



生物多样性 ›› 2011, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (1): 34-40. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07098 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2011.07098
所属专题: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全
收稿日期:2010-04-22
接受日期:2010-10-03
出版日期:2011-01-20
发布日期:2011-04-01
通讯作者:
包维楷
作者简介:*E-mail: baowk@cib.ac.cn基金资助:Received:2010-04-22
Accepted:2010-10-03
Online:2011-01-20
Published:2011-04-01
Contact:
Weikai Bao
摘要:
原始云杉林是青藏高原东部林区近林线森林的重要类型之一, 但关于其林分结构与多样性的科学认识到目前为止仍然是贫乏的。为了揭示云杉原始林的层次结构及其相互关系、维管植物组成特点, 选择四川省壤塘县北部日柯沟近林线的紫果云杉(Picea purpurea)原始林为对象, 调查了6个40 m×50 m样地的乔木层结构, 并在样地内采用机械布点的方法设置180个小样方, 调查了林下灌木层、草本层和苔藓层结构以及灌草层物种组成。结果显示: (1)云杉原始林为复层异龄林, 乔木层分化明显, 可划分为4个亚层; 幼树密度不高但集中分布于林窗及其边缘(144±93株/ha); (2)林下灌木盖度与物种丰富度低, 层片结构简单, 呈明显的斑块状分布; 而草本层与苔藓层发达, 盖度与物种丰富度均较高; (3)6个样地共发现维管植物124种, 隶属于30科68属。其中草本109种, 灌木15种, 以温带区系成分占优势, 特有性缺乏; 生活型以地面芽植物为主体(61.29%)。综合分析表明, 该林分为藓类云杉林, 群落结构完整、稳定, 自然更新能力强, 与本区域内亚高山或高山林线森林具有相似的物种组成和多样性特点, 但群落结构则明显不同。
刘鑫, 包维楷 (2011) 青藏高原东部近林线紫果云杉原始林的群落结构与物种组成. 生物多样性, 19, 34-40. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07098.
Xin Liu, Weikai Bao (2011) Community structure and vascular plant species composition of primary spruce forest near timberline in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 19, 34-40. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07098.
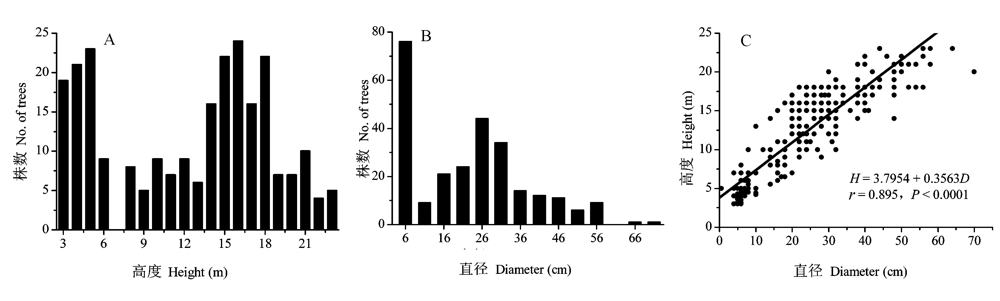
图1 青藏高原东部近林线云杉原始林乔木高度(A)和距地50 cm处直径(B)大小级分布及其关系(C)
Fig. 1 Size distribution of tree height (A), diameter at 50 cm height (B), and the height-diameter relationship (C) of trees in the primary spruce forest near timberline in the eastern Tibetan Plateau
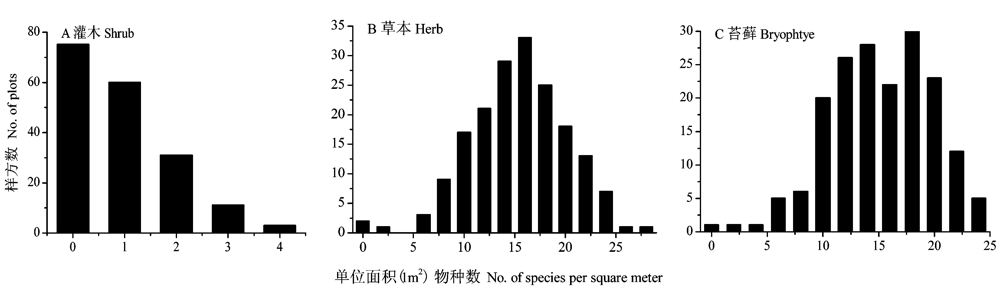
图2 青藏高原东部近林线云杉原始林下灌木(A)、草本(B)、苔藓植物(C)丰富度分布频率图(n=180)
Fig. 2 Frequency distribution of species richness of shrub (A), herb (B), bryophyte (C) under the primary spruce forest near timberline in the eastern Tibetan Plateau (180 subplots)
| 物种 Species | 生活型 Life form | 频度 Frequency | 重要值 Importance value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 草本层 Herb layer | ||||
| 明亮苔草 | Carex laeta | H 地面芽植物 | 0.8222 | 0.1616 |
| 狭苞橐吾 | Ligularia intermedia | H 地面芽植物 | 0.6278 | 0.1463 |
| 珠芽蓼 | Polygonum viviparum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.8278 | 0.1237 |
| 圆叶小堇菜 | Viola biflora var. rockiana | H 地面芽植物 | 0.8278 | 0.0891 |
| 细叶芨芨草 | Achnatherum chingii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2778 | 0.0804 |
| 箭叶橐吾 | Ligularia sagitta | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2667 | 0.0777 |
| 柳叶菜风毛菊 | Saussurea epilobioides | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3889 | 0.0620 |
| 梅氏雀麦 | Bromus mairei | H 地面芽植物 | 0.4333 | 0.0604 |
| 纤细草莓 | Fragaria gracilis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.6222 | 0.0567 |
| 东方草莓 | F. orientalis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.5278 | 0.0512 |
| 萎软紫菀 | Aster flaccidus | G 地下芽植物 | 0.5556 | 0.0491 |
| 喜巴早熟禾 | Poa hylobates | H 地面芽植物 | 0.4500 | 0.0488 |
| 紫花碎米荠 | Cardamine tangutorum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.5111 | 0.0449 |
| 高山露珠草 | Circaea alpina | H 地面芽植物 | 0.4500 | 0.0445 |
| 疏花剪股颖 | Agrostis hookeriana | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3833 | 0.0409 |
| 膨囊苔草 | Carex lehmanii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2556 | 0.0383 |
| 四齿无心菜 | Arenaria quadridentata | H 地面芽植物 | 0.6000 | 0.0378 |
| 弯齿风毛菊 | Saussurea przewalskii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2444 | 0.0337 |
| 狭叶红景天 | Rhodiola kirilowii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2333 | 0.0328 |
| 毛茛一种 | Ranunculus sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0278 | 0.0286 |
| 羊茅 | Festuca ovina | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1667 | 0.0274 |
| 高原毛茛 | Ranunculus tanguticus | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3889 | 0.0255 |
| 星叶草 | Circaeaster agrestis | Th 一年生植物 | 0.2389 | 0.0235 |
| 细毛拉拉藤 | Galium pusillosetosum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3111 | 0.0217 |
| 紫堇一种 | Corydalis sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2889 | 0.0199 |
| 湿地勿忘草 | Myosotis caespitosa | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2389 | 0.0190 |
| 条裂黄堇 | Corydalis linarioides | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2722 | 0.0182 |
| 肾叶金腰 | Chrysosplenium griffithii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2722 | 0.0181 |
| 长茎囊瓣芹 | Pternopetalum longicaule | G 地下芽植物 | 0.2722 | 0.0170 |
| 黄三七 | Souliea vaginata | G 地下芽植物 | 0.1722 | 0.0162 |
| 细柄茅 | Ptilagrostis mongholica | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1167 | 0.0157 |
| 微孔草 | Microula sikkimensis | Th 一年生植物 | 0.2278 | 0.0157 |
| 轮叶马先蒿 | Pedicularis verticillata | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1722 | 0.0144 |
| 小花缬草 | Valeriana minutiflora | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1611 | 0.0129 |
| 猪殃殃 | Galium aparine var. echinospermum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1778 | 0.0124 |
| 剪股颖一种 | Agrostis sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0833 | 0.0117 |
| 柔毛蓼 | Polygonum sparsipilosum | Th 一年生植物 | 0.1500 | 0.0115 |
| 异花孩儿参 | Pseudostellaria heterantha | G 地下芽植物 | 0.1611 | 0.0103 |
| 蕨叶千里光 | Senecio pteridophyllus | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0778 | 0.0098 |
| 大果红景天 | Rhodiola macrocarpa | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1056 | 0.0097 |
| 康定鼠尾草 | Salvia prattii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0944 | 0.0096 |
| 雀麦一种 | Bromux sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0722 | 0.0091 |
| 羌活 | Notopterygium incisum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0833 | 0.0089 |
| 单枝灯心草 | Juncus potaninii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0889 | 0.0082 |
| 耳蕨一种 | Polystichum sp. | G 地下芽植物 | 0.1056 | 0.0080 |
| 长叶微孔草 | Microula trichocarpa | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0667 | 0.0077 |
| 驴蹄草 | Caltha palustris | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0500 | 0.0073 |
| 唐古拉婆婆纳 | Veronica vandellioides | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1056 | 0.0072 |
| 早熟禾一种 | Poa sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0500 | 0.0072 |
| 毛脉柳叶菜 | Epilobium amurense | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0889 | 0.0068 |
| 阿洼早熟禾 | Poa araratica | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0667 | 0.0065 |
| 光籽柳叶菜 | Epilobium tibetanum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0944 | 0.0065 |
| 掌叶大黄 | Rheum palmatum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0061 |
| 二色香青同色变种 | Anaphalis bicolor var. subconcolor | Ch 地上芽植物 | 0.0667 | 0.0059 |
| 长芒披碱草 | Elymus dolichatherus | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0611 | 0.0056 |
| 针刺悬钩子 | Rubus pungens | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0054 |
| 黑水翠雀花 | Delphinium potaninii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0333 | 0.0051 |
| 甘青老鹳草 | Geranium pylzowianum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0722 | 0.0050 |
| 轮叶黄精 | Polygonatum verticillatum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0722 | 0.0049 |
| 单花拉拉藤 | Galium exile | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0667 | 0.0044 |
| 毛果婆婆纳 | Veronica eriogyne | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0611 | 0.0041 |
| 紫茎小芹 | Sinocarum coloratum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0444 | 0.0035 |
| 杯花韭 | Allium cyathophorum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0444 | 0.0031 |
| 柳兰 | Chamerion angustifolium subsp. angustifoliam | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0029 |
| 岩生剪股颖 | Agrostis rupestris | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0278 | 0.0027 |
| 曲枝早熟禾 | Poa pagophila | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0025 |
| 川西风毛菊 | Saussurea dzeurensis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0389 | 0.0025 |
| 毛葶苈 | Draba eriopoda | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0333 | 0.0023 |
| 簇生泉卷耳 | Cerastium fontanum subsp. vulgare | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0333 | 0.0023 |
| 玉山香青 | Anaphalis morrisonicola | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0167 | 0.0022 |
| 冷蕨 | Cystopteris fragilis | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0278 | 0.0020 |
| 丝叶苔草 | Carex capilliformis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0019 |
| 中华金腰 | Chrysosplenium sinicum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0018 |
| 肾叶毛茛 | Ranunculus sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0167 | 0.0017 |
| 多榔菊 | Doronicum stenoglossum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0017 |
| 异色红景天 | Rhodiola discolor | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0015 |
| 爪瓣虎耳草 | Saxifraga unguiculata | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0014 |
| 隐瓣蝇子草 | Silene gonosperma | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0167 | 0.0011 |
| 毛茛一种 | Ranunculus sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3778 | 0.0011 |
| 甘肃苔草 | Carex kansusis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0011 |
| 高山嵩草 | Kobresia pygmaea | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0011 |
| 苔草一种 | Carex sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0010 |
| 极丽马先蒿 | Pedicularis decorissima | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0010 |
| 大叶碎米荠 | Cardamine macrophylla | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0010 |
| 五脉绿绒蒿 | Meconopsis quintuplinervia | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0009 |
| 草玉梅 | Anemone rivularis | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0009 |
| 马先蒿一种 | Pedicularis sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0008 |
| 全冠黄堇 | Corydalis tongolensis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0008 |
| 中亚早熟禾 | Poa litwinowiana | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0008 |
| 具爪曲花紫堇 | Corydalis curviflora subsp. rosthornii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0008 |
| 腺毛蝇子草 | Silene yetii | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 东亚囊瓣芹 | Pternopetalum tanakae | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 滇藏无心菜 | Arenaria napuligera | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 假水生龙胆 | Gentiana pseudoaquatica | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 湿生扁蕾 | Gentianopsis paludosa | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 林地早熟禾 | Poa nemoralis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0005 |
| 史蒂瓦早熟禾 | Poa himalayana | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 菊状千里光 | Senecio laetus | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 短茎囊瓣芹 | Pternopetalum longicaule var. humile | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 沼兰 | Malaxis monophyllos | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 钻裂风铃草 | Campanula aristata | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 紫羊茅 | Festuca rubra | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 葱状灯心草 | Juncus allioides | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 双叉细柄茅 | Ptilagrostis dichotoma | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 长穗三毛草 | Trisetum clarkei | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0003 |
| 异叶囊瓣芹 | Pternopetalum heterophyllum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0003 |
| 椭圆叶花锚 | Halenia elliptica | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0003 |
| 长果母草 | Lindernia anagallis | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0003 |
| 灌木层 Shrub layer | ||||
| 云杉幼苗 | Picea spp. | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.1444 | 0.0227 |
| 银露梅 | Potentilla glabra | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.1389 | 0.0219 |
| 绵穗柳 | Salix eriostachya | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0778 | 0.0202 |
| 峨眉蔷薇 | Rosa omeiensis | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0611 | 0.0193 |
| 冰川茶藨子 | Ribes glaciale | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.1111 | 0.0187 |
| 细枝绣线菊 | Spiraea myrtilloides | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.1333 | 0.0132 |
| 华西忍冬 | Lonicera webbiana | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0556 | 0.0131 |
| 刚毛忍冬 | L. hispida | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0778 | 0.0124 |
| 金露梅 | Potentilla fruticosa | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0389 | 0.0114 |
| 唐古特忍冬 | Lonicera tangutica | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0042 |
| 细梗蔷薇 | Rosa graciliflora | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0278 | 0.0026 |
| 硬叶柳 | Salix sclerophylla | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0167 | 0.0025 |
| 川西樱桃 | Cerasus trichostoma | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0012 |
| 天山茶藨子 | Ribes meyeri | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0009 |
| 柳一种 | Salix sp. | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
附录I 四川壤塘县日柯沟高山近林线云杉原始林下维管植物物种组成及其重要值
Appendix I Species composition and their importance value of vascular plants under the primary spruce forests near alpine timberline in Zamtang County, Sichuan Province, China. (Ph, phanerophytes; Ch, chamaephytes; H, hemicryptophytes; C, cryptophytes; Th, therophytes)
| 物种 Species | 生活型 Life form | 频度 Frequency | 重要值 Importance value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 草本层 Herb layer | ||||
| 明亮苔草 | Carex laeta | H 地面芽植物 | 0.8222 | 0.1616 |
| 狭苞橐吾 | Ligularia intermedia | H 地面芽植物 | 0.6278 | 0.1463 |
| 珠芽蓼 | Polygonum viviparum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.8278 | 0.1237 |
| 圆叶小堇菜 | Viola biflora var. rockiana | H 地面芽植物 | 0.8278 | 0.0891 |
| 细叶芨芨草 | Achnatherum chingii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2778 | 0.0804 |
| 箭叶橐吾 | Ligularia sagitta | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2667 | 0.0777 |
| 柳叶菜风毛菊 | Saussurea epilobioides | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3889 | 0.0620 |
| 梅氏雀麦 | Bromus mairei | H 地面芽植物 | 0.4333 | 0.0604 |
| 纤细草莓 | Fragaria gracilis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.6222 | 0.0567 |
| 东方草莓 | F. orientalis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.5278 | 0.0512 |
| 萎软紫菀 | Aster flaccidus | G 地下芽植物 | 0.5556 | 0.0491 |
| 喜巴早熟禾 | Poa hylobates | H 地面芽植物 | 0.4500 | 0.0488 |
| 紫花碎米荠 | Cardamine tangutorum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.5111 | 0.0449 |
| 高山露珠草 | Circaea alpina | H 地面芽植物 | 0.4500 | 0.0445 |
| 疏花剪股颖 | Agrostis hookeriana | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3833 | 0.0409 |
| 膨囊苔草 | Carex lehmanii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2556 | 0.0383 |
| 四齿无心菜 | Arenaria quadridentata | H 地面芽植物 | 0.6000 | 0.0378 |
| 弯齿风毛菊 | Saussurea przewalskii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2444 | 0.0337 |
| 狭叶红景天 | Rhodiola kirilowii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2333 | 0.0328 |
| 毛茛一种 | Ranunculus sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0278 | 0.0286 |
| 羊茅 | Festuca ovina | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1667 | 0.0274 |
| 高原毛茛 | Ranunculus tanguticus | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3889 | 0.0255 |
| 星叶草 | Circaeaster agrestis | Th 一年生植物 | 0.2389 | 0.0235 |
| 细毛拉拉藤 | Galium pusillosetosum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3111 | 0.0217 |
| 紫堇一种 | Corydalis sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2889 | 0.0199 |
| 湿地勿忘草 | Myosotis caespitosa | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2389 | 0.0190 |
| 条裂黄堇 | Corydalis linarioides | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2722 | 0.0182 |
| 肾叶金腰 | Chrysosplenium griffithii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.2722 | 0.0181 |
| 长茎囊瓣芹 | Pternopetalum longicaule | G 地下芽植物 | 0.2722 | 0.0170 |
| 黄三七 | Souliea vaginata | G 地下芽植物 | 0.1722 | 0.0162 |
| 细柄茅 | Ptilagrostis mongholica | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1167 | 0.0157 |
| 微孔草 | Microula sikkimensis | Th 一年生植物 | 0.2278 | 0.0157 |
| 轮叶马先蒿 | Pedicularis verticillata | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1722 | 0.0144 |
| 小花缬草 | Valeriana minutiflora | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1611 | 0.0129 |
| 猪殃殃 | Galium aparine var. echinospermum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1778 | 0.0124 |
| 剪股颖一种 | Agrostis sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0833 | 0.0117 |
| 柔毛蓼 | Polygonum sparsipilosum | Th 一年生植物 | 0.1500 | 0.0115 |
| 异花孩儿参 | Pseudostellaria heterantha | G 地下芽植物 | 0.1611 | 0.0103 |
| 蕨叶千里光 | Senecio pteridophyllus | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0778 | 0.0098 |
| 大果红景天 | Rhodiola macrocarpa | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1056 | 0.0097 |
| 康定鼠尾草 | Salvia prattii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0944 | 0.0096 |
| 雀麦一种 | Bromux sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0722 | 0.0091 |
| 羌活 | Notopterygium incisum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0833 | 0.0089 |
| 单枝灯心草 | Juncus potaninii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0889 | 0.0082 |
| 耳蕨一种 | Polystichum sp. | G 地下芽植物 | 0.1056 | 0.0080 |
| 长叶微孔草 | Microula trichocarpa | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0667 | 0.0077 |
| 驴蹄草 | Caltha palustris | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0500 | 0.0073 |
| 唐古拉婆婆纳 | Veronica vandellioides | H 地面芽植物 | 0.1056 | 0.0072 |
| 早熟禾一种 | Poa sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0500 | 0.0072 |
| 毛脉柳叶菜 | Epilobium amurense | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0889 | 0.0068 |
| 阿洼早熟禾 | Poa araratica | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0667 | 0.0065 |
| 光籽柳叶菜 | Epilobium tibetanum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0944 | 0.0065 |
| 掌叶大黄 | Rheum palmatum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0061 |
| 二色香青同色变种 | Anaphalis bicolor var. subconcolor | Ch 地上芽植物 | 0.0667 | 0.0059 |
| 长芒披碱草 | Elymus dolichatherus | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0611 | 0.0056 |
| 针刺悬钩子 | Rubus pungens | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0054 |
| 黑水翠雀花 | Delphinium potaninii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0333 | 0.0051 |
| 甘青老鹳草 | Geranium pylzowianum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0722 | 0.0050 |
| 轮叶黄精 | Polygonatum verticillatum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0722 | 0.0049 |
| 单花拉拉藤 | Galium exile | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0667 | 0.0044 |
| 毛果婆婆纳 | Veronica eriogyne | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0611 | 0.0041 |
| 紫茎小芹 | Sinocarum coloratum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0444 | 0.0035 |
| 杯花韭 | Allium cyathophorum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0444 | 0.0031 |
| 柳兰 | Chamerion angustifolium subsp. angustifoliam | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0029 |
| 岩生剪股颖 | Agrostis rupestris | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0278 | 0.0027 |
| 曲枝早熟禾 | Poa pagophila | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0025 |
| 川西风毛菊 | Saussurea dzeurensis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0389 | 0.0025 |
| 毛葶苈 | Draba eriopoda | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0333 | 0.0023 |
| 簇生泉卷耳 | Cerastium fontanum subsp. vulgare | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0333 | 0.0023 |
| 玉山香青 | Anaphalis morrisonicola | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0167 | 0.0022 |
| 冷蕨 | Cystopteris fragilis | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0278 | 0.0020 |
| 丝叶苔草 | Carex capilliformis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0019 |
| 中华金腰 | Chrysosplenium sinicum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0018 |
| 肾叶毛茛 | Ranunculus sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0167 | 0.0017 |
| 多榔菊 | Doronicum stenoglossum | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0017 |
| 异色红景天 | Rhodiola discolor | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0015 |
| 爪瓣虎耳草 | Saxifraga unguiculata | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0014 |
| 隐瓣蝇子草 | Silene gonosperma | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0167 | 0.0011 |
| 毛茛一种 | Ranunculus sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.3778 | 0.0011 |
| 甘肃苔草 | Carex kansusis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0011 |
| 高山嵩草 | Kobresia pygmaea | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0011 |
| 苔草一种 | Carex sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0010 |
| 极丽马先蒿 | Pedicularis decorissima | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0010 |
| 大叶碎米荠 | Cardamine macrophylla | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0010 |
| 五脉绿绒蒿 | Meconopsis quintuplinervia | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0009 |
| 草玉梅 | Anemone rivularis | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0009 |
| 马先蒿一种 | Pedicularis sp. | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0008 |
| 全冠黄堇 | Corydalis tongolensis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0008 |
| 中亚早熟禾 | Poa litwinowiana | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0008 |
| 具爪曲花紫堇 | Corydalis curviflora subsp. rosthornii | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0008 |
| 腺毛蝇子草 | Silene yetii | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 东亚囊瓣芹 | Pternopetalum tanakae | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 滇藏无心菜 | Arenaria napuligera | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 假水生龙胆 | Gentiana pseudoaquatica | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 湿生扁蕾 | Gentianopsis paludosa | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0007 |
| 林地早熟禾 | Poa nemoralis | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0005 |
| 史蒂瓦早熟禾 | Poa himalayana | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 菊状千里光 | Senecio laetus | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 短茎囊瓣芹 | Pternopetalum longicaule var. humile | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 沼兰 | Malaxis monophyllos | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 钻裂风铃草 | Campanula aristata | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 紫羊茅 | Festuca rubra | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 葱状灯心草 | Juncus allioides | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 双叉细柄茅 | Ptilagrostis dichotoma | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| 长穗三毛草 | Trisetum clarkei | H 地面芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0003 |
| 异叶囊瓣芹 | Pternopetalum heterophyllum | G 地下芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0003 |
| 椭圆叶花锚 | Halenia elliptica | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0003 |
| 长果母草 | Lindernia anagallis | Th 一年生植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0003 |
| 灌木层 Shrub layer | ||||
| 云杉幼苗 | Picea spp. | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.1444 | 0.0227 |
| 银露梅 | Potentilla glabra | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.1389 | 0.0219 |
| 绵穗柳 | Salix eriostachya | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0778 | 0.0202 |
| 峨眉蔷薇 | Rosa omeiensis | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0611 | 0.0193 |
| 冰川茶藨子 | Ribes glaciale | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.1111 | 0.0187 |
| 细枝绣线菊 | Spiraea myrtilloides | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.1333 | 0.0132 |
| 华西忍冬 | Lonicera webbiana | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0556 | 0.0131 |
| 刚毛忍冬 | L. hispida | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0778 | 0.0124 |
| 金露梅 | Potentilla fruticosa | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0389 | 0.0114 |
| 唐古特忍冬 | Lonicera tangutica | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0222 | 0.0042 |
| 细梗蔷薇 | Rosa graciliflora | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0278 | 0.0026 |
| 硬叶柳 | Salix sclerophylla | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0167 | 0.0025 |
| 川西樱桃 | Cerasus trichostoma | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0012 |
| 天山茶藨子 | Ribes meyeri | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0111 | 0.0009 |
| 柳一种 | Salix sp. | Ph 高位芽植物 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| [1] | Bao WK (包维楷), Zhang YL (张镱锂), Wang Q (王乾), Bai WQ (摆万奇), Zheng D (郑度) (2002) Plant diversity along a time sequence (1-30 years) of artificial forest rehabilitation on subalpine cut land in the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 26,194-198. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [2] | Collaboration Group of Sichuan Vegetation (四川植被协作组) (1980) Sichuan Vegetation (四川植被). Sichuan People’s Publishing House, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [3] | Duan RY (段仁燕), Wang XA (王孝安), Huang MY (黄敏毅), Wang ZG (王志高), Wu GL (吴甘霖) (2010) Ecological characteristics of Larix chinensis population near timberline on Taibai Mountain in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 30,519-526. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] |
Gosz JR (1993) Ecotone hierarchies. Ecological Applications, 3,369-376.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] | Guan ZT (管中天) (2005) Forest Ecology Research and Application (森林生态研究与应用). Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [6] | Han JJ (韩景军), Xiao WF (肖文发), Luo JC (罗菊春) (2000) Effects of different cutting methods on regeneration and habitat for spruce-fir forests. Scientia Silvae Sinicae (林业科学), 36(1),90-96. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | He JC (何吉成), Luo TX (罗天祥), Xu YQ (徐雨晴) (2009) Characteristics of eco-climate at smith fir timberline in the Sergyemla Mountains, southeast Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 29,37-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Hooper DU, Chapin FS III, Ewel JJ, Hector A, Inchausti P, Lavorel S, Lawton JH, Lodge DM, Loreau M, Naeem S, Schmid B, Setala H, Symstad AJ, Vandermeer J, Wardle DA (2005) Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: a consensus of current knowledge. Ecological Monographs, 75,3-35. |
| [9] | Li MC (李明财), Luo TX (罗天祥), Liu XS (刘新圣), Kong GQ (孔高强) (2007) Distribution characteristics of δ 13C values in different organs of Abies georgei growing at alpine timberline. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 18,2654-2660. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [10] | Li MH (李迈和), Norbert K (2005) The state of knowledge on alpine treeline and suggestions for future research. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology (四川林业科技), 26(4),36-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Li WH (李文华) (1982) An overview of dark coniferous forest in Tibet. Journal of Natural Resources (自然资源), 6(2),1-16. (in Chinese) |
| [12] | Li WH (李文华), Zhou PC (周沛村) (1979) Study on the distribution of dark coniferous forests in Eurasia and its mathematical model. Journal of Natural Resources (自然资源), 3(1),21-34. (in Chinese) |
| [13] | Liu JH (刘俊华), Bao WK (包维楷), Li FL (李芳兰) (2005) Major bryophyte patch structures and their relationships with environmental factors under a coniferous forest of eastern Tibetan Plateau. Ecology and Environment (生态环境), 14,735-741. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Liu Q (刘庆) (2002) Ecological Research on Subalpine Coniferous Forests in China (亚高山针叶林生态学研究). Sichuan University Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [15] | Pang XY (庞学勇), Bao WK (包维楷), Zhang YM (张咏梅) (2005) Microclimate changes and plant succession in dark coniferous clear-cutting forestland in eastern Tibetan Plateau. World Science-Technology R & D (世界科技研究与发展), 27(3),47-53. |
| [16] | Qinghai Forest Editorial Committee (青海森林编辑委员会) (1993) Forest in Qinghai Province (青海森林). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [17] | Shi PL (石培礼) (1999) A Study on the Vegetation Ecology of Subalpine Timberline Ecotone (亚高山林线生态交错带的植被生态学研究). PhD dissertation, Institute of Geographic Science and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [18] | Shi PL (石培礼), Li WH (李文华), Wang JX (王金锡) (2002) Three-dimensional canopy structure in the timberline ecotone dominated by Abies faxoniana. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 11,1819-1824. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | The Editorial Board of Forests in Sichuan (四川森林编辑委员会) (1992) Forests in Sichuan (四川森林). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [20] | Theurillat JP, Guisan A (2001) Potential impact of climate change on vegetation in the European Alps: a review. Climate Change, 50,77-109. |
| [21] |
Tilman D, Reich PB, Knops JMH (2006) Biodiversity and ecosystem stability in a decade long grassland experiment. Nature, 441,629-632.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] | Wang JX (王金锡), Xu JD (许金铎), Hou GW (侯广维), Liu JB (刘建邦), Pu JT (蒲佳泰), Shi LX (史立新), Liao GY (廖光瑶) (1995) Ecology and Regeneration of Cutted Blank in Alpine and Plateau Region of the Upper Reach of Yangtze River (长江上游高山高原林区迹地生态与营林更新技术). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [23] | Wang XP (王襄平), Zhang L (张玲), Fang JY (方精云) (2004) Geographical differences in alpine timberline and its climatic interpretation in China. Acta Geographica Sinica (地理学报), 59,871-879. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] | Wu ZY (吴征镒) (1991) The areal-types of Chinese genera of seed plants. Acta Botanica Yunnanica (云南植物研究), 13 (Suppl., IV),1-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Wu ZY (吴征镒), Zhou ZK (周浙昆), Li DZ (李德铢), Peng H (彭华), Sun H (孙航) (2003) The areal-types of the world families of seed plants. Acta Botanica Yunnanica (云南植物研究), 25,245-257. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | Xu LJ (许林军), Peng H (彭鸿), Chen CG (陈存根), Tang HL (唐红亮), Yang YJ (杨亚娟) (2005) Quantitative analysis of the Larix chinensis forest’s distribution at Qinling Mountains and the character of the alpine timberline at Taibai Mountain. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica (西北植物学报), 25,968-972. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Yan XL (闫晓丽), Bao WK (包维楷) (2008) Evaluation of species composition and development of bryophyte community during early natural recovery progress of high-altitude spruce cutovers. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 16,110-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Zar JH (1999) Biostatistical Analysis. Prentcie Hall, New Jersey. |
| [29] | Zhang QY (张桥英), Luo P (罗鹏), Zhang YC (张运春), Shi FS (石福孙), Yi SL (易绍良), Wu N (吴宁) (2008) Ecological characteristics of Abies georgei population at timberline on the north-facing slope of Baima Snow Mountain, southwest China. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 28,129-135. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [30] | Zhang QY (张桥英), Zhang YC (张运春), Luo P (罗鹏), Wang Q (王乾), Wu N (吴宁) (2007) Ecological characteristics of a Sabina saltuaria population at timberline on the south-facing slope of Baima Snow Mountain, southwest China. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 31,857-864. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [2] | 仝淼, 王欢, 张文双, 王超, 宋建潇. 重金属污染土壤中细菌抗生素抗性基因分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [3] | 马文俊, 刘思嘉, 李柯懋, 简生龙, 薛长安, 韩庆祥, 魏金良, 陈生学, 牛依萌, 崔洲平, 隋瑞臣, 田菲, 赵凯. 青海省长江源区鱼类分布及多样性格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [4] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [5] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [6] | 时永强, 栾青杉, 单秀娟, 韦超, 赵永松, 孙策策, 金显仕. 长岛南部海域浮游动物多样性周年变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [7] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [8] | 倪艳梅, 陈莉, 董志远, 孙德斌, 李宝泉, 王绪敏, 陈琳琳. 黄河三角洲湿地生态修复区大型底栖动物群落结构与生态健康评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [9] | 魏嘉欣, 姜治国, 杨林森, 熊欢欢, 金胶胶, 罗方林, 李杰华, 吴浩, 徐耀粘, 乔秀娟, 魏新增, 姚辉, 余辉亮, 杨敬元, 江明喜. 湖北神农架中亚热带山地落叶阔叶林25 ha动态监测样地群落物种组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [10] | 林迪, 陈双林, 杜榷, 宋文龙, 饶固, 闫淑珍. 大别山黏菌的物种多样性调查[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23242-. |
| [11] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [12] | 吴芳芳, 刘娜, 何春梅, 原作强, 郝占庆, 尹秋龙. 秦岭山地木本植物群落结构及多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [13] | 单航, 雷祖培, 郑方东, 韦博良, 仲磊, 于明坚. 2013-2023年浙江乌岩岭次生常绿阔叶林群落动态变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24372-. |
| [14] | 姚嘉, 张聪伶, 李时轩, 林阳, 王震, 张煜涵, 周伟龙, 潘心禾, 朱珊, 吴逸卿, 王丹, 刘金亮, 谭珊珊, 沈国春, 于明坚. 百山祖连续海拔样带植物群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24052-. |
| [15] | 冯嘉谊, 练琚愉, 冯瑜莙, 张东旭, 曹洪麟, 叶万辉. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林群落垂直分层对群落结构及功能的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()
