



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (2): 22136. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022136 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022136
张伟1,2,#, 翟东东1,2,#, 熊飞1,2,*( ), 刘红艳1,2, 陈元元1, 王莹1,2, 廖传松3, 段辛斌4,*(
), 刘红艳1,2, 陈元元1, 王莹1,2, 廖传松3, 段辛斌4,*( ), 田辉伍4, 邓华堂4, 陈大庆4
), 田辉伍4, 邓华堂4, 陈大庆4
收稿日期:2022-03-27
接受日期:2022-09-21
出版日期:2023-02-20
发布日期:2022-12-05
通讯作者:
*熊飞, E-mail: xf9603@163.com;段辛斌 duan@yfi.ac.cn
作者简介:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
Wei Zhang1,2,#, Dongdong Zhai1,2,#, Fei Xiong1,2,*( ), Hongyan Liu1,2, Yuanyuan Chen1, Ying Wang1,2, Chuansong Liao3, Xinbin Duan4,*(
), Hongyan Liu1,2, Yuanyuan Chen1, Ying Wang1,2, Chuansong Liao3, Xinbin Duan4,*( ), Huiwu Tian4, Huatang Deng4, Daqing Chen4
), Huiwu Tian4, Huatang Deng4, Daqing Chen4
Received:2022-03-27
Accepted:2022-09-21
Online:2023-02-20
Published:2022-12-05
Contact:
*Fei Xiong, E-mail: xf9603@163.com;Xinbin Duan duan@yfi.ac.cn
About author:#Co-first authors
摘要:
物种的功能特征是联系群落结构和功能的关键因素, 开展功能多样性研究可以更好地理解群落结构和功能的关系。为了解三峡库区鱼类群落结构和功能多样性的空间格局, 作者于2019年和2020年对三峡库区库首秭归、库中云阳、库尾巴南及库首支流香溪河下游峡口、库中支流小江下游高阳、库尾支流嘉陵江下游合川等江段的鱼类进行调查, 分析了鱼类群落结构和多样性, 从摄食、运动和繁殖3个方面探讨了鱼类功能多样性空间格局。在三峡库区及主要支流共采集到鱼类78种, 隶属于6目15科56属。各江段以广适性和静水性鱼类为主, 其中库首秭归和支流香溪河下游峡口、小江下游高阳江段的短颌鲚(Coilia brachygnathus)和贝氏䱗(Hemiculter bleekeri)等静水性鱼类相对丰度较高, 库中云阳、库尾巴南和支流嘉陵江下游合川江段的蛇鮈(Saurogobio dabryi)和光泽黄颡鱼(Pelteobagrus nitidus)等广适性鱼类相对丰度较高。非度量多维尺度(non-metric multidimensional scale, NMDS)和Bray-Curtis相异性指数分析表明, 秭归和嘉陵江下游合川江段群落结构差异最大, 香溪河下游峡口和小江下游高阳江段群落最为相似。Margalef丰富度指数(D)、Shannon多样性指数(H')和Pielou均匀度指数(E)在干流江段为: 秭归 < 云阳 < 巴南, 支流江段为: 嘉陵下游合川 < 小江下游高阳 < 香溪河下游峡口。鱼类摄食、运动和繁殖相关的功能多样性在空间上的变化趋势较为一致, 库首秭归江段的功能多样性最高, 嘉陵江合川江段的功能多样性最低。总功能多样性和物种多样性变化趋势一致, 在干流江段为: 秭归 < 云阳 < 巴南, 在支流江段为: 嘉陵下游合川 < 小江下游高阳 < 香溪河下游峡口。研究结果可为三峡库区鱼类多样性保护和管理提供科学依据, 为长江“十年禁渔”效果评估提供本底资料。
张伟, 翟东东, 熊飞, 刘红艳, 陈元元, 王莹, 廖传松, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 邓华堂, 陈大庆 (2023) 三峡库区鱼类群落结构和功能多样性. 生物多样性, 31, 22136. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022136.
Wei Zhang, Dongdong Zhai, Fei Xiong, Hongyan Liu, Yuanyuan Chen, Ying Wang, Chuansong Liao, Xinbin Duan, Huiwu Tian, Huatang Deng, Daqing Chen (2023) Community structure and functional diversity of fishes in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22136. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022136.
| 种类 Species | 秭归 Zigui | 云阳 Yunyang | 巴南 Banan | 峡口 Xiakou | 高阳 Gaoyang | 合川 Hechuan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 短颌鲚 Coilia brachygnathus | 77.9 | 7.0 | - | 19.7 | 5.8 | - |
| 似鳊 Pseudobrama simoni | 4.4 | 8.4 | - | 20.0 | 15.1 | 6.1 |
| 贝氏? Hemiculter bleekeri | 3.5 | 28.5 | 5.0 | 32.1 | 53.2 | 2.2 |
| 银鮈 Squalidus argentatus | 2.8 | 3.9 | 1.9 | 3.3 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| 蛇鮈 Saurogobio dabryi | 2.5 | 16.5 | 31.3 | 1.8 | 5.7 | 34.6 |
| 子陵吻鰕虎鱼 Rhinogobius giurinus | 2.3 | 0.4 | 2.0 | 0.7 | - | - |
| 瓦氏黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus vachelli | 0.5 | 1.3 | 3.4 | 0.7 | 2.9 | 0.8 |
| 长须黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus eupogon | 0.4 | - | 2.0 | - | - | - |
| 鲤 Cyprinus carpio | 0.3 | 2.8 | 5.7 | - | 0.1 | - |
| ? Hemiculter leucisculus | 0.1 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 2.0 | - | 1.0 |
| 鲫 Carassius auratus | 0.04 | 2.3 | 10.6 | - | 1.4 | 0.6 |
| 飘鱼 Pseudolaubuca sinensis | 0.02 | - | 0.09 | 0.3 | - | 4.0 |
| 鲇 Silurus asotus | 0.01 | 2.1 | 1.5 | 0.07 | 0.1 | - |
| 张氏? Hemiculter tchangi | - | - | 3.8 | 2.0 | 6.6 | 0.4 |
| 黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus fulvidraco | - | 0.1 | 3.2 | - | 0.1 | - |
| 光泽黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus nitidus | - | 11.7 | 5.8 | 3.2 | 1.2 | 42.1 |
| 唇? Hemibarbus labeo | - | 0.03 | 3.8 | - | - | - |
| 大鳞副泥鳅 Paramisgurnus dabryanus | - | - | 2.6 | - | - | - |
| 黑尾近红鲌 Ancherythroculter nigrocauda | - | 0.5 | - | - | - | 5.9 |
| 其他 Others | 5.23 | 11.57 | 14.41 | 14.13 | 7.7 | 2.1 |
表1 三峡库区各江段渔获物数量百分比
Table 1 Abundance percentage (%) of fishery catches in each section of the Three Gorges Reservoir
| 种类 Species | 秭归 Zigui | 云阳 Yunyang | 巴南 Banan | 峡口 Xiakou | 高阳 Gaoyang | 合川 Hechuan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 短颌鲚 Coilia brachygnathus | 77.9 | 7.0 | - | 19.7 | 5.8 | - |
| 似鳊 Pseudobrama simoni | 4.4 | 8.4 | - | 20.0 | 15.1 | 6.1 |
| 贝氏? Hemiculter bleekeri | 3.5 | 28.5 | 5.0 | 32.1 | 53.2 | 2.2 |
| 银鮈 Squalidus argentatus | 2.8 | 3.9 | 1.9 | 3.3 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| 蛇鮈 Saurogobio dabryi | 2.5 | 16.5 | 31.3 | 1.8 | 5.7 | 34.6 |
| 子陵吻鰕虎鱼 Rhinogobius giurinus | 2.3 | 0.4 | 2.0 | 0.7 | - | - |
| 瓦氏黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus vachelli | 0.5 | 1.3 | 3.4 | 0.7 | 2.9 | 0.8 |
| 长须黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus eupogon | 0.4 | - | 2.0 | - | - | - |
| 鲤 Cyprinus carpio | 0.3 | 2.8 | 5.7 | - | 0.1 | - |
| ? Hemiculter leucisculus | 0.1 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 2.0 | - | 1.0 |
| 鲫 Carassius auratus | 0.04 | 2.3 | 10.6 | - | 1.4 | 0.6 |
| 飘鱼 Pseudolaubuca sinensis | 0.02 | - | 0.09 | 0.3 | - | 4.0 |
| 鲇 Silurus asotus | 0.01 | 2.1 | 1.5 | 0.07 | 0.1 | - |
| 张氏? Hemiculter tchangi | - | - | 3.8 | 2.0 | 6.6 | 0.4 |
| 黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus fulvidraco | - | 0.1 | 3.2 | - | 0.1 | - |
| 光泽黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus nitidus | - | 11.7 | 5.8 | 3.2 | 1.2 | 42.1 |
| 唇? Hemibarbus labeo | - | 0.03 | 3.8 | - | - | - |
| 大鳞副泥鳅 Paramisgurnus dabryanus | - | - | 2.6 | - | - | - |
| 黑尾近红鲌 Ancherythroculter nigrocauda | - | 0.5 | - | - | - | 5.9 |
| 其他 Others | 5.23 | 11.57 | 14.41 | 14.13 | 7.7 | 2.1 |
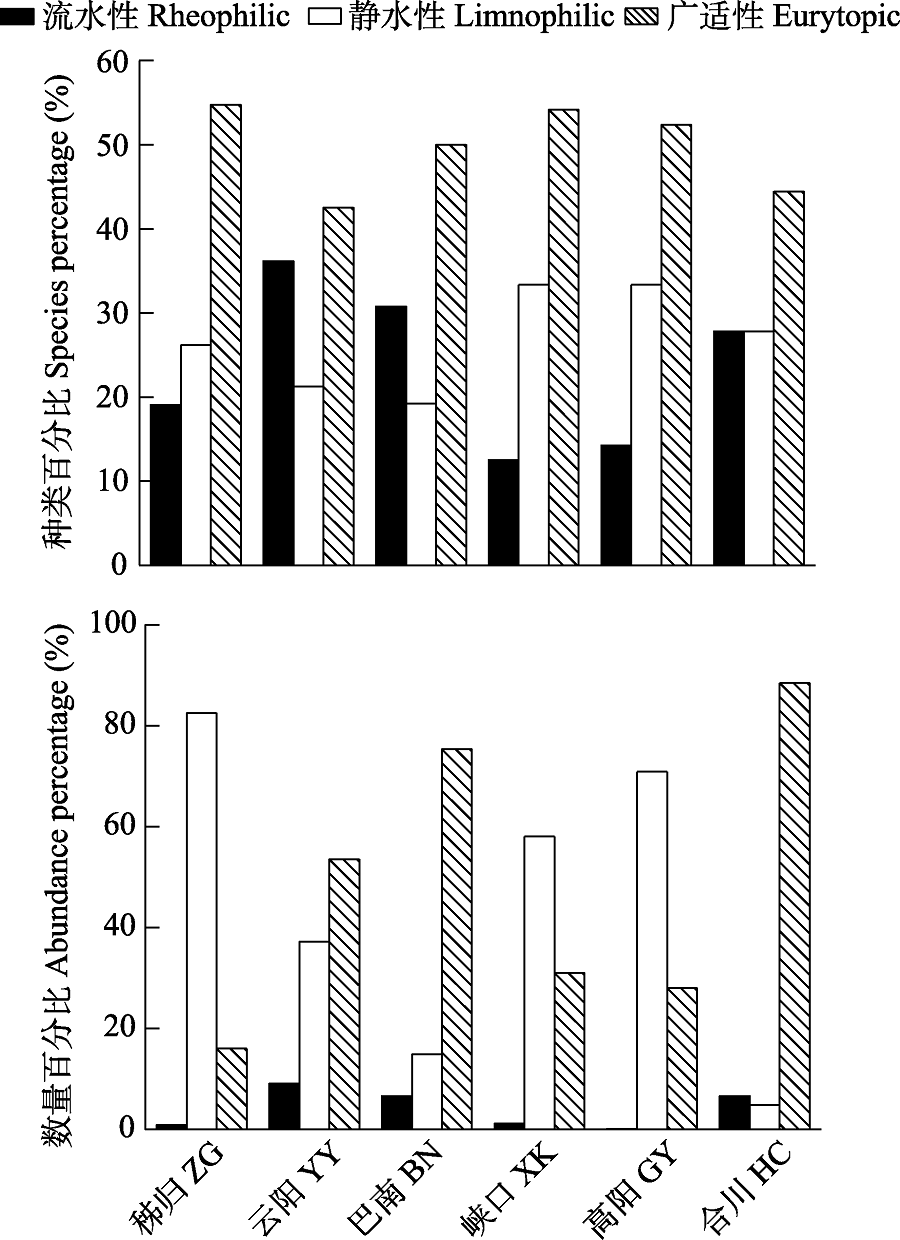
图2 三峡库区不同江段各鱼类生态类群的种类和数量百分比
Fig. 2 Percentages in species and abundance of each fish ecological group in different river section of the Three Gorges Reservoir. ZG, Zigui; YY, Yunyang; BN, Banan; XK, Xiakou; GY, Gaoyang; HC, Hechuan.
| 秭归 Zigui | 云阳 Yunyang | 巴南 Banan | 峡口 Xiakou | 高阳 Gaoyang | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 云阳 Yunyang | 0.77 | ||||
| 巴南 Banan | 0.88 | 0.59 | |||
| 峡口 Xiakou | 0.79 | 0.49 | 0.83 | ||
| 高阳 Gaoyang | 0.84 | 0.40 | 0.80 | 0.36 | |
| 合川 Hechuan | 0.94 | 0.73 | 0.79 | 0.85 | 0.84 |
表2 三峡库区各江段鱼类群落Bray-Curtis相异性指数
Table 2 Bray-Curtis dissimilarity index of fish communities in each river section of the Three Gorges Reservoir
| 秭归 Zigui | 云阳 Yunyang | 巴南 Banan | 峡口 Xiakou | 高阳 Gaoyang | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 云阳 Yunyang | 0.77 | ||||
| 巴南 Banan | 0.88 | 0.59 | |||
| 峡口 Xiakou | 0.79 | 0.49 | 0.83 | ||
| 高阳 Gaoyang | 0.84 | 0.40 | 0.80 | 0.36 | |
| 合川 Hechuan | 0.94 | 0.73 | 0.79 | 0.85 | 0.84 |
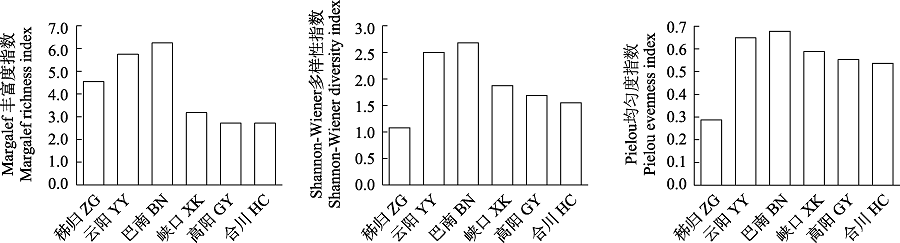
图4 三峡库区不同江段鱼类群落物种多样性空间变化
Fig. 4 Spatial variation of species diversity of fish communities in different river sections of the the Three Gorges Reservoir. ZG, Zigui; YY, Yunyang; BN, Banan; XK, Xiakou; GY, Gaoyang; HC, Hechuan.
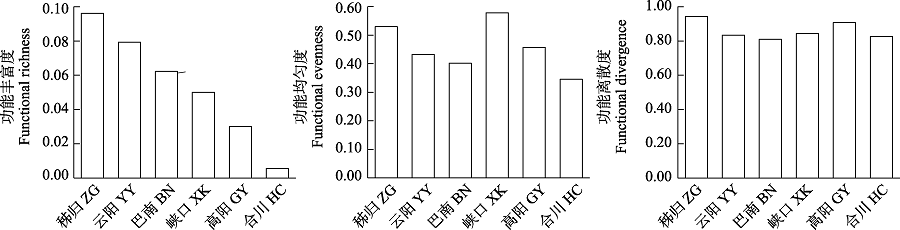
图5 三峡库区鱼类群落摄食功能多样性空间变化
Fig. 5 Spatial variation of food acquisition function diversity of fish communities in the Three Gorges Reservoir. ZG, Zigui; YY, Yunyang; BN, Banan; XK, Xiakou; GY, Gaoyang; HC, Hechuan.
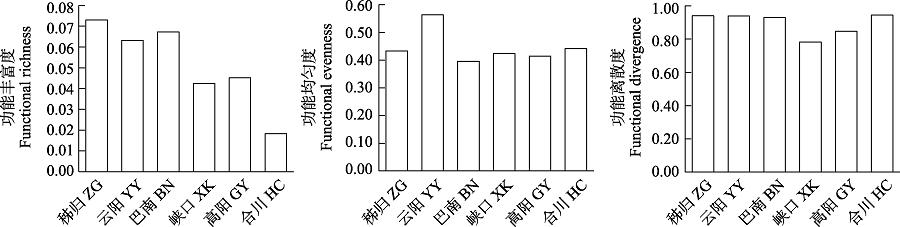
图6 三峡库区鱼类群落运动功能多样性空间变化
Fig. 6 Spatial variation of locomotion functional diversity of fish communities in the Three Gorges Reservoir. ZG, Zigui; YY, Yunyang; BN, Banan; XK, Xiakou; GY, Gaoyang; HC, Hechuan.
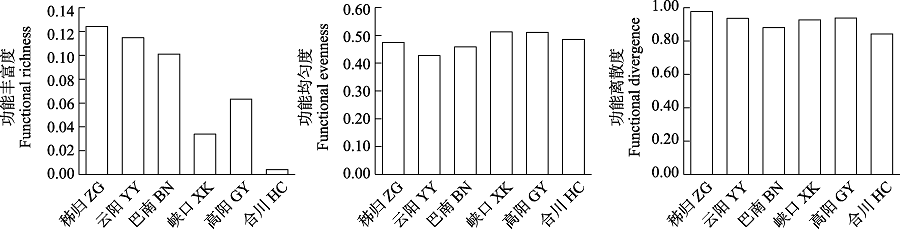
图7 三峡库区鱼类群落繁殖功能多样性空间变化
Fig. 7 Spatial variation of reproduction functional diversity of fish communities in the Three Gorges Reservoir. ZG, Zigui; YY, Yunyang; BN, Banan; XK, Xiakou; GY, Gaoyang; HC, Hechuan.
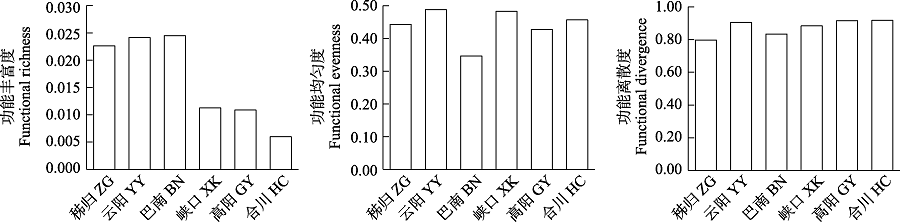
图8 三峡库区鱼类群落总功能多样性的空间变化
Fig. 8 Spatial variation of total functional diversity of fish communities in the Three Gorges Reservoir. ZG, Zigui; YY, Yunyang; BN, Banan; XK, Xiakou; GY, Gaoyang; HC, Hechuan.
| Margalef | Shannon | Pielou | T-FRic | T-FEve | T-FDiv | F-FRic | F-FEve | F-FDiv | L-FRic | L-FEve | L-FDiv | R-FRic | R-FEve | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon | 0.66 | |||||||||||||
| Pielou | 0.28 | 0.90* | ||||||||||||
| T-FRic | 0.94** | 0.44 | 0.02 | |||||||||||
| T-FEve | -0.41 | -0.33 | -0.19 | -0.33 | ||||||||||
| T-FDiv | -0.51 | 0.18 | 0.52 | -0.65 | 0.44 | |||||||||
| F-FRic | 0.71 | 0.09 | -0.31 | 0.89* | -0.01 | -0.73 | ||||||||
| F-FEve | -0.13 | -0.32 | -0.38 | 0.10 | 0.34 | -0.37 | 0.49 | |||||||
| F-FDiv | -0.29 | -0.76 | -0.84* | 0.04 | 0.13 | -0.37 | 0.35 | 0.51 | ||||||
| L-FRic | 0.79 | 0.24 | -0.17 | 0.94** | -0.33 | -0.74 | 0.93** | 0.35 | 0.32 | |||||
| L-FEve | 0.33 | 0.28 | 0.19 | 0.32 | 0.62 | 0.33 | 0.31 | -0.13 | -0.16 | 0.14 | ||||
| L-FDiv | 0.52 | 0.07 | -0.17 | 0.45 | -0.25 | -0.27 | 0.23 | -0.66 | -0.07 | 0.25 | 0.33 | |||
| R-FRic | 0.79 | 0.22 | -0.19 | 0.95** | -0.26 | -0.64 | 0.91* | 0.20 | 0.34 | 0.97** | 0.30 | 0.41 | ||
| R-FEve | -0.85* | -0.55 | -0.24 | -0.76 | 0.07 | 0.19 | -0.54 | 0.39 | 0.33 | -0.53 | -0.70 | -0.75 | -0.64 | |
| R-FDiv | 0.12 | -0.31 | -0.51 | 0.43 | 0.28 | -0.41 | 0.73 | 0.76 | 0.77 | 0.66 | 0.19 | -0.23 | 0.64 | 0.01 |
表3 不同多样性指数间的Pearson相关系数
Table 3 Pearson correlation coefficient among different diversity indices
| Margalef | Shannon | Pielou | T-FRic | T-FEve | T-FDiv | F-FRic | F-FEve | F-FDiv | L-FRic | L-FEve | L-FDiv | R-FRic | R-FEve | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon | 0.66 | |||||||||||||
| Pielou | 0.28 | 0.90* | ||||||||||||
| T-FRic | 0.94** | 0.44 | 0.02 | |||||||||||
| T-FEve | -0.41 | -0.33 | -0.19 | -0.33 | ||||||||||
| T-FDiv | -0.51 | 0.18 | 0.52 | -0.65 | 0.44 | |||||||||
| F-FRic | 0.71 | 0.09 | -0.31 | 0.89* | -0.01 | -0.73 | ||||||||
| F-FEve | -0.13 | -0.32 | -0.38 | 0.10 | 0.34 | -0.37 | 0.49 | |||||||
| F-FDiv | -0.29 | -0.76 | -0.84* | 0.04 | 0.13 | -0.37 | 0.35 | 0.51 | ||||||
| L-FRic | 0.79 | 0.24 | -0.17 | 0.94** | -0.33 | -0.74 | 0.93** | 0.35 | 0.32 | |||||
| L-FEve | 0.33 | 0.28 | 0.19 | 0.32 | 0.62 | 0.33 | 0.31 | -0.13 | -0.16 | 0.14 | ||||
| L-FDiv | 0.52 | 0.07 | -0.17 | 0.45 | -0.25 | -0.27 | 0.23 | -0.66 | -0.07 | 0.25 | 0.33 | |||
| R-FRic | 0.79 | 0.22 | -0.19 | 0.95** | -0.26 | -0.64 | 0.91* | 0.20 | 0.34 | 0.97** | 0.30 | 0.41 | ||
| R-FEve | -0.85* | -0.55 | -0.24 | -0.76 | 0.07 | 0.19 | -0.54 | 0.39 | 0.33 | -0.53 | -0.70 | -0.75 | -0.64 | |
| R-FDiv | 0.12 | -0.31 | -0.51 | 0.43 | 0.28 | -0.41 | 0.73 | 0.76 | 0.77 | 0.66 | 0.19 | -0.23 | 0.64 | 0.01 |
| [1] | Arantes CC, Fitzgerald DB, Hoeinghaus DJ, Winemiller KO (2019) Impacts of hydroelectric dams on fishes and fisheries in tropical rivers through the lens of functional traits. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 37, 28-40. |
| [2] | Chen J, Jiang WX, He SS, Wang HK, Zhuo LL, Chen Q, Wang HM (2018) Study of macroinvertebrate species and functional diversity in the New Xue River, Shandong Province, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 3328-3336. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈静, 蒋万祥, 贺诗水, 王洪凯, 卓丽玲, 陈青, 王红妹 (2018) 新薛河底栖动物物种多样性与功能多样性研究. 生态学报, 38, 3328-3336.] | |
| [3] | Chen YQ (2017) Functional diversity: A new view point in the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning research. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Sciences), 39, 1082-1088. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈又清 (2017) 功能多样性——生物多样性与生态系统功能关系研究的新视角. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 39, 1082-1088.] | |
| [4] | Chu XL, Zheng BS, Dai DY (1999) Fauna Sinica•Osteichthyes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [褚新洛, 郑葆珊, 戴定远 (1999) 中国动物志•硬骨鱼纲. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [5] |
Dı́az S, Cabido M (2001) Vive la différence: Plant functional diversity matters to ecosystem processes. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 16, 646-655.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Ding RH (1994) The Fishes of Sichuan. Sichuan Publishing House of Science & Technology, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [丁瑞华 (1994) 四川鱼类志. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [7] | Dong C, Yang Z, Gong Y, Tang HY (2019) Fish resource status and biodiversity conservation in the main channel of Three Gorges Reservoir. Journal of Hydroecology, 40(1), 15-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [董纯, 杨志, 龚云, 唐会元 (2019) 三峡库区干流鱼类资源现状与物种多样性保护. 水生态学杂志, 40(1), 15-21.] | |
| [8] | Esler K, Rebelo A (2014) Quantifying functional biodiversity. African Journal of Range & Forage Science, 31, 235-236. |
| [9] |
Feng C, He XB, Zhao CX, Li J, Kang B (2019) Functional diversity of fishes in the Minjiang Estuary, Southeast China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30, 3589-3595. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[冯晨, 何雄波, 招春旭, 李军, 康斌 (2019) 闽江口鱼类功能多样性. 应用生态学报, 30, 3589-3595.]
DOI |
|
| [10] | Feng HF, Lin WQ, Xue L (2021) Interactive effects of nitrogen and phosphorus additions and different stand densities on soil microbial functional diversity of Acacia auriculiformis stands. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41, 2305-2314. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [冯慧芳, 林婉奇, 薛立 (2021) 氮磷添加和栽植密度对大叶相思林土壤微生物群落功能多样性的影响. 生态学报, 41, 2305-2314.] | |
| [11] |
Gao X, Zeng Y, Wang JW, Liu HZ (2010) Immediate impacts of the second impoundment on fish communities in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 87, 163-173.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Hooper DU, Chapin FS III, Ewel JJ, Hector A, Inchausti P, Lavorel S, Lawton JH, Lodge DM, Loreau M, Naeem S, Schmid B, Setälä H, Symstad AJ, Vandermeer J, Wardle DA (2005) Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: A consensus of current knowledge. Ecological Monographs, 75, 3-35.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Huang XB, Su JR, Li SF, Liu WD, Lang XD (2019) Functional diversity drives ecosystem multifunctionality in a Pinus yunnanensis natural secondary forest. Scientific Reports, 9, 6979.
DOI |
| [14] | Lavorel S, Grigulis K, Mclntyre S, Williams NSG, Garden D, Dorrough J, Berman S, Quétier F, Thébault A, Bonis A (2008) Assessing functional diversity in the field-methodology matters. Functional Ecology, 22, 134-147. |
| [15] |
Lepš J, Brown VK, Len TAD, Gormsen D, Hedlund K, Kailová J, Korthals GW, Mortimer SR, Rodriguez-Barrueco C, Roy J, Santa Regina I, van Dijk C, van der Putten WH (2001) Separating the chance effect from other diversity effects in the functioning of plant communities. Oikos, 92, 123-134.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Lepš J, de Bello F, Lavorel S, Berman S (2006) Quantifying and interpreting functional diversity of natural communities: Practical considerations matter. Preslia, 78, 481-501. |
| [17] | Li T, Tang L, Wang L, An L, Wang J, Mo KL, Chen QW (2020) Distribution characteristics and ecological types changes in fish communities under hydropower development from Xiluodu to Xiangjiaba reach. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40, 1473-1485. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李婷, 唐磊, 王丽, 安磊, 王骏, 莫康乐, 陈求稳 (2020) 水电开发对鱼类种群分布及生态类型变化的影响——以溪洛渡至向家坝河段为例. 生态学报, 40, 1473-1485.] | |
| [18] | Liao CS, Chen SB, Ye SW, Lu T, Li W, Wang QD, Guo CB, Zhang TL, Liu JS (2021) Fish assemblage structure and age and growth of the primary fish populations in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 28, 695-702. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [廖传松, 陈思宝, 叶少文, 卢涛, 李为, 王齐东, 郭传波, 张堂林, 刘家寿 (2021) 三峡水库鱼类群落结构及主要鱼类种群年龄与生长. 中国水产科学, 28, 695-702.] | |
| [19] |
Liu XJ, Qin JJ, Xu Y, Ouyang S, Wu XP (2019) Biodiversity decline of fish assemblages after the impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 29, 177-195.
DOI |
| [20] | Liu YY, Li F, Xu XZ (2014) Impacts of hydropower development on hydrological regime in mainstream of mid-lower Jialing River. Yangtze River, 45(5), 10-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘扬扬, 李斐, 许秀贞 (2014) 嘉陵江中下游干流水电开发对水文情势的影响. 人民长江, 45(5), 10-15.] | |
| [21] |
Luck GW, Carter A, Smallbone L (2013) Changes in bird functional diversity across multiple land uses: Interpretations of functional redundancy depend on functional group identity. PLoS ONE, 8, e63671.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Ludwig JA, Reynolds JF (1988) Statistical Ecology, A Primer on Methods and Computing. John Wiley and Sons, New York. |
| [23] |
Mason NWH, Mouillot D, Lee WG, Wilson JB (2005) Functional richness, functional evenness and functional divergence: The primary components of functional diversity. Oikos, 111, 112-118.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Maureaud A, Hodapp D, van Denderen PD, Hillebrand H, Gislason H, Spaanheden Dencker T, Beukhof E, Lindegren M (2019) Biodiversity-ecosystem functioning relationships in fish communities:Biomass is related to evenness and the environment, not to species richness. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 286, 20191189. |
| [25] | Pan YF, Li JF, Yao YP, Jiang Y, Li HC, Wang XF, Lu GQ, Yang C, Huang SW, Jiang WP (2021) Changes in plant functional diversity and environmental factors of Cyclobalanopsis glauca community in response to slope gradient in Karst hills, Guilin. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41, 4484-4492. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [盘远方, 李娇凤, 姚玉萍, 姜勇, 利恒春, 王晓凤, 卢国琼, 杨晨, 黄诗雯, 蒋文平 (2021) 桂林岩溶石山青冈群落植物功能多样性和环境因子与坡向的关联研究. 生态学报, 41, 4484-4492.] | |
| [26] |
Parker J, Cao Y, Sass GG, Epifanio J (2018) Large river fish functional diversity responses to improved water quality over a 28 year period. Ecological Indicators, 88, 322-331.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Perera HACC, Li ZJ, De Silva SS, Zhang TL, Yuan J, Ye SW, Xia YG, Liu JS (2014) Effect of the distance from the dam on river fish community structure and compositional trends, with reference to the Three Gorges Dam. Yangtze River, China. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 38, 438-445. |
| [28] |
Petchey OL, Gaston KJ (2006) Functional diversity: Back to basics and looking forward. Ecology Letters, 9, 741-758.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Sankaran M, McNaughton SJ (1999) Determinants of biodiversity regulate compositional stability of communities. Nature, 401, 691-693.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Shuai FM, Li XH, Chen FC, Li YF, Yang JP, Li J, Wu Z (2017) Functional diversity of freshwater fishes and methods of measurement. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 5228-5237. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [帅方敏, 李新辉, 陈方灿, 李跃飞, 杨计平, 李捷, 武智 (2017) 淡水鱼类功能多样性及其研究方法. 生态学报, 37, 5228-5237.] | |
| [31] |
Teichert N, Lepage M, Lobry J (2018) Beyond classic ecological assessment: The use of functional indices to indicate fish assemblages sensitivity to human disturbance in estuaries. Science of the Total Environment, 639, 465-475.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Tilman D (2001) Functional diversity. Encyclopedia of Biodiversity, 3, 109-120.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Villéger S, Brosse S, Mouchet M, Mouillot D, Vanni MJ (2017) Functional ecology of fish: Current approaches and future challenges. Aquatic Sciences, 79, 783-801.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Villéger S, Mason NWH, Mouillot D (2008) New multidimensional functional diversity indices for a multifaceted framework in functional ecology. Ecology, 89, 2290-2301.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | Wei N, Zhang Y, Wu F, Shen ZW, Ru HJ, Ni ZH (2021) Current status and changes in fish assemblages in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 30, 1858-1869. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [魏念, 张燕, 吴凡, 沈子伟, 茹辉军, 倪朝辉 (2021) 三峡库区鱼类群落结构现状及变化. 长江流域资源与环境, 30, 1858-1869.] | |
| [36] | Wu H, Xiao NN, Lin TT (2020) Relationships between functional diversity and species diversity of pine-oak mixed forest in Qinling Mountains and their environmental explanations. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29, 1090-1100. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴昊, 肖楠楠, 林婷婷 (2020) 秦岭松栎林功能多样性与物种多样性和环境异质性的耦合关系. 生态环境学报, 29, 1090-1100.] | |
| [37] | Wu Q, Duan XB, Xu SY, Xiong CX, Chen DQ (2007) Studies on fishery resources in the Three Gorges Reservoir of the Yangtze River. Freshwater Fisheries, 37(2), 70-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴强, 段辛斌, 徐树英, 熊传喜, 陈大庆 (2007) 长江三峡库区蓄水后鱼类资源现状. 淡水渔业, 37(2), 70-75.] | |
| [38] | Xue QN, Yan M, Bi RC (2015) Functional diversity research of tree and shrub layers in forest communities of the Wulu Mountains Nature Reserve in Shanxi, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 7023-7032. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [薛倩妮, 闫明, 毕润成 (2015) 山西五鹿山森林群落木本植物功能多样性. 生态学报, 35, 7023-7032.] | |
| [39] | Yang F, Yao WZ, Deng HT, Chen DQ, Liu SP, Duan XB (2013) The current situation of fish resources in the Daning River after the impoundment of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Freshwater Fisheries, 43(4), 51-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨峰, 姚维志, 邓华堂, 陈大庆, 刘绍平, 段辛斌 (2013) 三峡库区蓄水后大宁河鱼类资源现状研究. 淡水渔业, 43(4), 51-57.] | |
| [40] | Yang Z, Tang HY, Gong Y, Dong C, Chen XJ, Wan CY, Chang JB (2017) The spatial-temporal distribution characteristics of the endemic fish in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River under the normal operation of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Ecology and Environmental Monitoring of Three Gorges, 2(1), 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨志, 唐会元, 龚云, 董纯, 陈小娟, 万成炎, 常剑波 (2017) 正常运行条件下三峡库区干流长江上游特有鱼类时空分布特征研究. 三峡生态环境监测, 2(1), 1-10.] | |
| [41] | Yang Z, Tang HY, Zhu D, Liu HG, Wan L, Tao JP, Qiao Y, Chang JB (2015) Spatiotemporal patterns of fish community structures in the Three Gorges Reservoir and its upstream during the 175-m-deep impoundment. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 5064-5075. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨志, 唐会元, 朱迪, 刘宏高, 万力, 陶江平, 乔晔, 常剑波 (2015) 三峡水库175 m试验性蓄水期库区及其上游江段鱼类群落结构时空分布格局. 生态学报, 35, 5064-5075.] | |
| [42] | Yang Z, Tao JP, Tang HY, Liu HG, Qiao Y, Chang JB (2012) Research on fish resources variation and protection in reservoir area of TGP after its operation. Yangtze River, 43(10), 62-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨志, 陶江平, 唐会元, 刘宏高, 乔晔, 常剑波 (2012) 三峡水库运行后库区鱼类资源变化及保护研究. 人民长江, 43(10), 62-67.] | |
| [43] | Zeng Y, Chen YB, Li ZJ (2014) Utilization and protection status of fish resources in Jialing River. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 20(2), 60-62, 87. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曾燏, 陈永柏, 李钟杰 (2014) 嘉陵江鱼类资源利用与保护现状. 天津农业科学, 20(2), 60-62, 87.] | |
| [44] | Zhang DC, Zheng JL (2019) Preliminary study on invasion of alien fish species after construction of hydropower projects. Yangtze River, 50(2), 83-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张登成, 郑娇莉 (2019) 水电工程建设前后外来鱼类入侵问题初步研究. 人民长江, 50(2), 83-89.] | |
| [45] | Zhao XN, Qin H, Zhang F (2017) Diversity of forest communities in the upstream and middle reaches of the Wenyu River watershed, Shanxi. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 1093-1102. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵小娜, 秦浩, 张峰 (2017) 山西文峪河上中游森林群落多样性. 生态学报, 37, 1093-1102.] | |
| [46] | Zou JX, Zhai HJ (2016) Impacts of Three Gorges Project on water environment and aquatic ecosystem and protective measures. Water Resources Protection, 32, 136-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邹家祥, 翟红娟 (2016) 三峡工程对水环境与水生态的影响及保护对策. 水资源保护, 32, 136-140.] |
| [1] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [2] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [3] | 仝淼, 王欢, 张文双, 王超, 宋建潇. 重金属污染土壤中细菌抗生素抗性基因分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [4] | 马文俊, 刘思嘉, 李柯懋, 简生龙, 薛长安, 韩庆祥, 魏金良, 陈生学, 牛依萌, 崔洲平, 隋瑞臣, 田菲, 赵凯. 青海省长江源区鱼类分布及多样性格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [5] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [6] | 刘志祥, 谢华, 张慧, 黄晓磊. 表皮碳氢化合物在社会性昆虫中的功能多样性及其调控[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24302-. |
| [7] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [8] | 孙智闲, 田晨, 王鑫, 方雨田, 李博, 赵亚辉. 热带沿海城市土著鱼类面临的威胁: 以海南省三亚市为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24165-. |
| [9] | 李雪原, 孙智闲, 王凤震, 席蕊, 方雨田, 郝浚源, 盛冬, 孙书雅, 赵亚辉. 城市发展对鱼类功能多样性的影响: 以超大城市北京为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24150-. |
| [10] | 时永强, 栾青杉, 单秀娟, 韦超, 赵永松, 孙策策, 金显仕. 长岛南部海域浮游动物多样性周年变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [11] | 张作鹏, 要晨阳, 吴玲, 罗遵兰, 孙光, 郭宗勇, 李晓思, 林峰, 陈小勇. 怒江云南段鱼类多样性现状与威胁因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24076-. |
| [12] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [13] | 王腾, 李纯厚, 王广华, 赵金发, 石娟, 谢宏宇, 刘永, 刘玉. 西沙群岛七连屿珊瑚礁鱼类的物种组成与演替[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 23481-. |
| [14] | 倪艳梅, 陈莉, 董志远, 孙德斌, 李宝泉, 王绪敏, 陈琳琳. 黄河三角洲湿地生态修复区大型底栖动物群落结构与生态健康评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [15] | 曹可欣, 王敬雯, 郑国, 武鹏峰, 李英滨, 崔淑艳. 降水格局改变及氮沉降对北方典型草原土壤线虫多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn