



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (5): 22566. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022566 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022566
所属专题: 数据论文
陈本平1, 陈建武1, 凌征文1, 杨旭2, 陈鑫2, 李生强3,4,*( ), 杨彪5,*(
), 杨彪5,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-10-06
接受日期:2023-03-18
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2023-05-19
通讯作者:
* E-mail: 基金资助:
Benping Chen1, Jianwu Chen1, Zhengwen Ling1, Xu Yang2, Xin Chen2, Shengqiang Li3,4,*( ), Biao Yang5,*(
), Biao Yang5,*( )
)
Received:2022-10-06
Accepted:2023-03-18
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-05-19
Contact:
* E-mail: 摘要:
物种编目是生物多样性研究和保护的基础, 开展野生动物多样性监测对更新本底物种编目至关重要。目前红外相机的应用十分普通, 已成为陆生大中型兽类和林下鸟类监测的最有效方法之一。老君山国家级自然保护区位于四川省屏山县, 面积35 km2, 是我国第一个以四川山鹧鸪(Arborophila rufipectus)等珍稀濒危雉科鸟类以及常绿阔叶林生态系统为主要保护对象的保护区。本文整理了保护区2013年4月至2020年9月的红外相机监测数据并进行了详细的物种鉴定, 提供了按照年度统计的红外相机监测数据集。本数据集展示了不同监测年度下的相机位点坐标和相机工作日、每个相机位点拍摄的兽类和鸟类物种数、独立有效记录数、整体鸟兽物种名录(包括分布海拔、分布区域以及不同年度下的网格占有率与相对多度指数等)、代表性物种的红外相机照片等。该数据集是保护区开展红外相机监测工作以来首次全面的成果汇总, 可为保护区制定针对性保护与管理决策提供重要科学依据。
数据库(集)基本信息简介
| 数据库(集)名称 | 四川老君山国家级自然保护区林下鸟兽多样性及动态变化数据集 | |
| 作者 | 陈本平, 陈建武, 凌征文, 杨旭, 陈鑫, 李生强, 杨彪 | |
| 通讯作者 | 李生强(shengqiang322@qq.com), 杨彪(yangb315@163.com) | |
| 时间范围 | 2013-2020年 | |
| 地理区域 | 1. 地理与管理单元: 四川老君山国家级自然保护区, 面积35 km2; 2. 经纬度范围: 103º57'-104º04' E, 28º39'-28º43' N; 3. 红外相机布设海拔跨度: 1,196-1,933 m | |
| 文件大小 | 数据文件: 918 KB; 代表性物种照片压缩包: 56.5 MB | |
| 数据格式 | 数据文件: *.doc; 代表性物种照片压缩包: *.rar | |
| 数据链接 | https://www.dataopen.info/home/datafile/index/id/286 https://doi.org/10.24889/do.202305001 https://www.biodiversity-science.net/fileup/1005-0094/DATA/2022566.zip | |
| 数据库(集)组成 | 数据集共包括1个数据文件和2个代表性物种照片压缩包。其中, 数据文件包括7个统计表格和2个分析图, 统计表格包括: 1. 总体监测概况; 2. 监测位点地理坐标; 3. 独立有效记录数; 4. 物种数; 5. 物种名录; 6. 不同区块下鸟兽物种分布; 7. 不同区块物种相对多度(RAI)前8位统计。分析图包括: 1. 兽类和鸟类物种数与有效相机工作日拟合曲线; 2. 相对多度指数前15位兽类物种以及前20位鸟类物种在不同年度下的比较。 |
陈本平, 陈建武, 凌征文, 杨旭, 陈鑫, 李生强, 杨彪 (2023) 四川老君山国家级自然保护区林下鸟兽多样性及动态变化数据集. 生物多样性, 31, 22566. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022566.
Benping Chen, Jianwu Chen, Zhengwen Ling, Xu Yang, Xin Chen, Shengqiang Li, Biao Yang (2023) Developing a dataset on the diversity and dynamic changes of mammals and birds recorded using camera traps in Laojun Mountain National Nature Reserve, Sichuan, China. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22566. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022566.
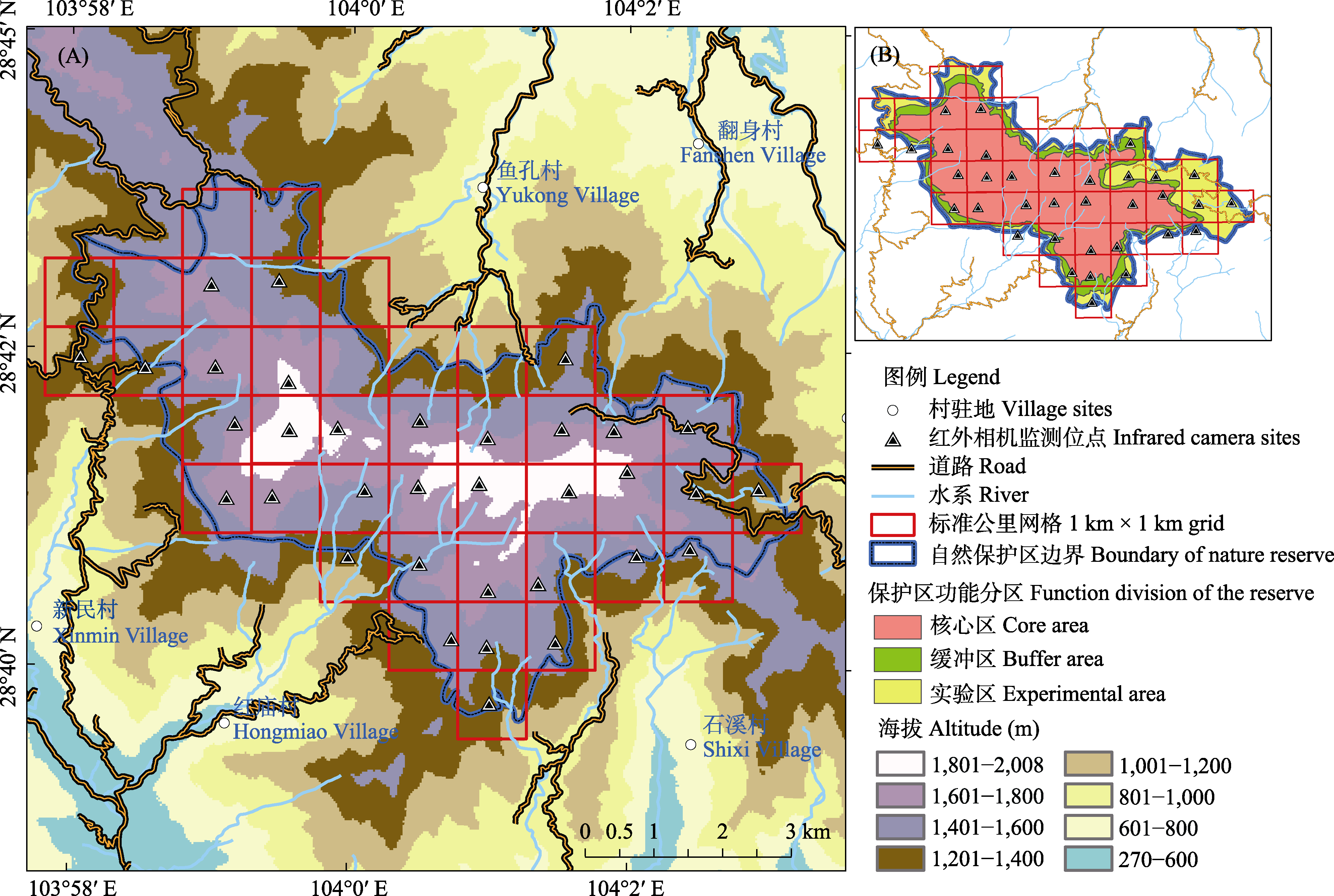
图1 四川老君山国家级自然保护区红外相机监测位点分布图。A: 保护区及周边海拔情况; B: 保护区功能区划情况。
Fig. 1 Distribution of infrared camera traps in Laojun Mountain National Nature Reserve. A, Altitude of Laojun Mountain National Nature Reserve and surrounding areas; B, Function division of Laojun Mountain National Nature Reserve.
| [1] | Chen BP, Ling ZW, Fu YQ (2015) The infrared camera monitoring in Sichuan Laojunshan National Nature Reserve has achieved fruitful results. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 34, 837. (in Chinese) |
| [陈本平, 凌征文, 付义强 (2015) 四川老君山国家级自然保护区红外相机监测取得丰硕成果. 四川动物, 34, 837.] | |
| [2] | Deng Y, Peng K, Yang X, Yang B, Li SQ (2022) Diversity and changes of mammals and birds in the Baishuihe National Nature Reserve (Sichuan) based on camera-trapping. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 41, 185-195. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邓玥, 彭科, 杨旭, 杨彪, 李生强 (2022) 基于红外相机监测四川白水河国家级自然保护区林下鸟兽多样性及其变化. 四川动物, 41, 185-195.] | |
| [3] | Fu LQ, Bai WK, Guo ZS, Huang YH, Li YWY, Yang B, Hou J, Dong X, Zhang JD, Zhou CQ (2020) Biodiversity and spatio-temporal patterns of mammals in the Mabian Dafengding National Nature Reserve using camera traps. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 39, 442-452. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [付励强, 白文科, 郭桢杉, 黄耀华, 立言伍叶, 杨彪, 侯金, 董鑫, 张晋东, 周材权 (2020) 利用红外相机调查四川马边大风顶国家级自然保护区兽类资源及时空分布特征. 四川动物, 39, 442-452.] | |
| [4] | Fu MD, Liu WW, Li BY, Ren YH, Li S, Bai X, Li JS, Zhu YP (2021) Construction and application of an evaluation index system for ecological and environmental protection effectiveness of national parks. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40, 4109-4118. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [付梦娣, 刘伟玮, 李博炎, 任月恒, 李爽, 白雪, 李俊生, 朱彦鹏 (2021) 国家公园生态环境保护成效评估指标体系构建与应用. 生态学杂志, 40, 4109-4118.] | |
| [5] | Fu YQ, Chen BP (2017) Report of Scientific Investigation of Sichuan Partridge (Arborophila rufipectus) in Laojun Mountain National Nature Reserve, Sichuan. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [付义强, 陈本平 (2017) 四川老君山国家级自然保护区四川山鹧鸪科学考察报告. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [6] | Fu YQ, Dai B, Wen LY (2018) Research progress of Sichuan partridge (Arborophila rufipectus). Journal of Leshan Normal University, 33(8), 37-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [付义强, 戴波, 文陇英 (2018) 四川山鹧鸪(Arborophila rufipectus)研究进展. 乐山师范学院学报, 33(8), 37-41.] | |
| [7] |
Fu YQ, Dai B, Wen LY, Chen BP, Dowell S, Zhang ZW (2017) Unusual incubation behavior and embryonic tolerance of hypothermia in the Sichuan partridge (Arborophila rufipectus). Journal of Ornithology, 158, 707-715.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Fu YQ, Zhang ZW, Chen BP, Ling ZW (2011) Winter habitat characteristics of red-winged laughingthrush at Laojunshan National Nature Reserve in China. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 46(5), 48-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [付义强, 张正旺, 陈本平, 凌征文 (2011) 四川老君山自然保护区红翅噪鹛冬季栖息地特征. 动物学杂志, 46(5), 48-54.] | |
| [9] | IUCN (2023) The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. https://www.iucnredlist.org. (accessed on 2023-03-08) |
| [10] | Li JW, Li YX, Zhang K, Luo W, Lan Q, He LY, Tang B, Yang ZS (2020) Preliminary camera-trapping survey on wild mammals and birds in Liziping National Nature Reserve. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 41(3), 7-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李健威, 李玉霞, 张勘, 骆伟, 兰琦, 何流洋, 唐博, 杨志松 (2020) 四川栗子坪国家级自然保护区野生鸟兽的红外相机初步监测. 四川林业科技, 41(3), 7-13.] | |
| [11] |
Li S (2020) Development progress and outlook of the wildlife camera-trapping networks in China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1045-1048. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[李晟 (2020) 中国野生动物红外相机监测网络建设进展与展望. 生物多样性, 28, 1045-1048.]
DOI |
|
| [12] |
Li S, Wang DJ, Xiao ZS, Li XH, Wang TM, Feng LM, Wang Y (2014) Camera-trapping in wildlife research and conservation in China: Review and outlook. Biodiversity Science, 22, 685-695. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[李晟, 王大军, 肖治术, 李欣海, 王天明, 冯利民, 王云 (2014) 红外相机技术在我国野生动物研究与保护中的应用与前景. 生物多样性, 22, 685-695.]
DOI |
|
| [13] | Liao WB (2010) A comparison of diversity for non-volant small mammal between high and low altitudes in Laojunshan Nature Reserve. Journal of China West Normal University (Natural Sciences), 31, 221-228. |
| [14] | Liao WB, Li C, Chen SY, Hu JC, Liu CZ, Jia YW (2006) Basic call of Leiothrix luteal in Sichuan Laojunshan Nature Reserve. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 25, 710-712. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [廖文波, 李操, 陈守云, 胡锦矗, 刘朝中, 贾延文 (2006) 红嘴相思鸟鸣声的初步探讨. 四川动物, 25, 710-712.] | |
| [15] | Liu BY, Zhang TY, Liang S, Bai XJ, Liu W (2020) Comparison of birds’ and mammals’ diversities using camera-trapping survey in Guizhou Chishui Alsophila National Nature Reserve and its surrounding areas. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 40, 503-519. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘邦友, 张廷跃, 梁盛, 白小节, 刘伟 (2020) 贵州赤水桫椤国家级自然保护区及其周边区域鸟兽多样性红外相机监测对比. 兽类学报, 40, 503-519.] | |
| [16] | Liu J, Ran JH, Yue XT, Mao YM, Ma XL, Zhang Y (2020) Diversity and changes of large and medium-sized mammals in the Heizhugou National Nature Reserve based on infrared cameras. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 39, 687-693. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘洁, 冉江洪, 岳先涛, 毛夜明, 马晓龙, 张尧 (2020) 基于红外相机监测四川黑竹沟国家级自然保护区的大中型兽类多样性及其变化. 四川动物, 39, 687-693.] | |
| [17] |
Liu P, Fu MX, Qi DW, Song XQ, Wei W, Yang WJ, Chen YX, Zhou YS, Liu JB, Ma R, Yu J, Yang H, Chen P, Hou R (2020) Camera-trapping survey of wild mammals and birds in Daxiangling Nature Reserve, Sichuan Province. Biodiversity Science, 28, 905-912. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[刘鹏, 付明霞, 齐敦武, 宋心强, 韦伟, 杨琬婧, 陈玉祥, 周延山, 刘家斌, 马锐, 余吉, 杨洪, 陈鹏, 侯蓉 (2020) 利用红外相机监测四川大相岭自然保护区鸟兽物种多样性. 生物多样性, 28, 905-912.]
DOI |
|
| [18] | Liu SY, Wu Y, Li S (2019) Handbook of the Mammals of China. The Straits Publishing & Distributing Group, Fuzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [刘少英, 吴毅, 李晟 (2019) 中国兽类图鉴. 海峡书局, 福州.] | |
| [19] | Liu Y, Chen SH (2021) The CNG Field Guide of the Birds of China. Hunan Science and Technology Press, Changsha. (in Chinese) |
| [刘阳, 陈水华 (2021) 中国鸟类观察手册. 湖南科学技术出版社, 长沙.] | |
| [20] |
Ma KP (2011) Assessing progress of biodiversity conservation with monitoring approach. Biodiversity Science, 19, 125-126. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[马克平 (2011) 监测是评估生物多样性保护进展的有效途径. 生物多样性, 19, 125-126.]
DOI |
|
| [21] | Ma KP (2015) Species Catalogue of China: A remarkable achievement in the field of biodiversity science in China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 137-138. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平 (2015) 中国生物多样性编目取得重要进展. 生物多样性, 23, 137-138.] | |
| [22] | Mao ZE, Bai WK, Fu LQ, Cai TG, Huang YH, Hong Y, Hou J, Luo H, Zhang JD, Zhou CQ (2022) Investigation on beasts of suspicious distribution in Mabian Dafengding Nature Reserve. Journal of China West Normal University (Natural Sciences), 43, 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [毛泽恩, 白文科, 付励强, 蔡天贵, 黄耀华, 洪洋, 侯金, 罗欢, 张晋东, 周材权 (2022) 马边大风顶自然保护区分布存疑兽类调查. 西华师范大学学报(自然科学版), 43, 1-8.] | |
| [23] |
Muldoon KM, Goodman SM (2015) Primates as predictors of mammal community diversity in the forest ecosystems of Madagascar. PLoS ONE, 10, e0136787.
DOI URL |
| [24] | National Forestry and Grassland Administration, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (2021) A List of Wildlife Under Key State Protection. (in Chinese) |
| [国家林业和草原局, 农业农村部 (2021) 国家重点保护野生动物名录. http://www.forestry.gov.cn/main/5461/20210205/122418860831352.html.] (accessed on 2021-02-08) | |
| [25] |
O’Brien TG, Kinnaird MF, Wibisono HT (2003) Crouching tigers, hidden prey: Sumatran tiger and prey populations in a tropical forest landscape. Animal Conservation, 6, 131-139.
DOI URL |
| [26] | O’Connell AF, Nichols JD, Karanth KU (2011) Camera Traps in Animal Ecology:Methods and Analyses. Springer Tokyo, Tokyo. |
| [27] | Peng B, Li SQ, Fu Y, Lei XJ, Zhao J, Meng QY, He F, Liao GJ, Yang X, Chen X, Yang ZS (2022) Diversity and distribution of wild mammals in Xiaozhaizigou National Nature Reserve in Sichuan Province based on infrared camera technology. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 43(3), 25-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [彭波, 李生强, 伏勇, 雷小军, 赵军, 孟庆玉, 贺飞, 廖光炯, 杨旭, 陈鑫, 杨志松 (2022) 基于红外相机技术的四川小寨子沟国家级自然保护区野生兽类种类与分布. 四川林业科技, 43(3), 25-35.] | |
| [28] |
Qiao J, Jia GQ, Zhou HM, Gong L, Jiang Y, Xiao NW, Gao XQ, Wen AX, Wang J (2022) Mammal and bird diversity recorded with camera traps in Gongga Mountain National Nature Reserve, Sichuan, China. Biodiversity Science, 30, 20395. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[乔江, 贾国清, 周华明, 龚林, 蒋勇, 肖能文, 高晓奇, 温安祥, 王杰 (2022) 四川贡嘎山国家级自然保护区鸟兽多样性. 生物多样性, 30, 20395.]
DOI |
|
| [29] | Qiao L, Yang Y, Shang K, Wang L, Li FJ, He S, Li J, Yue BS (2022) Investigation of small mammals and genetic diversity analysis of dominant species in the Laojunshan National Nature Reserve, Sichuan. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 41, 595-600. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [乔陆, 杨宇, 尚可, 王磊, 李凤君, 何松, 李健, 岳碧松 (2022) 四川老君山国家级自然保护区小型兽类调查及优势种遗传多样性分析. 四川动物, 41, 595-600.] | |
| [30] |
Qing J, Yang ZS, He K, Zhang ZJ, Gu XD, Yang XY, Zhang W, Yang B, Qi DW, Dai Q (2016) The minimum area requirements (MAR) for giant panda: An empirical study. Scientific Reports, 6, 37715.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Sichuan Forestry Department (2012) Giant Pandas in Sichuan—The Fourth Giant Panda Survey in Sichuan Province. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [四川省林业厅 (2012) 四川的大熊猫: 四川省第四次大熊猫调查报告. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [32] | Song Z, Dai J, Chen J, Zhang H, Tang XB, Yan SQ, Yan Y, Yang X, Yang B, Li SQ (2022) Preliminary investigation on mammal and bird resources using camera traps in the Xiaohegou Nature Reserve, Sichuan. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 41, 321-332. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋政, 代军, 陈娇, 张洪, 汤晓波, 鄢蜀歧, 严勇, 杨旭, 杨彪, 李生强 (2022) 利用红外相机对四川小河沟自然保护区兽类和鸟类资源的初步监测. 四川动物, 41, 321-332.] | |
| [33] | Wei FW, Yang QS, Wu Y, Jiang XL, Liu SY, Li BG, Yang G, Li M, Zhou J, Li S, Hu YB, Ge DY, Li S, Yu WH, Chen BY, Zhang ZJ, Zhou CQ, Wu SB, Zhang L, Chen ZZ, Chen SD, Deng HQ, Jiang TL, Zhang LB, Shi HY, Lu XL, Li Q, Liu Z, Cui YQ, Li YC (2021) Catalogue of mammals in China (2021). Acta Theriologica Sinica, 41, 487-501. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[魏辅文, 杨奇森, 吴毅, 蒋学龙, 刘少英, 李保国, 杨光, 李明, 周江, 李松, 胡义波, 葛德燕, 李晟, 余文华, 陈炳耀, 张泽钧, 周材权, 吴诗宝, 张立, 陈中正, 陈顺德, 邓怀庆, 江廷磊, 张礼标, 石红艳, 卢学理, 李权, 刘铸, 崔雅倩, 李玉春 (2021) 中国兽类名录(2021版). 兽类学报, 41, 487-501.]
DOI |
|
| [34] | Wei FW (2022) Taxonomy and Distribution of Mammals in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [魏辅文 (2022) 中国兽类分类与分布. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [35] | Wickham H (2023) Reshape2: Flexibly Reshape Data: A Reboot of the Reshape Package. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=reshape2. (accessed on 2023-02-06) |
| [36] | Wu PH, Hou J, Huang YH, Zhang DY, Bai WK, Fu LQ, Zhou CQ, Zhang JD (2020) Spatial-temporal distribution of birds using infrared camera traps in Mabian Dafengding Nature Reserve. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 41(1), 27-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴沛桦, 侯金, 黄耀华, 张栋耀, 白文科, 付励强, 周材权, 张晋东 (2020) 利用红外相机调查马边大风顶保护区鸟类资源的时空分布特征. 四川林业科技, 41(1), 27-35.] | |
| [37] | Wu YH, Kong CP, Xiang M, Fu YQ (2018) Breeding ecology of Trochalopteron formosum in Sichuan Laojunshan National Nature Reserve. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 37, 578-584. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴永恒, 孔赤平, 向明, 付义强 (2018) 四川老君山国家级自然保护区红翅噪鹛的繁殖生态研究. 四川动物, 37, 578-584.] | |
| [38] | Xi LYZ, Luo G, Ran JH, Feng SL, Chen JW, Chen BP (2020) Habitat use and change of Arborophila rufipectus during the breeding season in the Laojunshan National Nature Reserve, Sichuan. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 39, 258-265. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [西丽媛子, 罗概, 冉江洪, 冯盛林, 陈建武, 陈本平 (2020) 四川老君山国家级自然保护区四川山鹧鸪繁殖期的生境利用及其变化研究. 四川动物, 39, 258-265.] | |
| [39] |
Xiao ZS (2014) An introduction to wildlife camera trapping monitoring from Chinese Forest Biodiversity Monitoring Network (CForBio). Biodiversity Science, 22, 808-809. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[肖治术 (2014) 我国森林动态监测样地的野生动物红外相机监测. 生物多样性, 22, 808-809.]
DOI |
|
| [40] |
Xiao ZS, Li XH, Wang XZ, Zhou QH, Quan RC, Shen XL, Li S (2014) Developing camera-trapping protocols for wildlife monitoring in Chinese forests. Biodiversity Science, 22, 704-711. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[肖治术, 李欣海, 王学志, 周岐海, 权锐昌, 申小莉, 李晟 (2014) 探讨我国森林野生动物红外相机监测规范. 生物多样性, 22, 704-711.]
DOI |
|
| [41] | Xiao ZS (2016) Wildlife resource inventory using camera-trapping in natural reserves in China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 36, 270-271. (in Chinese) |
|
[肖治术 (2016) 红外相机技术促进我国自然保护区野生动物资源编目调查. 兽类学报, 36, 270-271.]
DOI |
|
| [42] |
Xiao ZS, Li XY, Xiang ZF, Li M, Jiang XL, Zhang LB (2017) Overview of the mammal diversity observation network of Sino BON. Biodiversity Science, 25, 237-245. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[肖治术, 李学友, 向左甫, 李明, 蒋学龙, 张礼标 (2017) 中国兽类多样性监测网的建设规划与进展. 生物多样性, 25, 237-245.]
DOI |
|
| [43] |
Xiao ZS (2019a) Application of camera trapping to species inventory and assessment of wild animals across China’s protected areas. Biodiversity Science, 27, 235-236. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
| [肖治术 (2019a) 红外相机技术在我国自然保护地野生动物清查与评估中的应用. 生物多样性, 27, 235-236.] | |
| [44] | Xiao ZS (2019b) Investigation and Evaluation of Wildlife and Habitat in Nature Reserve—A Case Study of Chebaling National Nature Reserve in Guangdong Province. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [肖治术 (2019b) 自然保护地野生动物及栖息地的调查与评估研究——广东车八岭国家级自然保护区案例分析. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [45] | Yang B, Li SQ, Yang X, Yang XY, Gu XD, Yang ZS, Dai Q (2021) Development and application of Sichuan Nature Conservation Infrared Camera Data Management System. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 42(1), 141-148. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨彪, 李生强, 杨旭, 杨旭煜, 古晓东, 杨志松, 戴强 (2021) 四川自然保护红外相机数据管理系统的研发及其应用. 四川林业科技, 42(1), 141-148.] | |
| [46] | Zheng GM (2017) A Checklist on the Classification and Distribution of the Birds of China, 3rd edn. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑光美 (2017) 中国鸟类分类与分布名录(第三版). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [47] | Zhou MQ, Yuan SB, Zhou CQ, Wang XL, Huang HS, Qi SF, Xiang M, Yan LB (2012) The preliminary study on breeding habit of Leiothrix lutea at Laojunshan Nature Reserve, Sichuan. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 31, 965-969, 1014. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周明强, 袁施彬, 周材权, 王夕龙, 黄泓升, 齐赛飞, 向明, 宴林波 (2012) 四川老君山自然保护区红嘴相思鸟繁殖生态初报. 四川动物, 31, 965-969, 1014.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [5] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [6] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [7] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [8] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [9] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [10] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [11] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [12] | 罗敏, 杨永川, 靳程, 周礼华, 龙宇潇. 城市森林兽类组成特征及人类活动的影响——以重庆中心城区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24402-. |
| [13] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [14] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [15] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()