



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (10): 1192-1201. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020063 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020063
张全建1,2, 杨彪3, 付强4, 王磊4, 龚旭1,2, 张远彬1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-02-27
接受日期:2020-05-09
出版日期:2020-10-20
发布日期:2020-10-20
通讯作者:
张远彬
作者简介:E-mail: zhangyb@imde.ac.cn基金资助:
Quanjian Zhang1,2, Biao Yang3, Qiang Fu4, Lei Wang4, Xu Gong1,2, Yuanbin Zhang1,*( )
)
Received:2020-02-27
Accepted:2020-05-09
Online:2020-10-20
Published:2020-10-20
Contact:
Yuanbin Zhang
摘要:
水鹿(Rusa unicolor)为珍稀濒危动物, 属国家II级重点保护野生动物, 其食物匮乏季的食性研究对其保护至关重要。本文以四川邛崃山系鞍子河保护地的水鹿为研究对象, 采用高通量测序(high-throughput sequencing, HTS)技术对其冬季18份有效粪便样品中的摄食植物进行了分析。结果表明: (1)水鹿摄食植物有50科94属; (2)水鹿冬季偏好食物为悬钩子属(Rubus)、山茱萸属(Cornus)、青荚叶属(Helwingia)、马蓝属(Strobilanthes)、荚蒾属(Viburnum)、清风藤属(Sabia)、旌节花属(Stachyurus)、菝葜属(Smilax)、槭属(Acer)和绣球属(Hydrangea)植物, 且蔷薇科悬钩子属植物为最重要的食物来源; (3)水鹿在冬季摄食植物多样性高、食物生态位宽; (4)水鹿具有强的环境适应性和资源利用能力, 在冬季会通过摄食更多的植物类型和适当调整生态位而适应环境变化。本研究结论将有利于水鹿及其同域生活的偶蹄目动物的管理策略制定。
张全建, 杨彪, 付强, 王磊, 龚旭, 张远彬 (2020) 邛崃山系水鹿的冬季食性. 生物多样性, 28, 1192-1201. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020063.
Quanjian Zhang, Biao Yang, Qiang Fu, Lei Wang, Xu Gong, Yuanbin Zhang (2020) The winter diet of sambar (Rusa unicolor) in the Qionglai Mountains. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1192-1201. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020063.
| 初冬样品编号 Sample code in early winter | 经度 Longitude (E) | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 采样时间 Sampling time | 冬季样品编号 Sample code in winter | 经度 Longitude (E) | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 采样时间 Sampling time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 103.19° | 30.81° | 1,990 | 2018.11.13 | 1 | 103.21° | 30.79° | 1,996 | 2018.12.1 |
| 5 | 103.15° | 30.80° | 2,429 | 2018.11.12 | 2 | 103.21° | 30.76° | 2,138 | 2018.12.1 |
| 6 | 103.17° | 30.81° | 2,060 | 2018.11.13 | 3 | 103.21° | 30.76° | 2,166 | 2018.12.28 |
| 7 | 103.16° | 30.80° | 2,280 | 2018.11.13 | 12 | 103.19° | 30.76° | 2,354 | 2018.12.1 |
| 8 | 103.19° | 30.81° | 1,979 | 2018.11.13 | 13 | 103.20° | 30.79° | 1,932 | 2018.12.1 |
| 9 | 103.15° | 30.80° | 2,453 | 2018.11.12 | 16 | 103.22° | 30.77° | 1,909 | 2019.1.5 |
| 10 | 103.27° | 30.81° | 1,734 | 2018.11.5 | 17 | 103.21° | 30.77° | 1,860 | 2018.12.4 |
| 11 | 103.27° | 30.81° | 1,798 | 2018.11.5 | 18 | 103.21° | 30.77° | 1,891 | 2018.12.16 |
| 14 | 103.21° | 30.77° | 1,923 | 2018.11.5 | |||||
| 15 | 103.21° | 30.76° | 1,998 | 2018.11.5 |
表1 鞍子河保护地经DNA鉴定筛选出的有效水鹿粪便样品
Table 1 The valid fecal samples of Rusa unicolor screened out through DNA identification at Anzihe protected area
| 初冬样品编号 Sample code in early winter | 经度 Longitude (E) | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 采样时间 Sampling time | 冬季样品编号 Sample code in winter | 经度 Longitude (E) | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 采样时间 Sampling time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 103.19° | 30.81° | 1,990 | 2018.11.13 | 1 | 103.21° | 30.79° | 1,996 | 2018.12.1 |
| 5 | 103.15° | 30.80° | 2,429 | 2018.11.12 | 2 | 103.21° | 30.76° | 2,138 | 2018.12.1 |
| 6 | 103.17° | 30.81° | 2,060 | 2018.11.13 | 3 | 103.21° | 30.76° | 2,166 | 2018.12.28 |
| 7 | 103.16° | 30.80° | 2,280 | 2018.11.13 | 12 | 103.19° | 30.76° | 2,354 | 2018.12.1 |
| 8 | 103.19° | 30.81° | 1,979 | 2018.11.13 | 13 | 103.20° | 30.79° | 1,932 | 2018.12.1 |
| 9 | 103.15° | 30.80° | 2,453 | 2018.11.12 | 16 | 103.22° | 30.77° | 1,909 | 2019.1.5 |
| 10 | 103.27° | 30.81° | 1,734 | 2018.11.5 | 17 | 103.21° | 30.77° | 1,860 | 2018.12.4 |
| 11 | 103.27° | 30.81° | 1,798 | 2018.11.5 | 18 | 103.21° | 30.77° | 1,891 | 2018.12.16 |
| 14 | 103.21° | 30.77° | 1,923 | 2018.11.5 | |||||
| 15 | 103.21° | 30.76° | 1,998 | 2018.11.5 |
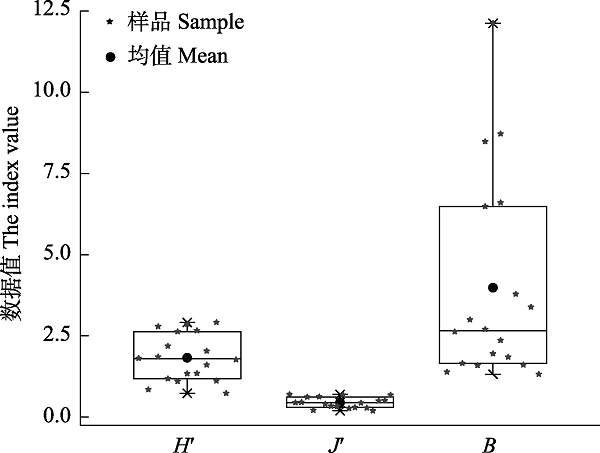
图3 水鹿粪便样品中植物的Shannon-Wiener指数(H')、Pielou均匀度指数(J')和食物生态位宽度(B)
Fig. 3 The Shannon-Wiener index (H'), Pielou evenness index (J') and dietary niche breadth (B) of plants in the fecal samples of Rusa unicolor
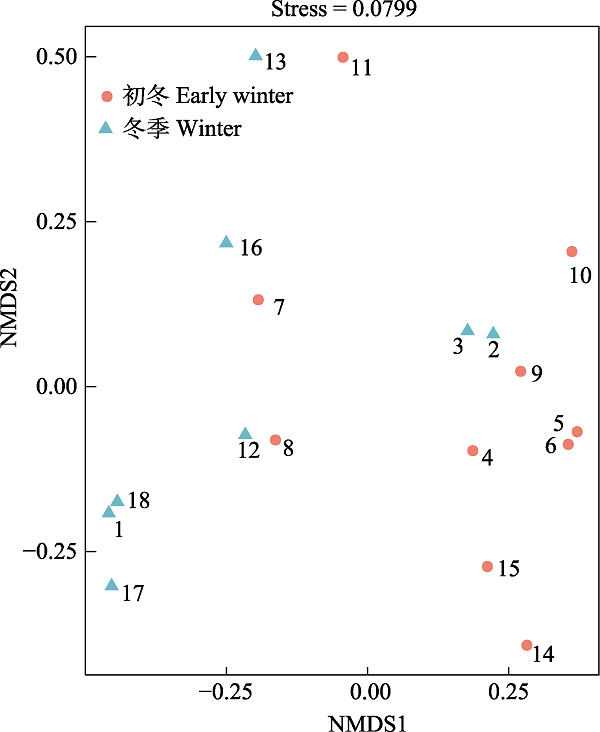
图4 初冬和冬季水鹿粪便样品的生态位分异图(1-18为样品编号)
Fig. 4 The niche differentiation between the fecal samples of Rusa unicolor at early winter and winter (1 to 18 are sample codes)
| 初冬样品编号 Sample code in early winter | OTU类型数 OTU type number | 冬季样品编号 Sample code in winter | OTU类型数 OTU type number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 55 | 1 | 66 |
| 5 | 54 | 2 | 55 |
| 6 | 53 | 3 | 66 |
| 7 | 70 | 12 | 55 |
| 8 | 68 | 13 | 54 |
| 9 | 53 | 16 | 53 |
| 10 | 55 | 17 | 70 |
| 11 | 44 | 18 | 68 |
| 14 | 52 | ||
| 15 | 55 | ||
| 均值 ± 标准误 Mean ± SE | 56 ± 8b | 均值 ± 标准误 Mean ± SE | 65 ± 8a |
表2 不同采样期水鹿粪便样品中OTU类型数比较
Table 2 The comparison of OTU type number in the fecal samples of Rusa unicolor between different sampling time
| 初冬样品编号 Sample code in early winter | OTU类型数 OTU type number | 冬季样品编号 Sample code in winter | OTU类型数 OTU type number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 55 | 1 | 66 |
| 5 | 54 | 2 | 55 |
| 6 | 53 | 3 | 66 |
| 7 | 70 | 12 | 55 |
| 8 | 68 | 13 | 54 |
| 9 | 53 | 16 | 53 |
| 10 | 55 | 17 | 70 |
| 11 | 44 | 18 | 68 |
| 14 | 52 | ||
| 15 | 55 | ||
| 均值 ± 标准误 Mean ± SE | 56 ± 8b | 均值 ± 标准误 Mean ± SE | 65 ± 8a |
| 研究对象 Study object | 数据来源 Data resource | 共食性植物 Shared plants |
|---|---|---|
| 中国海南水鹿 The Rusa unicolor in Hainan, China | 穇属 Eleusine, 稗属 Echinochloa | |
| 新西兰水鹿 The R. unicolor in New Zealand | 悬钩子属 Rubus, 繁缕属 Stellaria, 毛莨属 Ranunculus, 酸模属 Rumex | |
| 澳大利亚水鹿 The R. unicolor in Australia | 悬钩子属 Rubus, 繁缕属 Stellaria, 铁线莲属 Clematis, 蓟属 Cirsium, 酢浆草属 Oxalis | |
| 马来西亚水鹿 The R. unicolor in Malaysia | 木姜子属 Litsea | |
| 中国台湾水鹿 The R. unicolor in Taiwan, China | 悬钩子属 Rubus, 木姜子属 Litsea, 绣球属 Hydrangea, 杜鹃属 Rhododendron, 茶藨子属 Ribes, 槭属 Acer, 卫矛属 Euonymus, 鹅掌柴属 Schefflera, 忍冬属 Lonicera, 冬青属 Ilex, 勾儿茶属 Berchemia, 刚竹属 Phyllostachys, 小檗属 Berberis, 蔷薇属 Rosa, 旌节花属 Stachyurus, 樟属 Cinnamomum, 荚蒾属 Viburnum, 苹果属 Malus |
表3 邛崃山系水鹿与其他研究地水鹿共食植物表
Table 3 The shared plants of Rusa unicolor in the Qionglai Mountains and in other study places
| 研究对象 Study object | 数据来源 Data resource | 共食性植物 Shared plants |
|---|---|---|
| 中国海南水鹿 The Rusa unicolor in Hainan, China | 穇属 Eleusine, 稗属 Echinochloa | |
| 新西兰水鹿 The R. unicolor in New Zealand | 悬钩子属 Rubus, 繁缕属 Stellaria, 毛莨属 Ranunculus, 酸模属 Rumex | |
| 澳大利亚水鹿 The R. unicolor in Australia | 悬钩子属 Rubus, 繁缕属 Stellaria, 铁线莲属 Clematis, 蓟属 Cirsium, 酢浆草属 Oxalis | |
| 马来西亚水鹿 The R. unicolor in Malaysia | 木姜子属 Litsea | |
| 中国台湾水鹿 The R. unicolor in Taiwan, China | 悬钩子属 Rubus, 木姜子属 Litsea, 绣球属 Hydrangea, 杜鹃属 Rhododendron, 茶藨子属 Ribes, 槭属 Acer, 卫矛属 Euonymus, 鹅掌柴属 Schefflera, 忍冬属 Lonicera, 冬青属 Ilex, 勾儿茶属 Berchemia, 刚竹属 Phyllostachys, 小檗属 Berberis, 蔷薇属 Rosa, 旌节花属 Stachyurus, 樟属 Cinnamomum, 荚蒾属 Viburnum, 苹果属 Malus |
| [1] |
Ahrestani FS, Heitkonig IMA, Prins HHT ( 2012) Diet and habitat-niche relationships within an assemblage of large herbivores in a seasonal tropical forest. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 28, 385-394.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Aryal A, Panthi S, Barraclough RK, Bencini R, Adhikari B, Ji WH, Raubenheimer D ( 2015) Habitat selection and feeding ecology of dhole (Cuon alpinus) in the Himalayas. Journal of Mammalogy, 96, 47-53. |
| [3] |
Bokulich NA, Subramanian S, Faith JJ, Gevers D, Gordon JI, Knight R, Mills DA, Caporaso JG ( 2013) Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nature Methods, 10, 57-59.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] |
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R ( 2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods, 7, 335-336.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] |
Chen H, Jiang W ( 2014) Application of high-throughput sequencing in understanding human oral microbiome related with health and disease. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5, 508.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] |
Deagle BE, Thomas AC, Shaffer AK, Trites AW, Jarman SN ( 2013) Quantifying sequence proportions in a DNA-based diet study using ion torrent amplicon sequencing: Which counts count? Molecular Ecology Resources, 13, 620-633.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] | Delgiudice GD, Moen RA, Singer FJ, Riggs MR ( 2001) Winter nutritional restriction and simulated body condition of Yellowstone elk and bison before and after the fires of 1988. Wildlife Monographs, 147, 1-60. |
| [8] |
Duffy JE, Cardinale BJ, France KE, Mcintyre PB, Thebault E, Loreau M ( 2007) The functional role of biodiversity in ecosystems: Incorporating trophic complexity. Ecology Letters, 10, 522-538.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] |
Edgar RC ( 2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than blast. Bioinformatics, 26, 2460-2461.
DOI URL PMID |
| [10] |
Erickson DL, Reed E, Ramachandran P, Bourg NA, McShea WJ, Ottesen A ( 2017) Reconstructing a herbivore’s diet using a novel rbcL DNA mini-barcode for plants. AoB Plants, 9, plx015.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] | Forsyth DM, Davis NE ( 2011) Diets of non-native deer in Australia estimated by macroscopic versus microhistological rumen analysis. Journal of Wildlife Management, 75, 1488-1497. |
| [12] |
García-Robledo C, Erickson DL, Staines CL, Erwin TL, Kress WJ ( 2013) Tropical plant-herbivore networks: Reconstructing species interactions using DNA barcodes. PLoS ONE, 8, e52967.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
Gebremedhin B, Flagstad O, Bekele A, Chala D, Bakkestuen V, Boessenkool S, Popp M, Gussarova G, Schroder-Nielsen A, Nemomissa S, Brochmann C, Stenseth NC, Epp LS ( 2016) DNA metabarcoding reveals diet overlap between the endangered Walia ibex and domestic goats—Implications for conservation. PLoS ONE, 11, e0159133.
DOI URL PMID |
| [14] |
Gill SR, Pop M, Deboy RT, Eckburg PB, Turnbaugh PJ, Samuel BS, Gordon JI, Relman DA, Fraser-Liggett CM, Nelson KE ( 2006) Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science, 312, 1355-1359.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] | He XC, Fu Q, Wu YJ, Wang B, Chen X, Ran JH ( 2019) Population structure and activity rhythm of sambar deer (Rusa unicolor). Acta Theriologica Sinica, 39, 134-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 何兴成, 付强, 吴永杰, 王彬, 陈雪, 冉江洪 ( 2019) 水鹿的群体结构和活动节律分析. 兽类学报, 39, 134-141.] | |
| [16] | Holechek JL, Vavra M, Pieper RD ( 1982) Botanical composition determination of range herbivore diets—A review. Journal of Range Management, 35, 309-315. |
| [17] | Hollingsworth PM, Forrest LL, Spouge JL, Hajibabaei M, Ratnasingham S, van der Bank M, Chase MW, Cowan RS, Erickson DL, Fazekas AJ, Graham SW, James KE, Kim KJ, Kress WJ, Schneider H, van AlphenStahl J, Barrett SCH, van den Berg C, Bogarin D, Burgess KS, Cameron KM, Carine M, Chacon J, Clark A, Clarkson JJ, Conrad F, Devey DS, Ford CS, Hedderson TAJ, Hollingsworth ML, Husband BC, Kelly LJ, Kesanakurti PR, Kim JS, Kim YD, Lahaye R, Lee HL, Long DG, Madrinan S, Maurin O, Meusnier I, Newmaster SG, Park CW, Percy DM, Petersen G, Richardson JE, Salazar GA, Savolainen V, Seberg O, Wilkinson MJ, Yi DK, Little DP ( 2009) A DNA barcode for land plants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 106, 12794-12797. |
| [18] | Hu JC, Wang YZ ( 1984) Sichuan Resourceful Fauna (2nd vol.): Mammal. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [ 胡锦矗, 王酉之 ( 1984) 四川资源动物志(第2卷): 兽类. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [19] |
Ismail D, Jiwan D ( 2015) Browsing preference and ecological carrying capacity of sambar deer (Cervus unicolor Brookei) on secondary vegetation in forest plantation. Animal Science Journal, 86, 225-237.
URL PMID |
| [20] | Johnsingh AJT, Sankar K ( 1991) Food plants of chital, sambar and cattle on Mundanthurai Plateau, Tamil-Nadu, south India. Mammalia, 55, 57-66. |
| [21] | Kartzinel TR, Chen PA, Coverdale TC, Erickson DL, Kress WJ, Kuzmina ML, Rubenstein DI, Wang W, Pringle RM ( 2015) DNA metabarcoding illuminates dietary niche partitioning by African large herbivores. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 8019-8024. |
| [22] | Kelton SD, Skipworth JP ( 1987) Food of sambar deer (Cervus unicolor) in a Manawatu (New Zealand) flax swamp. New Zealand Journal of Ecology, 10, 149-152. |
| [23] | Khan JA ( 1994) Food-habits of ungulates in dry tropical forests of Gir Lion Sanctuary, Gujarat, India. Acta Theriologica, 39, 185-193. |
| [24] | Kowalczyk R, Taberlet P, Coissac E, Valentini A, Miquel C, Kaminski T, Wojcik JM ( 2011) Influence of management practices on large herbivore diet—Case of European bison in Bialowieza Primeval Forest (Poland). Forest Ecology and Management, 261, 821-828. |
| [25] |
Kress WJ, Garcia-Robledo C, Uriarte M, Erickson DL ( 2015) DNA barcodes for ecology, evolution, and conservation. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 30, 25-35.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | Liu G, Ning Y, Xia XF, Gong MH ( 2018) The application of high-throughput sequencing technologies to wildlife diet analysis. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 3347-3356. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘刚, 宁宇, 夏晓飞, 龚明昊 ( 2018) 高通量测序技术在野生动物食性分析中的应用. 生态学报, 38, 3347-3356.] | |
| [27] | Liu MC, Zou XY, Lin YT, Tang Z, Ma LP, Zhang JY, Wang PY ( 2018) The monitoring of licking salt behavior in takin and sambar in Wolong Nature Reserve. Bulletin of Biology, 53(12), 32-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘明冲, 邹晓艳, 林雨婷, 唐卓, 马联平, 张巨意, 王鹏彦 ( 2018) 卧龙保护区羚牛、水鹿舔盐活动监控统计初报. 生物学通报, 53(12), 32-35.] | |
| [28] |
Magoc T, Salzberg SL ( 2011) Flash: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics, 27, 2957-2963.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] |
Mata VA, Rebelo H, Amorim F, Mccracken GF, Jarman S, Beja P ( 2019) How much is enough? Effects of technical and biological replication on metabarcoding dietary analysis. Molecular Ecology, 28, 165-175.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] |
McClenaghan B, Gibson JF, Shokralla S, Hajibabaei M ( 2015) Discrimination of grasshopper (Orthoptera: Acrididae) diet and niche overlap using next-generation sequencing of gut contents. Ecology and Evolution, 5, 3046-3055.
DOI URL PMID |
| [31] | Newmaster SG, Thompson ID, Steeves RAD, Rodgers AR, Fazekas AJ, Maloles JR, Mcmullin RT, Fryxell JM ( 2013) Examination of two new technologies to assess the diet of woodland caribou: Video recorders attached to collars and DNA barcoding. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 43, 897-900. |
| [32] | Padmalal U, Takatsuki S, Jayasekara P ( 2003) Food habits of sambar Cervus unicolor at the Horton Plains National Park, Sri Lanka. Ecological Research, 18, 775-782. |
| [33] | Pielou EC ( 1969) An Introduction to Mathematical Ecology. Wiley-Interscience, New York. |
| [34] | Pompanon F, Deagle BE, Symondson WOC, Brown DS, Jarman SN, Taberlet P ( 2012) Who is eating what: Diet assessment using next generation sequencing. Molecular Ecology, 21, 1931-1950. |
| [35] | Pyke G, Pulliam H, Charnov EL ( 1977) Optimal foraging: A selective review of theory and tests. Quarterly Review of Biology, 52, 137-153. |
| [36] | Semiadi G, Barry TN, Muir PD, Hodgson J ( 1995) Dietary preferences of sambar (Cervus unicolor) and red deer (Cervus elaphus) offered browse, forage legume and grass species. Journal of Agricultural Science, 125, 99-107. |
| [37] | Severud WJ, Windels SK, Belant JL, Bruggink JG ( 2013) The role of forage availability on diet choice and body condition in American beavers (Castor canadensis). Mammalian Biology, 78, 87-93. |
| [38] | Shang YC ( 2010) General Ecology, 3rd edn. Peking University Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 尚玉昌 ( 2010) 普通生态学(第三版). 北京大学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [39] | Sheppard SK, Harwood JD ( 2005) Advances in molecular ecology: Tracking trophic links through predator-prey food-webs. Functional Ecology, 19, 751-762. |
| [40] | Smith EP ( 1982) Niche breadth, resource availability, and inference. Ecology, 63, 1675-1681. |
| [41] | Stafford KJ ( 1997) The diet and trace element status of sambar deer (Cervus unicolor) in Manawatu district, New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 24, 267-271. |
| [42] | Sun JX, Li JQ, Wan YQ, Li S, Guan TP, Wang J, Xia WC, Xu HG ( 2018) Study on the activity rhythms of vine ungulates in summer and autumn in Sichuan. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 34, 1003-1009. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙佳欣, 李佳琦, 万雅琼, 李晟, 官天培, 王杰, 夏万才, 徐海根 ( 2018) 四川9种有蹄类动物夏秋季活动节律研究. 生态与农村环境学报, 34, 1003-1009.] | |
| [43] |
Symondson WOC, Harwood JD ( 2014) Special issue on molecular detection of trophic interactions: Unpicking the tangled bank introduction. Molecular Ecology, 23, 3601-3604.
DOI URL PMID |
| [44] | Timmins R, Kawanishi K, Giman B, Lynam A, Chan B, Steinmetz R, Sagar Baral H, Kumar S ( 2015) Rusa unicolor (errata version published in 2015). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015, e.T41790A85628124. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T41790A22156247.en. (accessed on 2020-02-17) |
| [45] |
Valentini A, Miquel C, Nawaz MA, Bellemain E, Coissac E, Pompanon F, Gielly L, Cruaud C, Nascetti G, Wincker P, Swenson JE, Taberlet P ( 2009) New perspectives in diet analysis based on DNA barcoding and parallel pyrosequencing: The trnL approach. Molecular Ecology Resources, 9, 51-60.
DOI URL PMID |
| [46] | Wang P, Bai WK, Huang JY, Zhang JD, Liu D, Xia SS, Rao J, Zhou CQ ( 2018) Habitat use of differentiation between sympatric giant panda and sambar. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 5577-5583. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王盼, 白文科, 黄金燕, 张晋东, 刘巅, 夏珊珊, 饶佳, 周材权 ( 2018) 同域分布大熊猫和水鹿生境利用分异特征. 生态学报, 38, 5577-5583.] | |
| [47] | Wang XQ, Wang GH, Qiao F, Gao QK, Heong KL, Zhu ZR, Cheng JA ( 2017) Progress on high-throughput sequencing and its applications in food web analysis. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 2530-2539. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王雪芹, 王光华, 乔飞, 高其康, Heong KL, 祝增荣, 程家安 ( 2017) 高通量测序及其在食物网解析中的应用进展. 生态学报, 37, 2530-2539.] | |
| [48] | Weimerskirch H, Cherel Y, Cuenot-Chaillet F, Ridoux V ( 1997) Alternative foraging strategies and resource allocation by male and female wandering albatrosses. Ecology, 78, 2051-2063. |
| [49] | Williams RL, Goodenough AE, Stafford R ( 2012) Statistical precision of diet diversity from scat and pellet analysis. Ecological Informatics, 7, 30-34. |
| [50] |
Yin BF, Huai HY, Zhang YL, Zhou L, Wei WH ( 2007) Trophic niches of Pantholops hodgsoni, Procapra picticaudata and Equus kiang in Kekexili region. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 18, 766-770. (in Chinese with English abstract)
URL PMID |
|
[ 殷宝法, 淮虎银, 张镱锂, 周乐, 魏万红 ( 2007) 可可西里地区藏羚羊、藏原羚和藏野驴的营养生态位. 应用生态学报, 18, 766-770.]
PMID |
|
| [51] | Yao G, Li YH, Zhang JD, Li DY, Yang ZS, Hu J, Shi XG ( 2017) An investigation on population density and distribution of Rusa unicolor in Wolong National Nature Reserve. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 36, 588-592. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 姚刚, 李艳红, 张晋东, 黎大勇, 杨志松, 胡杰, 施小刚 ( 2017) 卧龙国家级自然保护区水鹿种群密度及分布调查. 四川动物, 36, 588-592.] | |
| [52] | Yen SC, Lin CY, Hew SW, Yang SY, Yeh CF, Weng GJ ( 2015) Characterization of debarking behavior by sambar deer (Rusa unicolor) in Taiwan. Mammal Study, 40, 167-179. |
| [53] | Yuan XC, Wang BL ( 1983) The sambar deer (Cervus unicolor) in Hainan Island. Chinese Wildlife, ( 6), 37-39. (in Chinese) |
| [ 袁喜才, 王宝琳 ( 1983) 海南岛水鹿. 野生动物, ( 6), 37-39.] | |
| [54] |
Zhang Y, Skaar I, Sulyok M, Liu X, Rao M, Taylor JW ( 2016) The microbiome and metabolites in fermented Pu-erh tea as revealed by high-throughput sequencing and quantitative multiplex metabolite analysis. PLoS ONE, 11, e0157847.
DOI URL PMID |
| [55] | Zhang YX, Liu Y, Liu PW, Fu CK, Lu LL, Wei JH ( 2020) Screening and identification on sequences of original plants of curcumae rhizoma. Guihaia, doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201912027. |
| [ 张玉秀, 刘杨, 刘培卫, 符传坤, 卢丽兰, 魏建和 ( 2020) 莪术基原植物DNA条形码序列的筛选与鉴定. 广西植物, doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201912027.] | |
| [56] | Zheng RQ, Bao YX ( 2004) Study methods and procedures for ungulate food habits. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24, 1532-1539. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郑荣泉, 鲍毅新 ( 2004) 有蹄类食性研究方法及研究进展. 生态学报, 24, 1532-1539.] |
| [1] | 龚翠凤, 韦伟, 罗概, 韩一敏, 吴鹏程, 何梦楠, 闵清悦, 付强, 陈鹏. 大熊猫国家公园崇州片区有蹄类动物空间分布及共存关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24260-. |
| [2] | 贺加贝, 柯可, 孙海明, 胡丽萍, 赵晓伟, 王文豪, 赵强. 基于DNA宏条形码技术分析香螺食性[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24403-. |
| [3] | 卢佳玉, 石小亿, 多立安, 王天明, 李治霖. 基于红外相机技术的天津城市地栖哺乳动物昼夜活动节律评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23369-. |
| [4] | 李佳琪, 冯一迪, 王蕾, 潘盆艳, 刘潇如, 李雪阳, 王怡涵, 王放. 上海城市环境中貉的食性分析及家域范围内的栖息地选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24131-. |
| [5] | 曲锐, 左振君, 王有鑫, 张良键, 吴志刚, 乔秀娟, 王忠. 基于元素组的生物地球化学生态位及其在不同生态系统中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23378-. |
| [6] | 吕晓波, 李东海, 杨小波, 张孟文. 红树林群落通过淹水时间及海水盐度的生态位分化实现物种共存[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23302-. |
| [7] | 杜聪聪, 冯学宇, 陈志林. 桥头堡效应中气候生态位差异的缩小促进了红火蚁的入侵[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24276-. |
| [8] | 赵榕江, 吴纪华, 何维明, 赵彩云, 周波, 李博, 杨强. 土壤生物多样性与外来植物入侵: 进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24243-. |
| [9] | 原雪姣, 张渊媛, 张衍亮, 胡璐祎, 桑卫国, 杨峥, 陈颀. 基于飞机草历史分布数据拟合的物种分布模型及其预测能力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24288-. |
| [10] | 谢将剑, 沈忱, 张飞宇, 肖治术. 融合音频及生态位信息的跨地域鸟类物种识别方法[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24259-. |
| [11] | 韩丽霞, 王永健, 刘宣. 外来物种入侵与本土物种分布区扩张的异同[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23396-. |
| [12] | 罗正明, 刘晋仙, 张变华, 周妍英, 郝爱华, 杨凯, 柴宝峰. 不同退化阶段亚高山草甸土壤原生生物群落多样性特征及驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23136-. |
| [13] | 刘志发, 王新财, 龚粤宁, 陈道剑, 张强. 基于红外相机监测的广东南岭国家级自然保护区鸟兽多样性及其垂直分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22689-. |
| [14] | 公欣桐, 陈飞, 高欢欢, 习新强. 两种果蝇成虫与幼虫期的竞争及其对二者共存的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22603-. |
| [15] | 湛振杰, 张超, 陈敏豪, 王嘉栋, 富爱华, 范雨薇, 栾晓峰. 基于DNA宏条形码技术的大兴安岭北部欧亚水獭冬季食性分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22586-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()