



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (2): 22394. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022394 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022394
李治中1,2, 彭帅3,4, 王青锋3,5, 李伟1, 梁士楚2,*( ), 陈进明1,*(
), 陈进明1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-07-11
接受日期:2022-09-05
出版日期:2023-02-20
发布日期:2022-09-19
通讯作者:
*陈进明, E-mail: jmchen@wbgcas.cn;梁士楚 gxlsc@sina.com
基金资助:
Zhizhong Li1,2, Shuai Peng3,4, Qingfeng Wang3,5, Wei Li1, Shichu Liang2,*( ), Jinming Chen1,*(
), Jinming Chen1,*( )
)
Received:2022-07-11
Accepted:2022-09-05
Online:2023-02-20
Published:2022-09-19
Contact:
*Jinming Chen, E-mail: jmchen@wbgcas.cn;Shichu Liang gxlsc@sina.com
摘要:
近20年来, 随着分子生物学的兴起, 越来越多的证据表明生命之树的各个分支中都存在大量的隐种多样性, 占据未被发现的生物多样性的极高比例。准确地评估濒危类群的隐种多样性水平, 不仅能更好地理解物种形成在生物多样性式样及过程中的异质性作用, 而且也更有利于生物多样性的有效保护及管理。海菜花属(Ottelia)是我国二级重点保护植物, 为泛热带水生植物类群, 我国云贵高原及其邻近区域为该属重要的物种多样性中心之一。由于该属具有高度的表型可塑性, 缺少明确的鉴别特征, 致使其属下分类一直未能很好解决, 这极大限制了相关保护措施的制定。因此, 本研究在对我国海菜花属植物广泛采样的基础上, 利用多位点联合贝叶斯方法对其进行物种划分研究。结果表明: 我国海菜花属植物至少包括14种, 分子证据支持将海菜花种下3个变种提升为种, 同时海菜花(O. acuminata)和靖西海菜花(O. jingxiensis)内存在隐种现象。喀斯特地区的异质性生境及西南地区水系间的地理隔离可能是我国海菜花属特有类群快速分化的主要原因。基于本研究结果, 我们建议将各分类群(包括存疑类群)分别作为独立单元就地保护。
李治中, 彭帅, 王青锋, 李伟, 梁士楚, 陈进明 (2023) 中国海菜花属植物隐种多样性. 生物多样性, 31, 22394. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022394.
Zhizhong Li, Shuai Peng, Qingfeng Wang, Wei Li, Shichu Liang, Jinming Chen (2023) Cryptic diversity of the genus Ottelia in China. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22394. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022394.

图1 本研究海菜花属居群采样点地图。居群和个体信息详见附录1。
Fig. 1 Map of sampled population site of Ottelia in this study. Information on populations and the individuals see Appendix 1.
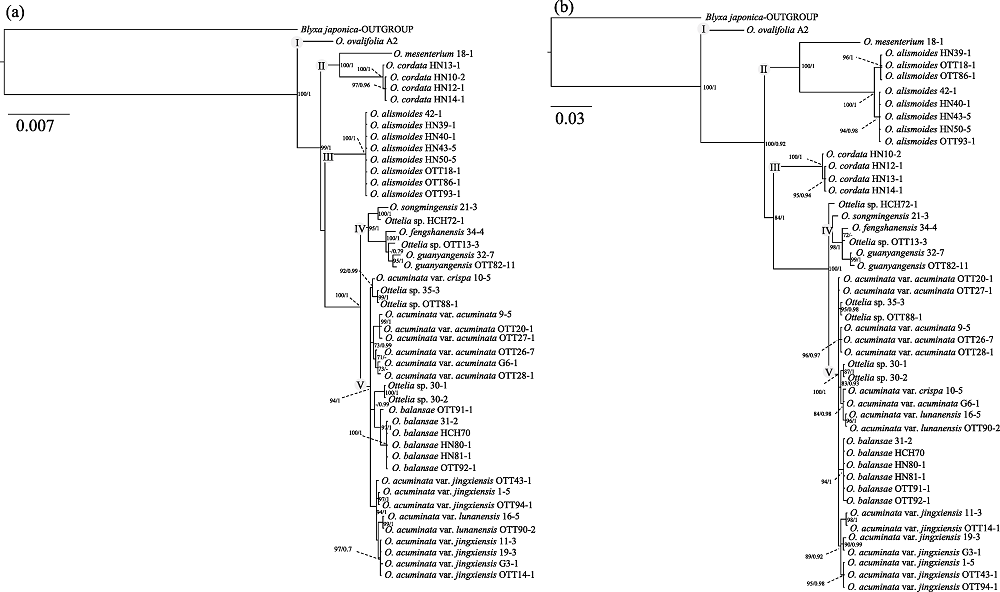
图2 基于叶绿体片段(a)及nrITS (b)对海菜花属植物构建的系统发育树。贝叶斯推理后验概率(PP)大于0.70及最大似然法分析支持度(BS)大于70展示在节点上。使用的物种、居群和个体信息见附录1, 水筛(Blyxa japonica)为外类群。
Fig. 2 Phylogenetic tree of Ottelia using ptDNA (a) and nrITS (b), respectively. Posterior probabilities (PP > 0.70) and bootstrap values (BS > 70) based on Bayesian Inference (BI) and Maximum Likelihood (ML) analysis are shown at nodes. Information on the individual code, population code, and species see Appendix 1. Blyxa japonica was included as outgroup.
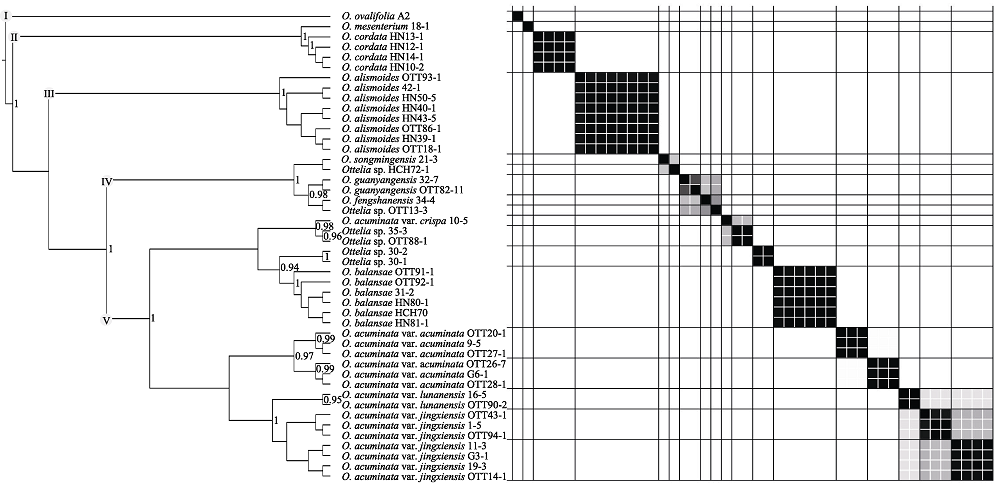
图3 基于多位点(8个叶绿体片段及nrITS)数据集最大置信树及STACEY结果。仅展示后验概率高于0.7的节点。黑、白阵列方格分别表示相似值1和0。使用的物种、居群和个体信息见附录1。
Fig. 3 Maximum credibility tree from STACEY analysis in BEAST2 based on multi-locus (nrITS and ptDNA). Only posterior probabilities higher than 0.7 were shown at nodes. Black and white matrix squares indicated posterior probabilities of 1 and 0, respectively. Information on the individual code, population code, and species see Appendix 1.
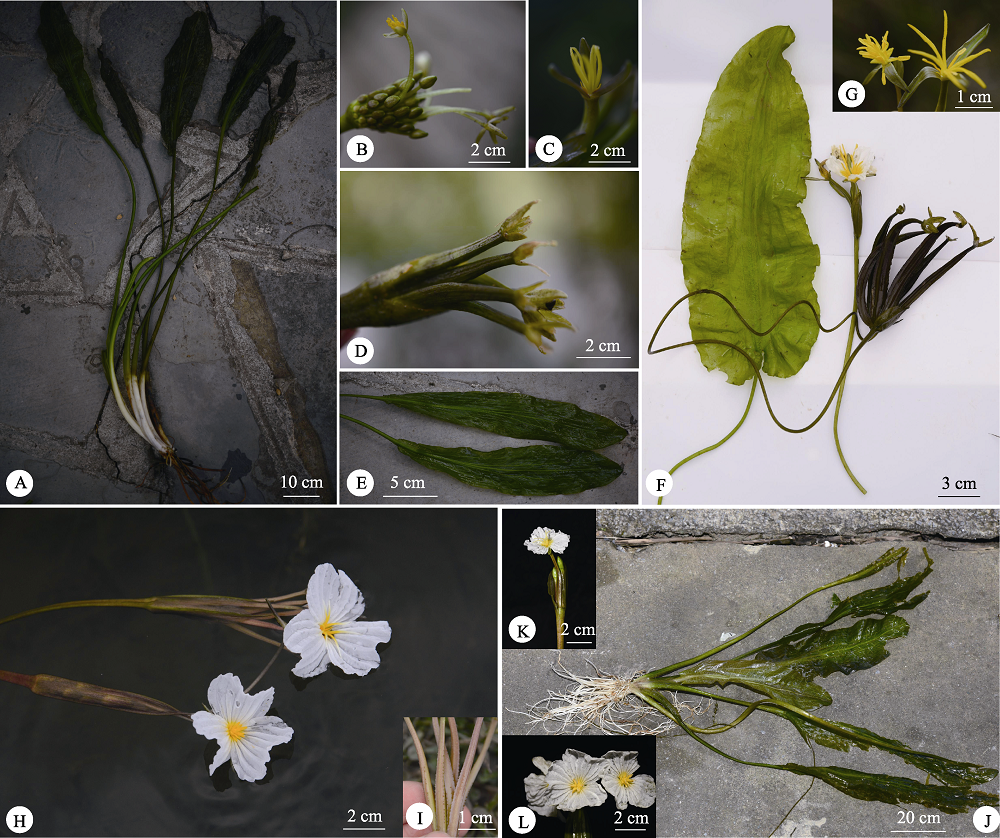

图4 本研究中4个海菜花属存疑类群。A?E: Ottelia sp. HCH72; F?G: Ottelia sp. 35; H?I: Ottelia sp. 30; J?L: Ottelia sp. OTT13。
Fig. 4 Four doubtful taxa in this study. A?E, Ottelia sp. HCH72; F?G, Ottelia sp. 35; H?I: Ottelia sp. 30; J?L, Ottelia sp. OTT13.
| [1] |
Barrett SCH, Eckert CG, Husband BC (1993) Evolutionary processes in aquatic plant populations. Aquatic Botany, 44, 105-145.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Chen YY, Li XL, Yin LY, Li W (2018) Genetic diversity of the threatened aquatic plant Ottelia alismoides in the Yangtze River. Aquatic Botany, 88, 10-16.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Delectis Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae Agendae Academiae Sinicae Edita (1992) Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae (Tomus 8). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国植物志编辑委员会 (1992) 中国植物志 (第8卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [4] |
Fan XR, Njeri HK, Li W, Chen YY (2019) Abundant historical gene flow within and among river systems for populations of Ottelia acuminata var. jingxiensis, an endangered macrophyte from south-west China. Aquatic Botany, 157, 1-9.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Fišer C, Robinson CT, Malard F (2018) Cryptic species as a window into the paradigm shift of the species concept. Molecular Ecology, 27, 613-635.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Guo JL, Yu YH, Zhang JW, Li ZM, Zhang YH, Volis S (2019) Conservation strategy for aquatic plants: Endangered Ottelia acuminata (Hydrocharitaceae) as a case study. Biodiversity and Conservation, 28, 1533-1548.
DOI |
| [7] | Guo YH, Huang SQ, Chen JK (1998) Breeding system and evolution of aquatic angiosperms. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 22, 79-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭友好, 黄双全, 陈家宽 (1998) 水生被子植物的繁育系统与进化. 水生生物学报, 22, 79-85.] | |
| [8] |
Ito Y, Tanaka N, Barfod AS, Bogner J, Li J, Yano O, Gale SW (2019) Molecular phylogenetic species delimitation in the aquatic genus Ottelia (Hydrocharitaceae) reveals cryptic diversity within a widespread species. Journal of Plant Research, 132, 335-344.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Jones GL (2017) Algorithmic improvements to species delimitation and phylogeny estimation under the multispecies coalescent. Journal of Mathematical Biology, 74, 447-467.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Kapli P, Lutteropp S, Zhang J, Kobert K, Pavlidis P, Stamatakis A, Flouri T (2017) Multi-rate Poisson tree processes for single-locus species delimitation under maximum likelihood and Markov Chain Monte Carlo. Bioinformatics, 33, 1630-1638.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Katoh K, Standley DM (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 777-780. |
| [12] |
Kaul RB (1969) Morphology and development of the flowers of Boottia cordata, Ottelia alismoides, and their synthetic hybrid (Hydrocharitaceae). American Journal of Botany, 56, 951-959.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Kong H, Condamine FL, Yang L, Harris AJ, Feng C, Wen F, Kang M (2022) Phylogenomic and macroevolutionary evidence for an explosive radiation of a plant genus in the Miocene. Systematic Biology, 71, 589-609.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Li H (1981) Classification, distribution and phylogeny of the genus Ottelia. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica, 19, 29-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李恒 (1981) 海菜花属的分类、地理分布和系统发育. 植物分类学报, 19, 29-42.] | |
| [15] |
Li ZZ, Liao K, Zou CY, Liu Y, Hu GW, Wang QF, Chen JM (2018) Ottelia guanyangensis (Hydrocharitaceae), a new species from southwestern China. Phytotaxa, 361, 294-300.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Li ZZ, Wu S, Zou CY, Liu Y, Hu GW, Lehtonen S, Wang QF, Chen JM (2019a) Ottelia fengshanensis, a new bisexual species of Ottelia (Hydrocharitaceae) from southwestern China. Phytokeys, 135, 1-10.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Li ZZ, Lu MX, Gichira AW, Islam MR, Wang QF, Chen JM (2019b) Genetic diversity and population structure of Ottelia acuminata var. jingxiensis, an endangered endemic aquatic plant from southwest China. Aquatic Botany, 152, 20-26.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Li ZZ, Lehtonen S, Martins K, Gichira AW, Wu S, Li W, Hu GW, Liu Y, Zou CY, Wang QF, Chen JM (2020a) Phylogenomics of the aquatic plant genus Ottelia (Hydrocharitaceae): Implications for historical biogeography. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 152, 106939.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Li ZZ, Ngarega BK, Lehtonen S, Gichira AW, Karichu MJ, Wang QF, Chen JM (2020b) Cryptic diversity within the African aquatic plant Ottelia ulvifolia (Hydrocharitaceae) revealed by population genetic and phylogenetic analyses. Journal of Plant Research, 133, 373-381.
DOI |
| [20] |
Li ZZ, Wang QF, Chen JM (2022a) Ottelia songmingensis, a new rank and combination of Hydrocharitaceae from China. Phytotaxa, 554, 101-102.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Li L, Chen X, Fang D, Dong S, Guo X, Li N, Campos-Dominguez L, Wang W, Liu Y, Lang X, Peng Y, Tian D, Thomas DC, Mu W, Liu M, Wu C, Yang T, Zhang S, Yang L, Yang J, Liu Z, Zhang L, Zhang X, Chen F, Jiao Y, Guo Y, Hughes M, Wang W, Liu X, Zhong C, Li A, Sahu SK, Yang H, Wu E, Sharbrough J, Lisby M, Liu X, Xu X, Soltis DE, de Peer YV, Kidner C, Zhang S, Liu H (2022b) Genomes shed light on the evolution of Begonia, a mega-diverse genus. New Phytologist, 234, 295-310.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Liu Y, Shen Z, Wang Q, Su X, Zhang W, Shrestha N, Xu X, Wang Z (2017) Determinants of richness patterns differ between rare and common species: Implications for Gesneriaceae conservation in China. Diversity and Distributions, 23, 235-246.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Loxdale HD, Davis BJ, Davis RA (2016) Known knowns and unknowns in biology. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 117, 386-398.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Lu YJ, Gu YF, Yan YH (2021) Isoetes baodongii (Isoetaceae), a new basic diploid quillwort from China. Novon, 29, 206-210.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Lu ZL, Qin HN, Jin XH, Zhang ZX, Yang QW, Hong DY, Li DZ, Li KF, Yuan LC, Zhou ZH (2021) On the necessity, principle, and process of updating the List of National Key Protected Wild Plants. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1577-1582. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[鲁兆莉, 覃海宁, 金效华, 张志翔, 杨庆文, 洪德元, 李德铢, 李开凡, 袁良琛, 周志华 (2021) 《国家重点保护野生植物名录》调整的必要性、原则和程序. 生物多样性, 29, 1577-1582.]
DOI |
|
| [26] | Ming QZ, Pan YJ (2002) The elementary acknowledge on the importance of environmental evolution of Yunnan Plateau. Journal of Geomechanics, 8, 361-368. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [明庆忠, 潘玉君 (2002) 对云南高原环境演化研究的重要性及环境演变的初步认知. 地质力学学报, 8, 361-368.] | |
| [27] |
Moonlight PW, Ardi WH, Padilla LA, Chung KF, Fuller D, Girmansyah D, Hollands R, Jara-Muñoz A, Kiew R, Leong W, Liu Y, Mahardika A, Marasinghe LDK, Connor MO, Peng C, Pérez AJ, Phutthai T, Pullan M, Rajbhandary S, Reynel C, Rubite RR, Sang J, Scherberich D, Shui Y, Tebbitt MC, Thomas DC, Wilson HP, Zaini NH, Hughes M (2018) Dividing and conquering the fastest-growing genus: Towards a natural sectional classification of the mega- diverse genus Begonia (Begoniaceae). Taxon, 67, 267-323.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Nguyen LT, Schmidt HA, Haeseler A, Minh BQ (2015) IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum likelihood phylogenies. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 32, 268-274.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Pante E, Puillandre N, Viricel A, Arnaud-Haond S, Aurelle D, Castelin M, Chenuil A, Destombe C, Forcioli D, Valero M, Viard F, Samadi S (2015) Species are hypotheses: Avoid connectivity assessments based on pillars of sand. Molecular Ecology, 24, 525-544.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Puillandre N, Lambert A, Brouillet S, Achaz GJME (2012) ABGD, Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery for primary species delimitation. Molecular Ecology, 21, 1864-1877.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Rambaut A (2009) FigTree ver. 1.3.1: Tree Figure Drawing Tool. http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/. (accessed on 2021-10-17) |
| [32] | Rambaut A, Suchard MA, Xie W, Drummond AJ (2014) Tracer ver. 1.6. http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer/. (accessed on 2021-10-17) |
| [33] | Rieseberg LH, Soltis DE (1991) Phylogenetic consequences of cytoplasmic gene flow in plants. Evolutionary Trends Plants, 5, 65-84. |
| [34] |
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, van der Mark P, Ayres DL, Darling A, Höhna S, Larget B, Liu L, Suchard MA, Huelsenbeck JP (2012) MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology, 61, 539-542.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Struck TH, Feder JL, Bendiksby M, Birkeland S, Cerca J, Gusarov VI, Kistenich S, Larsson K, Liow L, Nowak MD, Stedje B, Bachmann L, Dimitrov D (2018) Finding evolutionary processes hidden in cryptic species. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 33, 153-163.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Trontelj P, Fišer C (2009) Cryptic species diversity should not be trivialised. Systematics and Biodiversity, 7, 1-3.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Witt JDS, Threloff DL, Hebert PDN (2006) DNA barcoding reveals extraordinary cryptic diversity in an amphipod genus: Implications for desert spring conservation. Molecular Ecology, 15, 3073-3082.
PMID |
| [38] |
Xu W, Che J (2019) From cryptic species to biodiversity conservation in China: Status and prospects. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 49, 519-530. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [徐伟, 车静 (2019) 从隐存种到我国生物多样性保护研究: 现状与展望. 中国科学: 生命科学, 49, 519-530.] | |
| [39] |
Yang L, Kong H, Huang JP, Kang M (2019) Different species or genetically divergent populations? Integrative species delimitation of the Primulina hochiensis complex from isolated karst habitats. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 132, 219-231.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Yu JH, Zhang R, Liu QL, Wang FG, Yu XL, Dai XL, Liu YB, Yan YH (2022) Ceratopteris chunii and Ceratopteris chingii (Pteridaceae), two new diploid species from China, based on morphological, cytological, and molecular data. Plant Diversity, 44, 300-307.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Zhai SH, Yin GS, Yang XH (2018) Population genetics of the endangered and wild edible plant Ottelia acuminata in southwestern China using novel SSR markers. Biochemical Genetics, 56, 235-254.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
Zhang R, Yu JH, Shao W, Wang WQ, Shang H, Zheng XL, Yan YH (2020) Ceratopteris shingii, a new species of Ceratopteris with creeping rhizomes from Hainan, China. Phytotaxa, 449, 23-30.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 孙亚君. 何谓高等或低等生物——澄清《物种起源》所蕴含的生物等级性的涵义及其成立性[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24394-. |
| [2] | 艾妍雨, 胡海霞, 沈婷, 莫雨轩, 杞金华, 宋亮. 附生维管植物多样性及其与宿主特征的相关性: 以哀牢山中山湿性常绿阔叶林为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24072-. |
| [3] | 吕燕文, 王子韵, 肖钰, 何梓晗, 吴超, 胡新生. 谱系分选理论与检测方法的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23400-. |
| [4] | 曹可欣, 王敬雯, 郑国, 武鹏峰, 李英滨, 崔淑艳. 降水格局改变及氮沉降对北方典型草原土壤线虫多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [5] | 王斌, 钟艺倩, 杨美雪, 吴淼锐, 王艳萍, 陆芳, 陶旺兰, 李健星, 赵弘明, 刘晟源, 向悟生, 李先琨. 喀斯特季节性雨林优势树种叶片非结构性碳水化合物空间变异及生态驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24325-. |
| [6] | 杨向林, 赵彩云, 李俊生, 种方方, 李文金. 植物入侵导致群落谱系结构更加聚集: 以广西国家级自然保护区草本植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [7] | 何林君, 杨文静, 石宇豪, 阿说克者莫, 范钰, 王国严, 李景吉, 石松林, 易桂花, 彭培好. 火烧干扰下植物群落系统发育和功能多样性对紫茎泽兰入侵的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24269-. |
| [8] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [9] | 宋会银, 胡征宇, 刘国祥. 绿藻门小球藻科的分类学研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22083-. |
| [10] | 朱瑞良, 马晓英, 曹畅, 曹子寅. 中国苔藓植物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22378-. |
| [11] | 王婷, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 李艳清, 杨拓, 徐洲锋, 向建英, 张宪春, 严岳鸿. 中国石松类和蕨类植物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22381-. |
| [12] | 王健铭, 曲梦君, 王寅, 冯益明, 吴波, 卢琦, 何念鹏, 李景文. 青藏高原北部戈壁植物群落物种、功能与系统发育β多样性分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21503-. |
| [13] | 姜晓燕, 高圣杰, 蒋燕, 田赟, 贾昕, 查天山. 毛乌素沙地植被不同恢复阶段植物群落物种多样性、功能多样性和系统发育多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21387-. |
| [14] | 赵琦, 蒋际宝, 张曾鲁, 金清, 李佳丽, 邱江平. 海南岛蚯蚓物种组成及其系统发育分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22224-. |
| [15] | 栗冬梅, 杨卫红, 李庆多, 韩茜, 宋秀平, 潘虹, 冯云. 巴尔通体在滇西南蝙蝠中高度流行并具有丰富的遗传变异特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1245-1255. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn