



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 23246. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023246 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023246
收稿日期:2023-07-07
接受日期:2023-10-06
出版日期:2023-11-20
发布日期:2023-12-09
通讯作者:
* E-mail: 基金资助:Received:2023-07-07
Accepted:2023-10-06
Online:2023-11-20
Published:2023-12-09
Contact:
* E-mail: 摘要:
小型哺乳动物的群落结构可反映当地生境质量, 为生态保护提供数据支撑。为了解生境差异和人为干扰对云南省剑川县甸南镇小型哺乳动物群落结构以及多样性的影响, 本文于2005年1月至2017年12月, 选择4种典型生境(菜园地、耕地、灌丛和住家附近), 采用笼捕法对小型哺乳动物展开调查。共布设鼠笼195,612个, 捕获小型哺乳动物16,060只, 隶属4目7科22种。其中啮齿目捕获到3科15种15,777只, 大绒鼠(Eothenomys miletus)和高山姬鼠(Apodemus chevrieri)为甸南镇优势种。不同生境间小型哺乳动物数量差异极显著, 数量最多的是灌丛, 共5,760只; 最少的是住家附近, 仅2,160只。菜园地的Shannon-Wiener多样性指数最高(1.26), 住家附近最低(1.08)。菜园地和耕地的物种相似性系数最高, 为0.94。本研究结果表明, 小型哺乳动物的群落结构和多样性受生境差异和人类活动干扰影响: 植物资源少、人类活动干扰程度高的生境中多样性指数低; 环境条件好、人类活动干扰适度的生境中多样性指数较高; 食物资源较少、干扰较少的生境中(如灌丛)多样性指数略低。
杨瑾谕, 朱万龙 (2023) 生境差异和人类活动对云南剑川甸南镇小型哺乳动物群落结构和多样性的影响. 生物多样性, 31, 23246. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023246.
Jinyu Yang, Wanlong Zhu (2023) Impact of habitat variation and human activities on small mammal community structure and diversity in Diannan Town, Jianchuan County, Yunnan. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23246. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023246.
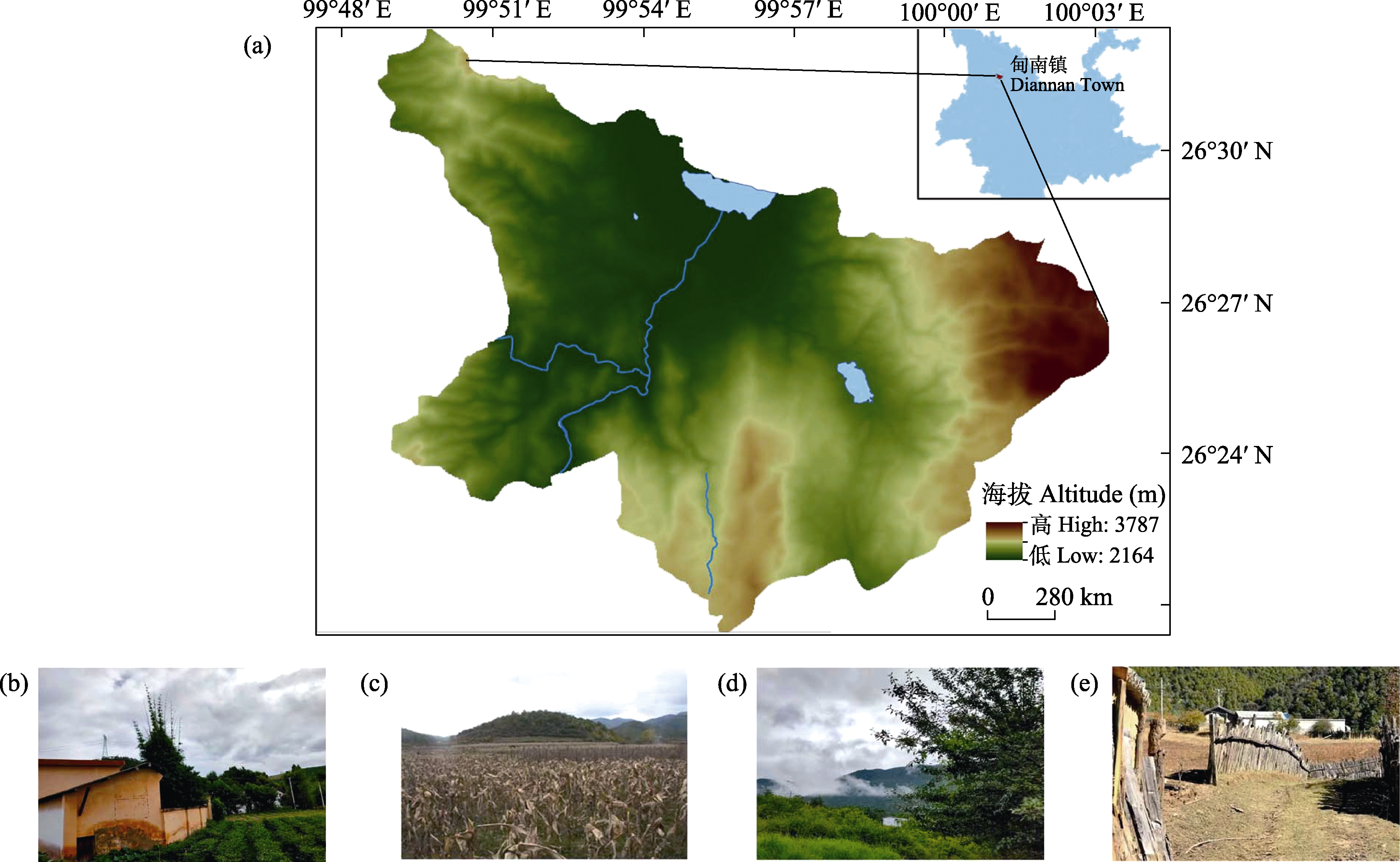
图1 云南省剑川县甸南镇地理位置(a)及调查样地(b: 菜园地; c: 耕地; d: 灌丛; e: 住家附近)照片
Fig. 1 Geographic location (a) and pictures of sampling sites (b, Vegetable garden; c, Cropland; d, Shrub; e, Neighborhood region) of Diannan Town, Jianchuan County, Yunnan
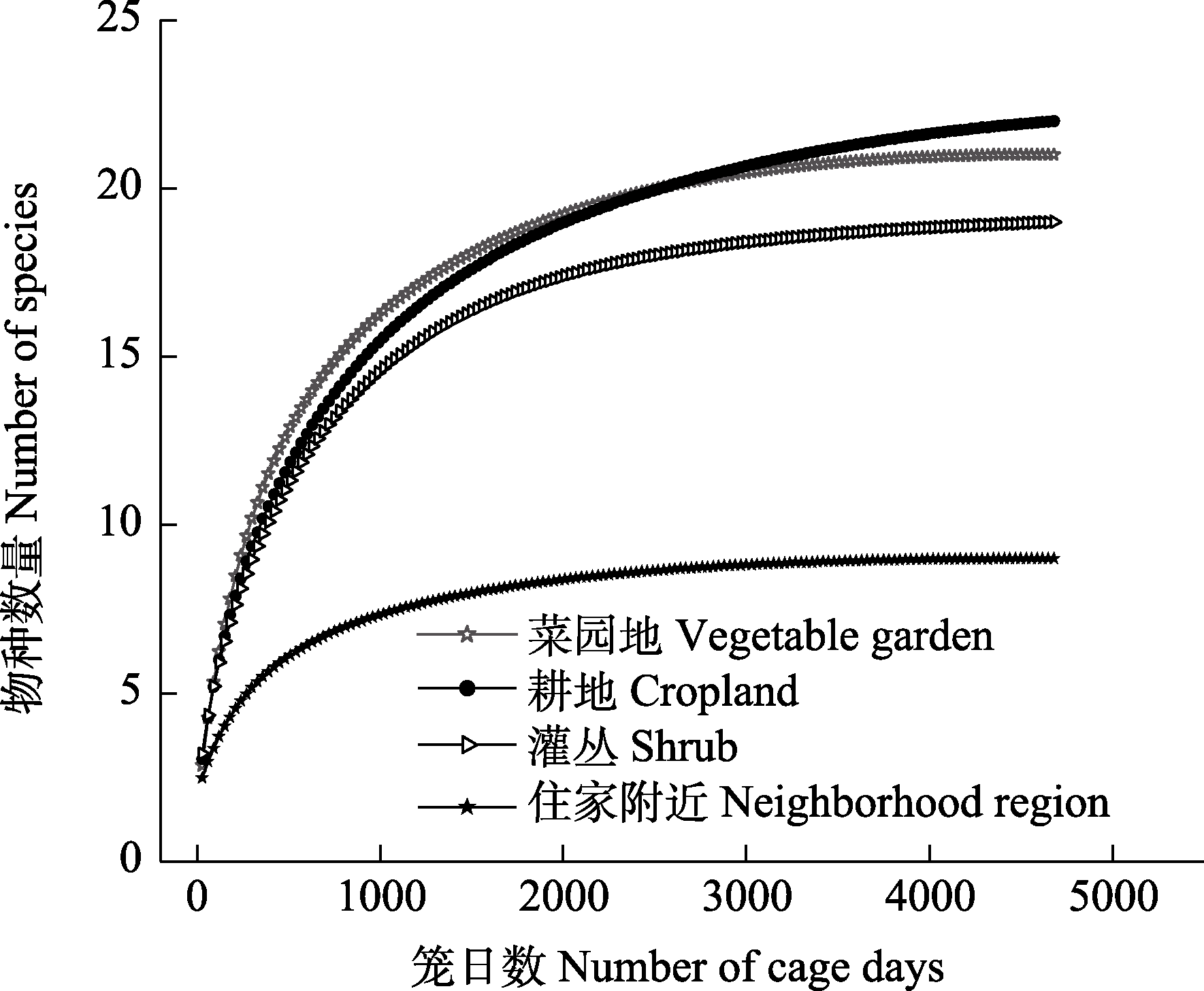
图2 云南省剑川县甸南镇不同生境小型哺乳动物调查的物种累积曲线
Fig. 2 Species accumulation curve for small mammals survey of different habitats in Diannan Town, Jianchuan County, Yunnan
| 生境 Habitat | 实际物种数 Actual number of species | Chao 2指数 Chao 2 index | Bootstrap指数 Bootstrap index | Jackknife 2指数 Jackknife 2 index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 菜园地 Vegetable garden | 21 | 21.08 | 22.05 | 23.56 |
| 耕地 Cropland | 22 | 24.45 | 23.40 | 27.50 |
| 灌丛 Shrub | 19 | 20.45 | 19.98 | 23.06 |
| 住家附近 Neighborhood region | 9 | 9.51 | 9.55 | 10.89 |
表1 云南省剑川县甸南镇不同生境小型哺乳动物实际物种丰富度和非参数估计丰富度
Table 1 Recorded species and non-parametric estimated richness of small mammals in different habitats in Diannan Town, Jianchuan County, Yunnan
| 生境 Habitat | 实际物种数 Actual number of species | Chao 2指数 Chao 2 index | Bootstrap指数 Bootstrap index | Jackknife 2指数 Jackknife 2 index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 菜园地 Vegetable garden | 21 | 21.08 | 22.05 | 23.56 |
| 耕地 Cropland | 22 | 24.45 | 23.40 | 27.50 |
| 灌丛 Shrub | 19 | 20.45 | 19.98 | 23.06 |
| 住家附近 Neighborhood region | 9 | 9.51 | 9.55 | 10.89 |
| 物种 Species | 捕获数量 Number of captures | 总捕获率 Capture rate (%) | 占捕获动物比例(P, %) | 物种 Species | 捕获数量 Number of captures | 总捕获率 Capture rate (%) | 占捕获动物比例(P, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 食肉目 Carnivora | 松鼠科 Sciuridae | ||||||
| 鼬科 Mustelidae | 侧纹岩松鼠 Sciurotamias forresti | 14 | 0.007 | 0.087 | |||
| 黄鼬 Mustela sibirica | 7 | 0.004 | 0.044 | 珀氏长吻松鼠 Dremomys pernyi | 12 | 0.006 | 0.075 |
| 劳亚食虫目 Eulipotyphla | 赤腹松鼠 Sciurus iginventris | 12 | 0.006 | 0.075 | |||
| 鼹科 Talpidae | 鼠科 Muridae | ||||||
| 白尾鼹 Parascaptor leucura | 6 | 0.003 | 0.037 | 高山姬鼠 Apodemus chevrieri | 6,719 | 3.435 | 41.837 |
| 鼩鼱科 Soricidae | 红耳巢鼠 Micromys erythrotis | 196 | 0.100 | 1.220 | |||
| 灰麝鼩 Crocidura attenuata | 53 | 0.027 | 0.330 | 大林姬鼠 Apodemus speciosus | 425 | 0.217 | 2.646 |
| 四川短尾鼩 Anourosorex squamipes | 29 | 0.015 | 0.181 | 小林姬鼠 Apodemus sylvaticus | 75 | 0.038 | 0.467 |
| 臭鼩 Suncus murinus | 33 | 0.017 | 0.205 | 褐家鼠 Rattus norvegicus | 1,162 | 0.594 | 7.235 |
| 攀鼩目 Scandentia | 黄胸鼠 Rattus flavipectus | 956 | 0.489 | 5.953 | |||
| 树鼩科 Tupalldae | 社鼠 Niviventer confucianus | 17 | 0.009 | 0.106 | |||
| 中缅树鼩 Tupaia belangeri | 15 | 0.008 | 0.965 | 大足鼠 Rattus nitidus | 94 | 0.048 | 0.585 |
| 啮齿目 Rodentia | 小家鼠 Mus musculus | 49 | 0.025 | 0.305 | |||
| 仓鼠科 Cricetidae | 安氏白腹鼠 Niviventer andersoni | 21 | 0.011 | 0.131 | |||
| 大绒鼠 Eothenomys miletus | 5,919 | 3.026 | 36.856 | 黑缘齿鼠 Rattus andamanensis | 102 | 0.052 | 0.635 |
| 针毛鼠 Niviventer fulvescens | 4 | 0.002 | 0.025 |
表2 云南省剑川县甸南镇小型哺乳动物种类组成
Table 2 Composition of small mammal community in Diannan Town, Jianchuan County, Yunnan
| 物种 Species | 捕获数量 Number of captures | 总捕获率 Capture rate (%) | 占捕获动物比例(P, %) | 物种 Species | 捕获数量 Number of captures | 总捕获率 Capture rate (%) | 占捕获动物比例(P, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 食肉目 Carnivora | 松鼠科 Sciuridae | ||||||
| 鼬科 Mustelidae | 侧纹岩松鼠 Sciurotamias forresti | 14 | 0.007 | 0.087 | |||
| 黄鼬 Mustela sibirica | 7 | 0.004 | 0.044 | 珀氏长吻松鼠 Dremomys pernyi | 12 | 0.006 | 0.075 |
| 劳亚食虫目 Eulipotyphla | 赤腹松鼠 Sciurus iginventris | 12 | 0.006 | 0.075 | |||
| 鼹科 Talpidae | 鼠科 Muridae | ||||||
| 白尾鼹 Parascaptor leucura | 6 | 0.003 | 0.037 | 高山姬鼠 Apodemus chevrieri | 6,719 | 3.435 | 41.837 |
| 鼩鼱科 Soricidae | 红耳巢鼠 Micromys erythrotis | 196 | 0.100 | 1.220 | |||
| 灰麝鼩 Crocidura attenuata | 53 | 0.027 | 0.330 | 大林姬鼠 Apodemus speciosus | 425 | 0.217 | 2.646 |
| 四川短尾鼩 Anourosorex squamipes | 29 | 0.015 | 0.181 | 小林姬鼠 Apodemus sylvaticus | 75 | 0.038 | 0.467 |
| 臭鼩 Suncus murinus | 33 | 0.017 | 0.205 | 褐家鼠 Rattus norvegicus | 1,162 | 0.594 | 7.235 |
| 攀鼩目 Scandentia | 黄胸鼠 Rattus flavipectus | 956 | 0.489 | 5.953 | |||
| 树鼩科 Tupalldae | 社鼠 Niviventer confucianus | 17 | 0.009 | 0.106 | |||
| 中缅树鼩 Tupaia belangeri | 15 | 0.008 | 0.965 | 大足鼠 Rattus nitidus | 94 | 0.048 | 0.585 |
| 啮齿目 Rodentia | 小家鼠 Mus musculus | 49 | 0.025 | 0.305 | |||
| 仓鼠科 Cricetidae | 安氏白腹鼠 Niviventer andersoni | 21 | 0.011 | 0.131 | |||
| 大绒鼠 Eothenomys miletus | 5,919 | 3.026 | 36.856 | 黑缘齿鼠 Rattus andamanensis | 102 | 0.052 | 0.635 |
| 针毛鼠 Niviventer fulvescens | 4 | 0.002 | 0.025 |
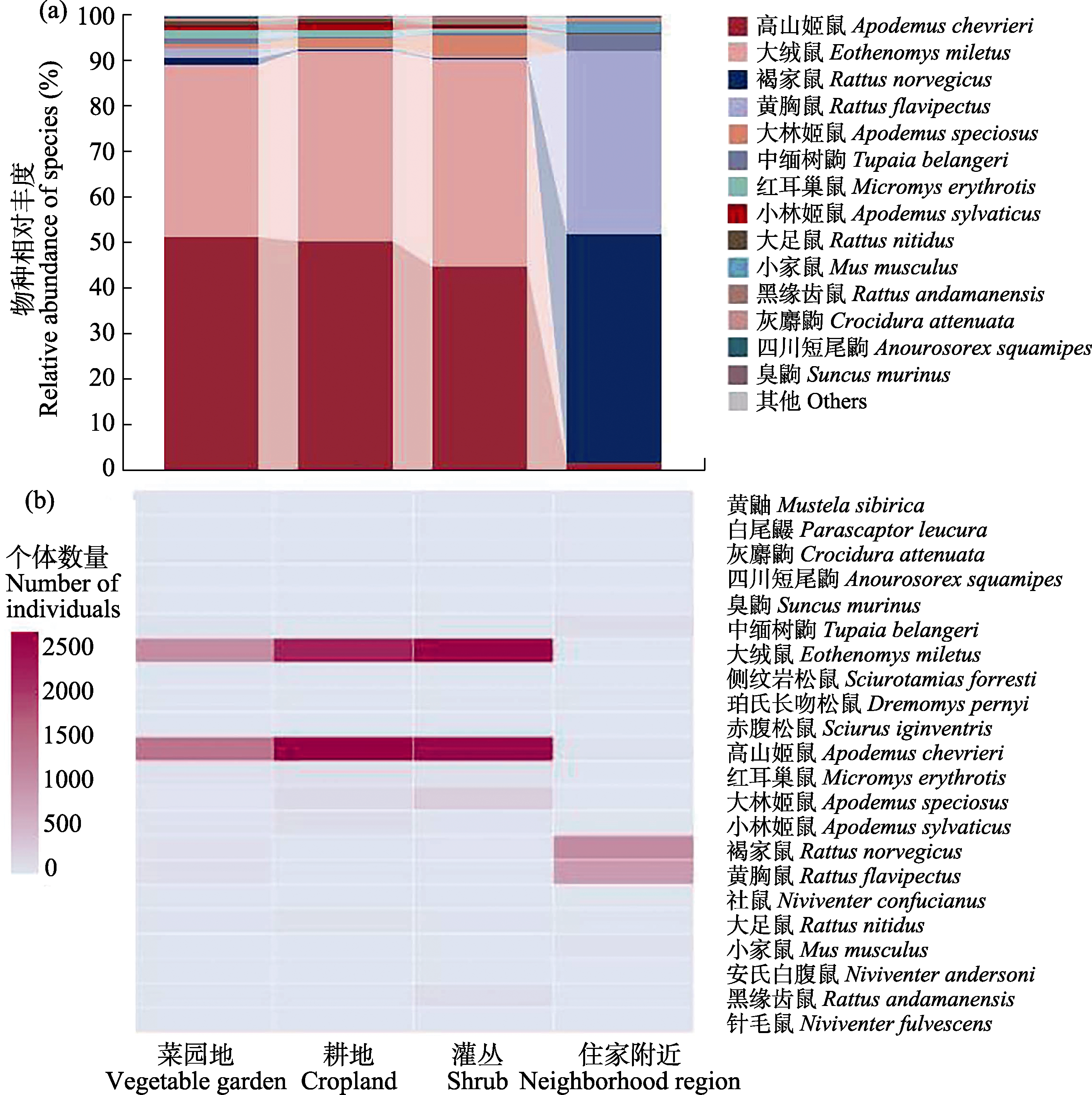
图3 云南省剑川县甸南镇不同生境小型哺乳动物的相对丰富度(a)和分布热图(b)
Fig. 3 The relative abundance of small mammals (a) and the heatmap of small mammal distribution (b) of different habitats in Diannan Town, Jianchuan County, Yunnan
| 生境 Habitat | Shannon-Wiener 多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index | Pielou 均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index | Simpson 优势度指数 Simpson dominance index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 菜园地 Vegetable garden | 1.26 | 0.41 | 1.59 |
| 耕地 Cropland | 1.09 | 0.35 | 1.18 |
| 灌丛 Shrub | 1.15 | 0.39 | 1.31 |
| 住家附近 Neighborhood region | 1.08 | 0.49 | 1.16 |
表3 云南省剑川县甸南镇不同生境小型哺乳动物的群落多样性
Table 3 Community diversity of small mammals of different habitats in Diannan Town, Jianchuan County, Yunnan
| 生境 Habitat | Shannon-Wiener 多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index | Pielou 均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index | Simpson 优势度指数 Simpson dominance index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 菜园地 Vegetable garden | 1.26 | 0.41 | 1.59 |
| 耕地 Cropland | 1.09 | 0.35 | 1.18 |
| 灌丛 Shrub | 1.15 | 0.39 | 1.31 |
| 住家附近 Neighborhood region | 1.08 | 0.49 | 1.16 |
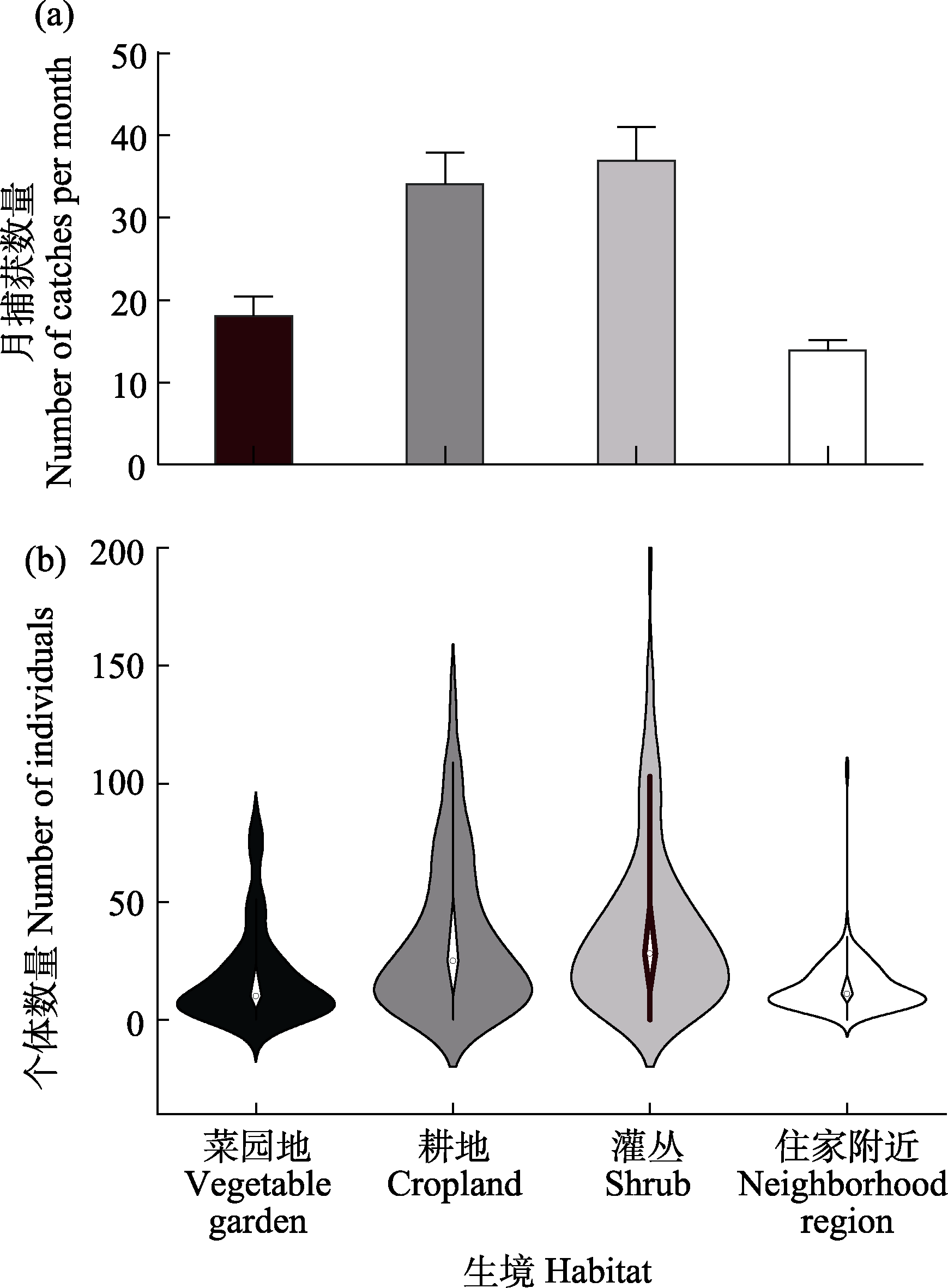
图4 云南省剑川县甸南镇不同生境小型哺乳动物的月捕获数量差异图(a)和个体数量小提琴图(b)
Fig. 4 Variation in monthly small mammal catches (a) and violin plot of individual number (b) of the small mammal population of different habitats in Diannan Town, Jianchuan County, Yunnan
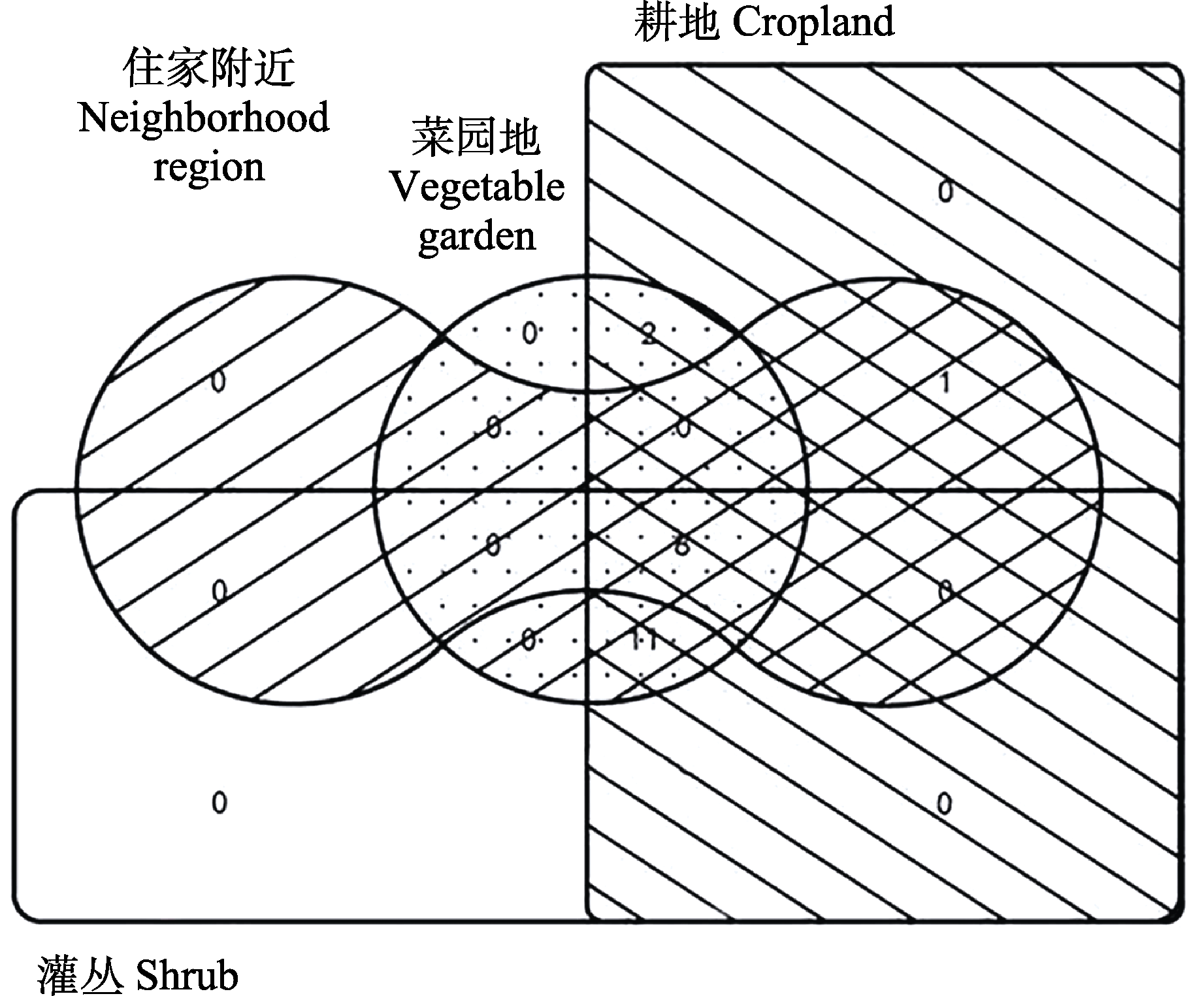
图5 云南省剑川县甸南镇不同生境小型哺乳动物分布情况Venn图
Fig. 5 Venn diagram of the distribution of small mammals in different habitats in Diannan Town, Jianchuan County, Yunnan
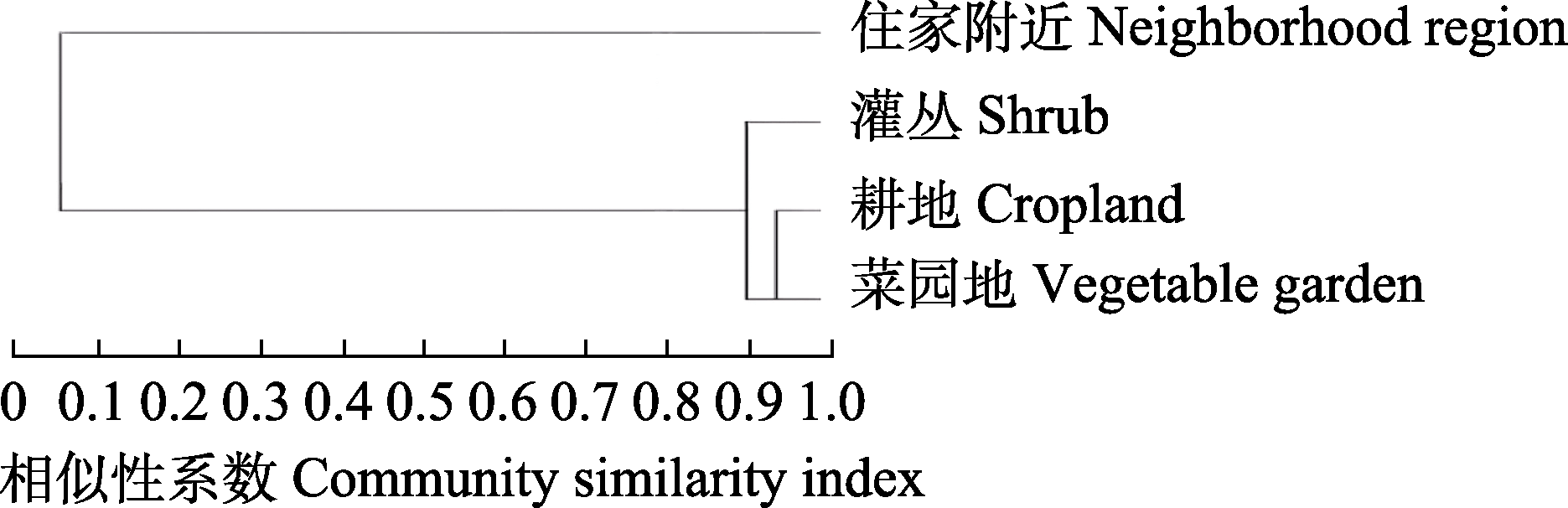
图6 云南省剑川县甸南镇不同生境小型哺乳动物群落聚类图
Fig. 6 Cluster of community similarity index of small mammals in different habitats in Diannan Town, Jianchuan County, Yunnan
| [1] |
Alexandre M, Hipólito D, Ferreira E, Fonseca C, Rosalino LM (2020) Humans do matter: Determinants of red fox (Vulpes vulpes) presence in a western Mediterranean landscape. Mammal Research, 65, 203-214.
DOI |
| [2] |
Ambec N, Bergeron Y, Fenton NJ (2023) Plant community and climate differ between former islands and submerged hills by proglacial Lake Ojibway in eastern boreal Canada. Biodiversity and Conservation, 32, 1709-1732.
DOI |
| [3] |
Aschwanden J, Holzgang O, Jenni L (2007) Importance of ecological compensation areas for small mammals in intensively farmed areas. Wildlife Biology, 13, 150-158.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Boufford DE (2014) Biodiversity hotspot: China’s Hengduan Mountains. Arnoldia, 72, 24-35. |
| [5] |
Chen ZZ, Li XY, Song WY, Li Q, Onditi K, Khanal L, Jiang XL (2020) Small mammal species richness and turnover along elevational gradient in Yulong Mountain, Yunnan, Southwest China. Ecology and Evolution, 10, 2545-2558.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Chu B, Ma SJ, Zhou YS, Ji CP, Zhou JW, Zhou R, Tian YL, Hua LM (2018) Relationship between the spatial distribution of the mounds of plateau zokor (Eospalax baileyi) and environmental factors in eastern Qilian Mountain. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 964-974. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [楚彬, 马素洁, 周延山, 姬程鹏, 周建伟, 周睿, 田永亮, 花立民 (2018) 祁连山东段高原鼢鼠(Eospalax baileyi)土丘空间分布格局及其与环境因子的空间关联性. 生态学报, 38, 964-974.] | |
| [7] | Colwell RK, Coddington JA (1994) Estimating terrestrial biodiversity through extrapolation. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B: Biological Sciences, 345, 101-118. |
| [8] | Dong DH (2019) Characteristics and Mechanism of Precipitation Change in Rainy Season in Hengduan Mountain Area. PhD dissertation, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [董丹宏 (2019) 横断山区雨季降水变化特征及其机制. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院大学, 北京.] | |
| [9] | Duan XD, Gong ZD, Feng XG, Yang GR, Luo DW, Li YH, Wu HY (2002) Investigation on community ecology of small mammals in the Lincang area of Yunnan. Endemic Diseases Bulletin, 17, 61-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [段兴德, 龚正达, 冯锡光, 杨贵荣, 罗大文, 李义和, 吴厚永 (2002) 云南临沧地区小型兽类的群落生态学研究. 地方病通报, 17, 61-66.] | |
| [10] |
Gong ZD, Wu HY, Duan XD, Feng XG, Zhang YZ, Liu Q (2001) The relationship between the geographical distribution trends of flea species diversity and the important environmental factor in the Hengduan Mountains, Yunnan. Biodiversity Science, 9, 319-328. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [龚正达, 吴厚永, 段兴德, 冯锡光, 张云智, 刘泉 (2001) 云南横断山区蚤类物种多样性的地理分布趋势与重要环境因素的关系. 生物多样性, 9, 319-328.] | |
| [11] | He XC, Wen ZX, Zhang DJ, Yang QS, Yin XD, Chen X, Ran JH (2023) Low impact of forest conversion on biodiversity: Evidence from small mammals in contrasting forests of Mt. Liangshan. Ecosphere, 14, e4570. |
| [12] |
Hortal J, Borges PAV, Gaspar C (2006) Evaluating the performance of species richness estimators: Sensitivity to sample grain size. Journal of Animal Ecology, 75, 274-287.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | Jiang XL (2000) Mammalian and Zonal Geographical Study of the Wuliang Mountains, Jingdong, Yunnan, China. PhD dissertation, Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蒋学龙 (2000) 景东无量山哺乳动物及区系地理学研究. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院昆明动物研究所, 昆明.] | |
| [14] |
Kelt DA, Van Vuren DH, Johnson ML, Wilson JA, Innes RJ, Jesmer BR, Ingram KP, Smith JR, Bigelow SW, Burnett RD, Stine PA (2013) Small mammals exhibit limited spatiotemporal structure in Sierra Nevada forests. Journal of Mammalogy, 94, 1197-1213.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Li Q (2011) Species accumulation curves and its application. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 48, 1882-1888. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李巧 (2011) 物种累积曲线及其应用. 应用昆虫学报, 48, 1882-1888.] | |
| [16] | Liu MQ, Liu ZX, Zhang CG, Shao ZT, Pu EN, Duan XD, Gao ZH (2021) Analysis on vertical spatial and seasonal ecological niche of small mammals in Yulong plague foci of Yunnan Province. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 56, 338-350. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘美琪, 刘正祥, 张长国, 邵宗体, 浦恩念, 段兴德, 高子厚 (2021) 云南省玉龙鼠疫疫源地小型兽类垂直空间与季节生态位分析. 动物学杂志, 56, 338-350.] | |
| [17] | Liu ZX, Gao ZH, Shao ZT, Duan XD, Li YQ, Pu EN, Chen X (2021) Composition and distribution of small-sized mammals in Baima Snow Mountain National Nature Reserve. Journal of Medical Pest Control, 37, 1025-1029. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘正祥, 高子厚, 邵宗体, 段兴德, 李玉琼, 浦恩念, 陈星 (2021) 白马雪山国家级自然保护区小型兽类的组成与分布. 医学动物防制, 37, 1025-1029.] | |
| [18] | Ma J, Li QF, Sun RY, Liu DZ (2004) Rodents as the key predators of ground seeds of Quercus liaotungensis in Xiaolongmen Forestry Centre, Beijing. Zoological Research, 25, 287-291. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马杰, 李庆芬, 孙儒泳, 刘定震 (2004) 啮齿动物对北京小龙门林场辽东栎地表种子的扩散. 动物学研究, 25, 287-291.] | |
| [19] | Ma KP, Liu YM (1994) Measurement of biotic community diversity. I. α diversity (Part 2). Chinese Biodiversity, 2, 231-239. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平, 刘玉明 (1994) 生物群落多样性的测度方法. I. α多样性的测度方法(下). 生物多样性, 2, 231-239.] | |
| [20] |
Mares MA, Ernest KA (1995) Population and community ecology of small mammals in a gallery forest of central Brazil. Journal of Mammalogy, 76, 750-768.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, da Fonseca GAB, Kent J (2000) Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature, 403, 853-858.
DOI |
| [22] |
Olson DM, Dinerstein E (1998) The global 200: A representation approach to conserving the earth’s most biologically valuable ecoregions. Conservation Biology, 12, 502-515.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Pan YS (1989) Division of geologic structure in the Hengduan Mountainous region. Mountain Research, 7, 3-12. (in Chinese) |
| [潘裕生 (1989) 横断山区地质构造分区. 山地研究, 7, 3-12.] | |
| [24] |
Peng BQ, Tao L, Li J, Fan RH, Chen SD, Fu CK, Wang Q, Tang KY (2023) DNA metabarcoding dietary analysis of six sympatric small mammals at the Laojunshan National Nature Reserve, Sichuan Province. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22474. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [彭步青, 陶玲, 李靖, 范荣辉, 陈顺德, 付长坤, 王琼, 唐刻意 (2023) 基于DNA宏条形码研究四川老君山国家级自然保护区6种同域共存小型哺乳动物的食性. 生物多样性, 31, 22474.] | |
| [25] |
Poe N, Stuble KL, Souza L (2019) Small mammal herbivores mediate the effects of soil nitrogen and invertebrate herbivores on grassland diversity. Ecology and Evolution, 9, 3577-3587.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Quan SY, Yue RP, Zhang LY, Lian HY, Zang YH, Bian CL, Li D, Ju JK, Gong ZD (2010) The composition and spatial distribution of small mammals in the Hengduan Mountains of Yunnan, China. Chinese Journal of Vector Biology and Control, 21, 16-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [权寿瑛, 岳仁苹, 张丽云, 连宏宇, 臧颖惠, 边长玲, 李栋, 琚俊科, 龚正达 (2010) 云南省横断山区小型兽类的组成及空间分布. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 21, 16-22.] | |
| [27] |
Song WY, Li XY, Wang HJ, Chen ZZ, He SW, Jiang XL (2021) Multi-dimensional evaluation of small mammal diversity in tree line habitats across the Three Parallel Rivers of Yunnan Protected Areas: Implications for conservation. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1215-1228. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[宋文宇, 李学友, 王洪娇, 陈中正, 何水旺, 蒋学龙 (2021) 三江并流区树线生境小型兽类多样性多维度评价及其保护启示. 生物多样性, 29, 1215-1228.]
DOI |
|
| [28] | Su XQ (2018) Study on the status of mammal species diversity in Gaoligong Mountain Nature Reserve. Environmental Impact Assessment, 40, 94-96. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [苏晓庆 (2018) 高黎贡山自然保护区兽类多样性现状研究. 环境影响评价, 40, 94-96.] | |
| [29] | Sun HL, Li WH, Zhang MT, Han YF (1986) Comprehensive scientific investigation of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Resources Science, (3), 22-30, 10. (in Chinese) |
| [孙鸿烈, 李文华, 章铭陶, 韩裕丰 (1986) 青藏高原综合科学考察. 资源科学, (3), 22-30, 10.] | |
| [30] | Sun ZY, Liu SY, Guo YS, Liu Y, Liao R, Guo ZW (2013) The faunal composition and distribution of small mammals in Erlang Mountains. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 33, 82-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙治宇, 刘少英, 郭延蜀, 刘洋, 廖锐, 郭振伟 (2013) 二郎山小型兽类区系及分布格局. 兽类学报, 33, 82-89.] | |
| [31] |
Talamoni SA, Dias MM (1999) Population and community ecology of small mammals in southeastern Brazil. Mammalia, 63, 167-182.
DOI URL |
| [32] | Tong L, Lu JQ (2010) Community structure and its seasonal variation of small mammals in Xishuangbanna of Yunnan, China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 29, 1770-1776. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [仝磊, 路纪琪 (2010) 西双版纳地区小型哺乳动物群落结构及其季节变动. 生态学杂志, 29, 1770-1776.] | |
| [33] | Wang YX (2009) Living habits, damage characteristics and control techniques of the white-tailed mole (Parascaptor leucura) in vegetable fields. China Plant Protection, 29, 19-20. (in Chinese) |
| [王玉兴 (2009) 菜田白尾鼹的生活习性、为害特点及其防治技术. 中国植保导刊, 29, 19-20.] | |
| [34] | Wang ZK, Gao WR, Zhu WL (2015) Progress of research on the metabolism characteristics in three small mammals in Hengduan Mountain region. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 35, 445-452. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王政昆, 高文荣, 朱万龙 (2015) 横断山区三种小型哺乳动物代谢特征的研究进展. 兽类学报, 35, 445-452.] | |
| [35] | Wei FW, Yang QS, Wu Y, Jiang XL, Liu SY, Li BG, Yang G, Li M, Zhou J, Li S, Hu YB, Ge DY, Li S, Yu WH, Chen BY, Zhang ZJ, Zhou CQ, Wu SB, Zhang L, Chen ZZ, Chen SD, Deng HQ, Jiang TL, Zhang LB, Shi HY, Lu XL, Li Q, Liu Z, Cui YQ, Li YC (2021) Catalogue of mammals in China (2021). Acta Theriologica Sinica, 41, 487-501. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[魏辅文, 杨奇森, 吴毅, 蒋学龙, 刘少英, 李保国, 杨光, 李明, 周江, 李松, 胡义波, 葛德燕, 李晟, 余文华, 陈炳耀, 张泽钧, 周材权, 吴诗宝, 张立, 陈中正, 陈顺德, 邓怀庆, 江廷磊, 张礼标, 石红艳, 卢学理, 李权, 刘铸, 崔雅倩, 李玉春 (2021) 中国兽类名录(2021版). 兽类学报, 41, 487-501.]
DOI |
|
| [36] | Wen ZX, Feijó A, Ke JZ, He XC, Cheng JL, Ge DY, Tian T, Xia L, Wu YJ, Ran JH, Yang QS (2022) Altitudinal dispersal process drives community assembly of montane small mammals. Ecography, 2022, e6318. |
| [37] | Wu YJ, Yang QS, Wen ZX, Xia L, Zhang QA, Zhou HM (2013) What drives the species richness patterns of non-volant small mammals along a subtropical elevational gradient? Ecography, 36, 185-196. |
| [38] |
Wu YJ, Yang QS, Xia L, Feng ZJ, Zhou HM (2012) Species diversity and distribution pattern of non-volant small mammals along the elevational gradient on eastern slope of Gongga Mountain. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 4318-4328. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [吴永杰, 杨奇森, 夏霖, 冯祚建, 周华明 (2012) 贡嘎山东坡非飞行小型兽类物种多样性的垂直分布格局. 生态学报, 32, 4318-4328.] | |
| [39] | Yin WS, Li M, Ao CH, Yang ZX (2023) Survey on the distribution of Niviventer fulvescen in Xifeng County of Guizhou Province. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 51(7), 88-89, 94. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [尹文书, 李梅, 敖成红, 杨再学 (2023) 贵州省息烽县针毛鼠分布调查. 安徽农业科学, 51(7), 88-89, 94.] | |
| [40] | Zhang YZ, Gong ZD, Feng XG, Duan XD, Wu HY, Weng X, Lü Y (2002) The community structure and vertical distribution of small mammal in Baicaoling Mt., Yunnan Province, China. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 37(2), 63-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张云智, 龚正达, 冯锡光, 段兴德, 吴厚永, 翁学, 吕元 (2002) 云南白草岭鼠形小兽群落结构及垂直分布. 动物学杂志, 37(2), 63-66.] | |
| [41] | Zhang YZ, Gong ZD, Wu HY, Cai QS, Luo HK, Li CC, Li ZP (2005) Community structure and vertical distribution of small mammals in Wuliang Mountain Nature Reserve, Yunnan Province, China. Endemic Disease Bulletin, 20(4), 13-15, 17. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张云智, 龚正达, 吴厚永, 蔡乔顺, 罗红开, 李昌朝, 李忠培 (2005) 云南省无量山自然保护区小型兽类群落结构及垂直分布研究. 地方病通报, 20(4), 13-15, 17.] | |
| [42] | Zhao WC, Li Q, Zhao YR, Bu SH (2021) Diversity and distribution characteristics of small mammals in the southern slope of middle and East Qinling Mountains. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 42, 1022-1029. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵文超, 李琦, 赵依然, 卜书海 (2021) 秦岭南麓中、东段小型兽类多样性及分布特征. 野生动物学报, 42, 1022-1029.] | |
| [43] |
Zhu WL, Cai JH, Lian X, Wang ZK (2010) Adaptive character of metabolism in Eothenomys miletus in Hengduan Mountains region during cold acclimation. Journal of Thermal Biology, 35, 417-421.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Zhu WL, Jia T, Lian X, Wang ZK (2008) Evaporative water loss and energy metabolic in two small mammals, voles (Eothenomys miletus) and mice (Apodemus chevrieri), in Hengduan Mountains region. Journal of Thermal Biology, 33, 324-331.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Zhu WL, Wang ZK (2015) Effects of cold exposure on maximum metabolic rate in Eothenomys miletus and Apodemus chevrieri. Journal of Green Science and Technology, (11), 24-26. (in Chinese) |
| [朱万龙, 王政昆 (2015) 低温暴露对大绒鼠和高山姬鼠最大代谢率的影响. 绿色科技, (11), 24-26.] | |
| [46] | Zhu WL, Zhang H, Meng LH, Cai JH, Wang ZK (2016) Composition and diversity of small mammals community in Shilong, Jianchuan area of Yunnan Province. Journal of Biology, 33(5), 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱万龙, 张浩, 孟丽华, 蔡金红, 王政昆 (2016) 云南剑川石龙地区小型哺乳动物群落组成和多样性研究. 生物学杂志, 33(5), 1-4.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 刘咏华, 童光蓉, 余航远, 王宁宁, 任海保, 陈磊, 马克平, 米湘成. 钱江源-百山祖国家公园候选区钱江源园区冠层三维结构及光谱特征对人为干扰的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24174-. |
| [3] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [4] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [5] | 刘志禹, 吉鑫, 隋国辉, 杨定, 李轩昆. 北京首都国际机场野牛草与杂草草坪无脊椎动物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [6] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [7] | 仝淼, 王欢, 张文双, 王超, 宋建潇. 重金属污染土壤中细菌抗生素抗性基因分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [8] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [9] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [10] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [11] | 李华亮, 张明军, 张熙斌, 谭荣, 李诗川, 冯尔辉, 林雪云, 陈珉, 颜文博, 曾治高. 海南东寨港国家级自然保护区两栖类群落组成及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24350-. |
| [12] | 王凤琼, 张心怡, 王鑫厅, 姜超, 侯亚丽, 包道日娜. 羊草草原原生群落羊草种群点格局分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24271-. |
| [13] | 弋维, 艾鷖, 吴萌, 田黎明, 泽让东科. 青藏高原高寒草甸土壤古菌群落对不同放牧强度的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24339-. |
| [14] | 刘源, 杜剑卿, 马丽媛, 杨刚, 田建卿. 纳木措流域岸边带湿地产甲烷古菌群落多样性与分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24247-. |
| [15] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
