



Biodiv Sci ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (9): 1245-1255. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021028 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021028
• Original Papers: Microbial Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Dongmei Li1,*( ), Weihong Yang2, Qingduo Li1, Xi Han2, Xiuping Song1, Hong Pan2, Yun Feng2,*(
), Weihong Yang2, Qingduo Li1, Xi Han2, Xiuping Song1, Hong Pan2, Yun Feng2,*( )
)
Received:2021-01-19
Accepted:2021-04-09
Online:2021-09-20
Published:2021-05-28
Contact:
Dongmei Li,Yun Feng
About author:First author contact:#Co-first authors
Dongmei Li, Weihong Yang, Qingduo Li, Xi Han, Xiuping Song, Hong Pan, Yun Feng. High prevalence and genetic variation of Bartonella species inhabiting the bats in southwestern Yunnan[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(9): 1245-1255.
| 蝙蝠种类 Species of bats | 感染率(阳性数/检测数) Infection rate (positive/detected) | 合计 Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 临沧市 Lincang City | 西双版纳州 Xishuangbanna Prefecture | 保山市 Baoshan City | 德宏州 Dehong Prefecture | ||
| 中菊头蝠 Rhinolophus affinis | 50.0% (22/44) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50.0% (22/44) |
| 小菊头蝠 Rhinolophus blythi | 0 | 0 | 62.1% (18/29) | 0 | 62.1% (18/29) |
| 棕果蝠 Rousettus leschenaultii | 0 | 61.7% (29/47) | 0 | 55.7% (103/185) | 56.9% (132/232) |
| 合计 Total | 50.0% (22/44) | 61.7% (29/47) | 62.1% (18/29) | 55.7% (103/185) | 56.4% (172/305) |
Table 1 Number of species and geographical origins of the bats infected with Bartonella spp.
| 蝙蝠种类 Species of bats | 感染率(阳性数/检测数) Infection rate (positive/detected) | 合计 Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 临沧市 Lincang City | 西双版纳州 Xishuangbanna Prefecture | 保山市 Baoshan City | 德宏州 Dehong Prefecture | ||
| 中菊头蝠 Rhinolophus affinis | 50.0% (22/44) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50.0% (22/44) |
| 小菊头蝠 Rhinolophus blythi | 0 | 0 | 62.1% (18/29) | 0 | 62.1% (18/29) |
| 棕果蝠 Rousettus leschenaultii | 0 | 61.7% (29/47) | 0 | 55.7% (103/185) | 56.9% (132/232) |
| 合计 Total | 50.0% (22/44) | 61.7% (29/47) | 62.1% (18/29) | 55.7% (103/185) | 56.4% (172/305) |
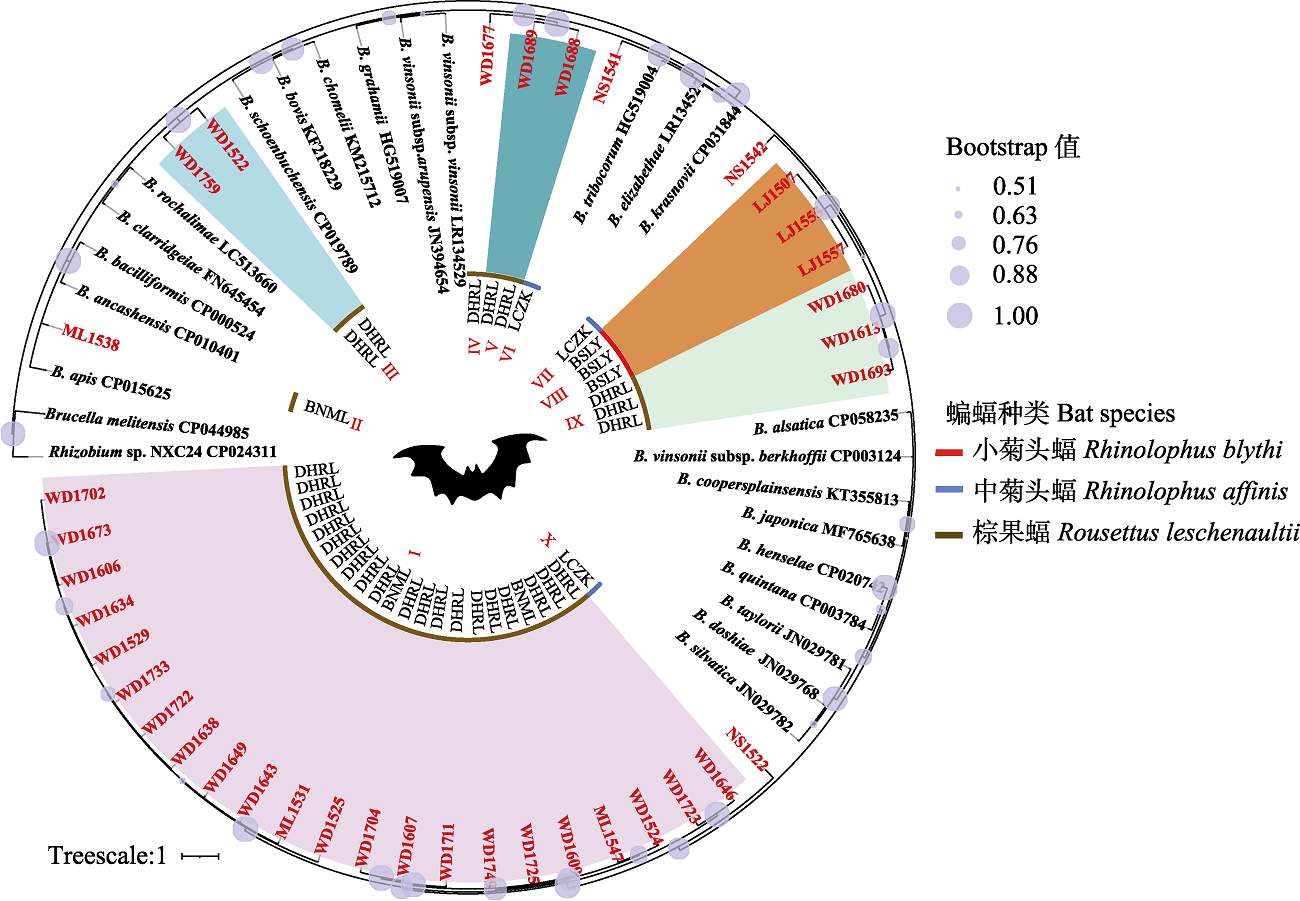
Fig. 1 Phylogenetic tree highlighting the position of ssrA sequences of Bartonella from bats relative to reference species of Bartonella spp. The bat species in the inner circle of the phylogenetic tree, represented by red, blue, and brown lines; bat sequence names in this study are marked with red font, the same as specimen no. in Appendix 2. BSLY, Lujiang Town, Longyang district, Baoshan City; LCZK, Nansan Town, Zhenkang County, Lincang City; BNML, Yaoqu Town, Mengla County, Xishuangbanna Prefecture; DHRL, Wanding Town, Ruili City, Dehong Prefecture; I-X in the center represent the phylogroups of ssrA sequence from bats in this study, while Brucella melitensis CP044985 and Rhizobuim sp. NXC24 CP024311 are outgroups.
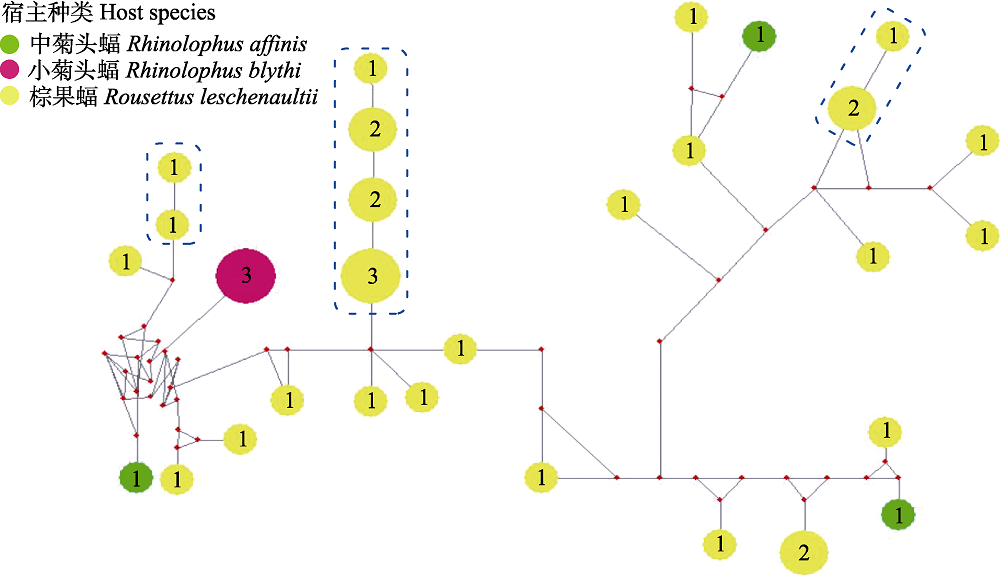
Fig. 2 Median-joining network of ssrA genotypes for Bartonella spp. from bat specimens in this study. Genotypes are denoted as pies, in which the numbers are number of individuals, with a size proportional to genotypic frequency.
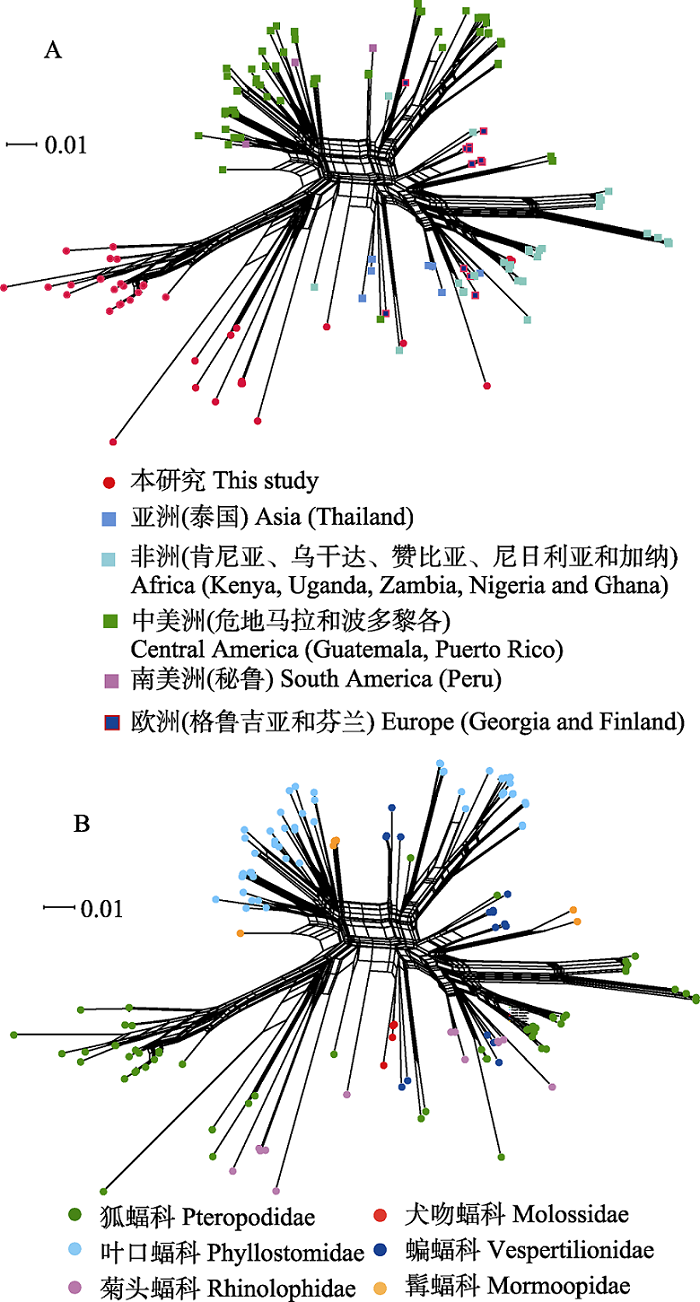
Fig. 3 Phylogenetic network diagram generated from ssrA sequences of Bartonella spp. from bat specimens in this study and GenBank using NeighborNet algorithm. There are 152 ssrA sequences of Bartonella spp. in the network diagram, including 37 sequences in this study and 115 sequences downloaded from the GenBank database. A and B are the networks of bat-borne Bartonella from the globe according to the geographic distributions and the host taxonomy associations.
| [1] |
Bai Y, Kosoy M, Recuenco S, Alvarez D, Moran D, Turmelle A, Ellison J, Garcia DL, Estevez A, Lindblade K, Rupprecht C (2011) Bartonella spp. in bats, Guatemala. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 17, 1269-1272.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Bai Y, Osinubi MOV, Osikowicz L, McKee C, Vora NM, Rizzo MR, Recuenco S, Davis L, Niezgoda M, Ehimiyein AM, Kia GSN, Oyemakinde A, Adeniyi OS, Gbadegesin YH, Saliman OA, Ogunniyi A, Ogunkoya AB, Kosoy MY, Team IBFI (2018) Human exposure to novel Bartonella species from contact with fruit bats. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 24, 2317-2323.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Becker DJ, Bergner LM, Bentz AB, Orton RJ, Altizer S, Streicker DG (2018) Genetic diversity, infection prevalence, and possible transmission routes of Bartonella spp. in vampire bats. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 12, e0006786.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Concannon R, Wynn-Owen K, Simpson VR, Birtles RJ (2005) Molecular characterization of haemoparasites infecting bats (Microchiroptera) in Cornwall, UK. Parasitology, 131, 489-496.
PMID |
| [5] |
Diaz MH, Bai Y, Malania L, Winchell JM, Kosoy MY (2012) Development of a novel genus-specific real-time PCR assay for detection and differentiation of Bartonella species and genotypes. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 50, 1645- 1649.
DOI URL |
| [6] | do Amaral RB, Lourenço EC, Famadas KM, Garcia AB, Machado RZ, André MR (2018) Molecular detection of Bartonella spp. and Rickettsia spp. in bat ectoparasites in Brazil. PLoS ONE, 13, e0198629. |
| [7] | Gutiérrez R, Vayssier-Taussat M, Buffet JP, Harrus S (2017) Guidelines for the isolation, molecular detection, and characterization of Bartonella species. Vector Borne and Zoonotic Diseases (Larchmont, NY), 17, 42-50. |
| [8] |
Han HJ, Wen HL, Zhao L, Liu JW, Luo LM, Zhou CM, Qin XR, Zhu YL, Zheng XX, Yu XJ (2017) Novel Bartonella species in insectivorous bats, Northern China. PLoS ONE, 12, e0167915.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Hornok S, Estók P, Kováts D, Flaisz B, Takács N, Szőke K, Krawczyk A, Kontschán J, Gyuranecz M, Fedák A, Farkas R, Haarsma AJ, Sprong H (2015) Screening of bat faeces for arthropod-borne apicomplexan protozoa: Babesia canis and Besnoitia besnoiti-like sequences from Chiroptera. Parasites & Vectors, 8, 1-6. |
| [10] |
Hornok S, Kovács R, Meli ML, Gönczi E, Hofmann-Lehmann R, Kontschán J, Gyuranecz M, Dán A, Molnár V (2012) First detection of bartonellae in a broad range of bat ectoparasites. Veterinary Microbiology, 159, 541-543.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Huson DH, Bryant D (2006) Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 23, 254-267.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Janssen BD, Hayes CS (2012) The tmRNA ribosome-rescue system. Advances in Protein Chemistry and Structural Biology, 86, 151-191.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Kosoy M, Bai Y, Lynch T, Kuzmin IV, Niezgoda M, Franka R, Agwanda B, Breiman RF, Rupprecht CE (2010) Bartonella spp. in bats, Kenya. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 16, 1875-1881.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Kosoy M, McKee C, Albayrak L, Fofanov Y (2018) Genotyping of Bartonella bacteria and their animal hosts: Current status and perspectives. Parasitology, 145, 543-562.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35, 1547-1549.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Kuncova K, Zemlickova H, Jager J, Ryskova L, Pliskova L, Bolehovska R, Pojar M (2019) Diagnosis and treatment of Bartonella endocarditis. Epidemiologie Mikrobiologie Imunologie, 68, 104-108. |
| [17] |
Lei BR, Olival KJ (2014) Contrasting patterns in mammal-bacteria coevolution: Bartonella and Leptospira in bats and rodents. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 8, e2738.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Li DM, Yu DZ, Liu QY, Gong ZD (2004) Study on the prevalence of Bartonella species in rodent hosts from different enviromental areas in Yunnan. Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 25, 934-937. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [栗冬梅, 俞东征, 刘起勇, 龚正达 (2004) 云南省不同环境鼠形动物巴尔通体感染情况的研究. 中华流行病学杂志, 25, 934-937.] | |
| [19] |
Lin JW, Hsu YM, Chomel BB, Lin LK, Pei JC, Wu SH, Chang CC (2012) Identification of novel Bartonella spp. in bats and evidence of Asian gray shrew as a new potential reservoir of Bartonella. Veterinary Microbiology, 156, 119-126.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
McKee CD, Hayman DTS, Kosoy MY, Webb CT (2016) Phylogenetic and geographic patterns of Bartonella host shifts among bat species. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 44, 382-394.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
McKee CD, Kosoy MY, Bai Y, Osikowicz LM, Franka R, Gilbert AT, Boonmar S, Rupprecht CE, Peruski LF (2017) Diversity and phylogenetic relationships among Bartonella strains from Thai bats. PLoS ONE, 12, e0181696.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Milne I, Lindner D, Bayer M, Husmeier D, McGuire G, Marshall DF, Wright F (2009) TOPALi v2: A rich graphical interface for evolutionary analyses of multiple alignments on HPC clusters and multi-core desktops. Bioinformatics, 25, 126-127.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Moratelli R, Calisher CH (2015) Bats and zoonotic viruses: Can we confidently link bats with emerging deadly viruses? Memórias Do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, 110, 1-22.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Morse SF, Olival KJ, Kosoy M, Billeter S, Patterson BD, Dick CW, Dittmar K (2012) Global distribution and genetic diversity of Bartonella in bat flies (Hippoboscoidea, Streblidae, Nycteribiidae). Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 12, 1717-1723.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Mühldorfer K (2013) Bats and bacterial pathogens: A review. Zoonoses and Public Health, 60, 93-103.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Mühldorfer K, Speck S, Wibbelt G (2011) Diseases in free-ranging bats from Germany. BMC Veterinary Research, 7, 61.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Reeves WK, Loftis AD, Gore JA, Dasch GA (2005) Molecular evidence for novel Bartonella species in Trichobius major (Diptera: Streblidae) and Cimex adjunctus (Hemiptera: Cimicidae) from two southeastern bat caves, U.S.A. Journal of Vector Ecology, 30, 339-341.
PMID |
| [28] |
Rodhain F (2015) Bats and viruses: Complex relationships. Bulletin de la Société de Pathologie Exotique, 108, 272-289.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Rozas J, Ferrer-Mata A, Sánchez-Delbarrio JC, Guirao-Rico S, Librado P, Ramos-Onsins SE, Sánchez-Gracia A (2017) DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 34, 3299-3302.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Sato S, Brinkerhoff RJ, Hollis E, Funada S, Shannon AB, Maruyama S (2020) Detection of zoonotic Bartonella pathogens in rabbit fleas, Colorado, USA. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 26, 778-781.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Shen B (2014) Molecular evolutionary studies of metabolic genes in bats. PhD dissertation, East China Normal University, Shanghai. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈斌 (2014) 蝙蝠代谢基因分子进化遗传学研究. 华东师范大学博士学位论文, 上海.] | |
| [32] |
Stuckey MJ, Boulouis HJ, Cliquet F, Picard-Meyer E, Servat A, Aréchiga-Ceballos N, Echevarría JE, Chomel BB (2017) Potentially zoonotic Bartonella in bats from France and Spain. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 23, 539-541.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Stuckey MJ, Chomel BB de Fleurieu EC, Aguilar-Setién A, Boulouis HJ, Chang CC (2017) Bartonella, bats and bugs: A review. Comparative Immunology, Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 55, 20-29.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Teeling EC, Springer MS, Madsen O, Bates P, O'Brien SJ, Murphy WJ (2005) A molecular phylogeny for bats illuminates biogeography and the fossil record. Science, 307, 580-584. |
| [35] |
Veikkolainen V, Vesterinen EJ, Lilley TM, Pulliainen AT (2014) Bats as reservoir hosts of human bacterial pathogen, Bartonella mayotimonensis. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 20, 960-967.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Wang YB, Yang FL, Peng HY, Yang XD, Yang H, Yu BB, Zhang Q, Li ZQ, Yang QJ, Xia ST (2014) Investigation of Bartonella infection in patients with fever of unknown origin in Yunnan Province. China Tropical Medicine, 14, 1446-1448. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王跃兵, 杨发莲, 彭海燕, 杨向东, 杨慧, 于彬彬, 张青, 李志强, 杨秋菊, 夏淑婷 (2014) 云南省不明原因发热病人巴尔通体感染调查. 中国热带医学, 14, 1446-1448.] | |
| [37] |
Wray AK, Olival KJ, Morán D, Lopez MR, Alvarez D, Navarrete-Macias I, Liang E, Simmons NB, Lipkin WI, Daszak P, Anthony SJ (2016) Viral diversity, prey preference, and Bartonella prevalence in Desmodus rotundus in Guatemala. EcoHealth, 13, 761-774.
PMID |
| [1] | Yaqing Liao, Zefeng Huang, Xiaoyun Wang, Libiao Zhang, Yi Wu, Wenhua Yu. An updated checklist of Chiroptera in Guangdong Province and a molecular barcode database [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24584-. |
| [2] | Jiachen Wang, Tangjun Xu, Wei Xu, Gaoji Zhang, Yijin You, Honghua Ruan, Hongyi Liu. Impact of urban landscape pattern on the genetic structure of Thereuopoda clunifera population in Nanjing, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [3] | Jiangtian Geng, Fei Wang, Huabin Zhao. Research progress on the impacts of urbanization on bats in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24109-. |
| [4] | Hua Ma, Changqing Li, Pinfeng Yu, Jie Chen, Tianyao He, Kehong Wang. Distribution patterns and impact factors of soil macrofauna communities in the riparian zone of the Pengxi River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 24117-. |
| [5] | Kexin Cao, Jingwen Wang, Guo Zheng, Pengfeng Wu, Yingbin Li, Shuyan Cui. Effects of precipitation regime change and nitrogen deposition on soil nematode diversity in the grassland of northern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [6] | Shiyi Long, Bobo Zhang, Yuchen Xia, Yangfan Fei, Yani Meng, Bingwei Lü, Yueqing Song, Pu Zheng, Taoran Guo, Jian Zhang, Shaopeng Li. Effects of diversity and temporal stability of native communities on the biomass of invasive species Solidago canadensis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24263-. |
| [7] | Linjun He, Wenjing Yang, Yuhao Shi, Kezhemo Ashuo, Yu Fan, Guoyan Wang, Jingji Li, Songlin Shi, Guihua Yi, Peihao Peng. Effects of plant community phylogeny and functional diversity on Ageratina adenophora invasion under fire disturbance [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24269-. |
| [8] | Yingying Liu, Lixin Gong, Hao Zeng, Jiang Feng, Yongjun Dong, Lei Wang, Tinglei Jiang. Application of passive acoustic monitoring in Chiropteran research [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24233-. |
| [9] | Qingduo Li, Dongmei Li. Analysis for the prevalence of global bat-borne Bartonella [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [10] | Chen Feng, Jie Zhang, Hongwen Huang. Parallel situ conservation: A new plant conservation strategy to integrate in situ and ex situ conservation of plants [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [11] | Hailing Qi, Pengzhen Fan, Yuehua Wang, Jie Liu. Genetic diversity and population structure of Juglans regia from six provinces in northern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [12] | Fei Xiong, Hongyan Liu, Dongdong Zhai, Xinbin Duan, Huiwu Tian, Daqing Chen. Population genetic structure of Pelteobagrus vachelli in the upper Yangtze River based on genome re-sequencing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [13] | Yuanyuan Xiao, Wei Feng, Yangui Qiao, Yuqing Zhang, Shugao Qin. Effects of soil microbial community characteristics on soil multifunctionality in sand-fixation shrublands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22585-. |
| [14] | Wei Zhang, Dongdong Zhai, Fei Xiong, Hongyan Liu, Yuanyuan Chen, Ying Wang, Chuansong Liao, Xinbin Duan, Huiwu Tian, Huatang Deng, Daqing Chen. Community structure and functional diversity of fishes in the Three Gorges Reservoir [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22136-. |
| [15] | Yiyue He, Yuying Liu, Fubin Zhang, Qiang Qin, Yu Zeng, Zhenyu Lü, Kun Yang. Genetic diversity and population structure of Saurogobio dabryi under cascade water conservancy projects in the Jialing River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()