



生物多样性 ›› 2013, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (3): 288-295. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.08258 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2013.08258
所属专题: 生物入侵
白尚斌1, 周国模2,*, 王懿祥2, 梁倩倩1, 陈娟1, 程艳艳1, 沈蕊1
收稿日期:2012-12-29
接受日期:2013-04-20
出版日期:2013-05-20
发布日期:2013-06-05
通讯作者:
周国模
基金资助:Shangbin Bai1, Guomo Zhou2,*, Yixiang Wang2, Qianqian Liang1, Juan Chen1, Yanyan Cheng1, Rui Shen1
Received:2012-12-29
Accepted:2013-04-20
Online:2013-05-20
Published:2013-06-05
Contact:
Zhou Guomo
摘要:
为探讨毛竹(Phyllostachys edulis)入侵对周围森林群落的影响, 作者于2005-2011年在天目山自然保护区进行了7年长期定位观测实验, 研究了毛竹入侵地森林群落的植物物种多样性变化。结果表明: 毛竹入侵对周围森林群落植物物种多样性产生了不利影响: 毛竹林乔木层和灌木层植物的Simpson指数小于针阔混交林和毛竹-针阔混交林, 而草本层的Simpson指数则大于针阔混交林和毛竹-针阔混交林。植物物种丰富度、Simpson指数和Pielou均匀度指数随时间发生了较大变化: 毛竹入侵的森林群落其乔木层和灌木层的物种丰富度、Simpson指数和Pielou均匀度指数显著降低(P<0.05), 草本层的物种丰富度显著提高(P<0.05), Simpson指数和Pielou均匀度指数未表现出明显的变化。毛竹-针阔混交林去除毛竹后, 乔木层和灌木层物种丰富度和Simpson指数增加, 草本层物种丰富度、Simpson指数和Pielou均匀度指数明显下降。可见, 毛竹入侵使森林群落植物多样性发生实质性的变化, 对自然保护区植物群落造成了重大影响。由此可见, 要使保护区物种多样性得到保护, 除进行科学的管理外, 还需要控制毛竹蔓延。
白尚斌, 周国模, 王懿祥, 梁倩倩, 陈娟, 程艳艳, 沈蕊 (2013) 天目山保护区森林群落植物多样性对毛竹入侵的响应及动态变化. 生物多样性, 21, 288-295. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.08258.
Shangbin Bai,Guomo Zhou,Yixiang Wang,Qianqian Liang,Juan Chen,Yanyan Cheng,Rui Shen (2013) Plant species diversity and dynamics in forests invaded by Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) in Tianmu Mountain Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 21, 288-295. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.08258.
| 时间 Time | 针阔混交林 Mixed conifer-broad- leaved forest | 毛竹-针阔混交林 Mixed bamboo and conifer-broad- leaved forest | 毛竹林 Bamboo forest | 竹针阔混交林去除毛竹 Removed bamboo from mixed bamboo and conifer-broad-leaved forest |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 0 | 400.0±34.2 | 4,233.3±94.3 | 1,300.0±107.5 |
| 2006 | 0 | 558.3±47.6 | 4,200.0±117.6 | 0 |
| 2007 | 0 | 633.3±59.8 | 4,391.6±89.3 | 0 |
| 2008 | 0 | 866.7±76.8 | 3,983.3±101.0 | 0 |
| 2009 | 0 | 1,033.3±108.4 | 4,075.0±110.2 | 0 |
| 2010 | 41.7±3.5 | 1,516.7±137.1 | 4,300.0±104.3 | 0 |
| 2011 | 100.0±8.7 | 1,775.0±145.2 | 4,491.7±82.5 | 0 |
表1 不同样地各年份毛竹立竹度变化(2005-2011)
Table 1 Moso bamboo culm density in different forests during monitoring time (inds./ha)
| 时间 Time | 针阔混交林 Mixed conifer-broad- leaved forest | 毛竹-针阔混交林 Mixed bamboo and conifer-broad- leaved forest | 毛竹林 Bamboo forest | 竹针阔混交林去除毛竹 Removed bamboo from mixed bamboo and conifer-broad-leaved forest |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 0 | 400.0±34.2 | 4,233.3±94.3 | 1,300.0±107.5 |
| 2006 | 0 | 558.3±47.6 | 4,200.0±117.6 | 0 |
| 2007 | 0 | 633.3±59.8 | 4,391.6±89.3 | 0 |
| 2008 | 0 | 866.7±76.8 | 3,983.3±101.0 | 0 |
| 2009 | 0 | 1,033.3±108.4 | 4,075.0±110.2 | 0 |
| 2010 | 41.7±3.5 | 1,516.7±137.1 | 4,300.0±104.3 | 0 |
| 2011 | 100.0±8.7 | 1,775.0±145.2 | 4,491.7±82.5 | 0 |
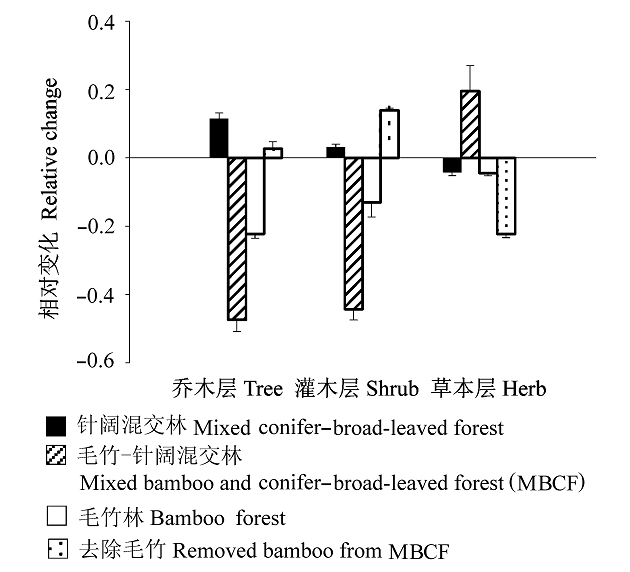
图2 不同群落乔、灌、草层物种丰富度相对变化(Ln(2011/ 2005))。
Fig. 2 Relative changes of species richness (Ln(2011/2005)) in the tree, shrub, and herb layers of different forests. Bars represent standard errors.
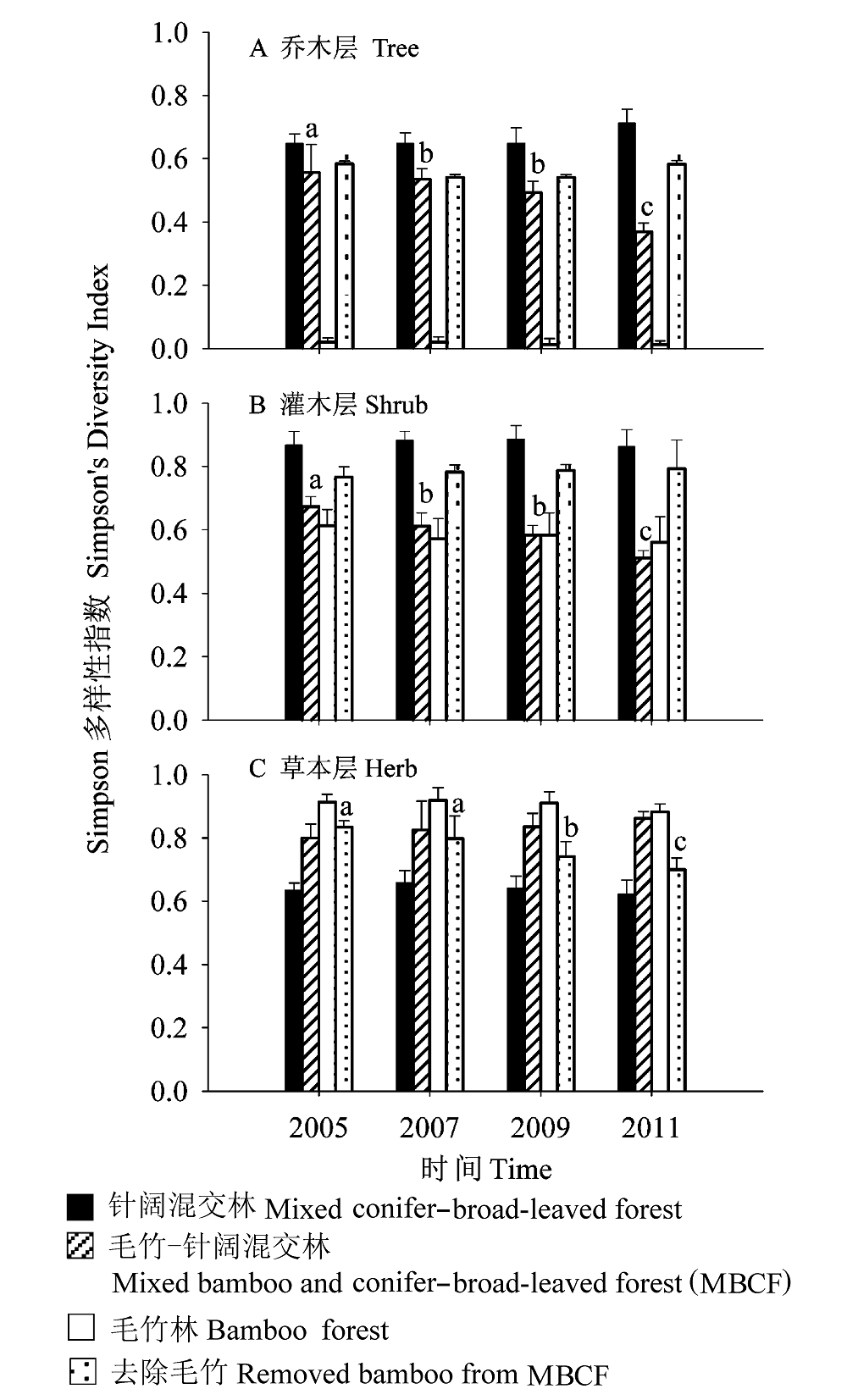
图3 不同群落乔、灌、草层Simpson指数的变化。
Fig. 3 Changes of Simpson’s Diversity Index in the tree, shrub, and herb layers of different forests over time. Bars labeled with different letters represent significantly different (P<0.05; LSD test). Bars represent standard errors.
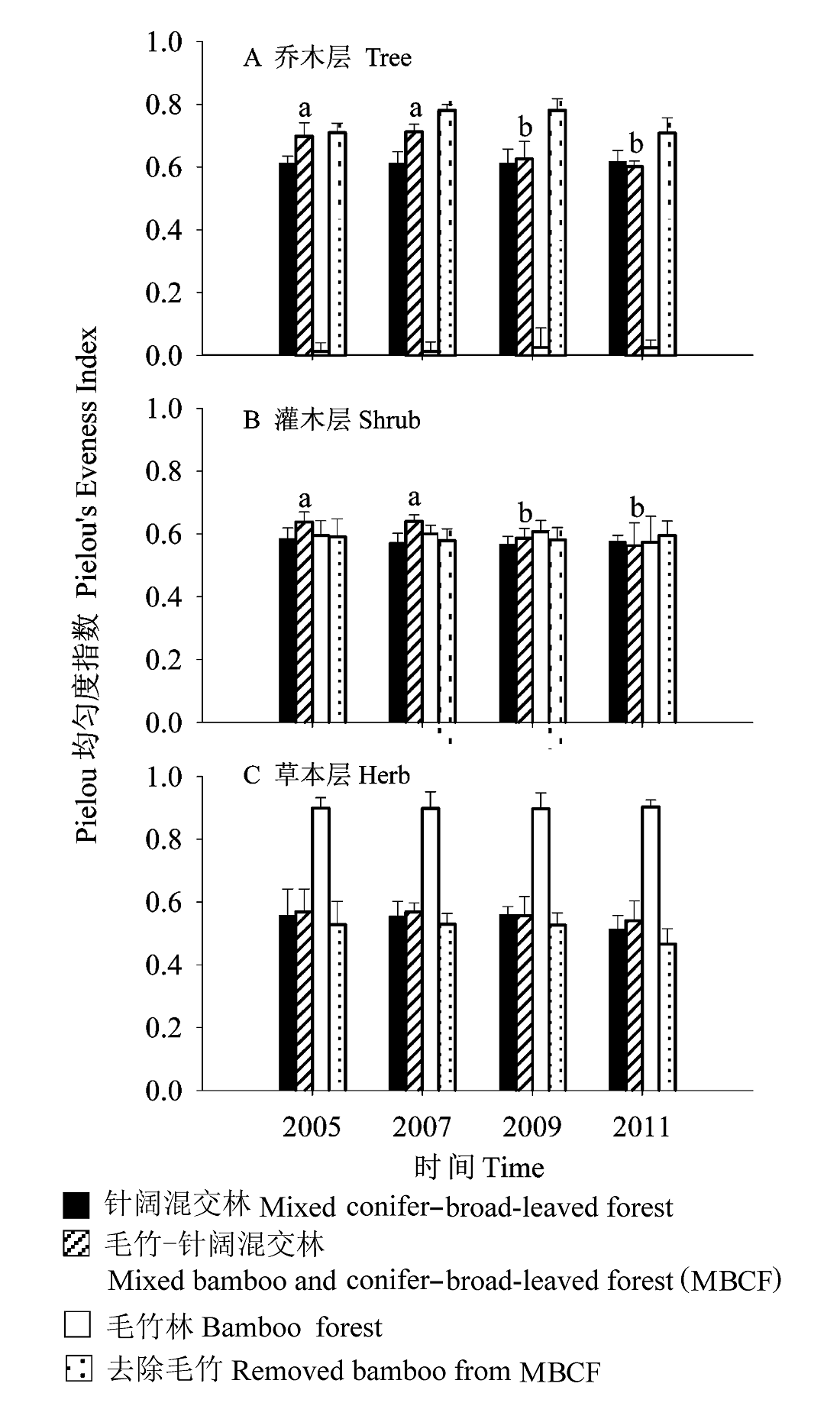
图4 不同群落乔、灌、草层Pielou均匀度指数的变化。
Fig. 4 Changes of Pielou’s Eveness Index in the tree, shrub, and herb layers of different forests over time. Bars labeled with different letters represent significantly different (P<0.05; LSD test). Bars represent standard errors.
| 1 | Bai SB (白尚斌), Zhou GM (周国模), Wang YX (王懿祥), Yu SQ (余树全), Li YH (李艳华), Fang FY (方飞燕) (2012) Stand structure change of Phyllostachys pubescens forest expansion in Tianmushan National Nature Reserve.Journal of West China Forestry Science(西部林业科学), 41(1), 77-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 2 | Cai L (蔡亮), Zhang RL (张瑞霖), Li CF (李春福), Ding Y (丁滪) (2003) A method to inhibit the expansion of Phyllo- stachys pubescens stand based on the analysis of underground rhizome.Journal of Northeast Forestry University(东北林业大学学报), 31(5), 68-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 3 | Cronk QCB, Fuller JL (1995) Plant Invaders: The Threat to Natural Ecosystem, p. 233. Chapman & Hall, London. |
| 4 | Cushman JH, Gaffney KA (2010) Community-level consequence of invasion: impacts of exotic clonal plants on riparian vegetation.Biological Invasions, 12, 2765-2776. |
| 5 | Ding LX (丁丽霞), Wang ZL (王祖良), Zhou GM (周国模), Du QZ (杜晴洲) (2006) Monitoring Phyllostachys pubescens stands expansion in National Nature Reserve of Mount Tianmu by remote sensing.Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College(浙江林学院学报), 23, 297-300. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 6 | Dong M (董鸣) (1996) Plant clonal growth in heterogeneous habitats: risk-spreading.Acta Phytoecologica Sinica(植物生态学报), 20, 543-548. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 7 | Fang FY (方飞燕), Bai SB (白尚斌), Zhou GM (周国模), Wang YX (王懿祥), Xie YM (谢一鸣) (2012) Effects of shading on growth of Phyllostachys pubescens.Journal of Northeast Forestry University(东北林业大学学报), 40(3), 11-13, 27. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 8 | Flory SL, Clay K (2009) Invasive plant removal method determines native plant community responses.Journal of Applied Ecology, 46, 434-442. |
| 9 | Flory SL, Clay K (2010) Non-native grass invasion alters native plant composition in experimental communities.Biological Invasions, 12, 1285-1294. |
| 10 | Hong W (洪伟), Hu XS (胡喜生), Wu CZ (吴承祯), Yan SJ (闫淑君), Feng L (封磊), Lin YM (林勇明) (2004) Comparison study on community structure features of the mixed forest of Phyllostachys pubescens in Fujian Province.Journal of Plant Resources and Environment(植物资源与环境学报), 13(1), 37-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 11 | Hulme PE, Bremner ET (2006) Assessing the impact of Impatiens glandulifera on riparian habitats: partitioning diversity components following species removal. Journal of Applied Ecology, 43, 43-50. |
| 12 | Isagi Y, Torii A (1998) Range expansion and its mechanisms in a naturalized bamboo species, Phyllostachys pubescens, in Japan.Journal of Sustainable Forestry, 6, 127-141. |
| 13 | Ito T (2006) Breeding characteristic, invasion prevention method, and its dissemination of Phyllostachys pubescens woods.Shinrin Gijyutsu, 772, 36-37. |
| 14 | Leps J (2004) Variability in population and community biomass in a grassland community affected by environmental productivity and diversity. Oikos, 107, 64-71. |
| 15 | Liu S (刘烁), Zhou GM (周国模), Bai SB (白尚斌) (2011) Light intensity changes on Cunninghamia lanceolata in mixed stands with different concentrations of Phyllostachys pubescens.Journal of Zhejiang A & F University(浙江农林大学学报), 28, 550-554. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 16 | Mack RN, Simberloff D, Lonsdale WM, Evans H, Clout M, Bazzaz FA (2000) Biotic invasions: causes, epidemiology, global consequences, and control.Ecological Applications, 10, 689-710. |
| 17 | Mclean MA, Parkinson D (1997) Changes in structure, organic matter and microbial activity in pine forest soil following the introduction of Dendrobaena oetaedra (Oligocbaeta: Lumbricidae).Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 29, 537-540. |
| 18 | Meghann EJ, Bradley JC (2009) Allelopathy as a mechanism for the invasion of Typha angustifolia.Plant Ecology, 204, 113-124. |
| 19 | Nakatsubo T, Suzuki T (1998) Ecological studies on the vegetation and management of the Yahagi River. I. The impact of bamboo cutting on the vegetation in Otsuridoba area.Report of Yahagi River Institute(矢作川研究), 2, 113-127. (in Japanese with English abstract) |
| 20 | Okutomi K, Shinoda S, Fukuda H (1996) Causal analysis of the invasion of broad-leaved forest by bamboo in Japan.Journal of Vegetation Science, 7, 723-728. |
| 21 | Pattison RR, Goldstein G, Ares A (1998) Growth, biomass allocation and photosynthesis of invasive and native Hawaiian rain-forest species.Oecologia, 117, 449-459. |
| 22 | Peng SL (彭少麟), Xiang YC (向言词) (1999) The invasion of exotic plants and effects of ecosystems.Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 19, 560-568. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 23 | Pennings SC, Callaway RM (2000) The advantages of clonal integration under different ecological conditions: a community-wide test.Ecology, 81, 709-716. |
| 24 | Ramula S, Pihlaja K (2012) Plant communities and the reproductive success of native plants after the invasion of an ornamental herb.Biological Invasions, 14, 2079-2090. |
| 25 | Ruiz-Pérez M, Fu M, Yang X, Belcher B (2001) Bamboo forestry in China: toward environmentally friendly expansion.Journal of Forestry, 99, 14-20. |
| 26 | Scott JM, Mary LC (2005) The relationship between community diversity and exotic plants: cause or consequence of invasion? In: Invasive Plants: Ecological and Agricultural Aspects (ed. Inderjit), pp. 97-100. Birkhäuser Verlag, Switzerland. |
| 27 | Smith MD, Knapp AK (1999) Exotic plant species in a C4-dominated grassland: invisibility, disturbance, and community structure.Oecologia, 120, 605-612. |
| 28 | Suzuki S, Nakagoshi N (2008) Expansion of bamboo forests caused by reduced bamboo-shoot harvest under different natural and artificial conditions.Ecological Research, 23, 641-647. |
| 29 | Suzuki T, Nakatsubo T (2001) Impact of the bamboo Phyuostaehys bambusoides on the light environment and plant communities on riverbanks.Journal of Forest Research, 6, 81-86. |
| 30 | van Kleuene M, Weber E, Fischer M (2010) A meta-analysis of trait differences between invasive and non-invasive plant species.Ecology Letters, 13, 235-245. |
| 31 | Vilà M, Espinar JL, Hejda M, Hulme PE, Jarošík V, Maron JL, Pergl J, Schaffner U, Sun Y, Pyšek P (2011) Ecological impacts of invasive alien plants: a meta-analysis of their effects on species, communities and ecosystems. Ecology Letters, 14, 702-708. |
| 32 | Wang CP, Stapleton C (2006) Phyllostackys. In: Flora of China (eds Wu CY, Raven PH), Vol. 22, pp. 163-180. Science Press, Beijing, Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis. |
| 33 | Yang H (杨怀), Li PX (李培学), Dai HT (戴慧堂), Liu D (刘丹), Yao XS (姚贤胜) (2010) Effects of Phyllostachys pubescens expansion on plant species diversity in Jigong Mountain and discussion of control measures. Journal of Xinyang Normal University (Natural Science Edition) (信阳师范学院学报(自然科学版)), 4, 553-557. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 34 | Zhang GH (张刚华), Xiao JH (萧江华), Nie JZ (聂洁珠), Chen SL (陈双林), Guo ZW (郭子武) (2007) Study on the species diversity at Moso bamboo stands of different types.Forest Research(林业科学研究), 20, 615-621. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 35 | Zhang JT (张金屯) (2011) Quantitative Ecology (数量生态学), pp. 83-107. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 36 | Zhou GM, Jiang PK, Mo LF (2009) Bamboo: a possible approach to the control of global warming.International Journal of Nonlinear Sciences & Numerical Simulation, 10, 547-550. |
| 37 | Zhu CL (朱长龙), Shangguan LP (上官林平) (2009) Preliminary study on the influence of the expansion edge on biodiversity of moso bamboo forest in Jinggang Mountain.Territory & Natural Resources Study(国土与自然资源研究), (3), 45-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 38 | Zhu JM (朱锦懋), Huang MT (黄茂提), Chen YQ (陈由强), Huang RZ (黄儒珠), Li XQ (李晓青) (2000) The structure of a culm and shoot producing stand of Phyllostachys pubescens.Acta Phytoecologica Sinica(植物生态学报), 24, 483-488. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| [2] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [3] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [4] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [5] | 连佳丽, 陈婧, 杨雪琴, 赵莹, 罗叙, 韩翠, 赵雅欣, 李建平. 荒漠草原植物多样性和微生物多样性对降水变化的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24044-. |
| [6] | 李雪萌, 蒋际宝, 张曾鲁, 刘晓静, 王亚利, 吴宜钊, 李银生, 邱江平, 赵琦. 宝天曼国家级自然保护区蚯蚓物种多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23352-. |
| [7] | 王启蕃, 刘小慧, 朱紫薇, 刘磊, 王鑫雪, 汲旭阳, 周绍春, 张子栋, 董红雨, 张明海. 黑龙江北极村国家级自然保护区鸟类与兽类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 24024-. |
| [8] | 万凤鸣, 万华伟, 张志如, 高吉喜, 孙晨曦, 王永财. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的应用潜力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23381-. |
| [9] | 所翟, 俞渃茜, 李媛辉, 徐基良. 基于实证分析中国自然保护区地方立法问题检视和优化路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23287-. |
| [10] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [11] | 黄小龙, 蒙秉顺, 李海波, 冉伟, 杨伟, 王丞, 谢波, 张旭, 冉景丞, 张明明. 基于红外相机的黔金丝猴及其同域分布物种种间关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23402-. |
| [12] | 张乃鹏, 梁洪儒, 张焱, 孙超, 陈勇, 王路路, 夏江宝, 高芳磊. 土壤类型和地下水埋深对黄河三角洲典型盐沼植物群落空间分异的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23370-. |
| [13] | 杨向林, 赵彩云, 李俊生, 种方方, 李文金. 植物入侵导致群落谱系结构更加聚集: 以广西国家级自然保护区草本植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [14] | 杜聪聪, 冯学宇, 陈志林. 桥头堡效应中气候生态位差异的缩小促进了红火蚁的入侵[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24276-. |
| [15] | 蒋陈焜, 郁文彬, 饶广远, 黎怀成, Julien B. Bachelier, Hartmut H. Hilger, Theodor C. H. Cole. 植物系统发生海报——以演化视角介绍植物多样性的科教资料项目[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24210-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()