



Biodiv Sci ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (9): 24180. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024180 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024180
• Microbial Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Shiyu Wei( ), Tianjiao Song, Jiayi Luo, Yan Zhang, Zixuan Zhao, Jingwen Ru, Hua Yi, Yanbing Lin*(
), Tianjiao Song, Jiayi Luo, Yan Zhang, Zixuan Zhao, Jingwen Ru, Hua Yi, Yanbing Lin*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-05-10
Accepted:2024-07-22
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-08-26
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:Shiyu Wei, Tianjiao Song, Jiayi Luo, Yan Zhang, Zixuan Zhao, Jingwen Ru, Hua Yi, Yanbing Lin. Altitudinal distribution patterns of soil bacterial communities in the Huoditang coniferous forests of the Qinling Mountains[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24180.
| 海拔 Altitude (m) | pH | 土壤有机质 SOM (g/kg) | 全氮 TN (g/kg) | 全磷 TP (g/kg) | 全钾 TK (g/kg) | 碱解氮 AN (mg/kg) | 速效磷 AP (mg/kg) | 速效钾 AK (mg/kg) | C/N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | 1582 | 5.95 ± 0.04b | 341.29 ± 13.57a | 14.1 ± 0.58a | 1.07 ± 0.03a | 12.61 ± 0.51b | 713.08 ± 24.31a | 35.76 ± 5.59a | 175 ± 7.81a | 24.21 ± 0.48b |
| 1874 | 7.26 ± 0.1a | 62.96 ± 29.31b | 2.36 ± 1.01b | 0.65 ± 0.26b | 13.91 ± 0.77b | 159.67 ± 50.58b | 34.87 ± 25.31a | 203.33 ± 104.84a | 26.25 ± 2.49b | |
| 2400 | 5.8 ± 0.27b | 91.64 ± 9.18b | 3 ± 0.28b | 0.78 ± 0.02ab | 22.51 ± 2.33a | 239.01 ± 47.34b | 43.8 ± 8.68a | 210.33 ± 15.82a | 30.49 ± 0.48a | |
| L | 1578 | 5.55 ± 0.26b | 70.36 ± 35.09a | 3.37 ± 1.84a | 0.67 ± 0.23a | 20.41 ± 1.03a | 228.16 ± 102.01a | 13.82 ± 5.89a | 239.33 ± 96.77a | 21.26 ± 1.21c |
| 1809 | 6.94 ± 0.36a | 58.22 ± 1.99a | 2.7 ± 0.05a | 0.81 ± 0.08a | 17.5 ± 1.29b | 178.89 ± 5.17a | 36.32 ± 13.6a | 222.33 ± 23.71a | 21.56 ± 0.64c | |
| 1979 | 5.67 ± 0.32b | 61.09 ± 43.85a | 2.02 ± 1.48a | 0.76 ± 0.05a | 19.67 ± 0.93ab | 146.36 ± 71.48a | 41.78 ± 18.87a | 186 ± 48.45a | 30.47 ± 0.6a |
Table 1 Changes of soil physical and chemical properties in two types of coniferous forests along the altitude gradients (mean ± SD)
| 海拔 Altitude (m) | pH | 土壤有机质 SOM (g/kg) | 全氮 TN (g/kg) | 全磷 TP (g/kg) | 全钾 TK (g/kg) | 碱解氮 AN (mg/kg) | 速效磷 AP (mg/kg) | 速效钾 AK (mg/kg) | C/N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | 1582 | 5.95 ± 0.04b | 341.29 ± 13.57a | 14.1 ± 0.58a | 1.07 ± 0.03a | 12.61 ± 0.51b | 713.08 ± 24.31a | 35.76 ± 5.59a | 175 ± 7.81a | 24.21 ± 0.48b |
| 1874 | 7.26 ± 0.1a | 62.96 ± 29.31b | 2.36 ± 1.01b | 0.65 ± 0.26b | 13.91 ± 0.77b | 159.67 ± 50.58b | 34.87 ± 25.31a | 203.33 ± 104.84a | 26.25 ± 2.49b | |
| 2400 | 5.8 ± 0.27b | 91.64 ± 9.18b | 3 ± 0.28b | 0.78 ± 0.02ab | 22.51 ± 2.33a | 239.01 ± 47.34b | 43.8 ± 8.68a | 210.33 ± 15.82a | 30.49 ± 0.48a | |
| L | 1578 | 5.55 ± 0.26b | 70.36 ± 35.09a | 3.37 ± 1.84a | 0.67 ± 0.23a | 20.41 ± 1.03a | 228.16 ± 102.01a | 13.82 ± 5.89a | 239.33 ± 96.77a | 21.26 ± 1.21c |
| 1809 | 6.94 ± 0.36a | 58.22 ± 1.99a | 2.7 ± 0.05a | 0.81 ± 0.08a | 17.5 ± 1.29b | 178.89 ± 5.17a | 36.32 ± 13.6a | 222.33 ± 23.71a | 21.56 ± 0.64c | |
| 1979 | 5.67 ± 0.32b | 61.09 ± 43.85a | 2.02 ± 1.48a | 0.76 ± 0.05a | 19.67 ± 0.93ab | 146.36 ± 71.48a | 41.78 ± 18.87a | 186 ± 48.45a | 30.47 ± 0.6a |
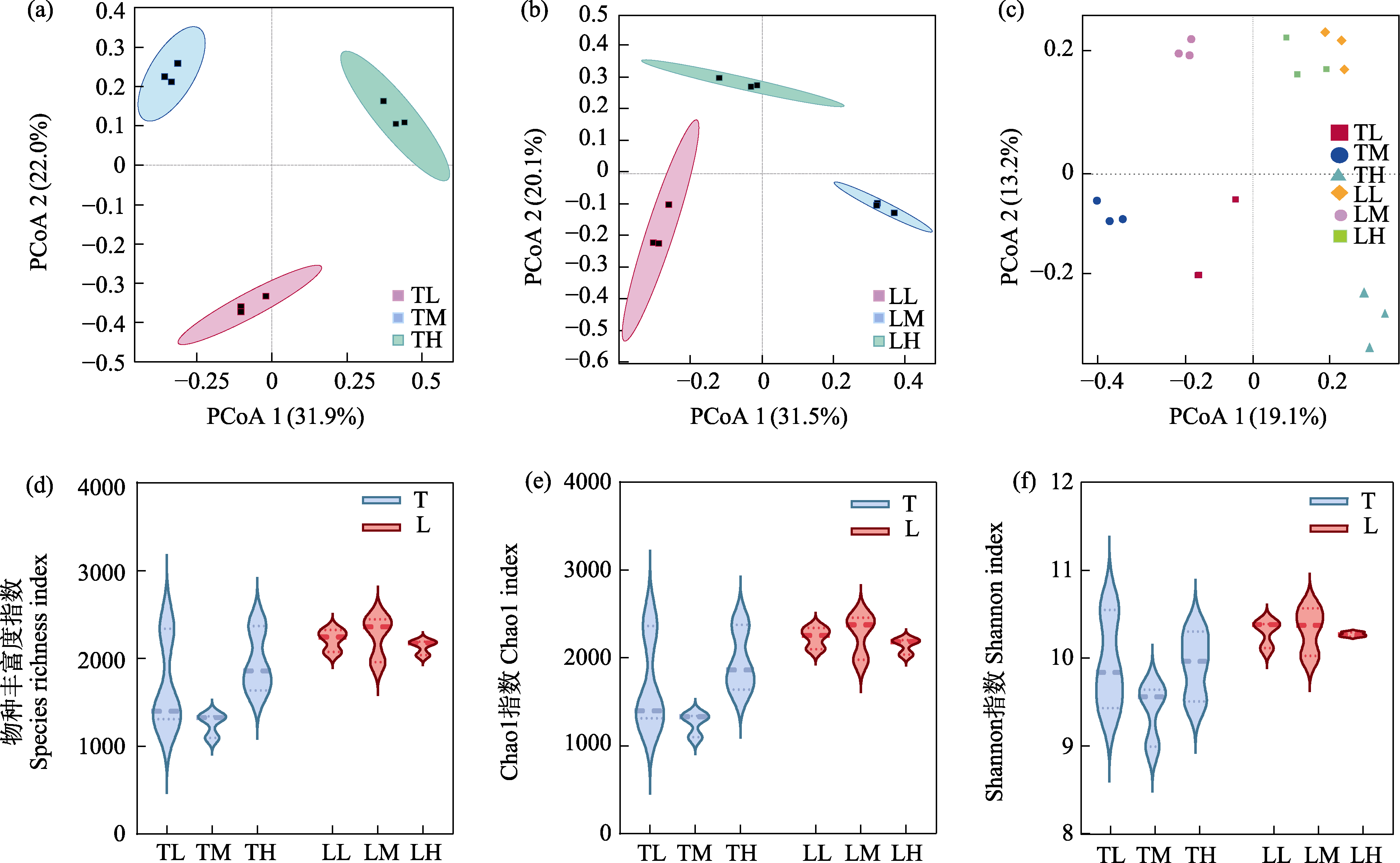
Fig. 1 Structure and diversity of soil microbial communities in two types of coniferous forests. (a-c), PcoA (principal co-ordinates analysis) based on Bray-Curtis; (d-f), α-diversity values. T, Tsuga chinensis forest; L, Larix principis-rupprechtii forest; TL, Low-altitude T. chinensis forest; TM, Mid-altitude T. chinensis forest; TH, High-altitude T. chinensis forest; LL, Low-altitude L. principis-rupprechtii forest; LM, Mid-altitude L. principis-rupprechtii forest; LH, High-altitude L. principis-rupprechtii forest.
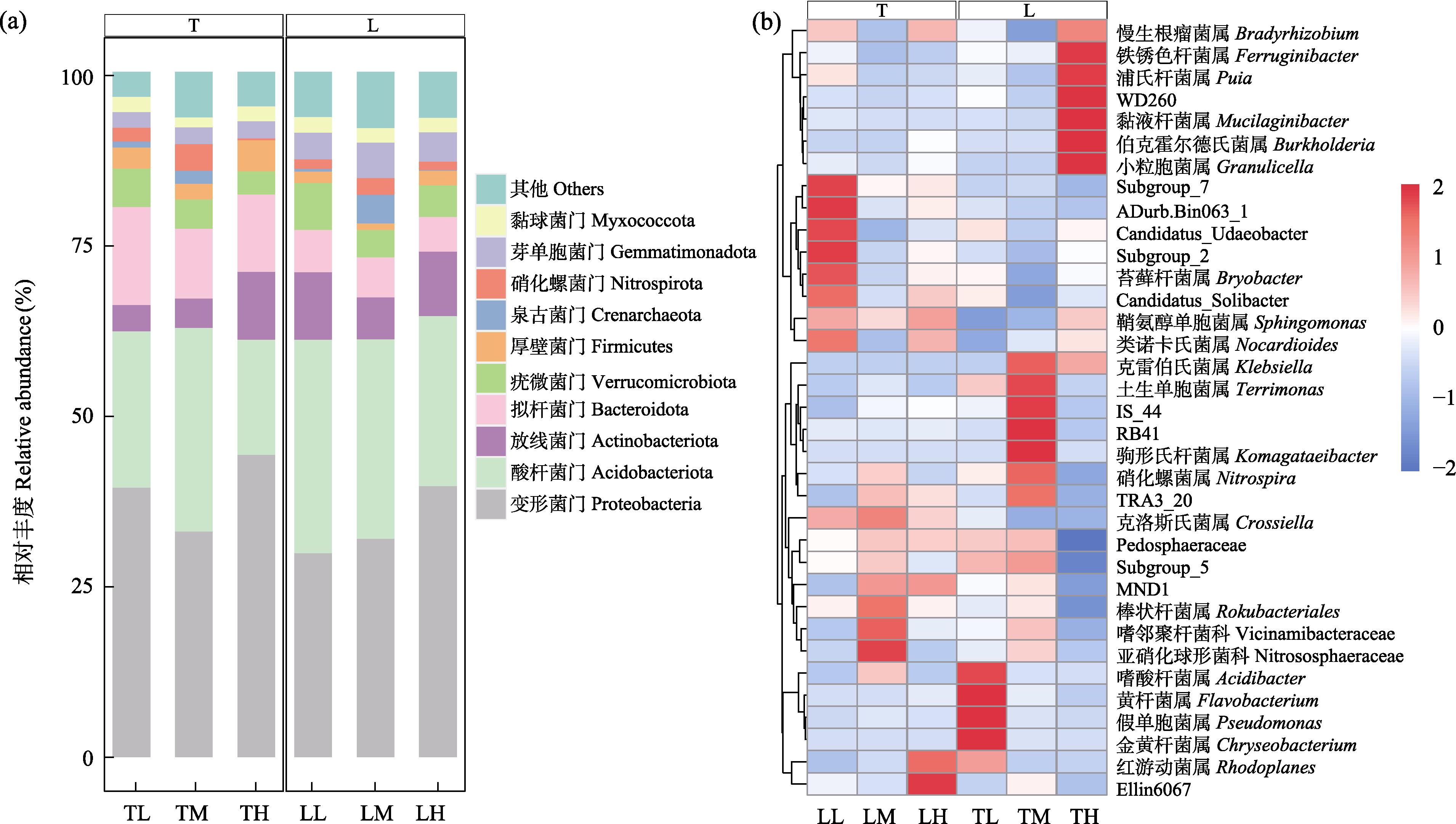
Fig. 2 Relative abundance of soil microbial communities at the phylum level (a) and genus level (b) in two types of coniferous forests. T, Tsuga chinensis forest; L, Larix principis-rupprechtii forest; TL, Low-altitude T. chinensis forest; TM, Mid-altitude T. chinensis forest; TH, High-altitude T. chinensis forest; LL, Low-altitude L. principis-rupprechtii forest; LM, Mid-altitude L. principis-rupprechtii forest; LH, High-altitude L. principis-rupprechtii forest. The colour shades in the scale bar on the right side of figure (b) indicate the degree of difference between the genus abundance and the mean value. Based on the mean value of genus abundance in the same sample, values above the mean are positive and marked in red; on the contrary, values below the mean are negative and marked in blue.
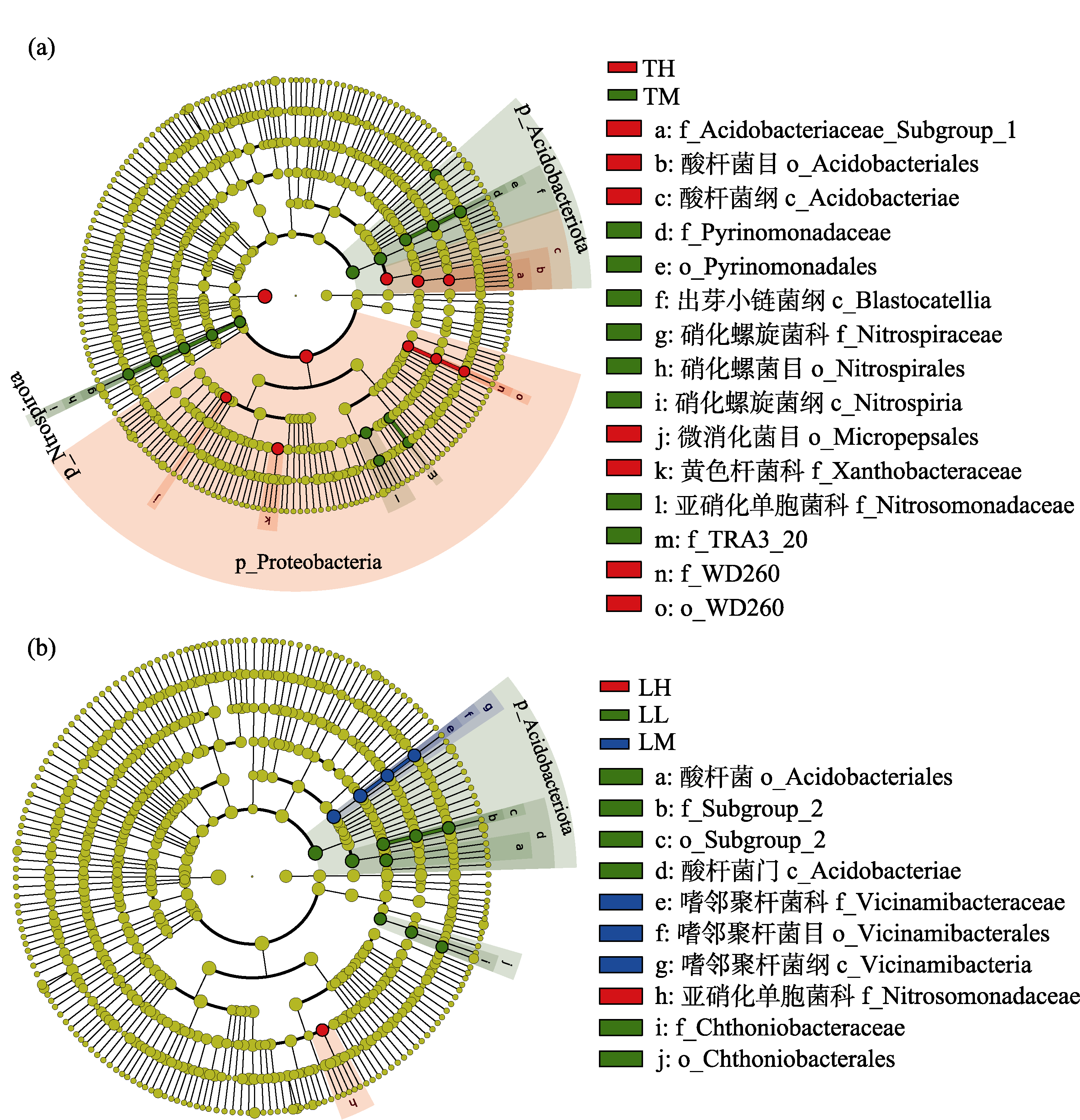
Fig. 3 LEfSe (linear discriminant analysis effect size ) showing soil community differences at different altitudes in Tsuga chinensis forest (a) and Larix principis-rupprechtii forest (b). Each circular ring deposits all taxa within a taxonomic level, and the circular ring from inside to outside represents supergroup, phylum, class, order, and family, respectively. The node on the circular ring represents taxon, affiliating within the taxonomic level. The diameter of each node is proportional to the abundance of the group. Taxa that have significantly higher relative abundance in a certain treatment within each altitude gradient are color-coded within the cladogram. TM, Mid-altitude T. chinensis forest; TH, High-altitude T. chinensis forest; LL, Low-altitude L. principis-rupprechtii forest; LM, Mid-altitude L. principis-rupprechtii forest; LH, High-altitude L. principis-rupprechtii forest.
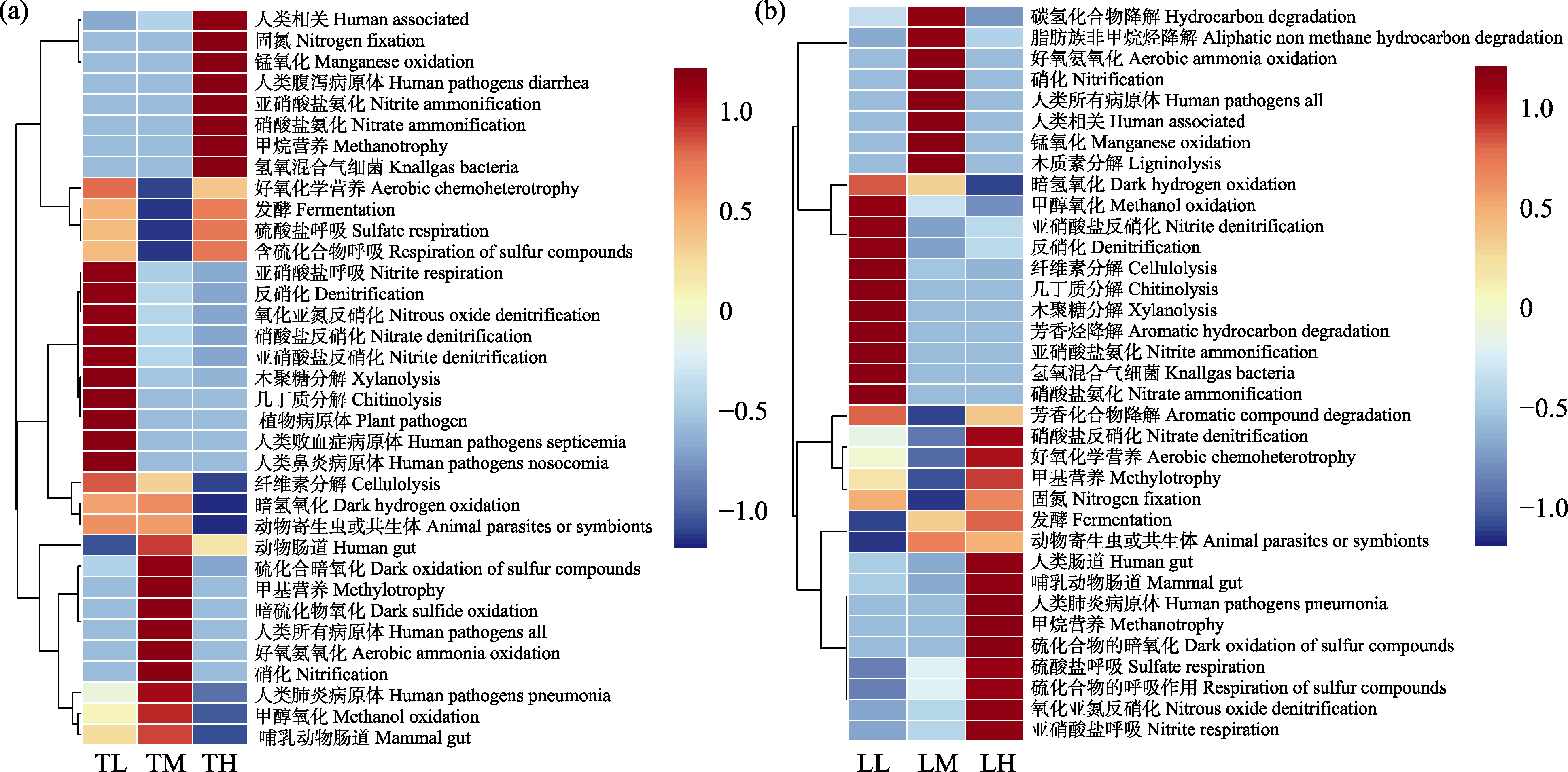
Fig. 4 FAPROTAX functional prediction of soil bacterial communities across different altitudinal gradients of Tsuga chinensis forest (a) and Larix principis-rupprechtii forest (b). The color shades indicate the degree of difference between the expression of metabolic function and the mean. The average value of gene expression in the same sample is used as the benchmark, and the expression above the average is positive, and the mark is red; conversely, the expression below the average is a negative value and marked as blue. TL, Low-altitude T. chinensis forest; TM, Mid-altitude T. chinensis forest; TH, High-altitude T. chinensis forest; LL, Low-altitude L. principis-rupprechti forest; LM, Mid-altitude L. principis-rupprechtii forest; LH, High-altitude L. principis-rupprechtii forest.
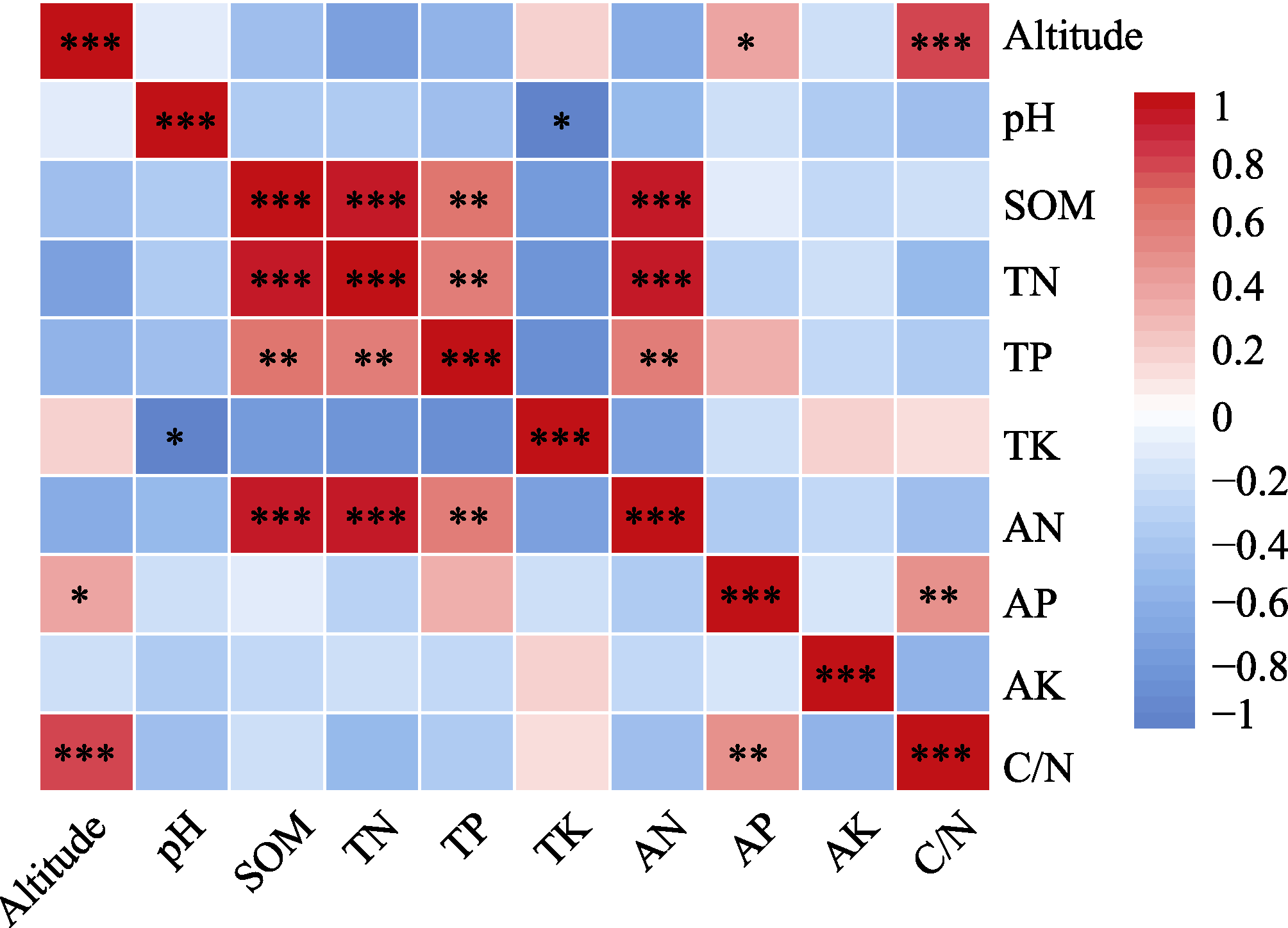
Fig. 5 Correlation analysis of environmental factors. Altitude, Altitude; pH, Soil pH; SOM, Soil organic matter; TN, Total nitrogen; TP, Total phosphorus; TK, Total potassium; AN, Available nitrogen; AP, Available phosphorus; AK, Available potassium; C/N, Carbon to nitrogen ratio. The values in the right scale bar indicate the Pearson correlation coefficients. The color of the square indicates the direction of the correlation, where red indicates positive correlation and blue indicates negative correlation, and the darker color indicates the stronger correlation. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.
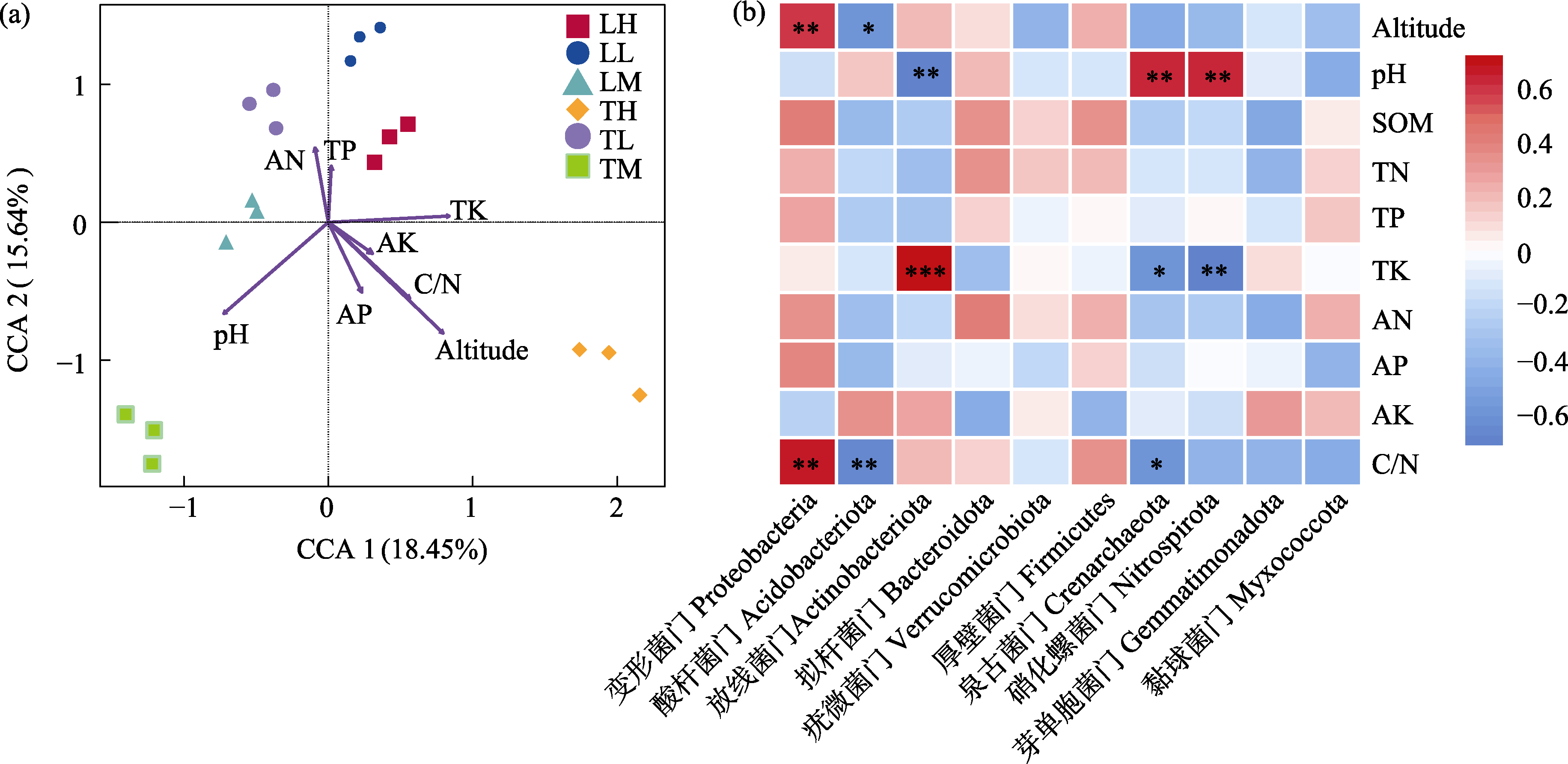
Fig. 6 Correlation analysis between environmental factors and soil microbial communities. (a) Canonical correspondence analysis; (b) Spearman correlation analysis. Altitude, Altitude; SOM, Soil organic matter; TN, Total nitrogen; TP, Total phosphorus; TK, Total potassium; AN, Available nitrogen; AP, Available phosphorus; AK, Available potassium; C/N, Carbon to nitrogen ratio. The color of the bar indicates the Spearman’s correlation coefficients, where red indicates positive correlation and blue indicates negative correlation, and the darker color indicates the stronger correlation. TL, Low-altitude Tsuga chinensis forest; TM, Mid-altitude T. chinensis forest; TH, High-altitude T. chinensis forest; LL, Low-altitude Larix principis-rupprechtii forest; LM, Mid-altitude L. principis-rupprechtii forest; LH, High-altitude L. principis-rupprechtii forest. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.
| [1] | Ahmedin AM, Elias E (2022) Effects of habitat gradient and agro-climatic variation on selected soil physical and chemical properties in the Bale Mountains National Park, south-eastern Ethiopia. BMC Ecology and Evolution, 22, 78. |
| [2] | Bardgett RD, Freeman C, Ostle NJ (2008) Microbial contributions to climate change through carbon cycle feedbacks. The ISME Journal, 2, 805-814. |
| [3] | Bay G, Lee C, Chen C, Mahal NK, Castellano MJ, Hofmockel KS, Halverson LJ (2021) Agricultural management affects the active rhizosphere bacterial community composition and nitrification. Msystems, 6, e0065121. |
| [4] | Chen JJ, Hou L, Li Y, Bai J, Zhang SX (2014) Soil microbes and enzymes in an oak-pine mixed forest in the Qinling Mountains. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 42(3), 103-106, 111. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈军军, 侯琳, 李银, 白娟, 张硕新 (2014) 秦岭松栎混交林土壤微生物及酶活性. 东北林业大学学报, 42(3), 103-106, 111.] | |
| [5] | Chen XB, Su YR, He XY, Qin WG, Wei YW, Liang YM, Wu JS (2012) Effect of human disturbance on composition of the dominant bacterial group proteobacteriain karst soil ecosystems. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 49, 354-363. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈香碧, 苏以荣, 何寻阳, 覃文更, 魏亚伟, 梁月明, 吴金水 (2012) 不同干扰方式对喀斯特生态系统土壤细菌优势类群——变形菌群落的影响. 土壤学报, 49, 354-363.] | |
| [6] | Cheng F (2015) Study on Microbial Community Characteristics of Main Forest Types in Huoditang Forest Region of Qinling Mountains. PhD dissertation, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, Shaanxi. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [程飞 (2015) 秦岭火地塘林区主要森林类型微生物群落特征研究. 博士学位论文, 西北农林科技大学, 陕西杨凌.] | |
| [7] | Cheng L, Wang LX, Wang XH, Ou Y, Liu HP, Hou X, Yan LM, Li XY (2023) The various effect of cow manure compost on the degradation of imazethapyr in different soil types. Chemosphere, 337, 139325. |
| [8] | Chisholm C, Di H, Cameron K, Podolyan A, Shen J, Zhang L, Sirisena K, Godsoe W (2024) Contrasting response of comammox Nitrospira, ammonia oxidising bacteria, and archaea to soil pH and nitrogen inputs. Science of the Total Environment, 924, 171627. |
| [9] |
Coluccia M, Besaury L (2023) Acidobacteria members harbour an abundant and diverse carbohydrate-active enzymes (cazyme) and secreted proteasome repertoire, key factors for potential efficient biomass degradation. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 298, 1135-1154.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Dai XJ (2023) Study on Nitrogen Leaching Loss and Crop Utilization in Soils with Different pH Values. PhD dissertation, Jiangxi Agricultural University, Nanchang. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [代新俊 (2023) 不同pH土壤的氮素淋溶损失和作物利用研究. 博士学位论文, 江西农业大学, 南昌.] | |
| [11] |
Chaves MGD, Silva GGZ, Rossetto R, Edwards RA, Navarrete AA (2019) Acidobacteria subgroups and their metabolic potential for carbon degradation in sugarcane soil amended with vinasse and nitrogen fertilizers. Frontiers in Microbiology. Front Microbiol, 10, 1680.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Guo HL, Qi W (2017) Forest stand structure optimization of Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation in the central area of Qinling Mountains. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 32(5), 144-149. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭怀林, 齐伟 (2017) 秦岭中段华北落叶松人工林林分结构优化研究. 西北林学院学报, 32(5), 144-149.] | |
| [13] | Huang YT, Lü YL, Ding Y, Yu ZB, Cheng H (2013) Comparison of soil nutrient status in four types of forests in Bawangling of Hainan Island. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 42(1), 64-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄永涛, 吕瑜良, 丁易, 余兆波, 程辉 (2013) 海南岛霸王岭4种热带森林类型林地土壤养分状况的比较分析. 西部林业科学, 42(1), 64-69.] | |
| [14] | Huber KJ, Overmann J (2017) Vicinamibacteraceae fam. nov., the first described family within the subdivision 6 Acidobacteria. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 67, 1408-1414. |
| [15] |
Kern M, Winkler C, Simon J (2011) Respiratory nitrogen metabolism and nitrosative stress defence in ϵ-proteobacteria: The role of NssR-type transcription regulators. Biochemical Society Transactions, 39, 299-302.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Lauber CL, Ramirez KS, Aanderud Z, Lennon J, Fierer N (2013) Temporal variability in soil microbial communities across land-use types. The ISME Journal, 7, 1641-1650. |
| [17] | Li C, Lu M, Ren YL, Du F, Tao H, Yang LP, Wang DX (2020) Distribution of soil nitrogen components of Wenshan typical subtropical forests along an altitude gradient and its influencing factors in Yunnan Province of southwestern China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 42(12), 63-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李聪, 陆梅, 任玉连, 杜凡, 陶海, 杨罗平, 王东旭 (2020) 文山典型亚热带森林土壤氮组分的海拔分布及其影响因子. 北京林业大学学报, 42(12), 63-73.] | |
| [18] | Li CN, Li JB, Li XZ (2017) Soil methanotrophic community structure and diversity in different vegetation types at elevation gradient of Gongga Mountain, Southwest China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28, 805-814. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[李超男, 李家宝, 李香真 (2017) 贡嘎山海拔梯度上不同植被类型土壤甲烷氧化菌群落结构及多样性. 应用生态学报, 28, 805-814.]
DOI |
|
| [19] | Li FL, Liu M, Li ZP, Jiang CY, Han FX, Che YP (2013) Changes in soil microbial biomass and functional diversity with a nitrogen gradient in soil columns. Applied Soil Ecology, 64, 1-6. |
| [20] | Li JY, Ren TB, Li YS, Chen N, Yin QY, Li MS, Liu HB, Liu GS (2022) Organic materials with high C/N ratio: More beneficial to soil improvement and soil health. Biotechnology Letters, 44, 1415-1429. |
| [21] | Li XM, Che KJ, Yang YH, Wang H, Ma WW, Wang H, Huang R (2014) Variation pattern of soil nutrients in forests at different altitudes at upstream of Bailongjiang River. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 49(6), 136-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李兴民, 车克钧, 杨永红, 王辉, 马维维, 王惠, 黄蓉 (2014) 白龙江上游不同海拔森林土壤养分变化规律研究. 甘肃农业大学学报, 49(6), 131-137.] | |
| [22] | Li XY, Zhang WY, Liu F, Zhang ZM, He TB, Lin CH (2016) The distribution characteristics of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus at different altitudes in Fanjingshan Mountain. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 23(3), 19-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李相楹, 张维勇, 刘峰, 张珍明, 何腾兵, 林昌虎 (2016) 不同海拔高度下梵净山土壤碳、氮、磷分布特征. 水土保持研究, 23(3), 19-24.] | |
| [23] | Li YJ, Zhao Y, Wang LM, Zhao GQ, Wei BC, Wang WG, Wu FZ (2016) A study of soil physicochemical property and soil enzyme along altitude gradient at Neixiang Baotianman Nature Reserve. Journal of Xinyang Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 29, 560-566. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李彦娇, 赵燕, 王立民, 赵干卿, 魏宝成, 王维刚, 吴福忠 (2016) 内乡宝天曼自然保护区土壤理化性质和酶活性的海拔特征研究. 信阳师范学院学报(自然科学版), 29, 560-566.] | |
| [24] | Liu SQ, Gao LL, Pu YL, Deng LJ, Zhang SR (2005) Status of soil P and K nutrient and their influencing factors in Tibet. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 19(1), 75-78, 88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘世全, 高丽丽, 蒲玉琳, 邓良基, 张世熔 (2005) 西藏土壤磷素和钾素养分状况及其影响因素. 水土保持学报, 19(1), 75-78, 88.] | |
| [25] | Liu YY, Wang S, Li SZ, Deng Y (2017) Advances in molecular ecology on microbial functional genes of carbon cycle. Microbiology China, 44, 1676-1689. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘洋荧, 王尚, 厉舒祯, 邓晔 (2017) 基于功能基因的微生物碳循环分子生态学研究进展. 微生物学通报, 44, 1676-1689.] | |
| [26] |
Louca S, Parfrey LW, Doebeli M (2016) Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science, 353, 1272-1277.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Lu RK (2000) Methods for Agrochemical Analysis of Soils. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [鲁如坤 (2000) 土壤农业化学分析方法. 中国农业科技出版社, 北京.] | |
| [28] | Luo L, Shen GZ, Xie ZQ, Yu J (2011) Leaf functional traits of four typical forests along the altitudinal gradients in Mt. Shennongjia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31, 6420-6428. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [罗璐, 申国珍, 谢宗强, 喻杰 (2011) 神农架海拔梯度上4种典型森林的乔木叶片功能性状特征. 生态学报, 31, 6420-6428.] | |
| [29] | Lü SL, Li XP, Li WB, Mu XY (2013) Forest soil nutrient characteristics at different altitudes in Niubeiliang National Natural Reserve. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 41(4), 161-168, 177. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吕世丽, 李新平, 李文斌, 慕小艳 (2013) 牛背梁自然保护区不同海拔高度森林土壤养分特征分析. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 41(4), 161-168, 177.] | |
| [30] | Naz M, Dai ZC, Hussain S, Tariq M, Danish S, Khan IU, Qi SS, Du DL (2022) The soil pH and heavy metals revealed their impact on soil microbial community. Journal of Environmental Management, 321, 115770. |
| [31] | Praeg N, Pauli H, Illmer P (2019) Microbial diversity in bulk and rhizosphere soil of Ranunculus glacialis along a high-alpine altitudinal gradient. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 1429. |
| [32] | Ren CJ, Zhang W, Zhong ZK, Han XH, Yang GH, Feng YZ, Ren GX (2018) Differential responses of soil microbial biomass, diversity, and compositions to altitudinal gradients depend on plant and soil characteristics. Science of the Total Environment, 610, 750-758. |
| [33] | Ren XM, Ren L (2023) Altitudinal variation of soil nitrogen content in subalpine shrub in the Xishui forest area of Qilian Mountains. Forest Science and Technology, (3), 4-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [任雪梅, 任龙 (2023) 祁连山西水林区亚高山灌丛土壤氮素含量海拔梯度变化特征. 林业科技通讯, (3), 4-7.] | |
| [34] |
Pedraza RO (2008) Recent advances in nitrogen-fixing acetic acid bacteria. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 125, 25-35.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | Shen CC, Shi Y, Fan KK, He JS, Adams JM, Ge Y, Chu HY (2019) Soil pH dominates elevational diversity pattern for bacteria in high elevation alkaline soils on the Tibetan Plateau. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 95, fiz003. |
| [36] | Shen CC, Xiong JB, Zhang HY, Feng YZ, Lin XG, Li XY, Liang WJ, Chu HY (2013) Soil pH drives the spatial distribution of bacterial communities along elevation on Changbai Mountain. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 57, 204-211. |
| [37] | Song XR, Shang ZY, Li XD, Fu H (2015) Soil phosphorus and influencing factors in the grasslands at different elevations on west-slope of Helan Mountain, Inner Mongolia. Pratacultural Science, 32, 1054-1060. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋雄儒, 尚振艳, 李旭东, 傅华 (2015) 贺兰山西坡不同海拔梯度草地土壤磷特征及其影响因素. 草业科学, 32, 1054-1060.] | |
| [38] | Sor R, Legendre P, Lek S (2018) Uniqueness of sampling site contributions to the total variance of macroinvertebrate communities in the Lower Mekong basin. Ecological Indicators, 84, 425-432. |
| [39] |
Stone BW, Li JH, Koch BJ, Blazewicz SJ, Dijkstra P, Hayer M, Hofmockel KS, Liu XJ, Mau RL, Morrissey EM, Pett-Ridge J, Schwartz E, Hungate BA (2021) Nutrients cause consolidation of soil carbon flux to small proportion of bacterial community. Nature Communications, 12, 3381.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | Tang ZY, Fang JY (2004) A review on the elevational patterns of plant species diversity. Biodiversity Science, 12, 20-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[唐志尧, 方精云 (2004) 植物物种多样性的垂直分布格局. 生物多样性, 12, 20-28.]
DOI |
|
| [41] | Tao J, Zang RG, Yu CY (2011) Altitudinal patterns of plant communities and species diversity in the Habaxueshan Mountains, Yunnan, China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 47(7), 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陶晶, 臧润国, 余昌元 (2011) 云南哈巴雪山植物群落和植物多样性海拔梯度分布格局. 林业科学, 47(7), 1-6.] | |
| [42] | Tripathi BM, Stegen JC, Kim M, Dong K, Adams JM, Lee YK (2018) Soil pH mediates the balance between stochastic and deterministic assembly of bacteria. The ISME Journal, 12, 1072-1083. |
| [43] | Wang GH, Liu JJ, Yu ZH, Wang XZ, Jin J, Liu XB (2016) Research progress of Acidobacteria ecology in soils. Biotechnology Bulletin, 32(2), 14-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[王光华, 刘俊杰, 于镇华, 王新珍, 金剑, 刘晓冰 (2016) 土壤酸杆菌门细菌生态学研究进展. 生物技术通报, 32(2), 14-20.]
DOI |
|
| [44] | Wei X, Zheng XF, Zhang SX (2014) Forest soil physicochemical properties along different altitudinal gradients at Huoditang in the Qinling Mountains. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 29(3), 9-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [魏新, 郑小锋, 张硕新 (2014) 秦岭火地塘不同海拔梯度森林土壤理化性质研究. 西北林学院学报, 29(3), 9-14.] | |
| [45] | Wu JY, Zhi XY, Li Y, Guan TW, Tang SK, Xu LH, Li WJ (2008) Comparison of actinobacterial diversity in Jiangcheng and Heijing saline mines in Yunnan by using culture-independent approach. Microbiology China, 35, 1550-1555. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴晋元, 职晓阳, 李岩, 关统伟, 唐蜀昆, 徐丽华, 李文均 (2008) 云南江城和黑井盐矿沉积物未培养放线菌多样性比较. 微生物学通报, 35, 1550-1555.] | |
| [46] | Xiang QS, Zhang DS, Sun K, Wang N (2021) Analysis of soil microbial community structure and diversity in Berberis vernae habitat at different altitudes in alpine region. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 41, 1036-1050. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [向前胜, 张登山, 孙奎, 王宁 (2021) 高寒地区不同海拔梯度西北小檗生境土壤微生物群落结构及多样性分析. 西北植物学报, 41, 1036-1050.] | |
| [47] | Xu N, Tan GC, Wang HY, Gai XP (2016) Effect of biochar additions to soil on nitrogen leaching, microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. European Journal of Soil Biology, 74, 1-8. |
| [48] | Yang F, Wu YH, Yuan XF, Fu ZC (2019) Status quo and protection countermeasures of hemlock ancient trees in south slope of Qinling Mountains. Modern Agriculture Research, (4), 54-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨芬, 吴玉华, 袁小峰, 付志超 (2019) 秦岭南坡铁杉古树群现状及保护对策. 现代农业研究, (4), 54-55.] | |
| [49] | Yao L, Hu LH, Zhang HC, Fang YM, Wang GM (2019) Elevational distribution characteristics of soil bacterial community and enzyme activities in Mount Huangshan. Environmental Science, 40, 859-868. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姚兰, 胡立煌, 张焕朝, 方炎明, 王艮梅 (2019) 黄山土壤细菌群落和酶活性海拔分布特征. 环境科学, 40, 859-868.] | |
| [50] | Zhang BY, Yu K (2020) Application of microbial gene databases in the annotation of nitrogen cycle functional genes. Microbiology China, 47, 3021-3038. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张博雅, 余珂 (2020) 微生物基因数据库在氮循环功能基因注释中的应用. 微生物学通报, 47, 3021-3038.] | |
| [51] | Zhang Q (2019) Study on the Difference of Soil Microbial Diversity and Nitrification at Different Altitudes in Yunhe Terrace. PhD dissertation, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张倩 (2019) 云和梯田不同海拔土壤微生物多样性及硝化作用差异研究. 博士学位论文, 浙江大学, 杭州.] | |
| [52] | Zhang X, Liu XQ, Wang YP, Li ZB, Li P (2012) Evaluation on benefits of soil and water conversation in ecological function region of Qinling Mountain. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 19(2), 86-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张霞, 刘晓清, 王亚萍, 李占斌, 李鹏 (2012) 秦岭生态功能区水土保持治理效益评价. 水土保持研究, 19(2), 86-90.] | |
| [53] | Zhou H (2019) Characteristics and Adaptive Mechanism of Soil Microorganisms in Alpine Grassland at Different Altitudes. PhD dissertation, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周恒 (2019) 不同海拔高寒草原土壤微生物特征及其适应机制. 博士学位论文, 甘肃农业大学, 兰州.] | |
| [54] | Zhou HK, Li S, Sun J, Qu JP, Zhang ZH, Ma L, Qin RM, Wei JJ, Chang T, Su HY, Hu X, A DHZ, Yuan F, Li HL (2023) Characteristics of plant community and soil physical and chemical properties in alpine meadow along altitude gradient in the headwaters region of Three-River on Tibetan Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 31, 1735-1743. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[周华坤, 李珊, 孙建, 曲家鹏, 张中华, 马丽, 秦瑞敏, 魏晶晶, 常涛, 苏洪烨, 胡雪, 阿的哈则, 袁访, 李宏林 (2023) 三江源区高寒草甸植物群落与土壤理化性质沿海拔梯度的变化特征. 草地学报, 31, 1735-1743.]
DOI |
| [1] | Tong Miao, Wang Huan, Zhang Wenshuang, Wang Chao, Song Jianxiao. Distribution characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes in soil bacterial communities exposed to heavy metal pollution [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [2] | Song Yuanhao, Gong Lü, Li Ben, Hu Yang, Li Xiuzhen. Impacts of different pond-to-wetland restoration methods on macrofauna in the Liao River Estuary, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24316-. |
| [3] | Zihong Chen, Yifei Zhang, Kai Chen, Jianying Chen, Ling Xu. Species diversity of entomopathogenic fungi and the influencing factors in the Southern Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [4] | Xuemeng Li, Jibao Jiang, Zenglu Zhang, Xiaojing Liu, Yali Wang, Yizhao Wu, Yinsheng Li, Jiangping Qiu, Qi Zhao. Earthworm biodiversity and its influencing factors in Baotianman National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23352-. |
| [5] | Xiaolin Liu, Yougui Wu, Minhua Zhang, Xiaorong Chen, Zhicheng Zhu, Dingyun Chen, Shu Dong, Buhang Li, Bingyang Ding, Yu Liu. Community composition and structure of a 25-ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical forest in Baishanzu, Zhejiang Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [6] | Fangfang Wu, Na Liu, Chunmei He, Zuoqiang Yuan, Zhanqing Hao, Qiulong Yin. Elevational gradient pattern of woody plant community structure and diversity in the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [7] | Yali Zhang, Bingchang Zhang, Kang Zhao, Kaikai Li, Yanjin Liu. Variation of bacterial communities and their driving factors in different types of biological soil crusts in Mu Us sandy land [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 23027-. |
| [8] | Yinger Mao, Xiumei Zhou, Nan Wang, Xiuxiu Li, Yuke You, Shangbin Bai. Impact of Phyllostachys edulis expansion to Chinese fir forest on the soil bacterial community [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 22659-. |
| [9] | Renxiu Yao, Yan Chen, Xiaoqin Lü, Jianghu Wang, Fujun Yang, Xiaoyue Wang. Altitude-related environmental factors shape the phenotypic characteristics and chemical profile of Rhododendron [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22259-. |
| [10] | Xiaofeng Wang, Jiesheng Rao, Tao Yang, Wencong Liu, Xi Tian, Xi Chen, Qiming Liu, Yanxiao Xu, Qiuyu Zhang, Hongqiang Zhang, Xu Zhang, Xiaokun Ou, Zehao Shen. Spatial variation and determinants of woody plant species diversity in a semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23217-. |
| [11] | Ruihe Gao, Shiming Fan, Jianghai Dong, Rongjiao Li, Zhiwei Zhang. Characteristics and vertical distribution of insect functional groups along an altitude gradient in Guandi Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(10): 23152-. |
| [12] | Chao Zhang, Juan Li, Haiyun Cheng, Jiachong Duan, Zhao Pan. Patterns and environmental drivers of the butterfly diversity in the western region of Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22272-. |
| [13] | Ting Wang, Lizhi Zhou. The spatial-temporal patterns of bird diversity and its determinants in the small wetlands in Hefei City [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(7): 21445-. |
| [14] | Wenkai Xue, Huadanshang Meng, Yanhong Wang, Pan Zhu, Ji De, Xiaofang Guo. Relationship between culturable filamentous fungal diversity and environmental factors in Nam Co Lake [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(6): 21473-. |
| [15] | Moxu Wu, Mingtai An, Li Tian, Feng Liu. Effects of environmental factors on quantitative characteristics of woody plant sexual system in Maolan karst forest [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(11): 22025-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()