



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 23400. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023400 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023400
吕燕文1,2( ), 王子韵1,2(
), 王子韵1,2( ), 肖钰1,2(
), 肖钰1,2( ), 何梓晗1,2(
), 何梓晗1,2( ), 吴超1,2(
), 吴超1,2( ), 胡新生1,2,*(
), 胡新生1,2,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2023-10-22
接受日期:2024-02-20
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-03-28
通讯作者:
* E-mail: 基金资助:
Yanwen Lv1,2( ), Ziyun Wang1,2(
), Ziyun Wang1,2( ), Yu Xiao1,2(
), Yu Xiao1,2( ), Zihan He1,2(
), Zihan He1,2( ), Chao Wu1,2(
), Chao Wu1,2( ), Xinsheng Hu1,2,*(
), Xinsheng Hu1,2,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-10-22
Accepted:2024-02-20
Online:2024-04-20
Published:2024-03-28
Contact:
* E-mail: 摘要:
谱系分选为理解物种形成机制提供了一个途径, 常被划分为复系、并系及单系3个阶段, 对应着不同的基因树与物种树关系。本文首先系统地探讨了不同进化属性(中性和选择性)的基因组位点在祖先群体中如何传递到子代群体中的相关理论, 分析了可能的基因树与物种树关系。其次探讨了基于中性序列谱系分选分析方法, 包括在不完全谱系分选下物种树构建和系统发育网络分析。进一步探讨了选择对谱系分选的影响, 基于基因树和物种树途径检测选择的方法, 包括定向选择和平衡选择检测。最后, 探讨了植物交配系统对谱系分选的影响, 不完全谱系分选检测存在的问题以及在花粉流和种子流及不完全谱系分选的综合条件下系统发育网络分析方法, 澄清这些问题有助于深度理解植物种的谱系分选过程。
吕燕文, 王子韵, 肖钰, 何梓晗, 吴超, 胡新生 (2024) 谱系分选理论与检测方法的研究进展. 生物多样性, 32, 23400. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023400.
Yanwen Lv, Ziyun Wang, Yu Xiao, Zihan He, Chao Wu, Xinsheng Hu (2024) Advances in lineage sorting theories and their detection methods. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23400. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023400.
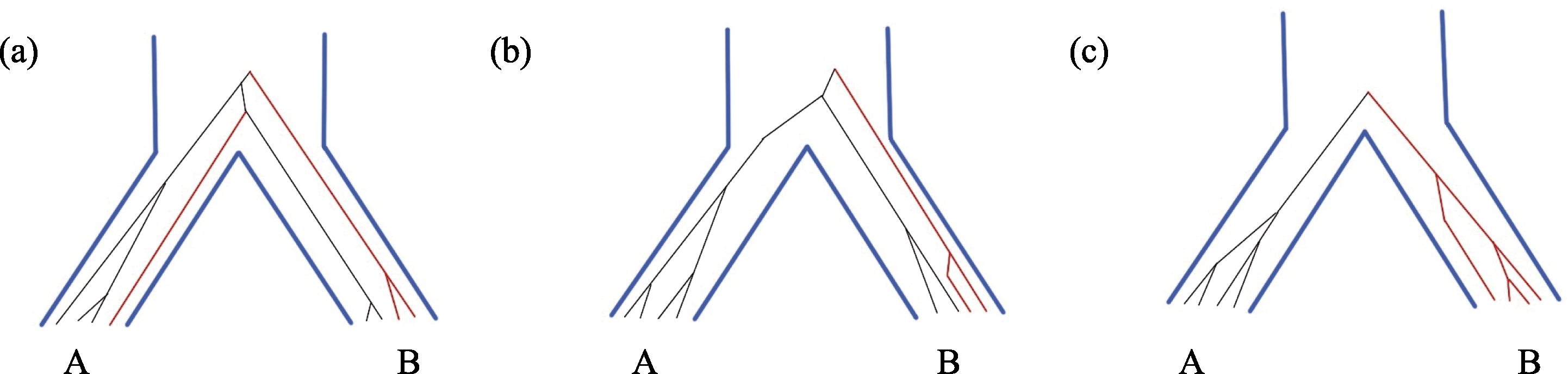
图1 两个物种的谱系分选过程: (a)复系; (b)并系; (c)单系。图中的蓝色粗线表示物种树(A和B物种), 黑色细线为物种A的等位基因, 红色细线为物种B的等位基因。
Fig. 1 Lineage sorting process of two species: (a) Polyphyly; (b) Paraphyly; (c) Monophyly. The blue bold lines in the figure indicate the tree of species A and B. The thin black lines represent the alleles of species A. The thin red lines represent the alleles of species B.
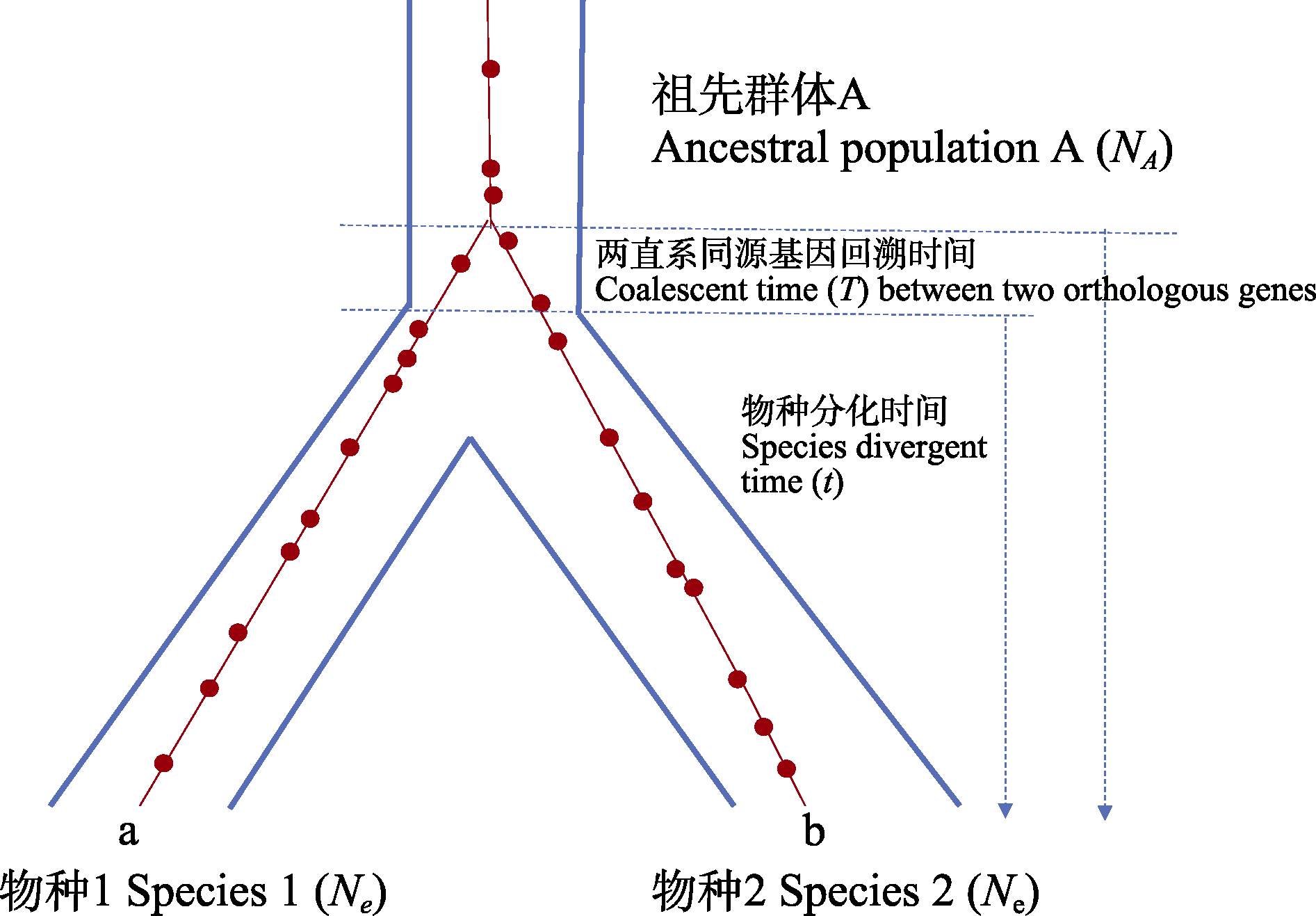
图2 两个子代物种(物种1, 物种2)在t世代前溯祖。种内所有基因来自单一祖先, 两直系基因回溯到物种分化前的祖先群体中(T世代)。在中性假设下, 两个子代物种直系同源基因间自物种分化后的突变数等于2μt。红点表示突变, 字母a、b表示两个直系同源基因。
Fig. 2 Two progeny species (species 1 and 2) descend from an ancestral population at t generations ago. All the genes within a species descend from a single lineage. Two orthologous genes coalesce to a single lineage in the ancestral population at T generations ago. Under the neutrality hypothesis, the two orthologous genes differ from each other by 2μt mutations since speciation. The red dots indicate mutations. Letters a and b indicate two orthologous genes.
| 祖先群体中选择类型 Selection type at a locus in the ancestral population | 子代物种间基因平均溯祖时间 Mean coalescent time between orthologous genes from descent species |
|---|---|
| 定向选择 Directional selection | 近似于在祖先群体时溯祖时间, 或长于物种分化时间 Approximate to the coalescent time in the ancestral population, or longer than the species divergence time |
| 平衡选择 Balancing selection | 远远大于物种分化时间 Much longer than the species divergence time |
| 歧化选择 Disruptive selection | 近似于物种分化时间 Approximate to the species divergence time |
| 正频率依赖选择 Positive frequency-dependent selection | 近似于在祖先群体时的溯祖时间 Approximate to the coalescent time in the ancestral population |
| 负频率依赖选择 Negative frequency-dependent selection | 远远大于物种分化时间 Much longer than the species divergence time |
| 随机选择 Stochastic selection | 近似于子代物种中性基因间溯祖时间, 大于物种分化时间 Approximate to the coalescent time of neutral genes in decent species but is longer than the species divergence time |
表1 在祖先群体中位点的选择类型及其在子代种间两直系同源基因的基因树与物种树的可能关系
Table 1 The type of selection at a locus in the ancestral population and the potential relationship between the gene tree of two orthologous genes and the descent species tree
| 祖先群体中选择类型 Selection type at a locus in the ancestral population | 子代物种间基因平均溯祖时间 Mean coalescent time between orthologous genes from descent species |
|---|---|
| 定向选择 Directional selection | 近似于在祖先群体时溯祖时间, 或长于物种分化时间 Approximate to the coalescent time in the ancestral population, or longer than the species divergence time |
| 平衡选择 Balancing selection | 远远大于物种分化时间 Much longer than the species divergence time |
| 歧化选择 Disruptive selection | 近似于物种分化时间 Approximate to the species divergence time |
| 正频率依赖选择 Positive frequency-dependent selection | 近似于在祖先群体时的溯祖时间 Approximate to the coalescent time in the ancestral population |
| 负频率依赖选择 Negative frequency-dependent selection | 远远大于物种分化时间 Much longer than the species divergence time |
| 随机选择 Stochastic selection | 近似于子代物种中性基因间溯祖时间, 大于物种分化时间 Approximate to the coalescent time of neutral genes in decent species but is longer than the species divergence time |
| 类型 Type | 输入/输出 Input/output | 方法 Method | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 汇总法 Summary method | 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | NJst | Liu & Yu, |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | wQMC | Avni et al, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | ASTRAL | Mirarab et al, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | ASTRAL-II | Mirarab & Warnow, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | ASTRID | Vachaspati & Warnow, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | DISTIQUE | Sayyari & Mirarab, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | ASTRAL-III | Zhang et al, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | USTAR/FastME | Allman et al, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | wQFM | Mahbub et al, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | ASTER | Zhang & Mirarab, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | TREE-QMC | Han & Molloy, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | Asteroid | Morel et al, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | wASTRID | Liu & Warnow, | |
| 有根基因树/有根物种树 RGT/RST | STEM | Kubatko et al, | |
| 有根基因树/有根物种树 RGT/RST | STAR/STEAC | Liu et al, | |
| 有根基因树/有根物种树 RGT/RST | MP-EST | Liu et al, | |
| 有根基因树/有根物种树 RGT/RST | STELLS | Wu, | |
| 有根基因树/有根物种树 RGT/RST | METAL | Dasarathy et al, | |
| 有根基因树/有根物种树 RGT/RST | STELLS2 | Pei & Wu, | |
| 有根基因树/有根物种树 RGT/RST | QR-STAR | Tabatabaee et al, | |
| 有根基因树/无根物种树 RGT/UST | STELAR | Islam et al, | |
| 共同估计法 Co-estimation of gene and species trees | 多序列比对/有根物种树和基因树分布 MSA/DRSGT | BEST | Liu, |
| 多序列比对/有根物种树和基因树分布 MSA/DRSGT | *BEAST | Heled & Drummond, | |
| 多序列比对/有根物种树和基因树分布 MSA/DRSGT | SNAP | Bryant et al, | |
| 多序列比对/有根物种树和基因树分布 MSA/DRSGT | BPP | Yang, | |
| 多序列比对/有根物种树和基因树分布 MSA/DRSGT | StarBEAST2 | Ogilvie et al, | |
| 基于位点法 Site-based method | 多位点比对/无根物种树 Multi-site alignments/UST | SVDquartets | Chifman & Kubatko, |
| 多位点比对/无根物种树 Multi-site alignments/UST | SVDquest | Vachaspati & Warnow, | |
| 独立溯祖位点/有根物种树 ICS/RST | Lily | Richards & Kubatko, |
表2 多物种溯祖模型下的物种树估计方法
Table 2 Methods for estimating species tree under multispecies coalescent model (MSC)
| 类型 Type | 输入/输出 Input/output | 方法 Method | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 汇总法 Summary method | 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | NJst | Liu & Yu, |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | wQMC | Avni et al, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | ASTRAL | Mirarab et al, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | ASTRAL-II | Mirarab & Warnow, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | ASTRID | Vachaspati & Warnow, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | DISTIQUE | Sayyari & Mirarab, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | ASTRAL-III | Zhang et al, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | USTAR/FastME | Allman et al, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | wQFM | Mahbub et al, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | ASTER | Zhang & Mirarab, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | TREE-QMC | Han & Molloy, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | Asteroid | Morel et al, | |
| 无根基因树/无根物种树 UGT/UST | wASTRID | Liu & Warnow, | |
| 有根基因树/有根物种树 RGT/RST | STEM | Kubatko et al, | |
| 有根基因树/有根物种树 RGT/RST | STAR/STEAC | Liu et al, | |
| 有根基因树/有根物种树 RGT/RST | MP-EST | Liu et al, | |
| 有根基因树/有根物种树 RGT/RST | STELLS | Wu, | |
| 有根基因树/有根物种树 RGT/RST | METAL | Dasarathy et al, | |
| 有根基因树/有根物种树 RGT/RST | STELLS2 | Pei & Wu, | |
| 有根基因树/有根物种树 RGT/RST | QR-STAR | Tabatabaee et al, | |
| 有根基因树/无根物种树 RGT/UST | STELAR | Islam et al, | |
| 共同估计法 Co-estimation of gene and species trees | 多序列比对/有根物种树和基因树分布 MSA/DRSGT | BEST | Liu, |
| 多序列比对/有根物种树和基因树分布 MSA/DRSGT | *BEAST | Heled & Drummond, | |
| 多序列比对/有根物种树和基因树分布 MSA/DRSGT | SNAP | Bryant et al, | |
| 多序列比对/有根物种树和基因树分布 MSA/DRSGT | BPP | Yang, | |
| 多序列比对/有根物种树和基因树分布 MSA/DRSGT | StarBEAST2 | Ogilvie et al, | |
| 基于位点法 Site-based method | 多位点比对/无根物种树 Multi-site alignments/UST | SVDquartets | Chifman & Kubatko, |
| 多位点比对/无根物种树 Multi-site alignments/UST | SVDquest | Vachaspati & Warnow, | |
| 独立溯祖位点/有根物种树 ICS/RST | Lily | Richards & Kubatko, |
| [1] |
Allman ES, Degnan JH, Rhodes JA (2018) Species tree inference from gene splits by unrooted STAR methods. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 15, 337-342.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Avise JC, Shapira JF, Daniel SW, Aquadro CF, Lansman RA (1983) Mitochondrial DNA differentiation during the speciation process in Peromyscus. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 1, 38-56.
PMID |
| [3] |
Avni E, Cohen R, Snir S (2015) Weighted quartets phylogenetics. Systematic Biology, 64, 233-242.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Barluenga M, Austerlitz F, Elzinga JA, Teixeira S, Goudet J, Bernasconi G (2011) Fine-scale spatial genetic structure and gene dispersal in Silene latifolia. Heredity, 106, 13-24.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Barton NH (1998) The effect of hitch-hiking on neutral genealogies. Genetics Research, 72, 123-133. |
| [6] | Barton NH, Briggs DEG, Eisen JA, Goldstein DB, Patel NH (2007) Evolution. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York. |
| [7] | Barton NH, Etheridge AM, Sturm AK (2004) Coalescence in a random background. Annals of Applied Probability, 14, 754-785. |
| [8] | Bayzid MS, Hunt T, Warnow T (2014) Disk covering methods improve phylogenomic analyses. BMC Genomics, 15, S7. |
| [9] | Berbel-Filho WM, Pacheco G, Tatarenkov A, Lira MG, Garcia de Leaniz C, Rodríguez López CM, Lima SMQ, Consuegra S (2022) Phylogenomics reveals extensive introgression and a case of mito-nuclear discordance in the killifish genus Kryptolebias. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 177, 107617. |
| [10] |
Bitarello BD, De Filippo C, Teixeira JC, Schmidt JM, Kleinert P, Meyer D, Andrés AM (2018) Signatures of long-term balancing selection in human genomes. Genome Biology and Evolution, 10, 939-955.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Blair C, Ané C (2020) Phylogenetic trees and networks can serve as powerful and complementary approaches for analysis of genomic data. Systematic Biology, 69, 593-601.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Bourret TB, Choudhury RA, Mehl HK, Blomquist CL, McRoberts N, Rizzo DM (2018) Multiple origins of downy mildews and mito-nuclear discordance within the paraphyletic genus Phytophthora. PLoS ONE, 13, e0192502. |
| [13] |
Bryant D, Bouckaert R, Felsenstein J, Rosenberg NA, RoyChoudhury A (2012) Inferring species trees directly from biallelic genetic markers: Bypassing gene trees in a full coalescent analysis. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 29, 1917-1932.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Burbrink FT, Guiher TJ (2015) Considering gene flow when using coalescent methods to delimit lineages of North American pitvipers of the genus Agkistrodon. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 173, 505-526. |
| [15] | Bustamante CD (2005) Population genetics of molecular evolution. In: Statistical Methods in Molecular Evolution (eds Mitchell H, Jonathan MS). Springer, New York. |
| [16] | Chan KO, Hutter CR, Wood PL Jr, Grismer LL, Das I, Brown RM (2020) Gene flow creates a mirage of cryptic species in a Southeast Asian spotted stream frog complex. Molecular Ecology, 29, 3970-3987. |
| [17] |
Chapurlat E, Le Roncé I, Ågren J, Sletvold N (2020) Divergent selection on flowering phenology but not on floral morphology between two closely related orchids. Ecology and Evolution, 10, 5737-5747.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Charlesworth B, Morgan MT, Charlesworth D (1993) The effect of deleterious mutations on neutral molecular variation. Genetics, 134, 1289-1303.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | Charlesworth D (2006) Balancing selection and its effects on sequences in nearby genome regions. PLoS Genetics, 2, e64. |
| [20] | Chen Q, Yang H, Feng X, Chen QJ, Shi SS, Wu CI, He ZW (2022) Two decades of suspect evidence for adaptive molecular evolution—Negative selection confounding positive-selection signals. National Science Review, 9, nwab217. |
| [21] | Cheng X, Li LL, Xiao Y, Chen XY, Hu XS (2020) Advances in the methods of detecting interspecific gene introgression and their applications. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 50, 1388-1404. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [程祥, 李玲玲, 肖钰, 陈晓阳, 胡新生 (2020) 种间基因渐渗检测方法及其应用研究进展. 中国科学: 生命科学, 50, 1388-1404.] | |
| [22] |
Cheng XH, DeGiorgio M (2019) Detection of shared balancing selection in the absence of trans-species polymorphism. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 36, 177-199.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Cheng XH, DeGiorgio M (2022) BalLeRMix+: Mixture model approaches for robust joint identification of both positive selection and long-term balancing selection. Bioinformatics, 38, 861-863. |
| [24] |
Chifman J, Kubatko L (2014) Quartet inference from SNP data under the coalescent model. Bioinformatics, 30, 3317-3324.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Chifman J, Kubatko L (2015) Identifiability of the unrooted species tree topology under the coalescent model with time-reversible substitution processes, site-specific rate variation, and invariable sites. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 374, 35-47.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Chung Y, Ané C (2011) Comparing two Bayesian methods for gene tree/species tree reconstruction: Simulations with incomplete lineage sorting and horizontal gene transfer. Systematic Biology, 60, 261-275.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Cui RF, Schumer M, Kruesi K, Walter RB, Andolfatto P, Rosenthal GC (2013) Phylogenomics reveals extensive reticulate evolution in Xiphophorus fishes. Evolution, 67, 2166-2179. |
| [28] |
Cutter AD (2019) Reproductive transitions in plants and animals: Selfing syndrome, sexual selection and speciation. New Phytologist, 224, 1080-1094.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Dasarathy G, Nowak R, Roch S (2015) Data requirement for phylogenetic inference from multiple loci: A new distance method. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 12, 422-432.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | De Maio N, Schlötterer C, Kosiol C (2013) Linking great apes genome evolution across time scales using polymorphism- aware phylogenetic models. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 2249-2262. |
| [31] |
De Maio N, Schrempf D, Kosiol C (2015) PoMo: An allele frequency-based approach for species tree estimation. Systematic Biology, 64, 1018-1031.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | DeGiorgio M, Lohmueller KE, Nielsen R (2014) A model-based approach for identifying signatures of ancient balancing selection in genetic data. PLoS Genetics, 10, e1004561. |
| [33] |
Degnan JH (2018) Modeling hybridization under the network multispecies coalescent. Systematic Biology, 67, 786-799.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | Degnan JH, Rosenberg NA (2009) Gene tree discordance, phylogenetic inference and the multispecies coalescent. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 24, 332-340. |
| [35] |
Disanto F, Schlizio A, Wiehe T (2013) Yule-generated trees constrained by node imbalance. Mathematical Biosciences, 246, 139-147.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Duan L, Fu L, Chen HF (2023) Phylogenomic cytonuclear discordance and evolutionary histories of plants and animals. Science China: Life Sciences, 66, 2946-2948. |
| [37] | Dutheil JY, Munch K, Nam K, Mailund T, Schierup MH (2015) Strong selective sweeps on the X chromosome in the human-chimpanzee ancestor explain its low divergence. PLoS Genetics, 11, e1005451. |
| [38] |
Edelman NB, Frandsen PB, Miyagi M, Clavijo B, Davey J, Dikow RB, García-Accinelli G, Van Belleghem SM, Patterson N, Neafsey DE, Challis R, Kumar S, Moreira GRP, Salazar C, Chouteau M, Counterman BA, Papa R, Blaxter M, Reed RD, Dasmahapatra KK, Kronforst M, Joron M, Jiggins CD, McMillan WO, Di Palma F, Blumberg AJ, Wakeley J, Jaffe D, Mallet J (2019) Genomic architecture and introgression shape a butterfly radiation. Science, 366, 594-599.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | Elworth RAL, Ogilvie HA, Zhu J, Nakhleh L (2019) Advances in computational methods for phylogenetic networks in the presence of hybridization. In: Bioinformatics and Phylogenetics (ed. Warnow T). Springer, Cham. |
| [40] |
Eyre-Walker A, Keightley PD (2009) Estimating the rate of adaptive molecular evolution in the presence of slightly deleterious mutations and population size change. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 26, 2097-2108.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
Fay JC, Wu CI (2000) Hitchhiking under positive Darwinian selection. Genetics, 155, 1405-1413.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
Ferretti L, Ledda A, Wiehe T, Achaz G, Ramos-Onsins SE (2017) Decomposing the site frequency spectrum: The impact of tree topology on neutrality tests. Genetics, 207, 229-240.
DOI PMID |
| [43] | Firneno TJ Jr, O’Neill JR, Portik DM, Emery AH, Townsend JH, Fujita MK (2020) Finding complexity in complexes: Assessing the causes of mitonuclear discordance in a problematic species complex of Mesoamerican toads. Molecular Ecology, 29, 3543-3559. |
| [44] | Fisher RA (1930) The Genetical Theory of Natural Selection. Clarendon Press, Oxford. |
| [45] |
Flouri T, Jiao XY, Rannala B, Yang ZH (2020) A Bayesian implementation of the multispecies coalescent model with introgression for phylogenomic analysis. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 37, 1211-1223.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
Forsythe ES, Nelson ADL, Beilstein MA (2020) Biased gene retention in the face of introgression obscures species relationships. Genome Biology and Evolution, 12, 1646-1663.
DOI PMID |
| [47] | Galtier N (2016) Adaptive protein evolution in animals and the effective population size hypothesis. PLoS Genetics, 12, e1005774. |
| [48] |
Gao ZY, Przeworski M, Sella G (2015) Footprints of ancient-balanced polymorphisms in genetic variation data from closely related species. Evolution, 69, 431-446.
DOI PMID |
| [49] | Gardner EM, Bruun-Lund S, Niissalo M, Chantarasuwan B, Clement WL, Geri C, Harrison RD, Hipp AL, Holvoet M, Khew G, Kjellberg F, Liao S, Pederneiras LC, Peng YQ, Pereira JT, Phillipps Q, Ahmad Puad AS, Rasplus JY, Sang J, Schou SJ, Velautham E, Weiblen GD, Zerega NJC, Zhang Q, Zhang Z, Baraloto C, Rønsted N (2023) Echoes of ancient introgression punctuate stable genomic lineages in the evolution of figs. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 120, e2222035120. |
| [50] | Gatesy J, Springer MS (2014) Phylogenetic analysis at deep timescales:Unreliable gene trees, bypassed hidden support, and the coalescence/concatalescence conundrum. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 80, 231-266. |
| [51] |
Guo C, Luo Y, Gao LM, Yi TS, Li HT, Yang JB, Li DZ (2023) Phylogenomics and the flowering plant tree of life. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 65, 299-323.
DOI |
| [52] | Gussow AB, Petrovski S, Wang QL, Allen AS, Goldstein DB (2016) The intolerance to functional genetic variation of protein domains predicts the localization of pathogenic mutations within genes. Genome Biology, 17, 9. |
| [53] | Haldane JBS (1927) A mathematical theory of natural and artificial selection, part V: Selection and mutation. Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 23, 838-844. |
| [54] |
Han YH, Molloy EK (2023) Improving quartet graph construction for scalable and accurate species tree estimation from gene trees. Genome Research, 33, 1042-1052.
DOI PMID |
| [55] |
Harris RB, Jensen JD (2020) Considering genomic scans for selection as coalescent model choice. Genome Biology and Evolution, 12, 871-877.
DOI PMID |
| [56] | Hayeck TJ, Stong N, Wolock CJ, Copeland B, Kamalakaran S, Goldstein DB, Allen AS (2019) Improved pathogenic variant localization via a hierarchical model of sub-regional intolerance. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 104, 299-309. |
| [57] | He B, Zhao YJ, Su CY, Lin GH, Wang YL, Li LY, Ma JY, Yang Q, Hao JS (2023) Phylogenomics reveal extensive phylogenetic discordance due to incomplete lineage sorting following the rapid radiation of alpine butterflies (Papilionidae: Parnassius). Systematic Entomology, 48, 585-599. |
| [58] |
Heled J, Drummond AJ (2010) Bayesian inference of species trees from multilocus data. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 27, 570-580.
DOI PMID |
| [59] |
Hey J, Chung Y, Sethuraman A, Lachance J, Tishkoff SA, Sousa VC, Wang Y (2018) Phylogeny estimation by integration over isolation with migration models. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35, 2805-2818.
DOI PMID |
| [60] | Hey J, Nielsen R (2004) Multilocus methods for estimating population sizes, migration rates and divergence time, with applications to the divergence of Drosophila pseudoobscura and D. persimilis. Genetics, 167, 747-760. |
| [61] | Hey J, Nielsen R (2007) Integration within the Felsenstein equation for improved Markov chain Monte Carlo methods in population genetics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 104, 2785-2790. |
| [62] | Hill M, Legried B, Roch S (2022) Species tree estimation under joint modeling of coalescence and duplication: Sample complexity of quartet methods. Annals of Applied Probability, 32, 4681-4705. |
| [63] | Hu XS (2015) Mating system as a barrier to gene flow. Evolution, 69, 1158-1177. |
| [64] | Hu XS, Ennos RA (1997) On estimation of the ratio of pollen to seed flow among plant populations. Heredity, 79, 541-552. |
| [65] |
Hu Y, Wang X, Zhang XX, Zhou W, Chen XY, Hu XS (2019) Advancing phylogeography with chloroplast DNA markers. Biodiversity Science, 27, 219-234. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[胡颖, 王茜, 张新新, 周玮, 陈晓阳, 胡新生 (2019) 叶绿体DNA标记在谱系地理学中的应用研究进展. 生物多样性, 27, 219-234.]
DOI |
|
| [66] |
Hudson RR, Kaplan NL (1988) The coalescent process in models with selection and recombination. Genetics, 120, 831-840.
DOI PMID |
| [67] | Hudson RR, Kaplan NL (1995a) The coalescent process and background selection. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 349, 19-23. |
| [68] | Hudson RR, Kaplan NL (1995b) Deleterious background selection with recombination. Genetics, 141, 1605-1617. |
| [69] |
Hudson RR, Kreitman M, Aguadé M (1987) A test of neutral molecular evolution based on nucleotide data. Genetics, 116, 153-159.
DOI PMID |
| [70] |
Hunter-Zinck H, Clark AG (2015) Aberrant time to most recent common ancestor as a signature of natural selection. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 32, 2784-2797.
DOI PMID |
| [71] | Isildak U, Stella A, Fumagalli M (2021) Distinguishing between recent balancing selection and incomplete sweep using deep neural networks. Molecular Ecology Resources, 21, 2706-2718. |
| [72] |
Islam M, Sarker K, Das T, Reaz R, Bayzid MS (2020) STELAR: A statistically consistent coalescent-based species tree estimation method by maximizing triplet consistency. BMC Genomics, 21, 136.
DOI PMID |
| [73] |
Jiang XD, Edwards SV, Liu L (2020) The multispecies coalescent model outperforms concatenation across diverse phylogenomic data sets. Systematic Biology, 69, 795-812.
DOI PMID |
| [74] | Joffard N, Le Roncé I, Langlois A, Renoult J, Buatois B, Dormont L, Schatz B (2020) Floral trait differentiation in Anacamptis coriophora: Phenotypic selection on scents, but not on colour. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 33, 1028-1038. |
| [75] | Johnson KE, Voight BF (2018) Patterns of shared signatures of recent positive selection across human populations. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2, 713-720. |
| [76] |
Jones G, Sagitov S, Oxelman B (2013) Statistical inference of allopolyploid species networks in the presence of incomplete lineage sorting. Systematic Biology, 62, 467-478.
DOI PMID |
| [77] |
Kamneva OK, Syring J, Liston A, Rosenberg NA (2017) Evaluating allopolyploid origins in strawberries (Fragaria) using haplotypes generated from target capture sequencing. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 17, 180.
DOI PMID |
| [78] | Kao TT, Wang TH, Ku C (2022) Rampant nuclear- mitochondrial-plastid phylogenomic discordance in globally distributed calcifying microalgae. New Phytologist, 235, 1394-1408. |
| [79] |
Kaplan N, Hudson RR, Iizuka M (1991) The coalescent process in models with selection, recombination and geographic subdivision. Genetics Research, 57, 83-91.
PMID |
| [80] |
Kaplan NL, Darden T, Hudson RR (1988) The coalescent process in models with selection. Genetics, 120, 819-829.
DOI PMID |
| [81] |
Kelly JK, Wade MJ (2000) Molecular evolution near a two-locus balanced polymorphism. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 204, 83-101.
PMID |
| [82] |
Kimura M (1954) Process leading to quasi-fixation of genes in natural populations due to random fluctuation of selection intensities. Genetics, 39, 280-295.
DOI PMID |
| [83] |
Kimura M (1962) On the probability of fixation of mutant genes in a population. Genetics, 47, 713-719.
PMID |
| [84] | Kingman JFC (1982) The coalescent. Stochastic Processes and Their Applications, 13, 235-248. |
| [85] | Klein J (1987) The major histocompatibility complex and protein recognition by T lymphocytes. In: Immunobiology of Proteins and Peptides IV: Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology (ed. Atassi MZ), Springer, Boston, MA. |
| [86] |
Koenen EJM, Ojeda DI, Steeves R, Migliore J, Bakker FT, Wieringa JJ, Kidner C, Hardy OJ, Pennington RT, Bruneau A, Hughes CE (2020) Large-scale genomic sequence data resolve the deepest divergences in the legume phylogeny and support a near-simultaneous evolutionary origin of all six subfamilies. New Phytologist, 225, 1355-1369.
DOI PMID |
| [87] |
Kubatko LS, Carstens BC, Knowles LL (2009) STEM: Species tree estimation using maximum likelihood for gene trees under coalescence. Bioinformatics, 25, 971-973.
DOI PMID |
| [88] |
Leaché AD, Harris RB, Rannala B, Yang ZH (2014) The influence of gene flow on species tree estimation: A simulation study. Systematic Biology, 63, 17-30.
DOI PMID |
| [89] | Li F, Rane RV, Luria V, Xiong ZJ, Chen JW, Li ZM, Catullo RA, Griffin PC, Schiffer M, Pearce S, Lee SF, McElroy K, Stocker A, Shirriffs J, Cockerell F, Coppin C, Sgrò CM, Karger A, Cain JW, Weber JA, Santpere G, Kirschner MW, Hoffmann AA, Oakeshott JG, Zhang GJ (2022) Phylogenomic analyses of the genus Drosophila reveals genomic signals of climate adaptation. Molecular Ecology Resources, 22, 1559-1581. |
| [90] | Li HP, Wiehe T (2013) Coalescent tree imbalance and a simple test for selective sweeps based on microsatellite variation. PLoS Computational Biology, 9, e1003060. |
| [91] | Li LL, Wang X, Xiao Y, Cheng X, Chen XY, Hu XS (2023) On the theories of plant mating system and molecular evolution and their applications. Science China (Vitae), 53, 50-63. (in Chinese with English abstract ) |
| [李玲玲, 王茜, 肖钰, 程祥, 陈晓阳, 胡新生 (2023) 植物交配系统与分子进化理论及其应用研究. 中国科学: 生命科学, 53, 50-63.] | |
| [92] | Li LL, Xiao Y, Wang X, He ZH, Lv YW, Hu XS (2023) The Ka/Ks and πa/πs ratios under different models of gametophytic and sporophytic selection. Genome Biology and Evolution, 15, evad151. |
| [93] |
Liang M, Nielsen R (2014) The lengths of admixture tracts. Genetics, 197, 953-967.
DOI PMID |
| [94] |
Liu BQ, Warnow T (2023) Weighted ASTRID: Fast and accurate species trees from weighted internode distances. Algorithms for Molecular Biology, 18, 6.
DOI PMID |
| [95] |
Liu L (2008) BEST: Bayesian estimation of species trees under the coalescent model. Bioinformatics, 24, 2542-2543.
DOI PMID |
| [96] |
Liu L, Yu L (2011) Estimating species trees from unrooted gene trees. Systematic Biology, 60, 661-667.
DOI PMID |
| [97] | Liu L, Yu L, Edwards SV (2010) A maximum pseudo- likelihood approach for estimating species trees under the coalescent model. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 10, 302. |
| [98] |
Liu L, Yu L, Pearl DK, Edwards SV (2009) Estimating species phylogenies using coalescence times among sequences. Systematic Biology, 58, 468-477.
DOI PMID |
| [99] |
Liu L, Yu LL (2010) Phybase: An R package for species tree analysis. Bioinformatics, 26, 962-963.
DOI PMID |
| [100] |
Long C, Kubatko L (2018) The effect of gene flow on coalescent-based species-tree inference. Systematic Biology, 67, 770-785.
DOI PMID |
| [101] |
Mahbub M, Wahab Z, Reaz R, Rahman MS, Bayzid MS (2021) wQFM: Highly accurate genome-scale species tree estimation from weighted quartets. Bioinformatics, 37, 3734-3743.
DOI PMID |
| [102] |
Mailund T, Munch K, Schierup MH (2014) Lineage sorting in apes. Annual Review of Genetics, 48, 519-535.
DOI PMID |
| [103] |
Mallet J, Besansky N, Hahn MW (2016) How reticulated are species? BioEssays, 38, 140-149.
DOI PMID |
| [104] | Mao Y, Economo EP, Satoh N (2018) The roles of introgression and climate change in the rise to dominance of Acropora corals. Current Biology, 28, 3373-3382. |
| [105] | Mao Y, Hou S, Shi J, Economo EP (2020) TREEasy: An automated workflow to infer gene trees, species trees, and phylogenetic networks from multilocus data. Molecular Ecology Resources, 20, 832-840. |
| [106] | Markin A, Eulenstein O (2021) Quartet-based inference is statistically consistent under the unified duplication-loss- coalescence model. Bioinformatics, 37, 4064-4074. |
| [107] | Messer PW, Petrov DA (2013) Frequent adaptation and the McDonald-Kreitman test. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 110, 8615-8620. |
| [108] | Mirarab S, Nakhleh L, Warnow T (2021) Multispecies coalescent: Theory and applications in phylogenetics. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 52, 247-268. |
| [109] |
Mirarab S, Reaz R, Bayzid MS, Zimmermann T, Swenson MS, Warnow T (2014) ASTRAL: Genome-scale coalescent- based species tree estimation. Bioinformatics, 30, 541-548.
DOI PMID |
| [110] |
Mirarab S, Warnow T (2015) ASTRAL-II: Coalescent-based species tree estimation with many hundreds of taxa and thousands of genes. Bioinformatics, 31, 44-52.
DOI PMID |
| [111] | Moghe GD, Shiu SH (2014) The causes and molecular consequences of polyploidy in flowering plants. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1320, 16-34. |
| [112] |
Molloy EK, Warnow T (2018) To include or not to include: The impact of gene filtering on species tree estimation methods. Systematic Biology, 67, 285-303.
DOI PMID |
| [113] | Moran PAP (1958) Random processes in genetics. Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 54, 60-71. |
| [114] | Moran PAP (1962) The Statistical Processes of Evolutionary Theory. Clarendon Press, Oxford. |
| [115] | Morel B, Williams TA, Stamatakis A (2023) Asteroid: A new algorithm to infer species trees from gene trees under high proportions of missing data. Bioinformatics, 39, btac832. |
| [116] | Munch K, Nam K, Schierup MH, Mailund T (2016) Selective sweeps across twenty million years of primate evolution. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33, 3065-3074. |
| [117] | Murga-Moreno J, Coronado-Zamora M, Casillas S, Barbadilla A (2022) impMKT: The imputed McDonald and Kreitman test, a straightforward correction that significantly increases the evidence of positive selection of the McDonald and Kreitman test at the gene level. G3: Genes|Genomes|Genetics, 12, jkac206. |
| [118] |
Neuhauser C, Krone SM (1997) The genealogy of samples in models with selection. Genetics, 145, 519-534.
DOI PMID |
| [119] |
Nilsson MA, Zheng Y, Kumar V, Phillips MJ, Janke A (2018) Speciation generates mosaic genomes in kangaroos. Genome Biology and Evolution, 10, 33-44.
DOI PMID |
| [120] |
Nute M, Chou J, Molloy EK, Warnow T (2018) The performance of coalescent-based species tree estimation methods under models of missing data. BMC Genomics, 19, 286.
DOI PMID |
| [121] |
Ogilvie HA, Bouckaert RR, Drummond AJ (2017) StarBEAST 2 brings faster species tree inference and accurate estimates of substitution rates. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 34, 2101-2114.
DOI PMID |
| [122] |
Olave M, Meyer A (2020) Implementing large genomic single nucleotide polymorphism data sets in phylogenetic network reconstructions: A case study of particularly rapid radiations of cichlid fish. Systematic Biology, 69, 848-862.
DOI PMID |
| [123] | Palamara PF, Terhorst J, Song YS, Price AL (2018) High- throughput inference of pairwise coalescence times identifies signals of selection and enriched disease heritability. Nature Genetics, 50, 1311-1317. |
| [124] |
Pamilo P, Nei M (1988) Relationships between gene trees and species trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 5, 568-83.
DOI PMID |
| [125] | Patwa Z, Wahl LM (2008) The fixation probability of beneficial mutations. Journal of the Royal Society, 5, 1279-1289. |
| [126] |
Pei JW, Wu YF (2017) STELLS2: Fast and accurate coalescent-based maximum likelihood inference of species trees from gene tree topologies. Bioinformatics, 33, 1789-1797.
DOI PMID |
| [127] | Poh YP, Domingues VS, Hoekstra HE, Jensen JD (2014) On the prospect of identifying adaptive loci in recently bottlenecked populations. PLoS ONE, 9, e110579. |
| [128] | Pollard DA, Iyer VN, Moses AM, Eisen MB (2006) Widespread discordance of gene trees with species tree in Drosophila: Evidence for incomplete lineage sorting. PLoS Genetics, 2, e173. |
| [129] | Poroshina AA, Sherbakov DY, Peretolchina TE (2020) Diagnosis of the mechanisms of different types of discordances between phylogenies inferred from nuclear and mitochondrial markers. Vavilov Journal of Genetics and Breeding, 24, 420-426. |
| [130] |
Przeworski M, Charlesworth B, Wall JD (1999) Genealogies and weak purifying selection. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 246-252.
PMID |
| [131] |
Rannala B, Yang ZH (2003) Bayes estimation of species divergence times and ancestral population sizes using DNA sequences from multiple loci. Genetics, 164, 1645-1656.
DOI PMID |
| [132] |
Reddy S, Kimball RT, Pandey A, Hosner PA, Braun MJ, Hackett SJ, Han KL, Harshman J, Huddleston CJ, Kingston S, Marks BD, Miglia KJ, Moore WS, Sheldon FH, Witt CC, Yuri T, Braun EL (2017) Why do phylogenomic data sets yield conflicting trees? Data type influences the avian tree of life more than taxon sampling. Systematic Biology, 66, 857-879.
DOI PMID |
| [133] | Rendón-Anaya M, Ibarra-Laclette E, Méndez-Bravo A, Lan T, Zheng C, Carretero-Paulet L, Perez-Torres CA, Chacón- López A, Hernandez-Guzmán G, Chang TH, Farr KM, Barbazuk WB, Chamala S, Mutwil M, Shivhare D, Alvarez- Ponce D, Mitter N, Hayward A, Fletcher S, Rozas J, Sánchez Gracia A, Kuhn D, Barrientos-Priego AF, Salojärvi J, Librado P, Sankoff D, Herrera-Estrella A, Albert VA, Herrera-Estrella L (2019) The avocado genome informs deep angiosperm phylogeny, highlights introgressive hybridization, and reveals pathogen-influenced gene space adaptation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 116, 17081-17089. |
| [134] | Rhodes JA, Nute MG, Warnow T (2020) NJst and ASTRID are not statistically consistent under a random model of missing data. ArXiv, doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2001.07844. |
| [135] |
Richards A, Kubatko L (2021) Bayesian-weighted triplet and quartet methods for species tree inference. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 83, 93.
DOI PMID |
| [136] |
Rifkin JL, Castillo AS, Liao IT, Rausher MD (2019) Gene flow, divergent selection and resistance to introgression in two species of morning glories (Ipomoea). Molecular Ecology, 28, 1709-1729.
DOI PMID |
| [137] | Roch S, Steel M (2015) Likelihood-based tree reconstruction on a concatenation of aligned sequence data sets can be statistically inconsistent. Theoretical Population Biology, 100, 56-62. |
| [138] | Sackton TB, Clark N (2019) Convergent evolution in the genomics era: New insights and directions. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 374, 20190102. |
| [139] |
Santos SHD, Peery RM, Miller JM, Dao A, Lyu FH, Li X, Li MH, Coltman DW (2021) Ancient hybridization patterns between bighorn and thinhorn sheep. Molecular Ecology, 30, 6273-6288.
DOI PMID |
| [140] |
Sarver BAJ, Keeble S, Cosart T, Tucker PK, Dean MD, Good JM (2017) Phylogenomic insights into mouse evolution using a pseudoreference approach. Genome Biology and Evolution, 9, 726-739.
DOI PMID |
| [141] |
Sawyer SA, Hartl DL (1992) Population genetics of polymorphism and divergence. Genetics, 132, 1161-1176.
DOI PMID |
| [142] |
Sayyari E, Mirarab S (2016) Anchoring quartet-based phylogenetic distances and applications to species tree reconstruction. BMC Genomics, 17, 783.
DOI PMID |
| [143] | Sheehan S, Song YS (2016) Deep learning for population genetic inference. Genome Biology and Evolution, 15, e1004845. |
| [144] | Shi CM, Yang ZH (2018) Coalescent-based analyses of genomic sequence data provide a robust resolution of phylogenetic relationships among major groups of gibbons. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35, 159-179. |
| [145] |
Siewert KM, Voight BF (2017) Detecting long-term balancing selection using allele frequency correlation. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 34, 2996-3005.
DOI PMID |
| [146] |
Slade PF (2000) Most recent common ancestor probability distributions in gene genealogies under selection. Theoretical Population Biology, 58, 291-305.
PMID |
| [147] | Smith JM, Haigh J (1974) The hitch-hiking effect of a favourable gene. Genetical Research, 23, 23-35. |
| [148] | Solís-Lemus C, Ané C (2016) Inferring phylogenetic networks with maximum pseudolikelihood under incomplete lineage sorting. PLoS Genetics, 12, e1005896. |
| [149] |
Solís-Lemus C, Bastide P, Ané C (2017) PhyloNetworks: A package for phylogenetic networks. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 34, 3292-3298.
DOI PMID |
| [150] | Soltis PS, Marchant DB, Van De Peer Y, Soltis DE (2015) Polyploidy and genome evolution in plants. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 35, 119-125. |
| [151] | Song S, Liu L, Edwards SV, Wu S (2012) Resolving conflict in eutherian mammal phylogeny using phylogenomics and the multispecies coalescent model. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 109, 14942-14947. |
| [152] | Stephens M, Donnelly P (2003) Ancestral inference in population genetics models with selection (with discussion). Australian & New Zealand Journal of Statistics, 45, 395-430. |
| [153] |
Stull GW, Pham KK, Soltis PS, Soltis DE (2023) Deep reticulation: The long legacy of hybridization in vascular plant evolution. The Plant Journal, 114, 743-766.
DOI PMID |
| [154] |
Sukumaran J, Holder MT (2010) DendroPy: A Python library for phylogenetic computing. Bioinformatics, 26, 1569-1571.
DOI PMID |
| [155] | Tabatabaee Y, Roch S, Warnow T (2023) Statistically consistent rooting of species trees under the multispecies coalescent model. In: Research in Computational Molecular Biology (ed. Tang H). Springer, Cham. |
| [156] |
Tajima F (1983) Evolutionary relationship of DNA sequences in finite populations. Genetics, 105, 437-460.
DOI PMID |
| [157] |
Tajima F (1989) Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics, 123, 585-595.
DOI PMID |
| [158] |
Takahata N, Nei M (1990) Allelic genealogy under overdominant and frequency-dependent selection and polymorphism of major histocompatibility complex loci. Genetics, 124, 967-978.
DOI PMID |
| [159] |
Thornton KR, Jensen JD (2007) Controlling the false-positive rate in multilocus genome scans for selection. Genetics, 175, 737-750.
PMID |
| [160] | To TH, Scornavacca C (2015) Efficient algorithms for reconciling gene trees and species networks via duplication and loss events. BMC Genomics, 16, S6. |
| [161] | Vachaspati P, Warnow T (2015) ASTRID: Accurate species TRees from internode distances. BMC Genomics, 16, S3. |
| [162] |
Vachaspati P, Warnow T (2018) SVDquest: Improving SVDquartets species tree estimation using exact optimization within a constrained search space. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 124, 122-136.
DOI PMID |
| [163] |
Wakeley J (2008) Conditional gene genealogies under strong purifying selection. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 25, 2615-2626.
DOI PMID |
| [164] |
Walczak AM, Nicolaisen LE, Plotkin JB, Desai MM (2012) The structure of genealogies in the presence of purifying selection: A fitness-class coalescent. Genetics, 190, 753-779.
DOI PMID |
| [165] |
Wang MX, Huang X, Li R, Xu HY, Jin L, He YG (2014) Detecting recent positive selection with high accuracy and reliability by conditional coalescent tree. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 31, 3068-3080.
DOI PMID |
| [166] | Wang X, Cheng X, Zhou W, Zhang XX, Hu Y, Chen XY, Hu XS (2019) Assessing the ecological and evolutionary processes underlying cytonuclear interactions. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 49, 951-964. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王茜, 程祥, 周玮, 张新新, 胡颖, 陈晓阳, 胡新生 (2019) 细胞核质互作形成的生态与进化过程分析. 中国科学: 生命科学, 49, 951-964.] | |
| [167] | Wang X, Xiao Y, He ZH, Li LL, Song HY, Zhang JJ, Cheng X, Chen XY, Li P, Hu XS (2022) A chromosome-level genome assembly of Toona ciliata (Meliaceae). Genome Biology and Evolution, 14, evac121. |
| [168] |
Wang Y, Hey J (2010) Estimating divergence parameters with small samples from a large number of loci. Genetics, 184, 363-379.
DOI PMID |
| [169] |
Wascher M, Kubatko L (2021) Consistency of SVDQuartets and maximum likelihood for coalescent-based species tree estimation. Systematic Biology, 70, 33-48.
DOI PMID |
| [170] |
Watterson GA (1975) On the number of segregating sites in genetical models without recombination. Theoretical Population Biology, 7, 256-276.
DOI PMID |
| [171] |
Wen D, Nakhleh L (2018) Coestimating reticulate phylogenies and gene trees from multilocus sequence data. Systematic Biology, 67, 439-457.
DOI PMID |
| [172] |
Wen D, Yu Y, Zhu J, Nakhleh L (2018) Inferring phylogenetic networks using PhyloNet. Systematic Biology, 67, 735-740.
DOI PMID |
| [173] | Wilson DJ, Hernandez RD, Andolfatto P, Przeworski M (2011) A population genetics-phylogenetics approach to inferring natural selection in coding sequences. PLoS Genetics, 7, e1002395. |
| [174] | Wright S (1942) Statistical genetics and evolution. Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society, 48, 223-246. |
| [175] |
Wu Y (2012) Coalescent-based species tree inference from gene tree topologies under incomplete lineage sorting by maximum likelihood. Evolution, 66, 763-775.
DOI PMID |
| [176] | Xi ZX, Liu L, Rest JS, Davis CC (2014) Coalescent versus concatenation methods and the placement of Amborella as sister to water lilies. Systematic Biology, 63, 919-932. |
| [177] |
Xiao Y, Wang X, He ZH, Li LL, Hu XS (2022) Advances in speciation theories and their verifications based on the biological species concept. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21480. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[肖钰, 王茜, 何梓晗, 李玲玲, 胡新生 (2022) 基于生物学物种定义探讨物种形成理论与验证的研究进展. 生物多样性, 30, 21480.]
DOI |
|
| [178] |
Xu L, Yu R, Lin X, Zhang BW, Li N, Lin K, Zhang DY, Bai WN (2021) Different rates of pollen and seed gene flow cause branch-length and geographic cytonuclear discordance within Asian butternuts. New Phytologist, 232, 388-403.
DOI PMID |
| [179] | Yan Z, Cao Z, Liu YS, Ogilvie HA, Nakhleh L (2022) Maximum parsimony inference of phylogenetic networks in the presence of polyploid complexes. Systematic Biology, 71, 706-720. |
| [180] |
Yang ZF, Li JR, Wiehe T, Li HP (2018) Detecting recent positive selection with a single locus test bipartitioning the coalescent tree. Genetics, 208, 791-805.
DOI PMID |
| [181] |
Yang ZH (2007) PAML 4: Phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24, 1586-1591.
DOI PMID |
| [182] | Yang ZH (2015) The BPP program for species tree estimation and species delimitation. Current Zoology, 61, 854-865. |
| [183] | Yu Y, Degnan JH, Nakhleh L (2012) The probability of a gene tree topology within a phylogenetic network with applications to hybridization detection. PLoS Genetics, 8, e1002660. |
| [184] | Yu Y, Dong JR, Liu KJ, Nakhleh L (2014) Maximum likelihood inference of reticulate evolutionary histories. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111, 16448-16453. |
| [185] | Yu Y, Nakhleh L (2015) A maximum pseudo-likelihood approach for phylogenetic networks. BMC Genomics, 16, S10. |
| [186] | Zhang C, Mirarab S (2022) Weighting by gene tree uncertainty improves accuracy of quartet-based species trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 39, msac215. |
| [187] | Zhang C, Ogilvie HA, Drummond AJ, Stadler T (2018a) Bayesian inference of species networks from multilocus sequence data. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35, 504-517. |
| [188] | Zhang C, Rabiee M, Sayyari E, Mirarab S (2018b) ASTRAL- III: Polynomial time species tree reconstruction from partially resolved gene trees. BMC Bioinformatics, 19, 153. |
| [189] | Zhou BF, Yuan S, Crowl AA, Liang YY, Shi Y, Chen XY, An QQ, Kang M, Manos PS, Wang BS (2022) Phylogenomic analyses highlight innovation and introgression in the continental radiations of Fagaceae across the Northern Hemisphere. Nature Communications, 13, 1320. |
| [190] |
Zhu JF, Nakhleh L (2018) Inference of species phylogenies from bi-allelic markers using pseudo-likelihood. Bioinformatics, 34, 376-385.
DOI PMID |
| [191] | Zhu JF, Wen DQ, Yu Y, Meudt HM, Nakhleh L (2018) Bayesian inference of phylogenetic networks from bi-allelic genetic markers. PLoS Computational Biology, 14, e1005932. |
| [192] | Zimmermann T, Mirarab S, Warnow T (2014) BBCA: Improving the scalability of *BEAST using random binning. BMC Genomics, 15, S11. |
| [193] | Zou XH, Ge S (2008) Conflicting gene trees and phylogenomics. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 46, 795-807. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邹新慧, 葛颂 (2008) 基因树冲突与系统发育基因组学研究. 植物分类学报, 46, 795-807.] |
| [1] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [2] | 曹东, 李焕龙, 彭扬, 魏存争. 植物基因组大小与性状关系的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24192-. |
| [3] | 孙亚君. 何谓高等或低等生物——澄清《物种起源》所蕴含的生物等级性的涵义及其成立性[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24394-. |
| [4] | 李佳琪, 冯一迪, 王蕾, 潘盆艳, 刘潇如, 李雪阳, 王怡涵, 王放. 上海城市环境中貉的食性分析及家域范围内的栖息地选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24131-. |
| [5] | 王瑞武, 于云云, 朱其凯, 王超, 李敏岚, 韩嘉旭. 路径依赖的选择——统一自然选择与中性选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24120-. |
| [6] | 张明军, 王合升, 颜文博, 符运南, 王琦, 曾治高. 海南大田国家级自然保护区小灵猫的活动节律与栖息地选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 23420-. |
| [7] | 艾妍雨, 胡海霞, 沈婷, 莫雨轩, 杞金华, 宋亮. 附生维管植物多样性及其与宿主特征的相关性: 以哀牢山中山湿性常绿阔叶林为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24072-. |
| [8] | 王鹏, 隋佳容, 丁欣瑶, 王伟中, 曹雪倩, 赵海鹏, 王彦平. 郑州城市公园鸟类群落嵌套分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23359-. |
| [9] | 曹可欣, 王敬雯, 郑国, 武鹏峰, 李英滨, 崔淑艳. 降水格局改变及氮沉降对北方典型草原土壤线虫多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [10] | 王斌, 钟艺倩, 杨美雪, 吴淼锐, 王艳萍, 陆芳, 陶旺兰, 李健星, 赵弘明, 刘晟源, 向悟生, 李先琨. 喀斯特季节性雨林优势树种叶片非结构性碳水化合物空间变异及生态驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24325-. |
| [11] | 杨向林, 赵彩云, 李俊生, 种方方, 李文金. 植物入侵导致群落谱系结构更加聚集: 以广西国家级自然保护区草本植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [12] | 何林君, 杨文静, 石宇豪, 阿说克者莫, 范钰, 王国严, 李景吉, 石松林, 易桂花, 彭培好. 火烧干扰下植物群落系统发育和功能多样性对紫茎泽兰入侵的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24269-. |
| [13] | 张梓欣, 张承云, 郝泽周, 何凯莹, 黄泳桥, 肖治术. 陆地生物声学数据采集设备的进展及展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24265-. |
| [14] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [15] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn