



生物多样性 ›› 2014, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 182-188. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13163 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2014.13163
所属专题: 生物入侵
张熙骜1,3, 隋晓云1,2,*( ), 吕植2, 陈毅峰1,*(
), 吕植2, 陈毅峰1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2013-07-15
接受日期:2013-12-09
出版日期:2014-03-20
发布日期:2014-04-03
通讯作者:
隋晓云,陈毅峰
基金资助:
Xi’ao Zhang1,3, Xiaoyun Sui1,2,*( ), Zhi Lü2, Yifeng Chen1,*(
), Zhi Lü2, Yifeng Chen1,*( )
)
Received:2013-07-15
Accepted:2013-12-09
Online:2014-03-20
Published:2014-04-03
Contact:
Sui Xiaoyun,Chen Yifeng
摘要:
受引种、贸易等人类活动的影响, 麦穗鱼(Pseudorasbora parva)和鲫(Carassius auratus)在全球范围内已经广泛分布并造成巨大的生态危害。根据野外采样和文献记录, 本文系统整理了麦穗鱼和鲫在世界各地的分布情况, 以高达2.5弧分分辨率的环境数据底图, 利用Maxent模型预测了麦穗鱼和鲫在全球的适生区, 以期为防控麦穗鱼和鲫的入侵提供早期预警。结果表明麦穗鱼和鲫在全球范围的分布区非常广泛, 除南极洲外的各个大洲均有其适生区, 因此这两种鱼还有继续扩散的潜力, 并可能在美国、巴西和阿根廷等国家出现由生物入侵导致的生态学问题。麦穗鱼的适生区主要集中在15º–55º N之间, 欧洲是麦穗鱼入侵的重灾区, 尤其是法国、荷兰周边的西欧国家和匈牙利、塞尔维亚周边的东欧国家; 而美国中部的密西西比河流域、东部及南部沿海, 以及西雅图至加拿大的温哥华之间是麦穗鱼潜在入侵风险性极高的区域。鲫自然分布于欧洲至东亚的广大地区, 目前已经在澳大利亚、加拿大、美国、马达加斯加、印度和越南等国家有分布, 未来还可能进一步扩散至大洋洲的新西兰和新喀里多尼亚, 北美洲的墨西哥至南美洲的阿根廷, 以及非洲的塞内加尔、几内亚和南非等国家; 尤其是南美洲的阿根廷和巴西, 非洲西部的几内亚、喀麦隆等国家将是鲫入侵风险极高的区域。
张熙骜, 隋晓云, 吕植, 陈毅峰 (2014) 基于Maxent的两种入侵性鱼类(麦穗鱼和鲫)的全球适生区预测. 生物多样性, 22, 182-188. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13163.
Xi’ao Zhang,Xiaoyun Sui,Zhi Lü,Yifeng Chen (2014) A prediction of the global habitat of two invasive fishes (Pseudorasbora parva and Carassius auratus) from East Asia using Maxent. Biodiversity Science, 22, 182-188. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13163.
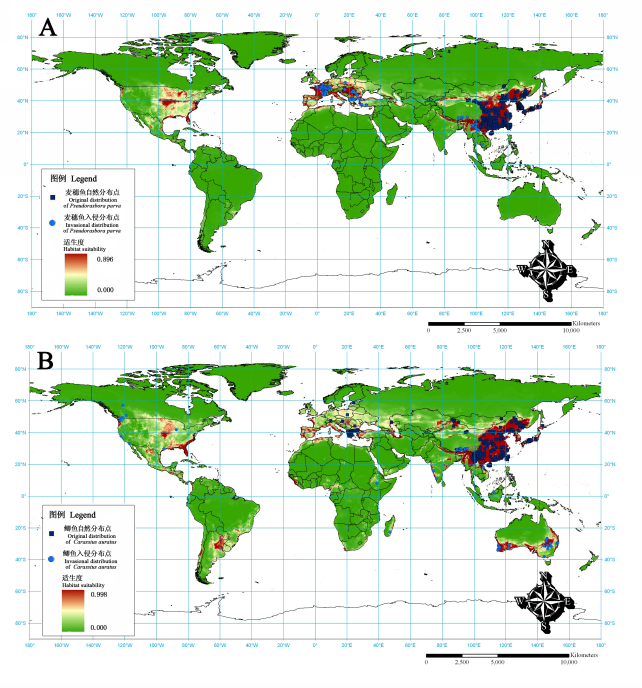
图1 麦穗鱼和鲫全球潜在分布区预测结果。A: 麦穗鱼; B: 鲫。
Fig. 1 The results of the potential habitat prediction of Pseudorasbora parva (A) and Carassius auratus (B) in the world
| 代码 Code | 数据描述 | Data description |
|---|---|---|
| BIO1 | 年均温 | Annual mean temperature |
| BIO2 | 平均温度月较差 | Mean diurnal range |
| (月最高温与月最低温的平均差) | (Mean of monthly (max temp–min temp)) | |
| BIO3 | 等温线 | Isothermality (BIO2/BIO7) (* 100) |
| BIO4 | 温度季节变化 | Temperature seasonality (standard deviation *100) |
| BIO5 | 最暖月最高温度 | Max temperature of warmest month |
| BIO6 | 最冷月最低温度 | Min temperature of coldest month |
| BIO7 | 温度全年波动范围 | Temperature annual range (BIO5–BIO6) |
| BIO8 | 最湿润季节平均温度 | Mean temperature of wettest quarter |
| BIO9 | 最干燥季节平均温度 | Mean temperature of driest quarter |
| BIO10 | 最暖月平均温度 | Mean temperature of warmest month |
| BIO11 | 最冷月平均温度 | Mean temperature of coldest month |
| BIO12 | 年降水量 | Annual precipitation |
| BIO13 | 最湿润月降雨量 | Precipitation of wettest month |
| BIO14 | 最干燥月降雨量 | Precipitation of driest month |
| BIO15 | 各季节降雨量 | Precipitation seasonality (coefficient of variation) |
| BIO16 | 最湿润季节降雨量 | Precipitation of wettest quarter |
| BIO17 | 最干燥季节降雨量 | Precipitation of driest quarter |
| BIO18 | 最暖季节平均温度 | Mean temperature of warmest quarter |
| BIO19 | 最冷季节平均温度 | Mean temperature of coldest quarter |
| Tmean1–12 | 1–12月平均温度 | Average monthly mean temperature |
| Tmin1–12 | 1–12月最小温度 | Average monthly minimum temperature |
| Tmax1–12 | 1–12月最大温度 | Average monthly maximum temperature |
| Prec1–12 | 1–12月平均降雨量 | Average monthly precipitation |
| Alt | 高程 | Altitude (elevation above sea level) |
附录I WorldClim气候数据名称及描述
Appendix I The name and description of WorldClim data
| 代码 Code | 数据描述 | Data description |
|---|---|---|
| BIO1 | 年均温 | Annual mean temperature |
| BIO2 | 平均温度月较差 | Mean diurnal range |
| (月最高温与月最低温的平均差) | (Mean of monthly (max temp–min temp)) | |
| BIO3 | 等温线 | Isothermality (BIO2/BIO7) (* 100) |
| BIO4 | 温度季节变化 | Temperature seasonality (standard deviation *100) |
| BIO5 | 最暖月最高温度 | Max temperature of warmest month |
| BIO6 | 最冷月最低温度 | Min temperature of coldest month |
| BIO7 | 温度全年波动范围 | Temperature annual range (BIO5–BIO6) |
| BIO8 | 最湿润季节平均温度 | Mean temperature of wettest quarter |
| BIO9 | 最干燥季节平均温度 | Mean temperature of driest quarter |
| BIO10 | 最暖月平均温度 | Mean temperature of warmest month |
| BIO11 | 最冷月平均温度 | Mean temperature of coldest month |
| BIO12 | 年降水量 | Annual precipitation |
| BIO13 | 最湿润月降雨量 | Precipitation of wettest month |
| BIO14 | 最干燥月降雨量 | Precipitation of driest month |
| BIO15 | 各季节降雨量 | Precipitation seasonality (coefficient of variation) |
| BIO16 | 最湿润季节降雨量 | Precipitation of wettest quarter |
| BIO17 | 最干燥季节降雨量 | Precipitation of driest quarter |
| BIO18 | 最暖季节平均温度 | Mean temperature of warmest quarter |
| BIO19 | 最冷季节平均温度 | Mean temperature of coldest quarter |
| Tmean1–12 | 1–12月平均温度 | Average monthly mean temperature |
| Tmin1–12 | 1–12月最小温度 | Average monthly minimum temperature |
| Tmax1–12 | 1–12月最大温度 | Average monthly maximum temperature |
| Prec1–12 | 1–12月平均降雨量 | Average monthly precipitation |
| Alt | 高程 | Altitude (elevation above sea level) |
| [40] | Yin MC (殷名称) (1995) Fish Ecology (鱼类生态学). China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [41] | .Yue PQ (乐佩琦) (2000) Fauna Sinica · Osteichthyes ·Cyprini-formes III (中国动物志・硬骨鱼纲・鲤形目(下卷)). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [42] | Zhang YP (张亚平), Jiang YX (蒋有绪), Zhang RZ (张润志), Sang WG (桑卫国), Chen YF (陈毅峰), Xue DY (薛大勇), Yang JX (杨君兴), Peng H (彭华), Zhang KQ (张克勤) (2009) Biological invasion in China: current situation and countermeasures. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences(中国科学院院刊), 24, 411–413. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | Austin MP (2002) Spatial prediction of species distribution: an interface between ecological theory and statistical modelling. Ecological Modelling, 157, 101–118. |
| [2] | Bănărescu P (2002) The Freshwater Fishes of Europe. Cyprinidae 2, Part Ⅲ: Carassius to Cyprinus. AULA, Wiebelsheim. |
| [3] | Berg LS (1949) Freshwater fishes of the USSR and adjacent countries. Guide to the Fauna of USSR, 27, 927–1382. |
| [4] | Britton JR, Davies GD, Brazier M (2009) Eradication of the invasive Pseudorasbora parva results in increased growth and production of native fishes. Ecology of Freshwater Fish, 18, 8–14. |
| [5] | Britton JR, Davies GD, Brazier M (2010a) Towards the successful control of the invasive Pseudorasbora parva in the UK. Biological Invasions, 12, 125–131. |
| [6] | Britton JR, Davies GD, Harrod C (2010b) Trophic interactions and consequent impacts of the invasive fish Pseudorasbora parva in a native aquatic foodweb: a field investigation in the UK. Biological Invasions, 12, 1533–1542. |
| [7] | Chen F (陈锋), Chen YF (陈毅峰) (2010) Investigation and protection strategies of fishes of Lhasa River. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica(水生生物学报), 34, 278–285. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Chen PX (陈佩薰) (1959) Fish biological research of Carassius auratus in Liangzi Lake. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica(水生生物学集刊), (4), 411–419. (in Chinese) |
| [9] | Chen XY (陈小勇) (2013) Checklist of fishes of Yunnan. Zoological Research(动物学研究), 34, 281–343. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [10] | Chen YY, Cui YB (1993) Some aspects of biological diversity in freshwater ecosystems. Chinese Biodiversity, 1(Suppl.), 46–49. |
| [11] | Chen YY (陈宜瑜) (1998) Fauna Sinica · Osteichthyes ·Cypriniformes II (中国动物志・硬骨鱼纲・鲤形目 (中卷)). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [12] | Cheng L (程磊), Chang YM (常玉梅), Lu CY (鲁翠云), Cao DC (曹顶臣), Sun XW (孙效文) (2012) DNA barcoding and species and subspecies classification within genus Carassius. Zoological Research(动物学研究), 33, 463–472. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Chu XL (禇新洛), Chen YR (陈银瑞) (1989) Fishes of Yunnan (云南鱼类志). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [14] | David LM, Howard SG, Mark GM, Stephen JB (2004) Distribution and impacts of introduced freshwater fishes in Western Australia. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 38, 511–523. |
| [15] | Dong CY (董存有) (1984) An observations of fish biology on Pseudorasbora parva. Fisheries Science & Technology(水产科技), (1), 50–53. (in Chinese) |
| [16] | Elith J, Graham CH, Anderson R, Dudík M, Ferrier S, Guisan A, Hijmans RJ, Huettmann F, Leathwick JR, Lehmann A, Li J, Lohmann LG, Loiselle BA, Manion G, Moritz C, Nakamura M, Nakazawa Y, Overton JMM, Peterson AT, Phillips SJ, Richardson K, Scachetti-Pereira R, Schapire RE, Soberón J, Williams S, Wisz MS, Zimmermann NE (2006) Novel methods improve prediction of species’ distributions from occurrence data. Ecography, 29, 129–151. |
| [17] | Froese R, Pauly D (2011) FishBase. . (2013. 04. 10 |
| [18] | Giovanelli JGR, Haddad CFB, Alexandrino J (2008) Predicting the potential distribution of the alien invasive American bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus) in Brazil. Biological Invasions, 10, 585–590. |
| [19] | Gozlan RE, Hilaire S, Feist SW, Martin P, Kent ML (2005) Biodiversity: disease threat to European fish. Nature, 435, 1046. |
| [20] | Gozlan RE, Andreou D, Asaeda T, Beyer K, Bouhadad R, Burnard D, Caiola N, Cakic P, Djikanovic V, Esmaeili HR, Falka I, Golicher D, Harka A, Jeney G, Kovac V, Musil J, Nocita A, Povz M, Poulet N, Virbickas T, Wolter C, Tarkan AS, Tricarico E, Trichkova T, Verreycken H, Witkowski A, Zhang CG, Zweimueller I, Britton JR (2010) Pan-contin- ental invasion of Pseudorasbora parva: towards a better understanding of freshwater fish invasions. Fish and Fisheries, 11, 315–340. |
| [21] | Hijmans R, Cameron S, Parra J, Jones P, Jarvis A (2004) The WorldClim interpolated global terrestrial climate surfaces. Version 1.3. . (2013. 04. 10 |
| [22] | Humphrey JD, Ashburner LD (1993) Spread of the bacterial fish pathogen Aeromonas salmonicida after importation of infected goldfish, Carassius auratus, into Australia. Australian Veterinary Journal, 70, 453–454. |
| [23] | Kalous L, Bohlen J, Rylková K, Petrtýl M (2012) Hidden diversity within the Prussian carp and designation of a neotype for Carassius gibelio (Teleostei: Cyprinidae). Ichthyological Exploration of Freshwaters, 21, 11–18. |
| [24] | Kim YU, Myung JG, Han KH, Koh JR (1996) The fish fauna of Namdae Stream in Kangreung, Korea. Journal of the Korean Fisheries Society, 29, 262–266. |
| [25] | Kolar CS, Lodge DM (2001) Progress in invasion biology: predicting invaders. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 16, 199–204. |
| [26] | Kottelat M, Freyhof J (2007) Handbook of European Fresh- water Fishes. Publications Kottelat, Cornol, Switzerland. |
| [27] | Lockwood J, Hoopes M, Marchetti M (2009) Invasion Ecology. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford. |
| [28] | Lusková V, Lusk S, Halačka K, Vetešnik L (2010) Carassius auratus gibelio: the most successful invasive fish in waters of the Czech Republic. Russian Journal of Biological Invasions, 1, 176–180. |
| [29] | Mack RN, Simberloff D, Lonsdale WM, Evans H, Clout M, Bazzaz FA (2000) Biotic invasions: causes, epidemiology, global consequences, and control. Ecological Applications, 10, 689–710. |
| [30] | Onikura N, Nakajima J (2013) Age, growth and habitat use of the topmouth gudgeon, Pseudorasbora parva in irrigation ditches on northwestern Kyushu Island, Japan. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 29, 186–192. |
| [31] | Pan Y (潘勇), Cao WX (曹文宣), Xu LP (徐立蒲), Yin SR (殷守仁) (2006) History and approach of invasion from domestic and abroad fishes. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University(大连水产学院学报), 21, 72–77. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Phillips SJ, Anderson RP, Schapire RE (2006) Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecological Modelling, 190, 231–259. |
| [33] | Sang WG (桑卫国), Zhu L (朱丽), Ma KP (马克平) (2006) Issues, phenomena and study emphases of alien species invasion in China. Advances in Earth Science(地球科学进展), 21, 305–312. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [34] | Suarez-Seoane S, de la Morena ELG, Prieto MBM, Osborne PE, de Juana E (2008) Maximum entropy niche-based modelling of seasonal changes in little bustard (Tetrax tetrax) distribution. Ecological Modelling, 219, 17–29. |
| [35] | Thuiller W, Richardson DM, Pysek P, Midgley GF, Hughes GO, Rouget M (2005) Niche-based modelling as a tool for predicting the risk of alien plant invasions at a global scale. Global Change Biology, 11, 2234–2250. |
| [36] | Wu XW (伍献文) (1977) The Cyprinid Fishes of China, Vol. 2 (中国鲤科鱼类志). Shanghai Science & Technogy Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [37] | Xie YH (解玉浩) (2007) Freshwater Fishes in Northeast Region of China (东北地区淡水鱼类). Liaoning Science and Technology Press, Shenyang. (in Chinese) |
| [38] | Xu RM (徐汝梅), Ye WH (叶万辉) (2003) Biological Invasions: Theory and Practice (生物入侵: 理论与实践). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [39] | Yang RB (杨瑞斌), Bian SJ (边书京), Zhou J (周洁), Xie CX (谢从新) (2004) Study on food habits of Pseudorasbora parva in Liangzi Lake. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University(华中农业大学学报), 23, 331–334. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 付梦娣, 朱彦鹏, 任月恒, 李爽, 秦乐, 谢正君, 王清春, 张立博. 新疆野生动物通道空间布局优化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24346-. |
| [2] | 杜聪聪, 冯学宇, 陈志林. 桥头堡效应中气候生态位差异的缩小促进了红火蚁的入侵[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24276-. |
| [3] | 原雪姣, 张渊媛, 张衍亮, 胡璐祎, 桑卫国, 杨峥, 陈颀. 基于飞机草历史分布数据拟合的物种分布模型及其预测能力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24288-. |
| [4] | 韩丽霞, 王永健, 刘宣. 外来物种入侵与本土物种分布区扩张的异同[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23396-. |
| [5] | 邓昶, 郝杰威, 高德, 任明迅, 张莉娜. 海南受威胁苔藓植物适生热点区域识别与保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22580-. |
| [6] | 张琼悦, 邓卓迪, 胡学斌, 丁志锋, 肖荣波, 修晨, 吴政浩, 汪光, 韩东晖, 张语克, 梁健超, 胡慧建. 粤港澳大湾区城市化进程对区域内鸟类分布及栖息地连通性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22161-. |
| [7] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [8] | 魏博, 刘林山, 谷昌军, 于海彬, 张镱锂, 张炳华, 崔伯豪, 宫殿清, 土艳丽. 紫茎泽兰在中国的气候生态位稳定且其分布范围仍有进一步扩展的趋势[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 21443-. |
| [9] | 刘艳杰, 黄伟, 杨强, 郑玉龙, 黎绍鹏, 吴昊, 鞠瑞亭, 孙燕, 丁建清. 近十年植物入侵生态学重要研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22438-. |
| [10] | 滕继荣, 刘兴明, 何礼文, 王钧亮, 黄建, 冯杰, 王放, 翁悦. 甘肃白水江国家级自然保护区林缘社区饲养犬只对大熊猫时空节律的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(1): 21204-. |
| [11] | 张晨, 马伟, 陈晨, 汪沐阳, 徐文轩, 杨维康. 重大工程影响下新疆卡拉麦里山有蹄类野生动物自然保护区鹅喉羚的生境格局变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(1): 21176-. |
| [12] | 马星, 王浩, 余蔚, 杜勇, 梁健超, 胡慧建, 邱胜荣, 刘璐. 基于MaxEnt模型分析广东省鸟类多样性热点分布及保护空缺[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(8): 1097-1107. |
| [13] | 周润, 慈秀芹, 肖建华, 曹关龙, 李捷. 气候变化对亚热带常绿阔叶林优势类群樟属植物的影响及保护评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 697-711. |
| [14] | 严靖, 闫小玲, 李惠茹, 杜诚, 马金双. 华东地区归化植物的组成特征、引入时间及时空分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 428-438. |
| [15] | 何维明. 生物入侵的影响是否准确可知?[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(2): 253-255. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn