



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (5): 629-646. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020273 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020273
陈旸康1, 王益1, 李家亮1, 王文韬1, 冯端宇2, 毛康珊1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-07-08
接受日期:2020-08-18
出版日期:2021-05-20
发布日期:2020-10-10
通讯作者:
毛康珊
作者简介:* E-mail: maokangshan@scu.edu.cn基金资助:
Yangkang Chen1, Yi Wang1, Jialiang Li1, Wentao Wang1, Duanyu Feng2, Kangshan Mao1,*( )
)
Received:2020-07-08
Accepted:2020-08-18
Online:2021-05-20
Published:2020-10-10
Contact:
Kangshan Mao
摘要:
近年来, 分子钟定年方法(molecular dating methods)得以广泛运用, 为宏观进化研究尤其是生物多样性及其格局形成历史的相关研究提供了不可或缺且十分详尽的进化时间框架。贝叶斯方法(Bayesian methods)和马尔可夫链蒙特卡罗方法 (Markov chain Monte Carlo)可容纳多维度、多类型的数据和参数设置, 因此以BEAST、PAML-MCMCTree等软件为代表的贝叶斯节点标记法(Bayesian node-dating methods)逐渐成为分子钟定年方法中最为广泛使用的类型。贝叶斯框架的优势之一在于其可以利用复杂模型考虑各种不确定性因素, 但是该类方法中各类模型和参数的设置都可能引入误差, 从而影响进化分化时间估算的可靠性。本文介绍了贝叶斯分子钟定年方法的原理和主要类型, 并以贝叶斯节点标记法为例, 重点讨论了分子钟模型、化石标记的选择与放置、采样频率及化石标记点年龄先验分布等因素对节点定年的影响; 提供了贝叶斯时间树构建软件的使用建议、节点年龄的讨论原则和不同模型下时间树的比较方法, 针对常见的引起节点年龄潜在高估和低估风险的情况作了分析并给出了合理化建议。我们认为, 合理整合多种贝叶斯方法和模型得出的结果并从中择优, 能够提高定年结果的可靠性; 研究人员应对时间树构建结果与其参数设置的关系开展讨论, 从而为其他学者提供参考; 化石记录的更新与分子钟定年方法的改进应同步不断跟进。
陈旸康, 王益, 李家亮, 王文韬, 冯端宇, 毛康珊 (2021) 主流分子钟定年方法的原理、误差来源和使用建议. 生物多样性, 29, 629-646. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020273.
Yangkang Chen, Yi Wang, Jialiang Li, Wentao Wang, Duanyu Feng, Kangshan Mao (2021) Principles, error sources and application suggestions of prevailing molecular dating methods. Biodiversity Science, 29, 629-646. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020273.
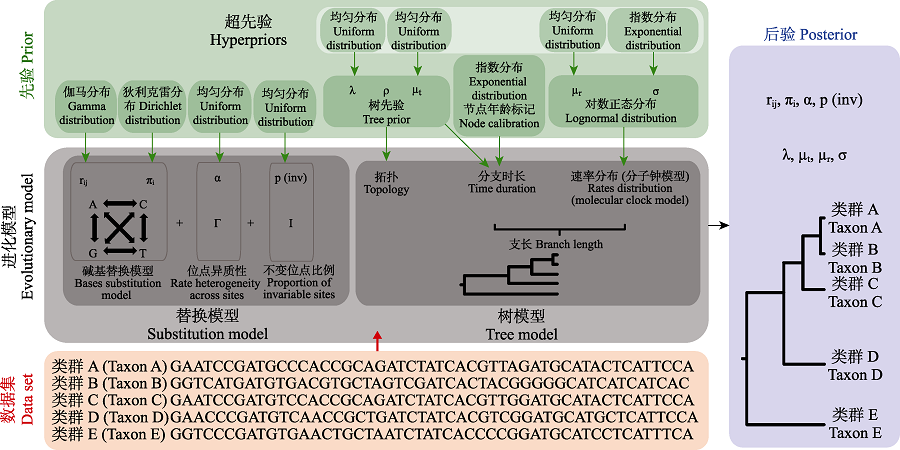
图1 贝叶斯法时间树构建过程示意图(改自: Bromham et al, 2018)。进化模型的参数设置是贝叶斯法系统发育树构建的关键步骤, 由替换模型和树模型组成。替换模型包括了碱基替换模型(包括碱基转换速率rij和碱基频率πi参数)、速率的位点(sites)异质型(如Γ分布)以及不变位点的比例p(inv)。树模型可以解构为结构与支长两个组份。结构由树先验决定, 图中使用的是生灭过程模型, 包含物种生成率(λ)、物种灭绝率(μt)和取样频率(ρ)三个参数。在“两步法”中, 结构还可以来自于树文件的输入。支长由分支时长与速率分布共同决定。分支时长一方面受树先验的影响, 另一方面与节点年龄标记密切相关; 速率分布即分子钟模型, 决定了进化速率在不同支上的分布格局。数据集与进化模型共同计算得到各参数的后验及时间树。
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of Bayesian time tree construction (modified from: Bromham et al, 2018). The parameter setting of evolutionary models is the key step of constructing phylogenetic tree based on Bayesian method, which is composed of substitution model and tree model. The substitution model includes base substitution model (including base conversion rate rij and base frequency πi as parameters), site heterogeneity of rate (such as Γ distribution) and proportion of invariant sites p(inv). The tree model can be decomposed into two components: structure and branch lengths. The structure is determined by tree priors (in this case the birth and death process model), which includes three parameters: species generation rate (λ), species extinction rate (μt) and sampling frequency (ρ). In the “two-step” method, the structure can also come from the input of the tree file. The branch length is determined by the branch duration and the rate distribution across branches. The branch duration is influenced by tree priors and node age calibration. The rate distribution is recognized as clock models, which determine the distribution pattern of evolution rate on different branches. The data set is applied to the evolutionary model to generate posteriors of each parameter and the time tree.
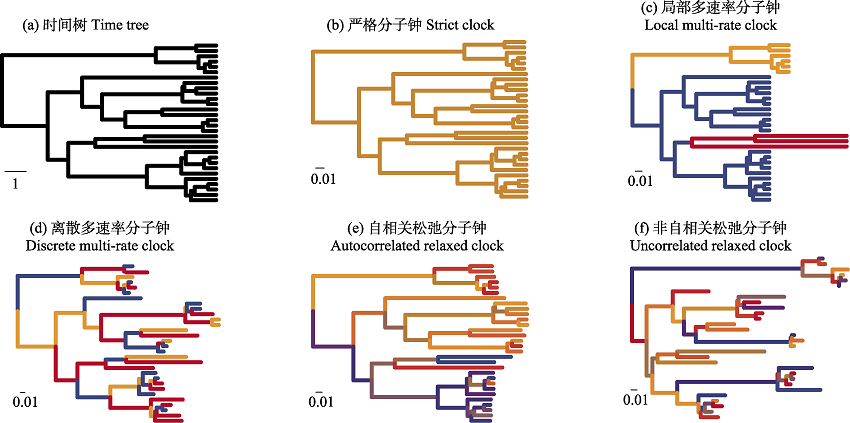
图2 不同的分子钟模型示意图(改自: Ho & Duchêne, 2014)。图中的6个时间树具有相同的结构, 但由于分子钟模型选择的不同, 支长有很大差异。(a)未添加分子钟模型的时间树, 比例尺显示了1个时间单位。(b)严格分子钟模型, 所有支的速率相等。(c)局部多速率分子钟, 允许一定量的速率存在, 并根据拓扑的聚类情况设置速率, 同一类群具有相同或相似的速率。(d)离散多速率分子钟, 允许一定量的速率存在, 不考虑拓扑聚类情况的模型。(e)自相关松弛分子钟, 允许最多等于支数的速率存在, 且邻近支的速率相关。(f)非自相关松弛分子钟, 没有任何对速率的数量、分布格局的限制, 是最宽松自由的模型设置。
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of different molecular clock models (modified from Ho & Duchêne, 2014). The six time trees in this figure have the same structure, but the branch length varies greatly due to different selection of molecular clock models. (a) The time tree without applying molecular clock model. The scale bar indicates one time unit. (b) In strict molecular clock model, all branches have the same rate. (c) Local multi-rate molecular clock allows a certain amount of rate and sets the rate according to the clustering situation of topology. The related branches have the same or similar rate. (d) Discrete multi-rate molecular clock, which also allows a certain amount of rate, does not consider the topological clustering. (e) The autocorrelated relaxed molecular clock allows the existence of a rate at most equal to the number of branches, and the rate dependence of adjacent branches. (f) The uncorrelated relaxed molecular clock, without any restrictions on the number and distribution pattern of rates, is the most relaxed and free model setting.
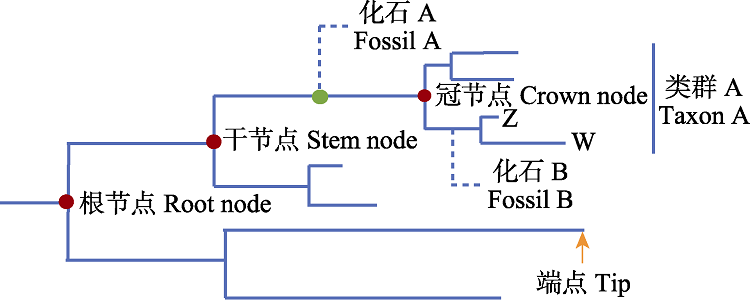
图3 系统发育树中部分术语示意图。图中冠节点的年龄代表了类群A现存所有物种最近共同祖先的节点, 而干节点代表了该类群最近共同祖先与其最近缘类群共祖的节点。以衍征法为例, 图中的化石A与类群A现存物种存在共同衍征, 因此可以作为类群A干节点的最小年龄限制; 而要为类群A的冠节点添加年龄限制, 需要获得与类群A的亚类群具有共同衍征的化石记录, 如图中的物种Z、W和化石B所表示的关系。系统发育法同理。
Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of some terms in phylogenetic tree. The age of the crown node in the figure represents the node of the nearest common ancestor of all species in group A, while the stem node represents the node of the nearest common ancestor of the group A and its nearest related group. Taking the apomorphy-based method as an example, fossil A in the figure has synapomorphies with the extant species of group A, so it can be used as the minimum age constraint for the stem node of group A. To apply age constraint to the crown node of group A, it is necessary to obtain fossil records sharing synapomorphies with subgroups of group A, as indicated by the relationship of species Z, W and fossil B in the figure. The same is true of phylogenetic method.
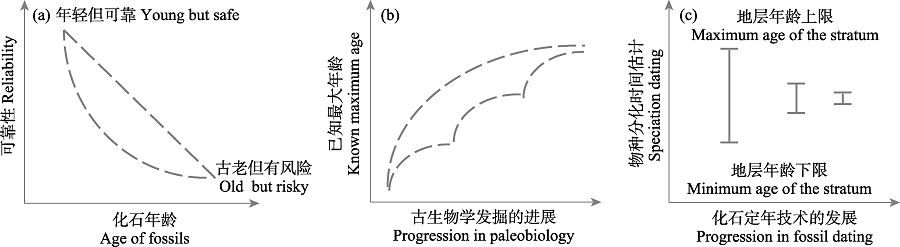
图4 化石年龄不确定性的3种情形。(a)“年轻但可靠”和“古老但有风险”的两种化石在化石年龄和可靠性两个维度上的分布, 其他大多数化石分布于两虚线围成的区域中。(b)某个类群已知最古老化石的年龄随着古生物学发掘过程不断扩展补充、逐步接近类群真实分化时间的趋势。(c)随着化石定年技术的发展, 化石年龄的精确度不断提升。
Fig. 4 Three cases of fossil age uncertainty. (a) The present of “young but safe” and “old but risky” fossils in two dimensions: age of fossils and reliability. Most of the other fossils are distributed in the area surrounded by the two dotted lines. (b) The age of the oldest known fossil of a certain group tends to be close to the real divergence time of the group as the paleobiological excavation continues to expand. (c) With the development of fossil dating technology, the accuracy of fossil age has been improved.
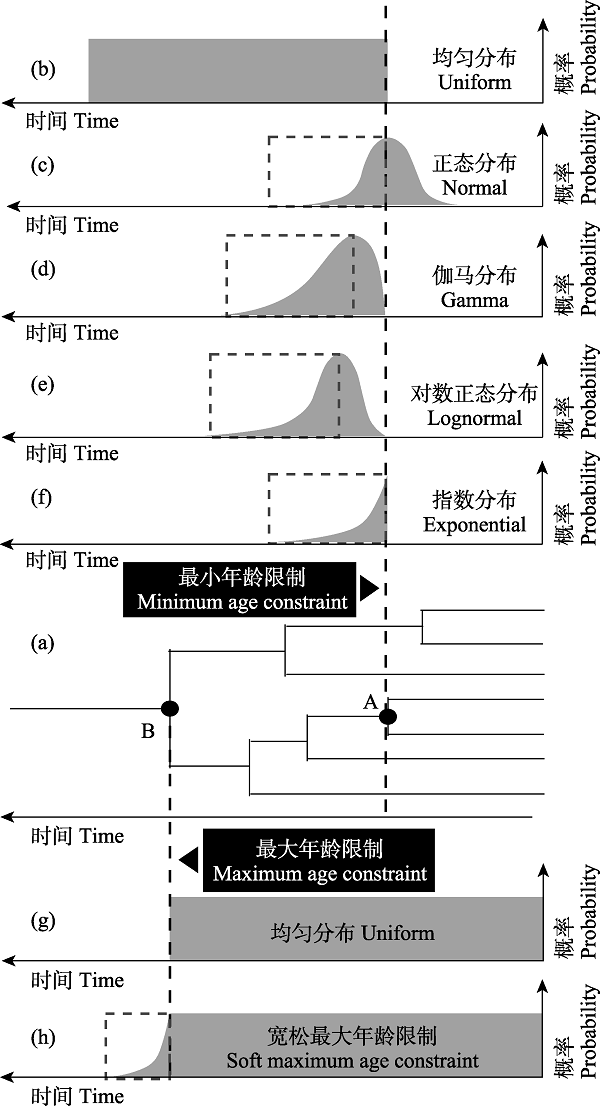
图5 节点年龄的概率分布。在不同节点设置最大或最小年龄限制, 可以采用不同的概率分布。其中(a)图表示系统发育树上设置最小和最大年龄限制的两个节点, (b)-(f)强调均匀、正态、伽马、对数正态和指数分布中的最小年龄限制, 而(g)和(h)则分别表示了均匀分布中的严格和宽松最大年龄限制(虚线及虚线框)。另外, (c)-(f)中虚线框强调的部分等同于宽松最大年龄限制。图中的soft maximum/minimum constraint又称软边界(soft bound)。
Fig. 5 Probability distribution of node age. The maximum or minimum age constraint can be set on different nodes, and different probability distribution can be adopted. Where (a) shows two nodes with minimum and maximum age constraint, respectively, in phylogenetic tree; (b)-(f) emphasize the minimum age constraints in uniform, normal, gamma, lognormal and exponential distribution, while (g) and (h) represent strict and relaxed maximum age constraints on uniform distribution, respectively. In addition, the part highlighted by the dotted box in (c)-(f) is equivalent to the relaxed maximum age constraint. The soft maximum/minimum constraint in the figure is also called soft bound.
| [1] |
Baele G, Lemey P, Bedford T, Rambaut A, Suchard MA, Alekseyenko AV (2012a) Improving the accuracy of demographic and molecular clock model comparison while accommodating phylogenetic uncertainty. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 29, 2157-2167.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Baele G, Li WLS, Drummond AJ, Suchard MA, Lemey P (2012b) Accurate model selection of relaxed molecular clocks in Bayesian phylogenetics. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 239-243.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Barba-Montoya J, dos Reis M, Yang ZH (2017) Comparison of different strategies for using fossil calibrations to generate the time prior in Bayesian molecular clock dating. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 114, 386-400.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Beerli P (2006) Comparison of Bayesian and maximum- likelihood inference of population genetic parameters. Bioinformatics, 22, 341-345.
PMID |
| [5] |
Benton MJ, Donoghue PCJ (2007) Paleontological evidence to date the tree of life. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24, 26-53.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Bouckaert R, Heled J, Kühnert D, Vaughan T, Wu CH, Xie D, Suchard MA, Rambaut A, Drummond AJ (2014) BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Computational Biology, 10, e1003537.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Bouckaert RR, Drummond AJ (2017) bModelTest: Bayesian phylogenetic site model averaging and model comparison. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 17, 42.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Brinkmann H, van der Giezen M, Zhou Y, De Raucourt GP, Philippe H (2005) An empirical assessment of long-branch attraction artefacts in deep eukaryotic phylogenomics. Systematic Biology, 54, 743-757.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Bromham L, Duchêne S, Hua X, Ritchie AM, Duchêne DA, Ho SYW (2018) Bayesian molecular dating: Opening up the black box. Biological Reviews, 93, 1165-1191.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Brooks DR, Bilewitch J, Condy C, Evans DC, Folinsbee KE, Fröbisch J, Halas D, Hill S, McLennan D, Mattern M, Tsuji LA, Ward J, Wahlberg N, Zamparo D, Zanatta D (2007) Quantitative phylogenetic analysis in the 21st century. Revista Mexicana de Biodiversidad, 78, 225-252. |
| [11] |
Brower AVZ (2018) Statistical consistency and phylogenetic inference: A brief review. Cladistics, 34, 562-567.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Brown RP, Yang ZH (2011) Rate variation and estimation of divergence times using strict and relaxed clocks. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 11, 271.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Chen MH, Shao QM (1999) Monte Carlo estimation of Bayesian credible and HPD intervals. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 8, 69-92. |
| [14] |
Claramunt S, Cracraft J (2015) A new time tree reveals Earth history’s imprint on the evolution of modern birds. Science Advances, 1, e1501005.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Condamine FL, Nagalingum NS, Marshall CR, Morlon H (2015) Origin and diversification of living cycads: A cautionary tale on the impact of the branching process prior in Bayesian molecular dating. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 15, 1-18.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Conroy CJ, van Tuinen M (2003) Extracting time from phylogenies: Positive interplay between fossil and genetic data. Journal of Mammalogy, 84, 444-455.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Cooper N, Thomas GH, Venditti C, Meade A, Freckleton RP (2016) A cautionary note on the use of Ornstein Uhlenbeck models in macroevolutionary studies. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 118, 64-77.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Crisp MD, Trewick SA, Cook LG (2011) Hypothesis testing in biogeography. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 26, 66-72.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2012) jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nature Methods, 9, 772.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Donoghue MJ, Doyle JA, Gauthier J, Kluge AG, Rowe T (1989) The importance of fossils in phylogeny reconstruction. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 20, 431-460.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Donoghue MJ, Moore BR (2003) Toward an integrative historical biogeography. Integrative and Comparative Biology, 43, 261-270.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
dos Reis M, Donoghue PCJ, Yang ZH (2016) Bayesian molecular clock dating of species divergences in the genomics era. Nature Reviews Genetics, 17, 71-80.
DOI URL |
| [23] | dos Reis M, Inoue J, Hasegawa M, Asher RJ, Donoghue PCJ, Yang ZH (2012) Phylogenomic datasets provide both precision and accuracy in estimating the timescale of placental mammal phylogeny. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 279, 3491-3500. |
| [24] |
dos Reis M, Thawornwattana Y, Angelis K, Telford MJ, Donoghue PCJ, Yang ZH (2015) Uncertainty in the timing of origin of animals and the limits of precision in molecular timescales. Current Biology, 25, 2939-2950.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Drummond AJ, Ho SYW, Phillips MJ, Rambaut A (2006) Relaxed phylogenetics and dating with confidence. PLoS Biology, 4, e88.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Drummond AJ, Suchard MA, Xie D, Rambaut A (2012) Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 29, 1969-1973.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Duchêne DA, Duchêne S, Ho SYW (2017) New statistical criteria detect phylogenetic bias caused by compositional heterogeneity. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 34, 1529-1534.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Duchêne S, Lanfear R, Ho SYW (2014) The impact of calibration and clock-model choice on molecular estimates of divergence times. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 78, 277-289.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Fan Y, Wu R, Chen MH, Kuo L, Lewis PO (2011) Choosing among partition models in Bayesian phylogenetics. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28, 523-532.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: A maximum likelihood approach. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 17, 368-376.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Fikáček M, Beutel RG, Cai C, Lawrence JF, Newton AF, Solodovnikov A, Ślipiński A, Thayer MK, Yamamoto S (2020) Reliable placement of beetle fossils via phylogenetic analyses—Triassic Leehermania as a case study (Staphylinidae or Myxophaga?). Systematic Entomology, 45, 175-187.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Friston KJ, Lawson R, Frith CD (2013) On hyperpriors and hypopriors: Comment on Pellicano and Burr. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 17, 1.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Good PI, Hardin JW (2012) Common Errors in Statistics (and How to Avoid Them). John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken. |
| [34] |
Graham TA, Sottoriva A (2017) Measuring cancer evolution from the genome. The Journal of Pathology, 241, 183-191.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Greenwood DR (1991) The taphonomy of plant macrofossils. In: The Processes of Fossilization (ed. Donovan SK), pp. 141-169. Columbia University Press, New York. |
| [36] |
Grimm GW, Kapli P, Bomfleur B, McLoughlin S, Renner SS (2015) Using more than the oldest fossils: Dating Osmundaceae with three Bayesian clock approaches. Systematic Biology, 64, 396-405.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Guillerme T, Cooper N (2016) Assessment of available anatomical characters for linking living mammals to fossil taxa in phylogenetic analyses. Biology Letters, 12, 20151003.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Hall BG (2005) Comparison of the accuracies of several phylogenetic methods using protein and DNA sequences. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 22, 792-802.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Halliday TJ, Goswami A (2016) The impact of phylogenetic dating method on interpreting trait evolution: A case study of Cretaceous-Palaeogene eutherian body-size evolution. Biology Letters, 12, 20160051.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Harwood DM, Nikolaev VA, Winter DM (2007) Cretaceous records of diatom evolution, radiation, and expansion. The Paleontological Society Papers, 13, 33-59.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Hasegawa M, Kishino H, Yano T (1985) Dating of the human-ape splitting by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 22, 160-174.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Heads M (2005) Dating nodes on molecular phylogenies: A critique of molecular biogeography. Cladistics, 21, 62-78.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Heath TA, Huelsenbeck JP, Stadler T (2014) The fossilized birth-death process for coherent calibration of divergence- time estimates. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111, E2957-E2966. |
| [44] |
Ho SYW, Duchêne S (2014) Molecular-clock methods for estimating evolutionary rates and timescales. Molecular Ecology, 23, 5947-5965.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Ho SYW, Phillips MJ (2009) Accounting for calibration uncertainty in phylogenetic estimation of evolutionary divergence times. Systematic Biology, 58, 367-380.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Höhna S, Landis MJ, Heath TA, Boussau B, Lartillot N, Moore BR, Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2016) RevBayes: Bayesian phylogenetic inference using graphical models and an interactive model-specification language. Systematic Biology, 65, 726-736.
DOI URL |
| [47] | Jeffreys H (1935) Some tests of significance, treated by the theory of probability. Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 31, 203-222. |
| [48] | Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Mammalian Protein Metabolism (ed. Munro HN), pp. 21-132. Academic Press, New York. |
| [49] |
Keane TM, Creevey CJ, Pentony MM, Naughton TJ, Mclnerney JO (2006) Assessment of methods for amino acid matrix selection and their use on empirical data shows that ad hoc assumptions for choice of matrix are not justified. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 6, 29.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 16, 111-120.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Korber B, Muldoon M, Theiler J, Gao F, Gupta R, Lapedes A, Hahn BH, Wolinsky S, Bhattacharya T (2000) Timing the ancestor of the HIV-1 pandemic strains. Science, 288, 1789-1796.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Kumar S (2005) Molecular clocks: Four decades of evolution. Nature Reviews Genetics, 6, 654-662.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Kumar S, Hedges SB (2016) Advances in time estimation methods for molecular data. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33, 863-869.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Kuo CH, Ochman H (2009) Inferring clocks when lacking rocks: The variable rates of molecular evolution in bacteria. Biology Direct, 4, 35.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Lanfear R, Calcott B, Ho SYW, Guindon S (2012) PartitionFinder: Combined selection of partitioning schemes and substitution models for phylogenetic analyses. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 29, 1695-1701.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Lartillot N, Philippe H (2006) Computing Bayes factors using thermodynamic integration. Systematic Biology, 55, 195-207.
DOI URL |
| [57] | Laws B (2010) Fifty Plants that Changed the Course of History. Firefly Books, Richmond Hill. |
| [58] |
Lee MSY (2016) Multiple morphological clocks and total-evidence tip-dating in mammals. Biology Letters, 12, 20160033.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
Lepage T, Lawi S, Tupper P, Bryant D (2006) Continuous and tractable models for the variation of evolutionary rates. Mathematical Biosciences, 199, 216-233.
DOI URL |
| [60] | Li KQ (2015) Quantitative analysis of relationship between absolute evolutionary rates and taxa divergence times. Journal of Biology, 32(2), 70-75, 79. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李可群 (2015) 分子绝对进化速率与物种分歧时间之间的定量关系. 生物学杂志, 32(2), 70-75, 79.] | |
| [61] |
Linder HP, Hardy CR, Rutschmann F (2005) Taxon sampling effects in molecular clock dating: An example from the African Restionaceae. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 35, 569-582.
DOI URL |
| [62] | Liu XF, Zhang AB (2016) The basic principle and application of the molecular clock hypothesis. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 55, 393-402. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘晓枫, 张爱兵 (2016) 分子钟假说的基本原理及在古生物等学科中的应用. 古生物学报, 55, 393-402.] | |
| [63] |
Lu LM, Sun M, Zhang JB, Li HL, Lin L, Yang T, Chen M, Chen ZD (2014) Tree of life and its applications. Biodiversity Science, 22, 3-20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 鲁丽敏, 孙苗, 张景博, 李洪雷, 林立, 杨拓, 陈闽, 陈之端 (2014) 生命之树及其应用. 生物多样性, 22, 3-20.] | |
| [64] |
Magallón S, Castillo A (2009) Angiosperm diversification through time. American Journal of Botany, 96, 349-365.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
Makowski D, Ben-Shachar M, Lüdecke D (2019) bayestestR: Describing effects and their uncertainty, existence and significance within the Bayesian framework. Journal of Open Source Software, 4, 1541.
DOI URL |
| [66] | Mao KS, Milne RI, Zhang LB, Peng YL, Liu JQ, Thomas P, Mill RR, Renner SS (2012) Distribution of living Cupressaceae reflects the breakup of Pangea. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 109, 7793-7798. |
| [67] |
Marshall CR (2008) A simple method for bracketing absolute divergence times on molecular phylogenies using multiple fossil calibration points. The American Naturalist, 171, 726-742.
DOI PMID |
| [68] |
Martin PG, Dowd JM (1993) Using sequences of rbcL to study phylogeny and biogeography of Nothofagus species. Australian Systematic Botany, 6, 441-447.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
Miller KB, Bergsten J (2012) Phylogeny and classification of whirligig beetles (Coleoptera: Gyrinidae): Relaxed-clock model outperforms parsimony and time-free Bayesian analyses. Systematic Entomology, 37, 706-746.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Morgan GJ (1998) Emile Zuckerkandl, Linus Pauling, and the molecular evolutionary clock, 1959-1965. Journal of the History of Biology, 31, 155-178.
PMID |
| [71] | Newton MA, Raftery AE (1994) Approximate Bayesian inference with the weighted likelihood bootstrap. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Statistical Methodology), 56, 3-26. |
| [72] |
Nie Y, Foster CSP, Zhu TQ, Yao R, Duchêne DA, Ho SYW, Zhong BJ (2020) Accounting for uncertainty in the evolutionary timescale of green plants through clock-partitioning and fossil calibration strategies. Systematic Biology, 69, 1-16.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
O’Reilly JE, Dos Reis M, Donoghue PCJ (2015) Dating tips for divergence-time estimation. Trends in Genetics, 31, 637-650.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
O’Reilly JE, Donoghue PCJ (2016) Tips and nodes are complementary not competing approaches to the calibration of molecular clocks. Biology Letters, 12, 20150975.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Parham JF, Donoghue PCJ, Bell CJ, Calway TD, Head JJ, Holroyd PA, Inoue JG, Irmis RB, Joyce WG, Ksepka DT, Patane JSL, Smith ND, Tarver JE, van Tuinen M, Yang ZH, Angielczyk KD, Greenwood JM, Hipsley CA, Jacobs L, Makovicky PJ, Müller J, Smith KT, Theodor JM, Warnock RCM, Benton MJ (2012) Best practices for justifying fossil calibrations. Systematic Biology, 61, 346-359.
DOI PMID |
| [76] | Pauling L, Zuckerkandl E (1962) Molecular paleontology. Acta Chemica Scandinavica, 17, S9-S16. |
| [77] | Raftery AE, Newton MA, Satagopan JM, Krivitsky PN (2006) Estimating the integrated likelihood via posterior simulation using the harmonic mean identity. Bayesian Statistics, 8, 1-45. |
| [78] | Rector A, Lemey P, Tachezy R, Mostmans S, Ghim SJ, Van Doorslaer K, Roelke M, Bush M, Montali RJ, Joslin J, Burk RD, Jenson AB, Sundberg JP, Shapiro B, van Ranst M (2007) Ancient papillomavirus-host co-speciation in Felidae. Genome Biology, 8, 1-12. |
| [79] |
Renner SS (2005) Relaxed molecular clocks for dating historical plant dispersal events. Trends in Plant Science, 10, 550-558.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
Reyes A, Pesole G, Saccone C (2000) Long-branch attraction phenomenon and the impact of among-site rate variation on rodent phylogeny. Gene, 259, 177-187.
PMID |
| [81] |
Ronquist F, Klopfstein S, Vilhelmsen L, Schulmeister S, Murray DL, Rasnitsyn AP (2012) A total-evidence approach to dating with fossils, applied to the early radiation of the Hymenoptera. Systematic Biology, 61, 973-999.
DOI PMID |
| [82] |
Sanders KL, Lee MSY (2007) Evaluating molecular clock calibrations using Bayesian analyses with soft and hard bounds. Biology Letters, 3, 275-279.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
Sauquet H (2013) A practical guide to molecular dating. Comptes Rendus Palevol, 12, 355-367.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
Sauquet H, Ho SYW, Gandolfo MA, Jordan GJ, Wilf P, Cantrill DJ, Bayly MJ, Bromham L, Brown GK, Carpenter RJ, Lee DM, Murphy DJ, Sniderman JMK, Udovicic F (2012) Testing the impact of calibration on molecular divergence times using a fossil-rich group: The case of Nothofagus (Fagales). Systematic Biology, 61, 289-313.
DOI PMID |
| [85] | Schaefer H, Heibl C, Renner SS (2009) Gourds afloat: A dated phylogeny reveals an Asian origin of the gourd family (Cucurbitaceae) and numerous oversea dispersal events. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 276, 843-851. |
| [86] |
Shapiro B, Rambaut A, Drummond AJ (2006) Choosing appropriate substitution models for the phylogenetic analysis of protein-coding sequences. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 23, 7-9.
DOI URL |
| [87] |
Sinsheimer JS, Lake JA, Little RJA (1996) Bayesian hypothesis testing of four-taxon topologies using molecular sequence data. Biometrics, 52, 193-210.
PMID |
| [88] |
Slack KE, Jones CM, Ando T, Harrison GL, Fordyce RE, Arnason U, Penny D (2006) Early penguin fossils, plus mitochondrial genomes, calibrate avian evolution. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 23, 1144-1155.
DOI URL |
| [89] | Smith SA, Beaulieu JM, Donoghue MJ (2010) An uncorrelated relaxed-clock analysis suggests an earlier origin for flowering plants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 107, 5897-5902. |
| [90] |
Steel M (2005) Should phylogenetic models be trying to ‘fit an elephant’? Trends in Genetics, 21, 307-309.
PMID |
| [91] |
Strugnell J, Norman M, Jackson J, Drummond AJ, Cooper A (2005) Molecular phylogeny of coleoid cephalopods (Mollusca: Cephalopoda) using a multigene approach: The effect of data partitioning on resolving phylogenies in a Bayesian framework. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 37, 426-441.
DOI URL |
| [92] | Suchard MA, Lemey P, Baele G, Ayres DL, Drummond AJ, Rambaut A (2018) Bayesian phylogenetic and phylodynamic data integration using BEAST 1.10. Virus Evolution, 4, vey016. |
| [93] |
Suchard MA, Weiss RE, Sinsheimer JS (2001) Bayesian selection of continuous-time Markov chain evolutionary models. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 18, 1001-1013.
DOI URL |
| [94] |
Susko E (2015) Bayesian long branch attraction bias and corrections. Systematic Biology, 64, 243-255.
DOI URL |
| [95] | Tavaré S (1986) Some probabilistic and statistical problems in the analysis of DNA sequences. Lectures on Mathematics in the Life Sciences, 17, 57-86. |
| [96] |
Thomas JA, Welch JJ, Lanfear R, Bromham L (2010) A generation time effect on the rate of molecular evolution in invertebrates. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 27, 1173-1180.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
Thorne JL, Kishino H, Painter IS (1998) Estimating the rate of evolution of the rate of molecular evolution. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 15, 1647-1657.
DOI URL |
| [98] | Van den Bergh D, Haaf JM, Ly A, Rouder JN, Wagenmakers EJ (2021) A cautionary note on estimating effect size. Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychological Science, 4, 1-8. |
| [99] |
Vijgen L, Keyaerts E, Moës E, Thoelen I, Wollants E, Lemey P, Vandamme AM, Van Ranst M (2005) Complete genomic sequence of human coronavirus OC43: Molecular clock analysis suggests a relatively recent zoonotic coronavirus transmission event. Journal of Virology, 79, 1595-1604.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
Wagenmakers EJ, Gronau QF, Dablander F, Etz A (2020) The support interval. Erkenntnis, 10.1007/s10670-019-00209-z.
DOI |
| [101] |
Wang Q, Mao KS (2016) Puzzling rocks and complicated clocks: How to optimize molecular dating approaches in historical phytogeography. New Phytologist, 209, 1353-1358.
DOI URL |
| [102] | Warnock RCM, Yang ZH, Donoghue PCJ (2017) Testing the molecular clock using mechanistic models of fossil preservation and molecular evolution. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 284, 20170227. |
| [103] | Wasserman L (2004) Bayesian Inference. In: All of Statistics, A Concise Course in Statistical Inference (ed. Wasserman L), pp. 175-190. Springer, New York. |
| [104] |
Wertheim JO, Sanderson MJ, Worobey M, Bjork A (2010) Relaxed molecular clocks, the bias-variance trade-off, and the quality of phylogenetic inference. Systematic Biology, 59, 1-8.
DOI PMID |
| [105] |
Wilf P, Escapa IH (2015) Green Web or megabiased clock? Plant fossils from Gondwanan Patagonia speak on evolutionary radiations. New Phytologist, 207, 283-290.
DOI URL |
| [106] |
Wu CH, Suchard MA, Drummond AJ (2013) Bayesian selection of nucleotide substitution models and their site assignments. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 669-688.
DOI URL |
| [107] |
Xie WG, Lewis PO, Fan Y, Kuo L, Chen MH (2011) Improving marginal likelihood estimation for Bayesian phylogenetic model selection. Systematic Biology, 60, 150-160.
DOI URL |
| [108] | Yang ZH (2006) Computational Molecular Evolution. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [109] |
Yang ZH, Rannala B (1997) Bayesian phylogenetic inference using DNA sequences: A Markov Chain Monte Carlo Method. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 14, 717-724.
DOI URL |
| [110] |
Yang ZH (2007) PAML 4: Phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24, 1586-1591.
DOI URL |
| [111] |
Yang ZH, Rannala B (2006) Bayesian estimation of species divergence times under a molecular clock using multiple fossil calibrations with soft bounds. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 23, 212-226.
DOI URL |
| [112] |
Yang ZH, Rannala B (2012) Molecular phylogenetics: Principles and practice. Nature Reviews Genetics, 13, 303-314.
DOI URL |
| [113] | Zhang C (2019) Molecular clock dating using MrBayes. Vertebrata PalaAsiatica, 57, 241-252. |
| [114] | Zhang Y, Chen ZD (2003) Recent progress of sequences analysis methods in molecular evolutionary biology. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 20, 462-467. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张原, 陈之端 (2003) 分子进化生物学中序列分析方法的新进展. 植物学通报, 20, 462-467.] | |
| [115] |
Zhu TQ (2019) Bayesian molecular dating with genomic data. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 49, 472-483. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 朱天琪 (2019) 使用基因组数据进行贝叶斯物种分化时间估计. 中国科学: 生命科学, 49, 472-483.] |
| [1] | 孙亚君. 何谓高等或低等生物——澄清《物种起源》所蕴含的生物等级性的涵义及其成立性[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24394-. |
| [2] | 艾妍雨, 胡海霞, 沈婷, 莫雨轩, 杞金华, 宋亮. 附生维管植物多样性及其与宿主特征的相关性: 以哀牢山中山湿性常绿阔叶林为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24072-. |
| [3] | 吕燕文, 王子韵, 肖钰, 何梓晗, 吴超, 胡新生. 谱系分选理论与检测方法的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23400-. |
| [4] | 曹可欣, 王敬雯, 郑国, 武鹏峰, 李英滨, 崔淑艳. 降水格局改变及氮沉降对北方典型草原土壤线虫多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [5] | 王斌, 钟艺倩, 杨美雪, 吴淼锐, 王艳萍, 陆芳, 陶旺兰, 李健星, 赵弘明, 刘晟源, 向悟生, 李先琨. 喀斯特季节性雨林优势树种叶片非结构性碳水化合物空间变异及生态驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24325-. |
| [6] | 杨向林, 赵彩云, 李俊生, 种方方, 李文金. 植物入侵导致群落谱系结构更加聚集: 以广西国家级自然保护区草本植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [7] | 何林君, 杨文静, 石宇豪, 阿说克者莫, 范钰, 王国严, 李景吉, 石松林, 易桂花, 彭培好. 火烧干扰下植物群落系统发育和功能多样性对紫茎泽兰入侵的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24269-. |
| [8] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [9] | 宋会银, 胡征宇, 刘国祥. 绿藻门小球藻科的分类学研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22083-. |
| [10] | 李治中, 彭帅, 王青锋, 李伟, 梁士楚, 陈进明. 中国海菜花属植物隐种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22394-. |
| [11] | 朱瑞良, 马晓英, 曹畅, 曹子寅. 中国苔藓植物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22378-. |
| [12] | 王婷, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 李艳清, 杨拓, 徐洲锋, 向建英, 张宪春, 严岳鸿. 中国石松类和蕨类植物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22381-. |
| [13] | 王健铭, 曲梦君, 王寅, 冯益明, 吴波, 卢琦, 何念鹏, 李景文. 青藏高原北部戈壁植物群落物种、功能与系统发育β多样性分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21503-. |
| [14] | 姜晓燕, 高圣杰, 蒋燕, 田赟, 贾昕, 查天山. 毛乌素沙地植被不同恢复阶段植物群落物种多样性、功能多样性和系统发育多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21387-. |
| [15] | 赵琦, 蒋际宝, 张曾鲁, 金清, 李佳丽, 邱江平. 海南岛蚯蚓物种组成及其系统发育分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22224-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()