



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (3): 331-339. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020081 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020081
卜向丽1, 王静1, 吴佳忆1, 孙太福1, 向荣伟1, 鲁庆斌2, 郝映红3, 崔绍朋4, 盛岩1, 孟秀祥1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-03-05
接受日期:2020-06-24
出版日期:2021-03-20
发布日期:2020-09-12
通讯作者:
孟秀祥
作者简介:E-mail: meng2014@ruc.edu.cn基金资助:
Xiangli Bu1, Jing Wang1, Jiayi Wu1, Taifu Sun1, Rongwei Xiang1, Qingbin Lu2, Yinghong Hao3, Shaopeng Cui4, Yan Sheng1, Xiuxiang Meng1,*( )
)
Received:2020-03-05
Accepted:2020-06-24
Online:2021-03-20
Published:2020-09-12
Contact:
Xiuxiang Meng
摘要:
为研究太行山东北部的哺乳动物区系及多样性格局, 2019年7月1日至10月30日间, 作者采用样线调查和红外相机监测、访谈、文献查阅等多种方法, 对该区域的哺乳动物进行调查, 分析了区系构成, 并基于多样性指数比较了太行山片区和燕山片区哺乳动物多样性及动物分布型的差异。结果表明: 太行山东北部区域分布有哺乳动物7目22科68种, 其中啮齿目种类最多(24种), 灵长目最少, 仅猕猴(Macaca mulatta) 1种; 区域内分布有2种国家I级(金钱豹Panthera pardus、豺Cuon alpinus)和10种国家II级重点保护野生动物。太行山片区和燕山片区的哺乳动物区系的平均动物区系相似性(average faunal resemblance)系数为0.844, 相似性较大, 太行山片区的哺乳动物种数(66)高于燕山片区(50), 其科的多样性指数(DF= 2.994 ± 0.251, n = 13)和属的多样性指数(DG = 2.443 ± 0.161, n = 13)也略高于燕山片区(DF = 2.458 ± 0.170, DG = 2.259 ± 0.149, n = 10), 但无显著差异(P> 0.05)。太行山片区哺乳动物G-F指数(DG-F= 0.145 ± 0.022, n = 13)显著高于燕山片区(0.078 ± 0.014, n = 10) (P< 0.05)。研究结果表明, 太行山片区和燕山片区的哺乳动物的科、属组成相同, 但太行山片区的物种多样性高于燕山片区; 太行山东北部区域分布的哺乳动物以古北界物种为主, 太行山片区和燕山片区均有10类动物分布型的哺乳动物; 因太行山片区的纬度相对较低, 其东洋界物种比例(19.11%)略高于燕山片区(17.64%)。
卜向丽, 王静, 吴佳忆, 孙太福, 向荣伟, 鲁庆斌, 郝映红, 崔绍朋, 盛岩, 孟秀祥 (2021) 太行山东北部哺乳动物区系及多样性. 生物多样性, 29, 331-339. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020081.
Xiangli Bu, Jing Wang, Jiayi Wu, Taifu Sun, Rongwei Xiang, Qingbin Lu, Yinghong Hao, Shaopeng Cui, Yan Sheng, Xiuxiang Meng (2021) Mammal fauna and biodiversity in the northeastern Taihang Mountains. Biodiversity Science, 29, 331-339. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020081.
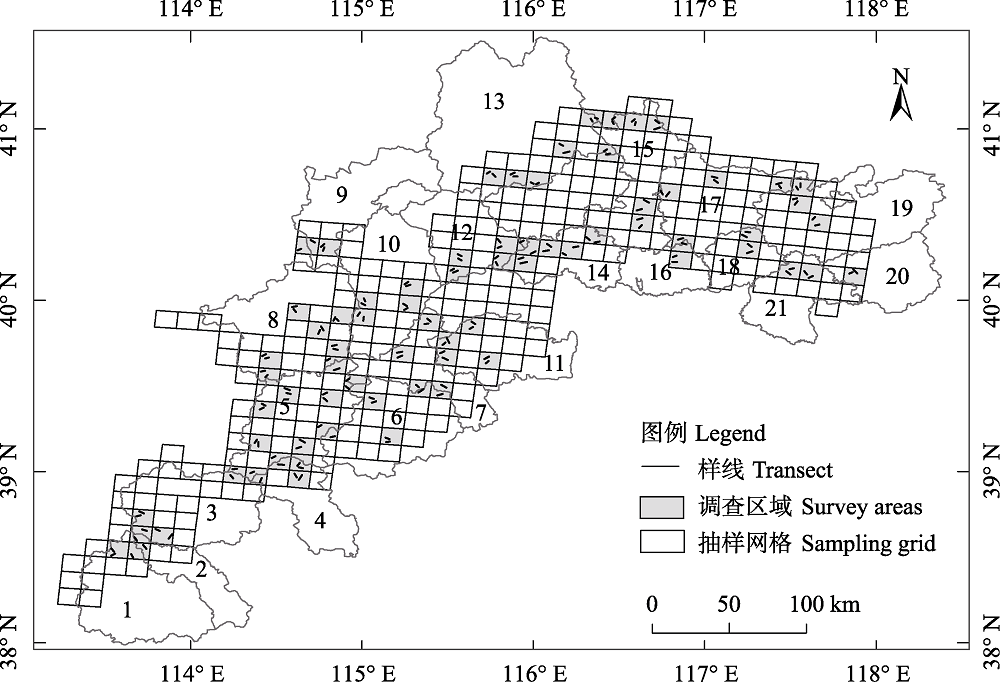
图1 太行山东北部调查区域及样线分布。1: 平山县; 2: 灵寿县; 3: 阜平县; 4: 唐县; 5: 涞源县; 6: 易县; 7: 涞水县; 8: 蔚县; 9: 宣化县; 10: 涿鹿县; 11: 房山区; 12: 怀来县; 13: 赤城县; 14: 昌平区; 15: 怀柔区; 16: 顺义区; 17: 密云区; 18: 平谷区; 19: 兴隆县; 20: 遵化市; 21: 蓟州区。
Fig. 1 Surveying area and transect lines distribution in northeastern Taihang Mountains. 1, Pingshan County; 2, Lingshou County; 3, Fuping County; 4, Tangxian County; 5, Laiyuan County; 6, Yixian County; 7, Laishui County; 8, Yuxian County; 9, Xuanhua County; 10, Zhuolu County; 11, Fangshan District; 12, Huailai County; 13, Chicheng County; 14, Changping District; 15, Huairou District; 16, Shunyi District; 17, Miyun District; 18, Pinggu District; 19, Xinglong County; 20, Zunhua City; 21, Jizhou District.
| 区系 Fauna | 分布型 Distribution type | 种数 No. of species (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 太行山东北部 Northeastern Taihang Mountains | 太行山片区 Taihang area | 燕山片区 Yanshan area | ||
| 古北界 Palaearctic realm | 古北型 Palaearctic type | 18 (26.47) | 18 (26.47) | 15 (22.06) |
| 华北型 North China type | 2 (2.94) | 2 (2.94) | 2 (2.94) | |
| 全北型 Holarctic type | 4 (5.88) | 4 (5.88) | 2 (2.94) | |
| 中亚型 Central-Asia type | 8 (11.76) | 8 (11.76) | 5 (7.35) | |
| 季风区型 Monsoon type | 9 (13.24) | 9 (13.24) | 6 (8.82) | |
| 东北-华北型 Northeast-north China type | 4 (5.88) | 4 (5.88) | 4 (5.88) | |
| 东洋界 Oriental realm | 南中国型 Southern China type | 3 (4.41) | 3 (4.41) | 1 (1.47) |
| 东洋型 Oriental type | 8 (11.76) | 7 (10.29) | 8 (11.76) | |
| 喜马拉雅-横断山区型 Himalaya-Hengduan Mountain type | 4 (5.88) | 3 (4.41) | 3 (4.41) | |
| 广布种 Wide spread | 不易归类的广布种 Inconvenience divide type and widely distributed species | 8 (11.76) | 8 (11.76) | 4 (5.88) |
表1 太行山东北部区域的哺乳动物区系组成
Table 1 Mammal fauna in the northeastern Taihang Mountains
| 区系 Fauna | 分布型 Distribution type | 种数 No. of species (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 太行山东北部 Northeastern Taihang Mountains | 太行山片区 Taihang area | 燕山片区 Yanshan area | ||
| 古北界 Palaearctic realm | 古北型 Palaearctic type | 18 (26.47) | 18 (26.47) | 15 (22.06) |
| 华北型 North China type | 2 (2.94) | 2 (2.94) | 2 (2.94) | |
| 全北型 Holarctic type | 4 (5.88) | 4 (5.88) | 2 (2.94) | |
| 中亚型 Central-Asia type | 8 (11.76) | 8 (11.76) | 5 (7.35) | |
| 季风区型 Monsoon type | 9 (13.24) | 9 (13.24) | 6 (8.82) | |
| 东北-华北型 Northeast-north China type | 4 (5.88) | 4 (5.88) | 4 (5.88) | |
| 东洋界 Oriental realm | 南中国型 Southern China type | 3 (4.41) | 3 (4.41) | 1 (1.47) |
| 东洋型 Oriental type | 8 (11.76) | 7 (10.29) | 8 (11.76) | |
| 喜马拉雅-横断山区型 Himalaya-Hengduan Mountain type | 4 (5.88) | 3 (4.41) | 3 (4.41) | |
| 广布种 Wide spread | 不易归类的广布种 Inconvenience divide type and widely distributed species | 8 (11.76) | 8 (11.76) | 4 (5.88) |
| 物种数 No. of species | 相同物种数 No. of common species | 平均动物区系相似性 Average faunal resemblance (AFR) | 科的多样性指数 Diversity of family index (DF) | 属的多样性指数 Diversity of genus index (DG) | G-F指数 G-F index (DG-F) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 太行山片区 Taihang area (n = 13) | 66 | 48 | 0.844 | 2.994 ± 0.251 | 2.443 ± 0.161 | 0.145 ± 0.022 |
| 燕山片区 Yanshan area (n = 10) | 50 | 2.458 ± 0.170 | 2.259 ± 0.149 | 0.078 ± 0.014 | ||
| P (t-test) | 0.157 | 0.572 | 0.046 |
表2 太行山片区与燕山片区哺乳动物物种多样性指数比较
Table 2 Comparison of mammal species diversity between Taihang area and Yanshan area
| 物种数 No. of species | 相同物种数 No. of common species | 平均动物区系相似性 Average faunal resemblance (AFR) | 科的多样性指数 Diversity of family index (DF) | 属的多样性指数 Diversity of genus index (DG) | G-F指数 G-F index (DG-F) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 太行山片区 Taihang area (n = 13) | 66 | 48 | 0.844 | 2.994 ± 0.251 | 2.443 ± 0.161 | 0.145 ± 0.022 |
| 燕山片区 Yanshan area (n = 10) | 50 | 2.458 ± 0.170 | 2.259 ± 0.149 | 0.078 ± 0.014 | ||
| P (t-test) | 0.157 | 0.572 | 0.046 |
| [1] | Chen W, Gao W (1991) Report of investigation on mammalian of Songshan Natural Conservancy of Beijing. Journal of Beijing Teachers College (Nature Sciences Edition), 12,64-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈卫, 高武 (1991) 北京松山自然保护区兽类调查报告. 北京师范学院学报(自然科学版), 12,64-69.]. | |
| [2] | Chen W, Gao W, Fu BQ (2004) Mammals and their geographical distribution in Beijing. Greening and Life, (6),42-43. (in Chinese) |
| [ 陈卫, 高武, 傅必谦 (2004) 北京地区兽类及其地理分布. 绿化与生活, (6),42-43.]. | |
| [3] | Cong MY, Cao D, Chen GP, Chen BZ, Sun FB (2017) Vertical characteristics of plant diversity in transition between Mount. Yan and Mount. Taihang. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 37,673-681. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 丛明旸, 曹迪, 陈国平, 陈宝政, 孙丰宾 (2017) 燕山和太行山过渡区植物多样性垂直变化特点. 植物研究, 37,673-681.]. | |
| [4] | Gao SP, Li DM, Gao YJ, Wang RJ, Li JY, Wu YF (2012) Species abundance and distribution patterns of vertebrates in Hebei Province. Journal of the Hebei Academy of Sciences, 29(3),62-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 高士平, 李东明, 高英杰, 王瑞君, 李巨勇, 吴跃峰 (2012) 河北省生物多样性动态监测指标设计: 以脊椎动物多样性分布的丰富度评价为例. 河北省科学院学报, 29(3),62-64.]. | |
| [5] | Gao XM, Ma KP, Chen LZ (2001) Species diversity of some deciduous broad-leaved forests in the warm-temperate zone and its relations to community dynamics. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 25,283-290. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 高贤明, 马克平, 陈灵芝 (2001) 暖温带若干落叶阔叶林群落物种多样性及其与群落动态的关系. 植物生态学报, 25,283-290.]. | |
| [6] | Jia YK, Gao YR, Chen CA, Zhou E (1999) Survey of rodent species and their zoogeographical distributions in Beijing Area. Chinese Journal of Vector Biology and Control, 10(2),87-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 贾延库, 高永荣, 陈长安, 周锷 (1999) 北京地区啮齿动物种类和地理分布调查. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 10(2),87-90.]. | |
| [7] | Jiang ZG, Ji LQ (1999) Avian-mammalian species diversity in nine representative sites in China. Chinese Biodiversity, 7,220-225. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋志刚, 纪力强 (1999) 鸟兽物种多样性测度的G-F指数方法. 生物多样性, 7,220-225.]. | |
| [8] | Jiang ZG, Li LL, Luo ZH, Tang SH, Li CW, Hu HJ, Ma Y, Wu Y, Wang YX, Zhou KY, Liu SY, Feng ZJ, Cai L, Zang CX, Zeng Y, Meng ZB, Ping XG, Fang HX (2016) Evaluating the status of China’s mammals and analyzing their causes of endangerment through the red list assessment. Biodiversity Science, 24,552-567. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋志刚, 李立立, 罗振华, 汤宋华, 李春旺, 胡慧建, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥, 周开亚, 刘少英, 冯祚建, 蔡蕾, 臧春鑫, 曾岩, 孟智斌, 平晓鸽, 方红霞 (2016) 通过红色名录评估研究中国哺乳动物受威胁现状及其原因. 生物多样性, 24,552-567.]. | |
| [9] | Jiang ZG, Liu SY, Wu Y, Jiang XL, Zhou KY (2017) China’s mammal diversity (2nd edition). Biodiversity Science, 25,886-895. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋志刚, 刘少英, 吴毅, 蒋学龙, 周开亚 (2017) 中国哺乳动物多样性(第2版). 生物多样性, 25,886-895.]. | |
| [10] | Jiang ZG, Ma Y, Wu Y, Wang YX, Feng ZJ, Zhou KY, Liu SY, Luo ZH, Li CW (2015) China’s mammal diversity. Biodiversity Science, 23,351-364. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋志刚, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥, 冯祚建, 周开亚, 刘少英, 罗振华, 李春旺, (2015) 中国哺乳动物多样性. 生物多样性, 23,351-364.]. | |
| [11] | Li DM, Wu YF, Sun LH, Zhang YW, Gao QH, Wu LN, Dong JX (2003) Analysis on avian-mammalian species diversity in Hebei Province. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 19(6),80-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李东明, 吴跃峰, 孙立汉, 张彦威, 高庆华, 武丽娜, 董建新 (2003) 河北省区域鸟兽物种多样性分析. 地理与地理信息科学, 19(6),80-82.]. | |
| [12] | Li JL, Zhao HS, Du J, Wan SX (2013) Threats to wildlife diversity and conservation strategies in the Xiaowutai Mountain National Nature Reserve, Hebei. Journal of Hebei Forestry Science and Technology, (1),35-37. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李吉利, 赵焕生, 杜娟, 万少欣 (2013) 河北小五台山国家级自然保护区野生动物多样性面临的威胁及保护对策. 河北林业科技, (1),35-37.]. | |
| [13] | Li Z, Sun RH, Zhang JC, Zhang C (2017) Temporal-spatial analysis of vegetation coverage dynamics in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei metropolitan regions. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37,7418-7426. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李卓, 孙然好, 张继超, 张翀 (2017) 京津冀城市群地区植被覆盖动态变化时空分析. 生态学报, 37,7418-7426.]. | |
| [14] | Lin X, Wang ZH, Tang ZY, Zhao SQ, Fang JY (2009) Geographic patterns and environmental correlates of terrestrial mammal species richness in China. Biodiversity Science, 17,652-663. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 林鑫, 王志恒, 唐志尧, 赵淑清, 方精云 (2009) 中国陆栖哺乳动物物种丰富度的地理格局及其与环境因子的关系. 生物多样性, 17,652-663.]. | |
| [15] | Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China (2011) China National Biodiversity Conservation Strategy and Action Plan (2011-2030). China Environmental Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 中华人民共和国环境保护部 (2011) 中国生物多样性保护战略与行动计划 (2011-2030年). 中国环境科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [16] | Pan QH, Wang YX, Yan K (2007) A Field Guide to the Mammals of China. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 潘清华, 王应祥, 岩崑 (2007) 中国哺乳动物彩色图鉴. 中国林业出版社, 北京. | |
| [17] | Post E, Stenseth NC (1999) Climatic variability, plant phenology, and northern ungulates. Ecology, 80,1322-1339. |
| [18] | Qin XB, Zhao TJ, Zhu JB (2008) Investigation of mammal resources in Baxianshan Nature Reserve. Science and Technology of Tianjin Agriculture and Forestry, (4),39-42. (in Chinese) |
| [ 覃雪波, 赵铁建, 朱金宝 (2008) 天津八仙山自然保护区兽类资源调查. 天津农林科技, (4),39-42.]. | |
| [19] | Smith AT, Xie Y, Hoffmann RS (2009) A Guide to the Mammals of China. Hunan Education Publishing House, Changsha. (in Chinese) |
| Smith A, 解焱, Hoffmann RS, (2009) 中国兽类野外手册. 湖南教育出版社, 长沙. | |
| [20] | Sun LH (1987) Eco-geographical division of small mammals in Hebei Province. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 3(2),55-57, 54. (in Chinese) |
| [ 孙立汉 (1987) 河北省小型兽类生态地理区划. 地理学与国土研究, 3(2),55-57, 54.]. | |
| [21] | Sun LH (2002) The research history of mammal and amphibious reptile and geographical division in Hebei Province. Geography and Territorial Research, 18(2),64-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙立汉 (2002) 河北哺乳及两栖爬行动物研究史与地理区划. 地理学与国土研究, 18(2),64-68.]. | |
| [22] | Tian Y, Feng YJ, Zhang CL, Yu BC, Tang XP, Hu HJ (2015) Effectiveness of line transects during wild animal surveys in mountain forests of South China. Biodiversity Science, 23,109-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 田园, 冯永军, 张春兰, 遇宝成, 唐小平, 胡慧建 (2015) 样线法在南方山地生态系统野生动物调查中的试点效果评价. 生物多样性, 23,109-115.]. | |
| [23] | Tong HW (2006) Mammalian faunal differentiations between North and South China during the Quaternary Period. L’Anthropologie, 110,870-887. (in French with English abstract). |
| [24] | Wang SW, Ye JL (1995) An analysis of global warming during the last one hundred years. Scientia Atmospherica Sinica, 19,545-553. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王绍武, 叶瑾琳 (1995) 近百年全球气候变暖的分析. 大气科学, 19,545-553.]. | |
| [25] | Wu ML, Wang XH, An CL, Zhao J, Fu YS, Mao FL, Shang XH, Wang ZP (2006) Investigation of mammal resources in Hebei Province. Journal of Hebei Forestry Science and Technology, (2),20-23. (in Chinese) |
| [ 武明录, 王秀辉, 安春林, 赵静, 付芸生, 毛富玲, 尚辛亥, 王振鹏 (2006) 河北省兽类资源调查. 河北林业科技, (2),20-23.]. | |
| [26] | Xiao ZS, Li XY, Xiang ZF, Li M, Jiang XL, Zhang LB (2017) Overview of the Mammal Diversity Observation Network of Sino BON. Biodiversity Science, 25,237-245. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 肖治术, 李学友, 向左甫, 李明, 蒋学龙, 张礼标 (2017) 中国兽类多样性监测网的建设规划与进展. 生物多样性, 25,237-245.]. | |
| [27] | Yang DD, Liu S, Fei DB, Yu XL, Gu YL, Lu HJ, Chen HM, Zhu JC (2008) Field survey and faunal analysis on herpetological resources in Qiyunshan Nature Reserve, Jiangxi Province. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 43(6),68-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨道德, 刘松, 费冬波, 喻兴雷, 谷颖乐, 卢何军, 陈辉敏, 朱家椿 (2008) 江西齐云山自然保护区两栖爬行动物资源调查与区系分析. 动物学杂志, 43(6),68-76.]. | |
| [28] | Yang SZ, An QX, Liu YR (2019) A survey and assessment of avian and mammalian resources in Xiaowutai International Hunting Ground, Hebei, China. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 40,332-344. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨守庄, 安琪瑄, 刘琰冉 (2019) 河北小五台国际狩猎场鸟兽资源调查与评价. 野生动物学报, 40,332-344.]. | |
| [29] | Zang CX, Cai L, Li JQ, Wu XP, Li XG, Li JS (2016) Preparation of the China Biodiversity Red List and its significance for biodiversity conservation within China. Biodiversity Science, 24,610-614. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 臧春鑫, 蔡蕾, 李佳琦, 吴晓莆, 李晓光, 李俊生 (2016) 《中国生物多样性红色名录》的制定及其对生物多样性保护的意义. 生物多样性, 24,610-614.]. | |
| [30] | Zhan YJ, Chen W, Gao W (2005) The status and conservation suggestions of Beijing Chiropteran. Journal of Capital Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 26(4),57-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 战永佳, 陈卫, 高武 (2005) 北京地区翼手类现状与保护. 首都师范大学学报(自然科学版), 26(4),57-59.]. | |
| [31] | Zhang J (1984) Characteristics of mammal fauna and eco-geography in Beijing area. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 4,187-195. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张洁 (1984) 北京地区的兽类区系及生态地理特征. 兽类学报, 4,187-195.]. | |
| [32] | Zhang J (1984) On the structure of rodent community in Beijing area. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 4,265-271. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张洁 (1984) 北京地区鼠类群落结构的研究. 兽类学报, 4,265-271.]. | |
| [33] | Zhang RZ (1978) On the zoogeographical characteristics of China: Mainly mammals. Acta Geographica Sinica, 33,85-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张荣祖 (1978) 试论中国陆栖脊椎动物地理特征——以哺乳动物为主. 地理学报, 33,85-101.]. | |
| [34] | Zhang RZ (2011) Zoogeography of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 张荣祖 (2011) 中国动物地理. 科学出版社, 北京. |
| [1] | 卢佳玉, 石小亿, 多立安, 王天明, 李治霖. 基于红外相机技术的天津城市地栖哺乳动物昼夜活动节律评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23369-. |
| [2] | 杨瑾谕, 朱万龙. 生境差异和人类活动对云南剑川甸南镇小型哺乳动物群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23246-. |
| [3] | 丁晨晨, 梁冬妮, 信文培, 李春旺, 蒋志刚. 中国哺乳动物形态、生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21520-. |
| [4] | 刘璐, 迟瑶, 吴朝宁, 钱天陆, 王结臣. 陆栖哺乳动物的地理隔离研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(8): 1134-1145. |
| [5] | 万雅琼, 李佳琦, 杨兴文, 李晟, 徐海根. 基于红外相机的中国哺乳动物多样性观测网络建设进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(9): 1115-1124. |
| [6] | 尚素琴, 吴兴波, 王召龙, 彭鹤年, 周惠丽, 张红勇, 白映禄. 兴隆山国家级自然保护区不同生境的蝴蝶群落结构与种-多度分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(8): 983-992. |
| [7] | 颜文博,吉晟男,帅凌鹰,赵雷刚,朱大鹏,曾治高. 秦岭南坡陕西洋县辖区哺乳动物物种多样性的空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(2): 177-185. |
| [8] | 陶夏秋, 崔绍朋, 蒋志刚, 初红军, 李娜, 杨道德, 李春旺. 新疆阿勒泰地区爬行动物区系及多样性海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(6): 578-589. |
| [9] | 胡一鸣, 梁健超, 金崑, 丁志锋, 周智鑫, 胡慧建, 蒋志刚. 喜马拉雅山哺乳动物物种多样性垂直分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(2): 191-201. |
| [10] | 蒋志刚, 李立立, 罗振华, 汤宋华, 李春旺, 胡慧建, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥, 周开亚, 刘少英, 冯祚建, 蔡蕾, 臧春鑫, 曾岩, 孟智斌, 平晓鸽, 方红霞. 通过红色名录评估研究中国哺乳动物受威胁现状及其原因[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(5): 552-567. |
| [11] | 黄备, 魏娜, 孟伟杰, 张明霞. 基于压力-状态-响应模型的辽宁省长海海域海洋生物多样性评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(1): 48-54. |
| [12] | 蒋志刚, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥, 冯祚建, 周开亚, 刘少英, 罗振华, 李春旺. 中国哺乳动物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(3): 351-364. |
| [13] | 苗林, 罗述金. 基因组时代的新视野: 东南亚哺乳动物类群在第四纪冰河时期多样性的起源与分化[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(1): 40-50. |
| [14] | 何锴, 王文智, 李权, 罗培鹏, 孙悦华, 蒋学龙. DNA条形码技术在小型兽类鉴定中的探索: 以甘肃莲花山为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(2): 197-205. |
| [15] | 孙工棋, 曲艺, 唐美庆, 刘晓, 栾晓峰. 基于我国陆生濒危哺乳动物保护的生态功能区优先保护规划[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(1): 47-53. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn