



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (5): 22407. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022407 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022407
鲍虞园1, 李银康2,3, 林吴颖4, 周志琴5, 肖晓波6, 颉晓勇2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-07-16
接受日期:2022-11-10
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2023-04-20
通讯作者:
* E-mail: 作者简介:# 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Yuyuan Bao1, Yinkang Li2,3, Wuying Lin4, Zhiqin Zhou5, Xiaobo Xiao6, Xiaoyong Xie2,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-07-16
Accepted:2022-11-10
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-04-20
Contact:
* E-mail: About author:# Co-first authors
摘要:
鲎是珍贵的海洋“活化石”生物, 由于过度捕捞、环境污染和栖息地丧失等原因, 中华鲎(Tachypleus tridentatus)数量呈现“断崖式”下降, 鲎资源和栖息地保护迫在眉睫。本研究对中国南海北部近海海域成鲎和北部湾沿岸潮间带幼鲎进行调查, 并基于幼鲎调查结果, 运用MaxEnt模型对北部湾沿岸中华鲎幼鲎潜在栖息地进行预测。2018年和2019年调查结果显示南海北部海域成鲎资源分布稀疏, 两次调查的99个站点中, 仅在15个站点累计发现18只成年中华鲎, 且主要集中在北部湾海域; 潮间带幼鲎调查显示, 2019年10个调查点幼鲎丰度为0.01-0.33 ind./100 m2, 2020年14个调查点幼鲎丰度为0.01-0.65 ind./100 m2, 其中北部湾海南沿岸海域发现鲎育幼场。根据中华鲎幼鲎潜在栖息地评估结果, 最湿季均温(bio 8)和平均海表温度(mean sea surface temperature, sst)是影响其分布的主要因子。北部湾中国沿岸海域潮间带的幼鲎高适宜区占比达18.39%, 主要为北部湾广西沿岸海域、广东遂溪县沿岸海域和海南新英湾, 这些区域值得重点保护。本研究结果可丰富中华鲎种群本底数据, 为今后鲎资源保护和恢复行动的布局提供科学依据和理论支撑。
鲍虞园, 李银康, 林吴颖, 周志琴, 肖晓波, 颉晓勇 (2023) 中国南海北部近海鲎资源调查及北部湾潮间带中华鲎幼鲎潜在栖息地评估. 生物多样性, 31, 22407. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022407.
Yuyuan Bao, Yinkang Li, Wuying Lin, Zhiqin Zhou, Xiaobo Xiao, Xiaoyong Xie (2023) The current situation of horseshoe crabs in the offshore waters of northern South China Sea with analysis of the potential habitat distribution of juvenile Tachypleus tridentatus in Beibu Gulf. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22407. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022407.
| 编号 Number | 站位 Survey station | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 平均高潮位 Mean high tide level (m) | 平均低潮位 Mean low tide level (m) | 参考潮汐站位 The closest tidal station |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 渔洲坪 Yuzhouping | 108°22′ E | 21°38′ N | 3.7 | 1.15 | 防城港 Fangchenggang |
| 2 | 螃蟹档 Pangxiedang | 108°49′ E | 21°37′ N | 3.88 | 1.37 | 龙门 Longmen |
| 3 | 中三墩 Zhongsandun | 108°52′ E | 21°37′ N | |||
| 4 | 西背岭 Xibeiling | 109°10′ E | 21°24′ N | 4.0 | 1.3 | 北海 Beihai |
| 5 | 下村 Xiacun | 109°12′ E | 21°25′ N | |||
| 6 | 竹林盐场 Zhulinyanchang | 109°16′ E | 21°25′ N | |||
| 7 | 坡尾底 Poweidi | 109°33′ E | 21°31′ N | 5.05 | 2.16 | 铁山港 Tieshangang (石头埠) (Shitoubu) |
| 8 | 沙田 Shatian | 109°39′ E | 21°30′ N | |||
| 9 | 榕根山 Ronggenshan | 109°40′ E | 21°29′ N | |||
| 10 | 乌坭 Wuni | 109°45′ E | 21°29′ N | |||
| 11 | 草潭 Caotan | 109°48′ E | 21°21′ N | 4.07 | 1.51 | 下泊 Xiabo |
| 12 | 澄迈湾 Chengmaiwan | 109°59′ E | 19°56′ N | 2.46 | 0.92 | 马村港 Macungang |
| 13 | 新盈 Xinying (I) | 109°31′ E | 19°54′ N | 3.15 | 1.07 | 新盈 Xinying |
| 14 | 新英 Xinying (II) | 109°16′ E | 19°43′ N | 3.07 | 1.05 | 洋浦 Yangpu |
表1 北部湾幼鲎调查站位潮位信息表
Table 1 Tide level information of survey stations of juvenile Tachypleus tridentatus in Beibu Gulf
| 编号 Number | 站位 Survey station | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 平均高潮位 Mean high tide level (m) | 平均低潮位 Mean low tide level (m) | 参考潮汐站位 The closest tidal station |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 渔洲坪 Yuzhouping | 108°22′ E | 21°38′ N | 3.7 | 1.15 | 防城港 Fangchenggang |
| 2 | 螃蟹档 Pangxiedang | 108°49′ E | 21°37′ N | 3.88 | 1.37 | 龙门 Longmen |
| 3 | 中三墩 Zhongsandun | 108°52′ E | 21°37′ N | |||
| 4 | 西背岭 Xibeiling | 109°10′ E | 21°24′ N | 4.0 | 1.3 | 北海 Beihai |
| 5 | 下村 Xiacun | 109°12′ E | 21°25′ N | |||
| 6 | 竹林盐场 Zhulinyanchang | 109°16′ E | 21°25′ N | |||
| 7 | 坡尾底 Poweidi | 109°33′ E | 21°31′ N | 5.05 | 2.16 | 铁山港 Tieshangang (石头埠) (Shitoubu) |
| 8 | 沙田 Shatian | 109°39′ E | 21°30′ N | |||
| 9 | 榕根山 Ronggenshan | 109°40′ E | 21°29′ N | |||
| 10 | 乌坭 Wuni | 109°45′ E | 21°29′ N | |||
| 11 | 草潭 Caotan | 109°48′ E | 21°21′ N | 4.07 | 1.51 | 下泊 Xiabo |
| 12 | 澄迈湾 Chengmaiwan | 109°59′ E | 19°56′ N | 2.46 | 0.92 | 马村港 Macungang |
| 13 | 新盈 Xinying (I) | 109°31′ E | 19°54′ N | 3.15 | 1.07 | 新盈 Xinying |
| 14 | 新英 Xinying (II) | 109°16′ E | 19°43′ N | 3.07 | 1.05 | 洋浦 Yangpu |
| 环境变量 Environmental variables | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | 重要性 Permutation importance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 平均海表温度 Mean sea surface temperature (sst) | 45.9 | 10.2 |
| 最湿季均温 Mean temperature of the wettest quarter (bio 8) | 36 | 21.3 |
| 距海岸线欧氏距离 Euclidean distance to the coastline (coastline) | 4.4 | 44.4 |
| 最暖月最高温 Max temperature of the warmest month (bio 5) | 3.1 | 3.9 |
| 降水季节性变化 Precipitation seasonality (bio 15) | 2.8 | 0.6 |
| 年平均气温 Annual mean temperature (bio 1) | 2.4 | 5.2 |
| 海底地形高程 Seabed topographic elevation (etopo 1) | 2.3 | 9.4 |
| 年平均降水量 Annual precipitation (bio 12) | 0.8 | 0.2 |
| 最干月降水量 Precipitation of the driest month (bio 14) | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| 平均海表盐度 Mean sea surface salinity (sss) | 0.5 | 2.2 |
| 气温季节性变化 Temperature seasonality (bio 4) | 0.4 | 1 |
| 等温性 Isothermality (bio 3) | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| 气温日较差 Mean diurnal range (bio 2) | 0.2 | 0.5 |
表2 主要环境变量对幼年中华鲎分布的贡献率及重要性
Table 2 Contribution and importance of major environmental variables to the distribution of juvenile Tachypleus tridentatus
| 环境变量 Environmental variables | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | 重要性 Permutation importance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 平均海表温度 Mean sea surface temperature (sst) | 45.9 | 10.2 |
| 最湿季均温 Mean temperature of the wettest quarter (bio 8) | 36 | 21.3 |
| 距海岸线欧氏距离 Euclidean distance to the coastline (coastline) | 4.4 | 44.4 |
| 最暖月最高温 Max temperature of the warmest month (bio 5) | 3.1 | 3.9 |
| 降水季节性变化 Precipitation seasonality (bio 15) | 2.8 | 0.6 |
| 年平均气温 Annual mean temperature (bio 1) | 2.4 | 5.2 |
| 海底地形高程 Seabed topographic elevation (etopo 1) | 2.3 | 9.4 |
| 年平均降水量 Annual precipitation (bio 12) | 0.8 | 0.2 |
| 最干月降水量 Precipitation of the driest month (bio 14) | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| 平均海表盐度 Mean sea surface salinity (sss) | 0.5 | 2.2 |
| 气温季节性变化 Temperature seasonality (bio 4) | 0.4 | 1 |
| 等温性 Isothermality (bio 3) | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| 气温日较差 Mean diurnal range (bio 2) | 0.2 | 0.5 |
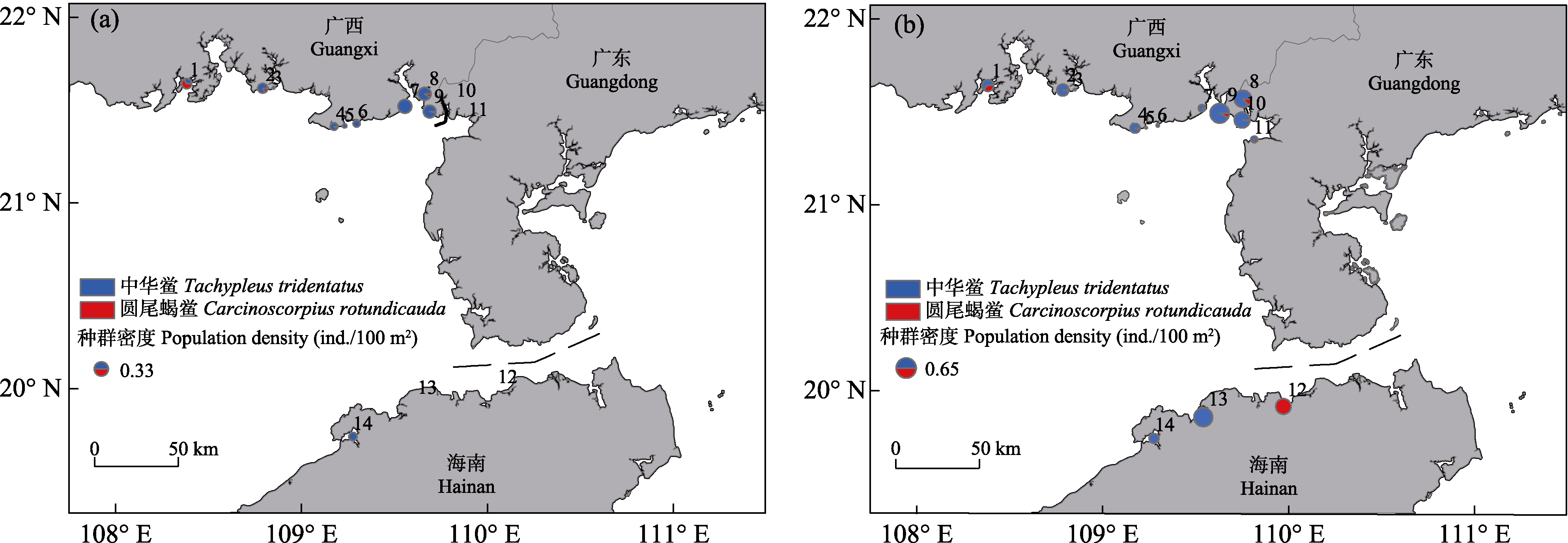
图3 2019年(a)和2020年(b)北部湾潮间带幼鲎分布。1: 渔洲坪; 2: 螃蟹档; 3: 中三墩; 4: 西背岭; 5: 下村; 6: 竹林盐场; 7: 坡尾底; 8: 沙田; 9: 榕根山; 10: 乌坭; 11: 草潭; 12: 澄迈湾; 13: 新盈; 14: 新英。
Fig. 3 Juvenile horseshoe crab distribution in the intertidal zone of Beibu Gulf in 2019 (a) and 2020 (b). 1, Yuzhouping; 2, Pangxiedang; 3, Zhongsandun; 4, Xibeiling; 5, Xiacun; 6, Zhulinyanchang; 7, Poweidi; 8, Shatian; 9, Ronggenshan; 10, Wuni; 11, Caotan; 12, Chengmaiwan; 13, Xinying (I); 14, Xinying (II).
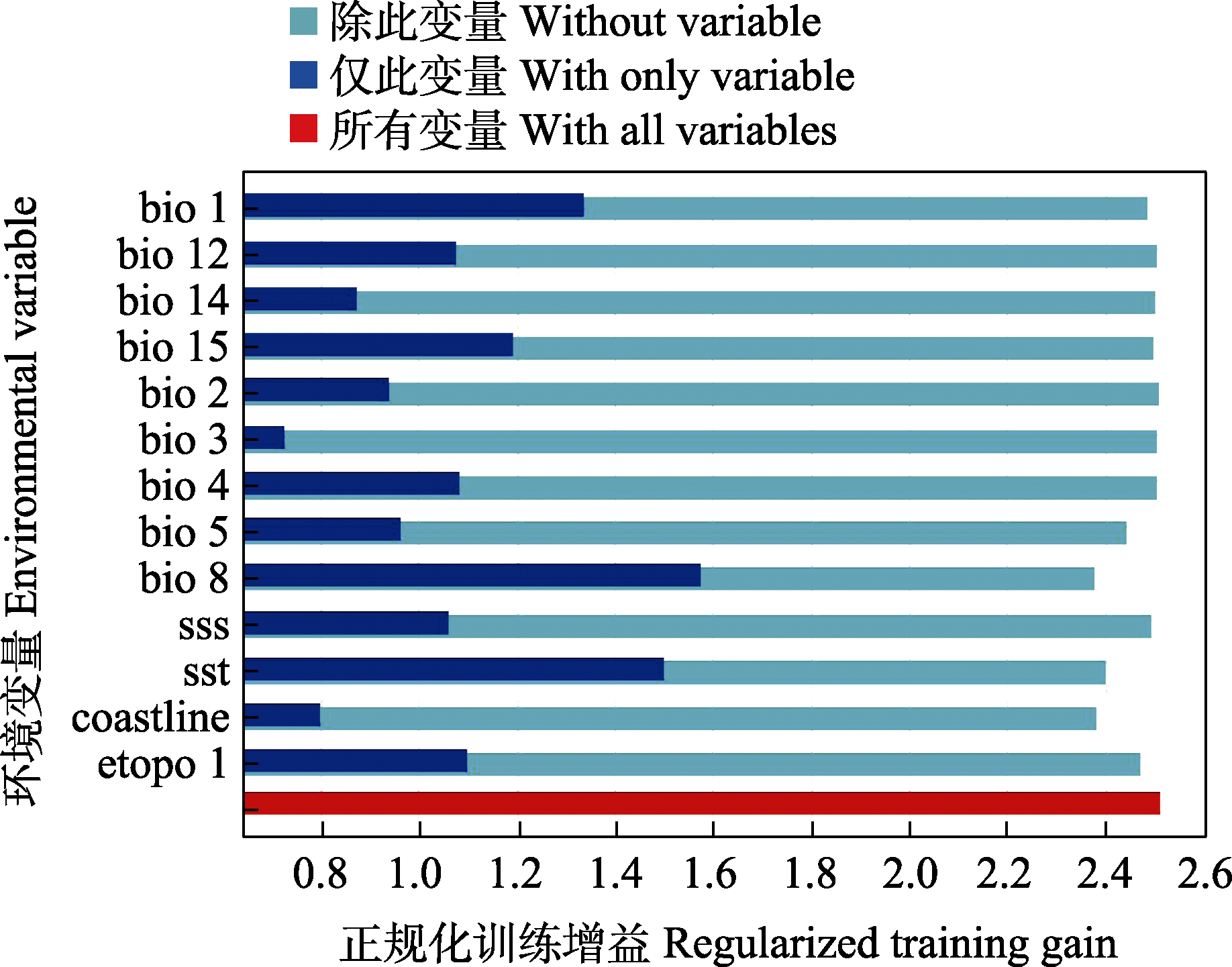
图4 基于刀切法的环境因子重要性分析。环境变量的含义见表2。
Fig. 4 Importance analysis of environmental factors based on Jackknife method. The meanings of the environmental variables are shown in Table 2.
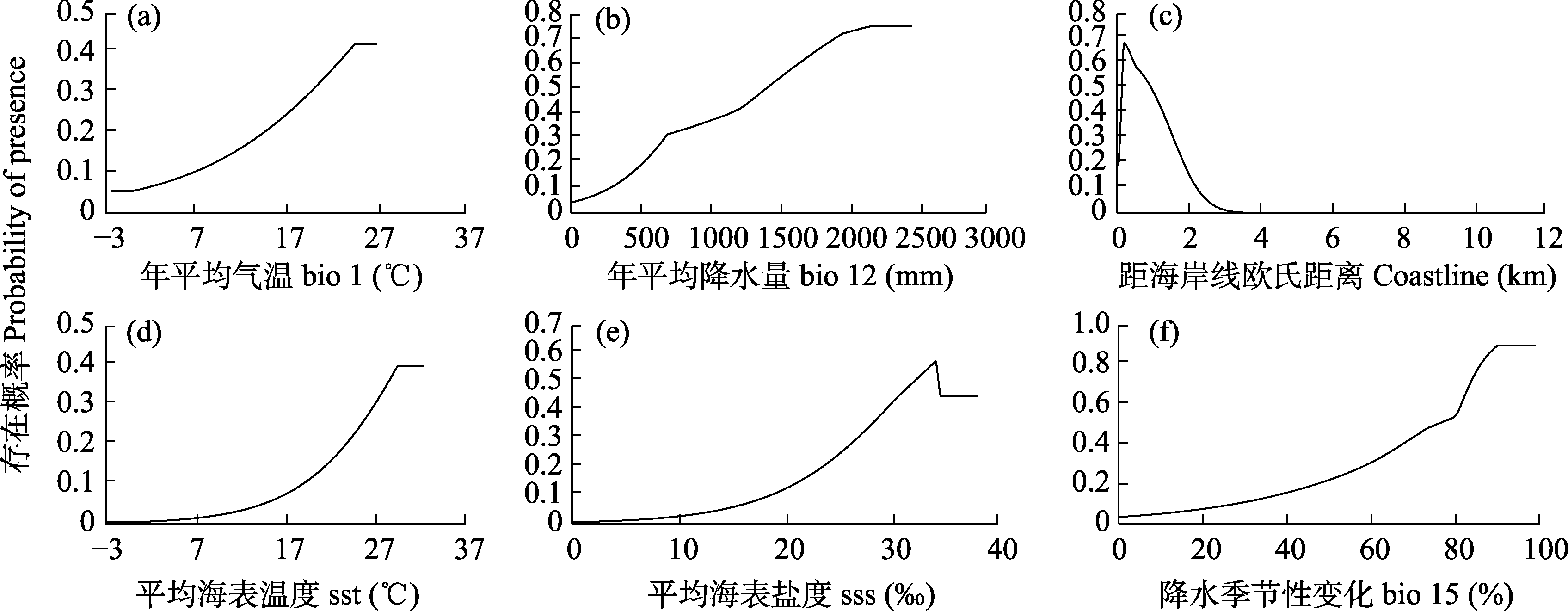
图5 MaxEnt模型中幼年中华鲎对环境变量的响应曲线。环境变量的含义见表2。
Fig. 5 Response curves of juvenile Tachypleus tridentatus to environmental variables in MaxEnt models. The meanings of the environmental variables are shown in Table 2.
| [1] | Arnold C (2020) Horseshoe crab blood is key to making a COVID-19 vaccined—but the ecosystem may suffer. https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/article/covid-vaccine-needs-horseshoe-crab-blood. (accessed on 2022-05-20) |
| [2] | Brockmann HJ, Smith MD (2009) Reproductive competition and sexual selection in horseshoe crabs. In: Biology and Conservation of Horseshoe Crabs (eds Tanacredi JT, Botton ML, Smith DR), pp. 199-221. Springer, New York. |
| [3] |
Cartwright-Taylor L, Yap VB, Hsu CC, Lou ST (2011) Distribution and abundance of horseshoe crabs Tachypleus gigas and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda around the main island of Singapore. Aquatic Biology, 13, 127-136.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Chakraborty A, Joshi PK, Sachdeva K (2016) Predicting distribution of major forest tree species to potential impacts of climate change in the central Himalayan region. Ecological Engineering, 97, 593-609.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Chao BX, Hu WJ, Chen B, Zhang D, Chen GC, Yu WW, Ma ZY, Lei GC, Wang YY (2020) Potential suitable habitat of mangroves and conservation gap analysis in Guangdong Province with MaxEnt Modeling. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39, 3785-3794. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [晁碧霄, 胡文佳, 陈彬, 张典, 陈光程, 俞炜炜, 马志远, 雷光春, 王玉玉 (2020) 基于MaxEnt模型的广东省红树林潜在适生区和保护空缺分析. 生态学杂志, 39, 3785-3794.] | |
| [6] |
Chen CP, Yang MC, Fan LF, Qiu G, Liao YY, Hsieh HL (2015) Co-occurrence of juvenile horseshoe crabs Tachypleus tridentatus and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda in an estuarine bay, southwestern China. Aquatic Biology, 24, 117-126.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Cheng H, Chabot CC, Watson WH (2015) The life history cycle of Limulus polyphemus in the Great Bay Estuary, New Hampshire, USA. In: Changing Global Perspectives on Horseshoe Crab Biology, Conservation and Management (eds Carmichael RH, Botton ML, Shin PKS, Cheung SG), pp.237-253. Springer, Cham. |
| [8] |
Chiu HMC, Morton B (2003) The morphological differentiation of two horseshoe crab species, Tachypleus tridentatus and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda (Xiphosura), in Hong Kong with a regional Asian comparison. Journal of Natural History, 37, 2369-2382.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Gallagher RV, Hughes L, Leishman MR, Wilson PD (2010) Predicted impact of exotic vines on an endangered ecological community under future climate change. Biological Invasions, 12, 4049-4063.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Gelviz-Gelvez SM, Pavón NP, Illoldi-Rangel P, Ballesteros-Barrera C (2015) Ecological niche modeling under climate change to select shrubs for ecological restoration in Central Mexico. Ecological Engineering, 74, 302-309.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Hong SG (2011) Biology of Horseshoe Crabs, Tachypleus tridentatus. Xiamen University Press, Xiamen. (in Chinese) |
| [洪水根 (2011) 中国鲎生物学研究. 厦门大学出版社, 厦门.] | |
| [12] | Hsieh HL, Chen CP (2015) Current status of Tachypleus tridentatus in Taiwan for Red List assessment. In: Changing Global Perspectives on Horseshoe Crab Biology, Conservation and Management (eds Carmichael RH, Botton ML, Shin PKS, Cheung SG), pp.383-396. Springer, Cham. |
| [13] | Hu MH, Kwan BKY, Wong YJ, Cheung SG, Shin PKS (2015) Population structure and growth of juvenile horseshoe crabs Tachypleus tridentatus and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda (Xiphosura) in Southern China. In: Changing Global Perspectives on Horseshoe Crab Biology, Conservation and Management (eds Carmichael RH, Botton ML, Shin PKS, Cheung SG), pp. 167-180. Springer, Cham. |
| [14] | International Union for Conservation of Nature IUCN (2012) IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria (Version 3.1), 2nd edn. https://portals.iucn.org/library/node/10315. (accessed on 2022-05-24) |
| [15] |
Jayasinghe SL, Kumar L (2019) Modeling the climate suitability of tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) in Sri Lanka in response to current and future climate change scenarios. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 272/273, 102-117.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Kwan BKY, Hsieh HL, Cheung SG, Shin PKS (2016) Present population and habitat status of potentially threatened Asian horseshoe crabs Tachypleus tridentatus and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda in Hong Kong: A proposal for marine protected areas. Biodiversity and Conservation, 25, 673-692.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Laurie K, Chen CP, Cheung SG, Do V, Hsieh HL, John AB, Mohamad F, Seino S, Nishida S, Shin PKS, Yang M (2019) Tachypleus tridentatus (errata version published in 2019). http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T21309A149768986.en. (accessed on 2022-05-24) |
| [18] |
Lee CNW, Morton B (2016) Changes in the distributions of juvenile horseshoe crabs (Arthropoda: Chelicerata) (2002-2014) related to environmental perturbations at Pak Nai and Ha Pak Nai, Deep Bay, Hong Kong SAR, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 108, 134-146.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Li XJ, Mao FJ, Du HQ, Zhou GM, Xing LQ, Liu TY, Han N, Liu YL, Zhu DE, Zheng JL, Dong LF, Zhang M (2019) Spatiotemporal evolution and impacts of climate change on bamboo distribution in China. Journal of Environmental Management, 248, 109265.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Liang GY (1985) Preliminary investigation on horseshoe crabs resources in Beibu Gulf. Guangxi Agricultural Science, (2), 18-20, 16. (in Chinese) |
| [梁广耀 (1985) 北部湾鲎资源的初步调查. 广西农业科学, (2), 18-20, 16.] | |
| [21] | Liao YY, Li XM (2001) Present situation of horseshoe crab resources in the sea area of China and tactics of preservation. Resources Science, 23(2), 53-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [廖永岩, 李晓梅 (2001) 中国海域鲎资源现状及保护策略. 资源科学, 23(2), 53-57.] | |
| [22] |
Liao YY, Hsieh HL, Xu SQ, Zhong QP, Lei J, Liang MZ, Fang HY, Xu LL, Lin WY, Xiao XB, Chen CP, Cheung SG, Kwan BKY (2019) Wisdom of crowds reveals decline of Asian horseshoe crabs in Beibu Gulf, China. Oryx, 53, 222-229.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Luo Z, Miao FZ, Hu MH, Wang YJ (2020) Research development on horseshoe crab: A 30-year bibliometric analysis. Frontiers in Marine Science, 7, 41.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Mamun MD, Kim S, An KG (2018) Distribution pattern prediction of an invasive alien species largemouth bass using a maximum entropy model (MaxEnt) in the Korean Peninsula. Journal of Asia-Pacific Biodiversity, 11, 516-524.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Merow C, Smith MJ, Silander JA (2013) A practical guide to MaxEnt for modeling species’ distributions: What it does, and why inputs and settings matter. Ecography, 36, 1058-1069.
DOI URL |
| [26] | National Marine Data and Information Service (2019) Tide Table 2020 (Vol. 3): From Taiwan Straits to the Beibu Gulf. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [国家海洋信息中心 (2019) 2020年潮汐表(第3册): 台湾海峡至北部湾. 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| [27] | Novitsky TJ (2015) Biomedical implications for managing the Limulus polyphemus harvest along the northeast coast of the United States. In: Changing Global Perspectives on Horseshoe Crab Biology, Conservation and Management (eds Carmichael RH, Botton ML, Shin PKS, Cheung SG), pp. 483-500. Springer, Cham. |
| [28] |
Padalia H, Srivastava V, Kushwaha SPS (2014) Modeling potential invasion range of alien invasive species, Hyptis suaveolens (L.) Poit. in India: Comparison of MaxEnt and GARP. Ecological Informatics, 22, 36-43.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Pati S, Shahimi S, Nandi D, Sarkar T, Acharya S, Sheikh H, Acharya DK, Choudhury T, John A, Nelson B, Dash BP, Edinur HA (2021) Predicting Tachypleus gigas spawning distribution with climate change in northeast coast of India. Journal of Ecological Engineering, 22, 211-220.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Rudkin DM, Young GA (2009) Horseshoe crabs—An ancient ancestry revealed. In: Biology and Conservation of Horseshoe Crabs (eds Tanacredi JT, Botton ML, Smith DR), pp.25-44. Springer, New York. |
| [31] | Seino S, Uda T, Maeda K, Yamaji K (2000) Dispersion mechanism of hatchlings of horseshoe crab Tachypleus tridentatus at tidal flat off the Yasaka rivermouth in Moriye Bay. Proceedings of Hydraulic Engineering, 44, 1209-1214. (in Japanese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Sekiguchi K (1988) Biology of Horseshoe Crabs. Science House Company Limited, Tokyo. |
| [33] | Sekiguchi K, Shuster CN Jr (2009) Limits on the global distribution of horseshoe crabs (Limulacea): Lessons learned from two lifetimes of observations:Asia and America. In: Biology and Conservation of Horseshoe Crabs (eds Tanacredi JT, Botton ML, Smith DR), pp. 5-24. Springer, New York. |
| [34] | Shuster CN, Sekiguchi K (2009) Basic habitat requirements of the extant species of horseshoe crabs (Limulacea). In: Biology and Conservation of Horseshoe Crabs (eds Tanacredi JT, Botton ML, Smith DR), pp.115-129. Springer, New York. |
| [35] | Tang QX, Wang YS (2021) Characteristics and distribution pattern of mangrove community in the Leizhou Peninsula. Ecological Science, 40(5), 23-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [唐秋霞, 王友绍 (2021) 雷州半岛红树林群落特征及其分布格局. 生态科学, 40(5), 23-32.] | |
| [36] | Wang DX, Su YQ, Wang J, Liang JR (2001) Influence of environmental factors on development of embryo and larvae in Tachypleus tridentatues. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 8(3), 10-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王德祥, 苏永全, 王军, 梁军荣 (2001) 几种因子对中国鲎胚胎和幼体发育的影响. 中国水产科学, 8(3), 10-14.] | |
| [37] | Wang T, Huang HH, Zhang P, Zhang SF, Wu FX, Liu QX, Liao XL, Xie B (2020) Acoustic survey of fisheries resources and spatial distribution in the Guishan wind farm area. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 27, 1496-1504. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王腾, 黄洪辉, 张鹏, 张书飞, 吴风霞, 刘庆霞, 廖秀丽, 谢斌 (2020) 珠海桂山风电场水域渔业资源声学评估与空间分布. 中国水产科学, 27, 1496-1504.] | |
| [38] | Wang YH (1984) The northern distribution of Tachypleus tridentatus leach in China Seas. Marine Sciences, 8(4), 38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王彝豪 (1984) 中国鲎在我国分布之北界. 海洋科学, 8(4), 38.] | |
| [39] | Waycott B (2020) Can Farming Horseshoe Crabs Help the COVID-19 Cause? https://www.aquaculturealliance.org/advocate/can-farming-horseshoe-crabs-help-the-covid-19-cause. (accessed on 2022-05-20) |
| [40] |
Wei B, Wang R, Hou K, Wang X, Wu W (2018) Predicting the current and future cultivation regions of Carthamus tinctorius L. using MaxEnt model under climate change in China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 16, e00477.
DOI URL |
| [41] | Weng ZH, Xie YJ, Xiao ZQ, Huang LM, Li J, Wang SH, Zhang YZ (2012) Distribution and resource of Chinese horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus) in Fujian and other coast water of China. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 47, 40-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [翁朝红, 谢仰杰, 肖志群, 黄良敏, 李军, 王淑红, 张雅芝 (2012) 福建及中国其他沿岸海域中国鲎资源分布现状调查. 动物学杂志, 47, 40-48.] | |
| [42] |
Xie XY, Wu Z, Wang CC, Fu YJ, Wang XP, Xu P, Huang X, Liao YY, Huang SL, Kwan KY (2020) Nursery habitat for Asian horseshoe crabs along the northern Beibu Gulf, China: Implications for conservation management under baseline gaps. Aquatic Conservation Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 30, 260-272.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Yan H, Feng L, Zhao Y, Feng L, Zhu C, Qu Y, Wang H (2020) Predicting the potential distribution of an invasive species, Erigeron canadensis L., in China with a maximum entropy model. Global Ecology and Conservation, 21, e00822. |
| [44] | Yan MY, Li QZ, Song J, Wang ZH, Wang YJ, Hu MH (2019) Prediction of potential distribution areas of Chinese horseshoe crab and mangrove horseshoe crab in the Beibu Gulf of Guangxi based on MaxEnt model and their population conservation strategies. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 3100-3109. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [颜明艳, 李琼珍, 宋洁, 王振华, 王有基, 胡梦红 (2019) 基于MaxEnt模型评估北部湾潮间带中国鲎和圆尾鲎稚鲎的潜在地理分布及种群保育对策. 生态学报, 39, 3100-3109.] | |
| [45] | Yan R, Fan JT, Xu SN, Xu YW, Sun MS, Chen ZZ (2018) Distribution characteristics of jack mackerel (Trachurus japonicus) habitat in the offshore waters of northern South China Sea. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37, 2430-2435. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [晏然, 范江涛, 徐姗楠, 许友伟, 孙铭帅, 陈作志 (2018) 南海北部近海竹荚鱼栖息地分布特征. 生态学杂志, 37, 2430-2435.] |
| [1] | 康燕 干靓 俞霖琳 何晨静 张理卿 吴婧彬. 基于自然解决方案的城市小微栖息地营造与网络构建模式:以上海市长宁区生境花园为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24528-. |
| [2] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [3] | 李佳琪, 冯一迪, 王蕾, 潘盆艳, 刘潇如, 李雪阳, 王怡涵, 王放. 上海城市环境中貉的食性分析及家域范围内的栖息地选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24131-. |
| [4] | 王艳丽, 张英, 戚春林, 张昌达, 史佑海, 杜彦君, 丁琼. 海南热带雨林国家公园生物多样性热点与保护空缺区域识别: 基于大型真菌与植物视角[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24081-. |
| [5] | 张明军, 王合升, 颜文博, 符运南, 王琦, 曾治高. 海南大田国家级自然保护区小灵猫的活动节律与栖息地选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 23420-. |
| [6] | 董廷玮, 黄美玲, 韦旭, 马硕, 岳衢, 刘文丽, 郑佳鑫, 王刚, 马蕊, 丁由中, 薄顺奇, 王正寰. 上海地区金线侧褶蛙种群的潜在空间分布格局及其景观连通性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22692-. |
| [7] | 刘伟, 王濡格, 范天巧, 娜依曼·阿不都力江, 宋新航, 肖书平, 郭宁, 帅凌鹰. 福建省明溪县黑冠鹃隼生境适宜性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22660-. |
| [8] | 邓昶, 郝杰威, 高德, 任明迅, 张莉娜. 海南受威胁苔藓植物适生热点区域识别与保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22580-. |
| [9] | 张琼悦, 邓卓迪, 胡学斌, 丁志锋, 肖荣波, 修晨, 吴政浩, 汪光, 韩东晖, 张语克, 梁健超, 胡慧建. 粤港澳大湾区城市化进程对区域内鸟类分布及栖息地连通性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22161-. |
| [10] | 王怡涵, 赵倩倩, 刁奕欣, 顾伯健, 翁悦, 张卓锦, 陈泳滨, 王放. 基于红外相机调查上海市区小灵猫的活动节律、栖息地利用及其对人类活动的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22294-. |
| [11] | 李婷婷, 朱锡红, 吴光年, 宋虓, 徐爱春. 镇海棘螈产卵场微生境选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(1): 22293-. |
| [12] | 王双贵, 郭志宏, 顾伯健, 李天醍, 苏玉兵, 马伯丞, 管宏信, 黄巧雯, 王放, 张卓锦. 六盘山华北豹的栖息地利用及保护建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22342-. |
| [13] | 马子驭, 何再新, 王一晴, 宋大昭, 夏凡, 崔士明, 苏红信, 邓建林, 李平, 李晟. 中国云豹种群分布现状与关键栖息地信息更新[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22349-. |
| [14] | 阿卜杜赛麦提·买尔迪亚力, 王云, 陶双成, 孔亚平, 王昊, 吕植. 我国道路对野生动物影响研究的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22209-. |
| [15] | 滕继荣, 刘兴明, 何礼文, 王钧亮, 黄建, 冯杰, 王放, 翁悦. 甘肃白水江国家级自然保护区林缘社区饲养犬只对大熊猫时空节律的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(1): 21204-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()