



生物多样性 ›› 2009, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (1): 69-75. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08218 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2009.08218
所属专题: 土壤生物与土壤健康
徐琳1,2, 徐佳洁1, 刘巧莉1, 谢瑞美1, 韦革宏1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2008-08-28
接受日期:2008-12-14
出版日期:2009-01-20
发布日期:2009-01-20
通讯作者:
韦革宏
作者简介:* E-mail: weigehong@yahoo.com.cn基金资助:
Lin Xu1,2, Jiajie Xu1, Qiaoli Liu1, Ruimei Xie1, Gehong Wei1,*( )
)
Received:2008-08-28
Accepted:2008-12-14
Online:2009-01-20
Published:2009-01-20
Contact:
Gehong Wei
摘要:
苦马豆(Sphaerophysa salsula)是荒漠区重要的豆科植物。为了研究其共生根瘤菌的多样性, 本试验采用16S rDNA PCR-RFLP和16S rDNA全序列分析方法, 对西北部分地区的苦马豆根瘤菌进行了遗传多样性及系统发育分析。结果表明, 57株供试菌株共产生了9种遗传图谱类型, 对每种图谱类型的代表性菌株进行16S rDNA全序列分析的结果表明, 它们分别归属于中慢生根瘤菌属(Mesorhizobium)、根瘤菌属(Rhizobium)、中华根瘤菌属(Sinorhizobium)、土壤杆菌属(Agrobacterium)、叶杆菌属(Phyllobacterium)和Shinella kummerowiae。不同地域的菌株在多样性方面也有明显差异: 分离自银川的苦马豆根瘤菌的Jaccard相似性系数较低; 而来自民乐县和临泽县的菌株有着非常丰富的遗传多样性, 其Simpson指数分别为0.826和0.710, Shannon-Wiener指数分别为1.831和1.530。以上结果为进一步确定西北地区豆科植物根瘤菌的系统分类地位提供了依据。
徐琳, 徐佳洁, 刘巧莉, 谢瑞美, 韦革宏 (2009) 西北部分地区苦马豆根瘤菌的遗传多样性. 生物多样性, 17, 69-75. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08218.
Lin Xu, Jiajie Xu, Qiaoli Liu, Ruimei Xie, Gehong Wei (2009) Genetic diversity in rhizobia isolated from Sphaerophysa salsula in several regions of northwestern China. Biodiversity Science, 17, 69-75. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08218.
酶切类型 Fingerprint pattern | 分离地 Location | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甘肃民乐县 Minle County, Gansu | 甘肃张掖市 Zhangye City, Gansu | 甘肃临泽县 Linze County, Gansu | 甘肃玉门市 Yumen City, Gansu | 宁夏银川市 Yinchuan City, Ningxia | 新疆伊犁市 Yili City, Xinjiang | |
| AAB | GS0181, GS0185, GS0188, GS0192, GS0198 | GS0215 | GS0240 | |||
| BBD | GS0184 | GS0218 | GS0237 | |||
| CCB | GS0170, GS0171 GS0168 | GS0219, GS0223, GS0227, GS0230, GS0231, GS0232 | NX0171, NX0172, NX0173 | XJ0216 | ||
| CEB | GS0176, GS0196, GS0199, GS0200, GS0201, GS0204 | GS0206, GS0209 GS0210, GS0214 | GS0216, GS0233 GS0234 | |||
| DDB | GS0228 | |||||
| DFB | GS0172, GS0202 | |||||
| EDB | GS0177, GS0178, GS0187 | GS0238 | ||||
| EDC | GS0166, GS0169, GS0173, GS0180 | GS0207, GS0211, GS0212, GS0213 | GS0220 | XJ0217, XJ0218, XJ0219, XJ0221 | ||
| FDC | XJ0229 | |||||
表1 采自西北部分地区的苦马豆根瘤菌菌株及其16S rDNA PCR-RFLP图谱类型(黑体为16S rDNA测序菌株)
Table 1 16S rDNA PCR-RFLP fingerprint patterns of the rhizobia collected from Sphaerophsa salsula nodules in different regions of northwestern China. The boldfaces are strains for 16S rDNA sequencing.
酶切类型 Fingerprint pattern | 分离地 Location | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甘肃民乐县 Minle County, Gansu | 甘肃张掖市 Zhangye City, Gansu | 甘肃临泽县 Linze County, Gansu | 甘肃玉门市 Yumen City, Gansu | 宁夏银川市 Yinchuan City, Ningxia | 新疆伊犁市 Yili City, Xinjiang | |
| AAB | GS0181, GS0185, GS0188, GS0192, GS0198 | GS0215 | GS0240 | |||
| BBD | GS0184 | GS0218 | GS0237 | |||
| CCB | GS0170, GS0171 GS0168 | GS0219, GS0223, GS0227, GS0230, GS0231, GS0232 | NX0171, NX0172, NX0173 | XJ0216 | ||
| CEB | GS0176, GS0196, GS0199, GS0200, GS0201, GS0204 | GS0206, GS0209 GS0210, GS0214 | GS0216, GS0233 GS0234 | |||
| DDB | GS0228 | |||||
| DFB | GS0172, GS0202 | |||||
| EDB | GS0177, GS0178, GS0187 | GS0238 | ||||
| EDC | GS0166, GS0169, GS0173, GS0180 | GS0207, GS0211, GS0212, GS0213 | GS0220 | XJ0217, XJ0218, XJ0219, XJ0221 | ||
| FDC | XJ0229 | |||||
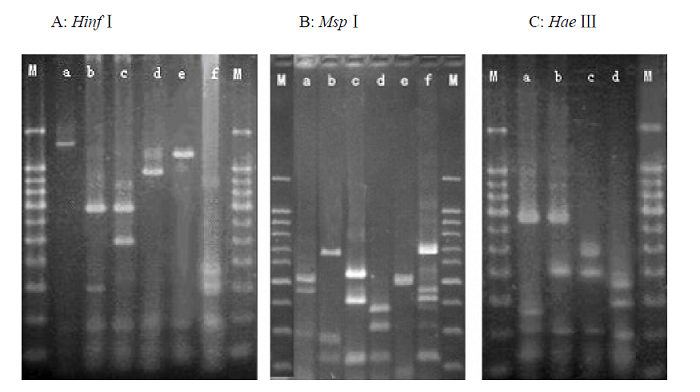
图1 供试菌株的16S rDNA酶切图谱
Fig. 1 16S rDNA PCR-RFLP fingerprint patterns of the tested strains. (A) Digested by Hinf Ⅰ; (B) Digested by MspⅠ; (C) Digested by HaeⅢ
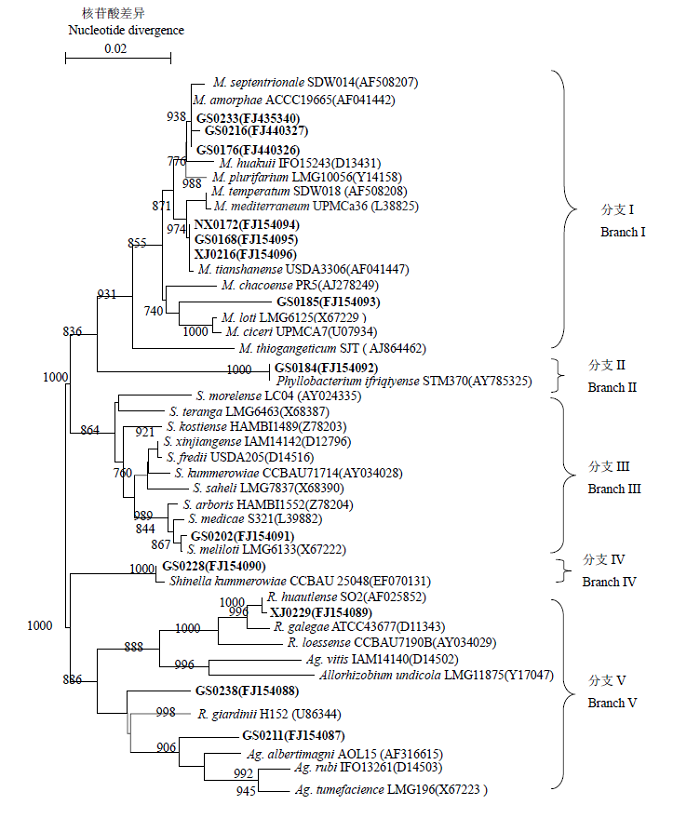
图2 16S rDNA基因系统发育树状图(图中分枝上数字表示树形可信度, 括号内为GenBank登录号。黑体为16S rDNA测序菌株)
Fig. 2 A phylogenetic tree based on 16S rDNA sequences using neighbour-joining method. The figures on the branches indicate the reliabilities. GenBank accession numbers are in the parenthesis. The boldfaces are strains for 16S rDNA sequencing.
| 来源 Location | Jaccard相似性系数 Jaccard similarity coefficient | Simpson 指数 Simpson index | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甘肃张掖市 Zhangye City, Gansu | 甘肃临泽县 Linze County, Gansu | 甘肃玉门市 Yumen City, Gansu | 宁夏银川市 Yinchuan City, Ningxia | 新疆伊犁市 Yili City, Xinjiang | |||
| 甘肃张掖市 Zhangye City, Gansu | 0.593 | 0. 965 | |||||
| 甘肃临泽县 Linze County, Gansu | 0.50 | 0.710 | 1.530 | ||||
| 甘肃玉门市 Yumen City, Gansu | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.500 | 0.693 | |||
| 宁夏银川市 Yinchuan City, Ningxia | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| 新疆伊犁市 Yili City, Xinjiang | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 0.500 | 0.868 | |
| 甘肃民乐县 Minle County, Gansu | 0.38 | 0.56 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.22 | 0.826 | 1.831 |
表2 分离自西北部分地区的苦马豆根瘤菌的16S rDNA相似性系数和多样性指数
Table 2 The Jaccard similarity coefficient and diversity indices of Sphaerophysa salsula rhizobia isolated from different regions of northwestern China
| 来源 Location | Jaccard相似性系数 Jaccard similarity coefficient | Simpson 指数 Simpson index | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甘肃张掖市 Zhangye City, Gansu | 甘肃临泽县 Linze County, Gansu | 甘肃玉门市 Yumen City, Gansu | 宁夏银川市 Yinchuan City, Ningxia | 新疆伊犁市 Yili City, Xinjiang | |||
| 甘肃张掖市 Zhangye City, Gansu | 0.593 | 0. 965 | |||||
| 甘肃临泽县 Linze County, Gansu | 0.50 | 0.710 | 1.530 | ||||
| 甘肃玉门市 Yumen City, Gansu | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.500 | 0.693 | |||
| 宁夏银川市 Yinchuan City, Ningxia | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| 新疆伊犁市 Yili City, Xinjiang | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 0.500 | 0.868 | |
| 甘肃民乐县 Minle County, Gansu | 0.38 | 0.56 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.22 | 0.826 | 1.831 |
| [1] | Beringer JE (1974) R-factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. Journal of General Microbiology, 84, 188-198. |
| [2] | Chen WX (陈文新), Wang ET (汪恩涛), Chen WF (陈文峰) (2004) The relationship between the symbiotic promiscuity of rhizobia and legumes and their geographical environments. Scientia Agricultura Sinica (中国农业科学), 37, 81-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Gao LF (高丽锋), Deng X (邓馨), Wang HX (王洪新) Hu ZA (胡志昂) (2004) Diversity and resistance of rhizobia isolated from Caragana intermedia in Maowusu sandland. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 15, 44-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] | Gaunt MW, Turner SL, Rigottier GL, Rigottier-Gois L, Lloyd-Macgilp SA, Young JPW (2001) Phylogenies of atpD and recA support the small subunit rRNA-based classification of rhizobia. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 51, 2037-2048. |
| [5] | Ma KP (马克平) (1994) The measurement of community diversity. In: Principles and Methodologies of Biodiversity Studies (生物多样性研究的原理与方法), pp. 141-165, China Science and Technology Press, Beijing. |
| [6] |
Mhamdi R, Mrabet M, Laguerre G, Tiwari R, Aouani ME (2005) Colonization of Phaseolus vulgaris nodules by Agrobacterium-like strains. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 51, 105-111.
URL PMID |
| [7] | Martens M, Dawyndt P, Coopman R, Gillis M, De Vos P, Willems A (2008) Advantages of multilocus sequence analysis for taxonomic studies: a case study using 10 housekeeping genes in the genus Ensifer (including former Sinorhizobium). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 58, 200-214. |
| [8] | Peng GX, Tan ZY, Wang ET, Reinhold-Hurek B, Chen WF and Chen WX (2002) Identification of isolates from soybean nodules in Xinjiang region as Sinorhizobium xinjiangense and genetic differentiation of S. xinjiangense from Sinorhizobium fredii. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 52, 457-462. |
| [9] | Selenska-Pobell S, Evguenieva-Hackenberg E, Radeva G, Squartini A (1996) Characterization of Rhizobium‘hedysari’by RFLP analysis of PCR amplified rDNA and by genomic PCR fingerprinting. Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 80, 517-528. |
| [10] |
Stackebrandt E, Frederiksen W, Garrity GM, Grimont PAD, Kampfer P, Maiden MCJ, Nesme X, Rossello-Mora R, Swings J, Truper HG, Vauterin L, Ward AC, Whitman WB (2002) Report of the ad hoc committee for the re-evaluation of the species definition in bacteriology. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 52, 1043-1047.
URL PMID |
| [11] | Tan ZY (谭志远), Chen WX (陈文新) (1997) Sequencing the 16S rDNA of representative strain of new rhizobial group and determining of its phylogenetic relationship. Acta Microbiologica Sinica (微生物学报), 37, 411-416. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] |
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X Windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 4876-4882.
URL PMID |
| [13] | van de Peer Y, De Wachter R (1994) TREECON for Windows: a software package for the construction and drawing of evolutionary trees for the Microsoft Windows environment. Computer Applications in the Bioscience, 10, 569-570. |
| [14] | Vandamme P, Pot B, Gillis M, de Vos P, Kersters K, Swings J (1996) Polyphasic taxonomy, a consensus approach to bacterial systematics. Microbiological Reviews, 60, 407-438. |
| [15] | Vincent JM (1970) A Manual for the Practical Study of Rroot-Nodule Bacteria. IBP Handbook 15. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford. |
| [16] | Wang LL, Wang ET, Liu J, Li Y, Chen WX (2006) Endophytic occupation of root nodules and roots of Melilotus dentatus by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Microbial Ecology, 52, 436-443. |
| [17] | Wu D (吴达), Shi YP (师彦平), Liang B (梁冰), Wang JH (王建华) (2003) Advances in studies on swainsonine. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs (中草药), 34, A5-7. (in Chinese) |
| [18] | Xu L (徐莉), Yang JK (杨江科), Zhang WT (张伟涛), Yuan TY (袁天英), Zhou JC (周俊初) (2007) Phenotypic and genetic diversity of cowpea rhizobia. Acta Ecologica Sinina (生态学报), 27, 3655-3662. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Yang J, Hu Z, Guo GQ, Zheng GC (2001) In vitro plant regeneration from cotyledon explants of Swainsona salsula Taubert. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, 66, 35-39. |
| [20] | Yao RC (姚荣成) (2003) Advances in studies on Swainsona salsula. The Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice (药学实践杂志), 21, 43-44. (in Chinese) |
| [21] | Zhang Y (张英) (1999) The nutrition and feed value of Sphaerophysa salsula Tauberts. Feed Research (饲料研究), (7), 22. (in Chinese) |
| [22] | Zou L (邹林), Yang MQ (杨鸣琦) (2006) Progress on anti-tumor activity of swainsonine. Progress in Veterinary Medicine (动物医学进展), 27(4), 36-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [2] | 孙亚君. 何谓高等或低等生物——澄清《物种起源》所蕴含的生物等级性的涵义及其成立性[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24394-. |
| [3] | 艾妍雨, 胡海霞, 沈婷, 莫雨轩, 杞金华, 宋亮. 附生维管植物多样性及其与宿主特征的相关性: 以哀牢山中山湿性常绿阔叶林为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24072-. |
| [4] | 吕燕文, 王子韵, 肖钰, 何梓晗, 吴超, 胡新生. 谱系分选理论与检测方法的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23400-. |
| [5] | 曹可欣, 王敬雯, 郑国, 武鹏峰, 李英滨, 崔淑艳. 降水格局改变及氮沉降对北方典型草原土壤线虫多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [6] | 王斌, 钟艺倩, 杨美雪, 吴淼锐, 王艳萍, 陆芳, 陶旺兰, 李健星, 赵弘明, 刘晟源, 向悟生, 李先琨. 喀斯特季节性雨林优势树种叶片非结构性碳水化合物空间变异及生态驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24325-. |
| [7] | 杨向林, 赵彩云, 李俊生, 种方方, 李文金. 植物入侵导致群落谱系结构更加聚集: 以广西国家级自然保护区草本植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [8] | 何林君, 杨文静, 石宇豪, 阿说克者莫, 范钰, 王国严, 李景吉, 石松林, 易桂花, 彭培好. 火烧干扰下植物群落系统发育和功能多样性对紫茎泽兰入侵的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24269-. |
| [9] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [10] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [11] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [12] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [13] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [14] | 李治中, 彭帅, 王青锋, 李伟, 梁士楚, 陈进明. 中国海菜花属植物隐种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22394-. |
| [15] | 宋会银, 胡征宇, 刘国祥. 绿藻门小球藻科的分类学研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22083-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn