



Biodiv Sci ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (5): 23462. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023462 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023462
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yongqiang Zhao1, Xiyu Yan1, Jiaqi Xie1, Mengting Hou1, Danmei Chen1,2,3, Lipeng Zang1,2,3, Qingfu Liu1,2,3, Mingzhen Sui1,2,3, Guangqi Zhang1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2023-12-07
Accepted:2024-02-28
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-05-17
Contact:
E-mail: Yongqiang Zhao, Xiyu Yan, Jiaqi Xie, Mengting Hou, Danmei Chen, Lipeng Zang, Qingfu Liu, Mingzhen Sui, Guangqi Zhang. Species diversity and community assembly of woody plants at different life history stages during the natural restoration of degraded karst forests[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23462.
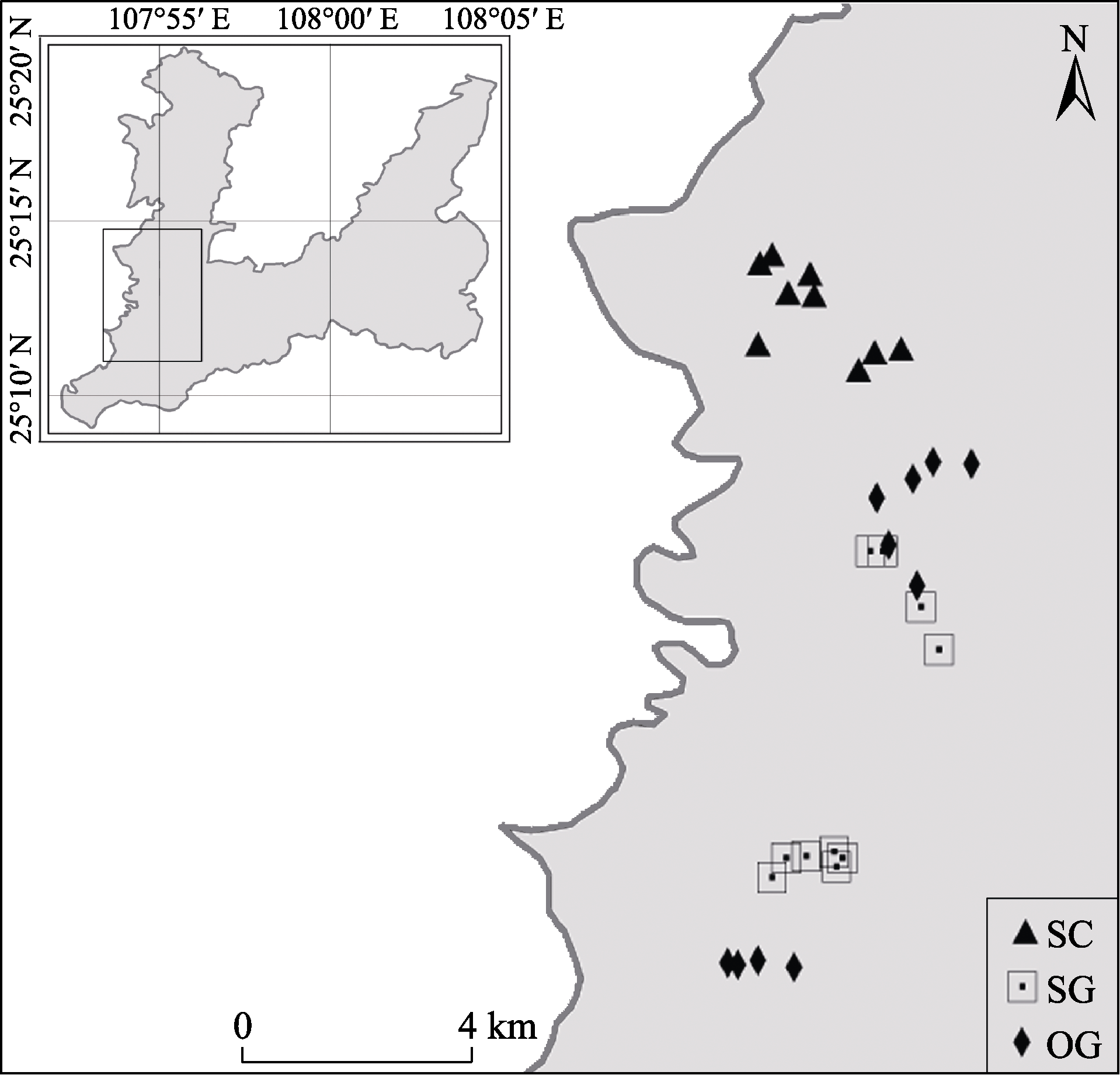
Fig. 1 Distribution of 30 fixed monitoring plots in Maolan National Nature Reserve. SC, Shrub-canopy mixed forest stage; SG, Secondary-growth forest stage; OG, Old-growth forest stage.
| 物种 Species | 乔灌混交林 SC | 先锋乔木林 SG | 老龄林 OG | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE | SA | TR | SE | SA | TR | SE | SA | TR | |
| 巴东荚蒾 Viburnum henryi | - | - | - | 0.032 | 0.043 | - | - | 0.033 | - |
| 薄叶山矾 Symplocos anomala | - | 0.025 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 齿叶黄皮 Clausena dunniana | - | - | - | 0.062 | 0.035 | 0.044 | 0.057 | 0.043 | 0.038 |
| 川桂 Cinnamomum wilsonii | 0.025 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 粗糠柴 Mallotus philippensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.033 | - | - |
| 冬青叶山茶 Camellia ilicifolia | - | 0.021 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 短刺米槠 Castanopsis carlesii var. spinulosa | 0.059 | 0.045 | 0.078 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 红山茶 Camellia japonica | - | 0.022 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 虎皮楠 Daphniphyllum oldhamii | 0.026 | 0.030 | 0.097 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 化香树 Platycarya strobilacea | - | - | - | 0.028 | - | 0.078 | - | - | 0.057 |
| 黄梨木 Boniodendron minus | - | - | - | 0.023 | 0.029 | 0.036 | - | 0.032 | 0.053 |
| 檵木 Loropetalum chinense | 0.035 | 0.081 | 0.067 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 榉树 Zelkova serrata | - | - | - | - | - | 0.025 | - | - | - |
| 柯 Lithocarpus glaber | - | - | 0.026 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 荔波鹅耳枥 Carpinus lipoensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.051 | - | - |
| 罗浮锥 Castanopsis faberi | 0.023 | 0.035 | 0.024 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 马尾松 Pinus massoniana | - | - | 0.041 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 南天竹 Nandina domestica | - | - | - | 0.051 | 0.035 | - | 0.025 | 0.028 | - |
| 朴树 Celtis sinensis | - | - | - | 0.022 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 黔蚊母树 Distylium tsiangii | - | - | - | - | 0.034 | - | - | - | - |
| 青檀 Pteroceltis tatarinowii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.024 |
| 三花冬青 Ilex triflora | 0.050 | 0.077 | 0.090 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 山矾 Symplocos sumuntia | 0.028 | 0.066 | 0.030 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 十大功劳 Mahonia fortunei | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.025 | - |
| 石斑木 Rhaphiolepis indica | 0.043 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 疏花卫矛 Euonymus laxiflorus | - | - | - | - | 0.023 | - | 0.027 | - | - |
| 天峨槭 Acer wangchii | - | - | - | - | 0.026 | 0.034 | 0.073 | 0.056 | 0.058 |
| 蚊母树 Distylium racemosum | - | - | - | 0.039 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 香叶树 Lindera communis | 0.043 | 0.069 | - | 0.048 | 0.055 | - | 0.031 | 0.043 | - |
| 小果润楠 Machilus microcarpa | - | - | 0.033 | - | - | 0.033 | - | - | 0.029 |
| 小花梾木 Cornus parviflora | - | - | - | 0.035 | 0.044 | 0.043 | 0.045 | 0.027 | 0.038 |
| 小叶青冈 Quercus myrsinifolia | - | - | - | - | 0.027 | - | - | - | - |
| 小叶润楠 Machilus microphylla | 0.028 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 岩柿 Diospyros dumetorum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.03 | - |
| 杨梅 Myrica rubra | - | - | 0.041 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 野独活 Miliusa balansae | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.028 | 0.033 | - |
| 野柿 Diospyros kaki var. silvestris | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.023 |
| 云贵鹅耳枥 Carpinus pubescens | - | - | - | - | - | 0.031 | - | - | 0.031 |
| 樟叶槭 Acer coriaceifolium | - | - | - | 0.032 | - | 0.027 | - | - | - |
| 长叶润楠 Machilus japonica | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.036 | - | - |
| 掌叶木 Handeliodendron bodinieri | - | - | - | - | - | 0.025 | - | - | 0.026 |
Table 1 The top 10 species with the highest importance values at different restoration stage and different life history stage
| 物种 Species | 乔灌混交林 SC | 先锋乔木林 SG | 老龄林 OG | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE | SA | TR | SE | SA | TR | SE | SA | TR | |
| 巴东荚蒾 Viburnum henryi | - | - | - | 0.032 | 0.043 | - | - | 0.033 | - |
| 薄叶山矾 Symplocos anomala | - | 0.025 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 齿叶黄皮 Clausena dunniana | - | - | - | 0.062 | 0.035 | 0.044 | 0.057 | 0.043 | 0.038 |
| 川桂 Cinnamomum wilsonii | 0.025 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 粗糠柴 Mallotus philippensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.033 | - | - |
| 冬青叶山茶 Camellia ilicifolia | - | 0.021 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 短刺米槠 Castanopsis carlesii var. spinulosa | 0.059 | 0.045 | 0.078 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 红山茶 Camellia japonica | - | 0.022 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 虎皮楠 Daphniphyllum oldhamii | 0.026 | 0.030 | 0.097 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 化香树 Platycarya strobilacea | - | - | - | 0.028 | - | 0.078 | - | - | 0.057 |
| 黄梨木 Boniodendron minus | - | - | - | 0.023 | 0.029 | 0.036 | - | 0.032 | 0.053 |
| 檵木 Loropetalum chinense | 0.035 | 0.081 | 0.067 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 榉树 Zelkova serrata | - | - | - | - | - | 0.025 | - | - | - |
| 柯 Lithocarpus glaber | - | - | 0.026 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 荔波鹅耳枥 Carpinus lipoensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.051 | - | - |
| 罗浮锥 Castanopsis faberi | 0.023 | 0.035 | 0.024 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 马尾松 Pinus massoniana | - | - | 0.041 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 南天竹 Nandina domestica | - | - | - | 0.051 | 0.035 | - | 0.025 | 0.028 | - |
| 朴树 Celtis sinensis | - | - | - | 0.022 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 黔蚊母树 Distylium tsiangii | - | - | - | - | 0.034 | - | - | - | - |
| 青檀 Pteroceltis tatarinowii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.024 |
| 三花冬青 Ilex triflora | 0.050 | 0.077 | 0.090 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 山矾 Symplocos sumuntia | 0.028 | 0.066 | 0.030 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 十大功劳 Mahonia fortunei | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.025 | - |
| 石斑木 Rhaphiolepis indica | 0.043 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 疏花卫矛 Euonymus laxiflorus | - | - | - | - | 0.023 | - | 0.027 | - | - |
| 天峨槭 Acer wangchii | - | - | - | - | 0.026 | 0.034 | 0.073 | 0.056 | 0.058 |
| 蚊母树 Distylium racemosum | - | - | - | 0.039 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 香叶树 Lindera communis | 0.043 | 0.069 | - | 0.048 | 0.055 | - | 0.031 | 0.043 | - |
| 小果润楠 Machilus microcarpa | - | - | 0.033 | - | - | 0.033 | - | - | 0.029 |
| 小花梾木 Cornus parviflora | - | - | - | 0.035 | 0.044 | 0.043 | 0.045 | 0.027 | 0.038 |
| 小叶青冈 Quercus myrsinifolia | - | - | - | - | 0.027 | - | - | - | - |
| 小叶润楠 Machilus microphylla | 0.028 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 岩柿 Diospyros dumetorum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.03 | - |
| 杨梅 Myrica rubra | - | - | 0.041 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 野独活 Miliusa balansae | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.028 | 0.033 | - |
| 野柿 Diospyros kaki var. silvestris | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.023 |
| 云贵鹅耳枥 Carpinus pubescens | - | - | - | - | - | 0.031 | - | - | 0.031 |
| 樟叶槭 Acer coriaceifolium | - | - | - | 0.032 | - | 0.027 | - | - | - |
| 长叶润楠 Machilus japonica | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.036 | - | - |
| 掌叶木 Handeliodendron bodinieri | - | - | - | - | - | 0.025 | - | - | 0.026 |
| 指数 Index | 生活史阶段 Life history stage | 恢复阶段 Restoration stage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乔灌混交林 SC | 先锋乔木林 SG | 老龄林 OG | ||
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index | 3.04 ± 0.38b | 3.53 ± 0.20a | 3.44 ± 0.18a | |
| 个体数 Number of individuals | 幼苗 Seedlings | 113 ± 36a | 59 ± 20b | 30 ± 10c |
| 幼树 Saplings | 615 ± 243a | 285 ± 100b | 176 ± 60b | |
| 成树 Adult tree | 196 ± 45a | 156 ± 44b | 144 ± 48b | |
| Margalef丰富度指数 Margalef richness index | 幼苗 Seedlings | 6.09 ± 0.84a | 5.66 ± 1.12a | 4.29 ± 0.68b |
| 幼树 Saplings | 7.97 ± 1.84b | 9.49 ± 2.00a | 8.27 ± 1.55b | |
| 成树 Adult tree | 5.68 ± 1.94b | 8.22 ± 1.06a | 8.26 ± 1.16a | |
| Fisher’s α指数 Fisher’s α index | 幼苗 Seedlings | 0.86 ± 0.16a | 0.68 ± 0.20b | 0.38 ± 0.16c |
| 幼树 Saplings | 2.48 ± 0.30a | 1.88 ± 0.35b | 1.71 ± 0.37b | |
| 成树 Adult tree | 1.59 ± 0.34a | 1.38 ± 0.23a | 1.33 ± 0.32a | |
Table 2 Statistics on species diversity, number of individuals and species richness at different life history stage and different restoration stage
| 指数 Index | 生活史阶段 Life history stage | 恢复阶段 Restoration stage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乔灌混交林 SC | 先锋乔木林 SG | 老龄林 OG | ||
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index | 3.04 ± 0.38b | 3.53 ± 0.20a | 3.44 ± 0.18a | |
| 个体数 Number of individuals | 幼苗 Seedlings | 113 ± 36a | 59 ± 20b | 30 ± 10c |
| 幼树 Saplings | 615 ± 243a | 285 ± 100b | 176 ± 60b | |
| 成树 Adult tree | 196 ± 45a | 156 ± 44b | 144 ± 48b | |
| Margalef丰富度指数 Margalef richness index | 幼苗 Seedlings | 6.09 ± 0.84a | 5.66 ± 1.12a | 4.29 ± 0.68b |
| 幼树 Saplings | 7.97 ± 1.84b | 9.49 ± 2.00a | 8.27 ± 1.55b | |
| 成树 Adult tree | 5.68 ± 1.94b | 8.22 ± 1.06a | 8.26 ± 1.16a | |
| Fisher’s α指数 Fisher’s α index | 幼苗 Seedlings | 0.86 ± 0.16a | 0.68 ± 0.20b | 0.38 ± 0.16c |
| 幼树 Saplings | 2.48 ± 0.30a | 1.88 ± 0.35b | 1.71 ± 0.37b | |
| 成树 Adult tree | 1.59 ± 0.34a | 1.38 ± 0.23a | 1.33 ± 0.32a | |
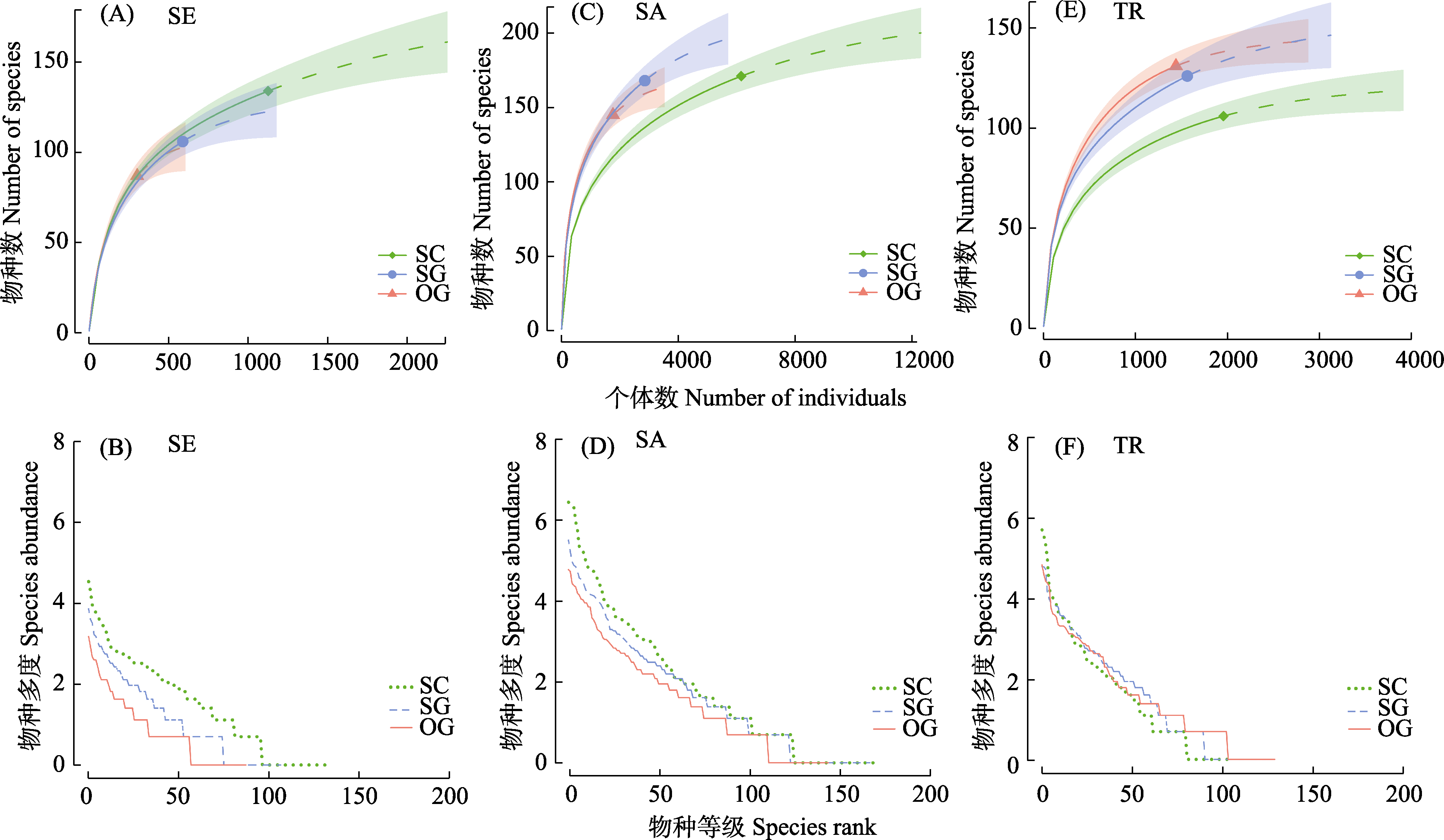
Fig. 2 Rarefaction and extrapolation species accumulation curves based on Hill number and species rank-abundance curves at different restoration stages and different life history stage. SC, Shrub-canopy mixed forest stage; SG, Secondary-growth forest stage; OG, Old-growth forest stage; SE, Seedlings; SA, Saplings; TR, Adult tree.
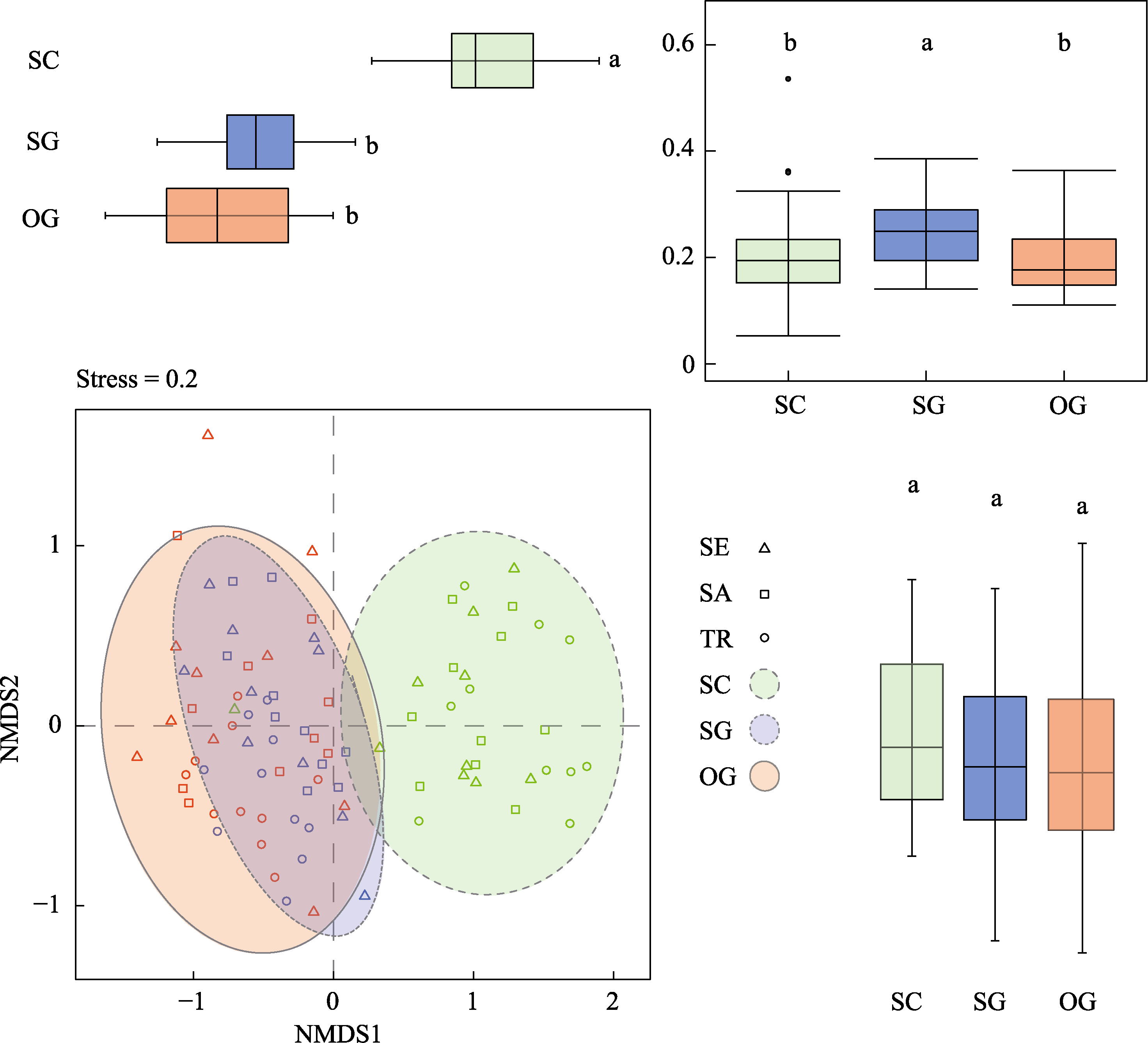
Fig. 3 Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) plots of different restoration stages based on the Horn similarity index. The plot in lower left corner is NMDS plot, the boxplot in the upper left corner and the lower right corner represent the values of NMDS1 and NMDS2, respectively; the boxplot in the upper right corner shows the similarity index comparison of the composition of 10 plot species in each restoration stage, and different letters indicate significant differences between the restoration stages. SC, Shrub-canopy mixed forest stage; SG, Secondary-growth forest stage; OG, Old-growth forest stage; SE, Seedlings; SA, Saplings; TR, Adult trees.
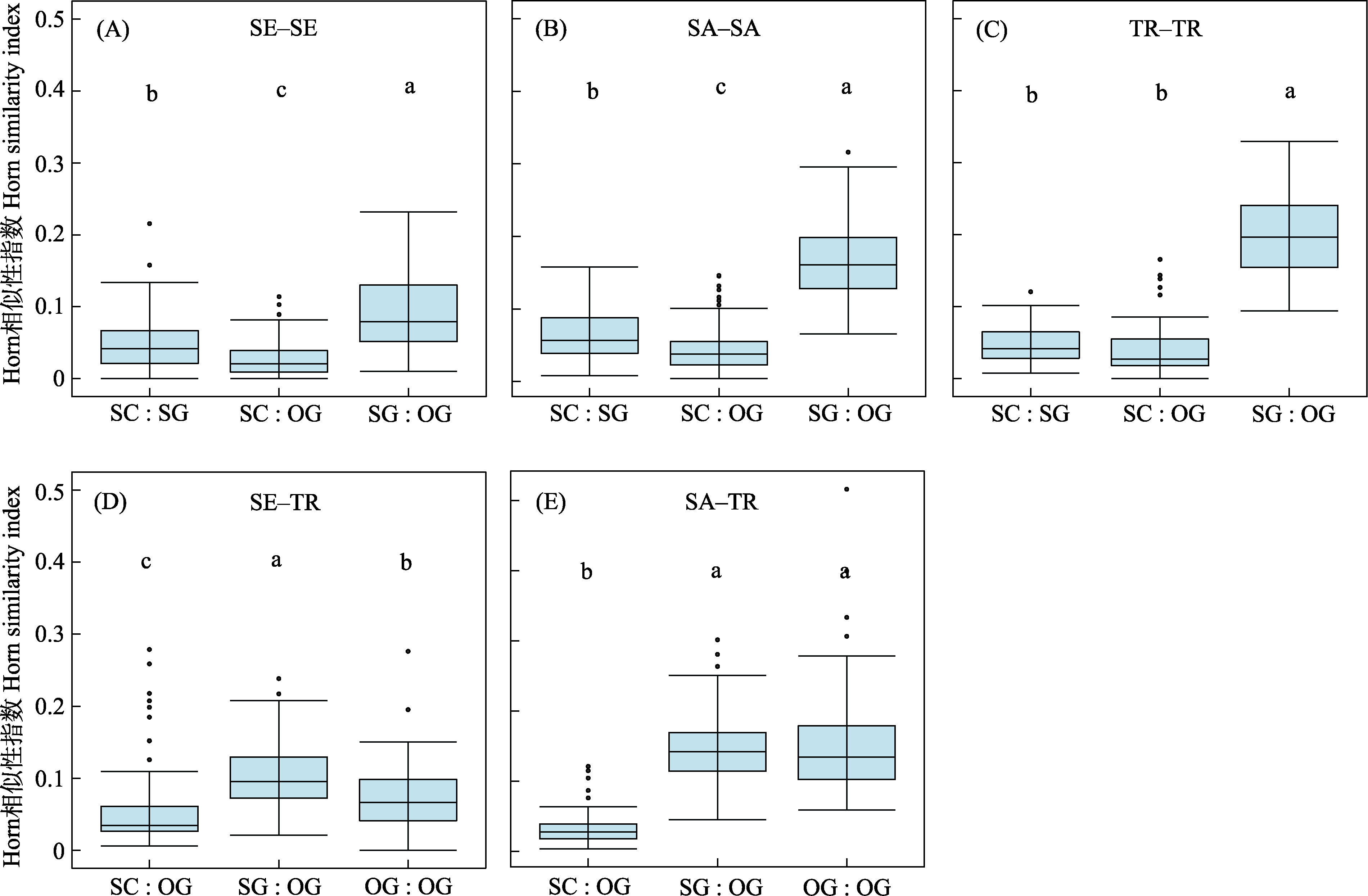
Fig. 4 The Horn similarity index of seedlings (A), saplings (B) and adult trees (C) at different recovery stages, as well as seedlings and OG adult trees (D), saplings and OG adult trees (E). SC: Shrub-canopy mixed forest stage; SG: Secondary-growth forest stage; OG: Old-growth forest stage; SE: Seedlings; SA: Saplings; TR: Adult trees. Different letters indicate significant differences between the restoration stages.
| [1] |
Adler PB, Hillerislambers J, Levine JM (2007) A niche for neutrality. Ecology Letters, 10, 95-104.
PMID |
| [2] |
Arroyo-Rodríguez V, Melo FPL, Martínez-Ramos M, Bongers F, Chazdon RL, Meave JA, Norden N, Santos BA, Leal IR, Tabarelli M (2017) Multiple successional pathways in human-modified tropical landscapes: New insights from forest succession, forest fragmentation and landscape ecology research. Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 92, 326-340.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | Barta KA, Hais M, Heurich M (2022) Characterizing forest disturbance and recovery with thermal trajectories derived from Landsat time series data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 282, 113274. |
| [4] | Brook BW, Bradshaw CJA, Koh LP, Sodhi NS (2006) Momentum drives the crash: Mass extinction in the tropics. Biotropica, 38, 302-305. |
| [5] | Bullock JM, Aronson J, Newton AC, Pywell RF, Rey-Benayas JM (2011) Restoration of ecosystem services and biodiversity: Conflicts and opportunities. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 26, 541-549. |
| [6] | Cao JH, Jiang ZC, Yang DS, Pei JG, Yang H, Luo WQ (2008) Grading of soil erosion intensity in southwest karst area of China. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 6(6), 1-7, 20. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曹建华, 蒋忠诚, 杨德生, 裴建国, 杨慧, 罗为群 (2008) 我国西南岩溶区土壤侵蚀强度分级标准研究. 中国水土保持科学, 6(6), 1-7, 20.] | |
| [7] | Chao A, Gotelli NJ, Hsieh TC, Sander EL, Ma KH, Colwell RK, Ellison AM (2014) Rarefaction and extrapolation with Hill numbers: A framework for sampling and estimation in species diversity studies. Ecological Monographs, 84, 45-67. |
| [8] | Chazdon RL (2008) Chance and determinism in tropical forest succession. In: Tropical Forest Community Ecology (eds Carson WP, Schnitzer SA, Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute), pp.384-408. Blackwell, Chichester. |
| [9] |
Chisholm RA, Lichstein JW (2009) Linking dispersal, immigration and scale in the neutral theory of biodiversity. Ecology Letters, 12, 1385-1393.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Chua SC, Ramage BS, Ngo KM, Potts MD, Lum SKY (2013) Slow recovery of a secondary tropical forest in Southeast Asia. Forest Ecology and Management, 308, 153-160. |
| [11] | Comita LS, Aguilar S, Pérez R, Lao S, Hubbell SP (2007) Patterns of woody plant species abundance and diversity in the seedling layer of a tropical forest. Journal of Vegetation Science, 18, 163-174. |
| [12] | Corlett RT (1995) Tropical secondary forests. Progress in Physical Geography: Earth and Environment, 19, 159-172. |
| [13] |
Cottenie K (2005) Integrating environmental and spatial processes in ecological community dynamics. Ecology Letters, 8, 1175-1182.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | De Cáceres M, Legendre P, Valencia R, Cao M, Chang LW, Chuyong G, Condit R, Hao ZQ, Hsieh CF, Hubbell S, Kenfack D, Ma KP, Mi XC, Supardi Noor MN, Kassim AR, Ren HB, Su SH, Sun IF, Thomas D, Ye WH, He FL (2012) The variation of tree beta diversity across a global network of forest plots. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 1191-1202. |
| [15] | Dent DH, DeWalt SJ, Denslow JS (2012) Secondary forests of central Panama increase in similarity to old-growth forest over time in shade tolerance but not species composition. Journal of Vegetation Science, 24, 530-542. |
| [16] |
Du H, Hu F, Zeng FP, Wang KL, Peng WX, Zhang H, Zeng ZX, Zhang F, Song TQ (2017) Spatial distribution of tree species in evergreen-deciduous broadleaf karst forests in Southwest China. Scientific Reports, 7, 15664.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Fisher RA, Corbet AS, Williams CB (1943) The relation between the number of species and the number of individuals in a random sample of an animal population. Journal of Animal Ecology, 12, 42-58. |
| [18] | Finegan B (1996) Pattern and process in neotropical secondary rain forests: The first 100 years of succession. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 11, 119-124. |
| [19] | Gilbert B, Lechowicz MJ (2004) Neutrality, niches, and dispersal in a temperate forest understory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 101, 7651-7656. |
| [20] | Grubb PJ (1977) The maintenance of species-richness in plant communities: The importance of the regeneration niche. Biological Reviews, 52, 107-145. |
| [21] | Guariguata MR, Ostertag R (2001) Neotropical secondary forest succession: Changes in structural and functional characteristics. Forest Ecology and Management, 148, 185-206. |
| [22] |
Guo YL, Wang B, Mallik AU, Huang FZ, Xiang WS, Ding T, Wen SJ, Lu SH, Li DX, He YL, Li XK (2017) Topographic species-habitat associations of tree species in a heterogeneous tropical karst seasonal rain forest, China. Journal of Plant Ecology, 10, 450-460.
DOI |
| [23] | Han TT, Ren H, Hui DF, Zhu YP, Lu HF, Guo QF, Wang J (2023) Dominant ecological processes and plant functional strategies change during the succession of a subtropical forest. Ecological Indicators, 146, 109885. |
| [24] | He YHZ, Wang L, Niu Z, Nath B (2022) Vegetation recovery and recent degradation in different karst landforms of Southwest China over the past two decades using GEE satellite archives. Ecological Informatics, 68, 101555. |
| [25] | Hill MO (1973) Diversity and evenness: A unifying notation and its consequences. Ecology, 54, 427-432. |
| [26] | Horn HS (1966) Measurement of “overlap” in comparative ecological studies. The American Naturalist, 100, 419-424. |
| [27] | Hu F, Zeng FP, Du H, Peng WX, Zhang F, Tan WN, Song TQ (2018) Scale-dependent spatial patterns for species diversity in a karst evergreen and deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest of northwest Guangxi. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 6074-6083. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [胡芳, 曾馥平, 杜虎, 彭晚霞, 张芳, 谭卫宁, 宋同清 (2018) 桂西北喀斯特常绿落叶阔叶混交林物种多样性分布格局的尺度效应. 生态学报, 38, 6074-6083.] | |
| [28] | Huang YF, Lu XH, Zang RG, Ding Y, Long WX, Wang JQ, Yang M, Huang YT (2013) Community assembly during recovery of tropical lowland rain forest from abandoned shifting cultivation lands on Hainan Island, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 37, 415-426. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[黄运峰, 路兴慧, 臧润国, 丁易, 龙文兴, 王进强, 杨民, 黄运天 (2013) 海南岛热带低地雨林刀耕火种弃耕地自然恢复过程中的群落构建. 植物生态学报, 37, 415-426.]
DOI |
|
| [29] | Hubbell SP (2001) The unified neutral theory of biodiversity and biogeography. Monographs in Population Biology, 32, 448. |
| [30] | Jost L (2006) Entropy and diversity. Oikos, 113, 363-375. |
| [31] | Kraft NJB, Adler PB, Godoy O, James EC, Fuller S, Levine JM (2015) Community assembly, coexistence and the environmental filtering metaphor. Functional Ecology, 29, 592-599. |
| [32] |
Kraft NJB, Valencia R, Ackerly DD (2008) Functional traits and niche-based tree community assembly in an Amazonian forest. Science, 322, 580-582.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Laurance WF (2007) Have we overstated the tropical biodiversity crisis? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 22, 65-70. |
| [34] | Letcher SG, Chazdon RL (2010) Rapid recovery of biomass, species richness, and species composition in a forest chronosequence in northeastern Costa Rica. Biotropica, 41, 608-617. |
| [35] | Levins R, Pielou EC (1970) An introduction to mathematical ecology. Evolution, 24, 482-482. |
| [36] | Li B, Zhao Y, Liu T, Chen XL, Gao BQ, Cao XW (2022) Characteristics of soil seed bank and their relationship with aboveground vegetation of Picea purpurea community in upstream of Taohe River. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 42, 705-714. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李波, 赵阳, 刘婷, 陈学龙, 高本强, 曹秀文 (2022) 洮河上游紫果云杉群落土壤种子库特征及其与地上植被的关系. 西北植物学报, 42, 705-714.] | |
| [37] | Li SP, Cadotte MW, Meiners SJ, Hua ZS, Jiang L, Shu WS, Holyoak M (2015) Species colonisation, not competitive exclusion, drives community overdispersion over long-term succession. Ecology Letters, 18, 964-973. |
| [38] | Li YB, Tan Q, Wang SJ (2005) Current status, problems analysis and basic framework of karst rocky desertification research. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 3(3), 27-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李阳兵, 谭秋, 王世杰 (2005) 喀斯特石漠化研究现状、问题分析与基本构架. 中国水土保持科学, 3(3), 27-34.] | |
| [39] | Lu MZ, Zeng FP, Song TQ, Peng WX, Su L, Liu KP, Tan WN, Du H (2022) Effects of tree mortality on the spatial patterns and interspecific associations of individuals in karst evergreen deciduous broad-leaved mixed forests. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 33, 2679-2686. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[鲁梦珍, 曾馥平, 宋同清, 彭晚霞, 苏樑, 刘坤平, 谭卫宁, 杜虎 (2022) 喀斯特常绿落叶阔叶林个体死亡对空间格局及种间关联性的影响. 应用生态学报, 33, 2679-2686.]
DOI |
|
| [40] | Lugo AE, Helmer E (2004) Emerging forests on abandoned land: Puerto Rico’s new forests. Forest Ecology and Management, 190, 145-161. |
| [41] | Luo J, Chen JY, Guo XM, Lei Y, Liu JC (2022) The characteristics of soil seed bank in karst area under different soil thickness niches. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 44(9), 2-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [罗杰, 陈金艺, 郭旭曼, 雷颖, 刘锦春 (2022) 喀斯特不同土壤厚度小生境下土壤种子库特征. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 44(9), 2-10.] | |
| [42] |
Ma RX, Guo YL, Li DX, Wang B, Xiang WS, Huang FZ, Lu F, Wen SJ, Li JX, Lu SH, Li XK (2023) Spatial distribution pattern and mechanism of sapling regeneration in karst seasonal rainforest in southwestern Guangxi. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22251. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[马瑞霞, 郭屹立, 李冬兴, 王斌, 向悟生, 黄甫昭, 陆芳, 文淑均, 李健星, 陆树华, 李先琨 (2023) 桂西南喀斯特季节性雨林幼树更新的空间分布格局及机制. 生物多样性, 31, 22251.]
DOI |
|
| [43] | Ma RX, Li JX, Guo YL, Wang B, Xiang WS, Li DX, Huang FZ, Lu F, Wen SJ, Lu SH, Li XK (2024) Recruitment dynamics in a tropical karst seasonal rain forest: Revealing complex processes from spatial patterns. Forest Ecology and Management, 553, 121610. |
| [44] | Ma XY, Tian X, Guo YT, Lin YM (2023) Effect of vegetation restoration on soil stoichiometry characteristics in southwestern China based on meta-analysis. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 29, 1058-1067. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马心雨, 田雪, 过怡婷, 林勇明 (2023) 中国西南地区植被恢复对土壤化学计量特征的影响——基于meta分析. 应用与环境生物学报, 29, 1058-1067.] | |
| [45] | Margalef R (1958) Information theory in ecology. General Systems, 3, 36-71. |
| [46] | Münkemüller T, Gallien L, Pollock LJ, Barros C, Carboni M, Chalmandrier L, Mazel F, Mokany K, Roquet C, Smyčka J, Talluto MV, Thuiller W (2020) Dos and don’ts when inferring assembly rules from diversity patterns. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 29, 1212-1229. |
| [47] | Nathan R, Muller-Landau HC (2000) Spatial patterns of seed dispersal, their determinants and consequences for recruitment. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 15, 278-285. |
| [48] |
Norden N, Chazdon RL, Chao A, Jiang YH, Vílchez-Alvarado B (2009) Resilience of tropical rain forests: Tree community reassembly in secondary forests. Ecology Letters, 12, 385-394.
DOI PMID |
| [49] | Punchi-Manage R, Getzin S, Wiegand T, Kanagaraj R, Savitri Gunatilleke CV, Nimal Gunatilleke IAU, Wiegand K, Huth A (2013) Effects of topography on structuring local species assemblages in a Sri Lankan mixed dipterocarp forest. Journal of Ecology, 101, 149-160. |
| [50] | Qi CH, Jin ZX, Li JM (2011) Small-scale spatial patterns of genetic structure in Castanopsis eyrei populations based on autocorrelation analysis in the Tiantai Mountain of Zhejiang Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31, 5130-5137. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [祁彩虹, 金则新, 李钧敏 (2011) 浙江天台山甜槠种群遗传结构的空间自相关分析. 生态学报, 31, 5130-5137.] | |
| [51] | R Core Team (2023) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. |
| [52] | Rosindell J, Hubbell SP, Etienne RS (2011) The unified neutral theory of biodiversity and biogeography at age ten. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 26, 340-348. |
| [53] |
Shen GC, He FL, Waagepetersen R, Sun IF, Hao ZQ, Chen ZS, Yu MJ (2013) Quantifying effects of habitat heterogeneity and other clustering processes on spatial distributions of tree species. Ecology, 94, 2436-2443.
PMID |
| [54] | Skeen JN (1973) An extension of the concept of importance value in analyzing forest communities. Ecology, 54, 655-656. |
| [55] | Su L, Du H, Zeng FP, Peng WX, Wang H, Wang KL, Lu MZ, Song TQ (2023) Environmental and spatial contributions to tree community assembly across life stages and scales in evergreen-deciduous broadleaf karst forests, Southwest China. Journal of Forestry Research, 34, 1323-1331. |
| [56] |
Tuomisto H, Ruokolainen K, Yli-Halla M (2003) Dispersal, environment, and floristic variation of western Amazonian forests. Science, 299, 241-244.
DOI PMID |
| [57] | Turner IM, Wong YK, Chew PT, bin Ibrahim A (1997) Tree species richness in primary and old secondary tropical forest in Singapore. Biodiversity and Conservation, 6, 537-543. |
| [58] | Wang MJ, Rong L, Ye TM, Wang Q, Li TT, Li X, Yang WS (2022) Dynamic characteristics of woody plant regeneration in karst secondary forests in central Guizhou. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 28, 1586-1593. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王梦洁, 容丽, 叶天木, 王琪, 李婷婷, 李璇, 杨文松 (2022) 黔中喀斯特次生林木本植物更新动态特征. 应用与环境生物学报, 28, 1586-1593.] | |
| [59] | Wang QG, Bao DC, Guo YL, Lu JM, Lu ZJ, Xu YZ, Zhang KH, Liu HB, Meng HJ, Jiang MX, Qiao XJ, Huang HD (2014) Species associations in a species-rich subtropical forest were not well-explained by stochastic geometry of biodiversity. PLoS ONE, 9, e97300. |
| [60] | Wright JS, Muller-Landau HC (2006) The future of tropical forest species. Biotropica, 38, 287-301. |
| [61] | Wu LH, Wang SJ, Bai XY, Tian YC, Luo GJ, Wang JF, Li Q, Chen F, Deng YH, Yang YJ, Hu ZY (2020) Climate change weakens the positive effect of human activities on karst vegetation productivity restoration in southern China. Ecological Indicators, 115, 106392. |
| [62] | Xie JY, Deng ZP (2003) Spatial pattern and size structure of Castanopsis carlesii population in Wuyun Mountain. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 22(5), 35-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谢佳彦, 邓志平 (2003) 杭州五云山米槠种群幼苗大小结构及空间分布格局研究. 生态学杂志, 22(5), 35-39.] | |
| [63] | Yu LF, Zhu SQ, Ye JZ, Wei LM, Chen ZR (2002) Dynamics of a degraded karst forest in the process of natural restoration. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 38(1), 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [喻理飞, 朱守谦, 叶镜中, 魏鲁明, 陈正仁 (2002) 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复过程中群落动态研究. 林业科学, 38(1), 1-7.] | |
| [64] | Zhu H (2007) The karst ecosystem of southern China and its biodiversity. Tropical Forestry, 35(S1), 44-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱华 (2007) 中国南方石灰岩(喀斯特)生态系统及生物多样性特征. 热带林业, 35(S1), 44-47.] | |
| [65] | Zhu JJ, Liu SR (2007) Conception of secondary forest and its relation to ecological disturbance degree. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 26, 1085-1093. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱教君, 刘世荣 (2007) 次生林概念与生态干扰度. 生态学杂志, 26, 1085-1093.] |
| [1] | Xiao-Qing Wu Meihui Zhang Suting Ge Manshu Li Kun Song Guochun Shen Jian Zhang. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Woody Plant Species Diversity and Aboveground Biomass during Near-Natural Forest Reconstruction in Shanghai: A Case Study from the Eco-Island in Minhang District [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | Tai Wang, Fujun Song, Yongsheng Zhang, Zhongyu Lou, Yanping Zhang, Yanyan Du. Fish diversity and resource status in interior drainage systems of Hexi Corridor [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | Jingyi Yuan, Xu Zhang, Zhenpeng Tian, Zizhe Wang, Yongping Gao, Dizhao Yao, Hongcan Guan, Wenkai Li, Jing Liu, Hong Zhang, Qin Ma. A comparison of methods for extracting tree species composition and quantitative characteristics in urban plant communities using UAV high-resolution RGB imagery and LiDAR point cloud [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24237-. |
| [5] | Ma Wenjun, Liu Sijia, Li Kemao, Jian Shenglong, Xue Chang’an, Han Qingxiango, Wei Jinliang, Chen Shengxue, Niu Yimeng, Cui Zhouping, Sui Ruichen, Tian Fei, Zhao Kai. Fish diversity and distribution in the source region of the Yangtze River in Qinghai Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [6] | Shang Huadan, Zhang Chuqing, Wang Mei, Pei Wenya, Li Guohong, Wang Hongbin. Species diversity and geographic distribution of poplar pests in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [7] | Wu Yuxuan, Wang Ping, Hu Xiaosheng, Ding Yi, Peng Tiantian, Zhi Qiuying, Bademu Qiqige, Li Wenjie, Guan Xiao, Li Junsheng. Evaluation of grassland degradation status and vegetation characteristics changes in Hulunbuir [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [8] | Zihong Chen, Yifei Zhang, Kai Chen, Jianying Chen, Ling Xu. Species diversity of entomopathogenic fungi and the influencing factors in the Southern Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [9] | Ke Tan, Yao Ning, Renfen Wang, Qing Wang, Danping Liang, Zibing Xin, Fang Wen. A dataset on the checklist and geographical distribution of Gesneriaceae in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [10] | Jianan Han, Yang Su, Fei Li, Junyan Liu, Yilin Zhao, Lin Li, Jiancheng Zhao, Hongzhu Liang, Min Li. Bryophytes diversity of Hebei Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [11] | Hongyu Niu, Lu Chen, Hengyue Zhao, Gulzar Abdukirim, Hongmao Zhang. Effects of urbanization on animals: From community to individual level [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [12] | Yongqiang Shi, Qingshan Luan, Xiujuan Shan, Chao Wei, Yongsong Zhao, Cece Sun, Xianshi Jin. Annual changes in zooplankton biodiversity in the southern waters of Changdao [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [13] | Xue Bai, Zhengfei Li, Yang Liu, Junqian Zhang, Duopeng Zhang, Xin Luo, Jiali Yang, Lina Du, Xuankong Jiang, Ruiwen Wu, Zhicai Xie. Species diversity and maintenance mechanisms of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Xijiang River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [14] | Jia Xu, Xiaojuan Cui, Yifei Zhang, Chang Wu, Yuandong Sun. Fish diversity and distribution in the Nanling region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [15] | Qiyu Kuang, Liang Hu. Species diversity and geographical distribution of marine benthic shell-bearing mollusks around Donghai Island and Naozhou Island, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()