



生物多样性 ›› 2009, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (5): 490-498. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09101
收稿日期:2009-04-16
接受日期:2009-06-24
出版日期:2009-09-20
发布日期:2009-09-20
通讯作者:
冯福应
作者简介:*E-mail: forefeng@hotmail.com基金资助:
Xinxin Sun, Huirong Liu, Fuying Feng( ), Jianyu Meng, Heng Li, Malina
), Jianyu Meng, Heng Li, Malina
Received:2009-04-16
Accepted:2009-06-24
Online:2009-09-20
Published:2009-09-20
Contact:
Fuying Feng
摘要:
水生生态系统富营养化与细菌群落之间的关系尚不明确。本文通过构建和分析16S rRNA基因片段克隆文库, 以期揭示乌梁素海富营养化水体细菌的多样性及其系统发育关系, 并探讨富营养化与细菌多样性之间的关系。利用HaeIII对文库中的87个克隆子进行单酶切, 产生了23种带型, 文库覆盖度达到了73.6%, 反映出文库有较好的代表性。选择每种OTU的一个代表克隆进行测序分析, 基因序列系统发育分析结果表明, 乌梁素海中多数细菌与淡水生态系统中常见的细菌门类相同, 即α-, β-, γ-Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, 它们分别占总菌数的10.3%、41.4%、4.6%和6.9%, 其中β-Proteobacteria和Bacteroidetes是优势细菌类群。与典型淡水生态系统细菌群落组成不同的是, 乌梁素海中存在约10.3%的轻度嗜盐碱细菌。水体中83.9%的细菌与已培养的细菌的同源性低于97%, 其中58.9%的细菌未能鉴定到属; 其余总菌数16.1%的克隆与具有降解污染物生物活性的已知菌相近。Bacteroidetes、Firmicutes和β-Proteobacteria中的某些类群成为优势菌群可能是对乌梁素海水体富营养化的响应。
孙鑫鑫, 刘惠荣, 冯福应, 孟建宇, 李蘅, 玛丽娜 (2009) 乌梁素海富营养化湖区浮游细菌多样性及系统发育分析. 生物多样性, 17, 490-498. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09101.
Xinxin Sun, Huirong Liu, Fuying Feng, Jianyu Meng, Heng Li, Malina (2009) Diversity and phylogenetic analysis of planktonic bacteria in eutrophic zone of Lake Wuliangsuhai. Biodiversity Science, 17, 490-498. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09101.
| 铵态氮 NH4+-N (mg/L) | 硝态氮 NO3--N (mg/L) | 总氮 Total N (mg/L) | 总磷 Total P (mg/L) | 硫化物 S (mg/L) | Na+ Na+ (mg/L) | 化学需氧量 CODMn (mg/L) | 溶解有机碳 DOC (mg/L) | 叶绿素a Chl a (mg/L) | 温度T Temperature (℃) | pH | 细菌数量 Bacterial number (cells/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.79 | 0.158 | 4.87 | 0.247 | 0.364 | 463 | 69.21 | 85.95 | 13.8 | 24.2 | 8.72 | 6.58×107 |
表1 乌梁素海水体水质参数及总细菌数量
Table 1 Water parameters and total bacterial numbers in Wuliangsuhai Lake
| 铵态氮 NH4+-N (mg/L) | 硝态氮 NO3--N (mg/L) | 总氮 Total N (mg/L) | 总磷 Total P (mg/L) | 硫化物 S (mg/L) | Na+ Na+ (mg/L) | 化学需氧量 CODMn (mg/L) | 溶解有机碳 DOC (mg/L) | 叶绿素a Chl a (mg/L) | 温度T Temperature (℃) | pH | 细菌数量 Bacterial number (cells/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.79 | 0.158 | 4.87 | 0.247 | 0.364 | 463 | 69.21 | 85.95 | 13.8 | 24.2 | 8.72 | 6.58×107 |
| OTU代表 Representatives of OTU | 克隆数 Clone number | RDP属 RDP genus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 属 Genus | 置信度 Confidence(%) | ||
| H0110 | 5 | Rhodobacter | 100 |
| H0015 | 4 | NC | 12 |
| H0080 | 5 | Hydrogenophaga | 100 |
| H0022 | 1 | Hydrogenophaga | 100 |
| H0061 | 1 | Curvibacter | 88 |
| H0108 | 5 | NC | 77 |
| H0035 | 9 | NC | 29 |
| H0051 | 9 | Curvibacter | 98 |
| H0074 | 6 | Methylophilus | 90 |
| H0068 | 3 | Aeromonas | 100 |
| H0030 | 1 | Shigella | 99 |
| H0041 | 10 | NC | 23 |
| H0002 | 3 | NC | 51 |
| H0017 | 2 | Fluviicola | 100 |
| H0093 | 1 | Flavobacterium | 100 |
| H0097 | 1 | NC | 67 |
| H0052 | 4 | Terrimonas | 96 |
| H0091 | 2 | NC | 33 |
| H0050 | 4 | NC | 76 |
| H0064 | 2 | NC | 31 |
| H0054 | 2 | Xi | 100 |
| H0057 | 4 | Exiguobacterium | 100 |
| H0011 | 3 | NC | 58 |
表2 16s rDNA的Hae III酶切类型、比例及其所属菌分类
Table 2 Digestion patterns and proportion of 16S rDNA by HaeIII and classification
| OTU代表 Representatives of OTU | 克隆数 Clone number | RDP属 RDP genus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 属 Genus | 置信度 Confidence(%) | ||
| H0110 | 5 | Rhodobacter | 100 |
| H0015 | 4 | NC | 12 |
| H0080 | 5 | Hydrogenophaga | 100 |
| H0022 | 1 | Hydrogenophaga | 100 |
| H0061 | 1 | Curvibacter | 88 |
| H0108 | 5 | NC | 77 |
| H0035 | 9 | NC | 29 |
| H0051 | 9 | Curvibacter | 98 |
| H0074 | 6 | Methylophilus | 90 |
| H0068 | 3 | Aeromonas | 100 |
| H0030 | 1 | Shigella | 99 |
| H0041 | 10 | NC | 23 |
| H0002 | 3 | NC | 51 |
| H0017 | 2 | Fluviicola | 100 |
| H0093 | 1 | Flavobacterium | 100 |
| H0097 | 1 | NC | 67 |
| H0052 | 4 | Terrimonas | 96 |
| H0091 | 2 | NC | 33 |
| H0050 | 4 | NC | 76 |
| H0064 | 2 | NC | 31 |
| H0054 | 2 | Xi | 100 |
| H0057 | 4 | Exiguobacterium | 100 |
| H0011 | 3 | NC | 58 |
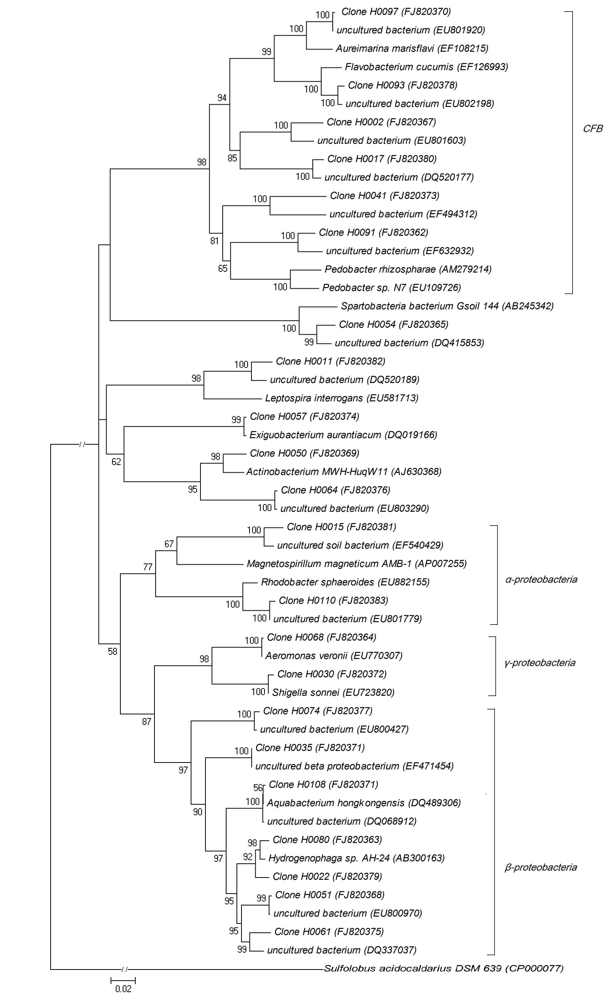
图1 基于乌梁素海环境水样细菌16S rDNA基因的系统发育树
Fig. 1 Phylogenetic tree of bacterial 16S rDNA gene sequences in Wuliangsuhai Lake water. Data in parentheses are the GenBank accession numbers. Numbers at the nodes indicate the levels of bootstrap support based on neighbor-joining analysis of 1,000 resampled datasets. Sulfolobus acidocaldarius DSM 639 serves as outgroup.
| [1] |
Acinas SG, Sarma-Rupavtarm R, Klepac-Ceraj V, Polz MF (2005) PCR-induced sequence artifacts and bias: insights from comparision of two 16S rRNA clone libraries constructed from the same sample. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71,8966-8969.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] | Amann RI, Ludwing W, Schleifer KH (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiologyical Reviews, 59,143-169. |
| [3] | Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (2002) Short Protocols in Molecular Biology. Wiley Press, New York. |
| [4] | Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, MacGarrell DM, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2009) The ribosomal database project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 37,D141-D145. |
| [5] |
Cottrell MT, Waidner LA, Yu LY, Kirchman DL (2005) Bacterial diversity of metagenomic and PCR libraries from the Delaware River. Environmental Microbiology, 7,1883-1895.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] |
Demergasso C, Casamayor EO, Chong G, Galleguillos P, Escudero L, Pedros-Alio C (2004) Distribution of prokaryotic genetic diversity in athalassohaline lakes of the Atacama Desert, Northern Chile. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 48,57-69.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] |
Dimitriu PA, Pinkart HC, Peyton BM, Mormile M (2008) Spatial and temporal patterns in the microbial diversity of a meromictic soda lake in Washington State. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74,4877-4888.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] | Duan XN (段晓男), Wang XK (王效科), Ouyang ZY (欧阳志云) (2005) Evaluation of wetland ecosystems services in Wuliangsuhai. Resources Science (资源科学), 27(2),110-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Felsenstein J (1989) PHYLIP–Phylogeny Inference Package (Version 3.2). Cladistics, 5,164-166. |
| [10] | Feng S (冯胜), Qin BQ (秦伯强), Gao G (高光) (2007) Response of bacterial communities to eutrophic water in Lake Taihu. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae (环境科学学报), 27,1823-1829. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] |
Frostegard A, Courtois S, Ramisse V, Clerc S, Bernillon D, Le Gall F, Jeannin P, Nesme X, Simonet P (1999) Quantification of bias related to the extraction of DNA directly from soils. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65,5409-5420.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] |
Giovannoni SJ, Sting U (2005) Molecular diversity and ecology of microbial plankton. Nature, 437,343-348.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
Glöckner FO, Zaichikov E, Belkova N, Denissova L, Pernthaler J, Pernthaler A, Amannl R (2000) Comparative 16S rRNA analysis of lake bacterioplankton reveals globally distributed phylogenetic clusters including an abundant group of Actinobacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66,5053-5065.
URL PMID |
| [14] | Grant S, Sorokin DY, Grant WD, Jones BE, Heaphy S (2004) A phylogenetic analysis of Wadi el Natrun soda lake cellulose enrichment cultures. Extremephiles, 8,421-429. |
| [15] |
Hill TCJ, Walsh KA, Harris JA, Moffett BF (2003) Using ecological diversity measures with bacterial communities. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 43,1-11.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] | Jenkins O, Byrom D, Jones D (1987) Methylophilus: a new genus of methanol-utilizing bacteria. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, 37,446-448. |
| [17] |
Kämpfer P, Schulze R, Jackel U, Malik KA, Amann R, Spring S (2005) Hydrogenophaga defluvii sp. nov. and Hydrogenophaga atypica sp. nov., isolated from activated sludge. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 55,341-344.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] |
Kumar S, Dudley J, Nei M, Tamura K (2008) MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 9,299-306.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] | Li CY (李畅游), Gao RZ (高瑞忠), Liu TX (刘廷玺), Ren CT (任春涛) (2005) Study on the eutrophication synthetical evaluation and the season-year change in Wuliangsuhai Lake. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering (水资源与水工程学报), 16(2),11-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] |
Lindström ES, Agterveld K-V MP, Zwart G (2005) Distribution of typical freshwater bacterial groups is associated with pH, temperature, and lake water retention time. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71,8201-8206.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] | Liu YQ, Yao TD, Zhu LP, Jiao NZ, Liu XB, Zeng YH, Jiang HC (2009) Bacterial diversity of freshwater alpine lake Puma Yumco on the Tibetan Plateau. Geomicrobiology Journal, 26,131-145. |
| [22] |
Lovejoy C, Massana R, Pedrós-Alió C (2006) Diversity and distribution of marine microbial eukaryotes in the Arctic Ocean and adjacent seas. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72,3085-3095.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] |
Ma YH, Zhang WZ, Xue YF, Zhou PJ, Ventosa A, Grant WD (2004) Bacterial diversity of the Inner Mongolian Baer soda lake as revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequence analyses. Extremophiles, 8,45-51.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] |
MacCann KS (2000) The diversity-stability debate. Nature, 405,228-233.
URL PMID |
| [25] |
Moyer CL, Tiedje JM, Dobbs FC (1996) A computer-simulated restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of bacterial small-subunit rRNA genes: efficacy of selected terameric restriction enzymes for studies of microbial diversity in nature. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62,2501-2507.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] |
Oda Y, Wanders W, Huisman LA, Meijer WG, Gottschal JC, Forney LJ (2002) Genotypic and phenotypic diversity within species of purple nonsulfur bacteria isolated from aquatic sediments. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68,3467-3477.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] |
Percent SF, Frischer ME, Vescio PA, Duffy VE, Milano V, McLellan M, Stevens BM, Boylen CW, Nierzwicki-Bauer SA (2008) Bacterial community structure of acid-impacted lakes: what controls diversity? Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74,1856-1868.
DOI URL PMID |
| [28] | Qin BQ, Yang LY, Chen FZ, Zhu GW, Zhang L, Chen YY (2006) Mechanism and control of lake eutrophication. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51,2401-2402. |
| [29] | Qu JH (屈建航), Yuan HL (袁红莉), Huang HC (黄怀曾), Wang ET (汪恩涛) (2005) Vertical distribution of bacterial community in sediment of Guantin Reservoir. Science in China Series D Earth Science(Suppl. I), 35,233-240. (in Chinese) |
| [30] |
Rodrigues DF, Goris J, Vishnivetskaya T, Gilichinsky D, Thomashow MF, Tiedje JM (2006) Characterization of Exiguobacterium isolates from the Siberian permafrost. Description of Exiguobacterium sibiricum sp. nov. Extremophiles, 10,285-294.
DOI URL PMID |
| [31] |
Sekiguchi H, Watanabe M, Nakahara T, Xu BH, Uchiyama H (2002) Succession of bacterial community structure along the Changjiang River determined by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and clone library analysis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68,5142-5150.
DOI URL PMID |
| [32] |
Shaw AK, Halpern AL, Beeson K, Tran B, Venter JC, Martiny JBH (2008) It’s all relative: ranking the diversity of aquatic bacterial communities. Environmental Microbiology, 10,2200-2210.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] | Shi XH (史小红) (2007) Modeling Analysis of Eutrophic Elements and Their Speciation for Wuliangsuhai Lake in Inner Mongolia (乌梁素海营养元素及其存在形态的数值模拟分析). PhD dissertation, Inner Mongolia Agriculture University, Huhhot. (in Chinese with English summary). |
| [34] |
Sipos R, Székely AJ, Palatinszky M, Révész S, Márialigeti K, Nikolausz M (2007) Effect of primer mismatch, annealing temperature and PCR cycle number on 16S rRNA gene-targeting bacterial community analysis. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 60,341-350.
DOI URL PMID |
| [35] |
Tamaki H, Sekiguchi Y, Hanada S, Nakamura K, Nomura N, Matsumura M, Kamagata Y (2005) Comparative analysis of bacteria diversity in freshwater sediment of a shallow eutrophic lake by molecular and improved cultivation-based techniques. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71,2162-2169.
DOI URL PMID |
| [36] |
Tiago I, Chung AP, Verissimo A (2004) Bacterial diversity in a nonsaline alkaline environment: heterotrophic aerobic populations. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70,7378-7387.
DOI URL PMID |
| [37] |
Vieira RP, Gonzalez AM, Cardoso AM, Oliverira DN, Albano RM, Clementino MM, Martins OB, Paranhos R (2008) Relationships between bacterial diversity and environmental variables in a tropical marine environment, Rio de Janeiro. Environmental Microbiology, 10,189-199.
DOI URL PMID |
| [38] |
von Wintzingerode F, Gobel UB, Stackebrandt E (1997) Determination of microbial diversity in environmental samples: pitfalls of PCR-based rRNA analysis. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 21,213-229.
DOI URL PMID |
| [39] | Wang LM (王丽敏), Shang SY (尚士友), Wu LB (吴利斌), Yue HJ (岳海军) (2004) Study on the nitrogen transformation in Wuliangsuhai, a grass-type lake. Environmental Science Trends (环境科学动态), (1),16-18. (in Chinese) |
| [40] | Wang ZW, Liu YH, Dai X, Wang BJ, Jiang CY, Liu SJ (2006) Flavobacterium saliperosum sp. nov., isolated from freshwater lake sediment. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, 56,439-442. |
| [41] |
Wu X, Xi WY, Ye WJ, Yang H (2007) Bacterial community composition of a shallow hypertrophic freshwater lake in China, revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequences. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 61,85-96.
URL PMID |
| [42] | Yachi S, Loreau M (1999) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in a fluctuating environment: the insurance hypothesis. Proceedings of the National Academy Sciences USA, 96,1463-1468. |
| [43] |
Yoon KS, Tsukada N, Sakai Y, Ishii M, Igarashi Y, Nishihara H (2008) Isolation and characterization of a new facultatively autotrophic hydrogen-oxidizing beta-proteobacterium, Hydrogenophaga sp. AH-24. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 278,94-100.
DOI URL PMID |
| [44] | Zhang WZ (张伟周), Mao WY (毛文扬), Xue YF (薛燕芬), Ma YH (马延和), Zhou PJ (周培瑾) (2001) The diversity of alkaliphiles from Hailaer Soda Lake, Inner Mongolia. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 9,44-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [45] | Zwart G, Crump BC, Agterveld M, Hagen F, Han SK (2002) Typical freshwater bacteria: an analysis of available 16S rRNA gene sequences from plankton of lakes and rivers. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 28,141-155. |
| [1] | 倪艳梅, 陈莉, 董志远, 孙德斌, 李宝泉, 王绪敏, 陈琳琳. 黄河三角洲湿地生态修复区大型底栖动物群落结构与生态健康评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [2] | 魏嘉欣, 姜治国, 杨林森, 熊欢欢, 金胶胶, 罗方林, 李杰华, 吴浩, 徐耀粘, 乔秀娟, 魏新增, 姚辉, 余辉亮, 杨敬元, 江明喜. 湖北神农架中亚热带山地落叶阔叶林25 ha动态监测样地群落物种组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [3] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [4] | 杨舒涵, 王贺, 陈磊, 廖蓥飞, 严光, 伍一宁, 邹红菲. 松嫩平原异质生境对土壤线虫群落特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23295-. |
| [5] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [6] | 张多鹏, 刘洋, 李正飞, 葛奕豪, 张君倩, 谢志才. 长江上游支流赤水河流域底栖动物物种多样性与保护对策[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22674-. |
| [7] | 刘彩莲, 许庆, 王林龙, 邢衍阔, 宋稼豪, 林柏岸, 康斌, 刘敏. 闽东近海春秋季游泳动物多样性、密度及群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22635-. |
| [8] | 朱晓华, 高程, 王聪, 赵鹏. 尿素对土壤细菌与真菌多样性影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22636-. |
| [9] | 毛莹儿, 周秀梅, 王楠, 李秀秀, 尤育克, 白尚斌. 毛竹扩张对杉木林土壤细菌群落的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22659-. |
| [10] | 陈哲涵, 尹进, 叶吉, 刘冬伟, 毛子昆, 房帅, 蔺菲, 王绪高. 增温对东北温带次生林草本群落季节动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23059-. |
| [11] | 张鹤露, 赵美红, 孙世春, 刘晓收. 西藏那曲市高原盐湖自由生活线虫群落多样性与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22533-. |
| [12] | 魏庐潞, 徐婷婷, 李媛媛, 艾喆, 马飞. 同质园环境和遗传分化影响锦鸡儿属植物根际土壤固氮菌多样性和群落结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22477-. |
| [13] | 林魏巍, 田呈明, 熊典广, 刘伟航, 热依汗古丽·斯地克, 梁英梅. 新疆杨树人工林中蜘蛛群落多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22493-. |
| [14] | 赵雯, 王丹丹, 热依拉·木民, 黄开钏, 刘顺, 崔宝凯. 阿尔山地区兴安落叶松林土壤微生物群落结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22258-. |
| [15] | 张伟, 翟东东, 熊飞, 刘红艳, 陈元元, 王莹, 廖传松, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 邓华堂, 陈大庆. 三峡库区鱼类群落结构和功能多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22136-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn