



生物多样性 ›› 2015, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (5): 610-618. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015051 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2015051
所属专题: 森林动态监测样地专题
金毅1, 陈建华2, 米湘成3, 任海保3, 马克平3, 于明坚1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2015-03-06
接受日期:2015-05-19
出版日期:2015-09-20
发布日期:2015-10-12
通讯作者:
于明坚
基金资助:
Yi Jin1, Jianhua Chen2, Xiangcheng Mi3, Haibao Ren3, Keping Ma3, Mingjian Yu1,*( )
)
Received:2015-03-06
Accepted:2015-05-19
Online:2015-09-20
Published:2015-10-12
Contact:
Yu Mingjian
摘要:
常绿阔叶林是我国亚热带地区的地带性植被, 其中最为典型而且分布最广泛的是中亚热带常绿阔叶林。为探讨2008年初我国南方发生的冰雪灾害对中亚热带常绿阔叶林的影响, 以浙江省古田山国家级自然保护区24 ha森林动态监测样地内的中亚热带常绿阔叶林为例, 研究了该森林在冰雪灾害前后(2005-2010年)的群落结构及物种组成动态。结果表明, 群落径级结构变化较小, 但群落整体补员不足且死亡率较高; 多个粒度上的群落动态显示出一致的衰退特征, 但不同生境间的群落动态存在差异; 物种多度和胸高截面积多呈减小趋势, 但频度和重要值变化不明显。同时, 物种的多度、胸高截面积、频度和重要值等次序均无明显变化。这说明2008年发生的冰雪灾害对古田山中亚热带常绿阔叶林群落的短期动态产生了较大的负面影响, 且其影响程度与植物胸径和地形等因素密切相关; 同时也反映了古田山中亚热带常绿阔叶林群落结构对冰雪灾害干扰具有一定的抵抗力。
金毅, 陈建华, 米湘成, 任海保, 马克平, 于明坚 (2015) 古田山24 ha森林动态监测样地常绿阔叶林群落结构和组成动态: 探讨2008年冰雪灾害的影响. 生物多样性, 23, 610-618. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015051.
Yi Jin, Jianhua Chen, Xiangcheng Mi, Haibao Ren, Keping Ma, Mingjian Yu (2015) Impacts of the 2008 ice storm on structure and composition of an evergreen broad-leaved forest community in eastern China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 610-618. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015051.
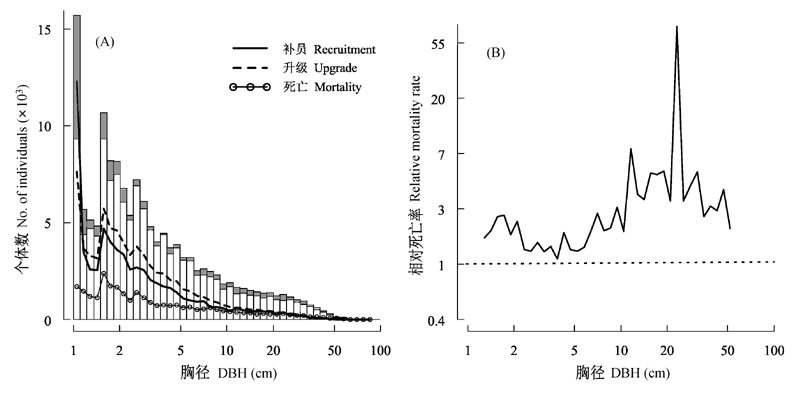
图1 2005-2010年群落径级结构动态。(A)显示了2005年及2010年的群落径级结构。柱形的白色部分为2010年各径级个体数, 白色部分加上灰色部分表示2005年各径级个体数, 灰色部分则表示2005-2010年间各径级个体数的减少数量。(B)显示了相对死亡率随着径级的变化情况。虚线分隔相对死亡率> 1和< 1的情况, 虚线上方数值表示观测死亡率大于预期死亡率, y值越大则差异越大; 虚线下方数值表示观测死亡率小于预期死亡率, y值越小则差异越大。
Fig. 1 Dynamics of DBH size class community structure between 2005 and 2010. Diagram (A) shows DBH size class community structures in 2005 and 2010. The empty part of the bar represents the number of individuals of a DBH size class in 2010, the empty plus the grey filled part represent the number of individuals of a DBH size class in 2005, and the grey filled part represents the decrease in number of individuals between 2005 and 2010. (B) shows the change in relative mortality rate with DBH size class. The dotted line divides relative mortality rate values > 1 from values < 1. Values above the dotted line indicate observed mortality rate > expected mortality rate, larger y value represent larger difference; values below the dotted line indicate observed mortality rate < expected mortality rate, smaller y value represent larger difference.
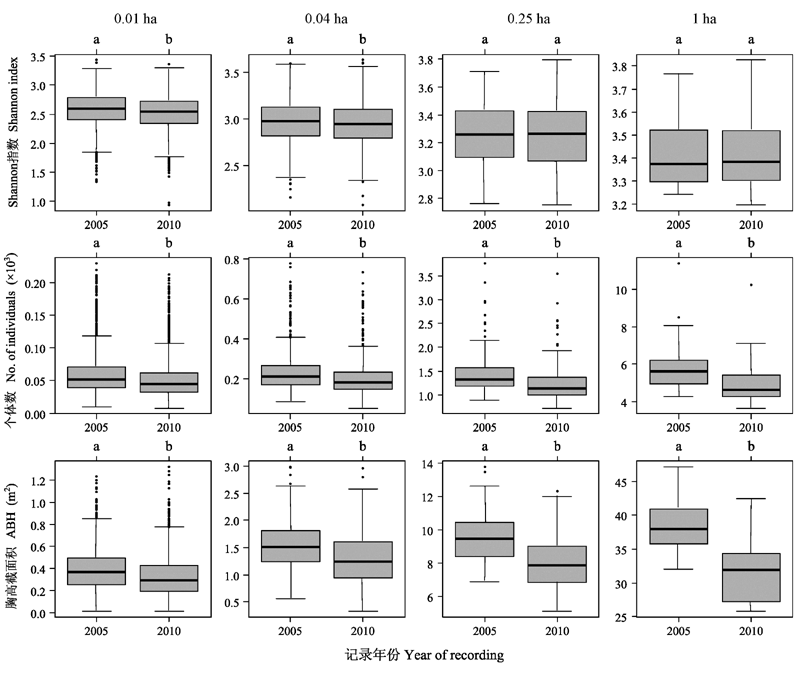
图2 2005年与2010年多个粒度群落生物多样性、个体数及胸高截面积的比较。箱形表示上下四分位数范围及中位数(粗线); 箱形上下方横线分别为上下四分位数加减1.5倍四分位距。图中不同字母表示组间差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 2 Comparisons of the biodiversity, number of individuals and area at breast height (ABH) of multiple grain sized assemblages between 2005 and 2010. Box represents the interquartile range and the median (the thick line); the two whiskers up and below the box represent the upper quantile plus 1.5 times interquantile range and the lower quantile minus 1.5 times interquantile range, respectively. Different letters represent significant difference (P < 0.05).
 |
表1 不同生境群落之间生物多样性、个体数及胸高截面积变化率的单因素方差分析结果
Table 1 One-way analysis of variance results of the rates of change in biodiversity, number of individuals and area at breast height (ABH) among different habitat assemblages
 |
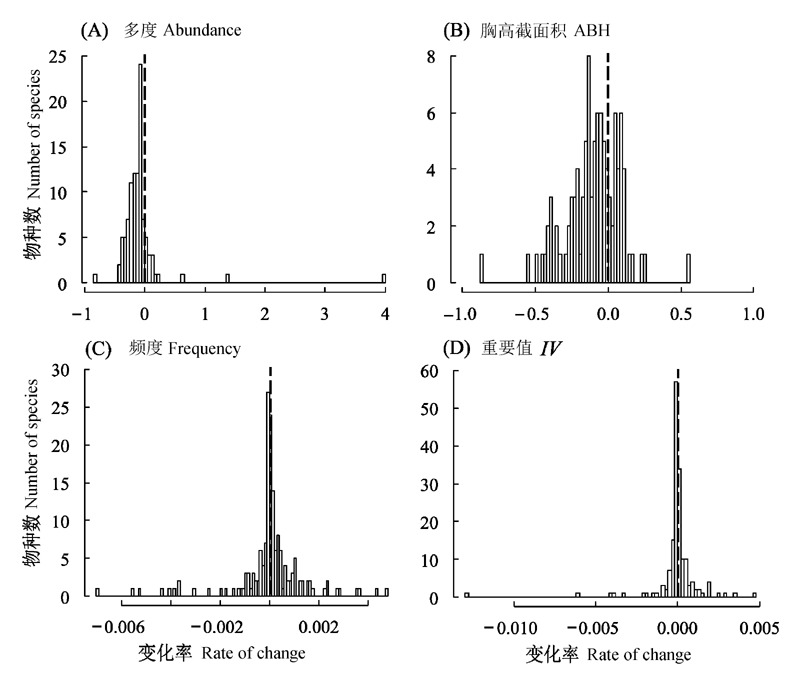
图3 2005-2010年间物种多度、胸高截面积、频度及重要值的变化率。竖直虚线右侧变化率为正值,左侧为负值。
Fig. 3 Rates of change in species abundance, area at breast height (ABH), frequency and importance value (IV) between 2005 and 2010. The right side of the vertical dotted line indicates positive rate of change, the left side indicates negative rate of change.
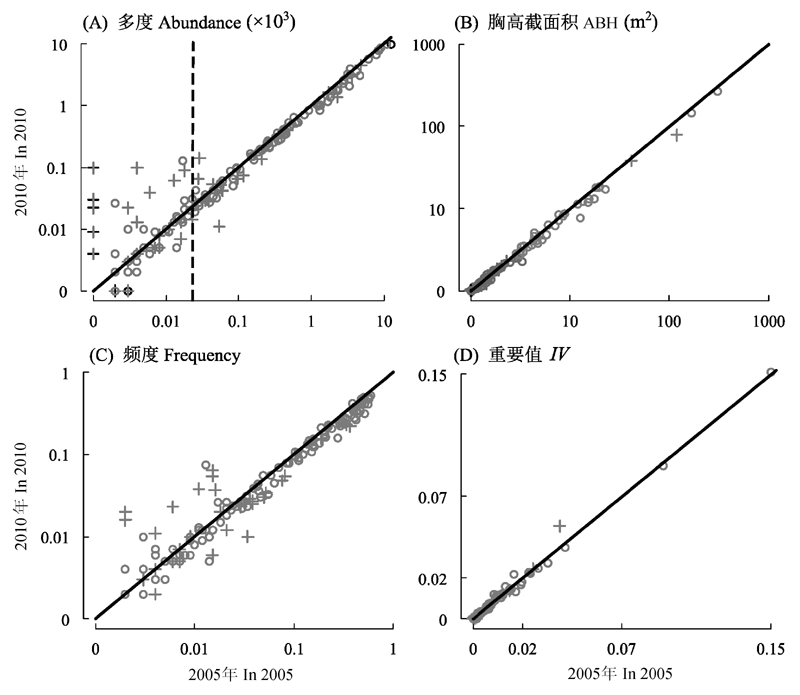
图4 2005年与2010年间物种多度、胸高截面积、频度以及重要值的相关性。○, 耐阴种, +, 阳性种。实线分隔2005-2010年间数值增大与减小的物种, 实线上方为增大种, 下方为减小种。(A)中, 虚线左侧为稀有种, 右侧为常见种。
Fig. 4 Correlations of species abundance, area at breast height (ABH), frequency and importance value (IV) between 2005 and 2010. ○, shade-tolerant species; +, shade-intolerant species. The solid line divides species increased in value from species decreased in value between 2005 and 2010. Values above the solid line indicate increase and below indicate decrease. In (A), on the left side of the dotted line are rare species and on the right side are common species.
| [1] | Amateis RL, Burkhart HE (1996) Impact of heavy glaze in a loblolly pine spacing trial.Southern Journal of Applied Forestry, 20, 151-155. |
| [2] | Boerner REJ, Runge SD, Cho DS, Kooser JG (1988) Localized ice storm damage in an Appalachian Plateau watershed.American Midland Naturalist, 119, 199-208. |
| [3] | Cao KF, Peters R (1997) Species diversity of Chinese beech forests in relation to warmth and climatic disturbances.Ecological Research, 12, 175-189. |
| [4] | Chen L, Mi XC, Comita LS, Zhang LW, Ren HB, Ma KP (2010) Community-level consequences of density dependence and habitat association in a subtropical broad-leaved forest.Ecology Letters, 13, 695-704. |
| [5] | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. |
| [6] | Darwin AT, Ladd D, Galdins R, Contreras TA, Fahrig L (2004) Response of forest understory vegetation to a major ice storm.Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society, 131, 45-52. |
| [7] | DeSteven D, Kline J, Matthiae PE (1991) Long-term changes in a Wisconsin Fagus-Acer forest in relation to glaze storm disturbance.Journal of Vegetation Science, 2, 201-208. |
| [8] | Guo SH (郭淑红), Xue L (薛立) (2012) Effects of ice-snow damage on forests.Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 32, 5242-5253. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Harms K, Condit R, Hubbell S, Foster R (2001) Habitat associations of trees and shrubs in a 50-ha neotropical forest plot.Journal of Ecology, 89, 947-959. |
| [10] | He J (何俊), Zhao XH (赵秀海), Zhang CY (张春雨), Jia YZ (贾玉珍), Fan J (范娟), Mao SY (毛双燕), Zhang ZB (张自斌), Liao CK (廖承开) (2011) Ice and snow disasters to the evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jiulianshan Nature Reserve in Jiangxi, China.Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology(应用与环境生物学报), 17, 180-185. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Hopkin A, Williams T, Sajan R, Pedlar J, Nielsen C (2003) Ice storm damage to eastern Ontario forests: 1998-2001.Forestry Chronicle, 79, 47-53. |
| [12] | Hu ZH (胡正华), Yu MJ (于明坚), Ding BY (丁炳扬), Fang T (方腾), Qian HY (钱海源), Chen QC (陈启瑺) (2003) Types of evergreen broad-leaved forests and their species diversity in Gutian Mountain National Nature Reserve.Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology(应用与环境生物学报), 9, 341-345. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Lafon CW (2004) Ice-storm disturbance and long-term forest dynamics in the Adirondack Mountains.Journal of Vegetation Science, 15, 267-276. |
| [14] | Lemon PC (1961) Forest ecology of ice storms.Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club, 88, 21-29. |
| [15] | Man XX (曼兴兴), Mi XC (米湘成), Ma KP (马克平) (2011) Effects of an ice storm on community structure of an evergreen broad-leaved forest in Gutianshan National Nature Reserve, Zhejiang Province.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 19, 197-205. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Proulx OJ, Greene DF (2001) The relationship between ice thickness and northern hardwood tree damage during ice storms.Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 31, 1758-1767. |
| [17] | R Development Core Team (2014) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. |
| [18] | Regan M (1998) Canadian ice storm.World Meteorological Organization, 47, 250-256. |
| [19] | Rhoads AG, Hamburg SP, Fahey TJ, Siccama TG, Hane EN, Battles J, Cogbill C, Randall J, Wilson G (2002) Effects of an intense ice storm on the structure of a northern hardwood forest.Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 32, 1763-1775. |
| [20] | Stone R (2008) Ecologists report huge storm losses in China’s forests.Science, 319, 1318-1319. |
| [21] | Su ZY (苏志尧), Liu G (刘刚), Ou YD (区余端), Dai ZH (戴朝晖), Li ZK (李镇魁) (2010) Storm damage in a montane evergreen broad-leaved forest of Chebaling National Nature Reserve, South China.Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology(植物生态学报), 34, 213-222. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [22] | Tremblay M, Messier C, Marceau DJ (2005) Analysis of deciduous tree species dynamics after a severe ice storm using SORTIE model simulations.Ecological Modelling, 187, 297-313. |
| [23] | Warrillow MP, Mou P (1999) Ice storm damage to forest tree species in the ridge and valley region of southwestern Virginia.Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society, 126, 147-158. |
| [24] | Wu KK (吴可可), Peng SL (彭少麟), Chen LY (陈蕾伊), Xu YW (徐雅雯), Zhu LR (朱丽蓉), Lin ZG (林真光) (2011) Characteristics of forest damage induced by frozen rain and snow in South China: a review.Chinese Journal of Ecology(生态学杂志), 30, 611-620. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Wu ZY (吴征镒) (1980) Vegetation of China (中国植被). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [26] | Vowels KM (2012) Ice storm damage to upland oak-hickory forest at Bernheim Forest, Kentucky.Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society, 139, 406-415. |
| [27] | Yang GY (杨灌英), Xu XL (徐小林), Yang LS (杨朗生), He XB (何兴炳) (2008) Bamboo forest damage caused by snow storm in Sichuan Province in 2008 and silvicultural reestablishment measures.Scientia Silvae Sinicae(林业科学), 44(11), 96-100. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Yu MJ (于明坚), Hu ZH (胡正华), Yu JP (余建平), Ding BY (丁炳扬), Fang T (方腾) (2001) Forest vegetation types in Gutianshan Nature Reserve in Zhejiang. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture & Life Science Edition) (浙江大学学报(农业和生命科学版)), 27, 375-380. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Zhang JG (张建国), Duan AG (段爱国), Tong SZ (童书振), Sun HG (孙洪刚), Deng ZF (邓宗富), Zhang SG (张守攻) (2008) Harm of frost and snow suppress to near mature stands of Cunninghamia lanceolata plantations.Scientia Silvae Sinicae(林业科学), 44(11), 18-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [30] | Zhou BZ, Gu LH, Ding YH, Shao L, Wu ZM, Yang XS, Li CZ, Li ZC, Wang XM, Cao YH, Zeng BS, Yu MK, Wang MY, Wang SK, Sun HG, Duan AG, An YF, Wang X, Kong WJ (2011) The Great 2008 Chinese storm: its socioeconomic-ecological impact and sustainability lessons learned.Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 92, 47-60. |
| [31] | Zhu Y (祝燕), Zhao GF (赵谷风), Zhang LW (张俪文), Shen GC (沈国春), Mi XC (米湘成), Ren HB (任海保), Yu MJ (于明坚), Chen JH (陈建华), Chen SW (陈声文), Fang T (方腾), Ma KP (马克平) (2008) Community composition and structure of Gutianshan forest dynamics plot in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest, East China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version) (植物生态学报), 32, 262-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 贾贞妮, 张意岑, 杜彦君, 任海保. 干扰对中亚热带森林群落物种多样性演替动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24078-. |
| [2] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [3] | 程建伟, 徐满厚, 窦永静, 王亚东, 王桠楠, 刘新民, 李永宏. 内蒙古典型草原马粪分解过程中节肢动物群落的季节动态变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24018-. |
| [4] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [5] | 单航, 雷祖培, 郑方东, 韦博良, 仲磊, 于明坚. 2013-2023年浙江乌岩岭次生常绿阔叶林群落动态变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24372-. |
| [6] | 姚嘉, 张聪伶, 李时轩, 林阳, 王震, 张煜涵, 周伟龙, 潘心禾, 朱珊, 吴逸卿, 王丹, 刘金亮, 谭珊珊, 沈国春, 于明坚. 百山祖连续海拔样带植物群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24052-. |
| [7] | 陈明苗, 张楚然, 邓云, 李生发, 李逢昌, 唐志忠, 魏兆喆, 张彩彩, 林露湘. 地形因子对亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林木本植物萌生特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24282-. |
| [8] | 张楚然, 李生发, 李逢昌, 唐志忠, 刘辉燕, 王丽红, 顾荣, 邓云, 张志明, 林露湘. 云南鸡足山亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地木本植物生境关联与群落数量分类[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23393-. |
| [9] | 王明慧, 陈昭铨, 李帅锋, 黄小波, 郎学东, 胡子涵, 尚瑞广, 刘万德. 云南普洱季风常绿阔叶林不同种子扩散方式的优势种空间点格局分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23147-. |
| [10] | 陈声文, 任海保, 童光蓉, 王宁宁, 蓝文超, 薛建华, 米湘成. 钱江源国家公园木本植物物种多样性空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22587-. |
| [11] | 徐学红, 王巍伟, 米湘成, 陈磊, 马克平. 中国森林生物多样性监测网络(CForBio): 二十年进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23354-. |
| [12] | 左艳洁, 彭明春, 王崇云, 沈泽昊, 李永萍, 周新茂, 周杰, 周光信, 任佳昕, 刘忠安. 滇中高原半湿润常绿阔叶林的岛屿化与物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23252-. |
| [13] | 田希, 刘文聪, 饶杰生, 王晓凤, 杨涛, 陈稀, 张秋雨, 刘其明, 徐衍潇, 张旭, 沈泽昊. 云南鸡足山半湿润常绿阔叶林的林隙干扰格局与成因[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23219-. |
| [14] | 杨涛, 沈泽昊, 王晓凤, 饶杰生, 刘文聪, 田希, 陈稀, 张秋雨, 刘倩, 钱恒君, 解宇阳, 刘其明, 徐衍潇, 涂梦灵, 单子铭, 张玉坤, 侯波, 李建斌, 欧晓昆. 滇中高原亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林植物群落多样性特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23238-. |
| [15] | 罗彩访, 杨涛, 张秋雨, 王馨培, 沈泽昊. 滇中半湿润常绿阔叶林木本植物的功能特征和功能多样性及其影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23215-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()