



Biodiv Sci ›› 2011, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (1): 34-40. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07098 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2011.07098
Special Issue: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全
• Special Issue • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2010-04-22
Accepted:2010-10-03
Online:2011-01-20
Published:2011-04-01
Contact:
Weikai Bao
Xin Liu, Weikai Bao. Community structure and vascular plant species composition of primary spruce forest near timberline in the eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2011, 19(1): 34-40.
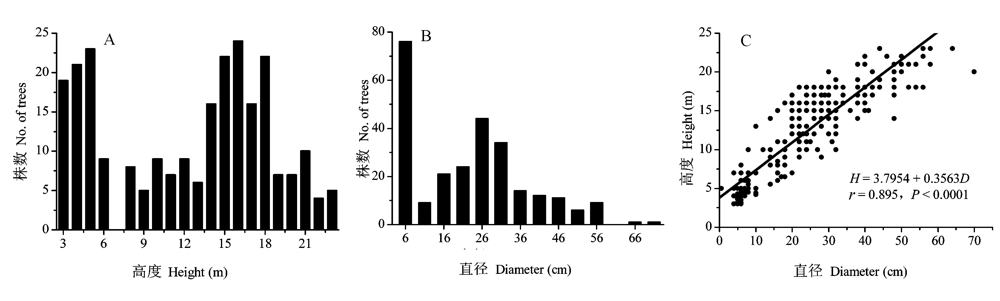
Fig. 1 Size distribution of tree height (A), diameter at 50 cm height (B), and the height-diameter relationship (C) of trees in the primary spruce forest near timberline in the eastern Tibetan Plateau
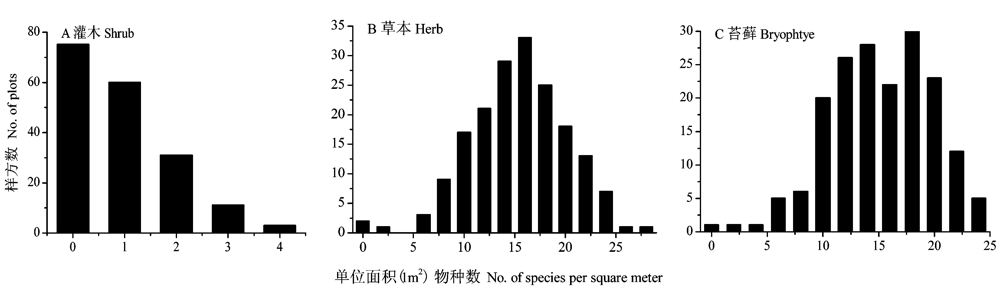
Fig. 2 Frequency distribution of species richness of shrub (A), herb (B), bryophyte (C) under the primary spruce forest near timberline in the eastern Tibetan Plateau (180 subplots)
| 物种 Species | 生活型 Life form | 频度 Frequency | 重要值 Importance value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 草本层 Herb layer | ||||
| 明亮苔草 | Carex laeta | H 地面芽植物 | 0.8222 | 0.1616 |
| 狭苞橐吾 | Ligularia intermedia | H 地面芽植物 | 0.6278 | 0.1463 |
| 珠芽蓼 | Polygonum viviparum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.8278 | 0.1237 |
| 圆叶小堇菜 | Viola biflora var. rockiana | H 地面芽植物 | 0.8278 | 0.0891 |
| 细叶芨芨草 | Achnatherum chingii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2778 | 0.0804 |
| 箭叶橐吾 | Ligularia sagitta | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2667 | 0.0777 |
| 柳叶菜风毛菊 | Saussurea epilobioides | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3889 | 0.0620 |
| 梅氏雀麦 | Bromus mairei | H 地面芽植物 | 0.4333 | 0.0604 |
| 纤细草莓 | Fragaria gracilis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.6222 | 0.0567 |
| 东方草莓 | F. orientalis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.5278 | 0.0512 |
| 萎软紫菀 | Aster flaccidus | G 地下芽植物 | 0.5556 | 0.0491 |
| 喜巴早熟禾 | Poa hylobates | H 地面芽植物 | 0.4500 | 0.0488 |
| 紫花碎米荠 | Cardamine tangutorum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.5111 | 0.0449 |
| 高山露珠草 | Circaea alpina | H 地面芽植物 | 0.4500 | 0.0445 |
| 疏花剪股颖 | Agrostis hookeriana | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3833 | 0.0409 |
| 膨囊苔草 | Carex lehmanii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2556 | 0.0383 |
| 四齿无心菜 | Arenaria quadridentata | H 地面芽植物 | 0.6000 | 0.0378 |
| 弯齿风毛菊 | Saussurea przewalskii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2444 | 0.0337 |
| 狭叶红景天 | Rhodiola kirilowii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2333 | 0.0328 |
| 毛茛一种 | Ranunculus sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0278 | 0.0286 |
| 羊茅 | Festuca ovina | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1667 | 0.0274 |
| 高原毛茛 | Ranunculus tanguticus | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3889 | 0.0255 |
| 星叶草 | Circaeaster agrestis | Th 一年生植物 | 0.2389 | 0.0235 |
| 细毛拉拉藤 | Galium pusillosetosum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3111 | 0.0217 |
| 紫堇一种 | Corydalis sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2889 | 0.0199 |
| 湿地勿忘草 | Myosotis caespitosa | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2389 | 0.0190 |
| 条裂黄堇 | Corydalis linarioides | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2722 | 0.0182 |
| 肾叶金腰 | Chrysosplenium griffithii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2722 | 0.0181 |
| 长茎囊瓣芹 | Pternopetalum longicaule | G 地下芽植物 | 0.2722 | 0.0170 |
| 黄三七 | Souliea vaginata | G 地下芽植物 | 0.1722 | 0.0162 |
| 细柄茅 | Ptilagrostis mongholica | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1167 | 0.0157 |
| 微孔草 | Microula sikkimensis | Th 一年生植物 | 0.2278 | 0.0157 |
| 轮叶马先蒿 | Pedicularis verticillata | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1722 | 0.0144 |
| 小花缬草 | Valeriana minutiflora | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1611 | 0.0129 |
| 猪殃殃 | Galium aparine var. echinospermum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1778 | 0.0124 |
| 剪股颖一种 | Agrostis sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0833 | 0.0117 |
| 柔毛蓼 | Polygonum sparsipilosum | Th 一年生植物 | 0.1500 | 0.0115 |
| 异花孩儿参 | Pseudostellaria heterantha | G 地下芽植物 | 0.1611 | 0.0103 |
| 蕨叶千里光 | Senecio pteridophyllus | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0778 | 0.0098 |
| 大果红景天 | Rhodiola macrocarpa | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1056 | 0.0097 |
| 康定鼠尾草 | Salvia prattii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0944 | 0.0096 |
| 雀麦一种 | Bromux sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0722 | 0.0091 |
| 羌活 | Notopterygium incisum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0833 | 0.0089 |
| 单枝灯心草 | Juncus potaninii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0889 | 0.0082 |
| 耳蕨一种 | Polystichum sp. | G 地下芽植物 | 0.1056 | 0.0080 |
| 长叶微孔草 | Microula trichocarpa | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0667 | 0.0077 |
| 驴蹄草 | Caltha palustris | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0500 | 0.0073 |
| 唐古拉婆婆纳 | Veronica vandellioides | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1056 | 0.0072 |
| 早熟禾一种 | Poa sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0500 | 0.0072 |
| 毛脉柳叶菜 | Epilobium amurense | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0889 | 0.0068 |
| 阿洼早熟禾 | Poa araratica | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0667 | 0.0065 |
| 光籽柳叶菜 | Epilobium tibetanum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0944 | 0.0065 |
| 掌叶大黄 | Rheum palmatum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0061 |
| 二色香青同色变种 | Anaphalis bicolor var. subconcolor | Ch 地上芽植物 | 0.0667 | 0.0059 |
| 长芒披碱草 | Elymus dolichatherus | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0611 | 0.0056 |
| 针刺悬钩子 | Rubus pungens | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0054 |
| 黑水翠雀花 | Delphinium potaninii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0333 | 0.0051 |
| 甘青老鹳草 | Geranium pylzowianum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0722 | 0.0050 |
| 轮叶黄精 | Polygonatum verticillatum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0722 | 0.0049 |
| 单花拉拉藤 | Galium exile | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0667 | 0.0044 |
| 毛果婆婆纳 | Veronica eriogyne | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0611 | 0.0041 |
| 紫茎小芹 | Sinocarum coloratum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0444 | 0.0035 |
| 杯花韭 | Allium cyathophorum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0444 | 0.0031 |
| 柳兰 | Chamerion angustifolium subsp. angustifoliam | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0029 |
| 岩生剪股颖 | Agrostis rupestris | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0278 | 0.0027 |
| 曲枝早熟禾 | Poa pagophila | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0025 |
| 川西风毛菊 | Saussurea dzeurensis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0389 | 0.0025 |
| 毛葶苈 | Draba eriopoda | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0333 | 0.0023 |
| 簇生泉卷耳 | Cerastium fontanum subsp. vulgare | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0333 | 0.0023 |
| 玉山香青 | Anaphalis morrisonicola | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0167 | 0.0022 |
| 冷蕨 | Cystopteris fragilis | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0278 | 0.0020 |
| 丝叶苔草 | Carex capilliformis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0019 |
| 中华金腰 | Chrysosplenium sinicum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0018 |
| 肾叶毛茛 | Ranunculus sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0167 | 0.0017 |
| 多榔菊 | Doronicum stenoglossum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0017 |
| 异色红景天 | Rhodiola discolor | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0015 |
| 爪瓣虎耳草 | Saxifraga unguiculata | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0014 |
| 隐瓣蝇子草 | Silene gonosperma | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0167 | 0.0011 |
| 毛茛一种 | Ranunculus sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3778 | 0.0011 |
| 甘肃苔草 | Carex kansusis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0011 |
| 高山嵩草 | Kobresia pygmaea | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0011 |
| 苔草一种 | Carex sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0010 |
| 极丽马先蒿 | Pedicularis decorissima | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0010 |
| 大叶碎米荠 | Cardamine macrophylla | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0010 |
| 五脉绿绒蒿 | Meconopsis quintuplinervia | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0009 |
| 草玉梅 | Anemone rivularis | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0009 |
| 马先蒿一种 | Pedicularis sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0008 |
| 全冠黄堇 | Corydalis tongolensis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0008 |
| 中亚早熟禾 | Poa litwinowiana | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0008 |
| 具爪曲花紫堇 | Corydalis curviflora subsp. rosthornii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0008 |
| 腺毛蝇子草 | Silene yetii | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 东亚囊瓣芹 | Pternopetalum tanakae | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 滇藏无心菜 | Arenaria napuligera | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 假水生龙胆 | Gentiana pseudoaquatica | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 湿生扁蕾 | Gentianopsis paludosa | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 林地早熟禾 | Poa nemoralis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0005 |
| 史蒂瓦早熟禾 | Poa himalayana | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 菊状千里光 | Senecio laetus | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 短茎囊瓣芹 | Pternopetalum longicaule var. humile | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 沼兰 | Malaxis monophyllos | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 钻裂风铃草 | Campanula aristata | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 紫羊茅 | Festuca rubra | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 葱状灯心草 | Juncus allioides | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 双叉细柄茅 | Ptilagrostis dichotoma | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 长穗三毛草 | Trisetum clarkei | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0003 |
| 异叶囊瓣芹 | Pternopetalum heterophyllum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0003 |
| 椭圆叶花锚 | Halenia elliptica | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0003 |
| 长果母草 | Lindernia anagallis | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0003 |
| 灌木层 Shrub layer | ||||
| 云杉幼苗 | Picea spp. | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.1444 | 0.0227 |
| 银露梅 | Potentilla glabra | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.1389 | 0.0219 |
| 绵穗柳 | Salix eriostachya | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0778 | 0.0202 |
| 峨眉蔷薇 | Rosa omeiensis | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0611 | 0.0193 |
| 冰川茶藨子 | Ribes glaciale | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.1111 | 0.0187 |
| 细枝绣线菊 | Spiraea myrtilloides | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.1333 | 0.0132 |
| 华西忍冬 | Lonicera webbiana | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0556 | 0.0131 |
| 刚毛忍冬 | L. hispida | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0778 | 0.0124 |
| 金露梅 | Potentilla fruticosa | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0389 | 0.0114 |
| 唐古特忍冬 | Lonicera tangutica | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0042 |
| 细梗蔷薇 | Rosa graciliflora | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0278 | 0.0026 |
| 硬叶柳 | Salix sclerophylla | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0167 | 0.0025 |
| 川西樱桃 | Cerasus trichostoma | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0012 |
| 天山茶藨子 | Ribes meyeri | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0009 |
| 柳一种 | Salix sp. | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
Appendix I Species composition and their importance value of vascular plants under the primary spruce forests near alpine timberline in Zamtang County, Sichuan Province, China. (Ph, phanerophytes; Ch, chamaephytes; H, hemicryptophytes; C, cryptophytes; Th, therophytes)
| 物种 Species | 生活型 Life form | 频度 Frequency | 重要值 Importance value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 草本层 Herb layer | ||||
| 明亮苔草 | Carex laeta | H 地面芽植物 | 0.8222 | 0.1616 |
| 狭苞橐吾 | Ligularia intermedia | H 地面芽植物 | 0.6278 | 0.1463 |
| 珠芽蓼 | Polygonum viviparum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.8278 | 0.1237 |
| 圆叶小堇菜 | Viola biflora var. rockiana | H 地面芽植物 | 0.8278 | 0.0891 |
| 细叶芨芨草 | Achnatherum chingii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2778 | 0.0804 |
| 箭叶橐吾 | Ligularia sagitta | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2667 | 0.0777 |
| 柳叶菜风毛菊 | Saussurea epilobioides | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3889 | 0.0620 |
| 梅氏雀麦 | Bromus mairei | H 地面芽植物 | 0.4333 | 0.0604 |
| 纤细草莓 | Fragaria gracilis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.6222 | 0.0567 |
| 东方草莓 | F. orientalis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.5278 | 0.0512 |
| 萎软紫菀 | Aster flaccidus | G 地下芽植物 | 0.5556 | 0.0491 |
| 喜巴早熟禾 | Poa hylobates | H 地面芽植物 | 0.4500 | 0.0488 |
| 紫花碎米荠 | Cardamine tangutorum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.5111 | 0.0449 |
| 高山露珠草 | Circaea alpina | H 地面芽植物 | 0.4500 | 0.0445 |
| 疏花剪股颖 | Agrostis hookeriana | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3833 | 0.0409 |
| 膨囊苔草 | Carex lehmanii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2556 | 0.0383 |
| 四齿无心菜 | Arenaria quadridentata | H 地面芽植物 | 0.6000 | 0.0378 |
| 弯齿风毛菊 | Saussurea przewalskii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2444 | 0.0337 |
| 狭叶红景天 | Rhodiola kirilowii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2333 | 0.0328 |
| 毛茛一种 | Ranunculus sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0278 | 0.0286 |
| 羊茅 | Festuca ovina | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1667 | 0.0274 |
| 高原毛茛 | Ranunculus tanguticus | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3889 | 0.0255 |
| 星叶草 | Circaeaster agrestis | Th 一年生植物 | 0.2389 | 0.0235 |
| 细毛拉拉藤 | Galium pusillosetosum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3111 | 0.0217 |
| 紫堇一种 | Corydalis sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2889 | 0.0199 |
| 湿地勿忘草 | Myosotis caespitosa | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2389 | 0.0190 |
| 条裂黄堇 | Corydalis linarioides | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2722 | 0.0182 |
| 肾叶金腰 | Chrysosplenium griffithii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2722 | 0.0181 |
| 长茎囊瓣芹 | Pternopetalum longicaule | G 地下芽植物 | 0.2722 | 0.0170 |
| 黄三七 | Souliea vaginata | G 地下芽植物 | 0.1722 | 0.0162 |
| 细柄茅 | Ptilagrostis mongholica | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1167 | 0.0157 |
| 微孔草 | Microula sikkimensis | Th 一年生植物 | 0.2278 | 0.0157 |
| 轮叶马先蒿 | Pedicularis verticillata | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1722 | 0.0144 |
| 小花缬草 | Valeriana minutiflora | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1611 | 0.0129 |
| 猪殃殃 | Galium aparine var. echinospermum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1778 | 0.0124 |
| 剪股颖一种 | Agrostis sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0833 | 0.0117 |
| 柔毛蓼 | Polygonum sparsipilosum | Th 一年生植物 | 0.1500 | 0.0115 |
| 异花孩儿参 | Pseudostellaria heterantha | G 地下芽植物 | 0.1611 | 0.0103 |
| 蕨叶千里光 | Senecio pteridophyllus | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0778 | 0.0098 |
| 大果红景天 | Rhodiola macrocarpa | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1056 | 0.0097 |
| 康定鼠尾草 | Salvia prattii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0944 | 0.0096 |
| 雀麦一种 | Bromux sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0722 | 0.0091 |
| 羌活 | Notopterygium incisum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0833 | 0.0089 |
| 单枝灯心草 | Juncus potaninii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0889 | 0.0082 |
| 耳蕨一种 | Polystichum sp. | G 地下芽植物 | 0.1056 | 0.0080 |
| 长叶微孔草 | Microula trichocarpa | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0667 | 0.0077 |
| 驴蹄草 | Caltha palustris | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0500 | 0.0073 |
| 唐古拉婆婆纳 | Veronica vandellioides | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1056 | 0.0072 |
| 早熟禾一种 | Poa sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0500 | 0.0072 |
| 毛脉柳叶菜 | Epilobium amurense | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0889 | 0.0068 |
| 阿洼早熟禾 | Poa araratica | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0667 | 0.0065 |
| 光籽柳叶菜 | Epilobium tibetanum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0944 | 0.0065 |
| 掌叶大黄 | Rheum palmatum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0061 |
| 二色香青同色变种 | Anaphalis bicolor var. subconcolor | Ch 地上芽植物 | 0.0667 | 0.0059 |
| 长芒披碱草 | Elymus dolichatherus | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0611 | 0.0056 |
| 针刺悬钩子 | Rubus pungens | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0054 |
| 黑水翠雀花 | Delphinium potaninii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0333 | 0.0051 |
| 甘青老鹳草 | Geranium pylzowianum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0722 | 0.0050 |
| 轮叶黄精 | Polygonatum verticillatum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0722 | 0.0049 |
| 单花拉拉藤 | Galium exile | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0667 | 0.0044 |
| 毛果婆婆纳 | Veronica eriogyne | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0611 | 0.0041 |
| 紫茎小芹 | Sinocarum coloratum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0444 | 0.0035 |
| 杯花韭 | Allium cyathophorum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0444 | 0.0031 |
| 柳兰 | Chamerion angustifolium subsp. angustifoliam | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0029 |
| 岩生剪股颖 | Agrostis rupestris | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0278 | 0.0027 |
| 曲枝早熟禾 | Poa pagophila | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0025 |
| 川西风毛菊 | Saussurea dzeurensis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0389 | 0.0025 |
| 毛葶苈 | Draba eriopoda | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0333 | 0.0023 |
| 簇生泉卷耳 | Cerastium fontanum subsp. vulgare | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0333 | 0.0023 |
| 玉山香青 | Anaphalis morrisonicola | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0167 | 0.0022 |
| 冷蕨 | Cystopteris fragilis | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0278 | 0.0020 |
| 丝叶苔草 | Carex capilliformis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0019 |
| 中华金腰 | Chrysosplenium sinicum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0018 |
| 肾叶毛茛 | Ranunculus sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0167 | 0.0017 |
| 多榔菊 | Doronicum stenoglossum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0017 |
| 异色红景天 | Rhodiola discolor | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0015 |
| 爪瓣虎耳草 | Saxifraga unguiculata | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0014 |
| 隐瓣蝇子草 | Silene gonosperma | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0167 | 0.0011 |
| 毛茛一种 | Ranunculus sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3778 | 0.0011 |
| 甘肃苔草 | Carex kansusis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0011 |
| 高山嵩草 | Kobresia pygmaea | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0011 |
| 苔草一种 | Carex sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0010 |
| 极丽马先蒿 | Pedicularis decorissima | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0010 |
| 大叶碎米荠 | Cardamine macrophylla | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0010 |
| 五脉绿绒蒿 | Meconopsis quintuplinervia | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0009 |
| 草玉梅 | Anemone rivularis | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0009 |
| 马先蒿一种 | Pedicularis sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0008 |
| 全冠黄堇 | Corydalis tongolensis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0008 |
| 中亚早熟禾 | Poa litwinowiana | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0008 |
| 具爪曲花紫堇 | Corydalis curviflora subsp. rosthornii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0008 |
| 腺毛蝇子草 | Silene yetii | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 东亚囊瓣芹 | Pternopetalum tanakae | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 滇藏无心菜 | Arenaria napuligera | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 假水生龙胆 | Gentiana pseudoaquatica | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 湿生扁蕾 | Gentianopsis paludosa | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 林地早熟禾 | Poa nemoralis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0005 |
| 史蒂瓦早熟禾 | Poa himalayana | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 菊状千里光 | Senecio laetus | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 短茎囊瓣芹 | Pternopetalum longicaule var. humile | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 沼兰 | Malaxis monophyllos | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 钻裂风铃草 | Campanula aristata | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 紫羊茅 | Festuca rubra | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 葱状灯心草 | Juncus allioides | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 双叉细柄茅 | Ptilagrostis dichotoma | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 长穗三毛草 | Trisetum clarkei | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0003 |
| 异叶囊瓣芹 | Pternopetalum heterophyllum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0003 |
| 椭圆叶花锚 | Halenia elliptica | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0003 |
| 长果母草 | Lindernia anagallis | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0003 |
| 灌木层 Shrub layer | ||||
| 云杉幼苗 | Picea spp. | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.1444 | 0.0227 |
| 银露梅 | Potentilla glabra | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.1389 | 0.0219 |
| 绵穗柳 | Salix eriostachya | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0778 | 0.0202 |
| 峨眉蔷薇 | Rosa omeiensis | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0611 | 0.0193 |
| 冰川茶藨子 | Ribes glaciale | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.1111 | 0.0187 |
| 细枝绣线菊 | Spiraea myrtilloides | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.1333 | 0.0132 |
| 华西忍冬 | Lonicera webbiana | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0556 | 0.0131 |
| 刚毛忍冬 | L. hispida | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0778 | 0.0124 |
| 金露梅 | Potentilla fruticosa | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0389 | 0.0114 |
| 唐古特忍冬 | Lonicera tangutica | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0042 |
| 细梗蔷薇 | Rosa graciliflora | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0278 | 0.0026 |
| 硬叶柳 | Salix sclerophylla | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0167 | 0.0025 |
| 川西樱桃 | Cerasus trichostoma | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0012 |
| 天山茶藨子 | Ribes meyeri | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0009 |
| 柳一种 | Salix sp. | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| [1] | Bao WK (包维楷), Zhang YL (张镱锂), Wang Q (王乾), Bai WQ (摆万奇), Zheng D (郑度) (2002) Plant diversity along a time sequence (1-30 years) of artificial forest rehabilitation on subalpine cut land in the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 26,194-198. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [2] | Collaboration Group of Sichuan Vegetation (四川植被协作组) (1980) Sichuan Vegetation (四川植被). Sichuan People’s Publishing House, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [3] | Duan RY (段仁燕), Wang XA (王孝安), Huang MY (黄敏毅), Wang ZG (王志高), Wu GL (吴甘霖) (2010) Ecological characteristics of Larix chinensis population near timberline on Taibai Mountain in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 30,519-526. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] |
Gosz JR (1993) Ecotone hierarchies. Ecological Applications, 3,369-376.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] | Guan ZT (管中天) (2005) Forest Ecology Research and Application (森林生态研究与应用). Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [6] | Han JJ (韩景军), Xiao WF (肖文发), Luo JC (罗菊春) (2000) Effects of different cutting methods on regeneration and habitat for spruce-fir forests. Scientia Silvae Sinicae (林业科学), 36(1),90-96. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | He JC (何吉成), Luo TX (罗天祥), Xu YQ (徐雨晴) (2009) Characteristics of eco-climate at smith fir timberline in the Sergyemla Mountains, southeast Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 29,37-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Hooper DU, Chapin FS III, Ewel JJ, Hector A, Inchausti P, Lavorel S, Lawton JH, Lodge DM, Loreau M, Naeem S, Schmid B, Setala H, Symstad AJ, Vandermeer J, Wardle DA (2005) Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: a consensus of current knowledge. Ecological Monographs, 75,3-35. |
| [9] | Li MC (李明财), Luo TX (罗天祥), Liu XS (刘新圣), Kong GQ (孔高强) (2007) Distribution characteristics of δ 13C values in different organs of Abies georgei growing at alpine timberline. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 18,2654-2660. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [10] | Li MH (李迈和), Norbert K (2005) The state of knowledge on alpine treeline and suggestions for future research. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology (四川林业科技), 26(4),36-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Li WH (李文华) (1982) An overview of dark coniferous forest in Tibet. Journal of Natural Resources (自然资源), 6(2),1-16. (in Chinese) |
| [12] | Li WH (李文华), Zhou PC (周沛村) (1979) Study on the distribution of dark coniferous forests in Eurasia and its mathematical model. Journal of Natural Resources (自然资源), 3(1),21-34. (in Chinese) |
| [13] | Liu JH (刘俊华), Bao WK (包维楷), Li FL (李芳兰) (2005) Major bryophyte patch structures and their relationships with environmental factors under a coniferous forest of eastern Tibetan Plateau. Ecology and Environment (生态环境), 14,735-741. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Liu Q (刘庆) (2002) Ecological Research on Subalpine Coniferous Forests in China (亚高山针叶林生态学研究). Sichuan University Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [15] | Pang XY (庞学勇), Bao WK (包维楷), Zhang YM (张咏梅) (2005) Microclimate changes and plant succession in dark coniferous clear-cutting forestland in eastern Tibetan Plateau. World Science-Technology R & D (世界科技研究与发展), 27(3),47-53. |
| [16] | Qinghai Forest Editorial Committee (青海森林编辑委员会) (1993) Forest in Qinghai Province (青海森林). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [17] | Shi PL (石培礼) (1999) A Study on the Vegetation Ecology of Subalpine Timberline Ecotone (亚高山林线生态交错带的植被生态学研究). PhD dissertation, Institute of Geographic Science and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [18] | Shi PL (石培礼), Li WH (李文华), Wang JX (王金锡) (2002) Three-dimensional canopy structure in the timberline ecotone dominated by Abies faxoniana. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 11,1819-1824. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | The Editorial Board of Forests in Sichuan (四川森林编辑委员会) (1992) Forests in Sichuan (四川森林). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [20] | Theurillat JP, Guisan A (2001) Potential impact of climate change on vegetation in the European Alps: a review. Climate Change, 50,77-109. |
| [21] |
Tilman D, Reich PB, Knops JMH (2006) Biodiversity and ecosystem stability in a decade long grassland experiment. Nature, 441,629-632.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] | Wang JX (王金锡), Xu JD (许金铎), Hou GW (侯广维), Liu JB (刘建邦), Pu JT (蒲佳泰), Shi LX (史立新), Liao GY (廖光瑶) (1995) Ecology and Regeneration of Cutted Blank in Alpine and Plateau Region of the Upper Reach of Yangtze River (长江上游高山高原林区迹地生态与营林更新技术). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [23] | Wang XP (王襄平), Zhang L (张玲), Fang JY (方精云) (2004) Geographical differences in alpine timberline and its climatic interpretation in China. Acta Geographica Sinica (地理学报), 59,871-879. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] | Wu ZY (吴征镒) (1991) The areal-types of Chinese genera of seed plants. Acta Botanica Yunnanica (云南植物研究), 13 (Suppl., IV),1-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Wu ZY (吴征镒), Zhou ZK (周浙昆), Li DZ (李德铢), Peng H (彭华), Sun H (孙航) (2003) The areal-types of the world families of seed plants. Acta Botanica Yunnanica (云南植物研究), 25,245-257. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | Xu LJ (许林军), Peng H (彭鸿), Chen CG (陈存根), Tang HL (唐红亮), Yang YJ (杨亚娟) (2005) Quantitative analysis of the Larix chinensis forest’s distribution at Qinling Mountains and the character of the alpine timberline at Taibai Mountain. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica (西北植物学报), 25,968-972. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Yan XL (闫晓丽), Bao WK (包维楷) (2008) Evaluation of species composition and development of bryophyte community during early natural recovery progress of high-altitude spruce cutovers. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 16,110-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Zar JH (1999) Biostatistical Analysis. Prentcie Hall, New Jersey. |
| [29] | Zhang QY (张桥英), Luo P (罗鹏), Zhang YC (张运春), Shi FS (石福孙), Yi SL (易绍良), Wu N (吴宁) (2008) Ecological characteristics of Abies georgei population at timberline on the north-facing slope of Baima Snow Mountain, southwest China. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 28,129-135. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [30] | Zhang QY (张桥英), Zhang YC (张运春), Luo P (罗鹏), Wang Q (王乾), Wu N (吴宁) (2007) Ecological characteristics of a Sabina saltuaria population at timberline on the south-facing slope of Baima Snow Mountain, southwest China. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 31,857-864. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | Mingyi Zhang, Xiaomei Wang, Yanxin Zheng, Nan Wu, Donghao Li, Enyuan Fan, Na Li, Xiujuan Shan, Tao Yu, Chunnuan Zhao, Bo Li, Shuai Xu, Yuping Wu, Liqun Ren. Resource status and habitat function of typical oyster reef areas in the Yellow River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [2] | Jingyi Yuan, Xu Zhang, Zhenpeng Tian, Zizhe Wang, Yongping Gao, Dizhao Yao, Hongcan Guan, Wenkai Li, Jing Liu, Hong Zhang, Qin Ma. A comparison of methods for extracting tree species composition and quantitative characteristics in urban plant communities using UAV high-resolution RGB imagery and LiDAR point cloud [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24237-. |
| [3] | Tong Miao, Wang Huan, Zhang Wenshuang, Wang Chao, Song Jianxiao. Distribution characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes in soil bacterial communities exposed to heavy metal pollution [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [4] | Ma Wenjun, Liu Sijia, Li Kemao, Jian Shenglong, Xue Chang’an, Han Qingxiango, Wei Jinliang, Chen Shengxue, Niu Yimeng, Cui Zhouping, Sui Ruichen, Tian Fei, Zhao Kai. Fish diversity and distribution in the source region of the Yangtze River in Qinghai Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [5] | Li Yanpeng, Chen Jie, Lu Chunyang, Xu Han. Community characteristics of a 64-ha secondary forest dynamics plot in a tropical montane rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [6] | Shiyu Wei, Tianjiao Song, Jiayi Luo, Yan Zhang, Zixuan Zhao, Jingwen Ru, Hua Yi, Yanbing Lin. Altitudinal distribution patterns of soil bacterial communities in the Huoditang coniferous forests of the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [7] | Yongqiang Shi, Qingshan Luan, Xiujuan Shan, Chao Wei, Yongsong Zhao, Cece Sun, Xianshi Jin. Annual changes in zooplankton biodiversity in the southern waters of Changdao [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [8] | Yongqiang Zhao, Xiyu Yan, Jiaqi Xie, Mengting Hou, Danmei Chen, Lipeng Zang, Qingfu Liu, Mingzhen Sui, Guangqi Zhang. Species diversity and community assembly of woody plants at different life history stages during the natural restoration of degraded karst forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [9] | Yanmei Ni, Li Chen, Zhiyuan Dong, Debin Sun, Baoquan Li, Xumin Wang, Linlin Chen. Community structure of macrobenthos and ecological health evaluation in the restoration area of the Yellow River Delta wetland [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [10] | Jiaxin Wei, Zhiguo Jiang, Linsen Yang, Huanhuan Xiong, Jiaojiao Jin, Fanglin Luo, Jiehua Li, Hao Wu, Yaozhan Xu, Xiujuan Qiao, Xinzeng Wei, Hui Yao, Huiliang Yu, Jingyuan Yang, Mingxi Jiang. Community composition and structure in a 25 ha mid-subtropical mountain deciduous broad-leaved forest dynamics plot in Shennongjia, Hubei, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [11] | Di Lin, Shuanglin Chen, Que Du, Wenlong Song, Gu Rao, Shuzhen Yan. Investigation of species diversity of myxomycetes in Dabie Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23242-. |
| [12] | Xiaolin Liu, Yougui Wu, Minhua Zhang, Xiaorong Chen, Zhicheng Zhu, Dingyun Chen, Shu Dong, Buhang Li, Bingyang Ding, Yu Liu. Community composition and structure of a 25-ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical forest in Baishanzu, Zhejiang Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [13] | Fangfang Wu, Na Liu, Chunmei He, Zuoqiang Yuan, Zhanqing Hao, Qiulong Yin. Elevational gradient pattern of woody plant community structure and diversity in the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [14] | Hang Shan, Zupei Lei, Fangdong Zheng, Boliang Wei, Lei Zhong, Mingjian Yu. Dynamic changes in the community of a secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest in Wuyanling, Zhejiang Province from 2013 to 2023 [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24372-. |
| [15] | Jia Yao, Congling Zhang, Shixuan Li, Yang Lin, Zhen Wang, Yuhan Zhang, Weilong Zhou, Xinhe Pan, Shan Zhu, Yiqing Wu, Dan Wang, Jinliang Liu, Shanshan Tan, Guochun Shen, Mingjian Yu. Characteristics of plant communities in the Baishanzu continuous elevational transect [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24052-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()
