



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 23352. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023352 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023352
李雪萌1,2, 蒋际宝1,2( ), 张曾鲁1,2, 刘晓静3(
), 张曾鲁1,2, 刘晓静3( ), 王亚利4, 吴宜钊1,2, 李银生1,2(
), 王亚利4, 吴宜钊1,2, 李银生1,2( ), 邱江平1,2(
), 邱江平1,2( ), 赵琦1,2,*(
), 赵琦1,2,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2023-09-20
接受日期:2024-03-17
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-04-26
通讯作者:
* E-mail: 基金资助:
Xuemeng Li1,2, Jibao Jiang1,2( ), Zenglu Zhang1,2, Xiaojing Liu3(
), Zenglu Zhang1,2, Xiaojing Liu3( ), Yali Wang4, Yizhao Wu1,2, Yinsheng Li1,2(
), Yali Wang4, Yizhao Wu1,2, Yinsheng Li1,2( ), Jiangping Qiu1,2(
), Jiangping Qiu1,2( ), Qi Zhao1,2,*(
), Qi Zhao1,2,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-09-20
Accepted:2024-03-17
Online:2024-04-20
Published:2024-04-26
Contact:
* E-mail: 摘要:
宝天曼国家级自然保护区独特的地理位置和气候条件使其成为生物多样性研究热点地区之一, 但关于该地区蚯蚓物种多样性的研究却十分匮乏。本研究在系统调查宝天曼国家级自然保护区蚯蚓物种的基础上, 联合5个线粒体基因(COI、COII、ND1、12S、16S)构建蚯蚓系统发育树, 并结合海拔、土壤、凋落物质量等环境因素建立结构方程模型, 初步探讨了宝天曼蚯蚓多样性形成的主要影响因素。研究结果表明: (1)宝天曼国家级自然保护区共记录到蚯蚓3科5属14种, 多为广布种, 其中巨蚓科为优势科; (2)蚯蚓物种数随海拔升高而增加, 但500-1,000 m海拔段的蚯蚓α多样性更高, 分布也更均匀, 符合中间高度膨胀格局; (3)在局域尺度上, 海拔高度对蚯蚓物种多样性和系统发育多样性的影响较大, 其次为土壤性质和凋落物质量。宝天曼国家级自然保护区蚯蚓物种组成及多样性成因的研究丰富了我国蚯蚓物种库和基因库。
李雪萌, 蒋际宝, 张曾鲁, 刘晓静, 王亚利, 吴宜钊, 李银生, 邱江平, 赵琦 (2024) 宝天曼国家级自然保护区蚯蚓物种多样性及其影响因素. 生物多样性, 32, 23352. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023352.
Xuemeng Li, Jibao Jiang, Zenglu Zhang, Xiaojing Liu, Yali Wang, Yizhao Wu, Yinsheng Li, Jiangping Qiu, Qi Zhao (2024) Earthworm biodiversity and its influencing factors in Baotianman National Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23352. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023352.
| 样方 Quadrat | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 地理坐标 Geographical coordinates | 植被 Vegetation | 土壤类型 Soil types | 凋落物厚度 Litter thickness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,352 | 111.93° E, 33.52° N | 锐齿槲栎和华山松混交林 Mixed forest of Quercus aliena var. acutiserrata and Pinus armandii | 潮湿黑壤 Moist black soil | 约5 cm厚 About 5 cm |
| 2 | 1,334 | 111.93° E, 33.51° N | 锐齿槲栎和华山松混交林 Mixed forest of Quercus aliena var. acutiserrata and Pinus armandii | 干硬黄棕壤 Dry hard yellow brown soil | 约5 cm厚 About 5 cm |
| 3 | 1,389 | 111.93° E, 33.50° N | 锐齿槲栎、短柄枹混交林 Mixed forest of Quercus aliena var. acutiserrata and Q. glandulifera var. brevipetiolata | 黄棕壤 Yellow brown soil | 约5 cm厚 About 5 cm |
| 4 | 1,401 | 111.93° E, 33.50° N | 锐齿槲栎林 Quercus aliena var. acutiserrata forest | 黄棕壤 Yellow brown soil | 约5 cm厚 About 5 cm |
| 5 | 1,360 | 111.74° E, 33.51° N | 短柄枹林 Quercus glandulifera var. brevipetiolata forest | 黄棕壤 Yellow brown soil | 约5 cm厚 About 5 cm |
| 6 | 1,074 | 111.92° E, 33.50° N | 锐齿槲栎、短柄枹混交林, 小溪旁 Mixed forest of Quercus aliena var. acutiserrata and Q. glandulifera var. brevipetiolata, beside the stream | 潮湿黄棕壤, 土层薄 Wet yellow brown soil, thin soil layer | 约20 cm厚, 下层凋落物腐烂 About 20 cm, the litter in the lower layer is rotten |
| 7 | 338 | 112.10° E, 33.57° N | 杨树林 Poplar forest | 黄棕壤 Yellow brown soil | 无凋落物覆盖 No litter cover |
| 8 | 557 | 112.05° E, 33.55° N | 野核桃树、草本植物, 小溪旁 Wild walnut trees, herbs, beside stream | 潮湿黑壤 Wet black soil | 无凋落物覆盖 No litter cover |
| 9 | 613 | 112.05° E, 33.55° N | 香樟和闽楠 Cinnamomum camphora and Phoebe bournei | 黄棕壤 Yellow brown soil | 少量凋落物覆盖 Small amount of litter cover |
表1 河南宝天曼国家级自然保护区蚯蚓、土壤和凋落物采样信息
Table 1 Sampling information of earthworm, soil and litter in Baotianman National Nature Reserve, Henan Province
| 样方 Quadrat | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 地理坐标 Geographical coordinates | 植被 Vegetation | 土壤类型 Soil types | 凋落物厚度 Litter thickness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,352 | 111.93° E, 33.52° N | 锐齿槲栎和华山松混交林 Mixed forest of Quercus aliena var. acutiserrata and Pinus armandii | 潮湿黑壤 Moist black soil | 约5 cm厚 About 5 cm |
| 2 | 1,334 | 111.93° E, 33.51° N | 锐齿槲栎和华山松混交林 Mixed forest of Quercus aliena var. acutiserrata and Pinus armandii | 干硬黄棕壤 Dry hard yellow brown soil | 约5 cm厚 About 5 cm |
| 3 | 1,389 | 111.93° E, 33.50° N | 锐齿槲栎、短柄枹混交林 Mixed forest of Quercus aliena var. acutiserrata and Q. glandulifera var. brevipetiolata | 黄棕壤 Yellow brown soil | 约5 cm厚 About 5 cm |
| 4 | 1,401 | 111.93° E, 33.50° N | 锐齿槲栎林 Quercus aliena var. acutiserrata forest | 黄棕壤 Yellow brown soil | 约5 cm厚 About 5 cm |
| 5 | 1,360 | 111.74° E, 33.51° N | 短柄枹林 Quercus glandulifera var. brevipetiolata forest | 黄棕壤 Yellow brown soil | 约5 cm厚 About 5 cm |
| 6 | 1,074 | 111.92° E, 33.50° N | 锐齿槲栎、短柄枹混交林, 小溪旁 Mixed forest of Quercus aliena var. acutiserrata and Q. glandulifera var. brevipetiolata, beside the stream | 潮湿黄棕壤, 土层薄 Wet yellow brown soil, thin soil layer | 约20 cm厚, 下层凋落物腐烂 About 20 cm, the litter in the lower layer is rotten |
| 7 | 338 | 112.10° E, 33.57° N | 杨树林 Poplar forest | 黄棕壤 Yellow brown soil | 无凋落物覆盖 No litter cover |
| 8 | 557 | 112.05° E, 33.55° N | 野核桃树、草本植物, 小溪旁 Wild walnut trees, herbs, beside stream | 潮湿黑壤 Wet black soil | 无凋落物覆盖 No litter cover |
| 9 | 613 | 112.05° E, 33.55° N | 香樟和闽楠 Cinnamomum camphora and Phoebe bournei | 黄棕壤 Yellow brown soil | 少量凋落物覆盖 Small amount of litter cover |
| 基因 Gene | 引物名称 Primer | 引物序列 Primer sequence | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| COI | LCO1490 | 5°-GGTCAACAAATCATAAAGATATTGG-3° | Folmer et al, |
| COI-E | 5°-TATACTTCTGGGTGTCCGAAGAATCA-3° | Bely & Wray, | |
| COII | COII-F | 5°-GGCACCTATTTGTTAATTAGG-3° | Pérez-Losada et al, |
| COII-R | 5°-GTGAGGCATAGAAATACACC-3° | ||
| ND1 | ND1-F | 5°-GAATAGTGCCACAGGTTTAAAC-3° | Pérez-Losada et al, |
| ND1-R | 5°-TTAACGTCATCAGAGTTATC-3° | ||
| 12S | 12S-F | 5°-CTTAAAGATTTTGGCGGTGTC-3° | Pérez-Losada et al, |
| 12S-R | 5°-CCTTTGCACGGTTAGGATAC-3° | ||
| 16S | 16SarL | 5°-CCGGTCTGAACTCAGATCACGT-3° | Moritz & Hillis, |
表2 线粒体5个基因引物序列
Table 2 The primers of 5 mitochondrial genes
| 基因 Gene | 引物名称 Primer | 引物序列 Primer sequence | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| COI | LCO1490 | 5°-GGTCAACAAATCATAAAGATATTGG-3° | Folmer et al, |
| COI-E | 5°-TATACTTCTGGGTGTCCGAAGAATCA-3° | Bely & Wray, | |
| COII | COII-F | 5°-GGCACCTATTTGTTAATTAGG-3° | Pérez-Losada et al, |
| COII-R | 5°-GTGAGGCATAGAAATACACC-3° | ||
| ND1 | ND1-F | 5°-GAATAGTGCCACAGGTTTAAAC-3° | Pérez-Losada et al, |
| ND1-R | 5°-TTAACGTCATCAGAGTTATC-3° | ||
| 12S | 12S-F | 5°-CTTAAAGATTTTGGCGGTGTC-3° | Pérez-Losada et al, |
| 12S-R | 5°-CCTTTGCACGGTTAGGATAC-3° | ||
| 16S | 16SarL | 5°-CCGGTCTGAACTCAGATCACGT-3° | Moritz & Hillis, |
| 物种名 Catalogue | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 数量 Number | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 巨蚓科 Megascolecidae | |||
| 远盲蚓属 Amynthas | |||
| 枯萎远盲蚓 A. emarcidus | 338 | 7 | |
| 无管远盲蚓 A. exsiphonus | 557、613、1,334、1,360、 1,389、1,401 | 44 | |
| 齿盲远盲蚓 A. filicinus | 557 | 5 | |
| 腔蚓属 Metaphire | |||
| Metaphire_W20519-01* | 1,334、1,360、1,389、1,401 | 22 | |
| Metaphire_W21111-05* | 557、613 | 6 | |
| 直隶腔蚓指名亚种 M. tschiliensis tschiliensis | 557、1,334 | 4 | |
| 通俗腔蚓 M. vulgaris | 338 | 1 | |
| 正蚓科 Lumbricidae | |||
| 丛林蚓属 Dendrodrilus | |||
| 红枝蚓 D. rubidus | 1,074、1,352 | 4 | |
| 爱胜蚓属 Eisenia | |||
| Eisenia_W20518-02* | 1,074、1,334、1,352、1,360、 1,389、1,401 | 105 | |
| 链胃蚓科 Moniligastridae | |||
| 杜拉蚓属 Drawida | |||
| 朝鲜杜拉蚓 D. koreana | 1,389 | 1 | |
| Drawida_W20518-01* | 1,334、1,352、1,360 | 13 | |
| Drawida_W20523-03* | 1,074 | 2 | |
| Drawida_W21110-03* | 338、557 | 12 | |
| Drawida_W21112-04* | 613 | 4 | |
表3 河南宝天曼国家级自然保护区蚯蚓物种名录(截至2022年10月)
Table 3 Checklist of earthworm species in Baotianman National Nature Reserve (until Oct. 2022)
| 物种名 Catalogue | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 数量 Number | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 巨蚓科 Megascolecidae | |||
| 远盲蚓属 Amynthas | |||
| 枯萎远盲蚓 A. emarcidus | 338 | 7 | |
| 无管远盲蚓 A. exsiphonus | 557、613、1,334、1,360、 1,389、1,401 | 44 | |
| 齿盲远盲蚓 A. filicinus | 557 | 5 | |
| 腔蚓属 Metaphire | |||
| Metaphire_W20519-01* | 1,334、1,360、1,389、1,401 | 22 | |
| Metaphire_W21111-05* | 557、613 | 6 | |
| 直隶腔蚓指名亚种 M. tschiliensis tschiliensis | 557、1,334 | 4 | |
| 通俗腔蚓 M. vulgaris | 338 | 1 | |
| 正蚓科 Lumbricidae | |||
| 丛林蚓属 Dendrodrilus | |||
| 红枝蚓 D. rubidus | 1,074、1,352 | 4 | |
| 爱胜蚓属 Eisenia | |||
| Eisenia_W20518-02* | 1,074、1,334、1,352、1,360、 1,389、1,401 | 105 | |
| 链胃蚓科 Moniligastridae | |||
| 杜拉蚓属 Drawida | |||
| 朝鲜杜拉蚓 D. koreana | 1,389 | 1 | |
| Drawida_W20518-01* | 1,334、1,352、1,360 | 13 | |
| Drawida_W20523-03* | 1,074 | 2 | |
| Drawida_W21110-03* | 338、557 | 12 | |
| Drawida_W21112-04* | 613 | 4 | |
| 海拔 Altitude (m) | Chao1 多样性指数 Chao1 diversity index | Shannon-Wiener 指数 Shannon- Wiener index | Simpson 多样性指数 Simpson diversity index | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-500 | 3.00 ± 0.01 | 0.90 ± 0.02 | 0.56 ± 0.01 | 0.82 ± 0.01 |
| 500-1,000 | 4.00 ± 1.00 | 1.25 ± 0.17 | 0.69 ± 0.04 | 0.93 ± 0.05 |
| 1,000-1,500 | 3.83 ± 1.07 | 0.91 ± 0.11 | 0.50 ± 0.08 | 0.72 ± 0.07 |
表4 河南宝天曼国家级自然保护区不同海拔蚯蚓α多样性指数(平均值 ± 标准差)
Table 4 The α diversity index of earthworms at different altitudes in Baotianman National Nature Reserve (mean ± SD)
| 海拔 Altitude (m) | Chao1 多样性指数 Chao1 diversity index | Shannon-Wiener 指数 Shannon- Wiener index | Simpson 多样性指数 Simpson diversity index | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-500 | 3.00 ± 0.01 | 0.90 ± 0.02 | 0.56 ± 0.01 | 0.82 ± 0.01 |
| 500-1,000 | 4.00 ± 1.00 | 1.25 ± 0.17 | 0.69 ± 0.04 | 0.93 ± 0.05 |
| 1,000-1,500 | 3.83 ± 1.07 | 0.91 ± 0.11 | 0.50 ± 0.08 | 0.72 ± 0.07 |
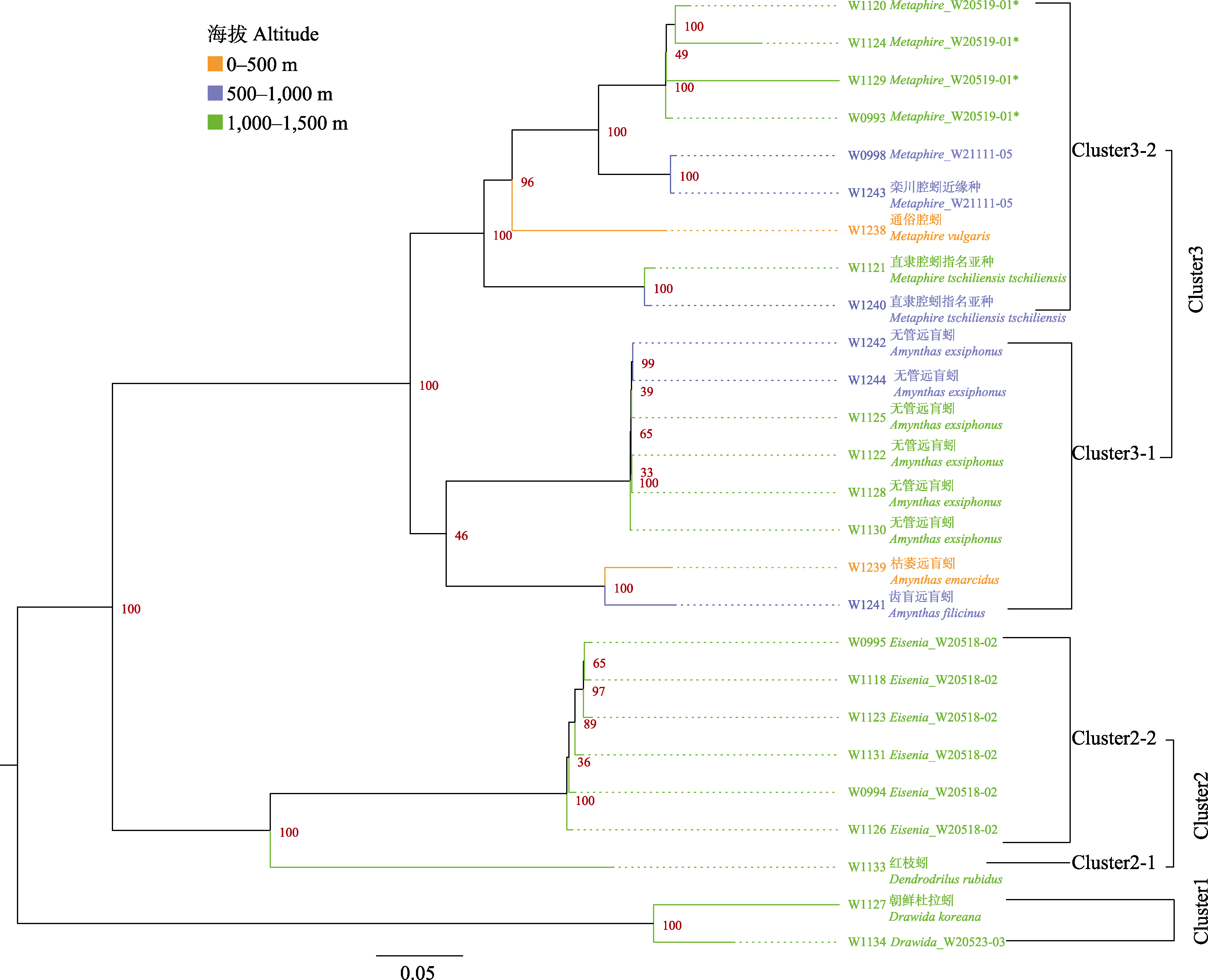
图1 基于5个基因联合构建的蚯蚓系统发育树。分支结点处的数字表示贝叶斯树的支持率。W加四位数字为样本编号。
Fig. 1 Phylogenetic tree of earthworms based on the combination of five genes. The number at the branch node represents the support percent of the Bayesian tree. W plus four digits is the sample number.
| 海拔 Altitude (m) | 系统发育多样性 标准化效应指数 Standardized effect size-phylogenetic diversity (SES-PD) | 净种间亲缘关系指数 Net relatedness index (NRI) | 净最近种间亲缘关系指数 Net nearest taxa index (NTI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-500 | -0.65 ± 0.00 | -0.65 ± 0.00 | -0.61 ± 0.00 | |
| 500-1,000 | -0.94 ± 0.32 | -0.99 ± 0.34 | -0.51 ± 0.14 | |
| 1,000-1,500 | 0.76 ± 0.70 | 0.73 ± 0.66 | 0.96 ± 0.61 | |
表5 宝天曼国家级自然保护区不同海拔段蚯蚓系统发育多样性指数(SES-PD)与系统发育结构(NRI和NTI)
Table 5 Phylogenetic diversity index and phylogenetic structure of earthworms at different altitudes in Baotianman National Nature Reserve
| 海拔 Altitude (m) | 系统发育多样性 标准化效应指数 Standardized effect size-phylogenetic diversity (SES-PD) | 净种间亲缘关系指数 Net relatedness index (NRI) | 净最近种间亲缘关系指数 Net nearest taxa index (NTI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-500 | -0.65 ± 0.00 | -0.65 ± 0.00 | -0.61 ± 0.00 | |
| 500-1,000 | -0.94 ± 0.32 | -0.99 ± 0.34 | -0.51 ± 0.14 | |
| 1,000-1,500 | 0.76 ± 0.70 | 0.73 ± 0.66 | 0.96 ± 0.61 | |
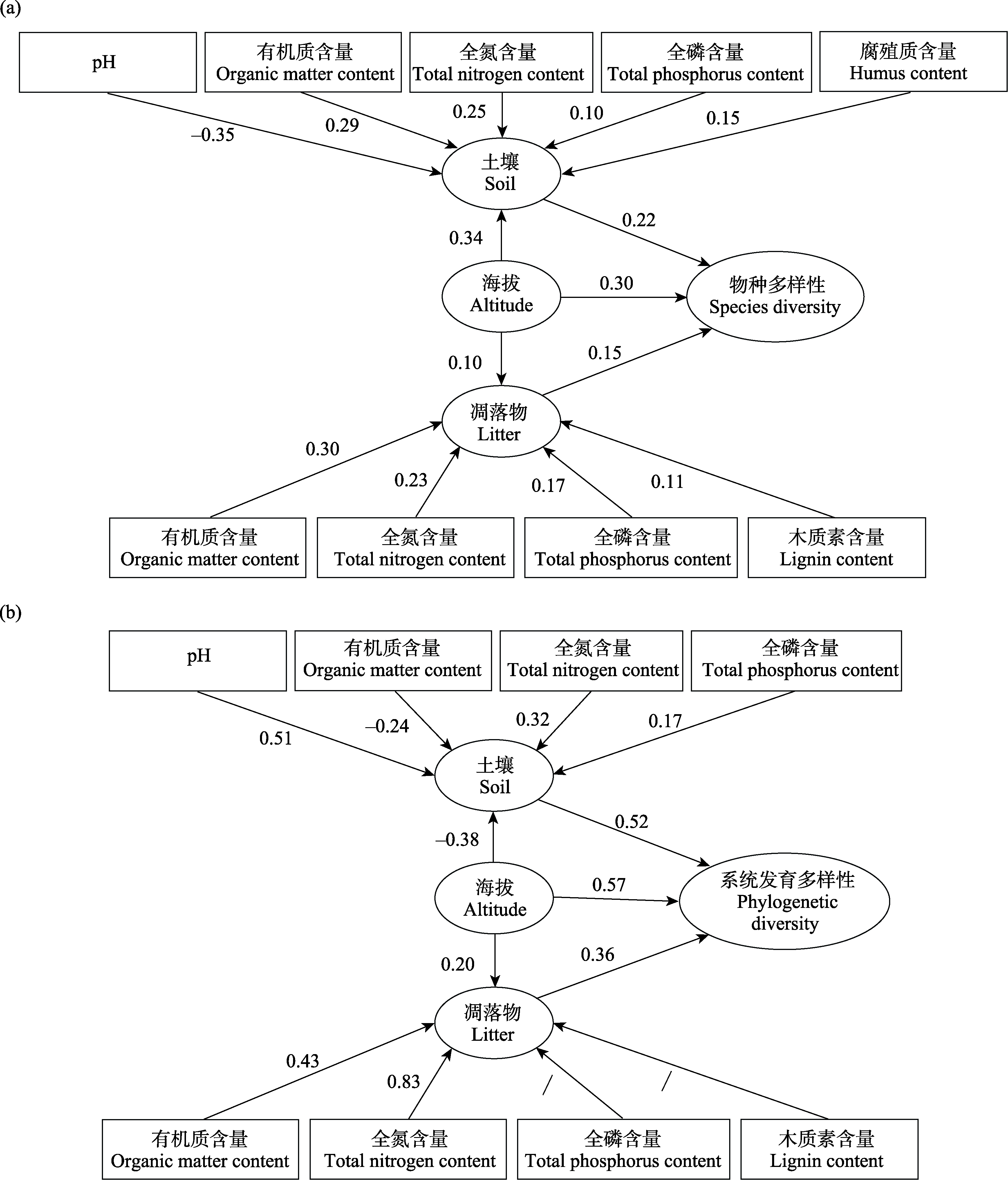
图2 土壤、海拔、凋落物对蚯蚓物种多样性(a)和系统发育多样性(b)影响的结构方程模型。“/”表示与对应变量的对应关系较弱。数字表示各变量间的路径系数。
Fig. 2 Structural equation model depicting the influences of soil, elevation and litter on species diversity (a) and phylogenetic diversity (b) of earthworms in Baotianman National Nature Reserve. “/” indicates a weak correlation with the corresponding variable. The number represents the path coefficient between the variables.
| [1] | Bao SD (2000) Soil Agricultural Chemistry Analysis. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [鲍士旦 (2000) 土壤农化分析. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [2] | Bazyari M, Etemad V, Kooch Y, Shirvany A (2021) Soil fauna communities and microbial activities response to litter and soil properties under degraded and restored forests of Hyrcania. iForest-Biogeosciences and Forestry, 14, 490-498. |
| [3] |
Bely AE, Wray GA (2004) Molecular phylogeny of naidid worms (Annelida: Clitellata) based on cytochrome oxidase I. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 30, 50-63.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Cao SP, Tan C, Wang H, Wu JP, Huang X, Liu CH (2018) Distribution of terrestrial earthworms and its influencing factors in the Nanniwan wetland. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 32(4), 80-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曹四平, 谭灿, 王欢, 吴金澎, 黄鑫, 刘长海 (2018) 南泥湾湿地陆栖蚯蚓的分布及其影响因素. 干旱区资源与环境, 32(4), 80-84.] | |
| [5] | Chaudhuri PS, Dey A (2013) Earthworm communities in the pineapple (Ananus comosus) and mixed fruit plantations of West Tripura, India. Proceedings of the Zoological Society, 66, 105-118. |
| [6] | Chen Q, Feng XY (1996) On Bucculenta species group of Metaphire and reproductive organ polymorphism (Oligochaeta: Megascolecidae). Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica, 21, 399-401. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈强, 冯孝义 (1996) 双腉腔蚓的生殖器官多态现象(寡毛纲: 巨蚓科). 动物分类学报, 21, 399-401.] | |
| [7] | Chen Y (1956) Zoological Atlas of China:Annelids (with Polypods). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [陈义 (1956) 中国动物图谱: 环节动物(附多足类). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [8] | Dhar S, Chaudhuri PS (2020) Earthworm communities in paddy (Oryza sativa) fields of West Tripura (India). Proceedings of the Zoological Society, 73, 273-284. |
| [9] | Dou S (2010) Soil Organic Matter. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [窦森 (2010) 土壤有机质. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [10] |
Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology, 3, 294-299.
PMID |
| [11] | Guo L, Chen XP, Shi L, Li L, Qiao L, Yang J, Chen XH (2012) Diversity and conservation of amphibians in Nanzhao Baotianman National Nature Reserve. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 51, 1413-1415. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭琳, 陈晓萍, 石灵, 李磊, 乔梁, 杨杰, 陈晓虹 (2012) 南召宝天曼国家级自然保护区两栖动物多样性与保护. 湖北农业科学, 51, 1413-1415.] | |
| [12] | Jiang JB (2016) Taxonomy and Molecular Phylogeny of the Family Megascolecidae Earthworms from China. PhD dissertation, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蒋际宝 (2016) 中国巨蚓科蚯蚓分类与分子系统发育研究. 博士学位论文, 上海交通大学, 上海.] | |
| [13] |
Jiang JB, Qiu JP (2018) Origin and evolution of earthworms belonging to the family Megascolecidae in China. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1074-1082. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[蒋际宝, 邱江平 (2018) 中国巨蚓科蚯蚓的起源与演化. 生物多样性, 26, 1074-1082.]
DOI |
|
| [14] | Kanianska R, Jaďuďová J, Makovníková J, Kizeková M (2016) Assessment of relationships between earthworms and soil abiotic and biotic factors as a tool in sustainable agricultural. Sustainability, 8, 906. |
| [15] | Korboulewsky N, Perez G, Chauvat M (2016) How tree diversity affects soil fauna diversity: A review. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 94, 94-106. |
| [16] | Liu BR (2021) Recent advances in altitudinal distribution patterns of biodiversity. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30, 438-444. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[刘秉儒 (2021) 生物多样性的海拔分布格局研究及进展. 生态环境学报, 30, 438-444.]
DOI |
|
| [17] | Liu T, Yao S, Yan MY, Li S, Bai BY (2023) Preliminary investigation and protection strategy of Capreolus capreolus Linnaeus in Baotianman Reserve. Animals Breeding and Feed, 22(2), 66-68. (in Chinese) |
| [刘统, 姚松, 闫满玉, 李舒, 白兵勇 (2023) 宝天曼保护区狍的初步调查及保护对策. 养殖与饲料, 22(2), 66-68.] | |
| [18] | Liu XJ, Ren SY, Li LX, Ye YZ, Yuan ZL, Wang T (2016) Detecting density dependence on tree survival in a deciduous broadleaved forest in Baotianman National Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 24, 639-648. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[刘晓静, 任思远, 李鹿鑫, 叶永忠, 袁志良, 王婷 (2016) 宝天曼国家级自然保护区落叶阔叶林密度制约效应对树木存活的影响. 生物多样性, 24, 639-648.]
DOI |
|
| [19] |
Liu Y, Zhan XJ, Wang N, Chang J, Zhang ZW (2010) Effect of geological vicariance on mitochondrial DNA differentiation in common pheasant populations of the Loess Plateau and eastern China. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 55, 409-417.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Liu YX (2020) Phylogeography of Four Cicada Species from China and Adaptive Evolution of Subpsaltria yangi. PhD dissertation, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, Shaanxi. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘雲祥 (2020) 四种中国蝉科昆虫谱系地理学研究暨枯蝉适应性进化研究. 博士学位论文, 西北农林科技大学, 陕西杨凌.] | |
| [21] | Lomolino MV (2001) Elevation gradients of species-density: Historical and prospective views. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 10, 3-13. |
| [22] | Ma YN, Filley TR, Szlavecz K, McCormick MK (2014) Controls on wood and leaf litter incorporation into soil fractions in forests at different successional stages. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 69, 212-222. |
| [23] | Moritz C, Hillis DM (1996) Molecular systematics:Context and controversies. In: Molecular Systematics (eds Hillis DM, Moritz C, Mable BK), pp. 1-13. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland. |
| [24] | Peng SL, Li MY, Song Y, Liang YZ, Song ZY, Ren DX, Ling CJ, Li SS, Liu C (2022) Species diversity and floristics seed plants in Baotianman Nature Reserve. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry Science and Technology, 42(3), 9-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [彭舜磊, 李满园, 宋莹, 梁亚珍, 宋子燕, 任德娴, 凌超杰, 李双双, 刘聪 (2022) 宝天曼国家级自然保护区种子植物物种多样性与区系分析. 浙江林业科技, 42(3), 9-16.] | |
| [25] |
Pérez-Losada M, Ricoy M, Marshall JC, Domínguez J (2009) Phylogenetic assessment of the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa species complex (Oligochaeta: Lumbricidae) based on mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 52, 293-302.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Phillips HRP, Guerra CA, Bartz MLC, Briones MJI, Brown G, Crowther TW, Ferlian O, Gongalsky KB, van den Hoogen J, Krebs J……Wackett AA, Warren MW, Wehr NH, Whalen JK, Wironen MB, Wolters V, Zenkova IV, Zhang WX, Cameron EK, Eisenhauer N (2019) Global distribution of earthworm diversity. Science, 366, 480-485.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Popovic F, Stojanovic M, Radosavljevic S, Trakic T, Sekulic J (2022) Earthworm community structure along altitudinal gradients on the western slopes of Kopaonik Mountain in Serbia. Turkish Journal of Zoology, 46, 103-114. |
| [28] | Qiu JP (2000) Earthworms and environmental protection. Guizhou Science, 18, 116-133. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邱江平 (2000) 蚯蚓与环境保护. 贵州科学, 18, 116-133.] | |
| [29] | Shi ZM (1998) Plant Community Diversity in Bao Tianman National Reserve, Henan Province. PhD dissertation, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [史作民 (1998) 河南宝天曼保护区植物群落多样性研究. 博士学位论文, 中国林业科学研究院, 北京.] | |
| [30] | Sims RW, Easton EG (1972) A numerical revision of the earthworm genus Pheretima auct. (Megascolecidae: Oligochaeta) with the recognition of new genera and an appendix on the earthworms collected by the Royal Society North Borneo Expedition. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 4, 169-268. |
| [31] |
Singh S, Sharma A, Khajuria K, Singh J, Vig AP (2020) Soil properties changes earthworm diversity indices in different agro-ecosystem. BMC Ecology, 20, 27.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | Song YG, Fang XM, Li JJ, An ZS, Miao XD (2001) The late Cenozoic uplift of the Liupan Shan, China. Science in China (Series D): Earth Sciences, 44, 176-184. |
| [33] | Talavera JA, Cunha L, Arévalo JR, Talavera IP, Kille P, Novo M (2020) Anthropogenic disturbance and environmental factors drive the diversity and distribution of earthworms in São Miguel Island (Azores, Portugal). Applied Soil Ecology, 145, 103301. |
| [34] | Wandeler HD, Sousa-Silva R, Ampoorter E, Bruelheide H, Carnol M, Dawud SM, Dǎnilǎ G, Finer L, Hättenschwiler S, Hermy M, Jaroszewicz B, Joly FX, Müller S, Pollastrini M, Ratcliffe S, Raulund-Rasmussen K, Selvi F, Valladares F, Meerbeek K, Verheyen K, Vesterdal L, Muys B (2016) Drivers of earthworm incidence and abundance across European forests. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 99, 167-178. |
| [35] | Wang JM, Wu FY, Zhang JJ, Khanal G, Yang L (2022) The Himalayan collisional orogeny: A metamorphic perspective. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96, 3128-3157. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王佳敏, 吴福元, 张进江, Khanal G, 杨雷 (2022) 喜马拉雅碰撞造山过程: 变质地质学视角. 地质学报, 96, 3128-3157.] | |
| [36] | Wang YG, Yang FW, Liu JJ, Mao ZC (2012) Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometric determination of total phosphorus in soil. Analysis and Testing Technology and Instruments, 18(3), 183-186. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王玉功, 杨发旺, 刘建军, 毛振才 (2012) 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定土壤中全磷. 分析测试技术与仪器, 18(3), 183-186.] | |
| [37] | Wu JH, Sun XD (1996) A new species of genus Drawida from the Changbai Mountains (Oligochaeta: Moniligasteridae). Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 15(3), 98-99, 117. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴纪华, 孙希达 (1996) 长白山杜拉属蚯蚓一新种(寡毛纲: 链胃蚓科). 四川动物, 15(3), 98-99, 117.] | |
| [38] | Xu SB, Li YH, Feng XY, Li L, Zhu LQ (2021) Research on functional groups of meso-micro soil fauna in Baotianman Nature Reserve. Journal of Nanyang Normal University, 20(1), 21-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐帅博, 李艳红, 冯小燕, 李理, 朱连奇 (2021) 宝天曼中小型土壤动物功能类群及其影响因素研究. 南阳师范学院学报, 20(1), 21-30.] | |
| [39] | Yakubchuk A (2017) Evolution of the central Asian orogenic supercollage since late Neoproterozoic revised again. Gondwana Research, 47, 372-398. |
| [40] | Yu CY, Li ZJ, Liu SY, Huang YD, Duan KJ, Li PL, Wang RH, Wang T, Liu XJ (2023) Altitudinal gradient pattern of woody species diversity and soil nutrients in Baotianman National Nature Reserve. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 51(9), 101-106, 119. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [于晨一, 李镇江, 刘升云, 黄玉蝶, 段科技, 李培琳, 王闰豪, 王婷, 刘晓静 (2023) 宝天曼国家级自然保护区木本植物多样性及土壤养分的海拔梯度格局. 东北林业大学学报, 51(9), 101-106, 119.] | |
| [41] | Yuan JJ, Ye Z, Bu WJ (2019) Phylogeography of widespread species in Eurasia: Current progress and future prospects. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 49, 1155-1164. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [袁娟娟, 叶瑱, 卜文俊 (2019) 欧亚大陆广布物种的谱系地理研究: 现状与发展趋势. 中国科学: 生命科学, 49, 1155-1164.] | |
| [42] | Zhang CS (2018) Study of Butterfly Diversity in Foping National Nature Reserve. PhD dissertation, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, Shaanxi. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张辰生 (2018) 佛坪国家级自然保护区蝶类多样性研究. 博士学位论文, 西北农林科技大学, 陕西杨凌.] | |
| [43] | Zhang N, Liao Y, Sun FL, Wang C, Sun ZJ (2012) Earthworm population characteristics in soils different in land use and their relationships with biological fertility of the soils. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 49, 364-372. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张宁, 廖燕, 孙福来, 王冲, 孙振钧 (2012) 不同土地利用方式下的蚯蚓种群特征及其与土壤生物肥力的关系. 土壤学报, 49, 364-372.] | |
| [44] | Zhang YF, Bi YM, Li GQ, Shen L (2017) Relationship between earthworm diversity and soil environment in Hebei area. Journal of China Agricultural University, 22(3), 60-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张玉峰, 毕艳孟, 李国强, 申磊 (2017) 河北地区不同农田蚯蚓多样性及其与土壤环境的关系. 中国农业大学学报, 22(3), 60-68.] | |
| [45] | Zhang YF, Wu YP, Sun Q, Sun ZJ (2014) Study of biodiversity of earthworm in Shandong and Liaodong Peninsulas. Journal of China Agricultural University, 19(4), 67-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张玉峰, 伍玉鹏, 孙倩, 孙振钧 (2014) 山东半岛与辽东半岛蚯蚓生物多样性研究. 中国农业大学学报, 19(4), 67-73.] | |
| [46] | Zhao HF, Fan SH, Aspe NM, Feng LC, Zhang YF (2022) Characterization of 15 earthworm mitogenomes from Northeast China and its phylogenetic implication (Oligochaeta: Lumbricidae, Moniligastridae). Diversity, 14, 714. |
| [47] | Zhong YH (1992) Description of two species of terrestrial Oligochaetes from Sichuan, China (Oligochaeta: Moniligastridae, Acanthodrilidae). Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica, 17, 268-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [钟远辉 (1992) 四川陆栖寡毛类两新种记述(寡毛纲: 链胃蚓科、棘蚓科). 动物分类学报, 17, 268-273.] | |
| [48] | Zhu XL, Yao ZC (2009) Distributing structure of biodiversity of edible mountain wild herbs along altitude gradient in Baotianman Nature Reserve. Journal of Henan University of Science & Technology (Natural Science), 30(2), 65-69, 113. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱学灵, 姚忠臣 (2009) 宝天曼自然保护区山野菜物种多样性的海拔梯度分布格局. 河南科技大学学报(自然科学版), 30(2), 65-69, 113.] |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn