



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 23393. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023393 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023393
张楚然1,2, 李生发3, 李逢昌3, 唐志忠3, 刘辉燕3, 王丽红3, 顾荣2, 邓云2,4,*( ), 张志明1,5, 林露湘2,4
), 张志明1,5, 林露湘2,4
收稿日期:2023-10-18
接受日期:2023-11-30
出版日期:2024-01-20
发布日期:2023-12-22
通讯作者:
*E-mail: dy@xtbg.org.cn
基金资助:
Churan Zhang1,2, Shengfa Li3, Fengchang Li3, Zhizhong Tang3, Huiyan Liu3, Lihong Wang3, Rong Gu2, Yun Deng2,4,*( ), Zhiming Zhang1,5, Luxiang Lin2,4
), Zhiming Zhang1,5, Luxiang Lin2,4
Received:2023-10-18
Accepted:2023-11-30
Online:2024-01-20
Published:2023-12-22
Contact:
*E-mail: dy@xtbg.org.cn
摘要:
亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林是中国西部中亚热带地区的地带性植被, 大理鸡足山是其连续分布面积最大的区域之一。本研究以云南鸡足山亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地为研究对象, 分析了木本植物分布与生境的关联性, 并对其进行群落数量分类。结果表明: 该样地中共有43,424个DBH ≥ 1 cm的独立生长的木本植物个体, 分属31科57属92种。科的区系成分以热带为主, 占67.7%; 属的区系成分以温带为主, 占50.9%; 种的区系成分以中国特有种为主, 占42.4%。物种-生境关联分析的结果表明, 在52个目标物种中, 有44个物种至少与一种生境具有显著正关联, 有35个物种至少与一种生境具有显著负关联, 说明生境过滤在该样地的木本植物分布中具有重要作用。低海拔山谷是具有显著关联物种最多的生境, 反映了该生境对物种具有强烈的过滤作用。该样地的群落分类主要受凹凸度和海拔这两个地形因素的影响, 可分为3个群丛: (1)紫药女贞+五柱滇山茶-白柯+银木荷群丛(Ligustrum delavayanum+Camellia yunnanensis-Lithocarpus dealbatus+Schima argentea Association); (2)珍珠花+美丽马醉木-银木荷+白柯群丛(Lyonia ovalifolia+Pieris Formosa-Schima argentea+Lithocarpus dealbatus Association); (3)云南金叶子+云南越桔-白柯+银木荷群丛(Craibiodendron yunnanense+Vaccinium duclouxii-Lithocarpus dealbatus+Schima argentea Association)。本研究可为进一步开展亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林的群落构建与物种共存研究提供科学基础。
张楚然, 李生发, 李逢昌, 唐志忠, 刘辉燕, 王丽红, 顾荣, 邓云, 张志明, 林露湘 (2024) 云南鸡足山亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地木本植物生境关联与群落数量分类. 生物多样性, 32, 23393. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023393.
Churan Zhang, Shengfa Li, Fengchang Li, Zhizhong Tang, Huiyan Liu, Lihong Wang, Rong Gu, Yun Deng, Zhiming Zhang, Luxiang Lin (2024) Habitat association and community classification of woody plants in the 20 ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23393. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023393.
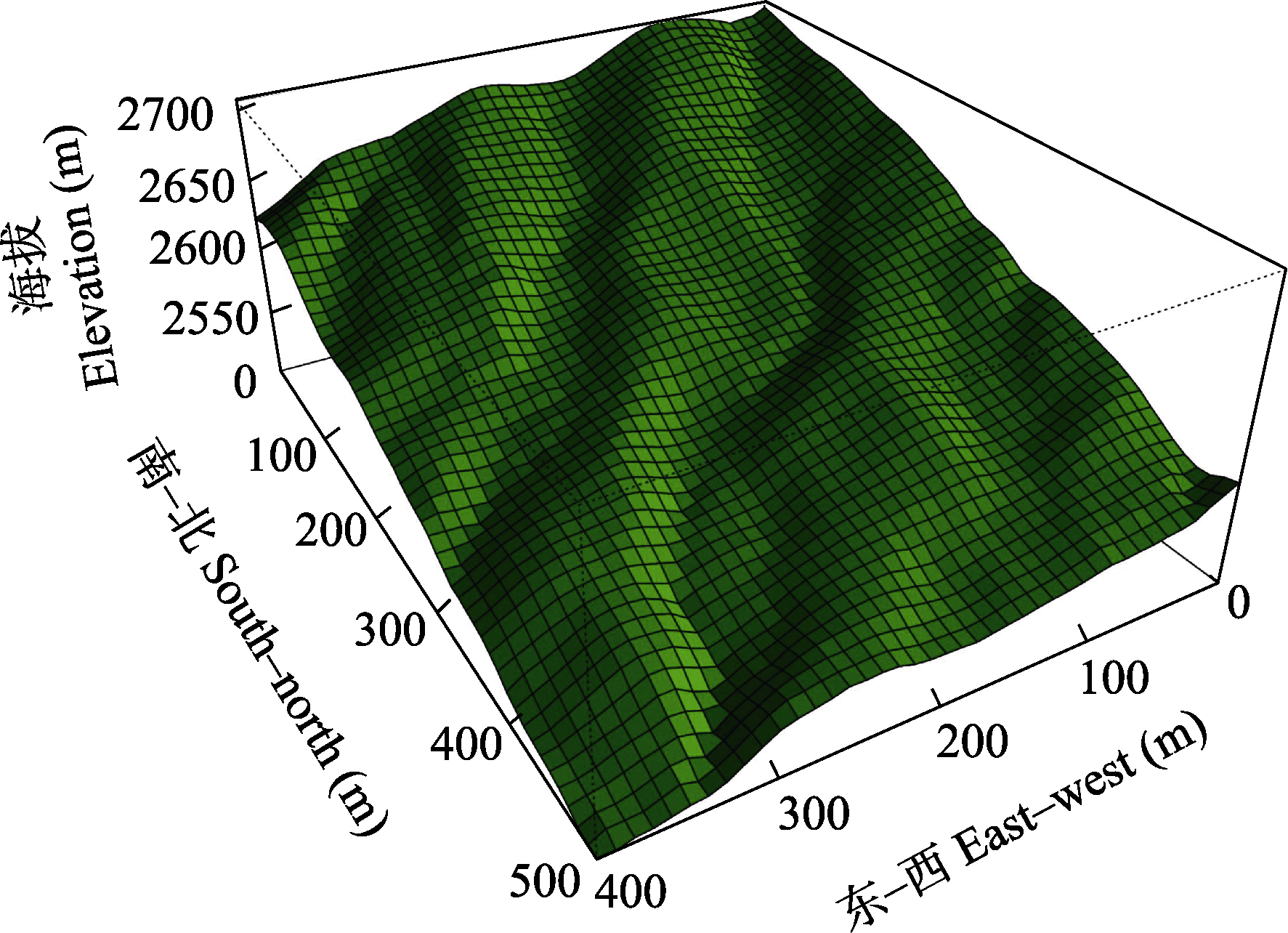
图1 云南鸡足山亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地的三维地形图
Fig. 1 Three-dimensional topographic map of the 20 ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan
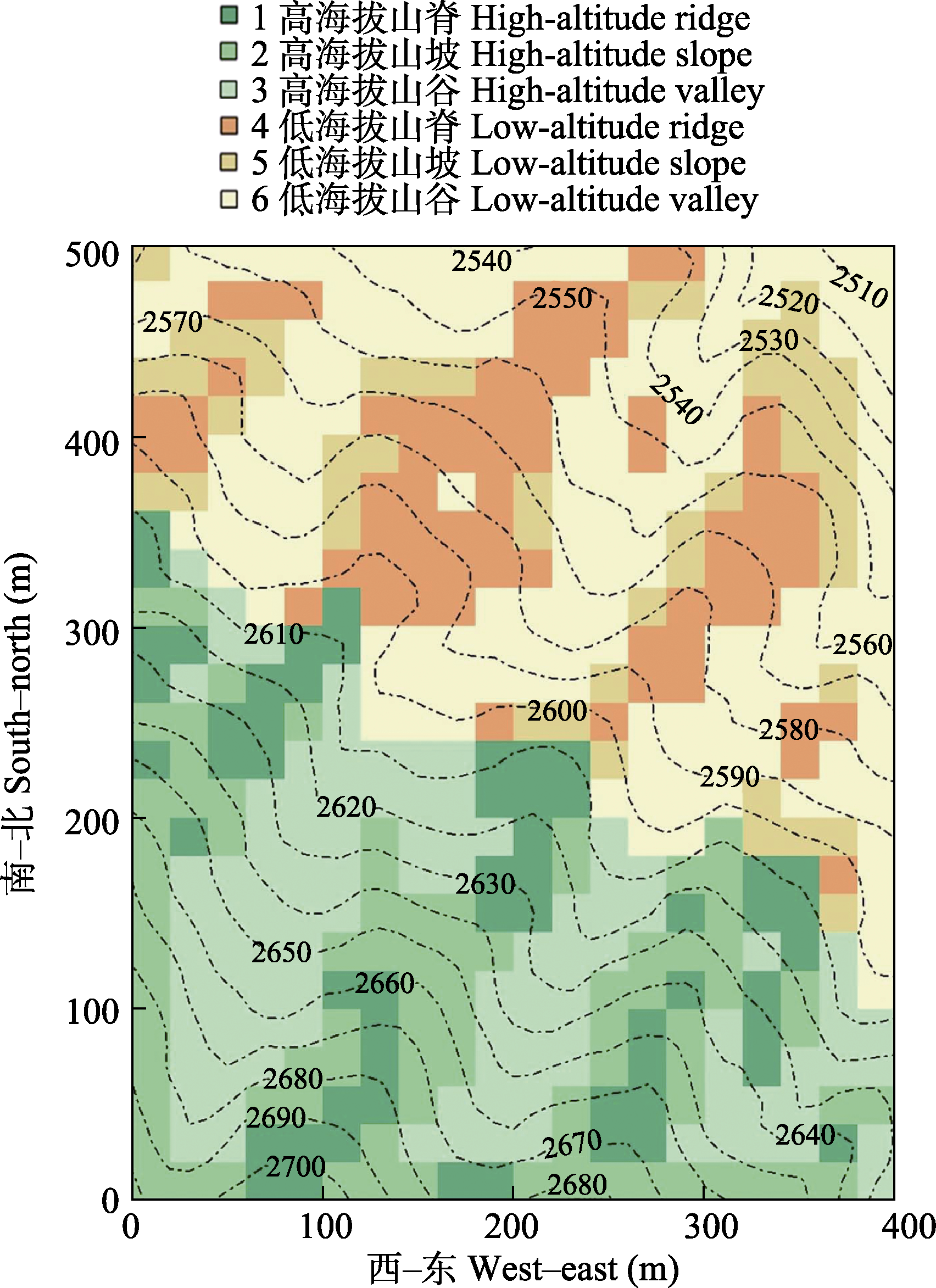
图2 云南鸡足山亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地的6类生境
Fig. 2 The six habitat types in the 20 ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan
| 序号 Rank | 物种 Species | 个体数 Individual no. | 相对多度 Relative abundance (%) | 相对胸高断面积 Relative basal area (%) | 重要值 Importance value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 银木荷 Schima argentea | 13,313 | 30.66 | 28.86 | 29.76 |
| 2 | 白柯 Lithocarpus dealbatus | 4,970 | 11.45 | 36.29 | 23.87 |
| 3 | 尼泊尔桤木 Alnus nepalensis | 516 | 1.19 | 10.87 | 6.03 |
| 4 | 响叶杨 Populus adenopoda | 2,958 | 6.81 | 4.13 | 5.47 |
| 5 | 五柱滇山茶 Camellia yunnanensis | 3,148 | 7.25 | 0.76 | 4.00 |
| 6 | 元江锥 Castanopsis orthacantha | 736 | 1.69 | 4.66 | 3.18 |
| 7 | 厚皮香 Ternstroemia gymnanthera | 1,952 | 4.50 | 1.08 | 2.79 |
| 8 | 云南越桔 Vaccinium duclouxii | 1,852 | 4.26 | 0.92 | 2.59 |
| 9 | 云南金叶子 Craibiodendron yunnanense | 1,401 | 3.23 | 1.09 | 2.16 |
| 10 | 云南凹脉柃 Eurya cavinervis | 1,571 | 3.62 | 0.44 | 2.03 |
| 11 | 紫药女贞 Ligustrum delavayanum | 1,569 | 3.61 | 0.21 | 1.91 |
| 12 | 云南松 Pinus yunnanensis | 248 | 0.57 | 3.24 | 1.91 |
| 13 | 蓝黑果荚蒾 Viburnum atrocyaneum | 1,334 | 3.07 | 0.33 | 1.70 |
| 14 | 白碎米花 Rhododendron spiciferum var. album | 1,295 | 2.98 | 0.10 | 1.54 |
| 15 | 山鸡椒 Litsea cubeba | 974 | 2.24 | 0.61 | 1.43 |
| 16 | 头状四照花 Cornus capitata | 300 | 0.69 | 1.85 | 1.27 |
| 17 | 锥序荚蒾 Viburnum pyramidatum | 524 | 1.21 | 0.75 | 0.98 |
| 18 | 怒江红山茶 Camellia saluenensis | 749 | 1.72 | 0.13 | 0.93 |
| 19 | 江南越桔 Vaccinium mandarinorum | 558 | 1.28 | 0.33 | 0.81 |
| 20 | 石灰花楸 Sorbus folgneri | 253 | 0.58 | 0.70 | 0.64 |
| 总计 Total | 40,221 | 92.62 | 97.33 | 94.98 | |
表1 云南鸡足山亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地重要值排名前20的物种
Table 1 Top 20 species with the highest importance values in the 20 ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan
| 序号 Rank | 物种 Species | 个体数 Individual no. | 相对多度 Relative abundance (%) | 相对胸高断面积 Relative basal area (%) | 重要值 Importance value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 银木荷 Schima argentea | 13,313 | 30.66 | 28.86 | 29.76 |
| 2 | 白柯 Lithocarpus dealbatus | 4,970 | 11.45 | 36.29 | 23.87 |
| 3 | 尼泊尔桤木 Alnus nepalensis | 516 | 1.19 | 10.87 | 6.03 |
| 4 | 响叶杨 Populus adenopoda | 2,958 | 6.81 | 4.13 | 5.47 |
| 5 | 五柱滇山茶 Camellia yunnanensis | 3,148 | 7.25 | 0.76 | 4.00 |
| 6 | 元江锥 Castanopsis orthacantha | 736 | 1.69 | 4.66 | 3.18 |
| 7 | 厚皮香 Ternstroemia gymnanthera | 1,952 | 4.50 | 1.08 | 2.79 |
| 8 | 云南越桔 Vaccinium duclouxii | 1,852 | 4.26 | 0.92 | 2.59 |
| 9 | 云南金叶子 Craibiodendron yunnanense | 1,401 | 3.23 | 1.09 | 2.16 |
| 10 | 云南凹脉柃 Eurya cavinervis | 1,571 | 3.62 | 0.44 | 2.03 |
| 11 | 紫药女贞 Ligustrum delavayanum | 1,569 | 3.61 | 0.21 | 1.91 |
| 12 | 云南松 Pinus yunnanensis | 248 | 0.57 | 3.24 | 1.91 |
| 13 | 蓝黑果荚蒾 Viburnum atrocyaneum | 1,334 | 3.07 | 0.33 | 1.70 |
| 14 | 白碎米花 Rhododendron spiciferum var. album | 1,295 | 2.98 | 0.10 | 1.54 |
| 15 | 山鸡椒 Litsea cubeba | 974 | 2.24 | 0.61 | 1.43 |
| 16 | 头状四照花 Cornus capitata | 300 | 0.69 | 1.85 | 1.27 |
| 17 | 锥序荚蒾 Viburnum pyramidatum | 524 | 1.21 | 0.75 | 0.98 |
| 18 | 怒江红山茶 Camellia saluenensis | 749 | 1.72 | 0.13 | 0.93 |
| 19 | 江南越桔 Vaccinium mandarinorum | 558 | 1.28 | 0.33 | 0.81 |
| 20 | 石灰花楸 Sorbus folgneri | 253 | 0.58 | 0.70 | 0.64 |
| 总计 Total | 40,221 | 92.62 | 97.33 | 94.98 | |
| 序号 Rank | 科名 Family | 属数 No. of genera | 种数 No. of species | 相对多样性 Relative diversity (%) | 相对密度 Relative density (%) | 相对优势度 Relative dominance (%) | 重要值 Importance value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 山茶科 Theaceae | 4 | 5 | 5.38 | 47.74 | 31.26 | 28.13 |
| 2 | 壳斗科 Fagaceae | 4 | 10 | 10.75 | 13.70 | 41.99 | 22.15 |
| 3 | 杜鹃花科 Ericaceae | 5 | 14 | 15.05 | 14.81 | 3.14 | 11.00 |
| 4 | 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 8 | 12 | 12.90 | 1.46 | 1.13 | 5.17 |
| 5 | 桦木科 Betulaceae | 1 | 1 | 1.08 | 1.19 | 10.87 | 4.38 |
| 6 | 杨柳科 Salicaceae | 2 | 2 | 2.15 | 6.81 | 4.14 | 4.37 |
| 7 | 忍冬科 Caprifoliaceae | 2 | 5 | 5.38 | 4.74 | 1.11 | 3.74 |
| 8 | 樟科 Lauraceae | 3 | 4 | 4.30 | 2.80 | 0.68 | 2.59 |
| 9 | 木樨科 Oleaceae | 2 | 3 | 3.23 | 3.65 | 0.22 | 2.37 |
| 10 | 松科 Pinaceae | 1 | 2 | 2.15 | 0.91 | 3.47 | 2.18 |
| 总计 Total | 32 | 58 | 62.37 | 97.82 | 98.00 | 86.08 | |
表2 云南鸡足山亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地重要值排名前10的科
Table 2 Top 10 families with the highest importance values in the 20 ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan
| 序号 Rank | 科名 Family | 属数 No. of genera | 种数 No. of species | 相对多样性 Relative diversity (%) | 相对密度 Relative density (%) | 相对优势度 Relative dominance (%) | 重要值 Importance value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 山茶科 Theaceae | 4 | 5 | 5.38 | 47.74 | 31.26 | 28.13 |
| 2 | 壳斗科 Fagaceae | 4 | 10 | 10.75 | 13.70 | 41.99 | 22.15 |
| 3 | 杜鹃花科 Ericaceae | 5 | 14 | 15.05 | 14.81 | 3.14 | 11.00 |
| 4 | 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 8 | 12 | 12.90 | 1.46 | 1.13 | 5.17 |
| 5 | 桦木科 Betulaceae | 1 | 1 | 1.08 | 1.19 | 10.87 | 4.38 |
| 6 | 杨柳科 Salicaceae | 2 | 2 | 2.15 | 6.81 | 4.14 | 4.37 |
| 7 | 忍冬科 Caprifoliaceae | 2 | 5 | 5.38 | 4.74 | 1.11 | 3.74 |
| 8 | 樟科 Lauraceae | 3 | 4 | 4.30 | 2.80 | 0.68 | 2.59 |
| 9 | 木樨科 Oleaceae | 2 | 3 | 3.23 | 3.65 | 0.22 | 2.37 |
| 10 | 松科 Pinaceae | 1 | 2 | 2.15 | 0.91 | 3.47 | 2.18 |
| 总计 Total | 32 | 58 | 62.37 | 97.82 | 98.00 | 86.08 | |
| 序号 Rank | 分布区类型 Areal-types | 科数 No. of families | 属数 No. of genera | 种数 No. of species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 世界广布 Widespread | 9 (29.0%) | 2 (3.5%) | 1 (1.1%) |
| 2 | 泛热带(热带广布) Pan Tropical | 7 (22.6%) | 4 (7.0%) | 5 (5.4%) |
| 2-1 热带亚洲-大洋洲和热带美洲 Tropical Asia-Australasia & Tropical America | 1 (3.1%) | 2 (3.5%) | 2 (2.2%) | |
| 2-2 热带亚洲-热带非洲-热带美洲 Tropical Asia-Tropical Africa-Tropical America | 1 (3.1%) | 1 (1.8%) | 1 (1.1%) | |
| 3 | 东亚(热带、亚热带)及南美间断 East Asia (Tropical & SubTropical) & Tropical South America disjuncted | 3 (9.7%) | 3 (5.3%) | 3 (3.3%) |
| 4 | 旧世界热带 Old World Tropical | - | 1 (1.8%) | 1 (1.1%) |
| 4-1 热带亚洲、非洲和大洋洲间断分布 Tropical Asia, Tropical Africa & Tropical Australasia disjuncted | - | 1 (1.8%) | 1 (1.1%) | |
| 5 | 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲 Tropical Asia to Tropical Australasia Oceania | - | 2 (3.5%) | 1 (1.1%) |
| 6 | 热带亚洲至热带非洲 Tropical Asia to Tropical Africa | - | - | - |
| 7 | 热带亚洲(即热带东南亚至印度-马来, 太平洋诸岛) Tropical Asia (Tropical Southeastern Asia to Indo-Malaya & Tropical Southwest Pacific Island) | - | 4 (7.0%) | 2 (2.2%) |
| 7-1 爪哇(或苏门答腊)、喜马拉雅间断或星散分布到我国西南、华南 Java or Sumatra, Himalaya to South & Southwest of China | - | 1 (1.8%) | 1 (1.1%) | |
| 7-3 缅甸、泰国至我国西南分布 Myanmar, Thailand to Southwest of China | - | 1 (1.8%) | 1 (1.1%) | |
| 热带成分(2-7)小计 Tropical elements (2-7) subtotal | 21 (67.7%) | 22 (38.6%) | 19 (20.7%) | |
| 8 | 北温带广布 North Temperate | 2 (6.5%) | 12 (21.0%) | 8 (8.7%) |
| 8-4 北温带和南温带间断分布 North Temperate & South Temperate disjuncted | 6 (19.4%) | 8 (14.0%) | 3 (3.3%) | |
| 8-5 欧亚和南美洲间断分布 Eurasia & Temperate South America disjuncted | 1 (3.1%) | 1 (1.8%) | - | |
| 9 | 东亚及北美间断分布 East Asia & North America disjuncted | - | 7 (12.3%) | 2 (2.2%) |
| 10 | 旧世界温带 Old World Temperate | - | 1 (1.8%) | - |
| 11 | 温带亚洲 Temperate Asia | - | - | - |
| 温带成分小计(8-11) Temperate elements (8-11) subtotal | 9 (29.0%) | 29 (50.9%) | 26 (28.3%) | |
| 12 | 东亚 East Asia | 1 (3.1%) | 2 (3.5%) | 4 (4.4%) |
| 14SH 中国-喜马拉雅 Sino-Himalaya | - | 2 (3.5%) | 14 (15.2%) | |
| 14SJ 中国-日本 Sino-Japan | - | 1 (1.8%) | 3 (3.3%) | |
| 13 | 中国特有 Endemic to China | - | 1 (1.8%) | 39 (42.4%) |
| 总计 Total | 100% | 100% | 100% |
表3 云南鸡足山亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地科、属、种的区系组成
Table 3 Areal types of families, genera and species in the 20 ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical semi-humid evergreen broad- leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan
| 序号 Rank | 分布区类型 Areal-types | 科数 No. of families | 属数 No. of genera | 种数 No. of species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 世界广布 Widespread | 9 (29.0%) | 2 (3.5%) | 1 (1.1%) |
| 2 | 泛热带(热带广布) Pan Tropical | 7 (22.6%) | 4 (7.0%) | 5 (5.4%) |
| 2-1 热带亚洲-大洋洲和热带美洲 Tropical Asia-Australasia & Tropical America | 1 (3.1%) | 2 (3.5%) | 2 (2.2%) | |
| 2-2 热带亚洲-热带非洲-热带美洲 Tropical Asia-Tropical Africa-Tropical America | 1 (3.1%) | 1 (1.8%) | 1 (1.1%) | |
| 3 | 东亚(热带、亚热带)及南美间断 East Asia (Tropical & SubTropical) & Tropical South America disjuncted | 3 (9.7%) | 3 (5.3%) | 3 (3.3%) |
| 4 | 旧世界热带 Old World Tropical | - | 1 (1.8%) | 1 (1.1%) |
| 4-1 热带亚洲、非洲和大洋洲间断分布 Tropical Asia, Tropical Africa & Tropical Australasia disjuncted | - | 1 (1.8%) | 1 (1.1%) | |
| 5 | 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲 Tropical Asia to Tropical Australasia Oceania | - | 2 (3.5%) | 1 (1.1%) |
| 6 | 热带亚洲至热带非洲 Tropical Asia to Tropical Africa | - | - | - |
| 7 | 热带亚洲(即热带东南亚至印度-马来, 太平洋诸岛) Tropical Asia (Tropical Southeastern Asia to Indo-Malaya & Tropical Southwest Pacific Island) | - | 4 (7.0%) | 2 (2.2%) |
| 7-1 爪哇(或苏门答腊)、喜马拉雅间断或星散分布到我国西南、华南 Java or Sumatra, Himalaya to South & Southwest of China | - | 1 (1.8%) | 1 (1.1%) | |
| 7-3 缅甸、泰国至我国西南分布 Myanmar, Thailand to Southwest of China | - | 1 (1.8%) | 1 (1.1%) | |
| 热带成分(2-7)小计 Tropical elements (2-7) subtotal | 21 (67.7%) | 22 (38.6%) | 19 (20.7%) | |
| 8 | 北温带广布 North Temperate | 2 (6.5%) | 12 (21.0%) | 8 (8.7%) |
| 8-4 北温带和南温带间断分布 North Temperate & South Temperate disjuncted | 6 (19.4%) | 8 (14.0%) | 3 (3.3%) | |
| 8-5 欧亚和南美洲间断分布 Eurasia & Temperate South America disjuncted | 1 (3.1%) | 1 (1.8%) | - | |
| 9 | 东亚及北美间断分布 East Asia & North America disjuncted | - | 7 (12.3%) | 2 (2.2%) |
| 10 | 旧世界温带 Old World Temperate | - | 1 (1.8%) | - |
| 11 | 温带亚洲 Temperate Asia | - | - | - |
| 温带成分小计(8-11) Temperate elements (8-11) subtotal | 9 (29.0%) | 29 (50.9%) | 26 (28.3%) | |
| 12 | 东亚 East Asia | 1 (3.1%) | 2 (3.5%) | 4 (4.4%) |
| 14SH 中国-喜马拉雅 Sino-Himalaya | - | 2 (3.5%) | 14 (15.2%) | |
| 14SJ 中国-日本 Sino-Japan | - | 1 (1.8%) | 3 (3.3%) | |
| 13 | 中国特有 Endemic to China | - | 1 (1.8%) | 39 (42.4%) |
| 总计 Total | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| 生境类型 Habitat types | 显著正关联物种数 No. of significant positive association species (%) | 显著负关联物种数 No. of significant negative association species (%) | 显著正/负生境关联的总物种数 Total no. of significant positive/ negative association species (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高海拔山脊 High-altitude ridge | 10 (19.2%) | 15 (28.9%) | 25 (48.1%) |
| 高海拔山坡 High-altitude slope | 8 (15.4%) | 17 (32.7%) | 25 (48.1%) |
| 高海拔山谷 High-altitude valley | 9 (17.3%) | 16 (30.8%) | 24 (46.2%) |
| 低海拔山脊 Low-altitude ridge | 11 (21.2%) | 12 (23.1%) | 23 (44.2%) |
| 低海拔山坡 Low-altitude slope | 12 (23.1%) | 11 (21.2%) | 23 (44.2%) |
| 低海拔山谷 Low-altitude valley | 16 (30.8%) | 11 (21.2%) | 27 (51.9%) |
| 总计 Total | 44 (84.6%) | 35 (67.3%) | 45 (86.5%) |
表4 云南鸡足山亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地物种-生境关联性检验结果
Table 4 Results of species-habitat association tests in the 20 ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan
| 生境类型 Habitat types | 显著正关联物种数 No. of significant positive association species (%) | 显著负关联物种数 No. of significant negative association species (%) | 显著正/负生境关联的总物种数 Total no. of significant positive/ negative association species (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高海拔山脊 High-altitude ridge | 10 (19.2%) | 15 (28.9%) | 25 (48.1%) |
| 高海拔山坡 High-altitude slope | 8 (15.4%) | 17 (32.7%) | 25 (48.1%) |
| 高海拔山谷 High-altitude valley | 9 (17.3%) | 16 (30.8%) | 24 (46.2%) |
| 低海拔山脊 Low-altitude ridge | 11 (21.2%) | 12 (23.1%) | 23 (44.2%) |
| 低海拔山坡 Low-altitude slope | 12 (23.1%) | 11 (21.2%) | 23 (44.2%) |
| 低海拔山谷 Low-altitude valley | 16 (30.8%) | 11 (21.2%) | 27 (51.9%) |
| 总计 Total | 44 (84.6%) | 35 (67.3%) | 45 (86.5%) |
| 物种名 Species | 高海拔山脊 High-altitude ridge | 高海拔山坡 High-altitude slope | 高海拔山谷 High-altitude valley | 低海拔山脊 Low-altitude ridge | 低海拔山坡 Low-altitude slope | 低海拔山谷 Low-altitude valley |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白柯 Lithocarpus dealbatus | + | + | + | - | - | - |
| 白碎米花 Rhododendron spiciferum var. album | - | - | - | + | + | n.s. |
| 刺叶高山栎 Quercus spinosa | - | - | n.s. | n.s. | - | + |
| 粗梗稠李 Prunus napaulensis | - | n.s. | + | - | - | n.s. |
| 大白杜鹃 Rhododendron decorum | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 大叶越桔 Vaccinium petelotii | n.s. | n.s. | - | n.s. | + | n.s. |
| 多依 Docynia indica | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 高盆樱桃 Prunus cerasoides | n.s. | - | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | + |
| 瓜馥木 Fissistigma oldhamii | - | - | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | + |
| 光亮山矾 Symplocos lucida | + | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 猴面柯 Lithocarpus balansae | n.s. | - | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 厚皮香 Ternstroemia gymnanthera | n.s. | - | - | n.s. | + | - |
| 槲树 Quercus dentata | n.s. | + | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 花椒簕 Zanthoxylum scandens | + | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 华山松 Pinus armandii | + | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | - |
| 江南越桔 Vaccinium mandarinorum | - | - | - | n.s. | + | + |
| 蓝黑果荚蒾 Viburnum atrocyaneum | - | - | - | + | - | + |
| 雷公藤 Tripterygium wilfordii | - | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | + |
| 柳叶润楠 Machilus salicina | n.s. | n.s. | + | n.s. | - | n.s. |
| 马缨杜鹃 Rhododendron delavayi | n.s. | + | n.s. | + | n.s. | - |
| 猫儿刺 Ilex pernyi | n.s. | n.s. | + | - | n.s. | n.s. |
| 毛葡萄 Vitis heyneana | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | - | n.s. | + |
| 毛瑞香 Daphne kiusiana var. atrocaulis | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | + |
| 美丽马醉木 Pieris formosa | n.s. | + | - | - | - | - |
| 南烛 Vaccinium bracteatum | + | n.s. | - | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 尼泊尔桤木 Alnus nepalensis | + | + | n.s. | + | - | - |
| 拟蚬壳花椒 Zanthoxylum laetum | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 怒江红山茶 Camellia saluenensis | - | - | n.s. | n.s. | + | + |
| 软条七蔷薇 Rosa henryi | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | + |
| 山鸡椒 Litsea cubeba | + | - | n.s. | - | + | n.s. |
| 珊瑚树 Viburnum odoratissimum | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | + |
| 石灰花楸 Sorbus folgneri | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | + | n.s. | - |
| 鼠李叶花楸 Sorbus rhamnoides | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 水红木 Viburnum cylindricum | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | + | n.s. | n.s. |
| 头状四照花 Cornus capitata | - | - | + | - | - | + |
| 尾叶樟 Camphora foveolata | n.s. | n.s. | + | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 五柱滇山茶 Camellia yunnanensis | - | - | + | - | - | + |
| 响叶杨 Populus adenopoda | - | - | - | - | - | + |
| 野花椒 Zanthoxylum simulans | n.s. | + | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 异叶梁王茶 Metapanax davidii | - | n.s. | + | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 银木荷 Schima argentea | + | + | - | + | + | - |
| 元江锥 Castanopsis orthacantha | + | n.s. | - | n.s. | + | n.s. |
| 云南凹脉柃 Eurya cavinervis | - | n.s. | + | - | + | n.s. |
| 云南杜鹃 Rhododendron yunnanense | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 云南金叶子 Craibiodendron yunnanense | + | - | - | + | n.s. | - |
| 云南松 Pinus yunnanensis | n.s. | n.s. | - | + | n.s. | - |
| 云南小檗 Berberis yunnanensis | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 云南越桔 Vaccinium duclouxii | - | - | - | + | + | n.s. |
| 云南樟 Camphora glandulifera | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 珍珠花 Lyonia ovalifolia | n.s. | + | - | + | - | - |
| 锥序荚蒾 Viburnum pyramidatum | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 紫药女贞 Ligustrum delavayanum | - | - | - | - | - | + |
表5 云南鸡足山亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地目标物种与6种生境的关联性
Table 5 The associations between targeted species and the six habitat types in the 20 ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical semi- humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan
| 物种名 Species | 高海拔山脊 High-altitude ridge | 高海拔山坡 High-altitude slope | 高海拔山谷 High-altitude valley | 低海拔山脊 Low-altitude ridge | 低海拔山坡 Low-altitude slope | 低海拔山谷 Low-altitude valley |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白柯 Lithocarpus dealbatus | + | + | + | - | - | - |
| 白碎米花 Rhododendron spiciferum var. album | - | - | - | + | + | n.s. |
| 刺叶高山栎 Quercus spinosa | - | - | n.s. | n.s. | - | + |
| 粗梗稠李 Prunus napaulensis | - | n.s. | + | - | - | n.s. |
| 大白杜鹃 Rhododendron decorum | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 大叶越桔 Vaccinium petelotii | n.s. | n.s. | - | n.s. | + | n.s. |
| 多依 Docynia indica | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 高盆樱桃 Prunus cerasoides | n.s. | - | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | + |
| 瓜馥木 Fissistigma oldhamii | - | - | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | + |
| 光亮山矾 Symplocos lucida | + | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 猴面柯 Lithocarpus balansae | n.s. | - | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 厚皮香 Ternstroemia gymnanthera | n.s. | - | - | n.s. | + | - |
| 槲树 Quercus dentata | n.s. | + | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 花椒簕 Zanthoxylum scandens | + | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 华山松 Pinus armandii | + | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | - |
| 江南越桔 Vaccinium mandarinorum | - | - | - | n.s. | + | + |
| 蓝黑果荚蒾 Viburnum atrocyaneum | - | - | - | + | - | + |
| 雷公藤 Tripterygium wilfordii | - | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | + |
| 柳叶润楠 Machilus salicina | n.s. | n.s. | + | n.s. | - | n.s. |
| 马缨杜鹃 Rhododendron delavayi | n.s. | + | n.s. | + | n.s. | - |
| 猫儿刺 Ilex pernyi | n.s. | n.s. | + | - | n.s. | n.s. |
| 毛葡萄 Vitis heyneana | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | - | n.s. | + |
| 毛瑞香 Daphne kiusiana var. atrocaulis | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | + |
| 美丽马醉木 Pieris formosa | n.s. | + | - | - | - | - |
| 南烛 Vaccinium bracteatum | + | n.s. | - | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 尼泊尔桤木 Alnus nepalensis | + | + | n.s. | + | - | - |
| 拟蚬壳花椒 Zanthoxylum laetum | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 怒江红山茶 Camellia saluenensis | - | - | n.s. | n.s. | + | + |
| 软条七蔷薇 Rosa henryi | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | + |
| 山鸡椒 Litsea cubeba | + | - | n.s. | - | + | n.s. |
| 珊瑚树 Viburnum odoratissimum | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | + |
| 石灰花楸 Sorbus folgneri | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | + | n.s. | - |
| 鼠李叶花楸 Sorbus rhamnoides | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 水红木 Viburnum cylindricum | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | + | n.s. | n.s. |
| 头状四照花 Cornus capitata | - | - | + | - | - | + |
| 尾叶樟 Camphora foveolata | n.s. | n.s. | + | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 五柱滇山茶 Camellia yunnanensis | - | - | + | - | - | + |
| 响叶杨 Populus adenopoda | - | - | - | - | - | + |
| 野花椒 Zanthoxylum simulans | n.s. | + | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 异叶梁王茶 Metapanax davidii | - | n.s. | + | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 银木荷 Schima argentea | + | + | - | + | + | - |
| 元江锥 Castanopsis orthacantha | + | n.s. | - | n.s. | + | n.s. |
| 云南凹脉柃 Eurya cavinervis | - | n.s. | + | - | + | n.s. |
| 云南杜鹃 Rhododendron yunnanense | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 云南金叶子 Craibiodendron yunnanense | + | - | - | + | n.s. | - |
| 云南松 Pinus yunnanensis | n.s. | n.s. | - | + | n.s. | - |
| 云南小檗 Berberis yunnanensis | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 云南越桔 Vaccinium duclouxii | - | - | - | + | + | n.s. |
| 云南樟 Camphora glandulifera | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 珍珠花 Lyonia ovalifolia | n.s. | + | - | + | - | - |
| 锥序荚蒾 Viburnum pyramidatum | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 紫药女贞 Ligustrum delavayanum | - | - | - | - | - | + |
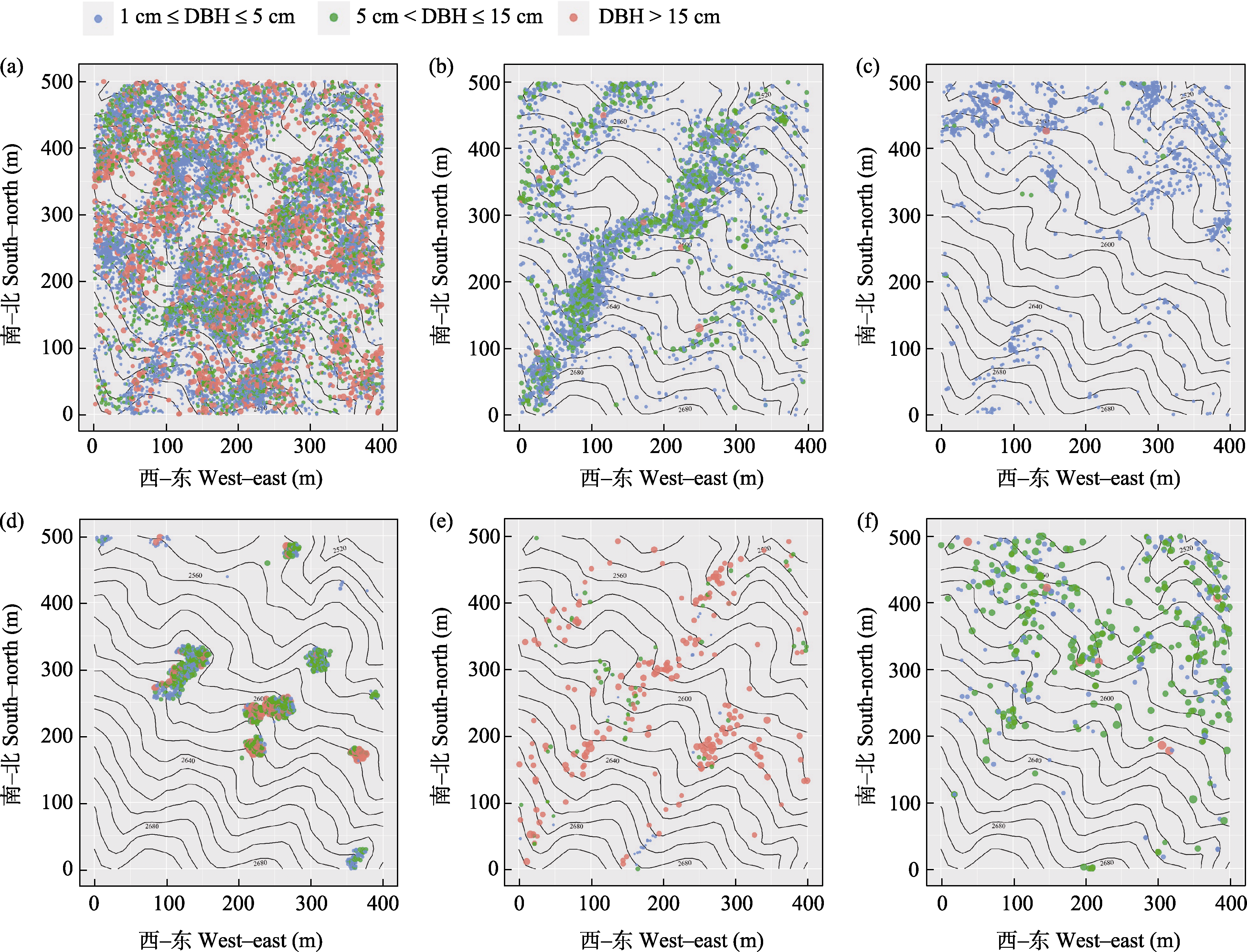
图3 云南鸡足山亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地代表性物种的空间分布图。(a)银木荷; (b)五柱滇山茶; (c)白碎米花; (d)云南金叶子; (e)头状四照花; (f)江南越桔。(a)和(d)是偏好山脊生境的物种; (b)和(e)是偏好山谷生境的物种; (d)和(f)是偏好低海拔生境的物种。
Fig. 3 The spatial distribution maps of representative species in the 20 ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan. (a) Schima argentea; (b) Camellia yunnanensis; (c) Rhododendron spiciferum var. album; (d) Craibiodendron yunnanense; (e) Cornus capitata; (f) Vaccinium mandarinorum. (a) and (d) are species that prefer ridge habitats; (b) and (e) are species that prefer valley habitats; (d) and (f) are species prefer low-altitude habitats.
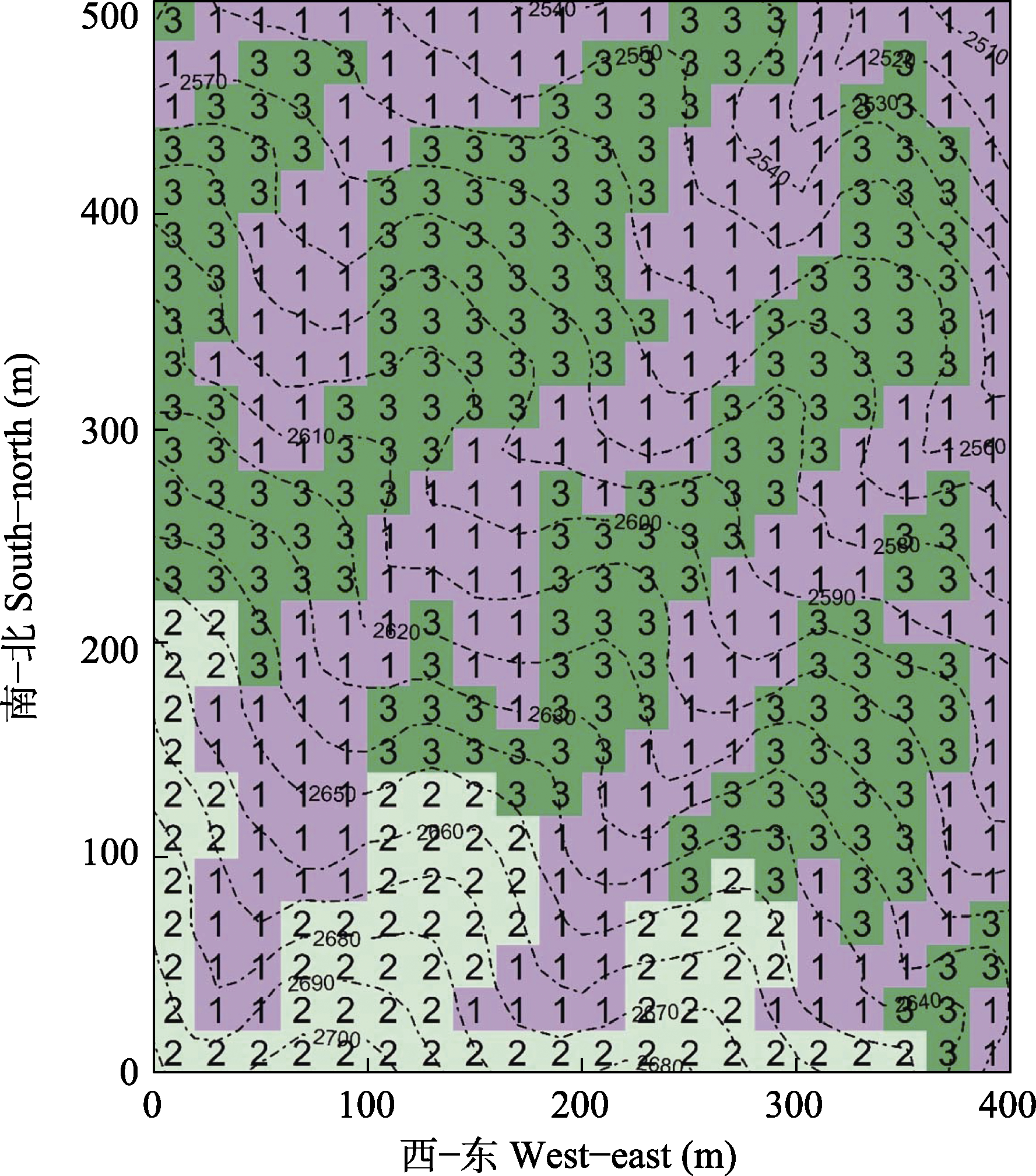
图4 云南鸡足山亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地3个群丛的空间分布图(1-3分别表示群丛1、2、3)
Fig. 4 The spatial distribution maps for the three associations in the 20 ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan (1-3, Association 1-3)
| [1] | Baddeley A, Turner R (2005) spatstat: An R package for analyzing spatial point patterns. Journal of Statistical Software, 12(6), 1-42. |
| [2] |
Chesson P (2000) Mechanisms of maintenance of species diversity. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 31, 343-366.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Comita LS, Condit R, Hubbll SP (2007) Developmental changes in habitat associations of tropical trees. Journal of Ecology, 95, 482-492.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and Comparison with Other Plots. Springer, Berlin. |
| [5] |
Condit R, Ashton PS, Baker P, Bunyavejchewin S, Gunatilleke S, Gunatilleke N, Hubbell SP, Foster RB, Itoh A, LaFrankie JV, Lee HS, Losos E, Manokaran N, Sukumar R, Yamakura T (2000) Spatial patterns in the distribution of tropical tree species. Science, 288, 1414-1418.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | De’Ath G (2002) Multivariate regression trees: A new technique for modeling species-environment relationships. Ecology, 83, 1105-1117. |
| [7] | De’Ath G (2006) mvpart: Multivariate partitioning. R package version 1.2-4. http://cran.r-project.org/. (accessed on 2023-09-15). |
| [8] |
De’Ath G, Fabricius KE (2000) Classification and regression trees: A powerful yet simple technique for ecological data analysis. Ecology, 81, 3178-3192.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Diamond JM (1975) Assembly of species communities. In: Ecology and Evolution of Communities (eds Cody M, Diamond JM), pp. 342-444. Harvard University Press, Cambridge. |
| [10] | Dufrêne M, Legendre P (1997) Species assemblages and indicator species: The need for a flexible asymmetrical approach. Ecological Monographs, 67, 345-366. |
| [11] |
Fick SE, Hijmans RJ (2017) WorldClim 2: New 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. International Journal of Climatology, 37, 4302-4315.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Gunatilleke CVS, Gunatilleke IAUN, Esufali S, Harms KE, Ashton PMS, Burslem DFRP, Ashton PS (2006) Species-habitat associations in a Sri Lankan Dipterocarp Forest. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 22, 371-384.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Guo YL, Wang B, Mallik AU, Huang FZ, Xiang WS, Ding T, Wen SJ, Lu SH, Li DX, He YL, Li XK (2016) Topographic species-habitat associations of tree species in a heterogeneous tropical karst seasonal rain forest, China. Journal of Plant Ecology, 10, 450-460. |
| [14] |
Grubb PJ (1977) The maintenance of species-richness in plant communities: The importance of the regeneration niche. Biological Reviews, 52, 107-145.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Harms KE, Condit R, Hubbell SP, Foster RB (2001) Habitat associations of trees and shrubs in a 50-ha neotropical forest plot. Journal of Ecology, 89, 947-959.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Hesselbarth MH (2021) shar: An R package to analyze species-habitat associations using point pattern analysis. Journal of Open Source Software, 6, 3811.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
HilleRisLambers J, Adler PB, Harpole WS, Levine JM, Mayfield MM (2012) Rethinking community assembly through the lens of coexistence theory. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 43, 227-248.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Huang FZ, Wang B, Ding T, Xiang WS, Li XK, Zhou AP (2014) Numerical classification of associations in a northern tropical karst seasonal rain forest and the relationships of these associations with environmental factors. Biodiversity Science, 22, 157-166. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[黄甫昭, 王斌, 丁涛, 向悟生, 李先琨, 周爱萍 (2014) 弄岗北热带喀斯特季节性雨林群丛数量分类及与环境的关系. 生物多样性, 22, 157-166.]
DOI |
|
| [19] | Hubbell SP, Foster RB (1986) Commonness and rarity in a neotropical forest:Implications for tropical tree conservation. In: Conservation Biology: Science of Scarcity and Diversity (ed. Soule ME), pp. 205-231. Sinauer Press, Sunderland, UK. |
| [20] | Jiang HQ (1980) Distributional features and zonal regularity of vegetation in Yunnan. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 2, 22-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姜汉侨 (1980) 云南植被分布的特点及其地带规律性. 云南植物研究, 2, 22-32.] | |
| [21] |
Keddy PA (1992) Assembly and response rules: Two goals for predictive community ecology. Journal of Vegetation Science, 3, 157-164.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Lai JS, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP (2010) Numerical classification of associations in subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest based on multivariate regression trees―A case study of 24 hm2 Gutianshan forest plot in China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 34, 761-769. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[赖江山, 米湘成, 任海保, 马克平 (2010) 基于多元回归树的常绿阔叶林群丛数量分类——以古田山24公顷森林样地为例. 植物生态学报, 34, 761-769.]
DOI |
|
| [23] |
Lai JS, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP (2009) Species-habitat associations change in a subtropical forest of China. Journal of Vegetation Science, 20, 415-423.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Li SF, Du F, Wang J, Yang YM (2008) Community characteristics and flora of semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in Yuanjiang Nature Reserve. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 37(1), 57-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李帅锋, 杜凡, 王娟, 杨宇明 (2008) 元江自然保护区半湿润常绿阔叶林的群落学及种子植物区系特征. 西部林业科学, 37(1), 57-63.] | |
| [25] |
Li SF, Lang XD, Huang XB, Wang YH, Liu WD, Xu CH, Su JR (2020) Association classification of a 30 hm2dynamics plot in the monsoon broad-leaved evergreen forest in Pu’er, Yunnan, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 44, 236-247. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[李帅锋, 郎学东, 黄小波, 王艳红, 刘万德, 徐崇华, 苏建荣 (2020) 云南普洱30 hm2季风常绿阔叶林动态监测样地群丛数量分类. 植物生态学报, 44, 236-247.]
DOI |
|
| [26] | Li XS, Song L, Chen JW, Yuan CM, Zhang L (2012) Seedling regeneration of the primary semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest and its secondary succession communities in Xishan, Kunming. Guihaia, 32, 475-482. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李小双, 宋亮, 陈军文, 袁春明, 张良 (2012) 昆明西山半湿润常绿阔叶林及其次生演替群落的更新特征. 广西植物, 32, 475-482.] | |
| [27] |
Linares-Palomino R, Alvarez SIP (2005) Tree community patterns in seasonally dry tropical forests in the Cerros de Amotape Cordilera, Tumbes, Peru. Forest Ecology and Management, 209, 261-272.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Liu YC, Miao SL (1992) The study on secondary succession of evergreen broad-leaved forests on Jinyun Mountain, The dynamics of communities and dominant populations. Acta Phytoeclogica et Geobotanica Sinica, 16, 26-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘玉成, 缪世利 (1992) 缙云山常绿阔叶林次生演替优势种群动态. 植物生态学与地植物学学报, 16, 26-35.] | |
| [29] |
Lu ZJ, Bao DC, Guo YL, Lu JM, Wang QG, He D, Zhang KH, Xu YZ, Liu HB, Meng HJ, Huang HD, Wei XZ, Liao JX, Qiao XJ, Jiang MX, Gu ZR, Liao CL (2013) Community composition and structure of Badagongshan (BDGS) Forest Dynamic Plot in a mid-subtropical mountain evergreen and deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest, Central China. Plant Science Journal, 31, 336-344. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [卢志军, 鲍大川, 郭屹立, 路俊盟, 王庆刚, 何东, 张奎汉, 徐耀粘, 刘海波, 孟红杰, 黄汉东, 魏新增, 廖建雄, 乔秀娟, 江明喜, 谷志容, 廖春林 (2013) 八大公山中亚热带山地常绿落叶阔叶混交林物种组成与结构. 植物科学学报, 31, 336-344.] | |
| [30] | Luo L, Song HZ, Liu ZC, Wang HW, Liao WB, Tang L (2019) Schima argentea communities in the middle Luoxiao Mountains. Guihaia, 39, 986-996. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [罗连, 宋含章, 刘忠成, 王浩威, 廖文波, 汤历 (2019) 罗霄山脉中段地区银木荷群落研究. 广西植物, 39, 986-996.] | |
| [31] |
Ma KP (2017) Forest dynamics plot is a crosscutting research platform for biodiversity science. Biodiversity Science, 25, 227-228. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[马克平 (2017) 森林动态大样地是生物多样性科学综合研究平台. 生物多样性, 25, 227-228.]
DOI |
|
| [32] |
Mi XC, Wang XG, Shen GC, Liu XB, Song XY, Qiao XJ, Feng G, Yang J, Mao ZK, Xu XH, Ma KP (2022) Chinese Forest Biodiversity Monitoring Network (CForBio): Twenty years of exploring community assembly mechanisms and prospects for future research. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22504. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[米湘成, 王绪高, 沈国春, 刘徐兵, 宋晓阳, 乔秀娟, 冯刚, 杨洁, 毛子昆, 徐学红, 马克平 (2022) 中国森林生物多样性监测网络: 二十年群落构建机制探索的回顾与展望. 生物多样性, 30, 22504.]
DOI |
|
| [33] | Peng H, Wu ZY (2001) The floristic characteristics and its significance in conservation of semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forests in Mt. Wuliangshan. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 23, 278-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [彭华, 吴征镒 (2001) 无量山半湿润常绿阔叶林的区系特征及保护生物学意义. 云南植物研究, 23, 278-286.] | |
| [34] | Peng MC, Dang CL (1999) The study on community diversity of both Castanopsis orthacantha and C. delavayi communities at Jizu Mountains, Yunnan. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Science Edition), 21, 156-159. (in Chinese) |
| [彭明春, 党承林 (1999) 云南鸡足山元江栲群落和高山栲群落的群落多样性研究. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 21, 156-159.] | |
| [35] | R Core Team (2022) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/. (accessed on 2023-09-15) |
| [36] | Roberts DW (2006) Labdsv: Laboratory for Dynamics Synthetic Vegephenomenology. R package version 1.2-2. . http://cran.r-project.org/. (accessed on 2023-09-15) |
| [37] |
Shi GS, Liu F, Chen D, Deng Y, Lin LX (2021) Species composition and community classification of the 20-ha tropical seasonal rainforest dynamics monitoring plot in the Naban River, Yunnan. Biodiversity Science, 29, 10-20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [施国杉, 刘峰, 陈典, 邓云, 林露湘 (2021) 云南纳板河热带季节雨林20 ha动态监测样地的树种组成与群落分类. 生物多样性, 29, 10-20.] | |
| [38] |
Silvertown J (2004) Plant coexistence and the niche. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 19, 605-611.
DOI URL |
| [39] | Song YC (2001) Vegetation Ecology, 2nd edn. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [宋永昌 (2001) 植被生态学(第二版). 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [40] | Song YC (2004) Tentative classification scheme of evergreen broad-leaved forests of China. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 28, 435-448. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[宋永昌 (2004) 中国常绿阔叶林分类试行方案. 植物生态学报, 28, 435-448.]
DOI |
|
| [41] | Song YC, Wang XH, Yan ER (2013) Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest in China: Classification, Ecology, Conservation. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [宋永昌, 王希华, 阎恩荣 (2013) 中国常绿阔叶林: 分类、生态、保育. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [42] |
Valencia R, Foster RB, Villa G, Condit R, Svenning JC, Hernández C, Romoleroux K, Losos E, Magård E, Balslev H (2004) Tree species distributions and local habitat variation in the Amazon: Large forest plot in eastern Ecuador. Journal of Ecology, 92, 214-229.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Vincent G, Molino JF, Marescot L, Barkaoui K, Sabatier D, Freycon V, Roelens JB (2011) The relative importance of dispersal limitation and habitat preference in shaping spatial distribution of saplings in a tropical moist forest: A case study along a combination of hydromorphic and canopy disturbance gradients. Annals of Forest Science, 68, 357-370.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Wen HD, Lin LX, Yang J, Hu YH, Cao M, Liu YH, Lu ZY, Xie YN (2018) Species composition and community structure of a 20 hm2 plot of mid-mountain moist evergreen broad-leaved forest on the Mts. Ailaoshan, Yunnan Province, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 42, 419-429. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[温韩东, 林露湘, 杨洁, 胡跃华, 曹敏, 刘玉洪, 鲁志云, 谢有能 (2018) 云南哀牢山中山湿性常绿阔叶林20 hm2动态监测样地的物种组成与群落结构. 植物生态学报, 42, 419-429.]
DOI |
|
| [45] |
Wright JS (2002) Plant diversity in tropical forests: A review of mechanisms of species coexistence. Oecologia, 130, 1-14.
DOI PMID |
| [46] | Wu ZY (1979) The regionalization of Chinese flora. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 1, 1-20. (in Chinese) |
| [吴征镒 (1979) 论中国植物区系的分区问题. 云南植物研究, 1, 1-20.] | |
| [47] | Wu ZY, Lu AM, Tang YC, Chen ZD, Li DZ (2003) The Families and Genera of Angiosperms in China:A Comprehensive Analysis. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [吴征镒, 路安民, 汤彦承, 陈之端, 李德铢 (2003) 中国被子植物科属综论. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [48] | Wu ZY, Zhou ZK, Sun H, Peng H (2006) The Areal Types of Seed Plants and Their Origin and Differentiation. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [吴征镒, 周浙昆, 孙航, 彭华 (2006) 种子植物分布区类型及其起源和分化. 云南科技出版社, 昆明.] | |
| [49] |
Yamada T, Zuidema PA, Itoh A, Yamakura T, Ohkubo T, Kanzaki M, Tan S, Ashton PS (2007) Strong habitat preference of a tropical rain forest tree does not imply large differences in population dynamics across habitats. Journal of Ecology, 95, 332-342.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Yang QS, Liu HM, Zhu TT, Zhang SH, Wang XH (2020) Interspecies associations and species-habitat associations in the evergreen broad-leaved forest of Tiantong National Forest Park, Zhejiang. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), (2), 110-119. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨庆松, 刘何铭, 朱彤彤, 张首和, 王希华 (2020) 浙江天童国家森林公园常绿阔叶林种间关联和种-生境关联. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (2), 110-119.] | |
| [51] |
Yang QS, Ma ZP, Xie YB, Zhang ZG, Wang ZH, Liu HM, Li P, Zhang N, Wang DL, Yang HB, Fang XF, Yan ER, Wang XH (2011) Community structure and species composition of an evergreen broad-leaved forest in Tiantong’s 20 ha dynamics plot, Zhejiang Province, eastern China. Biodiversity Science, 19, 215-223. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[杨庆松, 马遵平, 谢玉彬, 张志国, 王樟华, 刘何铭, 李萍, 张娜, 王达力, 杨海波, 方晓峰, 阎恩荣, 王希华 (2011) 浙江天童20 ha常绿阔叶林动态监测样地的群落特征. 生物多样性, 19, 215-223.]
DOI |
|
| [52] | Ye WH, Cao HL, Huang ZL, Lian JY, Wang ZG, Li L, Wei SG, Wang ZM (2008) Community structure of a 20 hm2 lower subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest plot in Dinghushan, China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32, 274-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[叶万辉, 曹洪麟, 黄忠良, 练琚愉, 王志高, 李林, 魏识广, 王章明 (2008) 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林20公顷样地群落特征研究. 植物生态学报, 32, 274-286.]
DOI |
|
| [53] | Zhang F, Zhang JT (2000) Research progress of numerical classification and ordination of vegetation in China. Journal of Shanxi University (Natural Science Edition), 23, 278-282. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张峰, 张金屯 (2000) 我国植被数量分类和排序研究进展. 山西大学学报(自然科学版), 23, 278-282.] | |
| [54] |
Zhang WJ, Zhang QD, Wang J, Feng F, Bi RC (2015) A comparison of multivariate regression tree and two-way indicator species analysis in plant community classification. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 39, 586-592. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[张文静, 张钦弟, 王晶, 冯飞, 毕润成 (2015) 多元回归树与双向指示种分析在群落分类中的应用比较. 植物生态学报, 39, 586-592.]
DOI |
|
| [55] |
Zhu H (2021) Vegetation geography of evergreen broad-leaved forests in Yunnan, southwestern China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 45, 224-241. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [朱华 (2021) 云南常绿阔叶林的植被地理研究. 植物生态学报, 45, 224-241.] | |
| [56] | Zhu Y, Zhao GF, Zhang LW, Shen GC, Mi XC, Ren HB, Yu MJ, Chen JH, Chen SW, Fang T, Ma KP (2008) Community composition and structure of Gutianshan forest dynamics plot in mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest, East China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32, 262-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[祝燕, 赵谷风, 张俪文, 沈国春, 米湘成, 任海保, 于明坚, 陈建华, 陈声文, 方腾, 马克平 (2008) 古田山中亚热带常绿阔叶林动态监测样地——群落组成与结构. 植物生态学报, 32, 262-273.]
DOI |
|
| [57] |
Zuleta D, Russo SE, Barona A, Barreto-Silva JS, Cardenas D, Castaño N, Davies SJ, Detto M, Sua S, Turner BL, Duque A (2020) Importance of topography for tree species habitat distributions in a terra firme forest in the Colombian Amazon. Plant and Soil, 450, 133-149.
DOI |
| [1] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [2] | 杨涛, 沈泽昊, 王晓凤, 饶杰生, 刘文聪, 田希, 陈稀, 张秋雨, 刘倩, 钱恒君, 解宇阳, 刘其明, 徐衍潇, 涂梦灵, 单子铭, 张玉坤, 侯波, 李建斌, 欧晓昆. 滇中高原亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林植物群落多样性特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23238-. |
| [3] | 王晓凤, 饶杰生, 杨涛, 刘文聪, 田希, 陈稀, 刘其明, 徐衍潇, 张秋雨, 张洪强, 张旭, 欧晓昆, 沈泽昊. 云南鸡足山半湿润常绿阔叶林群落木本植物多样性格局与环境解释[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23217-. |
| [4] | 鲁梦珍, 曾馥平, 宋同清, 彭晚霞, 张浩, 苏樑, 刘坤平, 谭卫宁, 杜虎. 喀斯特常绿落叶阔叶林死亡个体空间分布格局及生境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21340-. |
| [5] | 施国杉, 刘峰, 陈典, 邓云, 林露湘. 云南纳板河热带季节雨林20 ha动态监测样地的树种组成与群落分类[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(1): 10-20. |
| [6] | 李霞, 朱万泽, 孙守琴, 舒树淼, 盛哲良, 张军, 刘亭, 张志才. 大渡河中游干暖河谷区生境对植物群落分布格局和多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(2): 117-127. |
| [7] | 陈惠君, 杜虎, 宋同清, 彭晚霞, 张浩, 苏樑, 曾馥平. 木论喀斯特常绿落叶阔叶混交林群丛数量分类及稳定性[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(10): 1056-1068. |
| [8] | 龚雪伟, 吕光辉. 艾比湖流域杜加依林荒漠植物群落多样性及优势种生态位[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(1): 34-45. |
| [9] | 宋永昌, 阎恩荣, 宋坤. 中国常绿阔叶林8大动态监测样地植被的综合比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(2): 139-148. |
| [10] | 卢志军, 刘福玲, 吴浩, 江明喜. 八大公山常绿落叶阔叶混交林枯立木物种组成、大小级与分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(2): 167-173. |
| [11] | 黄甫昭, 王斌, 丁涛, 向悟生, 李先琨, 周爱萍. 弄岗北热带喀斯特季节性雨林群丛数量 分类及与环境的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(2): 157-166. |
| [12] | 谢玉彬, 马遵平, 杨庆松, 方晓峰, 张志国, 阎恩荣, 王希华. 基于地形因子的天童地区常绿树种和落叶树种共存机制研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2012, 20(2): 159-167. |
| [13] | 祝燕, 白帆, 刘海丰, 李文超, 李亮, 李广起, 王顺忠, 桑卫国. 北京暖温带次生林种群分布格局与种间空间关联性[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(2): 252-259. |
| [14] | 赖江山, 张谧, 谢宗强. 三峡库区世坪常绿阔叶林群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2006, 14(5): 435-443. |
| [15] | 赵淑清, 方精云, 宗占江, 朱彪, 沈海花. 长白山北坡植物群落组成、结构及物种多样性的垂直分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2004, 12(1): 164-173. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()