



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 22580. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022580 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022580
邓昶1,2, 郝杰威1, 高德3, 任明迅1,2, 张莉娜1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-10-16
接受日期:2023-02-16
出版日期:2023-04-20
发布日期:2023-04-20
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 基金资助:
Chang Deng1,2, Jiewei Hao1, De Gao3, Mingxun Ren1,2, Lina Zhang1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-10-16
Accepted:2023-02-16
Online:2023-04-20
Published:2023-04-20
Contact:
*E-mail: 摘要:
海南拥有丰富的热带苔藓植物, 已知受威胁苔藓植物多达29种, 但长期以来这些苔藓植物没有得到足够的关注和重视, 保护工作尚待推进。本研究利用最大熵(MaxEnt)模型模拟了其中27种海南受威胁苔藓植物的适生区, 并识别和划分了适生热点区域, 旨在提出海南受威胁苔藓植物保护优先区域和筛选重要区域, 为开展苔藓植物保护提供科学依据。结果表明: 不同苔藓植物的适生区面积和分布格局差异较大; 根据适生受威胁苔藓植物物种丰富度(species richness, SR)占丰富度峰值的比例区间(40% < SR ≤ 60%、60% < SR ≤ 80%及SR > 80%), 将适生热点区域划分为相对应的3级: (1)一般热点区域, 受威胁苔藓植物物种丰富度为11-15, 面积最大, 约2,527.2 km2; (2)显著热点区域, 丰富度为16-20, 面积约2,503.2 km2; (3)极热点区域, 丰富度为21-25, 面积最小, 约259.8 km2。各级热点区域主要分布在海南热带雨林国家公园范围内, 其中极热点区域集中在海拔约1,100 m (-1,300 m)以上的热带云雾林, 均属于该国家公园的核心区。各环境变量中, 昼夜温差月均值对11种苔藓植物的贡献率最大(46.2%-91.3%), 年温度变化范围对8种苔藓植物的贡献率最大(31.9%-82.2%), 二者对海南受威胁苔藓植物的分布影响较大。针对海南受威胁苔藓植物的保护提出相关建议: (1)通过本底调查掌握受威胁苔藓植物的分布信息和动态变化; (2)对部分物种的受威胁等级进行调整, 将受威胁苔藓植物列入海南野生植物保护名录; (3)将云雾林区域划为海南热带雨林国家公园的重要区域加以重点保护; (4)加强对适生热点区域森林维管植物的监护; (5)将国家公园范围外的热点区域设为生态恢复区, 加强对各热点区域次生林、人工林生态及苔藓植物群落恢复的科学研究。
邓昶, 郝杰威, 高德, 任明迅, 张莉娜 (2023) 海南受威胁苔藓植物适生热点区域识别与保护. 生物多样性, 31, 22580. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022580.
Chang Deng, Jiewei Hao, De Gao, Mingxun Ren, Lina Zhang (2023) Identification and protection of suitable habitat hotspots for threatened bryophytes in Hainan. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22580. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022580.
| 受威胁等级 Threat level | 数量 Number | 物种 Species | 生境 Habitat | 海南省内适生指数范围 Suitability index range in Hainan Province | 最小存在临界值 Lowest presence threshold | 适生区指数范围 Suitable area index range | AUC值 AUC value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 极危 Critically Endangered | 3 | 斜角角鳞苔 Drepanolejeunea obliqua | 树干、腐木 Trunk, rotten wood | 0.1026-0.9565 | 0.4524 | 0.4524-0.9565 | 0.9780 |
| 海南蓑藓 Macromitrium hainanense | 倒木 Fallen log | - | - | - | - | ||
| 齿边扁萼苔 Radula anceps | 树干、腐木、岩石 Trunk, rotten wood, rock | 0.1652-0.6665 | 0.4717 | 0.4717-0.6665 | 0.9140 | ||
| 濒危 Endangered | 9 | 南亚圆网藓 Cyclodictyon blumeanum | 腐木、湿石 Rotten wood, wet stone | 0.0003-0.7988 | 0.1641 | 0.1641-0.7988 | 0.9430 |
| 大角鳞苔 Drepanolejeunea grandis | 树干、倒木 Trunk, fallen log | 0.3659-0.9164 | 0.7709 | 0.7709-0.9164 | 0.9380 | ||
| 莫氏偏蒴藓 Ectropothecium moritzii | 腐木 Rotten wood | 0.0072-0.3969 | 0.1096 | 0.1096-0.3969 | 0.9130 | ||
| 爪哇扁锦藓 Glossadelphus similans | 树干、树枝、岩石 Trunk, branch, rock | 0.2851-0.9885 | 0.8539 | 0.8539-0.9885 | 0.9430 | ||
| 大胞密鳞苔 Pycnolejeunea grandiocellata | 树干 Trunk | 0.0013-0.9926 | 0.3570 | 0.3570-0.9926 | 0.9550 | ||
| 大扁萼苔 Radula sumatrana | 树干、岩石 Trunk, rock | 0.3742-0.9188 | 0.6959 | 0.6959-0.9188 | 0.9320 | ||
| 刺网藓 Syrrhopodon armatispinosus | 树干、腐木、土壤 Trunk, rotten wood, soil | 0.3782-1.0000 | 0.6886 | 0.6886-1.0000 | 0.9870 | ||
| 巴西网藓 Syrrhopodon prolifer | 树干、树基、腐木 Trunk, tree base, rotten wood | 0.5412-0.9990 | 0.7479 | 0.7479-0.9990 | 0.8990 | ||
| 东亚毛鳞苔 Thysananthus aculeatus | 树皮、树枝、湿石 Bark, branch, wet stone | 0.0232-0.9748 | 0.2159 | 0.2159-0.9748 | 0.9920 | ||
| 易危 Vulnerable | 17 | 顶胞藓粗枝变种 Acroporium stramineum var. turgidum | 树皮 Bark | 0.4362-0.8578 | 0.6608 | 0.6608-0.8578 | 0.8470 |
| 吊罗鞭苔 Bazzania tiaoloensis | 树干、腐木、岩石 Trunk, rotten wood, rock | - | - | - | - | ||
| 越南鞭苔 Bazzania vietnamica | 树基 Tree base | 0.3419-1.0000 | 0.5946 | 0.5946-1.0000 | 0.9530 | ||
| 带叶耳平藓 Calyptothecium phyllogonioides | 树干 Trunk | 0.1472-0.5241 | 0.4868 | 0.4868-0.5241 | 0.9220 | ||
| 尾枝耳平藓 Calyptothecium ramosii | 树干 Trunk | 0.5498-0.8135 | 0.7221 | 0.7221-0.8135 | 0.9380 | ||
| 假肋唇鳞苔 Cheilolejeunea falsinervis | 树干、树基 Trunk, tree base | 0.3472-0.9612 | 0.7415 | 0.7415-0.9612 | 0.9100 | ||
| 海南花锦藓 Chionostomum hainanense | 竹子 Bamboo | 0.6046-0.9956 | 0.9791 | 0.9791-0.9956 | 0.8540 | ||
| 海南疣鳞苔 Cololejeunea hainanensis | 叶片、树干 Leaf, trunk | 0.2855-0.9993 | 0.6199 | 0.6199-0.9993 | 0.8580 | ||
| 白绿细鳞苔 Lejeunea pallidevirens | 叶片、树干、石头、土壤、腐木 Leaf, trunk, stone, soil, rotten wood | 0.1007-1.0000 | 0.7678 | 0.7678-1.0000 | 0.9490 | ||
| 婆罗洲扁萼苔 Radula borneensis | 树干、树枝 Trunk, branch | 0.4270-0.9384 | 0.6275 | 0.6275-0.9384 | 0.8890 | ||
| 曲瓣扁萼苔 Radula kurzii | 树干、树枝、湿石 Trunk, branch, wet stone | 0.1590-0.9751 | 0.5964 | 0.5964-0.9751 | 0.9940 | ||
| 卷叶网藓 Syrrhopodon involutus | 树干 Trunk | 0.0128-0.8764 | 0.4580 | 0.4580-0.8764 | 0.8960 | ||
| 舌叶网藓 Syrrhopodon loreus | 树干 Trunk | 0.0453-0.5046 | 0.1213 | 0.1213-0.5046 | 0.9330 | ||
| 直叶网藓 Syrrhopodon muelleri | 树干、树基、树根 Trunk, tree base, root | 0.0017-0.4039 | 0.3037 | 0.3037-0.4039 | 0.9400 | ||
| 阔叶网藓 Syrrhopodon semiliber | 树干、树枝、石头、腐木 Trunk, branch, stone, rotten wood | 0.4755-0.8286 | 0.6888 | 0.6888-0.8286 | 0.9160 | ||
| 海南明叶藓 Vesicularia hainanensis | 土壤、岩面薄土 Soil, thin soil on rock | 0.4839-0.9814 | 0.8820 | 0.8820-0.9814 | 0.9170 | ||
| 东亚虫叶苔 Zoopsis liukiuensis | 腐木、树基 Rotten wood, tree base | 0.0033-0.9979 | 0.5574 | 0.5574-0.9979 | 0.9850 |
表1 海南29种受威胁苔藓植物模型模拟相关信息
Table 1 Information on the model stimulation of 29 threatened bryophyte species in Hainan
| 受威胁等级 Threat level | 数量 Number | 物种 Species | 生境 Habitat | 海南省内适生指数范围 Suitability index range in Hainan Province | 最小存在临界值 Lowest presence threshold | 适生区指数范围 Suitable area index range | AUC值 AUC value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 极危 Critically Endangered | 3 | 斜角角鳞苔 Drepanolejeunea obliqua | 树干、腐木 Trunk, rotten wood | 0.1026-0.9565 | 0.4524 | 0.4524-0.9565 | 0.9780 |
| 海南蓑藓 Macromitrium hainanense | 倒木 Fallen log | - | - | - | - | ||
| 齿边扁萼苔 Radula anceps | 树干、腐木、岩石 Trunk, rotten wood, rock | 0.1652-0.6665 | 0.4717 | 0.4717-0.6665 | 0.9140 | ||
| 濒危 Endangered | 9 | 南亚圆网藓 Cyclodictyon blumeanum | 腐木、湿石 Rotten wood, wet stone | 0.0003-0.7988 | 0.1641 | 0.1641-0.7988 | 0.9430 |
| 大角鳞苔 Drepanolejeunea grandis | 树干、倒木 Trunk, fallen log | 0.3659-0.9164 | 0.7709 | 0.7709-0.9164 | 0.9380 | ||
| 莫氏偏蒴藓 Ectropothecium moritzii | 腐木 Rotten wood | 0.0072-0.3969 | 0.1096 | 0.1096-0.3969 | 0.9130 | ||
| 爪哇扁锦藓 Glossadelphus similans | 树干、树枝、岩石 Trunk, branch, rock | 0.2851-0.9885 | 0.8539 | 0.8539-0.9885 | 0.9430 | ||
| 大胞密鳞苔 Pycnolejeunea grandiocellata | 树干 Trunk | 0.0013-0.9926 | 0.3570 | 0.3570-0.9926 | 0.9550 | ||
| 大扁萼苔 Radula sumatrana | 树干、岩石 Trunk, rock | 0.3742-0.9188 | 0.6959 | 0.6959-0.9188 | 0.9320 | ||
| 刺网藓 Syrrhopodon armatispinosus | 树干、腐木、土壤 Trunk, rotten wood, soil | 0.3782-1.0000 | 0.6886 | 0.6886-1.0000 | 0.9870 | ||
| 巴西网藓 Syrrhopodon prolifer | 树干、树基、腐木 Trunk, tree base, rotten wood | 0.5412-0.9990 | 0.7479 | 0.7479-0.9990 | 0.8990 | ||
| 东亚毛鳞苔 Thysananthus aculeatus | 树皮、树枝、湿石 Bark, branch, wet stone | 0.0232-0.9748 | 0.2159 | 0.2159-0.9748 | 0.9920 | ||
| 易危 Vulnerable | 17 | 顶胞藓粗枝变种 Acroporium stramineum var. turgidum | 树皮 Bark | 0.4362-0.8578 | 0.6608 | 0.6608-0.8578 | 0.8470 |
| 吊罗鞭苔 Bazzania tiaoloensis | 树干、腐木、岩石 Trunk, rotten wood, rock | - | - | - | - | ||
| 越南鞭苔 Bazzania vietnamica | 树基 Tree base | 0.3419-1.0000 | 0.5946 | 0.5946-1.0000 | 0.9530 | ||
| 带叶耳平藓 Calyptothecium phyllogonioides | 树干 Trunk | 0.1472-0.5241 | 0.4868 | 0.4868-0.5241 | 0.9220 | ||
| 尾枝耳平藓 Calyptothecium ramosii | 树干 Trunk | 0.5498-0.8135 | 0.7221 | 0.7221-0.8135 | 0.9380 | ||
| 假肋唇鳞苔 Cheilolejeunea falsinervis | 树干、树基 Trunk, tree base | 0.3472-0.9612 | 0.7415 | 0.7415-0.9612 | 0.9100 | ||
| 海南花锦藓 Chionostomum hainanense | 竹子 Bamboo | 0.6046-0.9956 | 0.9791 | 0.9791-0.9956 | 0.8540 | ||
| 海南疣鳞苔 Cololejeunea hainanensis | 叶片、树干 Leaf, trunk | 0.2855-0.9993 | 0.6199 | 0.6199-0.9993 | 0.8580 | ||
| 白绿细鳞苔 Lejeunea pallidevirens | 叶片、树干、石头、土壤、腐木 Leaf, trunk, stone, soil, rotten wood | 0.1007-1.0000 | 0.7678 | 0.7678-1.0000 | 0.9490 | ||
| 婆罗洲扁萼苔 Radula borneensis | 树干、树枝 Trunk, branch | 0.4270-0.9384 | 0.6275 | 0.6275-0.9384 | 0.8890 | ||
| 曲瓣扁萼苔 Radula kurzii | 树干、树枝、湿石 Trunk, branch, wet stone | 0.1590-0.9751 | 0.5964 | 0.5964-0.9751 | 0.9940 | ||
| 卷叶网藓 Syrrhopodon involutus | 树干 Trunk | 0.0128-0.8764 | 0.4580 | 0.4580-0.8764 | 0.8960 | ||
| 舌叶网藓 Syrrhopodon loreus | 树干 Trunk | 0.0453-0.5046 | 0.1213 | 0.1213-0.5046 | 0.9330 | ||
| 直叶网藓 Syrrhopodon muelleri | 树干、树基、树根 Trunk, tree base, root | 0.0017-0.4039 | 0.3037 | 0.3037-0.4039 | 0.9400 | ||
| 阔叶网藓 Syrrhopodon semiliber | 树干、树枝、石头、腐木 Trunk, branch, stone, rotten wood | 0.4755-0.8286 | 0.6888 | 0.6888-0.8286 | 0.9160 | ||
| 海南明叶藓 Vesicularia hainanensis | 土壤、岩面薄土 Soil, thin soil on rock | 0.4839-0.9814 | 0.8820 | 0.8820-0.9814 | 0.9170 | ||
| 东亚虫叶苔 Zoopsis liukiuensis | 腐木、树基 Rotten wood, tree base | 0.0033-0.9979 | 0.5574 | 0.5574-0.9979 | 0.9850 |
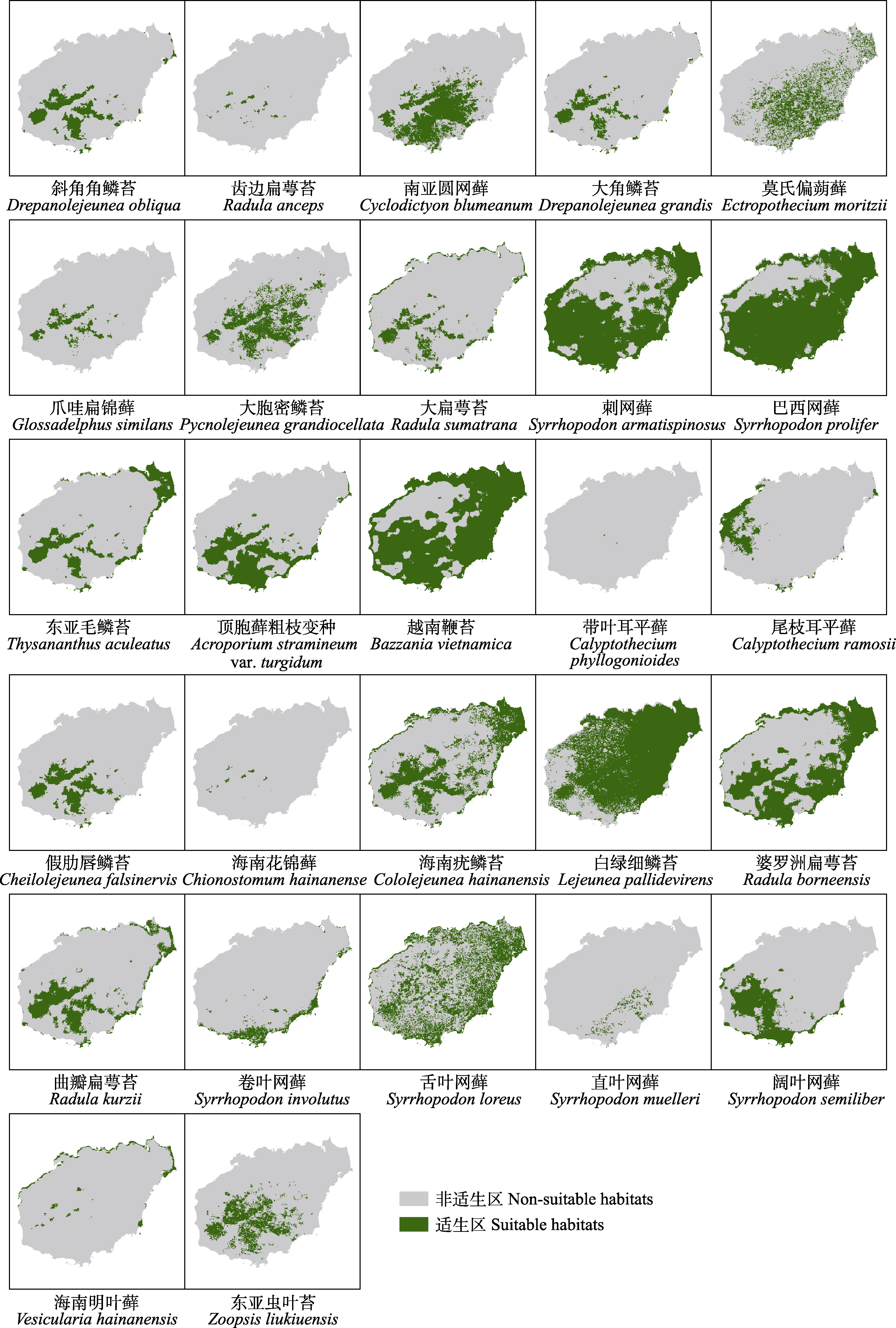
图1 海南27种受威胁苔藓植物适生区(仅截取有适生区分布的海南岛)
Fig. 1 The suitable habitats of 27 threatened bryophyte species in Hainan (Only Hainan Island with distribution of suitable habitats was intercepted)
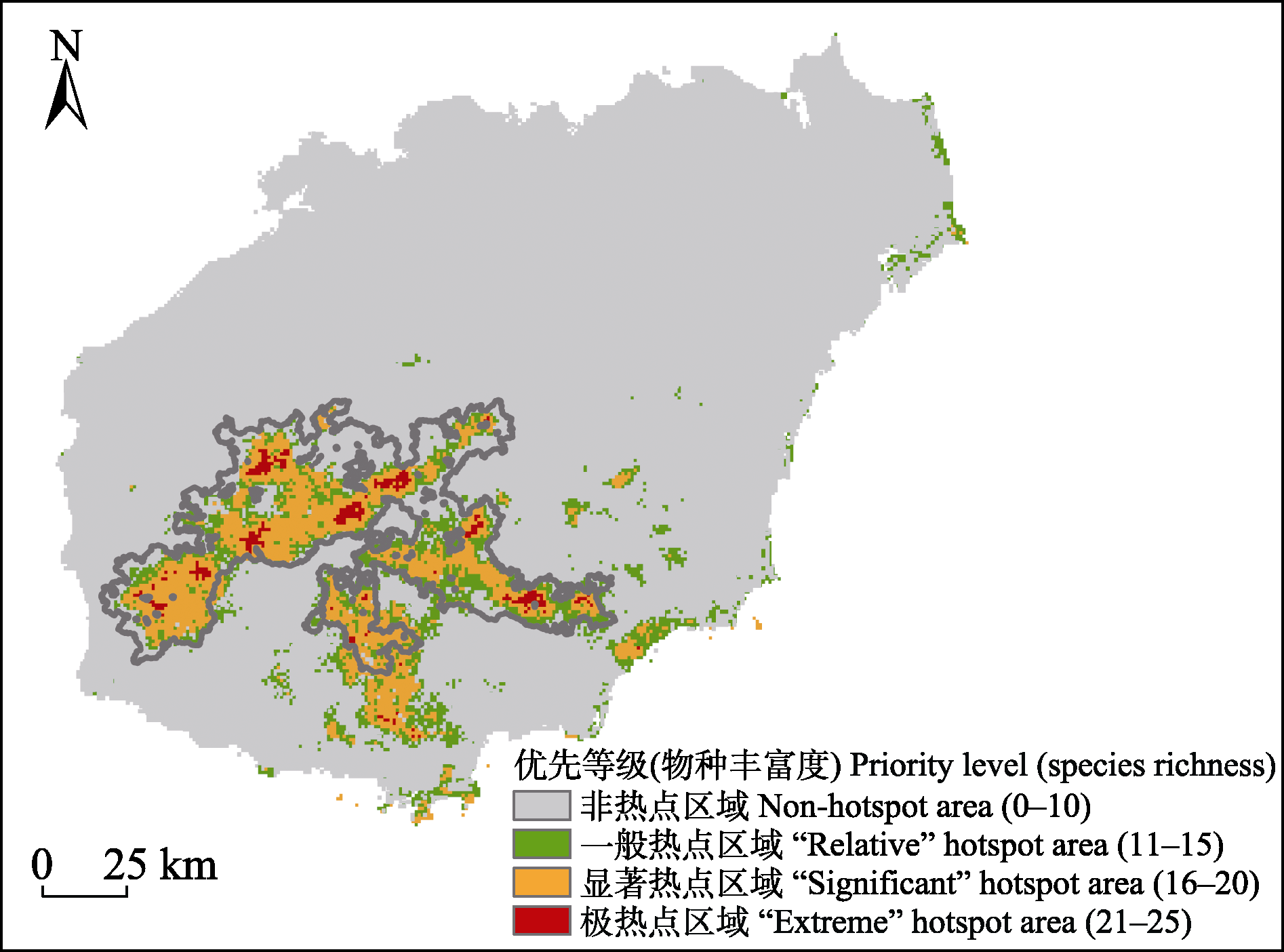
图2 海南27种受威胁苔藓植物适生热点图(仅截取有热点分布的海南岛)。灰色线为海南热带雨林国家公园边界。
Fig. 2 The map of suitable habitat hotspots of 27 threatened bryophyte species in Hainan (Only Hainan Island with distribution of hotspots was intercepted). The gray line depicting the boundary of National Park of Hainan Tropical Rainforest.
| [1] |
Bates JW, Thompson K, Grime JP (2005) Effects of simulated long-term climatic change on the bryophytes of a limestone grassland community. Global Change Biology, 11, 757-769.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Berdugo MB, Quant JM, Wason JW, Dovciak M (2018) Latitudinal patterns and environmental drivers of moss layer cover in extratropical forests. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 27, 1213-1224.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Bond-Lamberty B, Gower ST, Amiro B, Ewers BE (2011) Measurement and modelling of bryophyte evaporation in a boreal forest chronosequence. Ecohydrology, 4, 26-35.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Bubb P, May I, Miles L, Sayer J (2004) Cloud Forest Agenda. The UN Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC), Cambridge. |
| [5] |
Cañadas EM, Fenu G, Peñas J, Lorite J, Mattana E, Bacchetta G (2014) Hotspots within hotspots: Endemic plant richness, environmental drivers, and implications for conservation. Biological Conservation, 170, 282-291.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Cao T, Zhu RL, Guo SL, Zuo BR, Yu J (2006) A brief report of the first red list of endangered bryophytes in China. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 26, 756-762. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 曹同, 朱瑞良, 郭水良, 左本荣, 于晶 (2006) 中国首批濒危苔藓植物红色名录简报. 植物研究, 26, 756-762.]
DOI |
|
| [7] |
Ceballos G, Ehrlich PR, Barnosky AD, García A, Pringle RM, Palmer TM (2015) Accelerated modern human-induced species losses: Entering the sixth mass extinction. Science Advances, 1, e1400253.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Chen LD, Hu W, Li DQ, Cheng DM, Zhong AW (2019) Prediction of suitable distribution areas of the endangered plant wild Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. in China. Plant Science Journal, 37, 731-740. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈陆丹, 胡菀, 李单琦, 程冬梅, 钟爱文 (2019) 珍稀濒危植物野生莲的适生分布区预测. 植物科学学报, 37, 731-740.] | |
| [9] |
Cong MY, Jian MF, Xu YY, Tang LY, Li JJ, Yang WJ, Zhu YM (2021) Geographical distribution and migration routes of the medical bryophyte, Climacium dendroides, under climate warming in China. Plant Biosystems, 156, 663-670.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Deb CR, Jamir NS, Kikon ZP (2017) Distribution prediction model of a rare orchid species (Vanda bicolor Griff.) using small sample size. American Journal of Plant Sciences, 8, 1388-1398. |
| [11] |
Désamoré A, Laenen B, Stech M, Papp B, Hedenäs L, Mateo RG, Vanderpoorten A (2012) How do temperate bryophytes face the challenge of a changing environment? Lessons from the past and predictions for the future. Global Change Biology, 18, 2915-2924.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Du BM, Zhang N, Ji MC (2011) A review on the research of propagation and cultivation of bryophytes. Journal of Jiangsu Forestry Science & Technology, 38(2), 44-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杜宝明, 张楠, 季梦成 (2011) 苔藓植物的繁殖栽培研究进展. 江苏林业科技, 38(2), 44-48.] | |
| [13] |
Elith J, Graham CH, Anderson RP, Dudík M, Ferrier S, Guisan A, Hijmans RJ, Huettmann F, Leathwick JR, Lehmann A, Li J, Lohmann LG, Loiselle BA, Manion G, Moritz C, Nakamura M, Nakazawa Y, Overton JMcC, Peterson AT, Phillips SJ, Richardson K, Scachetti-Pereira R, Schapire RE, Soberón J, Williams S, Wisz MS, Zimmermann NE (2006) Novel methods improve prediction of species’ distributions from occurrence data. Ecography, 29, 129-151.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Ferretto A, Smith P, Genney D, Matthews R, Brooker R (2021) Modelling the future distribution of rare bryophytes in Scotland: Is inclusion of habitat loss important? bioRxiv, doi: 10.1101/2021.08.30.458156.
DOI |
| [15] |
Foster P (2001) The potential negative impacts of global climate change on tropical montane cloud forests. Earth-Science Reviews, 55, 73-106.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Francisco-Ortega J, Wang ZS, Wang FG, Xing FW, Liu H, Xu H, Xu WX, Luo YB, Song XQ, Gale S, Boufford DE, Maunder M, An SQ (2010) Seed plant endemism on Hainan Island: A framework for conservation actions. Botanical Review, 76, 346-376.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Gao Q (2003) Flora Bryophytorum Sinicorum, Vol. 9. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 高谦 (2003) 中国苔藓志 (第九卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [18] | Glime JM (2017) Bryophyte Ecology, Vol. 1. Physiological Ecology. Michigan Technological University & the International Association of Bryologists. https://digitalcommons.mtu.edu/bryophyte-ecology/. (accessed on 2021-04-25) |
| [19] | Gradstein SR, Griffin D, Morales MI, Nadkarni NM (2001) Diversity and habitat differentiation of mosses and liverworts in the cloud forest of Monteverde, Costa Rica. Caldasia, 23, 203-212. |
| [20] |
Gundale MJ, Deluca TH, Nordin A (2011) Bryophytes attenuate anthropogenic nitrogen inputs in boreal forests. Global Change Biology, 17, 2743-2753.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Guo SL, He S (2008) A new species of Macromitrium (Orthotrichaceae) from Hainan, China. The Bryologist, 111, 505-509.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Hao JW, Chu LM (2021) Short-term detrimental impacts of increasing temperature and photosynthetically active radiation on the ecophysiology of selected bryophytes in Hong Kong, southern China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 31, e1868. |
| [23] | He L, Guo SL, Xiong YX (2019) Applying MaxEnt model to predict geographical distribution of rare and endangered bryophytes Bryoxiphium norvegicum (Bryophyta: Bryaceae) in China. Ecological Science, 38(6), 46-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 何林, 郭水良, 熊源新 (2019) 应用MaxEnt模型预测濒危植物虾藓Bryoxiphium norvegicum在中国的分布范围. 生态科学, 38(6), 46-52.] | |
| [24] |
He Q, Jia Y (2017) Assessing the threat status of China’s bryophytes. Biodiversity Science, 25, 774-780. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 何强, 贾渝 (2017) 中国苔藓植物濒危等级的评估原则和评估结果. 生物多样性, 25, 774-780.]
DOI |
|
| [25] |
Hernandez PA, Graham CH, Master LL, Albert DL (2006) The effect of sample size and species characteristics on performance of different species distribution modeling methods. Ecography, 29, 773-785.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Hu JH, Liu Y (2014) Unveiling the conservation biogeography of a data-deficient endangered bird species under climate change. PLoS ONE, 9, e84529.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Hu YJ, Li YX (1992) The Tropical Rain Forest of Hainan Island. Guangdong Higher Education Press, Guangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 胡玉佳, 李玉杏 (1992) 海南岛热带雨林. 广东高等教育出版社, 广州.] | |
| [28] | IUCN (2012) IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria, Version 3.1, 2nd edn. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland & Cambridge, UK. |
| [29] | Jia Y, He S (2013) Species Catalogue of China (Vol. 1)•Plants•Bryophytes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 贾渝, 何思 (2013) 中国生物物种名录(第一卷)•植物•苔藓植物. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [30] |
Jiang YB, Fan M, Hu RG, Zhao JS, Wu YP (2018) Mosses are better than leaves of vascular plants in monitoring atmospheric heavy metal pollution in urban areas. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15, 1105.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Klopfer PH (1959) Environmental determinants of faunal diversity. The American Naturalist, 93, 337-342.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Kou J, Wang TJ, Yu FY, Sun YW, Feng C, Shao XM (2020) The moss genus Didymodon as an indicator of climate change on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecological Indicators, 113, 106204.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Li JL, Qin RP, Xu T, Liu H, Wang YQ (2022) Situations, problems and countermeasures of management and protection ability in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park. Tropical Forestry, 50(2), 73-76, 72. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李佳灵, 秦荣鹏, 徐涛, 刘辉, 王友强 (2022) 海南热带雨林国家公园管护能力建设现状、问题与对策. 热带林业, 50(2), 73-76, 72.] | |
| [34] |
Liao YJ, Song XT, Ye YH, Gu JQ, Wang RH, Zhuo gabayong, Zhao DP, Shao XM (2023) Climate change may pose additional threats to the endangered endemic species Encalypta buxbaumioidea in China. Diversity, 15, 269.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Liu WQ, Dai XH, Wang YF, Lei CY (2008) Analysis of environmental factors affecting the distribution of epiphytic bryophytes at Heishiding Nature Reserve, Guangdong Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28, 1080-1088. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘蔚秋, 戴小华, 王永繁, 雷纯义 (2008) 影响广东黑石顶树附生苔藓分布的环境因子. 生态学报, 28, 1080-1088.] | |
| [36] | Liu Y (2016) Predictions of suitable distribution of Meteorium in China under climate change. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), (6), 192-202. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘艳 (2016) 气候变化下我国蔓藓属(Meteorium)适生分布的预测. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (6), 192-202.] | |
| [37] | Liu Y, Atigul M, Sabiram S, Mamtimin S (2017) Modeling potential distributions of the desiccation-tolerant moss genus Schistidium in Xinjiang under climate change. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 37, 1881-1887. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘艳, 阿提古丽·毛拉, 沙毕热木·斯热义力, 买买提明·苏来曼, (2017) 气候变化下耐旱藓类连轴藓属在新疆的分布模拟. 西北植物学报, 37, 1881-1887.] | |
| [38] |
Long WX, Ding Y, Zang RG, Yang M, Chen SW (2011) Environmental characteristics of tropical cloud forests in the rainy season in Bawangling National Nature Reserve on Hainan Island, South China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 35, 137-146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 龙文兴, 丁易, 臧润国, 杨民, 陈少伟 (2011) 海南岛霸王岭热带云雾林雨季的环境特征. 植物生态学报, 35, 137-146.]
DOI |
|
| [39] | Ma KP (2001) Hotspots assessment and conservation priorities identification of biodiversity in China should be emphasized. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 25, 125, 124. (in Chinese) |
| [ 马克平 (2001) 中国生物多样性热点地区(Hotspot)评估与优先保护重点的确定应该重视. 植物生态学报, 25, 125, 124.] | |
| [40] |
Ma XY, Xu H, Cao ZY, Shu L, Zhu RL (2022) Will climate change cause the global peatland to expand or contract? Evidence from the habitat shift pattern of Sphagnum mosses. Global Change Biology, 28, 6419-6432.
DOI URL |
| [41] | Mao LH, Li Y, Liu C, Fang YM (2017) Predication of potential distribution of Haplocladium microphyllum in China based on MaxEnt model. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36, 54-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 毛俐慧, 李垚, 刘畅, 方炎明 (2017) 基于MaxEnt模型预测细叶小羽藓在中国的潜在分布区. 生态学杂志, 36, 54-60.] | |
| [42] | Ministry of Environmental Protection (2011) China National Biodiversity Conservation Strategy and Action Plan (2011-2030). China Environmental Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [环境保护部 (2011) 中国生物多样性保护战略与行动计划(2011-2030). 中国环境科学出版社, 北京. ] | |
| [43] |
Murray‐Smith C, Brummitt NA, Oliveira-Filho AT, Bachman S, Moat J, Lughadha EMN, Lucas EJ (2009) Plant diversity hotspots in the Atlantic coastal forests of Brazil. Conservation Biology, 23, 151-163.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, da Fonseca GAB, Kent J (2000) Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature, 403, 853-858.
DOI |
| [45] |
Nimis PL, Fumagalli F, Bizzotto A, Codogno M, Skert N (2002) Bryophytes as indicators of trace metals pollution in the River Brenta (NE Italy). Science of the Total Environment, 286, 233-242.
PMID |
| [46] |
Ning Y, Lei JR, Song XQ, Han SM, Zhong YF (2018) Modeling the potential suitable habitat of Impatiens hainanensis, a limestone-endemic plant. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 42, 946-954. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 宁瑶, 雷金睿, 宋希强, 韩淑梅, 钟云芳 (2018) 石灰岩特有植物海南凤仙花潜在适宜生境分布模拟. 植物生态学报, 42, 946-954.]
DOI |
|
| [47] |
Orme CDL, Davies RG, Burgess M, Eigenbrod F, Pickup N, Olson VA, Webster AJ, Ding TS, Rasmussen PC, Ridgely RS, Stattersfield AJ, Bennett PM, Blackburn TM, Gaston KJ, Owens IPF (2005) Global hotspots of species richness are not congruent with endemism or threat. Nature, 436, 1016-1019.
DOI |
| [48] |
Patiño J, Medina R, Vanderpoorten A, González-Mancebo JM, Werner O, Devos N, Mateo RG, Lara F, Ros RM (2013) Origin and fate of the single-island endemic moss Orthotrichum handiense. Journal of Biogeography, 40, 857-868.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Patiño J, Vanderpoorten A (2018) Bryophyte biogeography. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 37, 175-209.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Pearson RG, Raxworthy CJ, Nakamura M, Peterson AT (2007) Predicting species distributions from small numbers of occurrence records: A test case using cryptic geckos in Madagascar. Journal of Biogeography, 34, 102-117.
DOI URL |
| [51] | Peng Q, Chen Y (2007) Characteristics of bryophytes and artificial cultivation methods. Journal of Jiujiang University, (6), 71-72, 92. (in Chinese) |
| [ 彭琴, 陈晔 (2007) 苔藓植物的特性及人工培养方法. 九江学院学报, (6), 71-72, 92.] | |
| [52] |
Pertoldi C, Bach LA (2007) Evolutionary aspects of climate-induced changes and the need for multidisciplinarity. Journal of Thermal Biology, 32, 118-124.
DOI URL |
| [53] | Pimm SL, Jenkins CN, Abell R, Brooks TM, Gittleman JL, Joppa LN, Raven PH, Roberts CM, Sexton JO (2014) The biodiversity of species and their rates of extinction, distribution, and protection. Science, 344, 1246752. |
| [54] |
Pisarenko O, Makunina N (2020) Bioclimatic modeling of moss distribution: MaxEnt interpretation for test species. BIO Web of Conferences, 24, 00066.
DOI URL |
| [55] | Pócs T (1982) Tropical forest bryophytes. In: Bryophyte Ecology (ed. Smith AJE), pp. 59-104. Chapman and Hall, London. |
| [56] | Qian LY, Huang ZX, Yang SC, Cao WZ (2021) Study on spatial conservation priority pattern of key protected plants in Xiamen. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41, 4367-4378. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 钱灵颖, 黄智洵, 杨盛昌, 曹文志 (2021) 厦门市重点保护植物空间优先保护格局研究. 生态学报, 41, 4367-4378.] | |
| [57] |
Qin HN, Yang Y, Dong SY, He Q, Jia Y, Zhao LN, Yu SX, Liu HY, Liu B, Yan YH, Xiang JY, Xia NH, Peng H, Li ZY, Zhang ZX, He XJ, Yin LK, Lin YL, Liu QR, Hou YT, Liu Y, Liu QX, Cao W, Li JQ, Chen SL, Jin XH, Gao TG, Chen WL, Ma HY, Geng YY, Jin XF, Chang CY, Jiang H, Cai L, Zang CX, Wu JY, Ye JF, Lai YJ, Liu B, Lin QW, Xue NX (2017) Threatened species list of China’s higher plants. Biodiversity Science, 25, 696-744. (in Chinese and in English)
DOI URL |
|
[ 覃海宁, 杨永, 董仕勇, 何强, 贾渝, 赵莉娜, 于胜祥, 刘慧圆, 刘博, 严岳鸿, 向建英, 夏念和, 彭华, 李振宇, 张志翔, 何兴金, 尹林克, 林余霖, 刘全儒, 侯元同, 刘演, 刘启新, 曹伟, 李建强, 陈世龙, 金效华, 高天刚, 陈文俐, 马海英, 耿玉英, 金孝锋, 常朝阳, 蒋宏, 蔡蕾, 臧春鑫, 武建勇, 叶建飞, 赖阳均, 刘冰, 林秦文, 薛纳新 (2017) 中国高等植物受威胁物种名录. 生物多样性, 25, 696-744.]
DOI |
|
| [58] |
Sérgio C, Figueira R, Draper D, Menezes R, Sousa AJ (2007) Modelling bryophyte distribution based on ecological information for extent of occurrence assessment. Biological Conservation, 135, 341-351.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
Sérgio C, Garcia CA, Vieira C, Hespanhol H, Sim-Sim M, Stow S, Figueira R (2014) Conservation of Portuguese red-listed bryophytes species in Portugal: Promoting a shift in perspective on climate changes. Plant Biosystems, 148, 837-850.
DOI URL |
| [60] | Sha W, Li YY, Zhang ST, Zhang MJ, Zhang YF, Wang M, Ma TY (2021) Exploration of genetic diversity of Syrrhopodon prolifer var. prolifer based on ISSR markers. Molecular Plant Breeding, 19, 1366-1372. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 沙伟, 李莹莹, 张时通, 张梅娟, 张艳馥, 王曼, 马天意 (2021) 基于ISSR对巴西网藓原变种(Syrrhopodon prolifer var. prolifer)遗传多样性的探讨. 分子植物育种, 19, 1366-1372.] | |
| [61] | Shen Y, Yu J, Guo SL (2015) Macromitrium and Orthotrichum distribution patterns under different climate warming scenarios in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 6449-6459. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 沈阳, 于晶, 郭水良 (2015) 不同气候变化情境下中国木灵藓属和蓑藓属植物的潜在分布格局. 生态学报, 35, 6449-6459.] | |
| [62] | Soberón J, Peterson AT (2005) Interpretation of models of fundamental ecological niches and species’ distributional areas. Biodiversity Informatics, 2, 1-10. |
| [63] |
Still CJ, Foster PN, Schneider SH (1999) Simulating the effects of climate change on tropical montane cloud forests. Nature, 398, 608-610.
DOI |
| [64] | Vanderpoorten A, Goffinet B (2009) Introduction to Bryophytes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [65] | Wang Q, Guo SL (2016) Climate adaptability of Rhodobryum giganteum and its potential geographic distribution in China. Journal of Hangzhou Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 15, 368-376. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王强, 郭水良 (2016) 暖地大叶藓的气候适应性及其在中国的潜在分布区预测. 杭州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 15, 368-376.] | |
| [66] |
Wang XX, Long WX, Yang XB, Xiong MH, Kang Y, Huang J, Wang X, Hong XJ, Zhou ZL, Lu YQ, Fang J, Li SX (2016) Patterns of plant diversity within and among three tropical cloud forest communities in Hainan Island. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 40, 469-479. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 王茜茜, 龙文兴, 杨小波, 熊梦辉, 康勇, 黄瑾, 王旭, 洪小江, 周照骊, 陆雍泉, 方精, 李时兴 (2016) 海南岛3个林区热带云雾林植物多样性变化. 植物生态学报, 40, 469-479.]
DOI |
|
| [67] |
Wang ZM, Ye W, Xing FW (2019) Bryophyte diversity on a tropical continental island (Hainan, China): Potential vulnerable species and environmental indicators. Journal of Bryology, 41, 350-360.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
Wen C, Gu L, Wang H, Lü Z, Hu RC, Zhong J (2015) GAP analysis on national nature reserves in China based on the distribution of endangered species. Biodiversity Science, 23, 591-600. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 闻丞, 顾垒, 王昊, 吕植, 胡若成, 钟嘉 (2015) 基于最受关注濒危物种分布的国家级自然保护区空缺分析. 生物多样性, 23, 591-600.]
DOI |
|
| [69] |
Wierzcholska S, Dyderski MK, Jagodziński AM (2020) Potential distribution of an epiphytic bryophyte depends on climate and forest continuity. Global and Planetary Change, 193, 103270.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Wilbraham J (2018) Taxonomic notes on African Orthotrichaceae. 3. New synonymy in Madagascan Macromitrium. Journal of Bryology, 40, 393-398.
DOI URL |
| [71] | Wu DL, Zhang L (2013) Bryophyte Flora of Guangdong. Guangdong Science and Technology Press, Guangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 吴德邻, 张力 (2013) 广东苔藓志. 广东科技出版社, 广州.] | |
| [72] | Wu JY, Xue DY, Wang AH, Zhao FW (2016) Case studies on the identification of key biodiversity areas (KBAs) in foreign countries and progress and prospects in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 3108-3114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 武建勇, 薛达元, 王爱华, 赵富伟 (2016) 生物多样性重要区域识别——国外案例、国内研究进展. 生态学报, 36, 3108-3114.] | |
| [73] |
Wu XY, Dong SK, Liu SL, Liu QR, Han YH, Zhang XL, Su XK, Zhao HD, Feng J (2018) Identifying priority areas for grassland endangered plant species in the Sanjiangyuan Nature Reserve based on the MaxEnt model. Biodiversity Science, 26, 138-148. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 武晓宇, 董世魁, 刘世梁, 刘全儒, 韩雨晖, 张晓蕾, 苏旭坤, 赵海迪, 冯憬 (2018) 基于MaxEnt模型的三江源区草地濒危保护植物热点区识别. 生物多样性, 26, 138-148.]
DOI |
|
| [74] | Yang XB, Chen ZZ, Li DH, Li YD, Ding Q, Chen YK, Lin ZQ, Huang J, Zhang K, Long WX, Guo T, Xu ZL, Chen H, Wang LJ, Lu G (2019) Flora of Hainan, Vol. 1. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 杨小波, 陈宗铸, 李东海, 李意德, 丁琼, 陈玉凯, 林泽钦, 黄谨, 张凯, 龙文兴, 郭涛, 徐中亮, 陈辉, 王力军, 卢刚 (2019) 海南植被志(第一卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [75] |
Ye PC, Zhang GF, Zhao X, Chen H, Si Q, Wu JY (2021) Potential geographical distribution and environmental explanations of rare and endangered plant species through combined modeling: A case study of Northwest Yunnan, China. Ecology and Evolution, 11, 13052-13067.
DOI PMID |
| [76] | Zhang LN (2014) History, present situation and prospect of bryological research in Hainan Island, China. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 22, 643-652. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张莉娜 (2014) 海南岛苔藓植物研究历史、现状与展望. 热带亚热带植物学报, 22, 643-652.] | |
| [77] | Zhao DX, Wang C, Sun ZK, Hao ZZ (2020) Epiphytic bryophyte diversity and its influencing factors. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40, 2523-2532. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵德先, 王成, 孙振凯, 郝泽周 (2020) 树附生苔藓植物多样性及其影响因素. 生态学报, 40, 2523-2532.] | |
| [78] |
Zhu RL, Ma XY, Cao C, Cao ZY (2022) Advances in research on bryophyte diversity in China. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22378. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 朱瑞良, 马晓英, 曹畅, 曹子寅 (2022) 中国苔藓植物多样性研究进展. 生物多样性, 30, 22378.]
DOI |
|
| [79] | Zhu RL, So ML (1999) Additions of Lejeuneaceae taxa to the hepatic flora of Yunnan, China. Annales Botanici Fennici, 36, 219-229. |
| [80] | Zotz G, Bader MY (2009) Epiphytic plants in a changing world-global:Change effects on vascular and non-vascular epiphytes. In: Progress in Botany, Vol. 70 (eds Lüttge U, Beyschlag W, Büdel B, Francis D), pp.147-170. Springer, Berlin. |
| [1] | 刘咏华, 童光蓉, 余航远, 王宁宁, 任海保, 陈磊, 马克平, 米湘成. 钱江源-百山祖国家公园候选区钱江源园区冠层三维结构及光谱特征对人为干扰的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24174-. |
| [2] | 苏红巧, 余得光, 牟昆仑. 国家公园与国土空间规划和用途管制制度衔接路径探讨[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24570-. |
| [3] | 田志奇, 苏杨. 环境相关国际公约的中国履约模式和在《生物多样性公约》中的应用: 从完成《昆蒙框架》目标和发挥国家公园作用的角度[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24593-. |
| [4] | 张雨琦, 文君, 张引, 李晟之. 大熊猫国家公园全民公益性评价研究: 基于利益相关者感知视角[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24240-. |
| [5] | 王艳丽, 张英, 戚春林, 张昌达, 史佑海, 杜彦君, 丁琼. 海南热带雨林国家公园生物多样性热点与保护空缺区域识别: 基于大型真菌与植物视角[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24081-. |
| [6] | 王巍伟, 米湘成, 王宁宁, 任海保, 唐治喜, 张主宁, 马克平, 陈磊. 2005-2020年浙江古田山24 ha亚热带常绿阔叶林动态监测样地植物多样性数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24417-. |
| [7] | 杜宇晨, 刘蓓萌, 陈俊峰, 王浩, 谢屹. 基于结构方程模型的农户保护意愿影响因素分析: 以东北虎豹国家公园珲春片区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23155-. |
| [8] | 耿云, 寇一祎, 范新卓, 徐姝瑶, 丛丽, 张玉钧. 基于卡诺模型的大熊猫国家公园自然教育需求研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23101-. |
| [9] | 崔国发. 关于自然保护地整合优化工作中几个关键问题的讨论与建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 22447-. |
| [10] | 董廷玮, 黄美玲, 韦旭, 马硕, 岳衢, 刘文丽, 郑佳鑫, 王刚, 马蕊, 丁由中, 薄顺奇, 王正寰. 上海地区金线侧褶蛙种群的潜在空间分布格局及其景观连通性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22692-. |
| [11] | 刘伟, 王濡格, 范天巧, 娜依曼·阿不都力江, 宋新航, 肖书平, 郭宁, 帅凌鹰. 福建省明溪县黑冠鹃隼生境适宜性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22660-. |
| [12] | 李世东. 中国和美国国家公园时空发展及驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 23040-. |
| [13] | 鲍虞园, 李银康, 林吴颖, 周志琴, 肖晓波, 颉晓勇. 中国南海北部近海鲎资源调查及北部湾潮间带中华鲎幼鲎潜在栖息地评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22407-. |
| [14] | 龚心语, 黄宝荣. 国家公园全民公益性评估指标体系: 以青藏高原国家公园群为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22571-. |
| [15] | 陈天傲, 李想. 我国国家公园管理体系优化路径: 以中央层面为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22485-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()