 0.730 | |
| 焉耆马 YQ | 8.36 | 4.54 | 3 | 0.745 | 0.757 | 7.451 | 0.725 | |
| 伊犁马 YL | 8.40 | 4.61 | 2 | 0.757 | 0.763 | 7.464 | 0.732 | |
| 大通马 DT | 8.32 | 4.48 | 3 | 0.727 | 0.751 | 7.484 | 0.721 | |
| 柴达木马 CDM | 7.36 | 4.56 | 0 | 0.730 | 0.751 | 7.097 | 0.720 | |
| 河曲马 HQ | 6.76 | 4.40 | 0 | 0.755 | 0.730 | 6.760 | 0.695 | |
| 玉树马 YSH | 8.36 | 4.50 | 1 | 0.723 | 0.752 | 7.535 | 0.722 | |
| 西藏草地马 TGL | 8.24 | 4.23 | 3 | 0.739 | 0.745 | 7.295 | 0.713 | |
| 西藏河谷马 TRV | 7.88 | 4.49 | 2 | 0.742 | 0.756 | 7.253 | 0.725 | |
| 建昌马 JC | 7.60 | 4.57 | 1 | 0.729 | 0.761 | 7.025 | 0.731 | |
| 利川马 LCH | 7.72 | 4.62 | 3 | 0.749 | 0.752 | 7.130 | 0.723 | |
| 大理马 DL | 8.43 | 4.82 | 13 | 0.723 | 0.761 | 8.069 | 0.736 | |
| 文山马 WS | 7.84 | 4.42 | 2 | 0.747 | 0.765 | 7.301 | 0.724 | |
| 贵州马 GZ | 7.60 | 4.46 | 0 | 0.755 | 0.745 | 7.057 | 0.713 | |
| 百色马 BS | 8.24 | 4.56 | 2 | 0.734 | 0.749 | 7.364 | 0.721 | |
| 德保矮马 DBP | 8.80 | 4.66 | 6 | 0.737 | 0.755 | 7.602 | 0.728 | |
| 晋江马 JJ | 7.92 | 4.04 | 2 | 0.732 | 0.731 | 6.800 | 0.697 | |
| 英纯血马 THB | 4.68 | 3.07 | 0 | 0.667 | 0.632 | 4.551 | 0.577 | |
表2 24个马群体的遗传变异
Table 2 Basic genetic variation information of the 24 horse studied populations
| 代码 Code | 等位基因差异 Allelic diversity | 群体遗传多样性 Genetic diversity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNA | NEA | Pa | Ho | He | AR | PIC | ||
| 蒙古马 MG | 7.48 | 4.16 | 4 | 0.742 | 0.727 | 6.736 | 0.693 | |
| 锡泥河马 XNH | 7.88 | 4.25 | 0 | 0.723 | 0.746 | 7.081 | 0.712 | |
| 三河马 SH | 7.92 | 4.43 | 0 | 0.745 | 0.751 | 7.549 | 0.718 | |
| 黑河马 HH | 7.96 | 4.38 | 2 | 0.752 | 0.747 | 7.248 | 0.715 | |
| 鄂伦春马 ELC | 6.72 | 3.69 | 1 | 0.683 | 0.698 | 6.453 | 0.659 | |
| 吉林马 JL | 7.80 | 4.41 | 1 | 0.743 | 0.745 | 6.969 | 0.713 | |
| 哈萨克马 KZK | 8.36 | 4.81 | 2 | 0.766 | 0.760 | 7.558 | 0.730 | |
| 焉耆马 YQ | 8.36 | 4.54 | 3 | 0.745 | 0.757 | 7.451 | 0.725 | |
| 伊犁马 YL | 8.40 | 4.61 | 2 | 0.757 | 0.763 | 7.464 | 0.732 | |
| 大通马 DT | 8.32 | 4.48 | 3 | 0.727 | 0.751 | 7.484 | 0.721 | |
| 柴达木马 CDM | 7.36 | 4.56 | 0 | 0.730 | 0.751 | 7.097 | 0.720 | |
| 河曲马 HQ | 6.76 | 4.40 | 0 | 0.755 | 0.730 | 6.760 | 0.695 | |
| 玉树马 YSH | 8.36 | 4.50 | 1 | 0.723 | 0.752 | 7.535 | 0.722 | |
| 西藏草地马 TGL | 8.24 | 4.23 | 3 | 0.739 | 0.745 | 7.295 | 0.713 | |
| 西藏河谷马 TRV | 7.88 | 4.49 | 2 | 0.742 | 0.756 | 7.253 | 0.725 | |
| 建昌马 JC | 7.60 | 4.57 | 1 | 0.729 | 0.761 | 7.025 | 0.731 | |
| 利川马 LCH | 7.72 | 4.62 | 3 | 0.749 | 0.752 | 7.130 | 0.723 | |
| 大理马 DL | 8.43 | 4.82 | 13 | 0.723 | 0.761 | 8.069 | 0.736 | |
| 文山马 WS | 7.84 | 4.42 | 2 | 0.747 | 0.765 | 7.301 | 0.724 | |
| 贵州马 GZ | 7.60 | 4.46 | 0 | 0.755 | 0.745 | 7.057 | 0.713 | |
| 百色马 BS | 8.24 | 4.56 | 2 | 0.734 | 0.749 | 7.364 | 0.721 | |
| 德保矮马 DBP | 8.80 | 4.66 | 6 | 0.737 | 0.755 | 7.602 | 0.728 | |
| 晋江马 JJ | 7.92 | 4.04 | 2 | 0.732 | 0.731 | 6.800 | 0.697 | |
| 英纯血马 THB | 4.68 | 3.07 | 0 | 0.667 | 0.632 | 4.551 | 0.577 | |
| 基因座位 Locus | 所有中国群体 All Chinese horse populations | 群体 Population | 所有位点Fis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fit | Fst | Fis | All lociFis | ||
| HMS06 | 0.035** | 0.031*** | 0.004 | MG | -0.011 |
| HMS07 | 0.040** | 0.014*** | 0.026* | XNH | 0.041** |
| HTG07 | 0.028 | 0.026*** | 0.002 | SH | 0.005 |
| HMS03 | 0.080*** | 0.028*** | 0.054*** | HH | 0.039* |
| COR082 | 0.063*** | 0.031*** | 0.033*** | ELC | 0.012 |
| HTG04 | 0.035* | 0.024*** | 0.012 | JL | -0.091 |
| LEX54 | -0.016 | 0.024*** | -0.041 | KZK | 0.003 |
| ASB17 | 0.066*** | 0.021*** | 0.047*** | YQ | 0.026* |
| SGCV28 | 0.031* | 0.040*** | -0.010 | YL | 0.016 |
| HMS02 | 0.037** | 0.019*** | 0.019 | DT | 0.041** |
| COR022 | 0.014 | 0.015*** | -0.002 | CDM | 0.043** |
| HMS45 | -0.014 | 0.036*** | -0.052 | HQ | -0.013 |
| LEX34 | 0.018 | 0.027*** | -0.010 | YSH | 0.049*** |
| COR071 | 0.064*** | 0.019*** | 0.045*** | TGL | 0.016 |
| LEX73 | 0.064*** | 0.033*** | 0.033 | TRV | 0.029 |
| HTG10 | 0.109*** | 0.019*** | 0.091*** | JC | 0.051*** |
| COR007 | 0.021 | 0.026*** | -0.006 | LCH | 0.017 |
| LEX63 | 0.123*** | 0.026*** | 0.099*** | DL | 0.067*** |
| ASB23 | 0.045** | 0.031*** | 0.014 | WS | 0.024 |
| COR018 | 0.044** | 0.024*** | 0.021 | GZ | 0.001 |
| VHL20 | 0.046*** | 0.023*** | 0.024* | BS | 0.029 |
| AHT04 | 0.025* | 0.015*** | 0.010 | DBP | 0.031** |
| UCDEQ4 | 0.044** | 0.039*** | 0.005 | JJ | 0.007 |
| HTG06 | -0.033 | 0.018*** | -0.052 | ||
| ASB02 | 0.080*** | 0.020*** | 0.061*** | ||
| 总计 Total | 0.045*** | 0.024*** | 0.021*** | ||
表3 23个中国马群体25对微卫星座位的F-统计检验
Table 3 F-statistics for 23 Chinese horse populations at 25 microsatellite loci
| 基因座位 Locus | 所有中国群体 All Chinese horse populations | 群体 Population | 所有位点Fis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fit | Fst | Fis | All lociFis | ||
| HMS06 | 0.035** | 0.031*** | 0.004 | MG | -0.011 |
| HMS07 | 0.040** | 0.014*** | 0.026* | XNH | 0.041** |
| HTG07 | 0.028 | 0.026*** | 0.002 | SH | 0.005 |
| HMS03 | 0.080*** | 0.028*** | 0.054*** | HH | 0.039* |
| COR082 | 0.063*** | 0.031*** | 0.033*** | ELC | 0.012 |
| HTG04 | 0.035* | 0.024*** | 0.012 | JL | -0.091 |
| LEX54 | -0.016 | 0.024*** | -0.041 | KZK | 0.003 |
| ASB17 | 0.066*** | 0.021*** | 0.047*** | YQ | 0.026* |
| SGCV28 | 0.031* | 0.040*** | -0.010 | YL | 0.016 |
| HMS02 | 0.037** | 0.019*** | 0.019 | DT | 0.041** |
| COR022 | 0.014 | 0.015*** | -0.002 | CDM | 0.043** |
| HMS45 | -0.014 | 0.036*** | -0.052 | HQ | -0.013 |
| LEX34 | 0.018 | 0.027*** | -0.010 | YSH | 0.049*** |
| COR071 | 0.064*** | 0.019*** | 0.045*** | TGL | 0.016 |
| LEX73 | 0.064*** | 0.033*** | 0.033 | TRV | 0.029 |
| HTG10 | 0.109*** | 0.019*** | 0.091*** | JC | 0.051*** |
| COR007 | 0.021 | 0.026*** | -0.006 | LCH | 0.017 |
| LEX63 | 0.123*** | 0.026*** | 0.099*** | DL | 0.067*** |
| ASB23 | 0.045** | 0.031*** | 0.014 | WS | 0.024 |
| COR018 | 0.044** | 0.024*** | 0.021 | GZ | 0.001 |
| VHL20 | 0.046*** | 0.023*** | 0.024* | BS | 0.029 |
| AHT04 | 0.025* | 0.015*** | 0.010 | DBP | 0.031** |
| UCDEQ4 | 0.044** | 0.039*** | 0.005 | JJ | 0.007 |
| HTG06 | -0.033 | 0.018*** | -0.052 | ||
| ASB02 | 0.080*** | 0.020*** | 0.061*** | ||
| 总计 Total | 0.045*** | 0.024*** | 0.021*** | ||
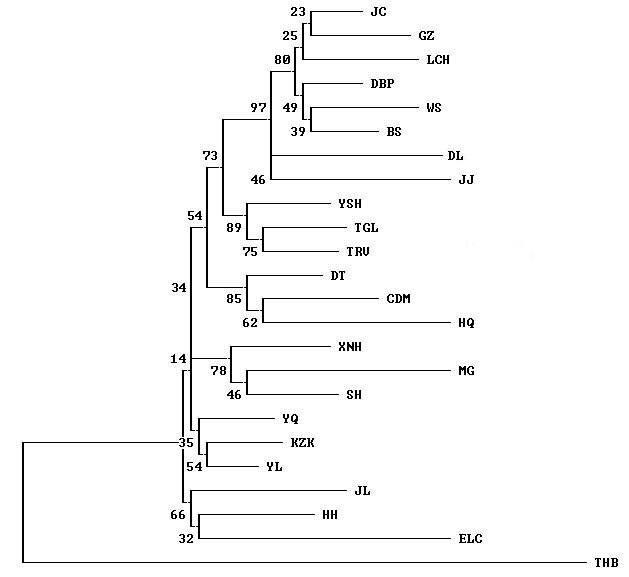
图1 基于Nei’s遗传距离(DA)构建的24个马群体的NJ聚类图(群体代号同表1)
Fig. 1 A neighbour-joining dendrogram of 24 horse populations based on Nei’s genetic distances (DA). Population codes see Table 1.
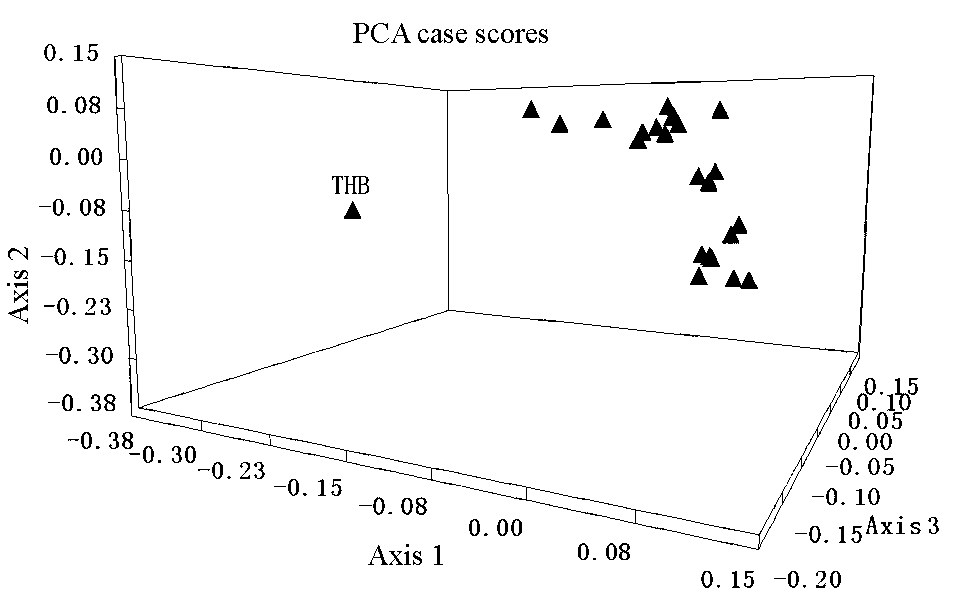
图2 24个马群体前三个主成分的三维散点图。Axis 1、Axis 2、Axis 3分别代表第1、第2、第3主成分。
Fig. 2 Three-dimensional scatter plot for the first three principal factors for 24 horse populations. Axis 1, Axis 2, and Axis 3 represent the first three principal factors, respectively.
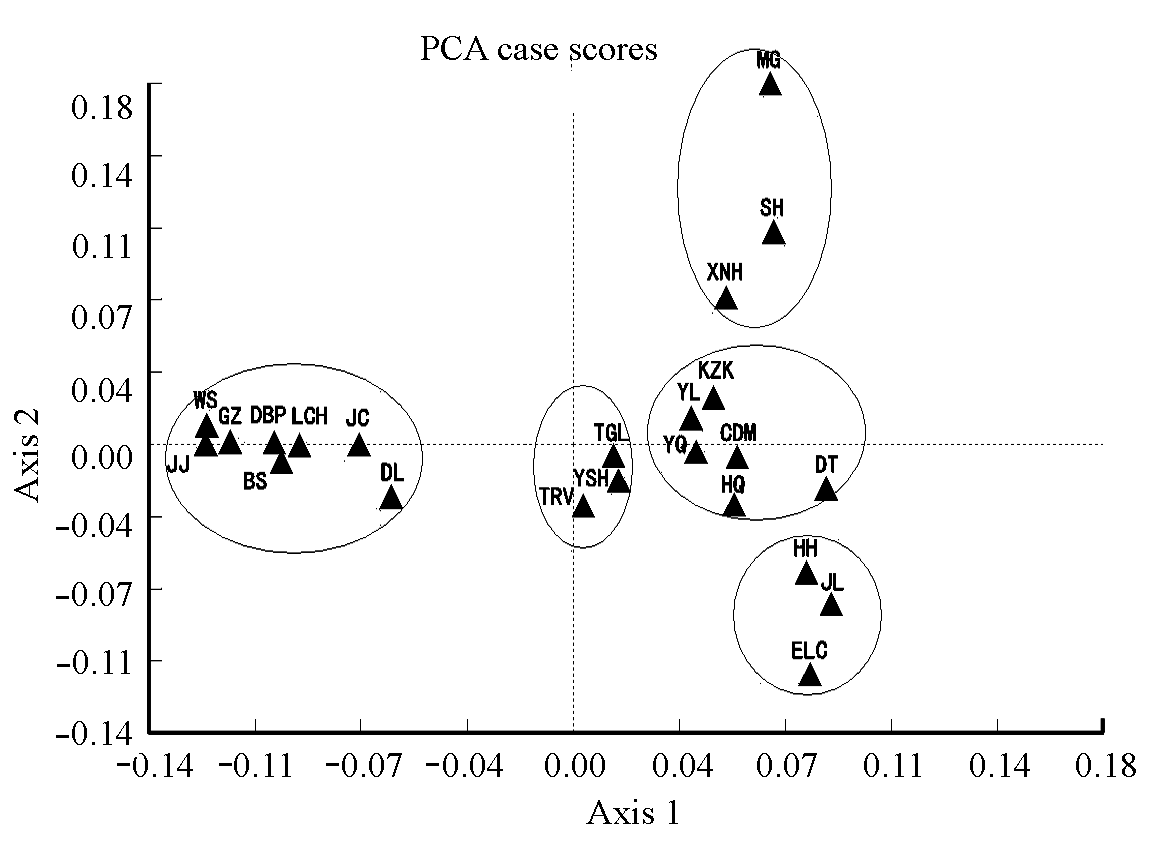
图3 23个中国马群体第一、二主成分的二维散点图。Axis 1和Axis 2分别代表第1主成分和第2主成分。
Fig. 3 Two-dimensional scatter plot for the first two principal factors for 23 Chinese horse populations. Axis 1 and Axis 2 represent the first two principal factors, respectively.
| [1] |
Aberle KS, Hamann H, Drogemuller C, Distl O (2004) Genetic diversity in German draught horse breeds compared with a group of primitive, riding and wild horses by means of microsatellite DNA markers. Animal Genetics, 35,270-277.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] |
Alvarez L, Royo J, Fernandez I, Gutierrez JP, Gomez E, Goyache F (2004) Genetic relationships and admixture among sheep breeds from northern Spain assessed using microsatellites. Journal of Animal Science, 82,2246-2252.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] |
Canon J, Checa ML, Carleos C, Vega-Pla JL, Vallejo M, Dunner S (2000) The genetic structure of Spanish Celtic horse breeds inferred from microsatellite data. Animal Genetics, 31,39-48.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] |
Dadi H, Tibbo M, Takahashi Y, Nomura K, Hanada H, Amano T (2008) Microsatellite analysis reveals high genetic diversity but low genetic structure in Ethiopian indigenous cattle populations. Animal Genetics, 39,425-431.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] |
Di R (狄冉), He XH (何晓红), Han JL (韩建林), Guan WJ (关伟军), Pu YB (浦亚斌), Zhao QJ (赵倩君), Fu BL (傅宝玲), Ma YH (马月辉) (2007) Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship of Chinese cashmere goats based on microsatellite DNA markers. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 15,470-478. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [6] | Editorial Committee of Horse and Ass Breeds in China (中国马驴品种志编写组) (1986) Horse and Ass Breeds in China (中国马驴品种志). Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [7] |
Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2003) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics, 164,1567-1587.
URL PMID |
| [8] | Geng SM (耿社民), Liu XL (刘小林) (2003) Compendium of Animal Breed Resources in China (中国家畜品种资源纲要). China Agricultural Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [9] | Goudet J (2001) FSTAT, a program to estimate and test gene diversities and fixation (version 2.9.3.2). http://www2.unil.ch/popgen/softwares/fstat.htm. |
| [10] |
Glowatzki ML, Muntwyler J, Pfister W, Marti E, Rieder S, Poncet PA, Gaillard C (2005) Genetic diversity among horse populations with a special focus on the Franches-Montagnes breed. Animal Genetics, 37,33-39.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] | Hou WT (侯文通), Sun C (孙超) (1995) Genetic diversity analysis of the eastern and western types of the Mongolian horse. Journal of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine (畜牧兽医杂志), 14(2),5-7. (in Chinese) |
| [12] | Hou WT (侯文通), Li XY (李相运), Li QR (李勤荣) (1993) Studies on the genetic differentiation and relationship of some local types in southwestern horses of China. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica (西北农业学报), 2(4),94-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] |
Iwañczyk E, Juras R, Cholewiñski G, Cothran EG (2006) Genetic structure and phylogenetic relationships of the Polish heavy horse. Journal of Applied Genetics, 47,353-359.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Jansen T, Forster P, Levine MA, Oelke H, Hurles M, Renfrew C, Weber J, Olek K (2002) Mitochondrial DNA and the origins of the domestic horse. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 16,10905-10910. |
| [15] | Li JL (李金莲), Mang L (芒来), Shi YF (石有斐) (2005) Evaluation of genetic diversity of Mongolian horse and Thoroughbred horse using microsatellite markers. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica (畜牧兽医学报), 36,6-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] |
Marletta D, Tupac-Yupanqui I, Bordonaro S, Garcia D, Guastella AM, Criscione A, Canon J, Dunner S (2006) Analysis of genetic diversity and the determination of relationships among western Mediterranean horse breeds using microsatellite markers. Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics, 123,315-325.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
Morais J, Maria M, Malta V, Luís C (2005) Genetic structure of an endangered Portuguese semiferal pony breed, the Garrano. Biochemical Genetics, 43,347-364.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Nei M (1972) Genetic distance between populations. The American Naturalist, 106,283-292. |
| [19] |
Nei M, Tajima F, Tateno Y (1983) Accuracy of estimated phylogenetic trees from molecular data. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 19,153-170.
URL PMID |
| [20] | Ota T (1993) DISPAN: Genetic Distance and Phylogenetic Analysis. Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA. |
| [21] |
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics, 155,945-959.
URL PMID |
| [22] | Qu LJ (曲鲁江), Li XY (李显耀), Xu GF (徐桂芳), Chen KW (陈宽维), Yang HJ (杨红杰), Zhang LC (张龙超), Wu GQ (吴桂琴), Hou ZC (侯卓成), Xu GY (徐桂云), Yang N (杨宁) (2006) Analysis of genetic diversity of Chinese native chicken breeds using microsatellite markers. Science in China (Series C) (中国科学C辑), 36,17-26. (in Chinese) |
| [23] | Sun HM (孙红梅), Xing XM (邢秀梅), Rong M (荣敏), Cong B (丛波) (2008) Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship of rabbit breeds based on microsatellite DNA markers. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 16,492-497. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] | Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, NY. |
| [25] |
Vila C, Leonard JA, Gotherstom A, Marklund S, Sandberg K, Linden K, Wayne RK, Ellegren H (2001) Widespread origins of domestic horse lineages. Science, 291,474-477.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | Wang ZS (王振山), Li JC (李建成), Guo YX (郭永新) (2001) Preliminary study on genetic polymorphism of transferrin in Chinese miniature horses. Heilongjiang Journal of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine (黑龙江畜牧兽医), 10,3-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] |
Weir BS, Cockerham CC (1984) Estimating F-statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evolution, 38,1358-70.
DOI URL PMID |
| [28] | Wright S (1977) Evolution and the Genetics of Populations, Volume 3: Experimental Results and Evolutionary Deductions. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [29] | Zhang CJ (张才骏), Yu BY (俞秉印), Wang YG (汪永贵), Chen F (陈福), Sun Y (孙瑛) (1995) Investigation on polymorphism of serum esterase in Huangzhong horse. Qinghai Journal of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine (青海畜牧兽医杂志), 25(4),19-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [30] | Zhong T (仲涛), Ma YH (马月辉), Guan WJ (关伟军), Ling YH (凌英会), Guo J (郭军), Zhao QJ (赵倩君), He XH (何晓红) (2008) Genetic diversity of microsatellite DNA among ten sheep breeds. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica (畜牧兽医学报), 39,555-561. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [2] | 王瑞武, 于云云, 朱其凯, 王超, 李敏岚, 韩嘉旭. 路径依赖的选择——统一自然选择与中性选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24120-. |
| [3] | 刘彩莲, 张雄, 樊恩源, 王松林, 姜艳, 林柏岸, 房璐, 李玉强, 刘乐彬, 刘敏. 中国海域海马的物种多样性、生态特征及保护建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23282-. |
| [4] | 罗小燕, 李强, 黄晓磊. 戴云山国家级自然保护区访花昆虫DNA条形码数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23236-. |
| [5] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [6] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [7] | 康敏. 论华莱士的人类学思想及其当代价值[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23304-. |
| [8] | 张琦. 关于规范涉及喜马拉雅山的物种中文命名的建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(1): 22131-. |
| [9] | 陶克涛, 白东义, 图格琴, 赵若阳, 安塔娜, 铁木齐尔·阿尔腾齐米克, 宝音德力格尔, 哈斯, 芒来, 韩海格. 基于基因组SNPs对东亚家马不同群体遗传多样性的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [10] | 王军, 赵超. 中国菌食性管蓟马物种多样性及分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22128-. |
| [11] | 李盼盼, 佟一杰, 曹浩宇, 容国森, 覃诗晴, 杨星科, 王国全, 白明. 广西花坪SITE100样地甲虫标本照片数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1165-1169. |
| [12] | 叶俊伟, 田斌. 中国西南地区重要木本油料植物扁核木的遗传结构及成因[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1629-1637. |
| [13] | 滕备, 杨海东, 佟一杰, 梁敏轩, 张嘉康, 李英铭, 白明. 三种被动式采集方法对甲虫收集效果的比较研究: 以香港城门样地为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(10): 1386-1395. |
| [14] | 陶克涛, 韩海格, 赵若阳, 图格琴, 芒来, 白东义. 家马的驯化起源与遗传演化特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(6): 734-748. |
| [15] | 翁茁先, 黄佳琼, 张仕豪, 余锴纯, 钟福生, 黄勋和, 张彬. 利用线粒体COI基因揭示中国乌骨鸡遗传多样性和群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(6): 667-676. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()