



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (8): 1134-1145. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020476 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020476
• 综述 • 上一篇
刘璐1, 迟瑶1, 吴朝宁1, 钱天陆1, 王结臣1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-12-24
接受日期:2021-06-21
出版日期:2021-08-20
发布日期:2021-08-06
通讯作者:
王结臣
作者简介:* E-mail: wangjiechen@nju.edu.cn基金资助:
Lu Liu1, Yao Chi1, Zhaoning Wu1, Tianlu Qian1, Jiechen Wang1,2,*( )
)
Received:2020-12-24
Accepted:2021-06-21
Online:2021-08-20
Published:2021-08-06
Contact:
Jiechen Wang
摘要:
地理隔离是驱动物种分布格局形成的主要因素之一。本文回顾和总结了近几十年来地理隔离影响陆栖哺乳动物空间分布的研究成果, 从自然因素和人为因素两方面就地理隔离对物种分布的影响研究进展进行了综述。自然因素包括山脉、水体、沙漠和其他极端环境、气候变化等, 这些要素通常是在陆栖哺乳动物的缓慢演化进程中发挥作用; 人为因素侧重于因人类活动参与导致的物种分布变化, 包括景观结构变化、交通设施建设等, 在短短几百年甚至几十年内, 可以使物种分布特征发生显著变化。地理隔离对陆栖哺乳动物分布的作用是普遍而相对的, 长期存在且处于动态变化中。多种地理隔离因素之间的尺度效应不同, 哺乳动物在适应地理隔离的过程中表现出了生物个体和种群的响应过程。最后, 建议今后重点开展以下几方面的研究: (1)基于历史动物地理学与生态动物地理学, 深入研究地理隔离与动物地理边界形成的原因; (2)微观尺度下, 借助分子生物学和各种组学技术探讨地理隔离对物种遗传和适应机制的影响; (3)借鉴其他动物类群的研究经验, 加强对我国陆生哺乳动物的跟踪监测; (4)以数据驱动为导向, 将动物地理学与数据科学相结合, 以更好地分析动物分布的变迁史。
刘璐, 迟瑶, 吴朝宁, 钱天陆, 王结臣 (2021) 陆栖哺乳动物的地理隔离研究进展. 生物多样性, 29, 1134-1145. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020476.
Lu Liu, Yao Chi, Zhaoning Wu, Tianlu Qian, Jiechen Wang (2021) Research progress on the geographical isolation of terrestrial mammals. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1134-1145. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020476.
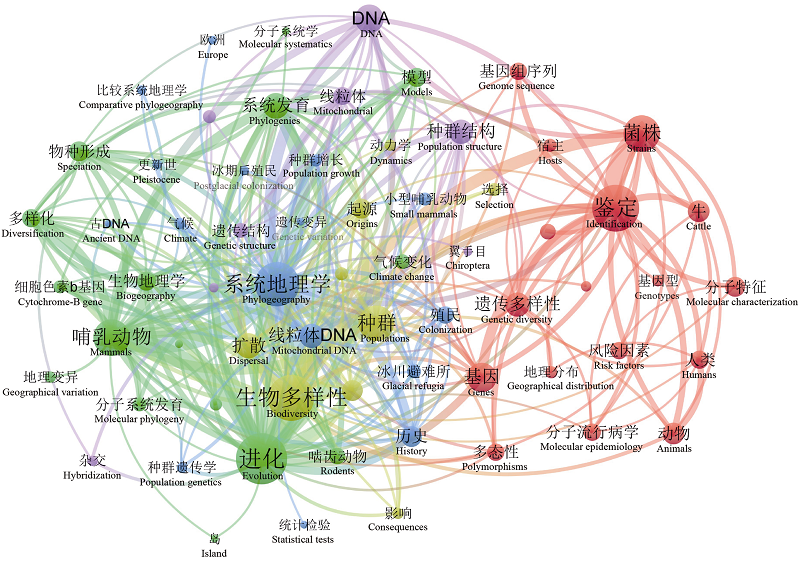
图1 陆栖哺乳动物的地理隔离研究关键词共现图谱。文献来源: Web of Science核心合集数据库; 时间: 1990-2021; 文献类型: ARTICLE。
Fig. 1 Keywords coexistence network of research on geographical isolation of terrestrial mammals. Literature source: Web of Science Core Collection; publication years: 1990-2021; document type: ARTICLE.
| 隔离因素 Isolation factors | 主要影响方式及强度 Main influence mode and intensity | |
|---|---|---|
| 自然因素 Natural factors | 山脉 Mountain range | 造成山脉两侧物种差异, 促进动物的支系分化, 形成“天空之岛”。但也有可能利于山地动物的扩散。It causes species differences on both sides of the mountain, promotes the divergence of branches, and forms “islands in the sky”. But it may also be conducive to the dispersals of mountain animals. |
| 江河 Rivers | 可能阻碍动物扩散, 促进两岸种群遗传分化。结冰期可为扩散提供条件。隔离效果差异与河流宽度有关。会驱动兽类群落分布格局的变化, 如“千岛湖”呈现出的典型嵌套格局。It inhibits the dispersals and intensifies genetic differentiation of cross-strait populations. The glaciation period can provide conditions for dispersal. And the difference of isolation effect is related to the width of river. It drives the change of the distribution pattern of mammal community, such as the typical nested pattern of “Thousand-Islet Lake”. | |
| 海洋 Oceans | 导致岛屿隔离, 隔离作用强于江河, 促进岛屿特有种的形成。It promotes the formation of endemic species on islands. The isolation effect of ocean is stronger than that of river. | |
| 沙漠 Deserts | 阻碍大多数哺乳动物的扩散, 促进动物分化形成不同的亚种, 但有利于沙漠动物范围的扩大。It inhibits the dispersals of most mammals and promotes the division of animals into different subspecies. However, it is conducive to the expansion of desert animal range. | |
| 其他极端环境与气候变化 Other extreme environments and climate change | 冰川扩张收缩加剧动物遗传分化, 气温波动影响物种分布。如全球变暖引起的北极海冰消融, 造成北极熊生境缩小且碎片化。The expansion and contraction of glaciers aggravate genetic differentiation. Temperature fluctuations affect the distribution of species. For example, the melting of Arctic sea ice caused by global warming leads to the shrinking and fragmentation of polar bear habitat. | |
| 人为因素 Human factors | 景观格局变化 Change of landscape pattern | 大规模森林砍伐导致树栖哺乳动物生境面积减少, 但可能促进非树栖动物的种群扩张。土地利用类型变化会影响物种分布, 重新造林会促进树栖动物的再次扩张。Large-scale deforestation reduces the habitat area of arboreal mammals, but it may promote the population expansion of non-arboreal mammals. Changes in land use types will affect species distribution and reforestation will promote the re-expansion of arboreal fauna. |
| 交通设施建设 Construction of transportation facilities | 阻碍动物迁徙, 导致动物生境破碎化程度加剧。不同物种对道路的响应不同。野生动物桥梁可为动物提供迁徙通道。It inhibits the migration of animals and leads to the fragmentation of the habitat. Different species respond differently to the road. Wildlife bridges can provide migration passages for mammals. | |
| 其他因素 Other factors | 水库修建、偷猎狩猎、人为火灾等均会影响动物分布和扩散。人为干预可打破地理隔离限制, 加强地理隔离可防治物种入侵。Reservoir construction, poaching, and man-made fires all affect the distribution and the dispersal of mammals. Human intervention can break the restriction of geographical isolation, and strengthening geographical isolation can prevent and control species invasion. | |
表1 不同地理隔离因素的主要影响方式及强度
Table 1 The main influence mode and intensity of different geographical isolation factors
| 隔离因素 Isolation factors | 主要影响方式及强度 Main influence mode and intensity | |
|---|---|---|
| 自然因素 Natural factors | 山脉 Mountain range | 造成山脉两侧物种差异, 促进动物的支系分化, 形成“天空之岛”。但也有可能利于山地动物的扩散。It causes species differences on both sides of the mountain, promotes the divergence of branches, and forms “islands in the sky”. But it may also be conducive to the dispersals of mountain animals. |
| 江河 Rivers | 可能阻碍动物扩散, 促进两岸种群遗传分化。结冰期可为扩散提供条件。隔离效果差异与河流宽度有关。会驱动兽类群落分布格局的变化, 如“千岛湖”呈现出的典型嵌套格局。It inhibits the dispersals and intensifies genetic differentiation of cross-strait populations. The glaciation period can provide conditions for dispersal. And the difference of isolation effect is related to the width of river. It drives the change of the distribution pattern of mammal community, such as the typical nested pattern of “Thousand-Islet Lake”. | |
| 海洋 Oceans | 导致岛屿隔离, 隔离作用强于江河, 促进岛屿特有种的形成。It promotes the formation of endemic species on islands. The isolation effect of ocean is stronger than that of river. | |
| 沙漠 Deserts | 阻碍大多数哺乳动物的扩散, 促进动物分化形成不同的亚种, 但有利于沙漠动物范围的扩大。It inhibits the dispersals of most mammals and promotes the division of animals into different subspecies. However, it is conducive to the expansion of desert animal range. | |
| 其他极端环境与气候变化 Other extreme environments and climate change | 冰川扩张收缩加剧动物遗传分化, 气温波动影响物种分布。如全球变暖引起的北极海冰消融, 造成北极熊生境缩小且碎片化。The expansion and contraction of glaciers aggravate genetic differentiation. Temperature fluctuations affect the distribution of species. For example, the melting of Arctic sea ice caused by global warming leads to the shrinking and fragmentation of polar bear habitat. | |
| 人为因素 Human factors | 景观格局变化 Change of landscape pattern | 大规模森林砍伐导致树栖哺乳动物生境面积减少, 但可能促进非树栖动物的种群扩张。土地利用类型变化会影响物种分布, 重新造林会促进树栖动物的再次扩张。Large-scale deforestation reduces the habitat area of arboreal mammals, but it may promote the population expansion of non-arboreal mammals. Changes in land use types will affect species distribution and reforestation will promote the re-expansion of arboreal fauna. |
| 交通设施建设 Construction of transportation facilities | 阻碍动物迁徙, 导致动物生境破碎化程度加剧。不同物种对道路的响应不同。野生动物桥梁可为动物提供迁徙通道。It inhibits the migration of animals and leads to the fragmentation of the habitat. Different species respond differently to the road. Wildlife bridges can provide migration passages for mammals. | |
| 其他因素 Other factors | 水库修建、偷猎狩猎、人为火灾等均会影响动物分布和扩散。人为干预可打破地理隔离限制, 加强地理隔离可防治物种入侵。Reservoir construction, poaching, and man-made fires all affect the distribution and the dispersal of mammals. Human intervention can break the restriction of geographical isolation, and strengthening geographical isolation can prevent and control species invasion. | |
| [1] |
Albert JS, Carvalho TP, Petry P, Holder MA, Maxime EL, Espino J, Corahua I, Quispe R, Rengifo B, Ortega H, Reis RE (2011) Aquatic biodiversity in the Amazon: Habitat specialization and geographic isolation promote species richness. Animals, 1, 205-241.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Baisero D, Visconti P, Pacifici M, Cimatti M, Rondinini C (2020) Projected global loss of mammal habitat due to land-use and climate change. One Earth, 2, 578-585.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Barton HD, Wisely SM (2012) Phylogeography of striped skunks (Mephitis mephitis) in North America: Pleistocene dispersal and contemporary population structure. Journal of Mammalogy, 93, 38-51.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Boubli JP, Ribas C, Lynch Alfaro JW, Alfaro MEda Silva MNF, Pinho GM, Farias IP (2015) Spatial and temporal patterns of diversification on the Amazon: A test of the riverine hypothesis for all diurnal primates of Rio Negro and Rio Branco in Brazil. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 82(B), 400-412.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Bruinderink GG, van der Sluis T, Lammertsma D, Opdam P, Pouwels R (2003) Designing a coherent ecological network for large mammals in northwestern Europe. Conservation Biology, 17, 549-557.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Buho H, Jiang Z, Liu C, Yoshida T, Mahamut H, Kaneko M, Asakawa M, Motokawa M, Kaji K, Wu X, Otaishi N, Ganzorig S, Masuda R (2011) Preliminary study on migration pattern of the Tibetan antelope (Pantholops hodgsonii) based on satellite tracking. Advances in Space Research, 48, 43-48.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Carmichael LE, Nagy JA, Larter NC, Strobeck C (2001) Prey specialization may influence patterns of gene flow in wolves of the Canadian Northwest. Molecular Ecology, 10, 2787-2798.
PMID |
| [8] |
Chen CW, Xu AC, Ding P, Wang YP (2019) The small-island effect and nestedness in assemblages of medium- and large-bodied mammals on Chinese reservoir land-bridge islands. Basic and Applied Ecology, 38, 47-57.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Cheng JL, Ge DY, Xia L, Wen ZX, Zhang Q, Lu L, Yang QS (2018) Phylogeny and taxonomic reassessment of jerboa, Dipus (Rodentia, Dipodinae), in inland Asia. Zoologica Scripta, 47, 630-644.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Corlatti L, Hackländer K, Frey-Roos F (2009) Ability of wildlife overpasses to provide connectivity and prevent genetic isolation. Conservation Biology, 23, 548-556.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Coster SS, Kovach AI (2012) Anthropogenic influences on the spatial genetic structure of black bears. Conservation Genetics, 13, 1247-1257.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Cronin DT, Riaco C, Linder JM, Bergl RA, Gonder MK, O'Connor MP, Hearn GW (2016) Impact of gun-hunting on monkey species and implications for primate conservation on Bioko Island, Equatorial Guinea. Biological Conservation, 197, 180-189.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Dellicour S, Frantz AC, Colyn M, Bertouille S, Chaumont F, Flamand MC (2011) Population structure and genetic diversity of red deer (Cervus elaphus) in forest fragments in north-western France. Conservation Genetics, 12, 1287-1297.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Deng T, Wang XM, Wang SQ, Li Q, Hou SK (2015) Evolution of the Chinese Neogene mammalian faunas and its relationship to uplift of the Tibetan Plateau. Advances in Earth Science, 30, 407-415. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 邓涛, 王晓鸣, 王世骐, 李强, 侯素宽 (2015) 中国新近纪哺乳动物群的演化与青藏高原隆升的关系. 地球科学进展, 30, 407-415.] | |
| [15] | Douady CJ, Catzeflis F, Raman J, Springer MS, Stanhope MJ (2003) The Sahara as a vicariant agent, and the role of Miocene climatic events, in the diversification of the mammalian order Macroscelidea (elephant shrews). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 100, 8325-8330. |
| [16] |
Duflot R, Avon C, Roche P, Bergès L (2018) Combining habitat suitability models and spatial graphs for more effective landscape conservation planning: An applied methodological framework and a species case study. Journal for Nature Conservation, 46, 38-47.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Endo H, Fukuta K, Kimura J, Sasaki M, Stafford BJ (2004) Geographical variation of the skull of the lesser mouse deer. Journal of Veterinary Medical Science, 66, 1229-1235.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Etherington TR (2015) Geographical isolation and invasion ecology. Progress in Physical Geography: Earth and Environment, 39, 697-710.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Feng XD, Liu X (2007) Modern traffic and endangered species of wild animals protection—A case study ofPantholops hodgsonii. Forestry Economics, 29(2),69-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 冯晓东, 刘欣 (2007) 现代交通建设与濒危野生动物的保护——以藏羚羊为例. 林业经济, 29(2),69-71.] | |
| [20] |
Frantz AC, Bertouille S, Eloy MC, Licoppe A, Chaumont F, Flamand MC (2012) Comparative landscape genetic analyses show a Belgian motorway to be a gene flow barrier for red deer (Cervus elaphus), but not wild boars (Sus scrofa). Molecular Ecology, 21, 3445-3457.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Goossens B, Chikhi L, Jalil MF, Ancrenaz M, Lackman-Ancrenaz I, Mohamed M, Andau P, Bruford MW (2005) Patterns of genetic diversity and migration in increasingly fragmented and declining orang-utan (Pongo pygmaeus) populations from Sabah, Malaysia. Molecular Ecology, 14, 441-456.
PMID |
| [22] | He K, Jiang XL (2014) Sky islands of southwest China. I. An overview of phylogeographic patterns. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 1055-1068. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 何锴, 蒋学龙 (2014) 中国西南地区的“天空之岛”: I 系统地理学研究概述. 科学通报, 59, 1055-1068.] | |
| [23] |
Hernández FA, Parker BM, Pylant CL, Smyser TJ, Piaggio AJ, Lance SL, Milleson MP, Austin JD, Wisely SM (2018) Invasion ecology of wild pigs (Sus scrofa) in Florida, USA: The role of humans in the expansion and colonization of an invasive wild ungulate. Biological Invasions, 20, 1865-1880.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Hewitt GM (1996) Some genetic consequences of ice ages, and their role in divergence and speciation. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 58, 247-276.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Hu ZJ, Yu CQ, Xu HF, Wang Y (2005) Ecological effects of roads on terrestrial animals. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 24, 433-437. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡忠军, 于长青, 徐宏发, 王淯 (2005) 道路对陆栖野生动物的生态学影响. 生态学杂志, 24, 433-437.] | |
| [26] | IUCN International Union for Conservation of Nature (2021) The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. https://www.iucnredlist.org/. (accessed on 2021-05-22) |
| [27] |
Krojerová-Prokešová J, Barančeková M, Kawata Y, Oshida T, Igota H, Koubek P (2017) Genetic differentiation between introduced Central European sika and source populations in Japan: Effects of isolation and demographic events. Biological Invasions, 19, 2125-2141.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Laidre KL, Born EW, Atkinson SN, Wiig Ø, Andersen LW, Lunn NJ, Dyck M, Regehr EV, McGovern R, Heagerty P (2018) Range contraction and increasing isolation of a polar bear subpopulation in an era of sea-ice loss. Ecology and Evolution, 8, 2062-2075.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Lei FM, Song G, Cai TL, Qu YH, Jia CX, Zhao YF, Zhang DZ (2021) Research progress and prospect on biogeography of birds in China. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 56, 265-289. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 雷富民, 宋刚, 蔡天龙, 屈延华, 贾陈喜, 赵义方, 张德志 (2021) 中国鸟类生物地理学研究回顾与展望. 动物学杂志, 56, 265-289.] | |
| [30] |
Li KY, Li KT, Yang CH, Hwang MH, Chang SW, Lin SM, Wu HJ, Basilio EB, Vega RSA, Laude RP, Ju YT (2017) Insular East Asia pig dispersal and vicariance inferred from Asian wild boar genetic evidence. Journal of Animal Science, 95, 1451-1466.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Li XH, Jiang GS, Tian HD, Xu L, Yan C, Wang ZW, Wei FW, Zhang ZB (2015) Human impact and climate cooling caused range contraction of large mammals in China over the past two millennia. Ecography, 38, 74-82.
DOI URL |
| [32] | Liu CX, Su JP, Zhang TZ, Lin GH (2013) The effect of Qingzang-Tibet Plateau geographical barrier on plateau pika population differentiation. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 32, 651-657. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘翠霞, 苏建平, 张同作, 林恭华 (2013) 青藏高原的地理屏障在高原鼠兔种群分化中的作用. 四川动物, 32, 651-657.] | |
| [33] | Liu JH, Lu JQ (2020) Multivariate similarity clustering analysis on zoogeographical distribution of mammals in China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 40, 271-281. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘嘉恒, 路纪琪 (2020) 中国哺乳动物地理分布的多元相似性聚类分析. 兽类学报, 40, 271-281.] | |
| [34] |
Lorenzini R, José CS, Braza F, Aragón S (2003) Genetic differentiation and phylogeography of roe deer in Spain, as suggested by mitochondrial DNA and microsatellite analysis. Italian Journal of Zoology, 70, 89-99.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Lynch Alfaro JW, Boubli JP, Paim FP, Ribas CC, da Silva MNF, Messias MR, Röhe F, Mercês MP, Silva JS Jr, Silva CR, Pinho GM, Koshkarian G, Nguyen MTT, Harada ML, Rabelo RM, Queiroz HL, Alfaro ME, Farias IP (2015a) Biogeography of squirrel monkeys (genusSaimiri): South-central Amazon origin and rapid Pan-Amazonian diversification of a lowland primate. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 82(B), 436-454.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Lynch Alfaro JW, Cortés-Ortiz L, Di Fiore A, Boubli JP (2015b) Special issue: Comparative biogeography of Neotropical primates. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 82(B), 518-529.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Mendoza M, Goodwin B, Criado C (2004) Emergence of community structure in terrestrial mammal-dominated ecosystems. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 230, 203-214.
PMID |
| [38] |
Millions DG, Swanson BJ (2007) Impact of natural and artificial barriers to dispersal on the population structure of bobcats. Journal of Wildlife Management, 71, 96-102.
DOI URL |
| [39] | Niu CJ, Lou AR, Sun RY, Li QF (2007) Basic Ecology, 2nd edn. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 牛翠娟, 娄安如, 孙儒泳, 李庆芬 (2007) 基础生态学(第2版). 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [40] |
Ntuli H, Jagers SC, Linell A, Sjöstedt M, Muchapondwa E (2019) Factors influencing local communities' perceptions towards conservation of transboundary wildlife resources: The case of the Great Limpopo Trans-frontier Conservation Area. Biodiversity and Conservation, 28, 2977-3003.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Onorato DP, Hellgren EC, van den Bussche RA, Doan-Crider DL (2004) Phylogeographic patterns within a metapopulation of black bears (Ursus americanus) in the American Southwest. Journal of Mammalogy, 85, 140-147.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Oshida T, Lee JK, Lin LK, Chen YJ (2006) Phylogeography of pallas's squirrel in Taiwan: Geographical isolation in an arboreal small mammal. Journal of Mammalogy, 87, 247-254.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Peng YX, Huang SJ (1997) Evolutionary Biology. Wuhan University Press, Wuhan. (in Chinese) |
| [ 彭奕欣, 黄诗笺 (1997) 进化生物学. 武汉大学出版社, 武汉.] | |
| [44] |
Penjor U, Wangdi S, Tandin T, MacDonald DW (2021) Vulnerability of mammal communities to the combined impacts of anthropic land-use and climate change in the Himalayan conservation landscape of Bhutan. Ecological Indicators, 121, 107085.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Peters W, Hebblewhite M, Cavedon M, Pedrotti L, Mustoni A, Zibordi F, Groff C, Zanin M, Cagnacci F (2015) Resource selection and connectivity reveal conservation challenges for reintroduced brown bears in the Italian Alps. Biological Conservation, 186, 123-133.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Puckett EE, Etter PD, Johnson EA, Eggert LS (2015) Phylogeographic analyses of American black bears (Ursus americanus) suggest four glacial refugia and complex patterns of postglacial admixture. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 32, 2338-2350.
DOI PMID |
| [47] | Qi C (2021) Survey and analysis of wild animal resources in Xinjiang Taxkorgan Wildlife Nature Reserve. Forest Resources Management, (3),145-148. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 齐成 (2021) 新疆塔什库尔干野生动物自然保护区动物资源调查与分析. 林业资源管理, (3),145-148.] | |
| [48] |
Reckless HJ, Murray M, Crowther MS (2017) A review of climatic change as a determinant of the viability of koala populations. Wildlife Research, 44, 458-470.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Rey-Iglesia A, Grandal-D'Anglade A, Campos PF, Hansen AJ (2017) Mitochondrial DNA of pre-last glacial maximum red deer from NW Spain suggests a more complex phylogeographical history for the species. Ecology and Evolution, 7, 10690-10700.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Riley SPD, Pollinger JP, Sauvajot RM, York EC, Bromley C, Fuller TK, Wayne RK (2006) A southern California freeway is a physical and social barrier to gene flow in carnivores. Molecular Ecology, 15, 1733-1741.
PMID |
| [51] |
Rodríguez D, Ojeda RA (2011) Patterns of diversity of the Monte Desert small mammals across multiple spatial scales. Journal of Arid Environments, 75, 424-431.
DOI URL |
| [52] | Rondinini C, di Marco M, Chiozza F, Santulli G, Baisero D, Visconti P, Hoffmann M, Schipper J, Stuart SN, Tognelli MF, Amori G, Falcucci A, Maiorano L, Boitani L (2011) Global habitat suitability models of terrestrial mammals. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 366, 2633-2641. |
| [53] | Rull V (2020) Quaternary Ecology, Evolution, and Biogeography, pp.173-221. Academic Press, Salt Lake City. |
| [54] | Rutten A, Cox K, Scheppers T, Broecke BV, Leirs H, Casaer J (2019) Analysing the recolonisation of a highly fragmented landscape by wild boar using a landscape genetic approach. Wildlife Biology, (1),1-11. |
| [55] | Shen ZH, Yang MZ, Feng JM, Li XH, Peng PH, Zheng Z (2017) Geographic patterns of alpine flora in China in relation to environmental and spatial factors. Biodiversity Science, 25, 182-194. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 沈泽昊, 杨明正, 冯建孟, 李新辉, 彭培好, 郑智 (2017) 中国高山植物区系地理格局与环境和空间因素的关系. 生物多样性, 25, 182-194.]
DOI |
|
| [56] |
Shi QJ, Guo YY, Engelhardt SC, Weladji RB, Zhou Y, Long M, Meng XX (2016) Endangered wild yak (Bos grunniens) in the Tibetan Plateau and adjacent regions: Population size, distribution, conservation perspectives and its relation to the domestic subspecies. Journal for Nature Conservation, 32, 35-43.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Skog A, Zachos FE, Rueness EK, Feulner PGD, Mysterud A, Langvatn R, Lorenzini R, Hmwe SS, Lehoczky I, Hartl GB, Stenseth NC, Jakobsen KS (2009) Phylogeography of red deer (Cervus elaphus) in Europe. Journal of Biogeography, 36, 66-77.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Small MP, Stone KD, Cook JA (2003) American marten (Martes americana) in the Pacific Northwest: Population differentiation across a landscape fragmented in time and space. Molecular Ecology, 12, 89-103.
DOI URL |
| [59] | Smith TB, Schneider CJ, Holder K (2001) Refugial isolation versus ecological gradients. Genetica, 112, 383-398. |
| [60] |
Song LL, Qin MZ (2016) Identification of ecological corridors and its importance by integrating circuit theory. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27, 3344-3352. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI PMID |
|
[ 宋利利, 秦明周 (2016) 整合电路理论的生态廊道及其重要性识别. 应用生态学报, 27, 3344-3352.]
PMID |
|
| [61] |
Stewart JR, Lister AM (2001) Cryptic northern refugia and the origins of the modern biota. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 16, 608-613.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Stricker HK, Gehring TM, Donner D, Petroelje T (2019) Multi-scale habitat selection model assessing potential gray wolf den habitat and dispersal corridors in Michigan, USA. Ecological Modelling, 397, 84-94.
DOI |
| [63] |
Sulloway FJ (1979) Geographic isolation in Darwin's thinking: The vicissitudes of a crucial idea. Studies in History of Biology, 3, 23-65.
PMID |
| [64] |
Supriatna J, Shekelle M, Fuad HAH, Winarni NL, Dwiyahreni AA, Farid M, Mariati S, Margules C, Prakoso B, Zakaria Z (2020) Deforestation on the Indonesian island of Sulawesi and the loss of primate habitat. Global Ecology and Conservation, 24, e01205.
DOI URL |
| [65] | Wang CS, Hazen RM, Cheng QM, Stephenson MH, Zhou CH, Fox P, Shen SZ, Oberhänsli R, Hou ZQ, Ma XG, Feng ZQ, Fan JX, Ma C, Hu XM, Luo B, Wang JL, Schiffries CM (2021) The Deep-Time Digital Earth Program: Data-driven discovery in geosciences. National Science Review, 8, nwab027. |
| [66] |
Wang GH, Munson SM, Yu KL, Chen N, Gou QQ (2020) Ecological effects of establishing a 40-year oasis protection system in a northwestern China desert. Catena, 187, 104374.
DOI URL |
| [67] | Wang JZ (2006) The Impacts of Constructing Three Gorges Dam to the Animals in Three Gorges Rivervoir. PhD dissertation, Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王建柱 (2006) 三峡大坝的修建对库区动物的影响. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院植物研究所, 北京.] | |
| [68] |
Wang Y, Guan L, Piao ZJ, Wang ZC, Kong YP (2017) Monitoring wildlife crossing structures along highways in Changbai Mountain, China. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 50, 119-128.
DOI URL |
| [69] | Wang Y, Li HF, Cui P, Wu H (2007) A study on wildlife passage along highway in Wolong National Nature Preserve. Highway, 52(1),99-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王云, 李海峰, 崔鹏, 吴浩 (2007) 卧龙自然保护区公路动物通道设置研究. 公路, 52(1),99-104.] | |
| [70] | Wang Y, Piao ZJ, Guan L, Wang XY, Kong YP, Chen JD (2013) Road mortalities of vertebrate species on Ring Changbai Mountain Scenic Highway, Jilin Province, China. North-Western Journal of Zoology, 9, 399-409. |
| [71] |
Weckworth BV, Talbot S, Sage GK, Person DK, Cook J (2005) A signal for independent coastal and continental histories among North American wolves. Molecular Ecology, 14, 917-931.
PMID |
| [72] |
Wen ZX, Quan Q, Du YB, Xia L, Ge DY, Yang QS (2016a) Dispersal, niche, and isolation processes jointly explain species turnover patterns of nonvolant small mammals in a large mountainous region of China. Ecology and Evolution, 6, 946-960.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
Wen ZX, Yang QS, Quan Q, Xia L, Ge DY, Lv X (2016b) Multiscale partitioning of small mammal β-diversity provides novel insights into the Quaternary faunal history of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and Hengduan Mountains. Journal of Biogeography, 43, 1412-1424.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Wereszczuk A, Leblois R, Zalewski A (2017) Genetic diversity and structure related to expansion history and habitat isolation: Stone marten populating rural-urban habitats. BMC Ecology, 17, 1-16.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
White TH Jr, Bowman JL, Leopold BD, Jacobson HA, Smith WP, Vilella FJ (2000) Influence of Mississippi alluvial valley rivers on black bear movements and dispersal: Implications for Louisiana black bear recovery. Biological Conservation, 95, 323-331.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Wilson GM, Den Bussche RA, McBee K, Johnson LA, Jones CA (2005) Intraspecific phylogeography of red squirrels (Tamiasciurus hudsonicus) in the central rocky mountain region of North America. Genetica, 125, 141-154.
DOI URL |
| [77] | Winarni NL, Supriatna J, Dwiyahreni AA (2017) Deforestation of primate habitat on Sumatra and adjacent islands, Indonesia. Primate Conservation, 31, 71-82. |
| [78] |
Xia L, Yang QS, Li ZC, Wu YH, Feng ZJ (2007) The effect of the Qinghai-Tibet railway on the migration of Tibetan antelopePantholops hodgsonii in Hoh-xil National Nature Reserve, China. Oryx, 41, 352-357.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
Xia WC, Zhang C, Zhuang HF, Ren BP, Zhou J, Shen J, Krzton A, Luan XF, Li DY (2020) The potential distribution and disappearing of Yunnan snub-nosed monkey: Influences of habitat fragmentation. Global Ecology and Conservation, 21, e00835.
DOI URL |
| [80] | Xie ZQ, Chen ZG, Fan DY, Xiong GM (2003) Global consequences and control strategies of biological invasion. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 14, 1795-1798. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谢宗强, 陈志刚, 樊大勇, 熊高明 (2003) 生物入侵的危害与防治对策. 应用生态学报, 14, 1795-1798.] | |
| [81] |
Yang SJ, Dong HL, Lei FM (2009) Phylogeography of regional fauna on the Tibetan Plateau: A review. Progress in Natural Science, 19, 789-799.
DOI URL |
| [82] | Yin YQ, Hu JC, Wu PW, Ai YB, Li YX (2009) Study on morphological characters ofApodemus agrarius andAnourosorex squamipes in lower reach of Jialing River. Journal of China West Normal University (Natural Sciences), 30(1),13-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 尹彦强, 胡锦矗, 吴攀文, 艾永斌, 黎运喜 (2009) 嘉陵江下游黑线姬鼠(Apodernus agrarius)和四川短尾鼩(Anourosorex squamipes)的形态学初步研究. 西华师范大学学报(自然科学版), 30(1),13-16.] | |
| [83] | Zeng ZY, Song ZM, Deng XZ, Sun QZ (1994) A study of the ungulate fauna in Sichuan. Journal of Sichuan University (Natural Science Edition), 31, 540-545. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 曾宗永, 宋志明, 邓小忠, 孙奇志 (1994) 四川有蹄动物区系形成的探讨. 四川大学学报(自然科学版), 31, 540-545.] | |
| [84] |
Zhang FF, Jiang ZG (2006) Mitochondrial phylogeography and genetic diversity of Tibetan gazelle (Procapra picticaudata): Implications for conservation. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 41, 313-321.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
Zhang FF, Jiang ZG, Xu AC, Zeng Y, Li CW (2013) Recent geological events and intrinsic behavior influence the population genetic structure of the chiru and Tibetan gazelle on the Tibetan Plateau. PLoS ONE, 8, e60712.
DOI URL |
| [86] |
Zhang K, Lenstra JA, Zhang S, Liu W, Liu J (2020) Evolution and domestication of the Bovini species. Animal Genetics, 51, 637-657.
DOI PMID |
| [87] |
Zhang Q, Xia L, Ma J, Wu PW, Yang QS (2009) Effects of the Qinghai-Tibet Railway on the community structure of rodents in Qaidam desert region. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29, 267-271.
DOI URL |
| [88] | Zhang RZ (2011) Zoogeography of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张荣祖 (2011) 中国动物地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [89] | Zhang WH, Chi Y, Qian TL, Xi CB, Wang JC (2019) Application of geographic information technology in terrestrial mammal habitat research: Retrospect and prospect. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38, 3839-3846. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张文涵, 迟瑶, 钱天陆, 席唱白, 王结臣 (2019) 地理信息技术在陆生哺乳动物栖息地研究中的应用: 回顾与展望. 生态学杂志, 38, 3839-3846.] | |
| [90] | Zhang YQ (2002) The significance of Qinghai-Xizang railway to economic development in Xizang. Journal of Xi'an Petrdleum Institute (Social Sciences Edition), 11(3),21-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张玉清 (2002) 青藏铁路对西藏经济发展的意义. 西安石油学院学报(社会科学版), 11(3),21-24.] | |
| [91] |
Zhao QY, Bao YX, Sun B, Zhang LL, Hu ZY (2009) Community distribution pattern and the affecting factors of small mammals in Qiandao Lake, Zhejiang. Zoological Research, 30, 671-678. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 赵庆洋, 鲍毅新, 孙波, 张龙龙, 胡知渊 (2009) 千岛湖岛屿小型兽类群落分布格局及其影响因素. 动物学研究, 30, 671-678.] |
| [1] | 罗敏, 杨永川, 靳程, 周礼华, 龙宇潇. 城市森林兽类组成特征及人类活动的影响——以重庆中心城区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24402-. |
| [2] | 马文俊, 刘思嘉, 李柯懋, 简生龙, 薛长安, 韩庆祥, 魏金良, 陈生学, 牛依萌, 崔洲平, 隋瑞臣, 田菲, 赵凯. 青海省长江源区鱼类分布及多样性格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [3] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [4] | 何泽嵘, 叶鹏, 王舒婷, 关永鑫, 闫淑君, 洪心茹. 中国城市草坪的杂草优势种组成及空间分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24133-. |
| [5] | 舒为杰, 何花, 曾罗, 谷志容, 谭敦炎, 杨晓琛. 雌雄异株物种一把伞南星雌雄株空间分布及性别二态性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24084-. |
| [6] | 钟超, 廖亚琴, 刘伟杰, 隋昊志, 陈清华. 广东沿海海草床的现状、面临的威胁与保护建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23201-. |
| [7] | 吴芳芳, 刘娜, 何春梅, 原作强, 郝占庆, 尹秋龙. 秦岭山地木本植物群落结构及多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [8] | 杨俊毅, 关潇, 李俊生, 刘晶晶, 郝颢晶, 王槐睿. 乌江流域生物多样性与生态系统服务的空间格局及相互关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23061-. |
| [9] | 董庆栋, 陈超男, 李艳红, 赵体侠, 孙梓欣, 张哲, 朱连奇. 基于NPP和人类扰动指数评估河南伏牛山地区国家级自然保护区群保护成效与溢出/泄漏效应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22503-. |
| [10] | 江艺欣, 时莹莹, 高朔, 王苏盆. 人为噪音、夜间人造光和路杀对两栖动物的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22427-. |
| [11] | 林木青, 张应明, 欧阳芳, 束祖飞, 朱朝东, 肖治术. 广东车八岭国家级自然保护区独栖性胡蜂多样性空间分布特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22310-. |
| [12] | 金恒镳. 从天择到人择: 在华莱士的肩膀上看地球的未来[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23267-. |
| [13] | 崔家鹤, 李智勇, 王宇池, 孙蔷, 莎娜, 李紫晶, 武艳涛, 史亚博, 韩瀛, 李明乐, 王立新, 赵利清, 梁存柱. 垫状驼绒藜群落特征及地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(10): 23172-. |
| [14] | 赵仁生, 许诗嘉, 宋鹏飞, 周翔, 张亚洲, 袁燕. 青藏高原药用植物分布格局及保护优先区[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21385-. |
| [15] | 王雅婷, 张定海, 张志山. 古尔班通古特沙漠固定沙丘上白梭梭和梭梭的空间分布及种间关联性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21280-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()