



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (2): 128-134. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019276 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019276
王鑫厅1,*( ), 柴静1, 姜超2,*(
), 柴静1, 姜超2,*( ), 邰阳3, 迟延艳4, 张维华1,3, 刘芳1, 李素英1
), 邰阳3, 迟延艳4, 张维华1,3, 刘芳1, 李素英1
收稿日期:2019-09-04
接受日期:2019-11-11
出版日期:2020-02-20
发布日期:2020-04-02
通讯作者:
王鑫厅,姜超
基金资助:
Xinting Wang1,*( ), Jing Chai1, Chao Jiang2,*(
), Jing Chai1, Chao Jiang2,*( ), Yang Tai3, Yanyan Chi4, Weihua Zhang1,3, Fang Liu1, Suying Li1
), Yang Tai3, Yanyan Chi4, Weihua Zhang1,3, Fang Liu1, Suying Li1
Received:2019-09-04
Accepted:2019-11-11
Online:2020-02-20
Published:2020-04-02
Contact:
Xinting Wang, Chao Jiang
摘要:
种群空间格局是生态学研究的基本问题之一。典型草原带由于过度放牧退化严重, 原生群落罕见, 探讨原生群落的种群空间格局具有重要生态学意义。大针茅(Stipa grandis)草原是典型草原区广泛分布的主要群落类型, 1979年围封的大针茅样地, 是目前保存完整的大针茅草原原生群落。本文选择大针茅草原原生群落和长期过度放牧群落, 应用O-Ring函数结合不同零假设模型分析了大针茅种群的空间格局。结果表明: 在原生群落中大针茅种群在小尺度范围内呈均匀分布, 而在长期过度放牧群落中则表现为聚集分布。这说明在大针茅草原原生群落中竞争是主要的相互作用, 而在长期过度放牧群落中正相互作用居主导, 验证了胁迫梯度假说; 同时证明长期过度放牧改变了种群空间格局。
王鑫厅, 柴静, 姜超, 邰阳, 迟延艳, 张维华, 刘芳, 李素英 (2020) 典型草原大针茅种群空间格局及对长期过度放牧的响应. 生物多样性, 28, 128-134. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019276.
Xinting Wang, Jing Chai, Chao Jiang, Yang Tai, Yanyan Chi, Weihua Zhang, Fang Liu, Suying Li (2020) Population spatial pattern of Stipa grandis and its response to long-term overgrazing. Biodiversity Science, 28, 128-134. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019276.
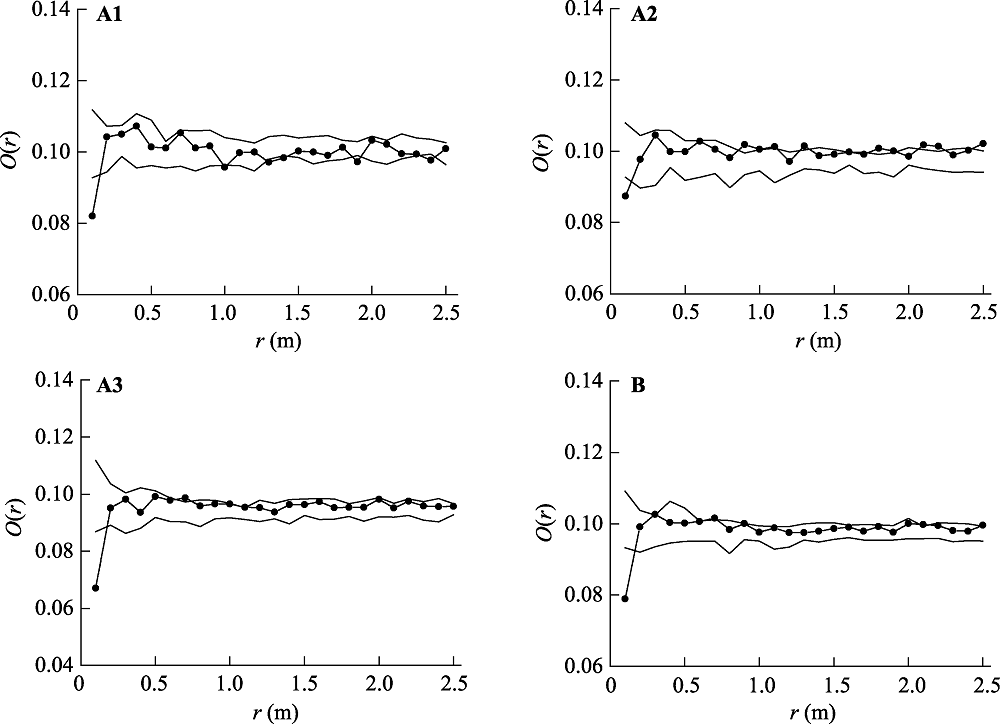
图1 原生群落中基于均质泊松零模型的大针茅种群点格局分析。-●- 实测数据; -- 99%置信区间。(A)每个重复的点格局分析, 下角标1, 2和3代表不同重复; (B)整合3个重复取样的点格局分析。
Fig. 1 Spatial pattern analysis of Stipa grandis in the primary community based on the homogeneous Poisson null model. -●- observational data; -- the confidence limits (99%). (A) Point pattern analysis in each replicate, subscripts 1, 2 and 3 refer to replicates; (B) Point pattern analysis by integrating data of three replicates.
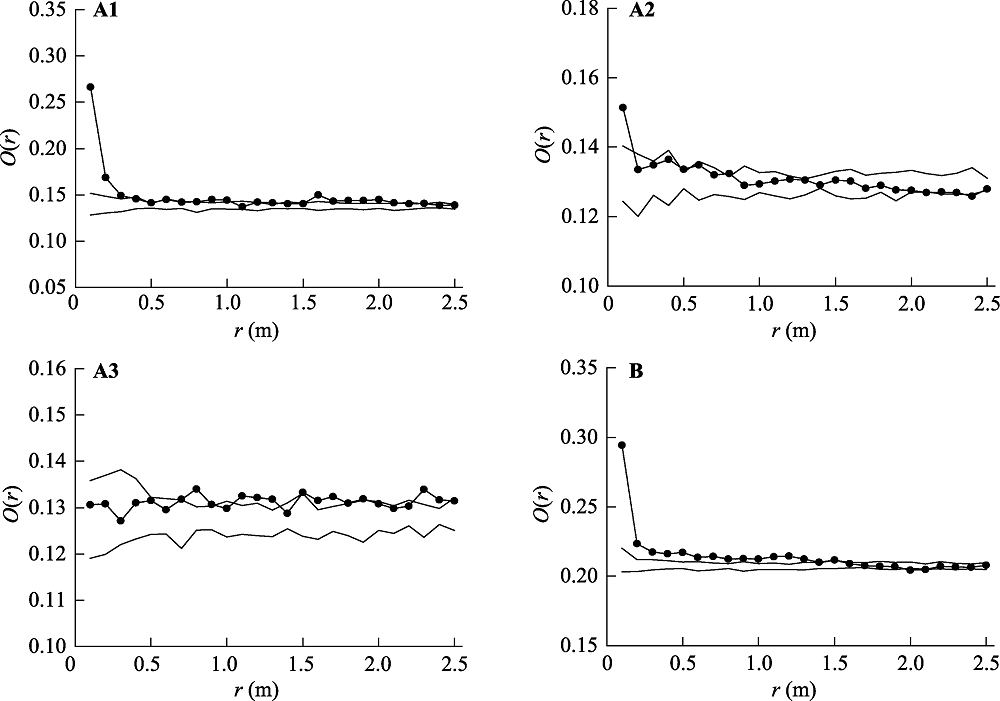
图2 放牧群落中基于均质泊松零模型的大针茅种群点格局分析。-●- 实测数据; -- 99%置信区间。(A)每个重复的点格局分析, 下角标1, 2和3代表不同重复; (B)整合3个重复取样的点格局分析。
Fig. 2 Spatial pattern analysis of Stipa grandis in the grazed community based on the homogeneous Poisson null model. -●- observational data; -- the confidence limits (99%). (A) Point pattern analysis in each replicate, subscripts 1, 2 and 3 refer to replicates; (B) Point pattern analysis by integrating data of three replicates.
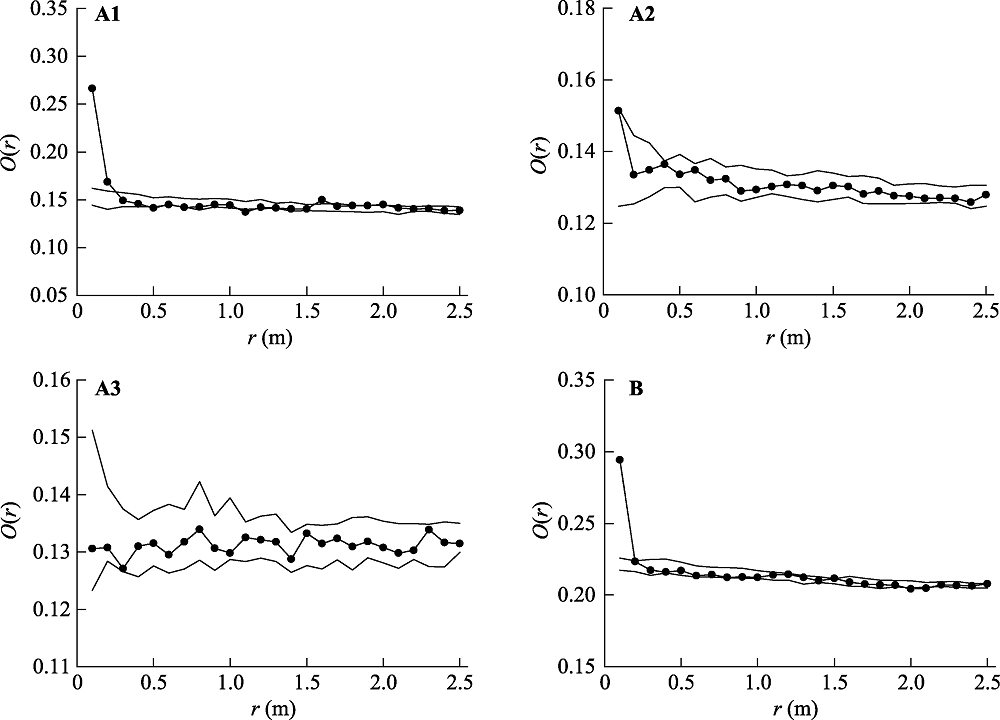
图3 原生群落中基于异质泊松零模型的大针茅种群点格局分析。-●- 实测数据; -- 99%置信区间。(A)每个重复的点格局分析, 下角标1, 2和3代表不同重复; (B)整合3个重复取样的点格局分析。
Fig. 3 Spatial pattern analysis of Stipa grandis in the primary community based on the heterogeneous Poisson null model. -●- observational data; -- the confidence limits (99%). (A) Point pattern analysis in each replicate, subscripts 1, 2 and 3 refer to replicates; (B) Point pattern analysis by integrating data of three replicates.
| [1] |
Bai Y, Han X, Wu J, Chen Z, Li L (2004) Ecosystem stability and compensatory effects in the Inner Mongolia grassland. Nature, 431, 181-184.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] |
Bertness MD, Callaway RM (1994) Positive interactions in communities. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 9, 191-193.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] | Callaway RM (2007) Positive Interactions and Interdependence in Plant Communities. Springer, Dordrecht. |
| [4] | Callaway RM, Walker LR (1997) Competition and facilitation: A synthetic approach to interactions in plant communities. Ecology, 78, 1958-1965. |
| [5] |
Chave J, Muller-Landau HC, Levin SA (2002) Comparing classical community models: Theoretical consequences for patterns of diversity. The American Naturalist, 159, 1-23.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] | Diggle PJ (2013) Statistical Analysis of Spatial and Spatio-Temporal Point Patterns, 3rd edn. CRC Press Boca Raton, Florida. |
| [7] | Grime JP (1973) Competitive exclusion in herbaceous vegetation. Nature, 242, 344-347. |
| [8] | Jia X, Dai X, Shen Z, Zhang JY, Wang GX (2011) Facilitation can maintain clustered spatial pattern of plant populations during density dependent mortality: Insights from a zone-of-influence model. Oikos, 120, 472-480. |
| [9] | Jiang Y, Bi XL, Huang JH, Bai YF (2010) Patterns and drivers of vegetation degradation in Xilin River Basin, Inner Mongolia, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 34, 1132-1141. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 姜晔, 毕晓丽, 黄建辉, 白永飞 (2010) 内蒙古锡林河流域植被退化的格局及驱动力分析, 植物生态学报, 34, 1132-1141.] | |
| [10] |
Shen GC, Yu MJ, Hu XS, Mi XC, Ren HB, Sun IF, Ma KP (2009) Species‒area relationships explained by the joint effects of dispersal limitation and habitat heterogeneity. Ecology, 90, 3033-3041.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] | Stoll P, Bergius E (2005) Pattern and process: Competition causes regular spacing of individuals within plant populations. Journal of Ecology, 93, 395-403. |
| [12] | Tilman D (1982) Resource Competition and Community Structure. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [13] | Ulrich W, Jabot F, Gotelli NJ (2017) Competitive interactions change the pattern of species co-occurrences under neutral dispersal. Oikos, 126, 91-100. |
| [14] | Velázquez E, Martínez I, Getzin S, Moloney KA, Wiegand T (2016) An evaluation of the state of spatial point pattern analysis in ecology. Ecography, 39, 1042-1055. |
| [15] | Wang W, Liang CZ, Liu ZL, Hao DY (2000a) Analysis of the plant individual behaviour during the degradation and restoring succession in steppe community. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 24, 268-274. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王炜, 梁存柱, 刘钟龄, 郝敦元 (2000a) 草原群落退化与恢复演替中的植物个体行为分析. 植物生态学报, 24, 268-274.] | |
| [16] | Wang W, Liang CZ, Liu ZL, Hao DY (2000b) Mechanism of degradation succession in Leymus chinensis and Stipa grandis steppe community. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 24, 468-472. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王炜, 梁存柱, 刘钟龄, 郝敦元 (2000b) 羊草+大针茅草原群落退化演替机理的研究. 植物生态学报, 24, 468-472.] | |
| [17] | Wang W, Liu ZL, Hao DY, Liang CZ (1996a) Research on the restoring succession of the degenerated grassland in Inner Mongolia. I. Basic characteristics and driving force for restoration of the degenerated grassland. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 20, 449-459. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王炜, 刘钟龄, 郝敦元, 梁存柱 (1996a) 内蒙古草原退化群落恢复演替的研究. I. 退化草原的基本特征与恢复演替动力. 植物生态学报, 20, 449-459.] | |
| [18] | Wang W, Liu ZL, Hao DY, Liang CZ (1996b) Research on the restoring succession of the degenerated grassland in Inner Mongolia. II. Analysis of the restoring processes. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 20, 460-471. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王炜, 刘钟龄, 郝敦元, 梁存柱 (1996b) 内蒙古草原退化群落恢复演替的研究. II. 恢复演替时间进程的分析. 植物生态学报, 20, 460-471.] | |
| [19] | Wang XT, Jiang C (2018) Spatial Point Pattern Analysis in Typical Steppe under Grazing Disturbance. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王鑫厅, 姜超 (2018) 典型草原放牧干扰下的点格局研究. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [20] | Wang XT, Wang W, Liu JH, Liang CZ, Zhang T (2006) A new method measuring plant population spatial patterns: Photography orientation. Atca Phytoecologica Sinica, 30, 571-575. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王鑫厅, 王炜, 刘佳慧, 梁存柱, 张韬 (2006) 植物种群空间分布格局测定的新方法: 摄影定位法. 植物生态学报, 30, 571-575.] | |
| [21] | Wang YF, Yong SP, Liu ZL (1985) Vegetation of Inner Mongolia. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王义凤, 雍世鹏, 刘钟龄 (1985) 内蒙古植被. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [22] | Wang XT, Zhang WH, Jiang C, Liang CZ (2017) Point pattern analysis under conditions of replicated sampling. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 41, 577-584. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王鑫厅, 张维华, 姜超, 梁存柱 (2017) 重复取样条件下的点格局分析. 植物生态学报, 41, 577-584.] | |
| [23] | Wiegand T, Moloney KA (2004) Rings, circles, and null-models for point pattern analysis in ecology. Oikos, 104, 209-229. |
| [24] | Wiegand T, Moloney KA (2014) A Handbook of Spatial Point Pattern Analysis in Ecology. Chapman and Hall / CRC Press, Boca Raton. |
| [25] | Yang C (1983) Studies on spatial pattern in Aneurolepidium chinensis steppe community. I. Use of contiguous grid guadrats. Journal of Inner Mongolia University (Natural Science Edition), 14, 245-254. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨持 (1983) 羊草草原群落水平格局的研究. I. 邻接格子样方的应用, 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 14, 245-254.] | |
| [26] | Yang C, Hao DY, Yang ZZ (1984) Studies on spatial pattern in Aneurolepidium chinensis steppe community. II. 2-dimension net function interpolation method. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 4, 237-247. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨持, 郝敦元, 杨在中 (1984). 羊草草原群落水平格局研究. I. 二维网函数插值法, 生态学报, 4, 237-247.] | |
| [27] | Yang HL, Rong YP, Mu Z (2016) Analysis of spatial heterogeneity of Leymus chinensis and Stipa grandis vegetation and soil nitrogen under different grazing intensities. Pratacultural Science, 10, 1035‒1043. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨合龙, 戎郁萍, 穆蓁 (2016) 不同放牧强度下羊草+大针茅草地植被与土壤氮素的空间异质性分析. 草业科学, 10, 1035‒1043.] |
| [1] | 易木荣, 卢萍, 彭勇, 汤勇, 许久恒, 尹浩萍, 张路杨, 翁晓东, 底明晓, 雷隽, 卢宸祺, 曹如君, 戴年华, 占德洋, 童媚, 楼智明, 丁永刚, 柴静, 车静. 北潦河金家水支流江西大鲵野外种群现状及栖息地评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24145-. |
| [2] | 王凤琼, 张心怡, 王鑫厅, 姜超, 侯亚丽, 包道日娜. 羊草草原原生群落羊草种群点格局分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24271-. |
| [3] | 邓洪, 钟占友, 寇春妮, 朱书礼, 李跃飞, 夏雨果, 武智, 李捷, 陈蔚涛. 基于线粒体全基因组揭示斑鳠的种群遗传结构与演化历史[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24241-. |
| [4] | 王明慧, 陈昭铨, 李帅锋, 黄小波, 郎学东, 胡子涵, 尚瑞广, 刘万德. 云南普洱季风常绿阔叶林不同种子扩散方式的优势种空间点格局分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23147-. |
| [5] | 陈嘉珈, 蒲真, 黄中鸿, 于凤琴, 张建军, 许东华, 徐俊泉, 尚鹏, 地里木拉提∙帕尔哈提, 李耀江, Jigme Tshering, 郭玉民. 全球黑颈鹤越冬种群分布与数量[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22400-. |
| [6] | 李苗, 要晨阳, 陈小勇. 环境RNA技术在水生生物监测中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23062-. |
| [7] | 李钊丞, 张燕雪丹. 基于物种濒危状况评价与种群增长的一种新评估方法在水生野生动物保护司法中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22319-. |
| [8] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [9] | 李珍珍, 杜梦甜, 朱原辛, 王大伟, 李治霖, 王天明. 基于红外相机的不可个体识别动物种群密度估算方法[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22422-. |
| [10] | 许再富. 对国家植物园体系建设“统筹原则”的一些见解[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(1): 22470-. |
| [11] | 杨剑焕, 李敬华, 杨浩炫, 欧梓键, 郑玺, Anthony J. Giordano, 陈辈乐. 基于红外相机数据评估华南地区豹猫的种群密度和活动节律[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 21357-. |
| [12] | 韦怡, 姜广顺. 虎豹及有蹄类猎物种群数量监测方法概述[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 21551-. |
| [13] | 夏凡, 杨婧, 李建, 史洋, 盖立新, 黄文华, 张经纬, 杨南, 高福利, 韩莹莹, 鲍伟东. 北京地区四个豹猫亚种群肠道菌群的组成[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22103-. |
| [14] | 初漠嫣, 梁书洁, 李沛芸, 贾丁, 阿卜杜赛麦提·买尔迪亚力, 李雪阳, 姜楠, 赵翔, 李发祥, 肖凌云, 吕植. 三江源国家级自然保护区内云塔村雪豹种群动态[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22157-. |
| [15] | 孙哲明, 刘亚恒, 彭秋桐, 徐芷妍, 杨予静, 欧文慧, 李中强. 湖北省极小种群野生植物在原生群落中的竞争地位及保护建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21517-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()