



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (10): 1202-1212. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020009 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020009
所属专题: 生物入侵
白敬沛1, 黄耿1,*( ), 蒋长军1, 章伟成1, 王齐东2, 姚伦广1,*(
), 蒋长军1, 章伟成1, 王齐东2, 姚伦广1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-01-08
接受日期:2020-05-19
出版日期:2020-10-20
发布日期:2020-10-20
通讯作者:
黄耿,姚伦广
作者简介:E-mail: wangyoukl@126.com;基金资助:
Jingpei Bai1, Geng Huang1,*( ), Changjun Jiang1, Weicheng Zhang1, Qidong Wang2, Lunguang Yao1,*(
), Changjun Jiang1, Weicheng Zhang1, Qidong Wang2, Lunguang Yao1,*( )
)
Received:2020-01-08
Accepted:2020-05-19
Online:2020-10-20
Published:2020-10-20
Contact:
Geng Huang,Lunguang Yao
摘要:
为了解丹江口水库鱼类群落现状及历史变化, 作者于2018-2019年采用多网目复合刺网采样和渔民渔获物调查的方式对丹江口水库进行了鱼类群落调查。本次调查共采集鱼类33种, 隶属5目11科29属, 以鲤科鱼类为主, 占总数的63.6%。基于多网目复合刺网采样的鱼类群落多样性指数和单位努力捕捞量(catch per unit effort, CPUE, g·day -1·m -2)在各采样点间具有一定的差异。目前丹江口水库以定居性、喜静缓流、杂食性和肉食性鱼类为主。与20世纪50年代和80年代的历史资料相比, 丹江口水库鱼类物种丰富度先升高后下降; 而生态类型则呈现杂食性鱼类、喜流水性鱼类和洄游性鱼类比例持续下降的趋势。2018-2019年丹江口水库鱼类组成与20世纪80年代的相似性指数为0.35 (中等不相似), 与20世纪50年代的相似性指数为0.29 (中等不相似)。调查结果表明半个世纪以来丹江口水库鱼类群落结构发生了较大变化, 目前趋于小型化和简单化。这些变化可能是由大坝建设、渔业放养、不合理捕捞、外来鱼类引入等人类活动所致。
白敬沛, 黄耿, 蒋长军, 章伟成, 王齐东, 姚伦广 (2020) 丹江口水库鱼类群落特征及其历史变化. 生物多样性, 28, 1202-1212. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020009.
Jingpei Bai, Geng Huang, Changjun Jiang, Weicheng Zhang, Qidong Wang, Lunguang Yao (2020) Characteristics and historical changes of the fish assemblage in the Danjiangkou Reservoir. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1202-1212. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020009.
| 地点 Sampling site | 马蹬镇 Madeng Town | 丹江口市 Danjiangkou City | 凉水河镇 Liangshuihe Town | 渠首 Headwork | 均县镇 Junxian Town |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 物种丰富度 Species richness (D) | 7.000 ± 0.892a | 8.000± 1.033a | 8.000 ± 0.813a | 10.000 ± 0.433a | 12.000 ± 1.031b |
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H') | 1.374 ± 0.173a | 1.408 ± 0.169a | 1.424 ± 0.182a | 1.436 ± 0.076a | 1.574 ± 0.226a |
| Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index (J) | 0.769 ± 0.067a | 0.636 ± 0.083a | 0.641 ± 0.069a | 0.614 ± 0.037a | 0.644 ± 0.070a |
| 单位努力捕捞量 CPUE (g·day-1·m-2) | 2.568 ± 0.977a | 3.735 ± 1.108ab | 3.846 ± 1.112ab | 4.298 ± 1.096ab | 4.841 ± 0.586b |
表1 基于多网目复合刺网采样的2018-2019年丹江口水库鱼类群落多样性指数及单位努力捕捞量的空间差异(不同小写字母表示各地点间具有显著性差异)
Table 1 Spatial variations of biodiversity indexes and catch per unit effort (CPUE) of fish in the Danjiangkou Reservoir in 2018-2019 based on multi-mesh gillnet samplings. Different lowercase letters indicate the significant differences among sites.
| 地点 Sampling site | 马蹬镇 Madeng Town | 丹江口市 Danjiangkou City | 凉水河镇 Liangshuihe Town | 渠首 Headwork | 均县镇 Junxian Town |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 物种丰富度 Species richness (D) | 7.000 ± 0.892a | 8.000± 1.033a | 8.000 ± 0.813a | 10.000 ± 0.433a | 12.000 ± 1.031b |
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H') | 1.374 ± 0.173a | 1.408 ± 0.169a | 1.424 ± 0.182a | 1.436 ± 0.076a | 1.574 ± 0.226a |
| Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index (J) | 0.769 ± 0.067a | 0.636 ± 0.083a | 0.641 ± 0.069a | 0.614 ± 0.037a | 0.644 ± 0.070a |
| 单位努力捕捞量 CPUE (g·day-1·m-2) | 2.568 ± 0.977a | 3.735 ± 1.108ab | 3.846 ± 1.112ab | 4.298 ± 1.096ab | 4.841 ± 0.586b |
| 科 Family | 种类数 Species number | 三个时期共有种数 | 相似性指数 Jaccard similarity index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950s | 1980s | 2018-2019 | Number of mutual species | 1950s vs. 1980s | 1950s vs. 2018-2019 | 1980s vs. 2018-2019 | |
| 鲤科 Cyprinidae | 28 | 42 | 21 | 12 | 0.46 | 0.36 | 0.43 |
| 鲟科 Acipenseridae | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 银鱼科 Salangidae | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 鳀科 Engraulidae | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 鳗鲡科 Anguillidae | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 鳅科 Cobitidae | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.33 |
| 平鳍鳅科 Balitoridae | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 鮰科 Ictaluridae | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 鲿科 Bagridae | 3 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 0.33 | 0.20 | 0.33 |
| 鲇科 Siluridae | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| 鮡科 Sisoridae | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 合鳃鱼科 Synbranchidae | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 刺鳅科 Mastacembelidae | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 鮨科 Serranidae | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| 虾虎鱼科 Gobiidae | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| 鳢科 Channidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| 塘鳢科 Eleotridae | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 太阳鱼科 Centrachidae | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 鱵科 Hemiramphidae | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 合计 Total | 43 | 67 | 33 | 18 | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.35 |
表2 丹江口水库不同时期鱼类组成相似性指数
Table 2 Variations of fish similarity index in different time periods in the Danjiangkou Reservoir
| 科 Family | 种类数 Species number | 三个时期共有种数 | 相似性指数 Jaccard similarity index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950s | 1980s | 2018-2019 | Number of mutual species | 1950s vs. 1980s | 1950s vs. 2018-2019 | 1980s vs. 2018-2019 | |
| 鲤科 Cyprinidae | 28 | 42 | 21 | 12 | 0.46 | 0.36 | 0.43 |
| 鲟科 Acipenseridae | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 银鱼科 Salangidae | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 鳀科 Engraulidae | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 鳗鲡科 Anguillidae | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 鳅科 Cobitidae | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.33 |
| 平鳍鳅科 Balitoridae | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 鮰科 Ictaluridae | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 鲿科 Bagridae | 3 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 0.33 | 0.20 | 0.33 |
| 鲇科 Siluridae | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| 鮡科 Sisoridae | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 合鳃鱼科 Synbranchidae | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 刺鳅科 Mastacembelidae | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 鮨科 Serranidae | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| 虾虎鱼科 Gobiidae | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| 鳢科 Channidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| 塘鳢科 Eleotridae | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 太阳鱼科 Centrachidae | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 鱵科 Hemiramphidae | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 合计 Total | 43 | 67 | 33 | 18 | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.35 |
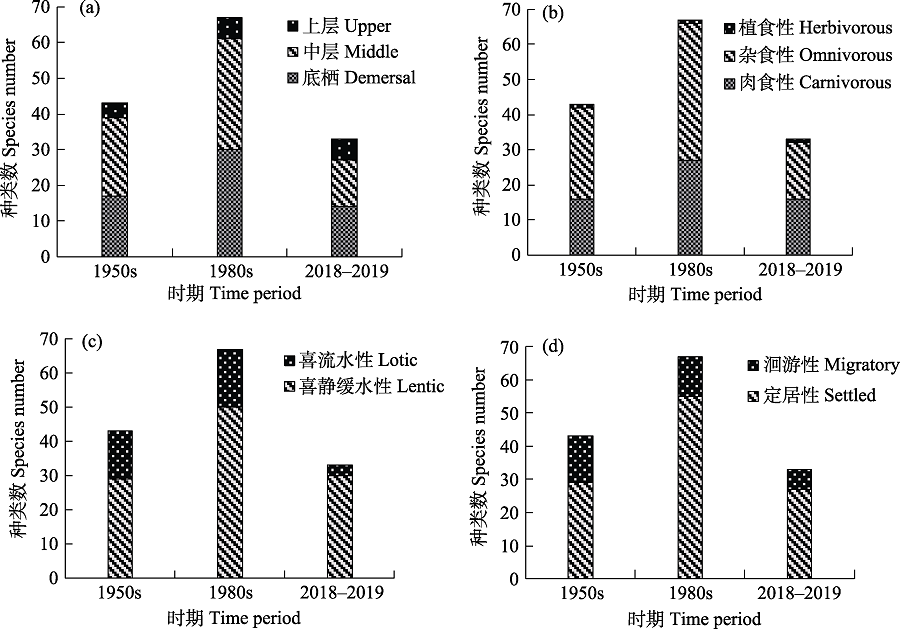
图3 丹江口水库不同生态类型鱼类组成比例的时间变化
Fig. 3 Temporal variations of fish species proportional composition for different ecological types in the Danjiangkou Reservoir
| [1] | Bao HF ( 2013) Influence Analysis on Biological Diversity of Danjiangkou Reservoir at the Middle Route South-to-North Water Transfer Project. PhD dissertation, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 包洪福 ( 2013) 南水北调中线工程对丹江口库区生物多样性的影响分析. 博士学位论文, 东北林业大学, 哈尔滨.] | |
| [2] | Bolotskiy EB, Wu XW, Bai GD, Ge MS, Wang QL, Wang SD, Chen SZ ( 1959) Hydrobiological survey of the region of the projected dam-reservoir of Danjiangkou, with propositions for fisheries management. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, ( 1), 33-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ E.B.波鲁茨基, 伍献文, 白国栋, 戈敏生, 王乾麟, 王士达, 陈受忠 ( 1959) 丹江口水库库区水生生物调查和渔业利用的意见. 水生生物学报, ( 1), 33-56.] | |
| [3] | Brandt SB ( 1993) The effect of thermal fronts on fish growth: A bioenergetics evaluation of food and temperature. Estuaries, 16, 142-159. |
| [4] |
Bruno JF, O’Connor MI ( 2005) Cascading effects of predator diversity and omnivory in a marine food web. Ecology Letters, 8, 1048-1056.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Chang JB, Chen YB, Gao Y, Zhu B, Qiao Y ( 2008) The influence of water conservancy and hydropower project on fish and countermeasures. In: Proceedings of the 2008 Annual Conference of Chinese Hydraulic Engineering Society (Vol. 1), pp. 685-696. China Water & Power Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 常剑波, 陈永柏, 高勇, 朱滨, 乔晔 ( 2008) 水利水电工程对鱼类的影响及减缓对策. 见: 中国水利学会2008年学术年会论文集(上册), 685-696页. 中国水利水电出版社, 北京.] | |
| [6] | Chen F, Zhao XF, Zhao JY, Li M ( 2012) Investigation of fish resources in the Oujiang River and its protection strategy. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 21, 934-941. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈锋, 赵先富, 赵进勇, 李敏 ( 2012) 瓯江鱼类资源调查及保护对策. 长江流域资源与环境, 21, 934-941.] | |
| [7] | Chen YY ( 1998) Fauna Sinica · Osteichthyes · Cypriniformes. II. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 陈宜瑜 ( 1998) 中国动物志 · 硬骨鱼纲 · 鲤形目(中卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [8] | Chu XL, Zheng BS, Dai DY ( 1999) Fauna Sinica · Osteichthyes · Siluriformes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 褚新洛, 郑葆珊, 戴定远 ( 1999) 中国动物志 · 硬骨鱼纲 · 鲇形目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [9] | Costedoat C, Pech N, Salducci MD, Chappaz R, Gilles A ( 2005) Evolution of mosaic hybrid zone between invasive and endemic species of Cyprinidae through space and time. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 85, 135-155. |
| [10] | Drake M, Valley R ( 2005) Validation and application of a fish-based index of biotic integrity for small central Minnesota lakes. North American Journal of Fisheries Management, 25, 1095-1111. |
| [11] |
Dugan PJ, Barlow C, Agostinho AA, Baran E, Cada GF, Chen DQ, Cowx GI, Ferguson JW, Jutagate TT, Marmulla G, Nestler J, Petrere M, Welcomme RL, Winemiller KO ( 2010) Fish migration, dams, and loss of ecosystem services in the Mekong basin. Ambio, 39, 344-348.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] | Fan ZH, Ba JW, Duan XB ( 2012) Studies on fish resources and species diversity in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River from Yichang to Chenglingji section. Freshwater Fisheries, 42, 20-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 范振华, 巴家文, 段辛斌 ( 2012) 长江宜昌至城陵矶江段鱼类资源现状及物种多样性研究. 淡水渔业, 42, 20-25.] | |
| [13] | Fish Laboratory of Institute of Hydrobiology in Hubei Province( 1976) Yangtze River Fish. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 湖北省水生生物研究所鱼类研究室( 1976) 长江鱼类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [14] | Fu JJ, Wang ML, Wang BH, Xie DX ( 2015) Operational management of Danjiangkou hydro-complex and its heightening works. Yangtze River, 46(6), 14-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 付建军, 王梦凉, 王保红, 谢丹雄 ( 2015) 丹江口大坝加高施工和枢纽运行管理. 人民长江, 46(6), 14-16.] | |
| [15] |
Gozlan RE, St-Hilaire S, Feist SW, Martin P, Kent ML ( 2005) Biodiversity: Disease threat to European fish. Nature, 435, 1046.
URL PMID |
| [16] | Jaccard P ( 1912) The distribution of flora in the alpine zone. New Phytologist, 11, 37-50. |
| [17] | Jia YT, Chen YF, Tao J, He DK ( 2013) Current status and historical changes in fish assemblages of the Zengjiang River. Resources Science, 35, 1490-1498. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 贾银涛, 陈毅峰, 陶捐, 何德奎 ( 2013) 增江鱼类群落特征及其历史变化. 资源科学, 35, 1490-1498.] | |
| [18] | Johnson JA, Kelsch SW ( 1998) Effects of evolutionary thermal environment on temperature-preference relationships in fishes. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 53, 447-458. |
| [19] | Kitchell JF, Schindler DE, Ogutu-Ohwayo R, Reinthal PN ( 1997) The Nile perch in Lake Victoria: Interactions between predation and fisheries. Ecological Applications, 7, 653-664. |
| [20] | Krebs CJ ( 1999) Ecological Methodology. Harper Collins, New York. |
| [21] | Liao CS, Xiong MT, Yin Z, Liu JS ( 2018) Studies on the fishery fishing and community structure of fish in the Danjiangkou Reservoir. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 46, 87-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 廖传松, 熊满堂, 殷战, 刘家寿 ( 2018) 丹江口水库渔业捕捞及鱼类群落结构研究. 安徽农业科学, 46, 87-90.] | |
| [22] | Liu QG ( 2005) Aquatic Environmental Protection Oriented Fishery in Lake Qiandaohu and Its Influences on Lake Ecosystem. PhD dissertation, East China Normal University, Shanghai. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘其根 ( 2005) 千岛湖保水渔业及其对湖泊生态系统的影响. 博士学位论文, 华东师范大学, 上海.] | |
| [23] | Ludwig JA, Reynolds JF ( 1988) Statistical Ecology: A Primer on Methods and Computing. John Wiley & Sons, New York. |
| [24] | Lun F, Li Z, Zhou BX, Wang CX, Li YY ( 2016) Investigation of fish resources in Danjiangkou Reservoir in Henan Province. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 45, 150-155. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 伦峰, 李峥, 周本翔, 王晨溪, 李玉英 ( 2016) 丹江口水库(河南辖区)鱼类资源调查. 河南农业科学, 45, 150-155.] | |
| [25] | Lyons J, Gutiérrez-Hernández A, Díaz-Pardo E, Soto-Galera E, Medina-Nava M, Raúl PL ( 2000) Development of a preliminary index of biotic integrity (IBI) based on fish assemblages to assess ecosystem condition in the lakes of central Mexico. Hydrobiologia, 418, 57-72. |
| [26] |
Magurran AE ( 1989) Ecological diversity and its measurement. Biometrics, 46, 81-99.
URL PMID |
| [27] | Pan YD, Guo SJ, Li YY, Yin W, Qi PC, Shi JW, Hu LQ, Li B, Bi SG, Zhu JY ( 2018) Effects of water level increase on phytoplankton assemblages in a drinking water reservoir. Water, 10, 256-274. |
| [28] | Petchey OL, Downing AL, Mittelbach GG, Persson L, Steiner CF, Warren PH ( 2004) Species loss and the structure and functioning of multitrophic aquatic systems. Oikos, 104, 467-478. |
| [29] | Pielou EC ( 1975) Ecological Diversity. John Wiley & Sons, New York. |
| [30] | Pinkas L, Oliphant MS, Iverson LK ( 1970) Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna, and bonito in California waters. Scripps Institution of Oceanography Library. Fish Bulletin, 152, 1-105. |
| [31] | Roberts TR ( 2001) On the river of no returns: Thailand’s Pak Mun Dam and its fish ladder. Natural History Bulletin of the Siam Society, 492, 189-230. |
| [32] | Ru HJ, Wang HJ, Zhao WH, Shen YQ, Wang Y, Zhang XK ( 2010) Fishes in the mainstream of the Yellow River: Assemblage characteristics and historical changes. Biodiversity Science, 18, 179-186. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 茹辉军, 王海军, 赵伟华, 沈亚强, 王勇, 张晓可 ( 2010) 黄河干流鱼类群落特征及其历史变化. 生物多样性, 18, 179-186.] | |
| [33] | Stanford JA, Ward JV, Zimmermann HJ, Cline LD ( 1986) Fish of the Colorado River system. In: The Ecology of River Systems (eds Davies BR, Walker KF), pp. 385-402. Dr W. Junk Publishers, Dordrecht. |
| [34] | Vehanen T, Sutela T, Korhonen H ( 2010) Environmental assessment of boreal rivers using fish data—A contribution to the Water Framework Directive. Fisheries Management & Ecology, 17, 165-175. |
| [35] | Wolter C ( 2007) Temperature influence on the fish assemblage structure in a large lowland river, the lower Oder River, Germany. Ecology of Freshwater Fish, 16, 492-503. |
| [36] | Xing DY, Yang GR ( 1992) The diet of six fierce fish in Danjiangkou Reservoir. Fishery of Water Conservancy, ( 3), 10-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 邢东耀, 杨干荣 ( 1992) 丹江口水库六种凶猛鱼的食性. 水利渔业, ( 3), 10-14.] | |
| [37] | Xu SN, Guo JZ, Chen ZZ, Zhang K, Xu YW, Cai YC, Li CH ( 2019) Tempo-spatial distribution characteristics of fish resources in Jiaozhou Bay. Journal of Fisheries of China, 43, 1615-1625. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐姗楠, 郭建忠, 陈作志, 张魁, 许友伟, 蔡研聪, 李纯厚 ( 2019) 胶州湾鱼类资源量的时空分布特征. 水产学报, 43, 1615-1625.] | |
| [38] | Yang ZW, Li ZJ, Liu JS, Zhang TL, Ye SW, Zhang H ( 2012) A comparative study on reproductive characteristics of different spawning stocks of the icefish (Neosalanx taihuensis) in the Danjiangkou Reservoir. Freshwater Fisheries, 42, 58-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨战伟, 李钟杰, 刘家寿, 张堂林, 叶少文, 张华 ( 2012) 丹江口水库太湖新银鱼不同繁殖群体的繁殖特征比较. 淡水渔业, 42, 58-62.] | |
| [39] | Yin MC ( 1995) Fish Ecology. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 殷名称 ( 1995) 鱼类生态学. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [40] | Yonekura R, Kohmatsu Y, Yuma M ( 2007) Difference in the predation impact enhanced by morphological divergence between introduced fish populations. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 91, 601-610. |
| [41] | Yu ZT ( 1982) Investigation of fish resources in the middle and lower reaches of the Hanjiang River and the impact assessment of the Danjiangkou water conservancy project on fish resources in the Hanjiang River. Fishery of Water Conservancy, ( 1), 19-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 余志堂 ( 1982) 汉江中下游鱼类资源调查以及丹江口水利枢纽对汉江鱼类资源影响的评价. 水库渔业, ( 1), 19-27.] | |
| [42] | Yuan FX, Huang DM ( 1989) Analysis of fish resources and composition in the Danjiangkou Reservoir. Fishery of Water Conservancy, ( 2), 35-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 袁凤霞, 黄道明 ( 1989) 丹江口水库鱼类资源及组成分析. 水利渔业, ( 2), 35-36.] | |
| [43] | Yuan J, Xia YG, Li ZJ, Yin Z, Liu JS ( 2016) Changes in fisheries resources in the Hanjiang River and Danjiangkou Reservoir, China. American Fisheries Society Symposium, 84, 179-191. |
| [44] | Yue PQ ( 2000) Fauna Sinica · Osteichthyes · Cypriniformes. III. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 乐佩琦 ( 2000) 中国动物志 · 硬骨鱼纲 · 鲤形目(下卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [45] | Zhang GH, Cao WX ( 1997) Effects of fish stocking on lake ecosystems in China. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 21, 271-280. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张国华, 曹文宣 ( 1997) 湖泊放养渔业对我国湖泊生态系统的影响. 水生生物学报, 21, 271-280.] | |
| [46] | Zhang JB ( 1999) Analysis of clustering on growth of predatory fish guild in the Danjiangkou Reservoir. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 23, 689-695. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张家波 ( 1999) 丹江口水库凶猛鱼集团生长特性组型的聚类分析. 水生生物学报, 23, 689-695.] | |
| [47] | Zhang QF, Su RH, Jiang MX, Li SY ( 2007) The South-to-north Water Transfer Project and its ecological security: The priorities. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 16, 217-221. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张全发, 苏荣辉, 江明喜, 李思悦 ( 2007) 南水北调工程及其生态安全: 优先研究领域. 长江流域资源与环境, 16, 217-221.] | |
| [48] | Zhu SQ ( 1995) Synopsis of Freshwater Fishes of China. Jiangsu Science and Technology Publishing House, Nanjing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 朱松泉 ( 1995) 中国淡水鱼类检索表. 江苏科技出版社, 南京.] |
| [1] | 罗敏, 杨永川, 靳程, 周礼华, 龙宇潇. 城市森林兽类组成特征及人类活动的影响——以重庆中心城区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24402-. |
| [2] | 钟超, 廖亚琴, 刘伟杰, 隋昊志, 陈清华. 广东沿海海草床的现状、面临的威胁与保护建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23201-. |
| [3] | 黄骏涵, 余梵冬, 王裕祥, 黄哲, 张铭斯, 房苗, 舒璐, 徐猛, 韦慧, 汪学杰, 顾党恩, 罗思. 花地河中下游外来鱼类入侵现状及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24249-. |
| [4] | 董庆栋, 陈超男, 李艳红, 赵体侠, 孙梓欣, 张哲, 朱连奇. 基于NPP和人类扰动指数评估河南伏牛山地区国家级自然保护区群保护成效与溢出/泄漏效应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22503-. |
| [5] | 江艺欣, 时莹莹, 高朔, 王苏盆. 人为噪音、夜间人造光和路杀对两栖动物的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22427-. |
| [6] | 沈梅, 郭宁宁, 罗遵兰, 郭晓晨, 孙光, 肖能文. 基于eDNA metabarcoding探究北京市主要河流鱼类分布及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22240-. |
| [7] | 赵仁生, 许诗嘉, 宋鹏飞, 周翔, 张亚洲, 袁燕. 青藏高原药用植物分布格局及保护优先区[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21385-. |
| [8] | 傅声雷, 刘满强, 张卫信, 邵元虎. 土壤动物多样性的地理分布及其生态功能研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22435-. |
| [9] | 刘璐, 迟瑶, 吴朝宁, 钱天陆, 王结臣. 陆栖哺乳动物的地理隔离研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(8): 1134-1145. |
| [10] | 李学友, 胡文强, 普昌哲, 李权, 于秋鹏, 胡哲畅, William V. Bleisch, 蒋学龙. 西南纵向岭谷区兽类及雉类红外相机监测平台:方案、进展与前景[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(9): 1090-1096. |
| [11] | 刘安榕, 杨腾, 徐炜, 上官子健, 王金洲, 刘慧颖, 时玉, 褚海燕, 贺金生. 青藏高原高寒草地地下生物多样性: 进展、问题与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(9): 972-987. |
| [12] | 许玥, 李鹏, 刘晔, 张婉君, 秦思雨, 沈泽昊. 怒江河谷入侵植物与乡土植物丰富度的分布格局与影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(4): 389-398. |
| [13] | 李渊, 张静, 张然, 宋普庆, 钟指挥, 王燕平, 林龙山. 南沙群岛西南部和北部湾口海域鱼类物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(2): 166-174. |
| [14] | 陈永俊, 张静, 宋普庆, 张然, 李渊, 钟指挥, 林龙山. 台湾海峡鱼类组成及其生态区系[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(4): 525-531. |
| [15] | 林杰, 徐文轩, 杨维康, 夏参军, 刘伟. 卡拉麦里山有蹄类自然保护区蒙古野驴生境适宜性评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2012, 20(4): 411-419. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()